S100A4/FSP1: A Prognostic Marker and a Promising Target for Antitumor Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
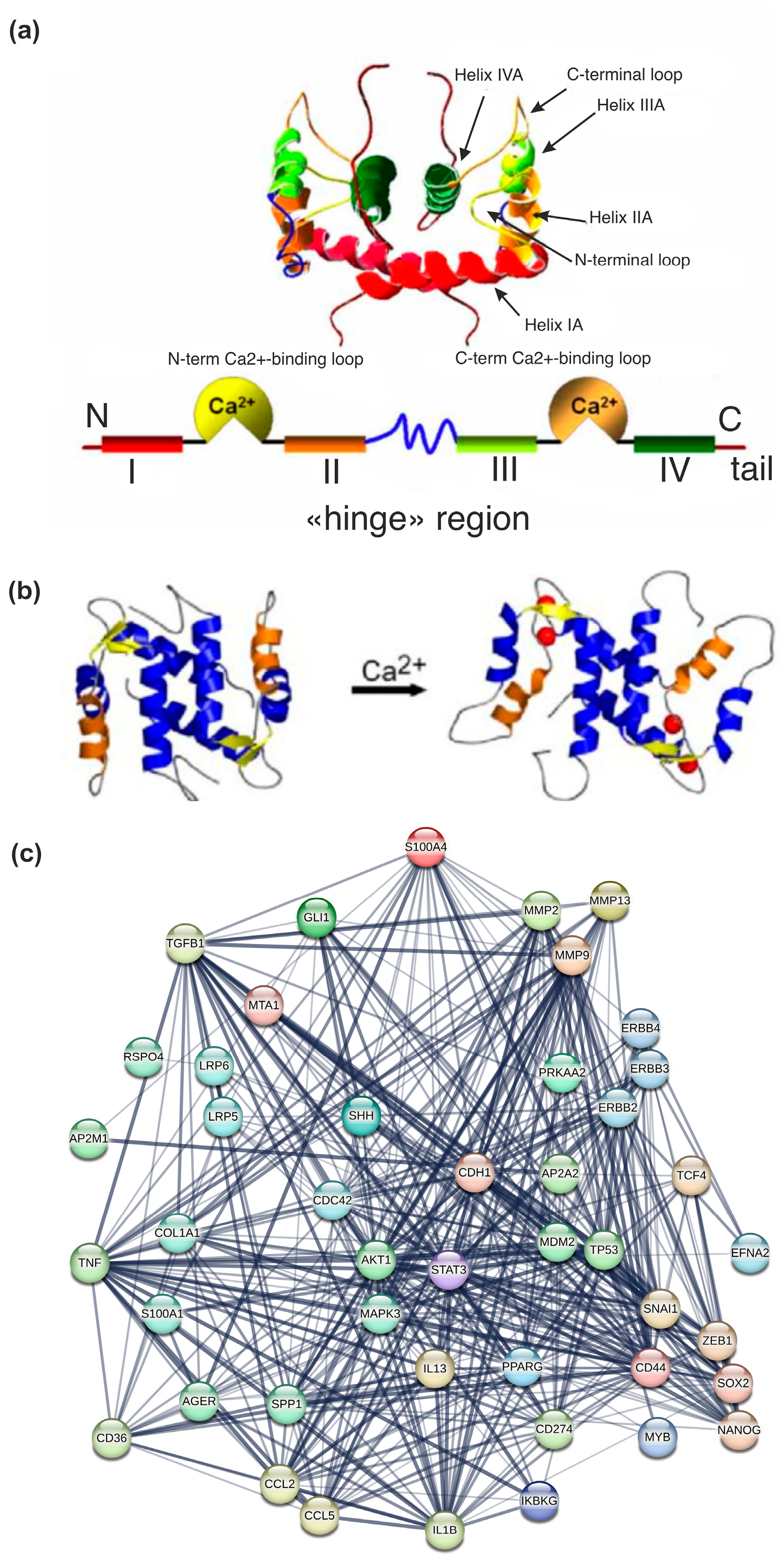
2. Structure of S100A4: Localization of the Gene and Regulation of Transcription of S100A4
3. S100A4: Significance for Oncogenesis and Prognosis of Cancer
3.1. Expression and Prognostic Significance of S100A4 in Tumor Tissues
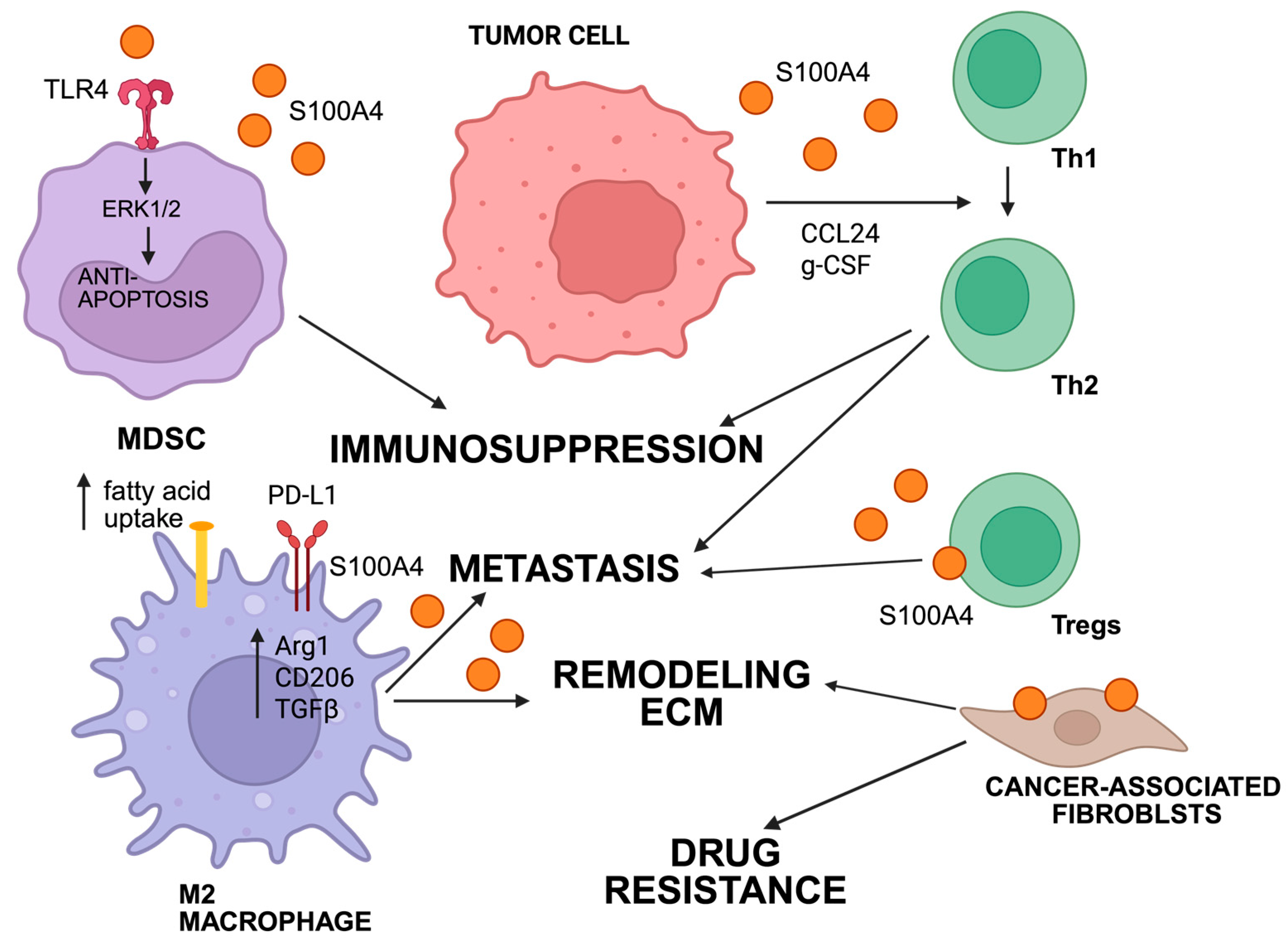
3.2. Signaling Pathways That Mediate S100A4 Functions in Tumors and Microenvironment
3.3. Intracellular Signaling Pathways for S100A4 Functions
4. The Importance of S100A4 in the Formation of Fibrotic Changes in Inflammatory Processes
- -
- Metalloproteases: S100A4 increases the expression of various metalloproteases in different types of cells, including smooth muscle cells (MMPs 1,2,3,9) and articular chondrocytes (MMP-13). Osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts treated with S100A4 oligomer can induce the expression and release of MMP-3 and other MMPs (MMP-1, MMP-9, and MMP-13), thereby promoting extracellular matrix remodeling;
- -
- Interaction with the RAGE receptor allows S100A4 to weaken autophagy, contributing to the development of fibrosis and angiogenesis.
5. Therapeutic Approaches to Targeting S100A4
6. Discussion and Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Newman, L.A.; Freedman, R.A.; Smith, R.A.; Star, J.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Breast Cancer Statistics 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 477–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azamjah, N.; Soltan-Zadeh, Y.; Zayeri, F. Global Trend of Breast Cancer Mortality Rate: A 25-Year Study. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 20, 2015–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, R.; Nevitt, S.; Liu, Y.; Harden, M.; Khouja, C.; Raine, G.; Churchill, R.; Dias, S. Multi-Cancer Early Detection Tests for General Population Screening: A Systematic Literature Review. Health Technol. Assess. 2025, 29, 1–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connal, S.; Cameron, J.M.; Sala, A.; Brennan, P.M.; Palmer, D.S.; Palmer, J.D.; Perlow, H.; Baker, M.J. Liquid Biopsies: The Future of Cancer Early Detection. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinstein, W.S.; Patriotis, C.; Dickherber, A.; Han, P.K.J.; Katki, H.A.; LeeVan, E.; Pinsky, P.F.; Prorok, P.C.; Skarlupka, A.L.; Temkin, S.M.; et al. Cancer Screening with Multicancer Detection Tests: A Translational Science Review. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 368–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinestrosa, J.P.; Kurzrock, R.; Lewis, J.M.; Schork, N.J.; Schroeder, G.; Kamat, A.M.; Lowy, A.M.; Eskander, R.N.; Perrera, O.; Searson, D.; et al. Early-Stage Multi-Cancer Detection Using an Extracellular Vesicle Protein-Based Blood Test. Commun. Med. 2022, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Fatima, K.; Aisha, S.; Malik, F. Unveiling the Mechanisms and Challenges of Cancer Drug Resistance. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karati, D.; Kumar, D. A Comprehensive Review on Targeted Cancer Therapy: New Face of Treatment Approach. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2023, 29, 3282–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Konig, M.F.; Pardoll, D.M.; Bettegowda, C.; Papadopoulos, N.; Wright, K.M.; Gabelli, S.B.; Ho, M.; van Elsas, A.; Zhou, S. Cancer Therapy with Antibodies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2024, 24, 399–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Bhardwaj, A.; Gupta, S. Cancer Treatment Therapies: Traditional to Modern Approaches to Combat Cancers. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 9663–9676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.; Li, N.; Zhang, Z. Emerging Therapies for Glioblastoma: Current State and Future Directions. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, R.; Dilabazian, H.; Bahr, H.; Barakat, A.; El-Sibai, M. A Guide through Conventional and Modern Cancer Treatment Modalities: A Specific Focus on Glioblastoma Cancer Therapy (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2022, 48, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresnick, A.R.; Weber, D.J.; Zimmer, D.B. S100 Proteins in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marenholz, I.; Heizmann, C.W.; Fritz, G. S100 Proteins in Mouse and Man: From Evolution to Function and Pathology (Including an Update of the Nomenclature). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 322, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Cui, P.; Dai, W.; Cao, B.; Zhao, H.; Jin, S.; Xu, D.; Shi, Y.; Yan, S. S100 Protein Family: Emerging Role and Mechanism in Digestive Tract Cancer (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2024, 64, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, R. S100 Protein Family in Lung Cancer: An Updated Narrative Review. Cancer Manag. Res. 2025, 17, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.W. A Soluble Protein Characteristic of the Nervous System. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1965, 19, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S100A4 Gene-S100 Calcium Binding Protein A4. Available online: https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=S100A4 (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- Ebralidze, A.; Tulchinsky, E.; Grigorian, M.; Afanasyeva, A.; Senin, V.; Revazova, E.; Lukanidin, E. Isolation and Characterization of a Gene Specifically Expressed in Different Metastatic Cells and Whose Deduced Gene Product Has a High Degree of Homology to a Ca2+-Binding Protein Family. Genes. Dev. 1989, 3, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, H.R.; Adhami, V.M.; Parray, A.; Johnson, J.J.; Siddiqui, I.A.; Shekhani, M.T.; Murtaza, I.; Ambartsumian, N.; Konety, B.R.; Mukhtar, H.; et al. The S100A4 Oncoprotein Promotes Prostate Tumorigenesis in a Transgenic Mouse Model: Regulating NFκB through the RAGE Receptor. Genes. Cancer 2013, 4, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, B.R.; Davies, M.P.; Gibbs, F.E.; Barraclough, R.; Rudland, P.S. Induction of the Metastatic Phenotype by Transfection of a Benign Rat Mammary Epithelial Cell Line with the Gene for P9Ka, a Rat Calcium-Binding Protein, but Not with the Oncogene EJ-Ras-1. Oncogene 1993, 8, 999–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, T.; Kang, R.; Yun, K. The Multi-Faceted Immune Modulatory Role of S100A4 in Cancer and Chronic Inflammatory Disease. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1525567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, F.; Qu, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S. S100A4 in Cancer Progression and Metastasis: A Systematic Review. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 73219–73239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorak, H.F. Tumors: Wounds That Do Not Heal—Redux. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, E.; Astsaturov, I.; Cukierman, E.; DeNardo, D.G.; Egeblad, M.; Evans, R.M.; Fearon, D.; Greten, F.R.; Hingorani, S.R.; Hunter, T.; et al. A Framework for Advancing Our Understanding of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akimoto, N.; Väyrynen, J.P.; Zhao, M.; Ugai, T.; Fujiyoshi, K.; Borowsky, J.; Zhong, R.; Haruki, K.; Arima, K.; Lau, M.C.; et al. Desmoplastic Reaction, Immune Cell Response, and Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 840198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Yu, H.; Zhou, D.; Fan, X.; Duan, Y.; Tan, Y.; Lang, M.; Shao, G. Cancer Stem Cell-Derived CHI3L1 Activates the MAF/CTLA4 Signaling Pathway to Promote Immune Escape in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulchinsky, E.; Grigorian, M.; Tkatch, T.; Georgiev, G.; Lukanidin, E. Transcriptional Regulation of the Mts1 Gene in Human Lymphoma Cells: The Role of DNA-Methylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gene Struct. Expr. 1995, 1261, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrosi, N.; Milani, M.; Apolloni, S. S100A4 in the Physiology and Pathology of the Central and Peripheral Nervous System. Cells 2021, 10, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, R.; Cannon, B.R.; Sorci, G.; Riuzzi, F.; Hsu, K.; Weber, D.J.; Geczy, C.L. Functions of S100 Proteins. Curr. Mol. Med. 2013, 13, 24–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heizmann, C.W.; Cox, J.A. New Perspectives on S100 Proteins: A Multi-Functional Ca2+-, Zn 2+- and Cu2+-Binding Protein Family. Biometals 1998, 11, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coser, M.; Neamtu, B.M.; Pop, B.; Cipaian, C.R.; Crisan, M. RAGE and Its Ligands in Breast Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Oncol. Rev. 2025, 18, 1507942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, R. RAGE: A Single Receptor for Several Ligands and Different Cellular Responses: The Case of Certain S100 Proteins. Curr. Mol. Med. 2007, 7, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambartsumian, N.; Klingelhöfer, J.; Grigorian, M. The Multifaceted S100A4 Protein in Cancer and Inflammation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1929, 339–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, R.H.; van Es, J.H.; Clevers, H. Caught up in a Wnt Storm: Wnt Signaling in Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Cancer 2003, 1653, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Chu, Q.; Shi, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, L. Wnt Signaling Pathways in Biology and Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Advances. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING Database in 2023: Protein–Protein Association Networks and Functional Enrichment Analyses for Any Sequenced Genome of Interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, U.; Arlt, F.; Walther, W.; Smith, J.; Waldman, T.; Harris, E.D.; Mertins, S.D.; Heizmann, C.W.; Allard, D.; Birchmeier, W.; et al. The Metastasis-Associated Gene S100A4 Is a Novel Target of β-Catenin/T-Cell Factor Signaling in Colon Cancer. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 1486–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sack, U.; Walther, W.; Scudiero, D.; Selby, M.; Aumann, J.; Lemos, C.; Fichtner, I.; Schlag, P.M.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Stein, U. S100A4-Induced Cell Motility and Metastasis Is Restricted by the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Inhibitor Calcimycin in Colon Cancer Cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 3344–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernan, R.; Fasheh, R.; Calabrese, C.; Frank, A.J.; Maclean, K.H.; Allard, D.; Barraclough, R.; Gilbertson, R.J. ERBB2 Up-Regulates S100A4 and Several Other Prometastatic Genes in Medulloblastoma. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 140–148. [Google Scholar]
- Rudland, P.S.; Platt-Higgins, A.; Renshaw, C.; West, C.R.; Winstanley, J.H.; Robertson, L.; Barraclough, R. Prognostic Significance of the Metastasis-Inducing Protein S100A4 (P9Ka) in Human Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Silva Rudland, S.; Martin, L.; Roshanlall, C.; Winstanley, J.; Leinster, S.; Platt-Higgins, A.; Carroll, J.; West, C.; Barraclough, R.; Rudland, P. Association of S100A4 and Osteopontin with Specific Prognostic Factors and Survival of Patients with Minimally Invasive Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt-Higgins, A.M.; Renshaw, C.A.; West, C.R.; Winstanley, J.H.; De Silva Rudland, S.; Barraclough, R.; Rudland, P.S. Comparison of the Metastasis-Inducing Protein S100A4 (P9ka) with Other Prognostic Markers in Human Breast Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 89, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.B.; Nesland, J.M.; Fodstad, Ø.; Mælandsmo, G.M. Expression of S100A4, E-Cadherin, α- and β-Catenin in Breast Cancer Biopsies. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 87, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorian, M.; Ambartsumian, N.; Lykkesfeldt, A.E.; Bastholm, L.; Elling, F.; Georgiev, G.; Lukanidin, E. Effect of Mts1 (S100A4) Expression on the Progression of Human Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 67, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitenko, L.L.; Lloyd, B.H.; Rudland, P.S.; Fear, S.; Barraclough, R. Localisation by in Situ Hybridisation of S100A4 (P9Ka) Mrna in Primary Human Breast Tumour Specimens. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 86, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.K.; Jung, W.H.; Koo, J.S. Expression of Cancer-Associated Fibroblast-Related Proteins Differs between Invasive Lobular Carcinoma and Invasive Ductal Carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 159, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, R.; Platt-Higgins, A.; Rathi, N.; Crooks, D.; Brodbelt, A.; Chavredakis, E.; Lawson, D.; Jenkinson, M.D.; Rudland, P.S. Metastasis-Inducing Proteins Are Widely Expressed in Human Brain Metastases and Associated with Intracranial Progression and Radiation Response. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, J.-S.; Deng, H.; Xiong, W.; Tran, H.N.; Hashimoto, C.; Leonard, F.; Wong, T.; Abdelfattah, N.; An, Z.; Zhang, N.; et al. Abstract A041: Combined Inhibition of S100A4 and TIGIT Suppresses Late-Stage Breast Cancer Metastasis to the Lung by Activating T and NK Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2025, 13, A041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Schlumbrecht, M.P.; Shipley, G.L.; Xie, S.; Bassett, R.L.; Broaddus, R.R. S100A4 Mediates Endometrial Cancer Invasion and Is a Target of TGF-Β1 Signaling. Lab. Investig. 2009, 89, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.; Chi, Y.B.; Sun, J.L. Effect of ShRNA-Mediated Regulation of S100A4 Gene Expression on Proliferation and Apoptosis of KLE Endometrial Cancer Cells. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 23, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H. Integrated Analysis of Lactate-Related Genes Identifies S100A4 as a Novel Marker Promoting the Migration and Invasion of Endometrial Stromal Cell in Endometriosis. Reprod. Sci. 2025, 32, 2558–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Nie, H.; Liu, Q.; Xu, C. Study on the Expression of S100A4 and HMGA1 in Endometrial Carcinoma and Their Correlation with Metastasis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2025, 17, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastrad, B.; Vastrad, C. Screening and Identification of Key Biomarkers Associated with Endometriosis Using Bioinformatics and Next-Generation Sequencing Data Analysis. Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2024, 25, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, T.; Kuhlmann, J.D.; Kobelt, D.; Herrmann, P.; Vassileva, Y.D.; Kramer, M.; Frank, K.; Göckenjan, M.; Wimberger, P.; Stein, U. Clinical Relevance of Circulating MACC1 and S100A4 Transcripts for Ovarian Cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 1268–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiralte, M.; Barquín, A.; Yagüe-Fernández, M.; Navarro, P.; Grazioso, T.P.; Sevillano-Fernández, E.; Rodriguez-Moreno, J.F.; Balarezo-Saldivar, A.; Peinado, H.; Izquierdo, E.; et al. Proteomic Profiles of Peritoneal Fluid-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Correlate with Patient Outcome in Ovarian Cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e176161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, M.; Yokoi, A.; Nakagawa, M.; Hashimura, M.; Oguri, Y.; Saegusa, M. Prognostic Significance of S100A4 in Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma: Its Relation to Tumor Progression and Chemoresistance. Cancers 2025, 17, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, F.; Pang, X.; Jin, F.; Luan, N.; Guo, H.; Zhu, L. Integration of ScRNA-Seq and Bulk RNA-Seq to Reveal the Association and Potential Molecular Mechanisms of Metabolic Reprogramming Regulated by Lactylation and Chemotherapy Resistance in Ovarian Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1513806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenaga, K.; Nakanishi, H.; Wada, K.; Suzuki, M.; Matsuzaki, O.; Matsuura, A.; Endo, H. Increased Expression of S100A4, a Metastasis-Associated Gene, in Human Colorectal Adenocarcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 1997, 3, 2309–2316. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.; Herrington, S.; Prime, W.; Rudland, P.S.; Barraclough, R. S100A4 (P9Ka) Protein in Colon Carcinoma and Liver Metastases: Association with Carcinoma Cells and T-Lymphocytes. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 86, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, W.-J.; Ji, M.; Lee, T.-G.; Son, B.-R.; Yoon, S.M.; Sung, R.; Lee, E.J.; Youn, S.J.; et al. Combined Aberrant Expression of E-Cadherin and S100A4, but Not β-Catenin Is Associated with Disease-Free Survival and Overall Survival in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Diagn. Pathol. 2013, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlmann, M.; Okhrimenko, A.; Marcinkowski, P.; Osterland, M.; Herrmann, P.; Smith, J.; Heizmann, C.W.; Schlag, P.M.; Stein, U. RAGE Mediates S100A4-Induced Cell Motility via MAPK/ERK and Hypoxia Signaling and Is a Prognostic Biomarker for Human Colorectal Cancer Metastasis. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 3220–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlmann, M.; Monks, A.; Harris, E.D.; Kobelt, D.; Osterland, M.; Khaireddine, F.; Herrmann, P.; Kemmner, W.; Burock, S.; Walther, W.; et al. Combination of Wnt/β-Catenin Targets S100A4 and DKK1 Improves Prognosis of Human Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlmann, M.; Kobelt, D.; Walther, W.; Mudduluru, G.; Stein, U. S100A4 in Cancer Metastasis: Wnt Signaling-Driven Interventions for Metastasis Restriction. Cancers 2016, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, K.; Jacob, H.; Frikstad, K.-A.M.; Nesland, J.M.; Mælandsmo, G.M.; Dahl, O.; Nesbakken, A.; Flatmark, K. Prognostic Significance of S100A4 Expression in Stage II and III Colorectal Cancer: Results from a Population-Based Series and a Randomized Phase III Study on Adjuvant Chemotherapy. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 1840–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, S.; Hussein, Z.; Ali, H.; Al Ismaeel, Q.; Al-Mahmoodi, H.; Yalda, M.; Najeeb, H. The Emerging Role of S100A4 and S100A14 Proteins in Colorectal Cancer Progression. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2024, 70, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, S.H. Correlation of S100A4 and S100A14 Expression with Clinico-Pathological Features and Tumor Location in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Cureus 2024, 16, e65615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Deng, Z.; Wu, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wen, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; et al. Low MiR-224–5p in Exosomes Confers Colorectal Cancer 5-FU Resistance by Upregulating S100A4. Drug Resist. Updat. 2025, 79, 101211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Ye, Z.-Y.; Zhao, Z.-S.; Tao, H.-Q.; Chu, Y.-Q. High-Level Expression of S100A4 Correlates with Lymph Node Metastasis and Poor Prognosis in Patients with Gastric Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Q. S100 Calcium-Binding Protein A4 Is a Novel Independent Prognostic Factor for the Poor Prognosis of Gastric Carcinomas. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.-Z.; Zheng, X.-Y.; Zhou, L.-X.; Fu, B.; Yu, Y.-W.; Lu, S.-C.; Cao, N.-S. Correlation between Expression of S100A4 and VEGF-C, and Lymph Node Metastasis and Prognosis in Gastric Carcinoma. J. Int. Med. Res. 2011, 39, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Z.; Li, R. Clinicopathological and Prognostic Value of S100A4 Expression in Gastric Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2014, 29, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treese, C.; Hartl, K.; Pötzsch, M.; Dahlmann, M.; von Winterfeld, M.; Berg, E.; Hummel, M.; Timm, L.; Rau, B.; Walther, W.; et al. S100A4 Is a Strong Negative Prognostic Marker and Potential Therapeutic Target in Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach and Esophagus. Cells 2022, 11, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Feng, J.; Wang, Z. Oncogene OSTM1 Promotes Gastric-Cancer Metastasis by Modulating the Metastatic Microenvironment Through Altered Tumor-Cell Autocrine Signaling. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, C.; Hu, B.; Gao, X.; Zou, T.; Luo, Q.; Chen, M.; Fu, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Zhang, K.; et al. Exosomal S100A4 Derived from Highly Metastatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Promotes Metastasis by Activating STAT3. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, S.; Zhou, J.; Li, S.; Ye, H. S100a4 Promotes Metastatic Transformation in Non-Metastatic Liver Cancer Cells through NMIIa Binding: Mechanistic Insights. BMC Cancer 2025, 25, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, N.; Egawa, S.; Akada, M.; Abe, K.; Saiki, Y.; Kaneko, N.; Yokoyama, S.; Shima, K.; Yamamura, A.; Motoi, F.; et al. The Expression of S100A4 in Human Pancreatic Cancer Is Associated With Invasion. Pancreas 2013, 42, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozono, S.; Ohuchida, K.; Ohtsuka, T.; Cui, L.; Eguchi, D.; Fujiwara, K.; Zhao, M.; Mizumoto, K.; Tanaka, M. S100A4 MRNA Expression Level Is a Predictor of Radioresistance of Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Yue, S.; Liu, J. Relationship between S100A4 Protein Expression and Pre-Operative Serum CA19.9 Levels in Pancreatic Carcinoma and Its Prognostic Significance. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 17, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Matoso, A.; Sciandra, K.T.; Yakirevich, E.; Sabo, E.; Zhang, Y.; Meitner, P.A.; Tavares, R.; Noble, L.; Pareek, G.; et al. Expression of S100A4 in Renal Epithelial Neoplasms. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2012, 20, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Jiao, B.; Tran, M.; Wang, Y. Pharmacological Inhibition of S100A4 Attenuates Fibroblast Activation and Renal Fibrosis. Cells 2022, 11, 2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, M.; Al-Baradie, R.S.; Al-Hindi, H.; Farid, N.R.; Shi, Y. S100A4 (Mts1) Gene Overexpression Is Associated with Invasion and Metastasis of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 93, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yu, M.; Hao, F.; Dong, A.; Chen, D. Knockdown of S100A4 Blocks Growth and Metastasis of Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cells in Vitro and in Vivo. Cancer Biomark. 2016, 17, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chng, C.-L.; Lai, O.F.; Seah, L.-L.; Yong, K.-L.; Chung, Y.H.-W.; Goh, R.; Lim, C.K. A Combined Transcriptomics and Proteomics Approach Reveals S100A4 as a Potential Biomarker for Graves’ Orbitopathy. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1342205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semov, A.; Moreno, M.J.; Onichtchenko, A.; Abulrob, A.; Ball, M.; Ekiel, I.; Pietrzynski, G.; Stanimirovic, D.; Alakhov, V. Metastasis-Associated Protein S100A4 Induces Angiogenesis through Interaction with Annexin II and Accelerated Plasmin Formation*. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 20833–20841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, N.; Luo, J.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, X.; He, T.; Xing, Y. Overexpression of S100A4 Protects Retinal Ganglion Cells against Retinal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Mice. Exp. Eye Res. 2020, 201, 108281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherbet, G. V Metastasis Promoter S100A4 Is a Potentially Valuable Molecular Target for Cancer Therapy. Cancer Lett. 2009, 280, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazilaty, H.; Rago, L.; Kass Youssef, K.; Ocaña, O.H.; Garcia-Asencio, F.; Arcas, A.; Galceran, J.; Nieto, M.A. A Gene Regulatory Network to Control EMT Programs in Development and Disease. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, F.S.; Culiersi, C.; Florido, A.; De Nadai, K.; Adamo, G.G.; Nasini, F.; Vivarelli, C.; Mura, M.; Parmeggiani, F. Genetic Features of Uveal Melanoma. Genes 2024, 15, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Shi, J.; Tang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Yao, X. Study on the Mechanism of S100A4-Mediated Cancer Oncogenesis in Uveal Melanoma Cells through the Integration of Bioinformatics and in Vitro Experiments. Gene 2024, 911, 148333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xiong, M.; Zhou, Q.; Ouyang, J. Construction of an Immune-Related Prognostic Model and Functional Analysis of CEBPB in Uveal Melanoma: A STROBE-Compliant Observational Study. Medicine 2025, 104, e42574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasanen, K.; Sriswasdi, S.; Valiga, A.; Tang, H.-Y.; Zhang, G.; Perego, M.; Somasundaram, R.; Li, L.; Speicher, K.; Klein-Szanto, A.J.; et al. Comparative Secretome Analysis of Epithelial and Mesenchymal Subpopulations of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Identifies S100A4 as a Potential Therapeutic Target*. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2013, 12, 3778–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, H.; Lai, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Miao, Z.; Rahman, S.U.; Zhang, H.; Qian, A.; Zhang, W. S100A10 Might Be a Novel Prognostic Biomarker for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Based on Bioinformatics Analysis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 149, 106000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decaestecker, C.; De Clercq, S.; Salmon, I. S100A4, a Key Factor in Glioblastoma Biology. Transl. Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 5360–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, K.-H.; Park, H.J.; George, J.; Yamamoto, K.; Gallup, A.D.; Graber, J.H.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, W.; Steindler, D.A.; Neilson, E.G.; et al. S100A4 Is a Biomarker and Regulator of Glioma Stem Cells That Is Critical for Mesenchymal Transition in Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5360–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inukai, M.; Yokoi, A.; Ishizuka, Y.; Hashimura, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Oguri, Y.; Nakagawa, M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Ito, T.; Kumabe, T.; et al. A Functional Role of S100A4/Non-Muscle Myosin IIA Axis for pro-Tumorigenic Vascular Functions in Glioblastoma. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.; Leu, J.-S.; Fan, X.; Leonard, F.; Faisal, M.; Kang, R.; Ali, Y.; Abdelfattah, N.; Zhang, N.; Yun, K. Abstract 6069: A Bispecific S100A4/TFR Antibody to Reprogram the GBM Tumor Microenvironment and Target GBM Stem Cells. Cancer Res. 2025, 85, 6069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Endo, Y.; Yonemura, Y.; Heizmann, C.W.; Schafer, B.W.; Watanabe, Y.; Sasaki, T. Clinical Significance of S100A4 and E-Cadherin-Related Adhesion Molecules in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2000, 16, 1125–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagimoto, A.; Tsutani, Y.; Kushitani, K.; Kambara, T.; Mimae, T.; Miyata, Y.; Takeshima, Y.; Okada, M. Usefulness of Serum S100A4 and Positron-Emission Tomography on Lung Cancer Accompanied by Interstitial Pneumonia. Thorac. Cancer 2023, 14, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, G.; Peng, M.; Li, C.; Lu, J.; Jiang, S.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Y. Exosome-Transmitted S100A4 Induces Immunosuppression and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Development by Activating STAT3. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2022, 210, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, A.N.; Thorat, R.; Dhadve, A.C.; De, A.; Rekhi, B.; Ray, P. IGF1R-A6 Integrin-S100A4 Network Governs the Organ-Specific Metastasis of Chemoresistant Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2022, 1868, 166282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, A.; Costa-Silva, B.; Shen, T.-L.; Rodrigues, G.; Hashimoto, A.; Tesic Mark, M.; Molina, H.; Kohsaka, S.; Di Giannatale, A.; Ceder, S.; et al. Tumour Exosome Integrins Determine Organotropic Metastasis. Nature 2015, 527, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruqui, T.; Khan, M.S.; Akhter, Y.; Khan, S.; Rafi, Z.; Saeed, M.; Han, I.; Choi, E.-H.; Yadav, D.K. RAGE Inhibitors for Targeted Therapy of Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-C.; Chen, K.-C.; Chang, G.-C.; Lin, H.; Wu, C.-C.; Kao, W.-H.; Teng, C.-L.J.; Hsu, S.-L.; Yang, T.-Y. RAGE Acts as an Oncogenic Role and Promotes the Metastasis of Human Lung Cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronowicka-Szydełko, A.; Kotyra, Ł.; Lewandowski, Ł.; Gamian, A.; Kustrzeba-Wójcicka, I. Role of Advanced Glycation End-Products and Other Ligands for AGE Receptors in Thyroid Cancer Progression. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medapati, M.R.; Dahlmann, M.; Ghavami, S.; Pathak, K.A.; Lucman, L.; Klonisch, T.; Hoang-Vu, C.; Stein, U.; Hombach-Klonisch, S. RAGE Mediates the Pro-Migratory Response of Extracellular S100A4 in Human Thyroid Cancer Cells. Thyroid 2015, 25, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herwig, N.; Belter, B.; Wolf, S.; Haase-Kohn, C.; Pietzsch, J. Interaction of Extracellular S100A4 with RAGE Prompts Prometastatic Activation of A375 Melanoma Cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, D.; Koziol, J.; ElShamy, W.M. Targeting AXL and RAGE to Prevent Geminin Overexpression-Induced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Gunst, S.J. S100A4 Is Secreted by Airway Smooth Muscle Tissues and Activates Inflammatory Signaling Pathways via Receptors for Advanced Glycation End Products. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2020, 319, L185–L195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Jung, S.; Kim, H.; Kwon, J.-O.; Song, M.-K.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.-H. The Role of S100A4 for Bone Metastasis in Prostate Cancer Cells. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.-Y.; Gray, J.M.; Holewinski, R.J.; Andresson, T.; So, J.Y.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; Hollander, M.C.; Yang, H.H.; Lee, M.; Kaplan, M.J.; et al. Apoptosis-Induced Nuclear Expulsion in Tumor Cells Drives S100a4-Mediated Metastatic Outgrowth through the RAGE Pathway. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Myrvang, H.K.; Dekker, L. V Annexin A2 Complexes with S100 Proteins: Structure, Function and Pharmacological Manipulation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 1664–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisz, J.; Uversky, V.N. Zooming into the Dark Side of Human Annexin-S100 Complexes: Dynamic Alliance of Flexible Partners. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, T.; Chen, G.; Liu, G.; Song, Q.; Li, G.; Xu, F.; Dong, X.; Yang, F.; et al. Annexin A Protein Family: Focusing on the Occurrence, Progression and Treatment of Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1141331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Fernández, L.; Menéndez, S.T.; Otero-Rosales, M.; Montoro-Jiménez, I.; Hermida-Prado, F.; García-Pedrero, J.M.; Álvarez-Teijeiro, S. Pathobiological Functions and Clinical Implications of Annexin Dysregulation in Human Cancers. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1009908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecsédi, P.; Kiss, B.; Gógl, G.; Radnai, L.; Buday, L.; Koprivanacz, K.; Liliom, K.; Leveles, I.; Vértessy, B.; Jeszenői, N.; et al. Regulation of the Equilibrium between Closed and Open Conformations of Annexin A2 by N-Terminal Phosphorylation and S100A4-Binding. Structure 2017, 25, 1195–1207.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecsédi, P.; Gógl, G.; Hóf, H.; Kiss, B.; Harmat, V.; Nyitray, L. Structure Determination of the Transactivation Domain of P53 in Complex with S100A4 Using Annexin A2 as a Crystallization Chaperone. Structure 2020, 28, 943–953.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriajevska, M.V.; Cardenas, M.N.; Grigorian, M.S.; Ambartsumian, N.S.; Georgiev, G.P.; Lukanidin, E.M. Non-Muscle Myosin Heavy Chain as a Possible Target for Protein Encoded by Metastasis-Related Mts-1 Gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 19679–19682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, P.R.; Irvine, A.F.; Jung, H.S.; Tozawa, K.; Pastok, M.W.; Picone, R.; Badyal, S.K.; Basran, J.; Rudland, P.S.; Barraclough, R.; et al. Asymmetric Mode of Ca2+-S100A4 Interaction with Nonmuscle Myosin IIA Generates Nanomolar Affinity Required for Filament Remodeling. Structure 2012, 20, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, H.L.; Silver, D.L.; Kachar, B.; Sellers, J.R.; Zain, S.B. Effect of Mts1 on the Structure and Activity of Nonmuscle Myosin II. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 16321–16327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, B.R.; O’Donnell, M.; Durkan, G.C.; Rudland, P.S.; Barraclough, R.; Neal, D.E.; Kilian Mellon, J. Expression of S100A4 Protein Is Associated with Metastasis and Reduced Survival in Human Bladder Cancer. J. Pathol. 2002, 196, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-H.; Spektor, A.; Varlamova, O.; Bresnick, A.R. Mts1 Regulates the Assembly of Nonmuscle Myosin-IIA. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 14258–14266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, B.; Duelli, A.; Radnai, L.; Kékesi, K.A.; Katona, G.; Nyitray, L. Crystal Structure of the S100A4–Nonmuscle Myosin IIA Tail Fragment Complex Reveals an Asymmetric Target Binding Mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6048–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramagopal, U.A.; Dulyaninova, N.G.; Varney, K.M.; Wilder, P.T.; Nallamsetty, S.; Brenowitz, M.; Weber, D.J.; Almo, S.C.; Bresnick, A.R. Structure of the S100A4/Myosin-IIA Complex. BMC Struct. Biol. 2013, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulyaninova, N.G.; Bresnick, A.R. The Heavy Chain Has Its Day. Bioarchitecture 2013, 3, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, G.; Fernig, D.G.; Rudland, P.S.; Webb, S.E.D.; Barraclough, R.; Martin-Fernandez, M. Interaction of Metastasis-Inducing S100A4 Protein in Vivo by Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy. Eur. Biophys. J. 2005, 34, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-H.; Bresnick, A.R. The S100A4 Metastasis Factor Regulates Cellular Motility via a Direct Interaction with Myosin-IIA. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5173–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tochimoto, M.; Oguri, Y.; Hashimura, M.; Konno, R.; Matsumoto, T.; Yokoi, A.; Kodera, Y.; Saegusa, M. S100A4/Non-Muscle Myosin II Signaling Regulates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness in Uterine Carcinosarcoma. Lab. Investig. 2020, 100, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiruta, A.; Oguri, Y.; Yokoi, A.; Matsumoto, T.; Oda, Y.; Tomohiro, M.; Hashimura, M.; Jiang, Z.; Tochimoto, M.; Nakagawa, M.; et al. S100A4/Nonmuscle Myosin IIA/P53 Axis Contributes to Aggressive Features in Ovarian High-Grade Serous Carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 2304–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Yu, C.; Li, F.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Ye, L. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Cancers and Targeted Therapies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Gao, Z.; Bao, Y.; Chen, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Q.; Wei, X. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Carcinogenesis and Cancer Therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 17, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Murkute, S.L.; Bhowmik, S.; Prasad, C.P.; Mohapatra, P. Belling the “Cat”: Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling and Its Significance in Future Cancer Therapies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Cancer 2024, 1879, 189195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, M.; Jiang, C.-H.; Li, N. Wnt Signaling in Cancer: From Biomarkers to Targeted Therapies and Clinical Translation. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niehrs, C. The Complex World of WNT Receptor Signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Yin, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; DiSanto, M.E.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X. S100A4 Modulates Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis and Fibrosis in the Hyperplastic Prostate. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2024, 169, 106551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, S.; Koran, S.; AlOmair, L. Insights Into the Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Cancer and Its Various Therapeutic Aspects: A Review. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 896099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Kweon, M.-H.; Johnson, J.J.; Adhami, V.M.; Elcheva, I.; Khan, N.; Bin Hafeez, B.; Bhat, K.M.R.; Sarfaraz, S.; Reagan-Shaw, S.; et al. S100A4 Accelerates Tumorigenesis and Invasion of Human Prostate Cancer through the Transcriptional Regulation of Matrix Metalloproteinase 9. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14825–14830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathisen, B.; Lindstad, R.I.; Hansen, J.; El-Gewely, S.A.; Maelandsmo, G.M.; Hovig, E.; Fodstad, Ø.; Loennechen, T.; Winberg, J.-O. S100A4 Regulates Membrane Induced Activation of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 in Osteosarcoma Cells. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2003, 20, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yammani, R.R.; Carlson, C.S.; Bresnick, A.R.; Loeser, R.F. Increase in Production of Matrix Metalloproteinase 13 by Human Articular Chondrocytes Due to Stimulation with S100A4: Role of the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2901–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furugaki, K.; Fujimura, T.; Mizuta, H.; Yoshimoto, T.; Asakawa, T.; Yoshimura, Y.; Yoshiura, S. FGFR Blockade Inhibits Targeted Therapy-Tolerant Persister in Basal FGFR1- and FGF2-High Cancers with Driver Oncogenes. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2023, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santolla, M.F.; Talia, M.; Maggiolini, M. S100A4 Is Involved in Stimulatory Effects Elicited by the FGF2/FGFR1 Signaling Pathway in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassin, O.; Oren, M. Drugging P53 in Cancer: One Protein, Many Targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, M.; Wei, H.; Chen, Y. Targeting P53 Pathways: Mechanisms, Structures and Advances in Therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orre, L.M.; Panizza, E.; Kaminskyy, V.O.; Vernet, E.; Gräslund, T.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Lehtiö, J. S100A4 Interacts with P53 in the Nucleus and Promotes P53 Degradation. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5531–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Chen, D.; Liu, S.; Chen, L.; Yu, A.; Fu, H.; Sun, X. S100A4 Interacts with Mutant P53 and Affects Gastric Cancer MKN1 Cell Autophagy and Differentiation. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 2123–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, Y.; Ikeda, S.; Kawabe, Y.; Oguri, Y.; Hashimura, M.; Yokoi, A.; Sida, A.; Fukagawa, N.; Hayashi, M.; Ono, M.; et al. S100A4 Contributes to Colorectal Carcinoma Aggressive Behavior and to Chemoradiotherapy Resistance in Locally Advanced Rectal Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 31338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derynck, R.; Turley, S.J.; Akhurst, R.J. TGFβ Biology in Cancer Progression and Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, A.B.; Rah, B.; Bhat, G.R.; Mushtaq, I.; Parveen, S.; Hassan, R.; Hameed Zargar, M.; Afroze, D. Transforming Growth Factor-Beta (TGF-β) Signaling in Cancer-A Betrayal Within. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 791272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yang, J.; Deng, S.; Xu, H.; Wu, D.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, S.; Hu, T.; Wu, F.; Zhou, H. TGF-β Signaling in the Tumor Metabolic Microenvironment and Targeted Therapies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Dong, H.; Lan, Y.; Bi, Y.; Gu, X.; Han, Y.; Yang, C.; Cheng, M.; Gao, J. Metformin Attenuates Fibroblast Activation during Pulmonary Fibrosis by Targeting S100A4 via AMPK-STAT3 Axis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1089812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-L.; Chen, H.-H.; Zheng, L.-L.; Sun, L.-P.; Shi, L. Angiogenic Signaling Pathways and Anti-Angiogenic Therapy for Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Osaki, M.; Yamagishi, M.; Onuma, K.; Ito, H.; Okada, F.; Endo, H. Correlation of Two Distinct Metastasis-Associated Proteins, MTA1 and S100A4, in Angiogenesis for Promoting Tumor Growth. Oncogene 2019, 38, 4715–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambartsumian, N.; Grigorian, M.; Lukanidin, E. Genetically Modified Mouse Models to Study the Role of Metastasis-Promoting S100A4(Mts1) Protein in Metastatic Mammary Cancer. J. Dairy. Res. 2005, 72, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hong, W.; Wei, X. The Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies of EMT in Tumor Progression and Metastasis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celià-Terrassa, T.; Kang, Y. How Important Is EMT for Cancer Metastasis? PLoS Biol. 2024, 22, e3002487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, G.; Aziz, S.G.-G.; Jaghi, N.Z.Z. EMT, Cancer Stem Cells and Autophagy; The Three Main Axes of Metastasis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Su, B.; Xie, C.; Wei, S.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Dai, W.; Cheng, P.; Wang, F.; Xu, X.; et al. Sonic Hedgehog-Gli1 Signaling Pathway Regulates the Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) by Mediating a New Target Gene, S100A4, in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X.; Guo, Y.; Huang, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Cai, L. S100A4 Suppresses Cancer Stem Cell Proliferation via Interaction with the IKK/NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, R.; Kang, L.; Han, J.-H.; Choi, J.-W.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, T.H.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, Y.S.; et al. Differential Expression of E-Cadherin, β-Catenin, and S100A4 in Intestinal Type and Nonintestinal Type Ampulla of Vater Cancers. Gut Liver 2014, 8, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shi, J.; Luo, Y.; Liao, Q.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Shao, Z.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, L. LIM and SH3 Protein 1 Induces TGFβ-Mediated Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Human Colorectal Cancer by Regulating S100A4 Expression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 5835–5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Liu, S.; Xin, X.; Cai, L.; Shi, R.; Chi, S.; Feng, D.; Wang, H. S100A4 Promotes Endometrial Cancer Progress through Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Regulation. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 3419–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Fan, Q. S100A4 Participates in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer via Targeting MMP2. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 2925–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, K.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Ni, C.; Zhai, W.; Liang, J.; Qin, Z.; et al. S100A4 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinogenesis by Intensifying Fibrosis-Associated Cancer Cell Stemness. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1725355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Han, F.; Du, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhou, W. Hypoxic Microenvironment in Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami Nejad, A.; Najafgholian, S.; Rostami, A.; Sistani, A.; Shojaeifar, S.; Esparvarinha, M.; Nedaeinia, R.; Haghjooy Javanmard, S.; Taherian, M.; Ahmadlou, M.; et al. The Role of Hypoxia in the Tumor Microenvironment and Development of Cancer Stem Cell: A Novel Approach to Developing Treatment. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Y.; Liu, K.; He, Q.; Gu, X.; Jiang, C.; Wu, J. Hypoxia Signaling in Cancer: Implications for Therapeutic Interventions. MedComm 2023, 4, e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Zhu, L.; Lei, N.; Wan, J.; Duan, X.; Liu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, M.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, H.; et al. S100A4-Dependent Glycolysis Promotes Lymphatic Vessel Sprouting in Tumor. Angiogenesis 2023, 26, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wan, D.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S.; Lin, S.; Qiao, Y. Extracellular Matrix and Its Therapeutic Potential for Cancer Treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Lee, B.; Jiang, Y. Extracellular Matrix in Cancer Progression and Therapy. Med. Rev. 2022, 2, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.J.; Ng, K.Y.; Bakhtiar, A. Extracellular Matrix: Unlocking New Avenues in Cancer Treatment. Biomark. Res. 2025, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, S. S100A4 a Classical DAMP as a Therapeutic Target in Fibrosis. Matrix Biol. 2024, 127, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louault, K.; Li, R.-R.; DeClerck, Y.A. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Understanding Their Heterogeneity. Cancers 2020, 12, 3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strutz, F.; Okada, H.; Lo, C.W.; Danoff, T.; Carone, R.L.; Tomaszewski, J.E.; Neilson, E.G. Identification and Characterization of a Fibroblast Marker: FSP1. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 130, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwano, M.; Plieth, D.; Danoff, T.M.; Xue, C.; Okada, H.; Neilson, E.G. Evidence That Fibroblasts Derive from Epithelium during Tissue Fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazakova, A.N.; Lukina, M.M.; Anufrieva, K.S.; Bekbaeva, I.V.; Ivanova, O.M.; Shnaider, P.V.; Slonov, A.; Arapidi, G.P.; Shender, V.O. Exploring the Diversity of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Insights into Mechanisms of Drug Resistance. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1403122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Liu, T.; Yin, R. Biomarkers for Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Biomark. Res. 2020, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nushtaeva, A.; Ermakov, M.; Abdurakhmanova, M.; Troitskaya, O.; Belovezhets, T.; Varlamov, M.; Gayner, T.; Richter, V.; Koval, O. “Pulsed Hypoxia” Gradually Reprograms Breast Cancer Fibroblasts into Pro-Tumorigenic Cells via Mesenchymal–Epithelial Transition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmick, N.A.; Chytil, A.; Plieth, D.; Gorska, A.E.; Dumont, N.; Shappell, S.; Washington, M.K.; Neilson, E.G.; Moses, H.L. TGF-ß Signaling in Fibroblasts Modulates the Oncogenic Potential of Adjacent Epithelia. Science 2004, 303, 848–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, H.; Mundel, T.M.; Kieran, M.W.; Kalluri, R. Identification of Fibroblast Heterogeneity in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2006, 5, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, J.T.; Sugimoto, H.; Cooke, V.G.; MacDonald, B.A.; Mehta, A.I.; LeBleu, V.S.; Dewar, R.; Rocha, R.M.; Brentani, R.R.; Resnick, M.B.; et al. VEGF-A and Tenascin-C Produced by S100A4+ Stromal Cells Are Important for Metastatic Colonization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16002–16007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Geng, Y.-H.; Yang, H.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Y.-T.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Tian, X.-X.; Fang, W.-G. Extracellular ATP Drives Breast Cancer Cell Migration and Metastasis via S100A4 Production by Cancer Cells and Fibroblasts. Cancer Lett. 2018, 430, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, M.; Pan, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.; Jin, Y.; Shao, C. Expression Pattern of Cancer-Associated Fibroblast and Its Clinical Relevance in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 65, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; González, Á.; Stevenson, H.L.; Gagea, M.; Sugimoto, H.; Kalluri, R.; Beretta, L. Depletion of S100A4+ Stromal Cells Does Not Prevent HCC Development but Reduces the Stem Cell-like Phenotype of the Tumors. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, e422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, A.; Kieffer, Y.; Scholer-Dahirel, A.; Pelon, F.; Bourachot, B.; Cardon, M.; Sirven, P.; Magagna, I.; Fuhrmann, L.; Bernard, C.; et al. Fibroblast Heterogeneity and Immunosuppressive Environment in Human Breast Cancer. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 463–479.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Hao, H. The Importance of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Targeted Therapies and Drug Resistance in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1333839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelon, F.; Bourachot, B.; Kieffer, Y.; Magagna, I.; Mermet-Meillon, F.; Bonnet, I.; Costa, A.; Givel, A.-M.; Attieh, Y.; Barbazan, J.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Heterogeneity in Axillary Lymph Nodes Drives Metastases in Breast Cancer through Complementary Mechanisms. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradovic, A.; Graves, D.; Korrer, M.; Wang, Y.; Roy, S.; Naveed, A.; Xu, Y.; Luginbuhl, A.; Curry, J.; Gibson, M.; et al. Immunostimulatory Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subpopulations Can Predict Immunotherapy Response in Head and Neck Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 2094–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbois, M.; Wang, Y. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Key Players in Shaping the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Immunol. Rev. 2021, 302, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givel, A.-M.; Kieffer, Y.; Scholer-Dahirel, A.; Sirven, P.; Cardon, M.; Pelon, F.; Magagna, I.; Gentric, G.; Costa, A.; Bonneau, C.; et al. MiR200-Regulated CXCL12β Promotes Fibroblast Heterogeneity and Immunosuppression in Ovarian Cancers. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, G.; Levi-Galibov, O.; David, E.; Bornstein, C.; Giladi, A.; Dadiani, M.; Mayo, A.; Halperin, C.; Pevsner-Fischer, M.; Lavon, H.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Compositions Change with Breast Cancer Progression Linking the Ratio of S100A4(+) and PDPN(+) CAFs to Clinical Outcome. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 692–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grum-Schwensen, B.; Klingelhöfer, J.; Beck, M.; Bonefeld, C.M.; Hamerlik, P.; Guldberg, P.; Grigorian, M.; Lukanidin, E.; Ambartsumian, N. S100A4-Neutralizing Antibody Suppresses Spontaneous Tumor Progression, Pre-Metastatic Niche Formation and Alters T-Cell Polarization Balance. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhao, T.; Li, R.; Han, M. Macrophage-Secreted S100A4 Supports Breast Cancer Metastasis by Remodeling the Extracellular Matrix in the Premetastatic Niche. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 9895504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bian, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Yao, X.; Wan, J.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; et al. S100A4 Enhances Protumor Macrophage Polarization by Control of PPAR-γ-Dependent Induction of Fatty Acid Oxidation. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Deng, Z.; Li, H. Single-Cell Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Key Genes Associated with Macrophage Polarization in Liver Cancer. Hepatol. Commun. 2023, 7, e0304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakova, E.; Rakina, M.; Sudarskikh, T.; Iamshchikov, P.; Tarasova, A.; Tashireva, L.; Afanasiev, S.; Dobrodeev, A.; Zhuikova, L.; Cherdyntseva, N.; et al. Angiogenesis Regulators S100A4, SPARC and SPP1 Correlate with Macrophage Infiltration and Are Prognostic Biomarkers in Colon and Rectal Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1058337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulton, A.; Murai, J.; Qian, D.; Thakkar, K.; Lewis, C.E.; Litchfield, K. Using a Pan-Cancer Atlas to Investigate Tumour Associated Macrophages as Regulators of Immunotherapy Response. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Mao, S.; Song, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Bu, H.; et al. S100a4(+) Alveolar Macrophages Accelerate the Progression of Precancerous Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia by Promoting the Angiogenic Function Regulated by Fatty Acid Metabolism. eLife 2025, 13, RP101731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenbacher, J.L.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Jahrsdörfer, B.; Kaltenmeier, C.; Rojewski, M.T.; Yildiz, T.; Beyer, T.; Erle, A.; Wiegmann, D.S.; Grassl, S.; et al. S100A4 and Uric Acid Promote Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Induction of IL-10+/IDO+ Lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 6102–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheiter, M.; Lau, U.; van Ham, M.; Bulitta, B.; Gröbe, L.; Garritsen, H.; Klawonn, F.; König, S.; Jänsch, L. Proteome Analysis of Distinct Developmental Stages of Human Natural Killer (NK) Cells. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 1099–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, A.; Lami, A.; Alhumaidi, A.; Madkhali, A.; Althaqib, A.; Aljarwan, N.; Alkharras, R. Blastic Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Neoplasm: A Case Report. Cureus 2023, 15, e37016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melsen, J.E.; van Ostaijen-ten Dam, M.M.; Schoorl, D.J.A.; Schol, P.J.; van den Homberg, D.A.L.; Lankester, A.C.; Lugthart, G.; Schilham, M.W. Single-Cell Transcriptomics in Bone Marrow Delineates CD56dimGranzymeK+ Subset as Intermediate Stage in NK Cell Differentiation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1044398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urlaub, D.; Höfer, K.; Müller, M.-L.; Watzl, C. LFA-1 Activation in NK Cells and Their Subsets: Influence of Receptors, Maturation, and Cytokine Stimulation. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1944–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebuffet, L.; Melsen, J.E.; Escalière, B.; Basurto-Lozada, D.; Bhandoola, A.; Björkström, N.K.; Bryceson, Y.T.; Castriconi, R.; Cichocki, F.; Colonna, M.; et al. High-Dimensional Single-Cell Analysis of Human Natural Killer Cell Heterogeneity. Nat. Immunol. 2024, 25, 1474–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Dai, C.; Xue, R.; Wang, P.; Chen, L.; Han, Y.; Erben, U.; Qin, Z. S100A4 Protects Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells from Intrinsic Apoptosis via TLR4–ERK1/2 Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfattah, N.; Kumar, P.; Wang, C.; Leu, J.-S.; Flynn, W.F.; Gao, R.; Baskin, D.S.; Pichumani, K.; Ijare, O.B.; Wood, S.L.; et al. Single-Cell Analysis of Human Glioma and Immune Cells Identifies S100A4 as an Immunotherapy Target. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, C.; Bai, J.; Li, Y.; Duan, J.; Fan, D.; Fu, W.; Liang, X.; et al. S100A4 Mediates the Accumulation and Functions of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells via GP130/JAK2/STAT3 Signaling in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2025, 1871, 167498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, Z.Z. Expression and Function of S100A4 in B-Cell Lymphomas. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Leicester, Leicester, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.-B.; Holmgren, J.; Larena, M.; Terrinoni, M.; Fang, Y.; Bresnick, A.R.; Xiang, Z. Deficiency in Calcium-Binding Protein S100A4 Impairs the Adjuvant Action of Cholera Toxin. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen Chaudhuri, A.; Yeh, Y.-W.; Zewdie, O.; Li, N.S.; Sun, J.-B.; Jin, T.; Wei, B.; Holmgren, J.; Xiang, Z. S100A4 Exerts Robust Mucosal Adjuvant Activity for Co-Administered Antigens in Mice. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 1028–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotfi, R.; Wiegmann, D.S.; Asseck, L.; Erle, A.; Yildiz, T.; Jahrsdörfer, B.; Schrezenmeier, H. Necrosis-Associated Factors (DAMPs) Including S100A4 Used to Pulse Dendritic Cells (DCs) Induce Regulatory T Cells. J. Cell Sci. Ther. 2012, 3, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Qin, Z. Extracellular S100A4 as a Key Player in Fibrotic Diseases. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 5973–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, Y.; Iwanaga, Y.; Niizuma, S.; Kawashima, T.; Kato, T.; Inuzuka, Y.; Horie, T.; Morooka, H.; Takase, T.; Akahashi, Y.; et al. Metastasis-Associated Protein, S100A4 Mediates Cardiac Fibrosis Potentially through the Modulation of P53 in Cardiac Fibroblasts. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2013, 57, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ošlejšková, L.; Grigorian, M.; Gay, S.; Neidhart, M.; Šenolt, L. The Metastasis Associated Protein S100A4: A Potential Novel Link to Inflammation and Consequent Aggressive Behaviour of Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šenolt, L.; Cerezo, L.A.; Šumová, B.; Pecha, O.; Pleštilová, L.; Forejtová, Š.; Růžičková, O.; Hušáková, M.; Závada, J.; Pavelka, K.; et al. High Levels of Metastasis-Inducing S100A4 Protein and Treatment Outcome in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: Data from the PERAC Cohort. Biomarkers 2015, 20, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingelhöfer, J.; Šenolt, L.; Baslund, B.; Nielsen, G.H.; Skibshøj, I.; Pavelka, K.; Neidhart, M.; Gay, S.; Ambartsumian, N.; Hansen, B.S.; et al. Up-Regulation of Metastasis-Promoting S100A4 (Mts-1) in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Putative Involvement in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šenolt, L.; Grigorian, M.; Lukanidin, E.; Simmen, B.; Michel, B.A.; Pavelka, K.; Gay, R.E.; Gay, S.; Neidhart, M. S100A4 Is Expressed at Site of Invasion in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovium and Modulates Production of Matrix Metalloproteinases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 1645–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlandsson, M.C.; Forslind, K.; Andersson, S.E.M.; Lund, A.; Bokarewa, M.I. Metastasin S100A4 Is Increased in Proportion to Radiographic Damage in Patients with RA. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, K.J.; Loeser, R.F.; Yammani, R.R. Sumoylation and Nuclear Translocation of S100A4 Regulate IL-1β-Mediated Production of Matrix Metalloproteinase-13*. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 31517–31524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Österreicher, C.H.; Penz-Österreicher, M.; Grivennikov, S.I.; Guma, M.; Koltsova, E.K.; Datz, C.; Sasik, R.; Hardiman, G.; Karin, M.; Brenner, D.A. Fibroblast-Specific Protein 1 Identifies an Inflammatory Subpopulation of Macrophages in the Liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Dai, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, Z.; Guo, H.; Wang, R.; Lu, S.; et al. S100A4 Promotes Liver Fibrosis via Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bao, J.; Bian, Y.; Erben, U.; Wang, P.; Song, K.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Gao, Z.; Qin, Z. S100A4+ Macrophages Are Necessary for Pulmonary Fibrosis by Activating Lung Fibroblasts. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ohno, S.; Steer, B.; Klee, S.; Staab-Weijnitz, C.A.; Wagner, D.; Lehmann, M.; Stoeger, T.; Königshoff, M.; Adler, H. S100a4 Is Secreted by Alternatively Activated Alveolar Macrophages and Promotes Activation of Lung Fibroblasts in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, W.E.; Polosukhin, V.V.; Zoia, O.; Stathopoulos, G.T.; Han, W.; Plieth, D.; Loyd, J.E.; Neilson, E.G.; Blackwell, T.S. Characterization of Fibroblast-Specific Protein 1 in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Gilbertsen, A.; Herrera, J.; Racila, E.; Smith, K.; Peterson, M.; Griffin, T.; Benyumov, A.; Yang, L.; Bitterman, P.B.; et al. Calcium-Binding Protein S100A4 Confers Mesenchymal Progenitor Cell Fibrogenicity in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 2586–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh-Minh, T.; Györfi, A.-H.; Tomcik, M.; Tran-Manh, C.; Zhou, X.; Dickel, N.; Tümerdem, B.S.; Kreuter, A.; Burmann, S.-N.; Borchert, S.V.; et al. Effect of Anti-S100A4 Monoclonal Antibody Treatment on Experimental Skin Fibrosis and Systemic Sclerosis-Specific Transcriptional Signatures in Human Skin. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Švec, X.; Štorkánová, H.; Trinh-Minh, T.; Tran, M.C.; Štorkánová, L.; Hulejová, H.; Oreská, S.; Heřmánková, B.; Bečvář, R.; Pavelka, K.; et al. S100A4-Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody 6B12 Counteracts the Established Experimental Skin Fibrosis Induced by Bleomycin. Rheumatology 2024, 63, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malashkevich, V.N.; Dulyaninova, N.G.; Ramagopal, U.A.; Liriano, M.A.; Varney, K.M.; Knight, D.; Brenowitz, M.; Weber, D.J.; Almo, S.C.; Bresnick, A.R. Phenothiazines Inhibit S100A4 Function by Inducing Protein Oligomerization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8605–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, S.C.; Hodgson, L.; Rybin, A.; Toutchkine, A.; Hahn, K.M.; Lawrence, D.S.; Bresnick, A.R. A Biosensor of S100A4 Metastasis Factor Activation: Inhibitor Screening and Cellular Activation Dynamics. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sack, U.; Walther, W.; Scudiero, D.; Selby, M.; Kobelt, D.; Lemm, M.; Fichtner, I.; Schlag, P.M.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Stein, U. Novel Effect of Antihelminthic Niclosamide on S100A4-Mediated Metastatic Progression in Colon Cancer. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 1018–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortüm, B.; Radhakrishnan, H.; Zincke, F.; Sachse, C.; Burock, S.; Keilholz, U.; Dahlmann, M.; Walther, W.; Dittmar, G.; Kobelt, D.; et al. Combinatorial Treatment with Statins and Niclosamide Prevents CRC Dissemination by Unhinging the MACC1-β-Catenin-S100A4 Axis of Metastasis. Oncogene 2022, 41, 4446–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, K.; Grotterød, I.; Aasheim, H.-C.; Hovig, E.; Mælandsmo, G.M. Activation of NF-ΚB by Extracellular S100A4: Analysis of Signal Transduction Mechanisms and Identification of Target Genes. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.L.; Carpenter, B.L.; West, D.S.; Knifley, T.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.; Weiss, H.L.; Gal, T.S.; Durbin, E.B.; Arnold, S.M.; et al. S100A4 Drives Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Invasion, Associates with Poor Prognosis, and Is Effectively Targeted by the FDA-Approved Anti-Helminthic Agent Niclosamide. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 34630–34642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burock, S.; Daum, S.; Keilholz, U.; Neumann, K.; Walther, W.; Stein, U. Phase II Trial to Investigate the Safety and Efficacy of Orally Applied Niclosamide in Patients with Metachronous or Sychronous Metastases of a Colorectal Cancer Progressing after Therapy: The NIKOLO Trial. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, U.; Arlt, F.; Smith, J.; Sack, U.; Herrmann, P.; Walther, W.; Lemm, M.; Fichtner, I.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Schlag, P.M. Intervening in β-Catenin Signaling by Sulindac Inhibits S100A4-Dependent Colon Cancer Metastasis. Neoplasia 2011, 13, 131–144, IN7–IN8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, T.; Ramachandran, V.; Gomez, S.B.; Schmidt, A.M.; Logsdon, C.D. S100P-Derived RAGE Antagonistic Peptide Reduces Tumor Growth and Metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4356–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, T.M.; Crick, R.G.; Du, M.; Shivkumar, U.; Carnell, A.; Barraclough, R.; Wang, G.; Cheng, Z.; Yu, W.; Platt-Higgins, A.; et al. Targeted Destruction of S100A4 Inhibits Metastasis of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailly, C. The Potential Value of Amlexanox in the Treatment of Cancer: Molecular Targets and Therapeutic Perspectives. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 197, 114895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganaie, A.A.; Mansini, A.P.; Hussain, T.; Rao, A.; Siddique, H.R.; Shabaneh, A.; Ferrari, M.G.; Murugan, P.; Klingelhöfer, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Anti-S100A4 Antibody Therapy Is Efficient in Treating Aggressive Prostate Cancer and Reversing Immunosuppression: Serum and Biopsy S100A4 as a Clinical Predictor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 2598–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochiya, T.; Takenaga, K.; Endo, H. Silencing of S100A4, a Metastasis-Associated Protein, in Endothelial Cells Inhibits Tumor Angiogenesis and Growth. Angiogenesis 2014, 17, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katte, R.H.; Chou, R.-H.; Yu, C. Pentamidine Inhibit S100A4-P53 Interaction and Decreases Cell Proliferation Activity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 691, 108442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katte, R.H.; Dowarha, D.; Chou, R.-H.; Yu, C. S100P Interacts with P53 While Pentamidine Inhibits This Interaction. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fares, J.; Fares, M.Y.; Khachfe, H.H.; Salhab, H.A.; Fares, Y. Molecular Principles of Metastasis: A Hallmark of Cancer Revisited. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Tao, L.; Qiu, J.; Xu, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, X.; Guan, X.; Cen, X.; Zhao, Y. Tumor Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Targeted Therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlDoughaim, M.; AlSuhebany, N.; AlZahrani, M.; AlQahtani, T.; AlGhamdi, S.; Badreldin, H.; Al Alshaykh, H. Cancer Biomarkers and Precision Oncology: A Review of Recent Trends and Innovations. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2024, 18, 11795549241298540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, A.; Al Bakir, M.; Hamilton, E.G.; Diehn, M.; André, F.; Roy-Chowdhuri, S.; Mountzios, G.; Wistuba, I.I.; Swanton, C.; Peters, S. Cancer Biomarkers: Emerging Trends and Clinical Implications for Personalized Treatment. Cell 2024, 187, 1617–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, K.; Mælandsmo, G.M. S100A4 and Metastasis: A Small Actor Playing Many Roles. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destek, S.; Gul, V.O. S100A4 May Be a Good Prognostic Marker and a Therapeutic Target for Colon Cancer. J. Oncol. 2018, 2018, 1828791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyina, A.; Leonteva, A.; Berezutskaya, E.; Abdurakhmanova, M.; Ermakov, M.; Mishinov, S.; Kuligina, E.; Vladimirov, S.; Bogachek, M.; Richter, V.; et al. Exploring the Heterogeneity of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts via Development of Patient-Derived Cell Culture of Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bogachek, M.; Kazakova, A.; Sergeevichev, D.; Vladimirov, S.; Richter, V.; Nushtaeva, A. S100A4/FSP1: A Prognostic Marker and a Promising Target for Antitumor Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9370. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199370
Bogachek M, Kazakova A, Sergeevichev D, Vladimirov S, Richter V, Nushtaeva A. S100A4/FSP1: A Prognostic Marker and a Promising Target for Antitumor Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9370. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199370
Chicago/Turabian StyleBogachek, Maria, Alina Kazakova, David Sergeevichev, Sergey Vladimirov, Vladimir Richter, and Anna Nushtaeva. 2025. "S100A4/FSP1: A Prognostic Marker and a Promising Target for Antitumor Therapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9370. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199370
APA StyleBogachek, M., Kazakova, A., Sergeevichev, D., Vladimirov, S., Richter, V., & Nushtaeva, A. (2025). S100A4/FSP1: A Prognostic Marker and a Promising Target for Antitumor Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9370. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199370







