Placental Dysfunction Is Associated with Dysregulated Fibrinolytic System Activation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of Patients
2.2. Thromboelastographic Analysis
2.3. Coagulation Markers
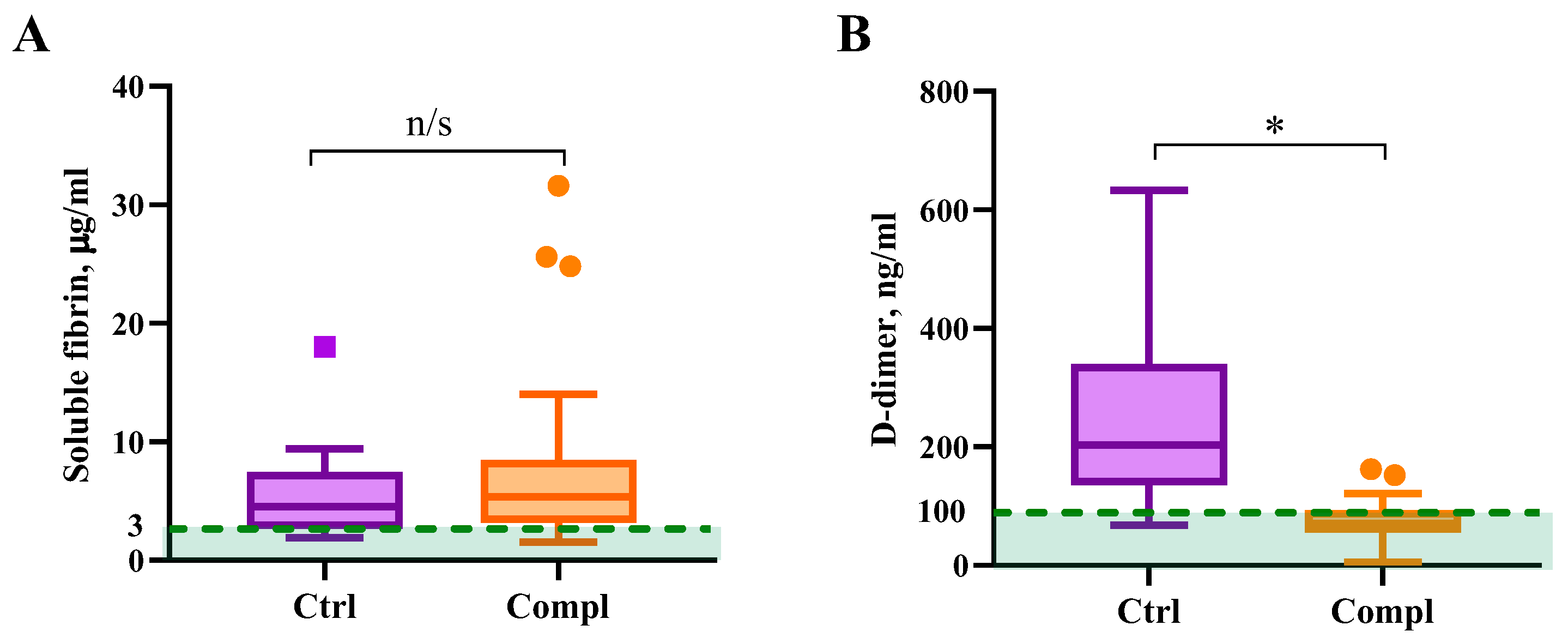
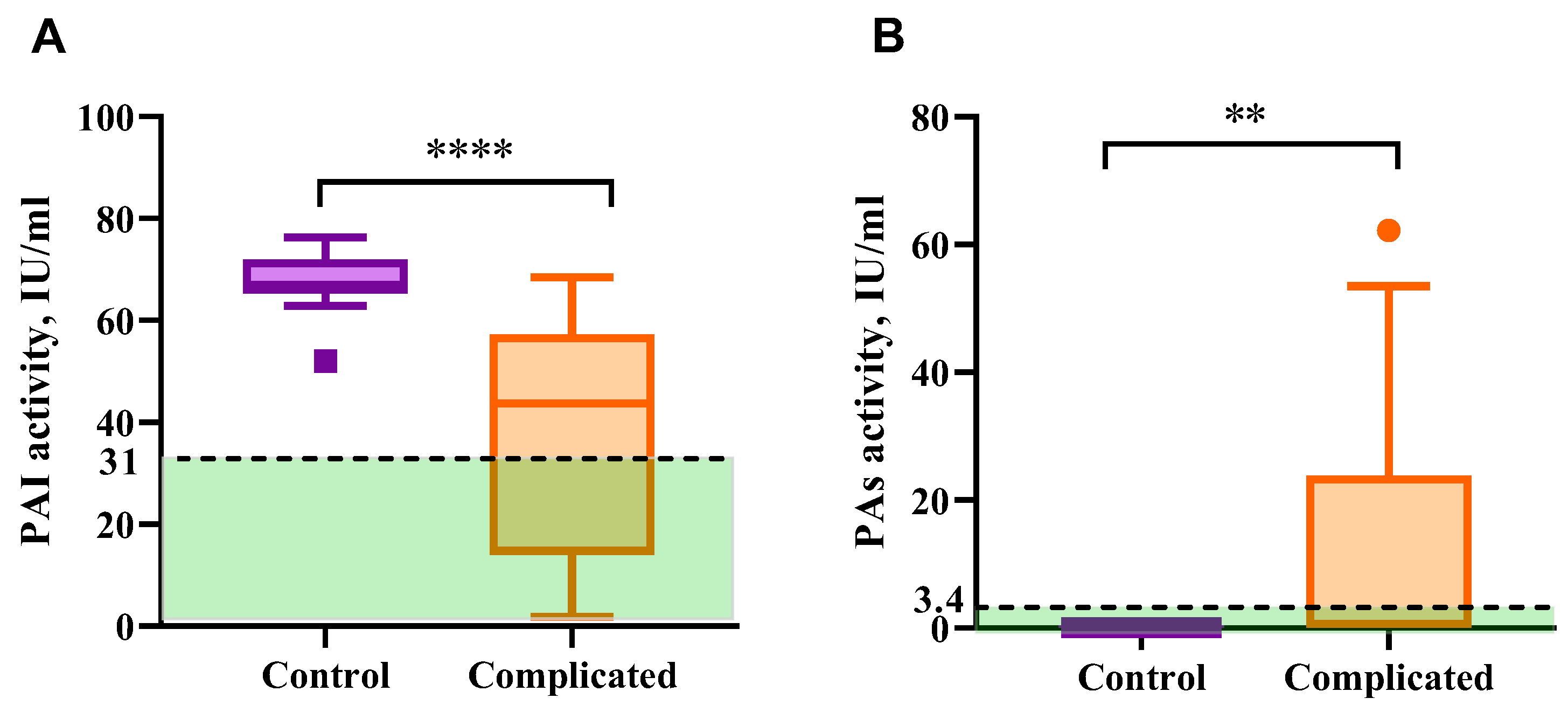
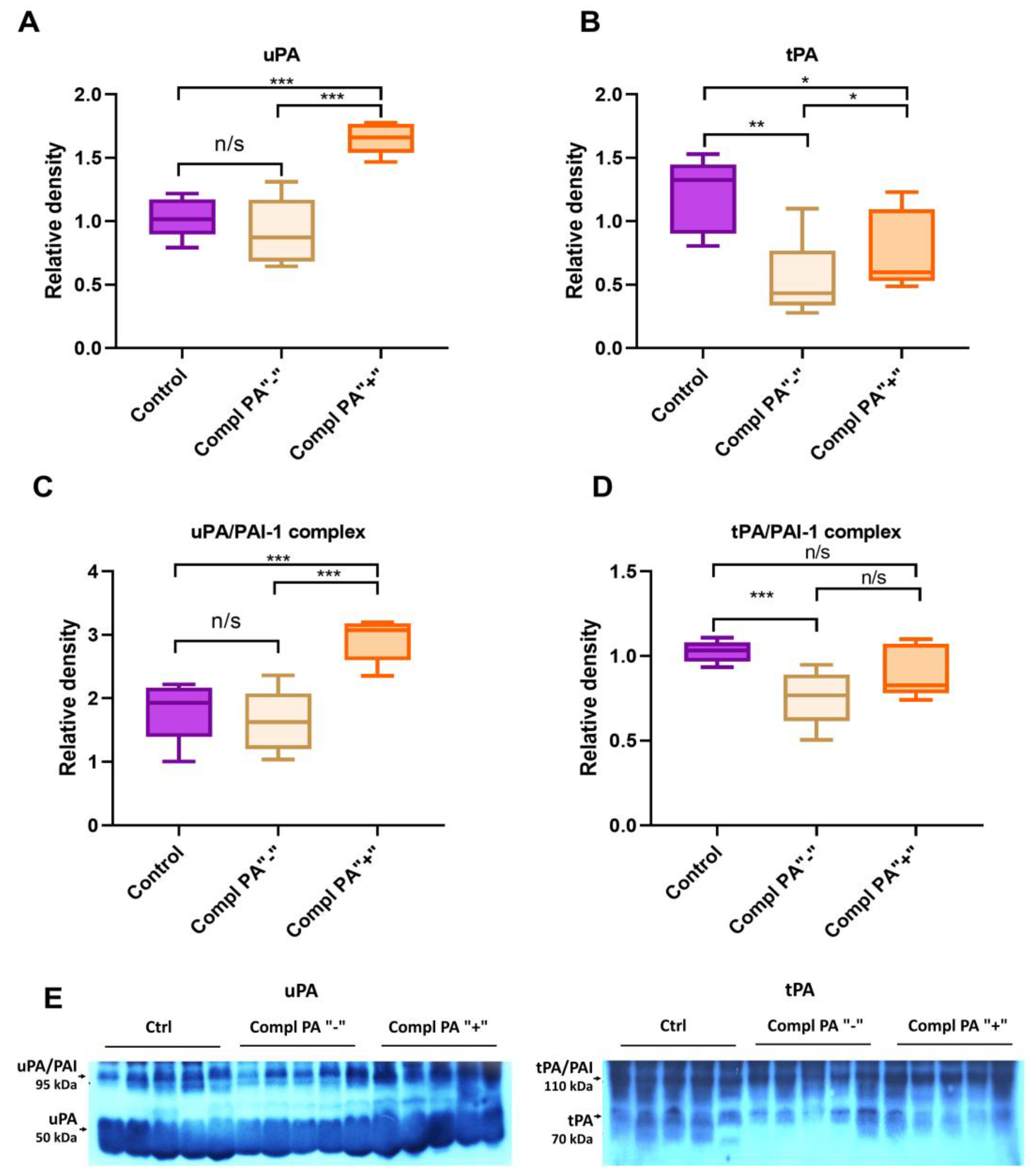
2.4. Fibrinolytic System Markers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Patient Groups
4.2. Blood Sample Collection and Plasma Preparation
4.3. Methods
4.3.1. Thromboelastography
4.3.2. Fibrinogen Assay
4.3.3. Protein C Assay
4.3.4. Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time Assay
4.3.5. Prothrombin Time Assay
4.3.6. Platelet Aggregation Measurement and Platelet Count
4.3.7. Soluble Fibrin Assay
4.3.8. D-Dimer Measurement
4.3.9. PAI and PA Activity Assay
4.3.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.3.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PAI | Plasminogen activator inhibitor |
| PA | Plasminogen activator |
| tPA | Tissue-type plasminogen activator |
| uPA | Urokinase-type plasminogen activator |
| aPTT | Activated partial thromboplastin time |
| PT | Prothrombin time |
| ROTEM | Rotational thromboelastography |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunoassay |
| TBS | Tris-buffered saline |
| ECL | Enhanced chemiluminescence |
References
- Hellgren, M. Hemostasis during Normal Pregnancy and Puerperium. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2003, 29, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolev, K.; Longstaff, C. Basic Mechanisms and Regulation of Fibrinolysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, S98–S105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szecsi, P.; Jørgensen, M.; Klajnbard, A.; Andersen, M.; Colov, N.; Stender, S. Haemostatic Reference Intervals in Pregnancy. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 103, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchini, M. Haemostasis and Pregnancy. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 95, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.-Y.; Liu, Y.-X.; Liu, K.; Byrne, S.; Ny, T.; Feng, Q.; Ockledorf, C.D. Expression of Tissue Type and Urokinase Type Plasminogen Activators as Well as Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor Type-1 and Type-2 in Human and Rhesus Monkey Placenta. J. Anat. 1999, 194, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardinger, J.; Ambati, S. Placental Insufficiency; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kornacki, J.; Gutaj, P.; Kalantarova, A.; Sibiak, R.; Jankowski, M.; Wender-Ozegowska, E. Endothelial Dysfunction in Pregnancy Complications. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saksela, O. Plasminogen Activation and Regulation of Pericellular Proteolysis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 1985, 823, 35–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görlinger, K.; Dirkmann, D.; Hanke, A.A. Rotational Thromboelastometry (ROTEM®). In Trauma Induced Coagulopathy; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzeraland, 2016; pp. 267–298. [Google Scholar]
- Us, I.; Zhuk, S.; Korolova, D.; Platonov, O.; Tsaryk, Y. Platelet Hemostasis in the Implementation of Placental Dysfunction. Reprod. Health Woman 2022, 6, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauthier, L.; Favresse, J.; Hardy, M.; Douxfils, J.; Le Gal, G.; Roy, P.M.; van Es, N.; Ay, C.; ten Cate, H.; Lecompte, T.; et al. D-Dimer Testing: A Narrative Review. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2023, 114, 151–223. [Google Scholar]
- Korolova, D.; Shevchuk, O.; Kostiuchenko, O.; Chernyshenko, T.; Klymenko, K.; Platonova, T.; Ivankiv, Y.; Palii, S.; Pak, A.; Chernyshenko, V.; et al. Hematological Findings in Post-COVID-19 Recovery Period: Three-Month Follow-Up Study. SSRN Electron. J. 2022, 4234239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugovskoy, E.; Gritsenko, P.; Kolesnikova, I.; Zolotarova, E.; Chernishov, V.; Nieuwenhuizen, W.; Komisarenko, S. Two Monoclonal Antibodies to D-Dimer-Specific Inhibitors of Fibrin Polymerization. Thromb. Res. 2004, 113, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaai, M.; Riley, P.; Mardovina, T.; Bell, P. The Clinical Significance of Fibrin Monomers. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 1856–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, K.; Muranishi, K.; Kawano, Y.; Hatomoto, H.; Yamasaki, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Ishikura, H. Soluble Fibrin Is a Useful Marker for Predicting Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Circuit Exchange Because of Circuit Clots. J. Artif. Organs 2018, 21, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.-S.; Lee, A.; Spencer, F.A.; Chunilal, S.; Crowther, M.; Wu, W.; Johnston, M.; Rodger, M.; Ginsberg, J.S. D-Dimer Testing in Pregnant Patients: Towards Determining the next ‘Level’ in the Diagnosis of Deep Vein Thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbassi-Ghanavati, M.; Greer, L.G.; Cunningham, F.G. Pregnancy and Laboratory Studies. Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 114, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xie, S.-B.; Wu, C.-H.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.; Fan, Y.-G.; Leng, R.-X.; Pan, H.-F.; Xiong, H.-B.; et al. Coagulation Cascade and Complement System in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 14862–14881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udovenko, A.; Makogonenko, Y.; Korolova, D.; Druzhyna, N.; Chernyshenko, V.; Komisarenko, S. Formation and Elimination of Soluble Fibrin and D-Dimer in the Bloodstream. Croat. Med. J. 2023, 64, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severens-Rijvers, C.A.H.; Al-Nasiry, S.; Vincken, A.; Haenen, G.; Winkens, B.; Ghossein-Doha, C.; Spaanderman, M.A.E.; Peeters, L.L.H. Early-Pregnancy Circulating Antioxidant Capacity and Hemodynamic Adaptation in Recurrent Placental Syndrome: An Exploratory Study. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2019, 84, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagana, K.D.; Pagana, T.J. Mosby’s Manual of Diagnostic and Laboratory Tests, 6th ed.; Elsevier Inc.: St Louis, MO, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-0-323-44663-1. [Google Scholar]
- Chmielewska, J.; Rånby, M.; Wiman, B. Evidence for a Rapid Inhibitor to Tissue Plasminogen Activator in Plasma. Thromb. Res. 1983, 31, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglés-Cano, E.; Boutière, B.; Arnoux, D.; Masson, C.; Contant, G.; Benchimol, P.; Sampol, J. Release Pattern of the Vascular Plasminogen Activator and Its Inbibitor in Human Postvenous Occlusion Plasma as Assessed by a Spectrophotometric Solid-Phase Fibrin-TPA Activity Assay. Thromb. Haemost. 1987, 58, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saes, J.L.; Schols, S.E.M.; van Heerde, W.L.; Nijziel, M.R. Hemorrhagic Disorders of Fibrinolysis: A Clinical Review. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolova, D.; Pavlenko, A.; Altorjay, A.; Zhuk, S.; Us, I.; Tsaryk, Y.; Suranyi, A.; Chernyshenko, V. Validation of the Diagnostics Algorithm to Monitor Coagulation Parameters in Pregnant Women. Ukr. Biochem. J. 2023, 95, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanjung, M.T.; Siddik, H.D.; Hariman, H.; Koh, S.C.L. Coagulation and Fibrinolysis in Preeclampsia and Neonates. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2005, 11, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, K.; Byrne, S.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Ockleford, C.D. Expression of Urokinase, Plasminogen Activator Inhibitors and Urokinase Receptor in Pregnant Rhesus Monkey Uterus During Early Placentation. Placenta 2000, 21, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, M.J. Embryo Implantation—Coordination of Maternal and Embryonic Adaptations. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2014, 58, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, P.; Black, S.; Huppertz, B. Endovascular Trophoblast Invasion: Implications for the Pathogenesis of Intrauterine Growth Retardation and Preeclampsia. Biol. Reprod. 2003, 69, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roes, E.M.; Sweep, C.G.F.; Thomas, C.M.; Zusterzeel, P.L.; Geurts-Moespot, A.; Peters, W.H.; Steegers, E.A. Levels of Plasminogen Activators and Their Inhibitors in Maternal and Umbilical Cord Plasma in Severe Preeclampsia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2002, 187, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzein, H.O.; Muddathir, A.R.M.; Rida, M.; Rayis, D.A.; Elhassan, E.M.; Adam, I. Fibrinolysis Parameters in Sudanese Women with Severe Preeclampsia. Hypertens. Pregnancy 2016, 35, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X. The Role of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 in Gynecological and Obstetrical Diseases: An Update Review. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2022, 150, 103490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Vattai, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Thaler, C.J.; Mahner, S.; Jeschke, U.; von Schönfeldt, V. Role of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor Type 1 in Pathologies of Female Reproductive Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Riordan, M.N.; Higgins, J.R. Haemostasis in Normal and Abnormal Pregnancy. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2003, 17, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, H.; Takashima, E.; Soma, M.; Murakami, M.; Maeda, Y.; Kasakura, S.; Takada, A.; Takada, Y. Source of Increased Plasminogen Activators during Pregnancy and Puerperium. Thromb. Res. 1989, 54, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coolman, M.; de Groot, C.J.M.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Geurts-Moespot, A.; Thomas, C.M.G.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M.; Sweep, F.C.G.J. Concentrations of Plasminogen Activators and Their Inhibitors in Blood Preconceptionally, during and after Pregnancy. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2006, 128, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoppelli, M.P. The Plasminogen Activation System in Cell Invasion. In Madame Curie Bioscience Database; Landes Bioscience: Austin, TX, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Uszyński, M.; Perlik, M.; Uszyński, W.; Żekanowska, E. Urokinase Plasminogen Activator (UPA) and Its Receptor (UPAR) in Gestational Tissues. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2004, 114, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korolova, D.; Parkhomenko, A.; Chernyshenko, V.; Chernyshenko, T.; Druzhyna, N.; Hornytska, O.; Platonova, T. Decrease of Prothrombin Level during Thrombolysis in Acute Myocardium Infarction. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2023, 70, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshan, T.M.; Stein, N.; Jiang, X.Y. Comparison of Clot-Based and Chromogenic Assay for the Determination of Protein c Activity. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2019, 30, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugovska, N.E.; Kolesnikova, I.M.; Stohnii, Y.M.; Chernyshenko, V.O.; Rebriev, A.V.; Kostiuchenko, O.P.; Gogolinska, G.K.; Dziubliuk, N.A.; Varbanets, L.D.; Platonova, T.M.; et al. Novel Monoclonal Antibody to Fibrin(Ogen) AC-Region for Detection of the Earliest Forms of Soluble Fibrin. Ukr. Biochem. J. 2020, 92, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolova, D.; Syrko, M.; Stohnii, Y.; Druzhyna, N.; Chernyshenko, T.; Gogolinska, G. Standardization of the Protein Calibrators Isolation Methodology for Thrombophilia Markers Detecting Immunodiagnostic Test Systems. Biotechnol. Acta 2022, 15, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuryata, O.; Sirenko, O.; Tykhomyrov, A.; Yatsenko, T. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 and Circulating Ceruloplasmin Levels in Men with Iron-Deficiency Anemia and Heart Failure with Concomitant Prostate Cancer and Their Dynamics after Treatment. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 42, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsenko, T.A.; Kharchenko, S.M. Polyclonal Antibodies against Human Plasminogen: Purification, Characterization and Application. Biotechnol. Acta 2020, 13, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ågren, A.; Kolmert, T.; Wiman, B.; Schulman, S. Low PAI-1 Activity in Relation to the Risk for Perioperative Bleeding Complications in Transurethral Resection of the Prostate. Thromb. Res. 2007, 119, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.; Befus, D.; O’Hashi, P.; Hart, F.; Schunk, M.; Fletch, A.; Griffin, G. CCAC Guidelines on: Antibody Production; Canadian Council on Animal Care: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2002; ISBN 0-919087-37-X. [Google Scholar]

| Control (n = 12) | Complicated (n = 32) | |
|---|---|---|
| Maternal Characteristics | ||
| Age at delivery (years), mean ± SD (range) | 31.3 ± 2.7 (29–35) | 32.0 ± 6.3 (18–45) |
| BMI | 20.4 ± 2.3 (17–23) | 23.6 ± 4.0 (18–31) |
| Chronic hypertension, n (%) | 0 | 1/32 (3.13%) |
| Tobacco smoking, n (%) | 0 | 1/32 (3.13%) |
| History of preeclampsia, n (%) | 0 | 2/32 (6.26%) |
| Nulliparous, n (%) | 1/12 (8.3%) | 12/32 (37.5%) |
| Pregnancy characteristics | ||
| Gestational age at admission, mean ± SD (range) | 32.9 ± 6.1 (24–40) | 30.7 ± 9 (12–38) |
| Gestational hypertension, n (%) | 0 | 2/32 (6.25%) |
| Preeclampsia, n (%) | 0 | 4/32 (12.5%) |
| Retrochorionic hematoma, n (%) | 0 | 1/32 (3.13%) |
| Delivery characteristics | ||
| Gestational age at the delivery, mean ± SD (range) | 37.4 ± 2.4 (30–40) | 37.4 ± 2.1 (29–41) |
| Cesarean section, n (%) | 1/12 (8.3%) | 7/32 (28.7%) |
| Vacuum extraction delivery, n (%) | 1/12 (8.3%) | 2/32 (6.25%) |
| Parameter | Control (n = 12) | Complicated (n = 32) |
|---|---|---|
| Fibrinogen, mg/mL | 3.7 ± 0.7 (2.6–4.8) * | 4.7 ± 0.9 (3.2–6.7) * |
| PT INR | 0.93 ± 0.10 (0.77–1.00) | 1.09 ± 0.11 (0.78–1.43) |
| APTT, sec | 31 ± 4 (26–35) | 30 ± 4 (25–40) |
| Protein C, % | 86.3 ± 16.0 (68.0–110.0) | 86.6 ± 13.0 (65.0–120.0) |
| Platelet count, ×109/L | 217 ± 83 (125–348) | 227 ± 55 (154–400) |
| Rate of ADP-induced platelet aggregation, % | 37 ± 9 (23–52) * | 47 ± 14 (20–80) * |
| Lag-phase of collagen-induced platelet aggregation, sec | 192 ± 74 (65–300) | 163 ± 87 (40–360) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yatsenko, T.; Us, I.; Korolova, D.; Zhuk, S.; Dziuba, H.; Nalbat, A.; Kharchenko, S.; Vari, S.G.; Chernyshenko, V. Placental Dysfunction Is Associated with Dysregulated Fibrinolytic System Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9339. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199339
Yatsenko T, Us I, Korolova D, Zhuk S, Dziuba H, Nalbat A, Kharchenko S, Vari SG, Chernyshenko V. Placental Dysfunction Is Associated with Dysregulated Fibrinolytic System Activation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9339. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199339
Chicago/Turabian StyleYatsenko, Tetiana, Iryna Us, Daria Korolova, Svitlana Zhuk, Halyna Dziuba, Alona Nalbat, Svitlana Kharchenko, Sandor George Vari, and Volodymyr Chernyshenko. 2025. "Placental Dysfunction Is Associated with Dysregulated Fibrinolytic System Activation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9339. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199339
APA StyleYatsenko, T., Us, I., Korolova, D., Zhuk, S., Dziuba, H., Nalbat, A., Kharchenko, S., Vari, S. G., & Chernyshenko, V. (2025). Placental Dysfunction Is Associated with Dysregulated Fibrinolytic System Activation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9339. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199339










