Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNA 00511 (LINC00511) Genetic Variations and Haplotypes in Breast Cancer: A Case-Controlled Study and Bioinformatics Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. In Silico Search and Bioinformatics Analysis Results (Accessed on 21 April 2025)
2.1.1. Differential Gene Expression (DGE) Analysis Results in BRCA (Figure 1a)
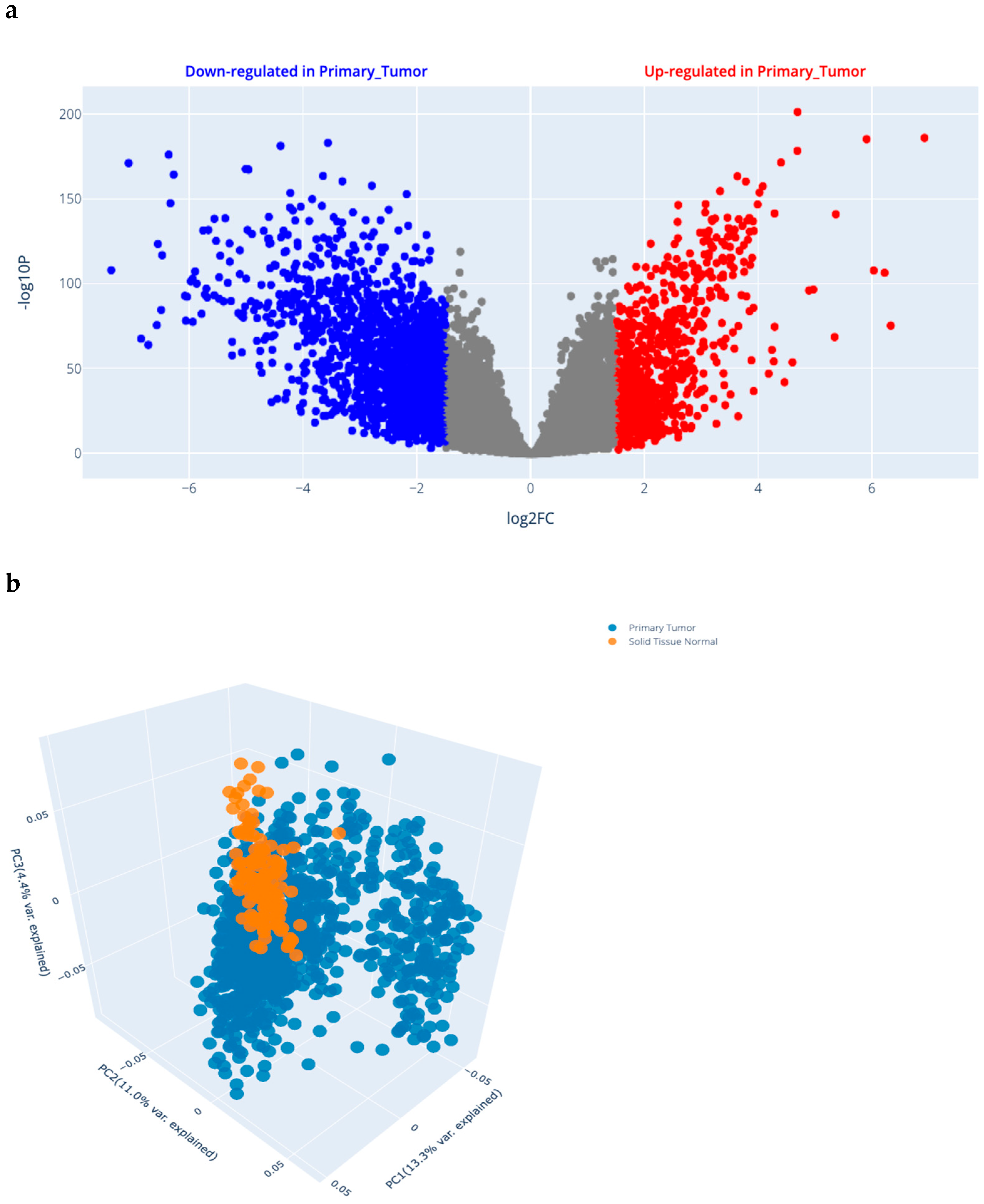
2.1.2. Selected SNP Criteria
2.2. Participants Demographic and Clinical Data
2.3. The Association Between LINC00511 SNPs and BC Susceptibility Using Different Genetic Models
2.4. Alleles Frequencies of the Five SNPs in All the Study Subjects and Their Association with BC
2.5. Stratification Analysis of the Relationship Between LINC00511 SNPs and BC Susceptibility Using Different Genetic Models
2.5.1. Stratification Analysis of the Relationship Between LINC00511 SNPs and BC Susceptibility Using the Codominant Model
2.5.2. Stratification Analysis of the Relationship Between LINC00511 SNPs and BC Susceptibility Using the Dominant Model
2.5.3. Stratification Analysis of the Relationship Between LINC00511 SNPs and BC Susceptibility Using the Recessive Model
2.5.4. Stratification Analysis of the Relationship Between LINC00511 SNPs and BC Susceptibility Using the Over-Dominant Model
2.6. The Associations of LINC00511 SNPs with ER, PR, and HER-2 Status of BC Patients
2.7. The Association Between LINC00511 SNPs and Tumor Stage
2.8. The Association Between LINC00511 SNPs and Lymph Node Metastasis
2.9. The Association Between LINC00511 SNPs and Tumor Grade
2.10. The Association Between BC Molecular Subtypes and LINC00511 SNPs, Relative to Controls
2.11. The Association Between LINC00511 SNPs and BC Molecular Subtypes “TNBC and Triple Positive BC”
2.12. The Association Between LINC00511 SNPs and BC Molecular Subtypes “Luminal B and Non-Luminal B BC”
2.13. Haplotype Analysis of the Five SNPs in LINC00511
2.14. Multifactor Dimensionality Reduction (MDR) Using a Three-Way Split Internal Validation Approach
2.15. Post Hoc Epistasis Analysis After MDR Model Fit with a Three-Way Split
2.16. Linkage Disequilibrium and Pairwise Correlation Coefficient
2.16.1. Population’s Linkage Disequilibrium
2.16.2. Testing for Linkage Disequilibrium and Pairwise Correlation Coefficient with Haplotypes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Size and Power of the Study
4.2. Study Design
4.3. Study Participants
4.3.1. Patient Group
Patients’ Inclusion Criteria
Patients’ Exclusion Criteria
Patients Pathological and Clinical Data
4.3.2. Control Group
4.4. In Silico Search and Bioinformatics Analysis
4.4.1. Differential Gene Expression of Different Genes from Online Datasets in BC
4.4.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4.5. LINC00511
4.6. SNP Selection
4.7. Blood Samples
4.8. Routine Biochemical Testing
4.9. DNA Extraction from Whole Blood
4.10. Quantitation of Purified DNA
4.11. SNPs Genotyping
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| BC | Breast Cancer |
| BIRADS | Breast-Imaging Reporting and Data System |
| bp | Base Pair |
| CA15-3 | Cancer Antigen 15-3 |
| CEA | Carcinoembryonic Antigen |
| ceRNA | Competing Endogenous RNA |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| dbSNP | SNP Database |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| E2F1 | E2F Transcription Factor 1 |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid |
| ER | Estrogen Receptor |
| HER-2 | Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 |
| IGSR | International Genome Sample Resource |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| LINC00511 | Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNA 00511 |
| LincRNAs | Long intergenic non-coding RNAs |
| LncRNAs | Long non-coding RNAs |
| LNM | Lymph Node Metastasis |
| MAF | Minor Allele Frequency |
| miR | micro-RNA |
| MDR | Multifactor Dimensionality Reduction |
| MMP13 | Matrix Metallopeptidase 13 |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| mRNAs | Messenger RNAs |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology information |
| NCI | National Cancer Institute |
| NIH | National Institutes of Health |
| ncRNAs | Non-coding RNAs |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| PR | Progesterone Receptor |
| qPCR | Quantitative Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| RNA | Ribonucleic Acid |
| SNPs | Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| TNBC | Triple-Negative BC |
| TNM | Tumor–Node–Metastasis |
| UV-Vis | Ultraviolet–Visible |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Laversanne, M.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Tomorrow. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/tomorrow/ (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Edition, S. Breast Cancer Metastasis and Drug Resistance; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; ISBN 9783030203009. [Google Scholar]
- Smolarz, B.; Zadrożna Nowak, A.; Romanowicz, H. Breast Cancer—Epidemiology, Classification, Pathogenesis and Treatment (Review of Literature). Cancers 2022, 14, 2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.-F.; Huang, K.-C.; Chen, H.-Y.; Hamdy, N.M.; Huang, T.-C.; Chang, H.-Y.; Shieh, T.-M.; Huang, Y.-J.; Hsia, S.-M. Hinokitiol Inhibits Breast Cancer Cells In Vitro Stemness-Progression and Self-Renewal with Apoptosis and Autophagy Modulation via the CD44/Nanog/SOX2/Oct4 Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Newman, L.A.; Freedman, R.A.; Smith, R.A.; Star, J.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Breast Cancer Statistics 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 477–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, N.M.; Zaki, M.B.; Abdelmaksoud, N.M.; Ismail, R.A.; Abd-Elmawla, M.A.; Rizk, N.I.; Fathi, D.; Abulsoud, A.I. Insights into the Genetic and Epigenetic Mechanisms Governing X-Chromosome-Linked-MiRNAs Expression in Cancer; a Step-toward NcRNA Precision. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 289, 138773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, F.H.; Sanad, E.F.; Elghazaly, H.; Hsia, S.M.; Hamdy, N.M. PiR-823 Tale as Emerging Cancer-Hallmark Molecular Marker in Different Cancer Types: A Step-toward NcRNA-Precision. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 398, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammad, R.; Eldosoky, M.A.; Lambert, C.; Sack, U.; Kujumdshiev, S.; Abd Elhamed, S.S.; Elfishawi, S.; Mohamed, E.F.; Kandeel, E.Z.; Lotfy, A.W.; et al. Hsa-MiR-21-5p Reflects Synovitis and Tenosynovitis Components of Musculoskeletal Ultrasonography Seven-Joint Scores in Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease and Predicts the Disease Flare. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2024, 253, 154960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattick, J.S.; Amaral, P.P.; Carninci, P.; Carpenter, S.; Chang, H.Y.; Chen, L.-L.; Chen, R.; Dean, C.; Dinger, M.E.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; et al. Long Non-Coding RNAs: Definitions, Functions, Challenges and Recommendations. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nukala, S.B.; Jousma, J.; Cho, Y.; Lee, W.H.; Ong, S.G. Long Non-Coding RNAs and MicroRNAs as Crucial Regulators in Cardio-Oncology. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wen, L.; Zhu, H. Unveiling the Hidden Function of Long Non-Coding RNA by Identifying Its Major Partner-Protein. Cell Biosci. 2015, 5, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Shi, L.; Luo, Z. Long Non-Coding RNAs in Cancer: Implications for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapy. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 612393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, N.I.; Kassem, D.H.; Abulsoud, A.I.; AbdelHalim, S.; Yasser, M.B.; Kamal, M.M.; Hamdy, N.M. Revealing the Role of Serum Exosomal Novel Long Non-Coding RNA NAMPT-AS as a Promising Diagnostic/Prognostic Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Life Sci. 2024, 352, 122850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, N.M.; Zaki, M.B.; Rizk, N.I.; Abdelmaksoud, N.M.; Abd-Elmawla, M.A.; Ismail, R.A.; Abulsoud, A.I. Unraveling the NcRNA Landscape That Governs Colorectal Cancer: A Roadmap to Personalized Therapeutics. Life Sci. 2024, 354, 122946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, R.; Aglan, R.B.; Mohammed, S.A.; Awad, E.A.-E.; Elsaid, M.A.; Bedair, H.M.; Khirala, S.K.; Selim, M.A.; Abo Elqasem, A.A.; Rushdi, A.; et al. Cytotoxic T Cell Expression of Leukocyte-Associated Immunoglobulin-Like Receptor-1 (LAIR-1) in Viral Hepatitis C-Mediated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, N.M.; Basalious, E.B.; El-Sisi, M.G.; Nasr, M.; Kabel, A.M.; Nossier, E.S.; Abadi, A.H. Advancements in Current One-Size-Fits-All Therapies Compared to Future Treatment Innovations for Better Improved Chemotherapeutic Outcomes: A Step-toward Personalized Medicine. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2024, 40, 1943–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolov, D.; Sharda, N.; Banerjee, A.; Denisenko, K.; Basalious, E.B.; Shukla, H.; Waddell, J.; Hamdy, N.M.; Banerjee, A. Differential Signaling Pathways in Medulloblastoma: Nano-Biomedicine Targeting Non-Coding Epigenetics to Improve Current and Future Therapeutics. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2024, 30, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atta, H.; Alzahaby, N.; Hamdy, N.M.; Emam, S.H.; Sonousi, A.; Ziko, L. New trends in synthetic drugs and natural products targeting 20S proteasomes in cancers. Bioorganic Chem. 2023, 133, 106427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mesallamy, H.O.; Hamdy, N.M.; Zaghloul, A.S.; Sallam, A.M. Serum retinol binding protein-4 and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin are interrelated in pancreatic cancer patients. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2012, 72, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, S.M.; Hamdy, N.M.; Hegab, H.M.; El-Mesallamy, H.O. Beclin-1 and Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Genes Expression: Potential Biomarkers in Acute Leukemia Patients. Cancer Biomark. 2016, 16, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, D.; Sun, G.; Wu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, G.; Jiang, W.; Li, X.; Zhong, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhang, C.; et al. Epigenetics: Roles and Therapeutic Implications of Non-Coding RNA Modifications in Human Cancers. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 25, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Gonzalez, E.A.; Rameshwar, P.; Etchegaray, J.-P. Non-Coding RNAs as Mediators of Epigenetic Changes in Malignancies. Cancers 2020, 12, 3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, N.; Mohammad Abadi, M.; Baghizadeh, A. ISSR Markers for Assessing DNA Polymorphism and Genetic Characterization of Cattle, Goat and Sheep Populations. Iran. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 9, 222–229. [Google Scholar]
- Barazandeh, A.; Mohammadabadi, M.R.; Ghaderi-Zefrehei, M.; Nezamabadi-pour, H. Genome-Wide Analysis of CpG Islands in Some Livestock Genomes and Their Relationship with Genomic Features. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 61, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri Roudbar, M.; Mohammadabadi, M.R.; Ayatollahi Mehrgardi, A.; Abdollahi-Arpanahi, R.; Momen, M.; Morota, G.; Brito Lopes, F.; Gianola, D.; Rosa, G.J.M. Integration of Single Nucleotide Variants and Whole-Genome DNA Methylation Profiles for Classification of Rheumatoid Arthritis Cases from Controls. Heredity 2020, 124, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, M.; Mozafari, M.R.; Ghaemi, S.; Ashengroph, M.; Hasanzadeh Davarani, F.; Mohammadabadi, M. Interaction of Epigallocatechin Gallate and Quercetin with Spike Glycoprotein (S-Glycoprotein) of SARS-CoV-2: In Silico Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarpour, F.; Mohammadabadi, M.R.; Zaidul, I.S.M.; Maherani, B.; Saari, N.; Hamid, A.A.; Abas, F.; Manap, M.Y.A.; Mozafari, M.R. Use of Prebiotics in Oral Delivery of Bioactive Compounds: A Nanotechnology Perspective. Pharmazie 2011, 66, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabiri, A.; Toroghi, R.; Mohammadabadi, M.; Tabatabaeizadeh, S.-E. Introduction of a Newcastle Disease Virus Challenge Strain (Sub-Genotype VII.1.1) Isolated in Iran. Vet. Res. Forum 2023, 14, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, B.M.; Shahin, M.H.; Solayman, M.H.; Langaee, T.; Schaalan, M.F.; Gong, Y.; Hammad, L.N.; Al-Mesallamy, H.O.; Hamdy, N.M.; El-Hammday, W.A.; et al. Genetic and Nongenetic Factors Affecting Clopidogrel Response in the Egyptian Population. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2016, 9, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fattah, Y.K.A.; Abulsoud, A.I.; AbdelHamid, S.G.; AbdelHalim, S.; Hamdy, N.M. CCDC144NL-AS1/hsa-miR-143-3p/HMGA2 interaction: In-silico and clinically implicated in CRC progression, correlated to tumor stage and size in case-controlled study; step toward ncRNA precision. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253 Pt 2, 126739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordbar, F.; Mohammadabadi, M.; Jensen, J.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, L. Identification of Candidate Genes Regulating Carcass Depth and Hind Leg Circumference in Simmental Beef Cattle Using Illumina Bovine Beadchip and Next-Generation Sequencing Analyses. Animals 2022, 12, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Koganti, P.P.; Yao, J. Systematic Identification of Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNAs Expressed in Bovine Oocytes. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2020, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plewka, P.; Raczynska, K.D. Long Intergenic Noncoding RNAs Affect Biological Pathways Underlying Autoimmune and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 5785–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.M.; Sanad, E.F.; Elshimy, R.A.A.; Hamdy, N.M. Competitive Endogenous Role of the LINC00511/MiR-185-3p Axis and MiR-301a-3p From Liquid Biopsy as Molecular Markers for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 749753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldash, S.; Sanad, E.F.; Nada, D.; Hamdy, N.M. The Intergenic Type LncRNA (LINC RNA) Faces in Cancer with In Silico Scope and a Directed Lens to LINC00511: A Step toward NcRNA Precision. Non-Coding RNA 2023, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Qin, Q.; Zhao, L.; Huang, Q.; Luo, Z.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA LINC00511 Contributes to Breast Cancer Tumourigenesis and Stemness by Inducing the MiR-185-3p/E2F1/Nanog Axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.H.; Cheng, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, R.; Li, S.; Hong, X. Long Non-Coding RNA LINC00511/MiR-150/MMP13 Axis Promotes Breast Cancer Proliferation, Migration and Invasion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 165957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Zhou, H.; Fan, H.; Yuan, Y. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Cancer Susceptibility. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 110635–110649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Børsting, C.; Pereira, V.; Andersen, J.D.; Morling, N. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism. In Wiley Encyclopedia of Forensic Science; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–18. ISBN 9780470061589. [Google Scholar]
- Bahreini, F.; Rayzan, E.; Rezaei, N. MicroRNA-Related Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Breast Cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboouf, M.A.; Hamdy, N.M.; Amin, A.I.; El-Mesallamy, H.O. Genotype Screening of APLN Rs3115757 Variant in Egyptian Women Population Reveals an Association with Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 109, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, P.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, L.; Guo, X.; Hao, Z.; Wang, X.; Ye, Y. Association of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) with Gastric Cancer Susceptibility and Prognosis in Population in Wuwei, Gansu, China. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 20, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.; Clements, J.A.; Batra, J. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Clinics: Fantasy or Reality for Cancer? Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2016, 53, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Mesallamy, H.O.; Rashed, W.M.; Hamdy, N.M.; Hamdy, N. High-Dose Methotrexate in Egyptian Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: The Impact of ABCG2 C421A Genetic Polymorphism on Plasma Levels, What Is Next? J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 140, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swellam, M.; Hamdy, N. Association of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with a Single Nucleotide Polymorphism on the Gene Encoding Leptin Receptor. IUBMB Life 2012, 64, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minotti, L.; Agnoletto, C.; Baldassari, F.; Corrà, F.; Volinia, S. SNPs and Somatic Mutation on Long Non-Coding RNA: New Frontier in the Cancer Studies? High-Throughput 2018, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei Chong, F.; Jing Cao, J.; Li Wang, Y.; Yu Sun, Q.; Meng Song, M.; Ru Jiang, X.; Juan Wang, K.; Ping Xu, L.; Hua Song, C. The Association between LINC00511 Variants and Breast Cancer Susceptibility among the Han Chinese Population. J. Nutr. Oncol. 2020, 5, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCBI-dbSNP SNP; Rs11657109, Rs17780195, Rs9906859, Rs4432291, Rs1558535. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/snp/ (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- Ensemble Human Variant; Rs11657109, Rs17780195, Rs9906859, Rs4432291, Rs1558535. Available online: https://www.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Variation/Explore?db=core;r=17:72624475-72625475;v=rs11657109;vdb=variation;vf=959746270 (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- National Institutes of Health. LDpair Tool. Available online: https://ldlink.nih.gov/?tab=ldpair (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Azim, H.A.; Elghazawy, H.; Ghazy, R.M.; Abdelaziz, A.H.; Abdelsalam, M.; Elzorkany, A.; Kassem, L. Clinicopathologic Features of Breast Cancer in Egypt—Contemporary Profile and Future Needs: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2023, 9, e2200387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behravan, H.; Hartikainen, J.M.; Tengström, M.; Kosma, V.-M.; Mannermaa, A. Predicting Breast Cancer Risk Using Interacting Genetic and Demographic Factors and Machine Learning. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, N.; Dutton, B.; Weng, S.; Sheehan, C.; Chorley, W.; Robertson, J.F.R.; Kendrick, D.; Kai, J. Improving Primary Care Identification of Familial Breast Cancer Risk Using Proactive Invitation and Decision Support. Fam. Cancer 2021, 20, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, V.; Rama, P.; Mohammed, S.; John, S.; Sivakumar, V.; Rodrigues, P.A. Association of Reproductive Risk Factors and Comorbidities among Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer in a Tertiary Care Hospital. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 58, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Omeogu, C.; Karanth, S.; Joshi, A.; Meernik, C.; Wilson, L.; Clark, A.; Deveaux, A.; He, C.; Johnson, T.; et al. Association of Reproductive Risk Factors and Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heer, E.; Harper, A.; Escandor, N.; Sung, H.; McCormack, V.; Fidler-Benaoudia, M.M. Global Burden and Trends in Premenopausal and Postmenopausal Breast Cancer: A Population-Based Study. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e1027–e1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellingjord-Dale, M.; Vos, L.; Tretli, S.; Hofvind, S.; Dos-Santos-Silva, I.; Ursin, G. Parity, Hormones and Breast Cancer Subtypes—Results from a Large Nested Case-Control Study in a National Screening Program. Breast Cancer Res. 2017, 19, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simbar, M.; Nazarpour, S.; KhodaKarami, N.; Nasiri, Z.; Rashidi Fakari, F.; Kiani, Z.; Keyvanfar, S.; Alavi Majd, H. A Situation Analysis on Postmenopausal Women’s Self-Care Needs and Priorities in Tehran: A Population-Based Study. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabat, G.C.; Kim, M.; Phipps, A.I.; Li, C.I.; Messina, C.R.; Wactawski-Wende, J.; Kuller, L.; Simon, M.S.; Yasmeen, S.; Wassertheil-Smoller, S.; et al. Smoking and Alcohol Consumption in Relation to Risk of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer in a Cohort of Postmenopausal Women. Cancer Causes Control 2011, 22, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millikan, R.C.; Newman, B.; Tse, C.-K.; Moorman, P.G.; Conway, K.; Dressler, L.G.; Smith, L.V.; Labbok, M.H.; Geradts, J.; Bensen, J.T.; et al. Epidemiology of Basal-like Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 109, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute. Reproductive History and Cancer Risk. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/hormones/reproductive-history-fact-sheet (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- Barnard, M.E.; Boeke, C.E.; Tamimi, R.M. Established Breast Cancer Risk Factors and Risk of Intrinsic Tumor Subtypes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Rev. Cancer 2015, 1856, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, A.I.; Buist, D.S.M.; Malone, K.E.; Barlow, W.E.; Porter, P.L.; Kerlikowske, K.; Li, C.I. Reproductive History and Risk of Three Breast Cancer Subtypes Defined by Three Biomarkers. Cancer Causes Control 2011, 22, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sukhun, S.; Tbaishat, F.; Hammad, N. Breast Cancer Priorities in Limited-Resource Environments: The Price-Efficacy Dilemma in Cancer Care. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. B 2022, 42, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Ursin, G.; Xu, X.; Lee, E.; Togawa, K.; Duan, L.; Lu, Y.; Malone, K.E.; Marchbanks, P.A.; McDonald, J.A.; et al. Reproductive Factors and the Risk of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer in White Women and African-American Women: A Pooled Analysis. Breast Cancer Res. 2017, 19, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youness, R.A.; Hassan, H.A.; Abaza, T.; Hady, A.A.; El Magdoub, H.M.; Ali, M.; Vogel, J.; Thiersch, M.; Gassmann, M.; Hamdy, N.M.; et al. A Comprehensive Insight and In Silico Analysis of CircRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Step toward NcRNA-Based Precision Medicine. Cells 2024, 13, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, N.M.; El-Sisi, M.G.; Ibrahim, S.M.; ElNokoudy, H.; Hady, A.A.; Abd-Ellatef, G.E.F.; Sallam, A.-A.M.; Barakat, B.M. In Silico Analysis and Comprehensive Review of Circular-RNA Regulatory Roles in Breast Diseases; a Step-toward Non-Coding RNA Precision. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2024, 263, 155651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, N.M.; Zaki, M.B.; Abdelmaksoud, N.M.; Elshaer, S.S.; Abd-Elmawla, M.A.; Rizk, N.I.; Fathi, D.; Doghish, A.S.; Abulsoud, A.I. Comprehensive Insights and In Silico Analysis into the Emerging Role of LincRNAs in Lung Diseases Pathogenesis; a Step toward NcRNA Precision. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2025, 25, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Safarzadeh, A.; Hussen, B.M.; Taheri, M.; Ayatollahi, S.A. A Review on the Role of LINC00511 in Cancer. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1116445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Feng, N.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Zhang, F.; Qian, Y.; Gao, M.; Yu, H.; Zhou, B.; Qian, B. SNPs in LncRNA Genes Are Associated with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in a Chinese Population. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kumar, S. Effect of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms on the Structure of Long Noncoding RNAs and Their Interaction with RNA Binding Proteins. Biosystems 2023, 233, 105021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhu, B.; Xu, L.; Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhou, P.; Gao, H.; Guo, P.; Chen, Y.; Gao, X.; et al. Genomic Prediction Using LD-Based Haplotypes Inferred From High-Density Chip and Imputed Sequence Variants in Chinese Simmental Beef Cattle. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Ma, Y.; Huang, Z. Advanced Stratification Analyses in Molecular Association Meta-Analysis: Methodology and Application. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2020, 20, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Wang, L.; Xuan, Y.; Zhai, Z. Identification of Genes and Pathways Associated with Menopausal Status in Breast Cancer Patients Using Two Algorithms. BMC Womens. Health 2024, 24, 665382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.R.; Hong, C.-C.; Edge, S.B.; Yao, S.; Bshara, W.; Higgins, M.J.; Freudenheim, J.L.; Ambrosone, C.B. Case-Only Analyses of the Associations between Polymorphisms in the Metastasis-Modifying Genes BRMS1 and SIPA1 and Breast Tumor Characteristics, Lymph Node Metastasis, and Survival. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 139, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstein, B.S. Identification of SNPs Associated with Susceptibility for Development of Adverse Reactions to Radiotherapy. Pharmacogenomics 2011, 12, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanchbury, J.S.; Pederson, H.J. An Apparent Quandary: Adoption of Polygenics and Gene Panels for Personalised Breast Cancer Risk Stratification. BJC Rep. 2023, 1, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orrantia-Borunda, E.; Anchondo-Nuñez, P.; Acuña-Aguilar, L.E.; Gómez-Valles, F.O.; Ramírez-Valdespino, C.A. Subtypes of Breast Cancer. In Breast Cancer; Exon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Pelizzola, M.; Futschik, A. Haplotype Based Testing for a Better Understanding of the Selective Architecture. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCBI. Homo Sapiens Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 511 (LINC00511), Long Non-Coding RNA. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/NR_033876 (accessed on 31 March 2024).
- GeneCaRNA LINC00511. Available online: https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=LINC00511 (accessed on 31 March 2024).
- Fairley, S.; Lowy-Gallego, E.; Perry, E.; Flicek, P. The International Genome Sample Resource (IGSR) Collection of Open Human Genomic Variation Resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D941–D947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| SNP | Genetic Model | Genotype | Cases (%) | Controls (%) | p * | Adjusted OR (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs11657109 | Codominant | AA | 66 (24.7) | 55 (36.7) | 1 | |
| AT | 120 (44.9) | 64 (42.7) | 0.062 | 1.562 (0.977–2.498) | ||
| TT | 81 (30.3) | 31 (20.7) | 0.005 | 2.177 (1.260–3.763) | ||
| Dominant | AA | 66 (24.7) | 55 (36.7) | 1 | ||
| AT + TT | 201 (75.3) | 95 (63.3) | 0.01 | 1.763 (1.143–2.719) | ||
| Recessive | AA + AT | 186 (69.7) | 119 (79.3) | 1 | ||
| TT | 81 (30.3) | 31 (20.7) | 0.033 | 1.672 (1.041–2.684) | ||
| Over-dominant | AA + TT | 147 (55.1) | 86 (57.3) | 1 | ||
| AT | 120 (44.9) | 64 (42.7) | 0.653 | 1.097 (0.733–1.642) | ||
| rs9906859 | Codominant | CC | 114 (42.7) | 55 (36.7) | 1 | |
| CT | 105 (39.3) | 55 (36.7) | 0.725 | 0.921 (0.582–1.456) | ||
| TT | 48 (18) | 40 (26.7) | 0.043 | 0.579 (0.341–0.982) | ||
| Dominant | CC | 114 (42.7) | 55 (36.7) | 1 | ||
| CT + TT | 153 (57.3) | 95 (63.3) | 0.229 | 0.777 (0.515–1.172) | ||
| Recessive | CC + CT | 219 (82) | 110 (73.3) | 1 | ||
| TT | 48 (18) | 40 (26.7) | 0.038 | 0.603 (0.374–0.972) | ||
| Over-dominant | CC + TT | 162 (60.7) | 95 (63.3) | 1 | ||
| CT | 105 (39.3) | 55 (36.7) | 0.592 | 1.120 (0.741–1.692) | ||
| rs17780195 | Codominant | AA | 136 (50.9) | 87 (58) | 1 | |
| AG | 106 (39.7) | 52 (34.7) | 0.223 | 1.304 (0.851–1.999) | ||
| GG | 25 (9.4) | 11 (7.3) | 0.334 | 1.454 (0.681–3.104) | ||
| Dominant | AA | 136 (50.9) | 87 (58) | 1 | ||
| AG + GG | 131 (49.1) | 63 (42) | 0.166 | 1.330 (0.889–1.991) | ||
| Recessive | AA + AG | 242 (90.6) | 139 (92.7) | 1 | ||
| GG | 25 (9.4) | 11 (7.3) | 0.48 | 1.305 (0.623–2.734) | ||
| Over-dominant | AA + GG | 161 (60.3) | 98 (65.3) | 1 | ||
| AG | 106 (39.7) | 52 (34.7) | 0.310 | 1.241 (0.818–1.881) | ||
| rs1558535 | Codominant | AA | 60 (22.5) | 43 (28.7) | 1 | |
| AT | 134 (50.2) | 64 (42.7) | 0.106 | 1.501 (0.917–2.454) | ||
| TT | 73 (27.3) | 43 (28.7) | 0.479 | 1.217 (0.707–2.095) | ||
| Dominant | AA | 60 (22.5) | 43 (28.7) | 1 | ||
| AT + TT | 207 (77.5) | 107 (71.3) | 0.160 | 1.386 (0.879–2.187) | ||
| Recessive | AA + AT | 194 (72.7) | 107 (71.3) | 1 | ||
| TT | 73 (27.3) | 43 (28.7) | 0.772 | 0.936 (0.600–1.461) | ||
| Over-dominant | AA + TT | 133 (49.8) | 86 (57.3) | 1 | ||
| AT | 134 (50.2) | 64 (42.7) | 0.14 | 1.354 (0.905–2.025) | ||
| rs4432291 | Codominant | GG | 93 (34.8) | 49 (32.7) | 1 | |
| AG | 124 (46.4) | 67 (44.7) | 0.914 | 0.975 (0.618–1.539) | ||
| AA | 50 (18.7) | 34 (22.7) | 0.369 | 0.775 (0.444–1.352) | ||
| Dominant | GG | 93 (34.8) | 49 (32.7) | 1 | ||
| AG + AA | 174 (65.2) | 101 (67.3) | 0.654 | 0.908 (0.594–1.387) | ||
| Recessive | GG + AG | 217 (81.3) | 116 (77.3) | 1 | ||
| AA | 50 (18.7) | 34 (22.7) | 0.336 | 0.786 (0.481–1.284) | ||
| Over-dominant | GG + AA | 143 (53.6) | 83 (55.3) | 1 | ||
| AG | 124 (46.4) | 67 (44.7) | 0.727 | 1.074 (0.719–1.605) |
| SNP | Alleles | Allele Frequency | p * | OR (95%CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases (%) | Controls (%) | ||||
| rs11657109 | A | 47 | 58 | 0.003 | 1.545 (1.162–2.056) |
| T | 53 | 42 | |||
| rs9906859 | C | 62 | 55 | 0.038 | 0.738 (0.554–0.983) |
| T | 38 | 45 | |||
| rs17780195 | A | 71 | 75 | 0.159 | 1.26 (0.913–1.739) |
| G | 29 | 25 | |||
| rs1558535 | A | 48 | 5 | 0.5 | 1.102 (.831–1.463) |
| T | 52 | 5 | |||
| rs4432291 | G | 58 | 45 | 0.393 | 0.883 (0.664–1.174) |
| A | 42 | 55 | |||
| SNP | Genetic Model of the SNP | Geno-Type | Controls | Luminal A BC | p * | OR (95%CI) | Luminal B BC | p * | OR (95%CI) | HER-2 BC | p * | OR (95%CI) | TNBC | p * | OR (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 150 n (%) | n = 175 n (%) | n = 64 n (%) | n = 16 n (%) | n = 12 n (%) | |||||||||||
| rs11657109 | Codominant | AA | 55 (36.7) | 38 (21.7) | 1 | 16 (25) | 1 | 7 (43.8) | 1 | 5 (41.7) | 1 | ||||
| AT | 64 (42.7) | 80 (45.7) | 0.028 | 1.809 (1.067–3.068) | 29 (45.3) | 0.220 | 1.558 (0.767–3.164) | 5 (31.3) | 0.427 | 0.614 (0.184–2.044) | 6 (50) | 0.691 | 1.031 (0.298–3.565) | ||
| TT | 31 (20.7) | 57 (32.6) | 0.011 | 2.661 (1.458–4.858) | 19 (29.7) | 0.067 | 2.107 (0.949–4.677) | 4 (25) | 0.984 | 1.014 (0.275–3.739) | 1 (8.3) | 0.354 | 0.355 (0.040–3.176) | ||
| Dominant | AA | 55 (36.7) | 38 (21.7) | 1 | 16 (25) | 1 | 7 (43.8) | 1 | 5 (41.7) | 1 | |||||
| AT + TT | 95 (63.3) | 137 (78.3) | 0.003 | 2.087 (1.280–3.405) | 48 (75) | 0.099 | 1.737 (0.901–3.347) | 9 (56.3) | 0.579 | 0.744 (0.263–2.110) | 7 (58.3) | 0.730 | 0.811 (0.245–2.677) | ||
| Recessive | AA + AT | 119 (79.3) | 118 (67.4) | 1 | 45 (70.3) | 1 | 12 (75) | 1 | 11 (91.7) | 1 | |||||
| TT | 31 (20.7) | 57 (32.6) | 0.017 | 1.854 (1.118–3.076) | 19 (29.7) | 0.155 | 1.621 (0.833–3.155) | 4 (25) | 0.687 | 1.280 (0.386–4.242) | 1 (8.3) | 0.322 | 0.349 (0.043–2.807) | ||
| Over-dominant | AA + TT | 86 (57.3) | 95 (54.3) | 1 | 35 (54.7) | 1 | 11 (68.8) | 1 | 6 (50) | 1 | |||||
| AT | 64 (42.7) | 80 (45.7) | 0.581 | 1.132 (0.729–1.756) | 29 (45.3) | 0.721 | 1.113 (0.618–2.007) | 5 (31.3) | 0.382 | 0.611 (0.202–1.845) | 6 (50) | 0.623 | 1.344 (0.414–4.360) | ||
| rs9906859 | Codominant | CC | 55 (36.7) | 78 (44.6) | 1 | 27 (42.2) | 1 | 4 (25) | 1 | 5 (41.7) | 1 | ||||
| CT | 55 (36.7) | 64 (36.6) | 0.437 | 0.821 (0.498–1.351) | 28 (43.8) | 0.912 | 1.037 (0.543–1.981) | 8 (50) | 0.280 | 2.000 (0.569–7.030) | 5 (41.7) | 1 | 1.000 (0.274–3.650) | ||
| TT | 40 (26.7) | 33 (18.9) | 0.065 | 0.582 (0.327–1.035) | 9 (14.1) | 0.074 | 0.458 (0.194–1.080) | 4 (25) | 0.666 | 1.375 (0.324–5.830) | 2 (16.7) | 0.488 | 0.550 (0.102–2.980) | ||
| Dominant | CC | 55 (36.7) | 78 (44.6) | 1 | 27 (42.2) | 1 | 4 (25) | 1 | 5 (41.7) | 1 | |||||
| CT + TT | 95 (63.3) | 97 (55.4) | 0.149 | 0.720 (0.461–1.125) | 37 (57.8) | 0.447 | 0.793 (0.437–1.441) | 12 (75) | 0.359 | 1.737 (0.534–5.648) | 7 (58.3) | 0.730 | 0.811 (0.245–2.677) | ||
| Recessive | CC + CT | 110 (73.3) | 142 (81.1) | 1 | 55 (85.9) | 1 | 12 (75) | 1 | 10 (83.3) | 1 | |||||
| TT | 40 (26.7) | 33 (18.9) | 0.094 | 0.639 (0.378–1.079) | 9 (14.1) | 0.048 | 0.450 (0.204–0.994) | 4 (25) | 0.868 | 0.917 (0.279–3.007) | 2 (16.7) | 0.453 | 0.550 (0.115–2.619) | ||
| Over-dominant | CC + TT | 95 (63.3) | 111 (63.4) | 1 | 36 (56.3) | 1 | 8 (50) | 1 | 7 (58.3) | 1 | |||||
| CT | 55 (36.7) | 64 (36.6) | 0.986 | 0.996 (0.633–1.566) | 28 (43.8) | 0.331 | 1.343 (0.741–2.436) | 8 (50) | 0.301 | 1.727 (0.614–4.861) | 5 (41.7) | 0.730 | 1.234 (0.374–4.075) | ||
| rs17780195 | Codominant | AA | 87 (58) | 97 (55.4) | 1 | 28 (43.8) | 1 | 6 (37.5) | 1 | 5 (41.7) | 1 | ||||
| AG | 52 (34.7) | 64 (36.6) | 0.678 | 1.104 (0.692–1.760) | 28 (43.8) | 0.107 | 1.673 (0.894–3.130) | 8 (50) | 0.158 | 2.231 (0.733–6.788) | 6 (50) | 0.269 | 2.008 (0.584–6.907) | ||
| GG | 11 (7.3) | 14 (8) | 0.753 | 1.142 (0.492–2.647) | 8 (12.5) | 0.112 | 2.260 (0.827–6.176) | 2 (12.5) | 0.269 | 2.636 (0.473–14.706) | 1 (8.3) | 0.688 | 1.582 (0.169–14.811) | ||
| Dominant | AA | 87 (58) | 97 (55.4) | 1 | 28 (43.8) | 1 | 6 (37.5) | 1 | 5 (41.7) | 1 | |||||
| AG + GG | 63 (42) | 78 (44.6) | 0.641 | 1.110 (0.715–1.725) | 36 (56.3) | 0.05 | 1.776 (1.100–3.206) | 10 (62.5) | 0.124 | 2.302 (0.795–6.662) | 7 (58.3) | 0.279 | 1.933 (0.587–6.371) | ||
| Recessive | AA + AG | 139 (92.7) | 161 (92) | 1 | 56 (87.5) | 1 | 14 (87.5) | 1 | 11 (91.7) | 1 | |||||
| GG | 11 (7.3) | 14 (8) | 0.822 | 1.099 (0.483–2.499) | 8 (12.5) | 0.229 | 1.805 (0.690–4.725) | 2 (12.5) | 0.470 | 1.805 (0.363–8.975) | 1 (8.3) | 0.899 | 1.149 (0.136–9.736) | ||
| Over-dominant | AA + GG | 98 (65.3) | 111 (63.4) | 1 | 36 (56.3) | 1 | 8 (50) | 1 | 6 (50) | 1 | |||||
| AG | 52 (34.7) | 64 (36.6) | 0.721 | 1.087 (0.689–1.714) | 28 (43.8) | 0.210 | 1.466 (0.806–2.664) | 8 (50) | 0.231 | 1.885 (0.669–5.311) | 6 (50) | 0.293 | 1.885 (0.579–6.136) | ||
| rs1558535 | Codominant | AA | 43 (28.7) | 39 (22.3) | 1 | 13 (20.3) | 1 | 7 (43.8) | 1 | 1 (8.3) | 1 | ||||
| AT | 64 (42.7) | 88 (50.3) | 0.131 | 1.516 (0.884–2.601) | 34 (53.1) | 0.139 | 1.757 (0.833–3.708) | 7 (43.8) | 0.485 | 0.672 (0.220–2.052) | 5 (41.7) | 0.276 | 3.359 (0.379–29.764) | ||
| TT | 43 (28.7) | 48 (27.4) | 0.496 | 1.231 (0.677–2.237) | 17 (26.6) | 0.530 | 1.308 (0.566–3.019) | 2 (12.5) | 0.131 | 0.286 (0.056–1.454) | 6 (50) | 0.104 | 6.000 (0.693–51.964) | ||
| Dominant | AA | 43 (28.7) | 39 (22.3) | 1 | 13 (20.3) | 1 | 7 (43.8) | 1 | 1 (8.3) | 1 | |||||
| AT + TT | 107 (71.3) | 136 (77.7) | 0.188 | 1.401 (0.848–2.315) | 51 (79.7) | 0.205 | 1.577 (0.780–3.189) | 9 (56.3) | 0.217 | 0.517 (0.181–1.475) | 11 (91.7) | 0.161 | 4.421 (0.554–35.295) | ||
| Recessive | AA + AT | 107 (71.3) | 127 (72.6) | 1 | 47 (73.4) | 1 | 14 (87.5) | 1 | 6 (50) | 1 | |||||
| TT | 43 (28.7) | 48 (27.4) | 0.804 | 0.940 (0.579–1.528) | 17 (26.6) | 0.754 | 0.900 (0.466–1.738) | 2 (12.5) | 0.183 | 0.355 (0.077–1.631) | 6 (50) | 0.132 | 2.488 (0.760–8.144) | ||
| Over-dominant | AA + TT | 86 (57.3) | 87 (49.7) | 1 | 30 (46.9) | 1 | 9 (56.3) | 1 | 7 (58.3) | 1 | |||||
| AT | 64 (42.7) | 88 (50.3) | 0.170 | 1.359 (0.876–2.108) | 34 (53.1) | 0.161 | 1.523 (0.846–2.742) | 7 (43.8) | 0.934 | 1.045 (0.370–2.955) | 5 (41.7) | 0.946 | 0.960 (0.291–3.163) | ||
| rs4432291 | Codominant | GG | 49 (32.7) | 64 (36.6) | 1 | 20 (31.3) | 1 | 3 (18.8) | 1 | 6 (50) | 1 | ||||
| AG | 67 (44.7) | 81 (46.3) | 0.759 | 0.926 (0.565–1.516) | 31 (48.4) | 0.715 | 1.134 (0.579–2.220) | 7 (43.8) | 0.455 | 1.706 (0.420–6.932) | 5 (41.7) | 0.435 | 0.609 (0.176–2.112) | ||
| AA | 34 (22.7) | 30 (17.1) | 0.212 | 0.676 (0.365–1.251) | 13 (20.3) | 0.877 | 0.937 (0.411–2.135) | 6 (37.5) | 0.153 | 2.882 (0.674–12.329) | 1 (8.3) | 0.196 | 0.240 (0.028–2.086) | ||
| Dominant | GG | 49 (32.7) | 64 (36.6) | 1 | 20 (31.3) | 1 | 3 (18.8) | 1 | 6 (50) | 1 | |||||
| AG + AA | 101 (67.3) | 111 (63.4) | 0.461 | 0.841 (0.531–1.332) | 44 (68.8) | 0.839 | 1.067(0.569–2.002) | 13 (81.3) | 0.263 | 2.102 (0.572–7.721) | 6 (50) | 0.230 | 0.485 (0.149–1.582) | ||
| Recessive | GG + AG | 116 (77.3) | 145 (82.9) | 1 | 51 (79.7) | 1 | 10 (62.5) | 1 | 11 (91.7) | 1 | |||||
| AA | 34 (22.7) | 30 (17.1) | 0.213 | 0.706 (0.408–1.221) | 13 (20.3) | 0.703 | 0.870 (0.424–1.785) | 6 (37.5) | 0.194 | 2.047 (0.694–6.039) | 1 (8.3) | 0.271 | 0.310 (0.039–2.489) | ||
| Over-dominant | GG + AA | 83 (55.3) | 94 (53.7) | 1 | 33 (51.6) | 1 | 9 (56.3) | 1 | 7 (58.3) | 1 | |||||
| AG | 67 (44.7) | 81 (46.3) | 0.770 | 1.067 (0.689–1.654) | 31 (48.4) | 0.612 | 1.164 (0.647–2.092) | 7 (43.8) | 0.944 | 0.964 (0.341–2.723) | 5 (41.7) | 0.841 | 0.885 (0.269–2.914) |
| Haplotype | Cases (%) | Controls (%) | χ2 | p Value | OR (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A A A A T | 23.76 | 36.67 | 9.058 | 0.003 | 0.617 (0.450–0.846) |
| T G T A C | 19.69 | 12.78 | 10.628 | 0.001 | 1.945 (1.298–2.915) |
| T G T G C | 16.18 | 16.86 | 0.201 | 0.654 | 1.092 (0.744–1.603) |
| A G T A C | 5.56 | 9.06 | 2.206 | 0.138 | 0.664 (0.386–1.143) |
| A A A G T | 5.26 | 0 | 18.382 | <0.001 | NA |
| T G A A C | 4.19 | 7.23 | 2.231 | 0.135 | 0.630 (0.342–1.160) |
| T A A A C | 3.68 | 1.33 | 4.869 | 0.027 | 3.191 (1.077–9.453) |
| A G T A T | 2.44 | 3.67 | 0.539 | 0.463 | 0.737 (0.326–1.669) |
| A G T G C | 2.39 | 3.3 | 0.254 | 0.615 | 0.805 (0.346–1.873) |
| A A T A T | 1.04 | 3.33 | 4.454 | 0.035 | 0.340 (0.119–0.970) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eldash, S.; Sanad, E.F.; Elshimy, R.A.A.; Hady, A.A.; Nada, D.; Hamdy, N.M. Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNA 00511 (LINC00511) Genetic Variations and Haplotypes in Breast Cancer: A Case-Controlled Study and Bioinformatics Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199328
Eldash S, Sanad EF, Elshimy RAA, Hady AA, Nada D, Hamdy NM. Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNA 00511 (LINC00511) Genetic Variations and Haplotypes in Breast Cancer: A Case-Controlled Study and Bioinformatics Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199328
Chicago/Turabian StyleEldash, Shorouk, Eman F. Sanad, Reham A. A. Elshimy, Ahmad A. Hady, Dina Nada, and Nadia M. Hamdy. 2025. "Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNA 00511 (LINC00511) Genetic Variations and Haplotypes in Breast Cancer: A Case-Controlled Study and Bioinformatics Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199328
APA StyleEldash, S., Sanad, E. F., Elshimy, R. A. A., Hady, A. A., Nada, D., & Hamdy, N. M. (2025). Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNA 00511 (LINC00511) Genetic Variations and Haplotypes in Breast Cancer: A Case-Controlled Study and Bioinformatics Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199328







