The Role of Skin Microbiota in Facial Dermatoses and Related Factors: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Role of the Skin Barrier
3. The Role of the Immune System
4. The Microbiome of Healthy Skin
5. Methods for Studying the Microbiome
6. The Role of the Skin Microbiome in the Most Common Inflammatory Skin Diseases
6.1. The Skin Microbiome in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis
6.2. The Skin Microbiome in Patients with Seborrheic Dermatitis
6.3. The Skin Microbiome in Patients with Acne Vulgaris
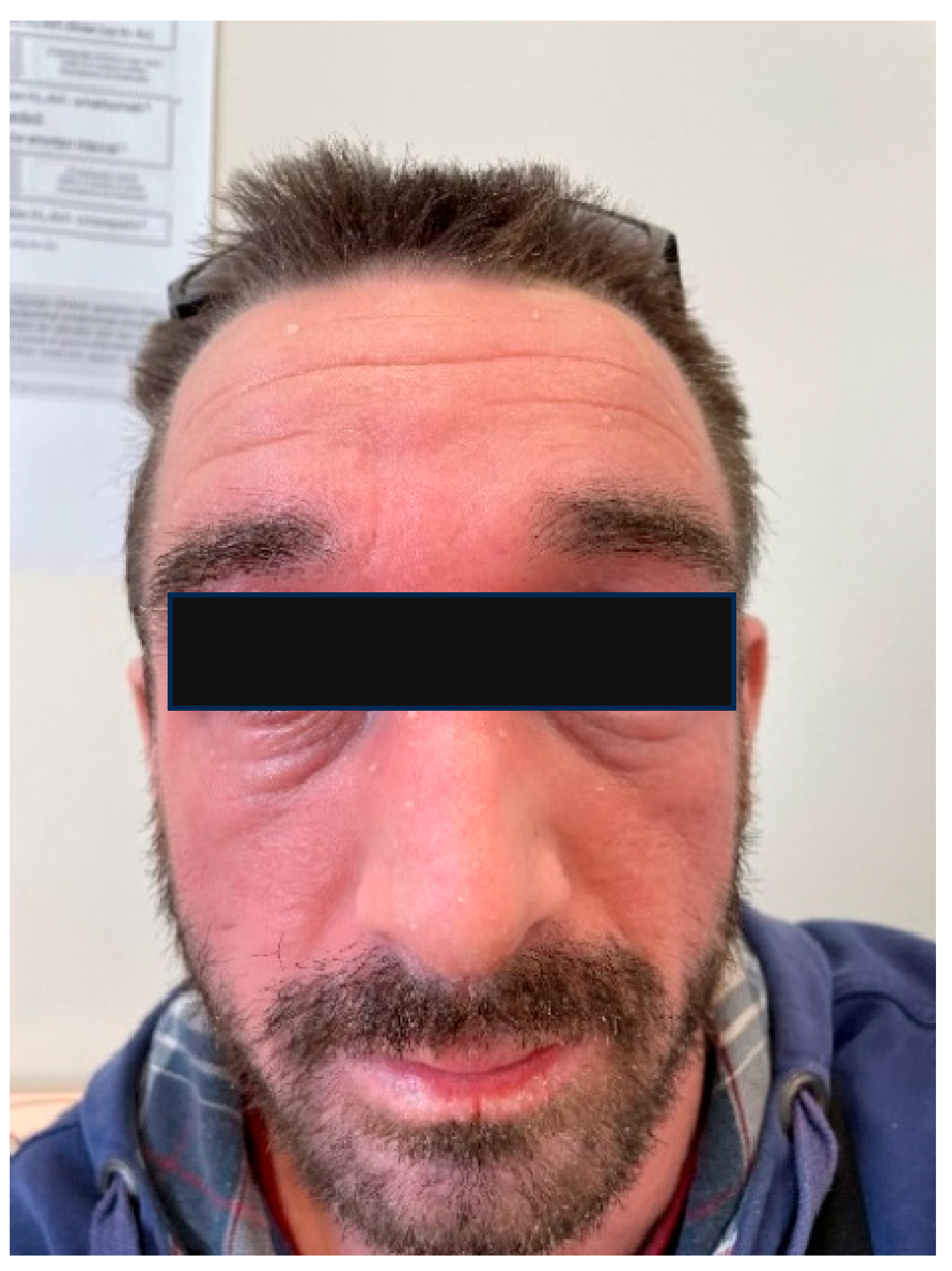
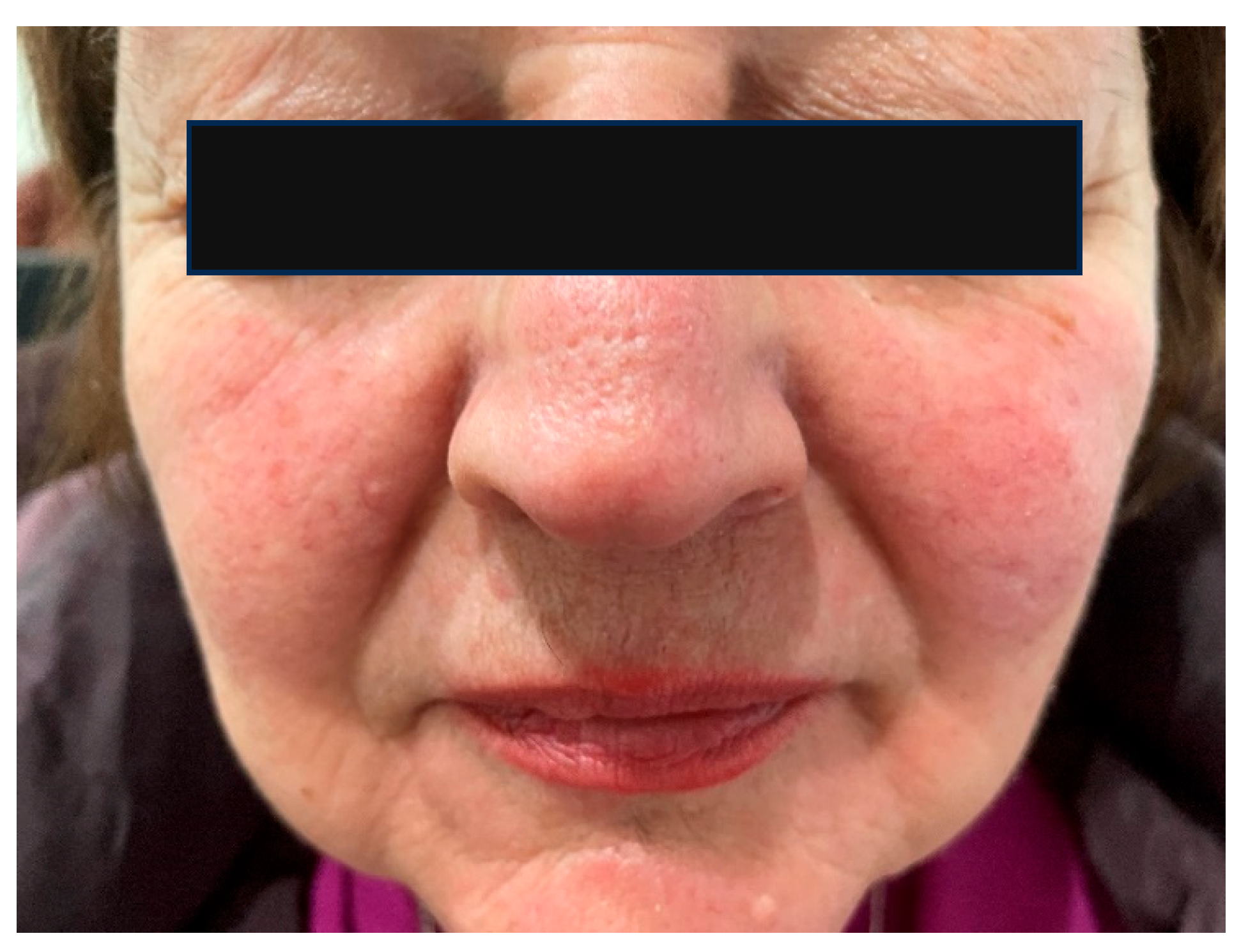
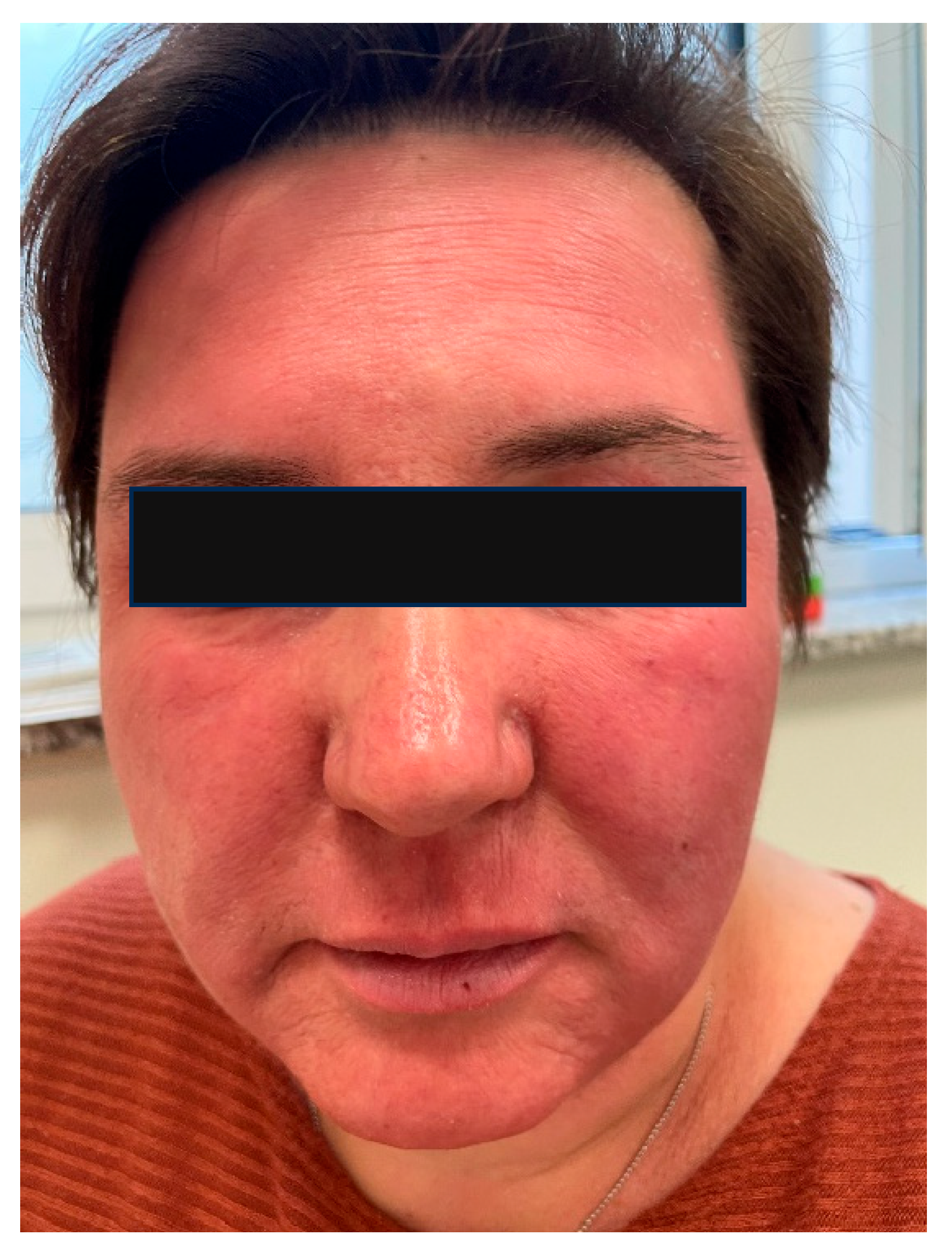
6.4. The Skin Microbiome in Patients with Rosacea
6.5. The Skin Microbiome in Patients with Contact Dermatitis
6.6. The Skin Microbiome in Patients with Periorificial Dermatitis, Including Perioral and Periocular Dermatitis
7. A Review of the Studies on the Role of the Skin Microbiome in Facial Dermatoses
8. New Treatment Options Based on the Skin Microbiome and Perspectives in This Field
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richard, M.; Paul, C.; Nijsten, T.; Gisondi, P.; Salavastru, C.; Taieb, C.; Trakatelli, M.; Puig, L.; Stratigos, A.; EADV Burden Of Skin Diseases Project Team. Prevalence Of Most Common Skin Diseases In Europe: A Population-Based Study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujiie, H.; Rosmarin, D.; Schön, M.P.; Ständer, S.; Boch, K.; Metz, M.; Maurer, M.; Thaci, D.; Schmidt, E.; Cole, C.; et al. Unmet Medical Needs in Chronic, Non-Communicable Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 875492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Moreno-Coutiño, G. Periocular Dermatoses. Int. J. Womens Dermatol. 2017, 3, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferček, I.; Lugović-Mihić, L.; Tambić-Andrašević, A.; Ćesić, D.; Grginić, A.G.; Bešlić, I.; Mravak-Stipetić, M.; Mihatov-Štefanović, I.; Buntić, A.-M.; Čivljak, R. Features of the Skin Microbiota in Common Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Life 2021, 11, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landeck, L.; Schalock, P.C.; Baden, L.A.; Gonzalez, E. Periorbital Contact Sensitization. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 150, 366–370.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garlet, A.; Andre-Frei, V.; Del Bene, N.; Cameron, H.J.; Samuga, A.; Rawat, V.; Ternes, P.; Leoty-Okombi, S. Facial Skin Microbiome Composition and Functional Shift with Aging. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warshaw, E.M.; Voller, L.M.; Maibach, H.I.; Zug, K.A.; DeKoven, J.G.; Atwater, A.R.; Sasseville, D.; Fowler, J.F.; Taylor, J.S.; Yiannias, J.A.; et al. Eyelid Dermatitis in Patients Referred for Patch Testing: Retrospective Analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group Data, 1994–2016. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 84, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavuoto, K.M.; Mendez, R.; Miller, D.; Galor, A.; Banerjee, S. Effect of Clinical Parameters on the Ocular Surface Microbiome in Children and Adults. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2018, 12, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, E.A.; Segre, J.A. The Skin Microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in Health and Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesi, J.R.; Ravel, J. The Vocabulary of Microbiome Research: A Proposal. Microbiome 2015, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuji, T.; Chen, T.H.; Narala, S.; Chun, K.A.; Two, A.M.; Yun, T.; Shafiq, F.; Kotol, P.F.; Bouslimani, A.; Melnik, A.V.; et al. Antimicrobials from Human Skin Commensal Bacteria Protect against Staphylococcus aureus and Are Deficient in Atopic Dermatitis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaah4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-E.; Zheng, P.; Ye, S.-Z.; Ma, X.; Liu, E.; Pang, Y.-B.; He, Q.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Li, W.-Q.; Zeng, J.-H.; et al. Microbiome: Role in Inflammatory Skin Diseases. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 1057–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreouzi, M.; Theodorakis, N.; Nikolaou, M.; Feretzakis, G.; Anastasiou, A.; Kalodanis, K.; Sakagianni, A. Skin Microbiota: Mediator of Interactions Between Metabolic Disorders and Cutaneous Health and Disease. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
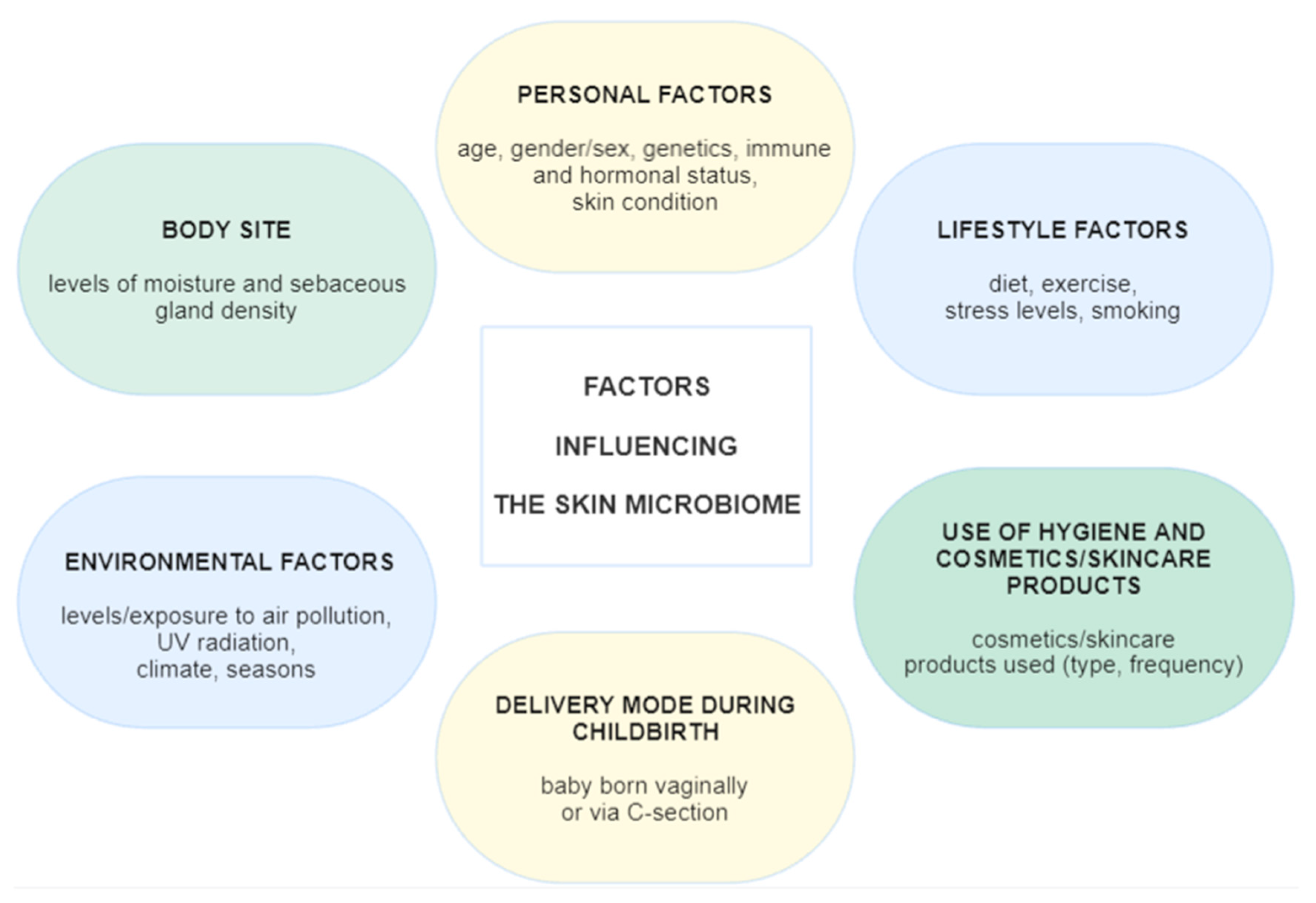
- Skowron, K.; Bauza-Kaszewska, J.; Kraszewska, Z.; Wiktorczyk-Kapischke, N.; Grudlewska-Buda, K.; Kwiecińska-Piróg, J.; Wałecka-Zacharska, E.; Radtke, L.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. Human Skin Microbiome: Impact of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors on Skin Microbiota. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Cruz, S.; Orozco-Covarrubias, L.; Sáez-de-Ocariz, M. The Human Skin Microbiome in Selected Cutaneous Diseases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 834135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mim, M.F.; Sikder, M.H.; Chowdhury, M.Z.H.; Bhuiyan, A.U.A.; Zinan, N.; Islam, S.M.N. The Dynamic Relationship between Skin Microbiomes and Personal Care Products: A Comprehensive Review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smythe, P.; Wilkinson, H.N. The Skin Microbiome: Current Landscape and Future Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanovic, N.; Irvine, A.D. Filaggrin and Beyond: New Insights into the Skin Barrier in Atopic Dermatitis and Allergic Diseases, from Genetics to Therapeutic Perspectives. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024, 132, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pondeljak, N.; Lugović-Mihić, L.; Tomić, L.; Parać, E.; Pedić, L.; Lazić-Mosler, E. Key Factors in the Complex and Coordinated Network of Skin Keratinization: Their Significance and Involvement in Common Skin Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, I.H.; Yoshida, T.; De Benedetto, A.; Beck, L.A. The Cutaneous Innate Immune Response in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkiewicz, M.; Majewski, S. The Role of Antimicrobial Peptides in Chronic Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Postep. Dermatol. Alergol. 2016, 33, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Yamasaki, K. Psoriasis and Antimicrobial Peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harder, J.; Dressel, S.; Wittersheim, M.; Cordes, J.; Meyer-Hoffert, U.; Mrowietz, U.; Fölster-Holst, R.; Proksch, E.; Schröder, J.M.; Schwarz, T.; et al. Enhanced Expression and Secretion of Antimicrobial Peptides in Atopic Dermatitis and after Superficial Skin Injury. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harder, J.; Tsuruta, D.; Murakami, M.; Kurokawa, I. What Is the Role of Antimicrobial Peptides (AMP) in Acne Vulgaris? Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, K.; Di Nardo, A.; Bardan, A.; Murakami, M.; Ohtake, T.; Coda, A.; Dorschner, R.A.; Bonnart, C.; Descargues, P.; Hovnanian, A.; et al. Increased Serine Protease Activity and Cathelicidin Promotes Skin Inflammation in Rosacea. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matejuk, A. Skin Immunity. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2018, 66, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.E.; Fischbach, M.A.; Belkaid, Y. Skin Microbiota-Host Interactions. Nature 2018, 553, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, E.A.; Kong, H.H.; Conlan, S.; Deming, C.B.; Davis, J.; Young, A.C.; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program; Bouffard, G.G.; Blakesley, R.W.; Murray, P.R.; et al. Topographical and Temporal Diversity of the Human Skin Microbiome. Science 2009, 324, 1190–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, A.L.; Deming, C.; Cassidy, S.K.B.; Harrison, O.J.; Ng, W.I.; Conlan, S.; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A.; Kong, H.H. Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis Strain Diversity Underlying Pediatric Atopic Dermatitis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaal4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, E.A. The Skin Microbiome: Potential for Novel Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Cutaneous Disease. Semin. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2014, 33, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournière, M.; Latire, T.; Souak, D.; Feuilloley, M.G.J.; Bedoux, G. Staphylococcus epidermidis and Cutibacterium acnes: Two Major Sentinels of Skin Microbiota and the Influence of Cosmetics. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridaura, V.K.; Bouladoux, N.; Claesen, J.; Chen, Y.E.; Byrd, A.L.; Constantinides, M.G.; Merrill, E.D.; Tamoutounour, S.; Fischbach, M.A.; Belkaid, Y. Contextual control of skin immunity and inflammation by Corynebacterium. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzatti, G.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Gibiino, G.; Binda, C.; Gasbarrini, A. Proteobacteria: A Common Factor in Human Diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9351507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabataş, N.; Doğan, A.Ş.; Kabataş, E.U.; Acar, M.; Biçer, T.; Gürdal, C. The Effect of Demodex Infestation on Blepharitis and the Ocular Symptoms. Eye Contact Lens 2017, 43, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chudzicka-Strugała, I.; Gołębiewska, I.; Brudecki, G.; Elamin, W.; Zwoździak, B. Demodicosis in Different Age Groups and Alternative Treatment Options-A Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rather, P.A.; Hassan, I. Human demodex mite: The versatile mite of dermatological importance. Indian J. Dermatol. 2014, 59, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forton, F.M.N. The Pathogenic Role of Demodex Mites in Rosacea: A Potential Therapeutic Target Already in Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea? Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 10, 1229–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, M.J.; Derebecka, N.; Żaba, R.; Wesoły, J.; Pawlak, P.; Szkaradkiewicz-Karpińska, A.; Maher, A.; Kavanagh, K. Novel Demodex detection method involving non-invasive sebum collection and next-generation sequencing. Postep. Dermatol. Alergol. 2022, 39, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannigan, G.D.; Duhaime, M.B.; Koutra, D.; Schloss, P.D. Biogeography and environmental conditions shape bacteriophage-bacteria networks across the human microbiome. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santus, W.; Devlin, J.R.; Behnsen, J. Crossing Kingdoms: How the Mycobiota and Fungal-Bacterial Interactions Impact Host Health and Disease. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e00648-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limon, J.J.; Skalski, J.H.; Underhill, D.M. Commensal Fungi in Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamczyk, K.; Garncarczyk, A.; Antończak, P.; Wcisło-Dziadecka, D. The foot microbiome. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparber, F.; LeibundGut-Landmann, S. Host Responses to Malassezia spp. in the Mammalian Skin. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Park, S.; Jung, W.H. Skin Commensal Fungus Malassezia and Its Lipases. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, J.J.; Monir, R.L.; Satcher, K.G.; Harris, J.; Triplett, E.; Neu, J. The infantile cutaneous microbiome: A review. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2019, 36, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pammi, M.; O’Brien, J.L.; Ajami, N.J.; Wong, M.C.; Versalovic, J.; Petrosino, J.F. Development of the Cutaneous Microbiome in the Preterm Infant: A Prospective Longitudinal Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, E.K.; Carlisle, E.M.; Bik, E.M.; Morowitz, M.J.; Relman, D.A. Microbiome Assembly across Multiple Body Sites in Low-Birthweight Infants. mBio 2013, 4, e00782-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Schwardt, N.H.; Jo, J.H.; Zhang, Z.; Pillai, V.; Phang, S.; Brady, S.M.; Portillo, J.A.; MacGibeny, M.A.; Liang, H.; et al. Shifts in the Skin Bacterial and Fungal Communities of Healthy Children Transitioning through Puberty. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.J.; Myeong, N.R.; Kim, T.; Kim, D.; An, S.; Kim, H.; Park, T.; Jang, S.I.; Yeon, J.H.; et al. Segregation of Age-Related Skin Microbiome Characteristics by Functionality. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paller, A.S.; Kong, H.H.; Seed, P.; Naik, S.; Scharschmidt, T.C.; Gallo, R.L.; Luger, T.; Irvine, A.D. The Microbiome in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Peng, G.; Abudouwanli, A.; Yang, M.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, W.; Ikeda, A.; Tan, Y.; Ma, L.; Ogawa, H.; et al. The Interaction Between The Skin Microbiome And Antimicrobial Peptides Within The Epidermal Immune Microenvironment: Bridging Insights Into Atopic Dermatitis. Allergol Int. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thio, H.B. The Microbiome in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: The Skin Perspective. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 2018, 94, 30–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langan, E.A.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Solbach, W.; Knobloch, J.K.; Zillikens, D.; Thaçi, D. The Role of the Microbiome in Psoriasis: Moving from Disease Description to Treatment Selection? Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 178, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, J.U. The Microbiome in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: Joints. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 2018, 94, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Cho, O.; Saito, C.; Saito, M.; Tsuboi, R.; Sugita, T. Comprehensive Pyrosequencing Analysis of the Bacterial Microbiota of the Skin of Patients with Seborrheic Dermatitis. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 60, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrestak, D.; Matijašić, M.; Čipčić Paljetak, H.; Ledić Drvar, D.; Ljubojević Hadžavdić, S.; Perić, M. Skin Microbiota in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Krieken, D.A.; Rikken, G.; Ederveen, T.H.A.; Jansen, P.A.M.; Rodijk-Olthuis, D.; Meesters, L.D.; van Vlijmen-Willems, I.M.J.J.; van Cranenbroek, B.; van der Molen, R.G.; Schalkwijk, J.; et al. Gram-Positive Anaerobic Cocci Guard Skin Homeostasis by Regulating Host-Defense Mechanisms. iScience 2023, 26, 106483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.H.; Oh, J.; Deming, C.; Conlan, S.; Grice, E.A.; Beatson, M.A.; Nomicos, E.; Polley, E.C.; Komarow, H.D.; NISC Comparative Sequence Program; et al. Temporal Shifts in the Skin Microbiome Associated with Disease Flares and Treatment in Children with Atopic Dermatitis. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callewaert, C.; Nakatsuji, T.; Knight, R.; Kosciolek, T.; Vrbanac, A.; Kotol, P.; Ardeleanu, M.; Hultsch, T.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Bissonnette, R.; et al. IL-4Rα Blockade by Dupilumab Decreases Staphylococcus aureus Colonization and Increases Microbial Diversity in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 191–202.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baurecht, H.; Rühlemann, M.C.; Rodríguez, E.; Thielking, F.; Harder, I.; Erkens, A.S.; Stölzl, D.; Ellinghaus, E.; Hotze, M.; Lieb, W.; et al. Epidermal Lipid Composition, Barrier Integrity, and Eczematous Inflammation are Associated with Skin Microbiome Configuration. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1668–1676.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Rho, M.; Choi, J.P.; Choi, H.I.; Park, H.K.; Song, W.J.; Min, T.K.; Cho, S.H.; Cho, Y.J.; Kim, Y.K.; et al. A Metagenomic Analysis Provides a Culture-Independent Pathogen Detection for Atopic Dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2017, 9, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, M.L.; Edslev, S.M.; Andersen, P.S.; Clemmensen, K.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Agner, T. Staphylococcus aureus Colonization in Atopic Eczema and Its Association with Filaggrin Gene Mutations. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, V.D.; Key, F.M.; Romo-González, C.; Martínez-Gayosso, A.; Campos-Cabrera, B.L.; Gerónimo-Gallegos, A.; Lynn, T.C.; Durán-McKinster, C.; Coria-Jiménez, R.; Lieberman, T.D.; et al. The Skin Microbiome of Patients with Atopic Dermatitis Normalizes Gradually During Treatment. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 720674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chng, K.R.; Tay, A.S.; Li, C.; Ng, A.H.; Wang, J.; Suri, B.K.; Matta, S.A.; McGovern, N.; Janela, B.; Wong, X.F.; et al. Whole Metagenome Profiling Reveals Skin Microbiome-Dependent Susceptibility to Atopic Dermatitis Flare. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosbrugger-Martinz, V.; Hackl, H.; Gruber, R.; Pilecky, M.; Knabl, L.; Orth-Höller, D.; Dubrac, S. Initial Evidence of Distinguishable Bacterial and Fungal Dysbiosis in the Skin of Patients with Atopic Dermatitis or Netherton Syndrome. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seite, S.; Flores, G.E.; Henley, J.B.; Martin, R.; Zelenkova, H.; Aguilar, L.; Fierer, N. Microbiome of Affected and Unaffected Skin of Patients with Atopic Dermatitis before and after Emollient Treatment. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2014, 13, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar]
- Tauber, M.; Balica, S.; Hsu, C.Y.; Jean-Decoster, C.; Lauze, C.; Redoules, D.; Viodé, C.; Schmitt, A.M.; Serre, G.; Simon, M.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Density on Lesional and Nonlesional Skin is Strongly Associated with Disease Severity in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1272–1274.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Lv, Z.; Liang, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, P.; Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Tao, A. Exploring the Role of Staphylococcus aureus in Inflammatory Diseases. Toxins 2022, 14, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galizia, G.; Belloni Fortina, A.; Semenzato, A. Seborrheic Dermatitis: From Microbiome and Skin Barrier Involvement to Emerging Approaches in Dermocosmetic Treatment. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikramanayake, T.C.; Borda, L.J.; Miteva, M.; Paus, R. Seborrheic Dermatitis—Looking beyond Malassezia. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adalsteinsson, J.A.; Kaushik, S.; Muzumdar, S.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Ungar, J. An Update on the Microbiology, Immunology and Genetics of Seborrheic Dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.G.H.; Nijsten, T.; Verlouw, J.; Kraaij, R.; Pardo, L.M. Composition of Cutaneous Bacterial Microbiome in Seborrheic Dermatitis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Panchamukhi, A.; Li, P.; Shan, W.; Zhou, H.; Hou, L.; Chen, W. Malassezia and Staphylococcus Dominate Scalp Microbiome for Seborrheic Dermatitis. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, R.; Mittal, P.; Clavaud, C.; Dhakan, D.B.; Hegde, P.; Veeranagaiah, M.M.; Saha, S.; Souverain, L.; Roy, N.; Breton, L. Comparison of Healthy and Dandruff Scalp Microbiome Reveals the Role of Commensals in Scalp Health. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, C.; Liu, X.; Yang, F.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Manabe, K.; Qin, O.; Wang, X. Dandruff Is Associated with the Conjoined Interactions Between Host and Microorganisms. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacentini, F.; Camera, E.; Di Nardo, A.; Dell’Anna, M.L. Seborrheic Dermatitis: Exploring the Complex Interplay with Malassezia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.; Kim, H.J.; Myeong, N.R.; Lee, H.G.; Kwack, I.; Lee, J.; Kim, B.J.; Sul, W.J.; An, S. Collapse of Human Scalp Microbiome Network in Dandruff and Seborrhoeic Dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimshaw, S.G.; Smith, A.M.; Arnold, D.S.; Xu, E.; Hoptroff, M.; Murphy, B. The Diversity and Abundance of Fungi and Bacteria on the Healthy and Dandruff-Affected Human Scalp. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qi, F.; Hu, Z.; Sweren, E.; Reddy, S.K.; Chen, L.; Feng, X.; Grice, E.A.; Garza, L.A.; et al. Commensal Microbe Regulation of Skin Cells In Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2024, 32, 1264–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.B.; Byun, E.J.; Kim, H.S. Potential Role of the Microbiome in Acne: A Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.J.; Li, B.Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Qi, F.W.; Meng, H. Analysis of Skin Microbiome in Facial and Back Acne Patients Based on High-Throughput Sequencing. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2025, 24, e70259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gether, L.; Overgaard, L.K.; Egeberg, A.; Thyssen, J.P. Incidence and Prevalence of Rosacea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 179, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daou, H.; Paradiso, M.; Hennessy, K.; Seminario-Vidal, L. Rosacea and the Microbiome: A Systematic Review. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, e00460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, C.; Paul, C.; Lahfa, M.; Livideanu, B.; Lejeune, O.; Alvarez-Georges, S.; Saint-Martory, C.; Degouy, A.; Mengeaud, V.; Ginisty, H.; et al. Quantification of Demodex folliculorum by PCR in Rosacea and Its Relationship to Skin Innate Immune Activation. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asees, A.; Sadur, A.; Choudhary, S. The Skin Microbiome in Rosacea: Mechanisms, Gut-Skin Interactions, and Therapeutic Implications. Cutis 2025, 116, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainer, B.M.; Wangpson, K.G.; Antonescu, C.; Florea, L.; Mongodin, E.F.; Bui, J.; Fischer, A.H.; Pasieka, H.B.; Garza, L.A.; Kang, S.; et al. Characterization and Analysis of the Skin Microbiota in Rosacea: A Case-Control Study. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, A.K.; Spaunhurst, K.; Sprockett, D.; Thomason, Y.; Mann, M.W.; Fu, P.; Ammons, C.; Gerstenblith, M.; Tuttle, M.S.; Popkin, D.L. Characterization of the Facial Microbiome in Twins Discordant for Rosacea. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Y.R.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, H.S. Characterization and Analysis of the Skin Microbiota in Rosacea: Impact of Systemic Antibiotics. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, J.D.; Bonefeld, C.M.; Schwensen, J.F.B.; Thyssen, J.P.; Uter, W. Novel Insights into Contact Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mraz, V.; Geisler, C.; Bonefeld, C.M. Dendritic Epidermal T Cells in Allergic Contact Dermatitis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak-Bilić, G.; Vučić, M.; Japundžić, I.; Meštrović-Štefekov, J.; Stanić-Duktaj, S.; Lugović-Mihić, L. Irritant and Allergic Contact Dermatitis—Skin Lesion Characteristics. Acta Clin. Croat. 2018, 57, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesqué, D.; Aerts, O.; Bizjak, M.; Gonçalo, M.; Dugonik, A.; Simon, D.; Ljubojević-Hadzavdić, S.; Malinauskiene, L.; Wilkinson, M.; Czarnecka-Operacz, M.; et al. Differential Diagnosis of Contact Dermatitis: A Practical-Approach Review by the EADV Task Force on Contact Dermatitis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38, 1704–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonsen, A.B.; Johansen, J.D.; Deleuran, M.; Mortz, C.G.; Sommerlund, M. Contact Allergy in Children with Atopic Dermatitis: A Systematic Review. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, J.L.; Vakharia, P.P.; Silverberg, J.I. The Role and Diagnosis of Allergic Contact Dermatitis in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 19, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurakić Tončić, R.; Ljubojević Hadžavdić, S.; Pustišek, N.; Marinović Kulišić, S.; Švigir, A. Contact Sensitivity in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. 2020, 28, 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.X.; Yiannias, J.A.; Killian, J.M.; Shen, J.F. Seven Common Allergen Groups Causing Eyelid Dermatitis: Education and Avoidance Strategies. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2021, 15, 1477–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørreslet, L.B.; Ingham, A.C.; Agner, T.; Olesen, C.M.; Bregnhøj, A.; Sommerlund, M.; Andersen, P.S.; Stegger, M.; Mørtz, C.G.; Edslev, S.M. Hand Eczema and Changes in the Skin Microbiome after 2 Weeks of Topical Corticosteroid Treatment. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2025, 39, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørreslet, L.B.; Lilje, B.; Ingham, A.C.; Edslev, S.M.; Clausen, M.L.; Plum, F.; Andersen, P.S.; Agner, T. Skin Microbiome in Patients with Hand Eczema and Healthy Controls: A Three-Week Prospective Study. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2022, 102, adv00633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petek, T.H.; Petek, M.; Petek, T.; Varda, N.M. Emerging Links between Microbiome Composition and Skin Immunology in Diaper Dermatitis: A Narrative Review. Children 2022, 9, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugović-Mihić, L.; Špiljak, B.; Blagec, T.; Delaš Aždajić, M.; Franceschi, N.; Gašić, A.; Parać, E. Factors Participating in the Occurrence of Inflammation of the Lips (Cheilitis) and Perioral Skin. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.; Neill, B.; Whitsitt, J.; Rajpara, A.; Aires, D. Exacerbation of Pediatric Periorificial Dermatitis: A Novel Adverse Reaction. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2020, 19, 428. [Google Scholar]
- Tolaymat, L.; Hall, M.R. Perioral Dermatitis. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525968/ (accessed on 17 October 2024).
- Contento, M.; Maher, J.; Cline, A.; Rose, S. Why Does Facial Eczema Differ from Body Eczema? J. Drugs Dermatol. 2022, 21, 1119–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago-Rodriguez, T.M.; Le François, B.; Macklaim, J.M.; Doukhanine, E.; Hollister, E.B. The Skin Microbiome: Current Techniques, Challenges, and Future Directions. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rungjang, A.; Meephansan, J.; Payungporn, S.; Sawaswong, V.; Chanchaem, P.; Pureesrisak, P.; Wongpiyabovorn, J.; Thio, H.B. Skin Microbiota Profiles from Tape Stripping and Skin Biopsy Samples of Patients with Psoriasis Treated with Narrowband Ultraviolet B. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 15, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prast-Nielsen, S.; Tobin, A.M.; Adamzik, K.; Powles, A.; Hugerth, L.W.; Sweeney, C.; Kirby, B.; Engstrand, L.; Fry, L. Investigation of the Skin Microbiome: Swabs vs. Biopsies. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandwein, M.; Fuks, G.; Israel, A.; Hodak, E.; Sabbah, F.; Steinberg, D.; Bentwich, Z.; Shental, N.; Meshner, S. Biogeographical Landscape of the Human Face Skin Microbiome Viewed in High Definition. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2021, 101, adv00603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferček, I.; Ozretić, P.; Tambić-Andrašević, A.; Trajanoski, S.; Ćesić, D.; Jelić, M.; Geber, G.; Žaja, O.; Paić, J.; Lugović-Mihić, L.; et al. Comparison of the Skin Microbiota in the Periocular Region between Patients with Inflammatory Skin Diseases and Healthy Participants: A Preliminary Study. Life 2024, 14, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C.; Cascella, F.; Mellai, M.; Barizzone, N.; Mignone, F.; Massa, N.; Nobile, V.; Bona, E. Influence of Sex on the Microbiota of the Human Face. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Bangayan, N.J.; Curd, E.; Taylor, P.A.; Gallo, R.L.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Li, H. The skin microbiome is different in pediatric versus adult atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1233–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyhrquist, N.; Muirhead, G.; Prast-Nielsen, S.; Jeanmougin, M.; Olah, P.; Skoog, T.; Jules-Clement, G.; Feld, M.; Barrientos-Somarribas, M.; Sinkko, H.; et al. Microbe-Host Interplay in Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, B.E.; Ahn, K.; Leung, D.Y.M. Interactions Between Atopic Dermatitis and Staphylococcus aureus Infection: Clinical Implications. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2019, 11, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Farhat, M.; Na, J.; Li, R.; Wu, Y. Bacterial and Fungal Microbiome Characterization in Patients with Rosacea and Healthy Controls. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 1112–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, K.G.; Rainer, B.M.; Antonescu, C.; Florea, L.; Mongodin, E.F.; Kang, S.; Chien, A.L. Comparison of the Skin Microbiota in Acne and Rosacea. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condrò, G.; Guerini, M.; Castello, M.; Perugini, P. Acne Vulgaris, Atopic Dermatitis and Rosacea: The Role of the Skin Microbiota—A Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Wang, H.L.; Bu, X.L.; Zhang, J.B.; Lu, Y.G. A Narrative Review of Research Progress on the Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Acne Vulgaris. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Son, S.M.; Park, H.; Kim, B.K.; Choi, I.S.; Kim, H.; Huh, C.S. Taxonomic Profiling of Skin Microbiome and Correlation with Clinical Skin Parameters in Healthy Koreans. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Y. (Eds.) Atlas of Oral Microbiology: From Healthy Microflora to Disease; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-0-12-802234-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wieërs, G.; Belkhir, L.; Enaud, R.; Leclercq, S.; Philippart de Foy, J.-M.; Dequenne, I.; de Timary, P.; Cani, P.D. How Probiotics Affect the Microbiota. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 9, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćesić, D.; Lugović-Mihić, L.; Ozretić, P.; Lojkić, I.; Buljan, M.; Šitum, M.; Zovak, M.; Vidović, D.; Mijić, A.; Galić, N.; et al. Association of Gut Lachnospiraceae and Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria. Life 2023, 13, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krišto, M.; Lugović-Mihić, L.; Muñoz, M.; Rupnik, M.; Mahnic, A.; Ozretić, P.; Jaganjac, M.; Ćesić, D.; Kuna, M. Gut Microbiome Composition in Patients with Chronic Urticaria: A Review of Current Evidence and Data. Life 2023, 13, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myles, I.A.; Earland, N.J.; Anderson, E.D.; Moore, I.N.; Kieh, M.D.; Williams, K.W.; Saleem, A.; Fontecilla, N.M.; Welch, P.A.; Darnell, D.A.; et al. First-in-human topical microbiome transplantation with Roseomonas mucosa for atopic dermatitis. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e120608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet-Réthoré, S.; Bourdès, V.; Mercenier, A.; Haddar, C.H.; Verhoeven, P.O.; Andres, P. Effect of a lotion containing the heat-treated probiotic strain Lactobacillus johnsonii NCC 533 on Staphylococcus aureus colonization in atopic dermatitis. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 10, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notay, M.; Saric-Bosanac, S.; Vaughn, A.R.; Dhaliwal, S.; Trivedi, M.; Reiter, P.N.; Rybak, I.; Li, C.C.; Weiss, L.B.; Ambrogio, L.; et al. The use of topical Nitrosomonas eutropha for cosmetic improvement of facial wrinkles. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wensel, C.R.; Pluznick, J.L.; Salzberg, S.L.; Sears, C.L. Next-Generation Sequencing: Insights to Advance Clinical Investigations of the Microbiome. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e154944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Atopic Dermatitis | Seborrheic Dermatitis | Acne Vulgaris | Rosacea | Contact Dermatitis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ↑ Increased | Staphylococcus spp. Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus epidermidis | Malassezia spp. Staphylococcus spp. Staphylococcus epidermidis Streptococcus spp. Pseudomonas spp. Acinetobacter | Cutibacterium acnes (IA1) Cutibacterium granulosum Staphylococcus epidermidis Proteobacteria Firmicutes Streptococcus spp. Malassezia spp. | Demodex folliculorum Staphylococcus epidermidis Corynebacterium kroppenstedtii | Staphylococcus aureus Enterococcus spp. Erwinia spp. Pseudomonas spp. |
| Decreased ↓ | Streptococcus spp. Cutibacterium spp. Corynebacterium spp. | Cutibacterium spp. | Actinobacteria | Roseomonas spp. Cutibacterium acnes Cutibacterium avidum | Clostridium spp. Actinomyces spp. Staphylococcus epidermidis Bifidobacterium spp. Anaerococcus spp. Staphylococcus haemolyticus |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferček, I.; Ozretić, P.; Zanze, L.; Zoričić, Z.; Dolački, L.; Čivljak, R.; Lugović-Mihić, L. The Role of Skin Microbiota in Facial Dermatoses and Related Factors: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188857
Ferček I, Ozretić P, Zanze L, Zoričić Z, Dolački L, Čivljak R, Lugović-Mihić L. The Role of Skin Microbiota in Facial Dermatoses and Related Factors: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):8857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188857
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerček, Iva, Petar Ozretić, Lucija Zanze, Zoran Zoričić, Lorena Dolački, Rok Čivljak, and Liborija Lugović-Mihić. 2025. "The Role of Skin Microbiota in Facial Dermatoses and Related Factors: A Narrative Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 8857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188857
APA StyleFerček, I., Ozretić, P., Zanze, L., Zoričić, Z., Dolački, L., Čivljak, R., & Lugović-Mihić, L. (2025). The Role of Skin Microbiota in Facial Dermatoses and Related Factors: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 8857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188857









