Age-Driven Genetic and Epigenetic Heterogeneity in B-ALL
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Genetics and Transcriptomics of Pediatrics vs. Adult B-ALL
3. Epigenetics of Pediatric vs. Adult B-ALL
3.1. Genetic Mutations in Epigenetic Regulators
3.2. DNA Methylation
3.2.1. Specific Gene Promoter Methylation
3.2.2. Genome-Wide Approaches
3.2.3. Repetitive Elements
3.3. Histone Marks
3.3.1. Epigenetic Writers
3.3.2. Epigenetic Readers and Remodelers
3.3.3. Additional Histone Modifications Remarks
3.3.4. Translational Gaps for Clinical Application of Histone PTMs-Related Epigenetic Therapies
3.4. ncRNAs
4. Concluding Remarks and Future Directions
- How do genetic and epigenetic programs evolve across age groups, and which features are true drivers of prognosis and treatment response?
- What mechanisms underlie clonal heterogeneity and relapse biology, and how can they be therapeutically intercepted?
- Can age-adapted, multi-omic biomarkers improve early diagnosis, risk stratification, and MRD monitoring in a minimally invasive manner?
- How can rational combinations of epigenetic drugs, targeted inhibitors, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy be optimized for AYAs and elderly patients?
- What strategies will ensure global accessibility and equitable implementation of precision-based therapies?
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pagliaro, L.; Chen, S.J.; Herranz, D.; Mecucci, C.; Harrison, C.J.; Mullighan, C.G.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Z.; Boissel, N.; Winter, S.S.; et al. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2024, 10, 1146–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terwilliger, T.; Abdul-Hay, M. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Comprehensive Review and 2017 Update. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7, e577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K.G.; Mullighan, C.G. Genomics in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: Insights and Treatment Implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drożak, P.; Bryliński, Ł.; Zawitkowska, J. A Comprehensive Overview of Recent Advances in Epigenetics in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers 2022, 14, 5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, K.G. Genetics and Prognosis of ALL in Children vs Adults. Hematology 2018, 2018, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Filho, A.; Piñeros, M.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Monnereau, A.; Bray, F. Epidemiological Patterns of Leukaemia in 184 Countries: A Population-Based Study. Lancet Haematol. 2018, 5, e14–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SEER*Explorer Application. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statistics-network/explorer/application.html (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Kantarjian, H.; Jabbour, E. Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: 2025 Update on Diagnosis, Therapy, and Monitoring. Am. J. Hematol. 2025, 100, 1205–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczewska, M.; Kośmider, K.; Bednarz, K.; Ostapińska, K.; Lejman, M.; Zawitkowska, J. Recent Advances in Treatment Options for Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers 2022, 14, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Makimoto, A.; Yuza, Y. Treatment of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Historical Perspective. Cancers 2024, 16, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucre, O.; Pamulapati, S.; Muzammil, Z.; Bitran, J. Advances in Therapy of Adult Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cells 2025, 14, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kegyes, D.; Ghiaur, G.; Bancos, A.; Tomuleasa, C.; Gale, R.P. Immune therapies of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in children and adults. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2024, 196, 104317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Rastogi, P.; Shah, B.; Zhang, L. B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma: New insights into genetics, molecular aberrations, subclassification and targeted therapy. Oncotarget. 2017, 8, 66728–66741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, S.; Li, Z.; Gocho, Y.; Yang, W.; Crews, K.R.; Lee, S.H.R.; Roberts, K.G.; Mullighan, C.G.; Relling, M.V.; Yu, J.; et al. Impact of Age on Pharmacogenomics and Treatment Outcomes of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 3478–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passet, M.; Kim, R.; Clappier, E. Genetic Subtypes of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Adults. Blood 2025, 145, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paietta, E.; Roberts, K.G.; Wang, V.; Gu, Z.; Buck, G.A.N.; Pei, D.; Cheng, C.; Levine, R.L.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Cheng, Z.; et al. Molecular Classification Improves Risk Assessment in Adult BCR-ABL1–Negative B-ALL. Blood 2021, 138, 948–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K.G.; Mullighan, C.G. The Biology of B-Progenitor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Med. 2020, 10, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Churchman, M.L.; Roberts, K.G.; Moore, I.; Zhou, X.; Nakitandwe, J.; Hagiwara, K.; Pelletier, S.; Gingras, S.; Berns, H.; et al. PAX5-Driven Subtypes of B-Progenitor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, S.W.; Roberts, K.G.; Gu, Z.; Shi, L.; Pounds, S.; Pei, D.; Cheng, C.; Dai, Y.; Devidas, M.; Qu, C.; et al. The Genomic Landscape of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteller, M.; Dawson, M.A.; Kadoch, C.; Rassool, F.V.; Jones, P.A.; Baylin, S.B. The Epigenetic Hallmarks of Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2024, 14, 1783–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mar, B.G.; Bullinger, L.B.; McLean, K.M.; Grauman, P.V.; Harris, M.H.; Stevenson, K.; Neuberg, D.S.; Sinha, A.U.; Sallan, S.E.; Silverman, L.B.; et al. Mutations in Epigenetic Regulators Including SETD2 Are Gained during Relapse in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Wang, L.M.; Luo, Y.; Lai, X.; Li, C.; Shi, J.; Tan, Y.; Fu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, N.; et al. Mutations in Epigenetic Regulators Are Involved in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Relapse Following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Oncotarget 2015, 7, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Deng, S.; Ding, C.; Cai, Z.; Chen, J.; Huang, Z.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Tang, B.; et al. Mutations of Epigenetic Modifier Genes Predict Poor Outcome in Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Ann. Hematol. 2024, 103, 3639–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Wang, B.Y.; Zhang, W.N.; Huang, J.Y.; Li, B.S.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, L.; Li, J.F.; Wang, M.J.; Dai, Y.J.; et al. Genomic Profiling of Adult and Pediatric B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. eBioMedicine 2016, 8, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, M.E.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Lu, C.; Ward, P.S.; Patel, J.; Shih, A.; Li, Y.; Bhagwat, N.; Vasanthakumar, A.; Fernandez, H.F.; et al. Leukemic IDH1 and IDH2 Mutations Result in a Hypermethylation Phenotype, Disrupt TET2 Function, and Impair Hematopoietic Differentiation. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Ward, P.S.; Kapoor, G.S.; Rohle, D.; Turcan, S.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Edwards, C.R.; Khanin, R.; Figueroa, M.E.; Melnick, A.; et al. IDH Mutation Impairs Histone Demethylation and Results in a Block to Cell Differentiation. Nature 2012, 483, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, T.; Sanada, M.; Kawazu, M.; Kojima, S.; Tsuzuki, S.; Ueno, H.; Iwamoto, E.; Iijima-Yamashita, Y.; Yamada, T.; Kanamori, T.; et al. Two Novel High-Risk Adult B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Subtypes with High Expression of CDX2 and IDH1/2 Mutations. Blood 2022, 139, 1850–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leegwater, P.A.J.; Lambooy, L.H.J.; De Abreu, R.A.; Bökkerink, J.P.M.; Van Den Heuvel, L.P. DNA Methylation Patterns in the Calcitonin Gene Region at First Diagnosis and at Relapse of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL). Leukemia 1997, 11, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Corn, P.G.; Kuerbitz, S.J.; Van Noesel, M.M.; Esteller, M.; Compitello, N.; Baylin, S.B.; Herman, J.G. Transcriptional Silencing of the P73 Gene in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Burkitt’s Lymphoma Is Associated with 5′ CpG Island Methylation. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 3352–3356. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Garcia-Manero, G.; Daniel, J.; Smith, T.L.; Kornblau, S.M.; Lee, M.-S.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Issa, J.-P.J. DNA Methylation of Multiple Promoter-Associated CpG Islands in Adult Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 2217–2224. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Shen, L.L.; Toyota, M.; Kondo, Y.; Obata, T.; Daniel, S.; Pierce, S.; Imai, K.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Issa, J.P.J.; Garcia-Manero, G. Aberrant DNA Methylation of P57KIP2 Identifies a Cell-Cycle Regulatory Pathway with Prognostic Impact in Adult Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia. Blood 2003, 101, 4131–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueso-Ramos, C.; Xu, Y.; McDonnell, T.J.; Brisbay, S.; Pierce, S.; Kantarjian, H.; Rosner, G.; Garcia-Manero, G. Protein Expression of a Triad of Frequently Methylated Genes, P73, P57Kip2, and P15, Has Prognostic Value in Adult Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia Independently of Its Methylation Status. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 3932–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, M.I.; Siraj, A.K.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Hussain, A.; Bhatia, K. Childhood and Adult ALL: Differences in Epigenetic Lesions Associated with Cell Cycle Genes. Am. J. Hematol. 2005, 80, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumpel, D.J.P.M.; Schneider, P.; Seslija, L.; Osaki, H.; Williams, O.; Pieters, R.; Stam, R.W. Connectivity Mapping Identifies HDAC Inhibitors for the Treatment of t(4;11)-Positive Infant Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia 2011, 26, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Brennan, S.; Milne, T.A.; Chen, W.Y.; Li, Y.; Hurtz, C.; Kweon, S.M.; Zickl, L.; Shojaee, S.; Neuberg, D.; et al. Integrative Epigenomic Analysis Identifies Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets in Adult B-Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunwell, T.L.; Dickinson, R.E.; Stankovic, T.; Dallol, A.; Weston, V.; Austen, B.; Catchpoole, D.; Maher, E.R.; Lalif, F. Frequent Epigenetic Inactivation of the SLIT2 Gene in Chronic and Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia. Epigenetics 2009, 4, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, L.E.; Meyer, J.A.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Wong, N.; Yang, W.; Condos, G.; Hunger, S.P.; Raetz, E.; Saffery, R.; et al. Integrated Genomic Analysis of Relapsed Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Reveals Therapeutic Strategies. Blood 2011, 118, 5218–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatla, T.; Wang, J.; Morrison, D.J.; Raetz, E.A.; Burke, M.J.; Brown, P.; Carroll, W.L. Epigenetic Reprogramming Reverses the Relapse-Specific Gene Expression Signature and Restores Chemosensitivity in Childhood B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2012, 119, 5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musialik, E.; Bujko, M.; Kober, P.; Wypych, A.; Gawle-Krawczyk, K.; Matysiak, M.; Siedlecki, J.A. Promoter Methylation and Expression Levels of Selected Hematopoietic Genes in Pediatric B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood Res. 2015, 50, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kuang, S.Q.; Fang, Z.; Zweidler-McKay, P.A.; Yang, H.; Wei, Y.; Gonzalez-Cervantes, E.A.; Boumber, Y.; Garcia-Manero, G. Epigenetic Inactivation of Notch-Hes Pathway in Human B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, M.; Choo, C.W.; Alias, H.; Abdul Rahman, E.J.; Mohd Ibrahim, H.; Jamal, R.; Hussin, N.H. ADAMTSL5 and CDH11: Putative Epigenetic Markers for Therapeutic Resistance in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Hematology 2017, 22, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yan, C.; Yu, Z.; He, C.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Yan, M.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, Z. Downregulation of CDH11 Promotes Metastasis and Resistance to Paclitaxel in Gastric Cancer Cells. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lei, P.; Samuel, R.Z.; Kashyap, A.M.; Groth, T.; Bshara, W.; Neelamegham, S.; Andreadis, S.T. Cadherin-11 Increases Tumor Cell Proliferation and Metastatic Potential via Wnt Pathway Activation. Mol. Oncol. 2023, 17, 2056–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arechederra, M.; Bazai, S.K.; Abdouni, A.; Sequera, C.; Mead, T.J.; Richelme, S.; Daian, F.; Audebert, S.; Dono, R.; Lozano, A.; et al. ADAMTSL5 Is an Epigenetically Activated Gene Underlying Tumorigenesis and Drug Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeff, F.C.; Rijs, K.; van Egmond, E.H.M.; Zoutman, W.H.; Qiao, X.; Kroes, W.G.M.; Veld, S.A.J.; Griffioen, M.; Vermeer, M.H.; Neefjes, J.; et al. Loss of the GPI-Anchor in B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia by Epigenetic Downregulation of PIGH Expression. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghantous, A.; Nusslé, S.G.; Nassar, F.J.; Spitz, N.; Novoloaca, A.; Krali, O.; Nickels, E.; Cahais, V.; Cuenin, C.; Roy, R.; et al. Epigenome-Wide Analysis across the Development Span of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Backtracking to Birth. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, F.; Pandith, A.A.; Rasool, S.U.A.; Guru, F.R.; Qasim, I.; Geelani, S.; Nisar, S.; Baba, S.M.; Ganie, F.A.; Kouser, S.; et al. Significance and Implications of FHIT Gene Expression and Promoter Hypermethylation in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL). Discover. Oncol. 2024, 15, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, J.; Heyn, H.; Méndez-González, J.; Gomez, A.; Moran, S.; Baiget, M.; Melo, M.; Badell, I.; Nomdedéu, J.F.; Esteller, M. Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Profiling Predicts Relapse in Childhood B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 160, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordlund, J.; Bäcklin, C.L.; Wahlberg, P.; Busche, S.; Berglund, E.C.; Eloranta, M.L.; Flaegstad, T.; Forestier, E.; Frost, B.M.; Harila-Saari, A.; et al. Genome-Wide Signatures of Differential DNA Methylation in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Genome. Biol. 2013, 14, r105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordlund, J.; Bäcklin, C.L.; Zachariadis, V.; Cavelier, L.; Dahlberg, J.; Öfverholm, I.; Barbany, G.; Nordgren, A.; Övernäs, E.; Abrahamsson, J.; et al. Dna Methylation-Based Subtype Prediction for Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clin. Epigenet. 2015, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.S.; Lafta, F.M.; Schwalbey, E.C.; Nakjang, S.; Cockell, S.J.; Iliasova, A.; Enshaei, A.; Schwab, C.; Rand, V.; Clifford, S.C.; et al. Epigenetic Landscape Correlates with Genetic Subtype but Does Not Predict Outcome in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Epigenetics 2015, 10, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, M.E.; Chen, S.C.; Andersson, A.K.; Phillips, L.A.; Li, Y.; Sotzen, J.; Kundu, M.; Downing, J.R.; Melnick, A.; Mullighan, C.G. Integrated Genetic and Epigenetic Analysis of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.T.; Muench, M.O.; Fomin, M.E.; Xiao, J.; Zhou, M.; De Smith, A.; Martín-Subero, J.I.; Heath, S.; Houseman, E.A.; Roy, R.; et al. Epigenetic Remodeling in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Occurs in Two Tracks and Employs Embryonic Stem Cell-like Signatures. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2015, 43, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejedor, J.R.; Bueno, C.; Vinyoles, M.; Petazzi, P.; Agraz-Doblas, A.; Cobo, I.; Torres-Ruiz, R.; Bayón, G.F.; Pérez, R.F.; López-Tamargo, S.; et al. Integrative Methylome-Transcriptome Analysis Unravels Cancer Cell Vulnerabilities in Infant MLL-Rearranged B Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e138833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Liu, T.; Hao, Q.; Fang, Q.; Gong, X.; Li, Y.; Tian, Z.; Wei, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; et al. Comprehensive Omics-Based Classification System in Adult Patients with B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Mol. Oncol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujko, M.; Musialik, E.; Olbromski, R.; Przestrzelska, M.; Libura, M.; Pastwińska, A.; Juszczyński, P.; Zwierzchowski, L.; Baranowski, P.; Siedlecki, J.A. Repetitive Genomic Elements and Overall DNA Methylation Changes in Acute Myeloid and Childhood B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients. Int. J. Hematol. 2014, 100, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, M.J.; Bhatla, T. Epigenetic Modifications in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Pediatr. 2014, 2, 82871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janczar, S.; Janczar, K.; Pastorczak, A.; Harb, H.; Paige, A.J.W.; Zalewska-Szewczyk, B.; Danilewicz, M.; Mlynarski, W. The Role of Histone Protein Modifications and Mutations in Histone Modifiers in Pediatric B-Cell Progenitor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers 2017, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivtsov, A.V.; Armstrong, S.A. MLL Translocations, Histone Modifications and Leukaemia Stem-Cell Development. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, J.D.; Wang, Y.; Chan, H.M.; Zhang, J.; Huether, R.; Kryukov, G.V.; Bhang, H.E.C.; Taylor, J.E.; Hu, M.; Englund, N.P.; et al. Global Chromatin Profiling Reveals NSD2 Mutations in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, J.; Han, Q.; Sun, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, R.C.H. Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 Is Overexpressed and Contributes to Epigenetic Inactivation of P21 and Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Exp. Biol. Med. 2012, 237, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zheng, M.; Ma, S.; Nie, F.; Yin, Z.; Liang, Y.; Yan, X.; Wen, W.; Yu, J.; Liang, Y.; et al. YTHDC1 Is a Therapeutic Target for B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia by Attenuating DNA Damage Response through the KMT2C-H3K4me1/Me3 Epigenetic Axis. Leukemia 2024, 39, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advani, A.S.; Gibson, S.E.; Douglas, E.; Jin, T.; Zhao, X.; Kalaycio, M.; Copelan, E.; Sobecks, R.; Sekeres, M.; Sungren, S.; et al. Histone H4 Acetylation by Immunohistochemistry and Prognosis in Newly Diagnosed Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) Patients. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janczar, K.; Janczar, S.; Pastorczak, A.; Mycko, K.; Paige, A.J.W.; Zalewska-Szewczyk, B.; Wagrowska-Danilewicz, M.; Danilewicz, M.; Mlynarski, W. Preserved Global Histone H4 Acetylation Linked to ETV6-RUNX1 Fusion and PAX5 Deletions Is Associated with Favorable Outcome in Pediatric B-Cell Progenitor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2015, 39, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chang, N.; Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, R.; Liao, P.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; et al. Histone Acetylation by HBO1 (KAT7) Activates Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling to Promote Leukemogenesis in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, C.J.; Kopp, N.; Bird, L.; Paranal, R.M.; Qi, J.; Bowman, T.; Rodig, S.J.; Kung, A.L.; Bradner, J.E.; Weinstock, D.M. BET Bromodomain Inhibition Targets Both C-Myc and IL7R in High-Risk Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2012, 120, 2843–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, D.; Agathanggelou, A.; Perry, T.; Weston, V.; Petermann, E.; Zlatanou, A.; Oldreive, C.; Wei, W.; Stewart, G.; Longman, J.; et al. BET Inhibition as a Single or Combined Therapeutic Approach in Primary Paediatric B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Blood Cancer J. 2013, 3, e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Lu, J.; Ling, J.; Chu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, Y.; Li, X.; Tian, Y.; et al. BRD4 PROTAC Degrader MZ1 Exhibits Anti-B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Effects via Targeting CCND3. Hematology 2023, 28, 2247253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, P.; Roberts, C.W.M. The SWI/SNF Complex in Cancer—Biology, Biomarkers and Therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Modak, S.B.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Purohit, J.S. SWI/SNF Chromatin Remodelers: Structural, Functional and Mechanistic Implications. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2023, 81, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Q.; Ma, D.; Zhao, P.; Chai, X.; Huang, Y.; Gao, R.; Zhang, T.; Liu, P.; Deng, B.; Feng, C.; et al. BRG1 Promotes Progression of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia by Disrupting PPP2R1A Transcription. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Shao, Y.; Nance, S.; Dang, J.; Xu, B.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Ju, B.; Dong, L.; Newman, S.; et al. Long-Read Sequencing Unveils IGH-DUX4 Translocation into the Silenced IGH Allele in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, A.D.; Hoff, F.W.; Qiu, Y.H.; Chandra, J.; Jabbour, E.; de Bont, E.S.J.M.; Horton, T.M.; Kornblau, S.M. Loss of H3K27 Methylation Identifies Poor Outcomes in Adult-Onset Acute Leukemia. Clin. Epigenet. 2021, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, W.P.J.; Evander, N.; van Ingen Schenau, D.S.; Stoll, G.R.; Anderson, N.; de Groot, L.; Grünewald, K.J.T.; Hagelaar, R.; Butler, M.; Kuiper, R.P.; et al. Histone Deacetylase Inhibition Sensitizes P53-Deficient B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia to Chemotherapy. Haematologica 2024, 109, 1755–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, M.S.; Sanaat, Z.; Akbarzadeh, M.A.; Vaez-Gharamaleki, Y.; Akbarzadeh, M. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors for Leukemia Treatment: Current Status and Future Directions. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, Z.C.; Wu, Y.Y.; Pi, Y.N.; Lou, S.H.; Liu, T.B.; Lou, G.; Yang, C. Bromodomain and Extraterminal (BET) Proteins: Biological Functions, Diseases, and Targeted Therapy. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, K.; Bayraktar, R.; Ferracin, M.; Calin, G.A. Non-Coding RNAs in Disease: From Mechanisms to Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2024, 25, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Kim, V.N. Small and Long Non-Coding RNAs: Past, Present, and Future. Cell 2024, 187, 6451–6485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisignano, G.; Michael, D.C.; Visal, T.H.; Pirlog, R.; Ladomery, M.; Calin, G.A. Going Circular: History, Present, and Future of CircRNAs in Cancer. Oncogene 2023, 42, 2783–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.L. Cellular Functions of Long Noncoding RNAs. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2019, 21, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Esmaeili, M.; Taheri, M. Expression of Non-Coding RNAs in Hematological Malignancies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 875, 172976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbar, R.; Karimian, A.; Aghaie Fard, A.; Tourani, M.; Majidinia, M.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Yousefi, B. The Importance of MiRNAs and Epigenetics in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Prognosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 3216–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, P.D.; Paculova, H.; Kogut, S.; Heath, J.; Schjerven, H.; Frietze, S. Non-Coding RNA Signatures of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziętara, K.J.; Lejman, J.; Wojciechowska, K.; Lejman, M. The Importance of Selected Dysregulated MicroRNAs in Diagnosis and Prognosis of Childhood B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers 2023, 15, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illarregi, U.; Telleria, J.; Bilbao-Aldaiturriaga, N.; Lopez-Lopez, E.; Ballesteros, J.; Martin-Guerrero, I.; Gutierrez-Camino, A. LncRNA Deregulation in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Oncol. 2022, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakidis, I.; Kyriakidis, K.; Tsezou, A. MicroRNAs and the Diagnosis of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Re-Analysis with Novel Small RNA-Seq Tools. Cancers 2022, 14, 3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Navarrete-Meneses, M.P.; Pérez-Vera, P. Epigenetic Alterations in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Bol. Méd. Hosp. Infant. Méx. (Engl. Ed.) 2017, 74, 243–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.R.; Schroeder, M.P.; Neumann, M.; Bastian, L.; Eckert, C.; Gökbuget, N.; Tanchez, J.O.; Schlee, C.; Isaakidis, K.; Schwartz, S.; et al. Long Non-Coding RNAs Defining Major Subtypes of B Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, H. Long Non-Coding RNA RP11-252C15.1 Is a Potential Biomarker of Prognosis and Hallmark for Leukemogenesis in Children with B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Acta Haematol. 2024, 147, 646–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Du, X.; Yang, M.; Xiao, S.; Cao, J.; Song, J.; Wang, L. LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 Contributes to STAT3 Activation by Associating with IL-11 in B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Biotechnol. Lett. 2017, 39, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Feng, X.; Liu, Z.; Liao, Y.; Pu, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhai, Z.; Xiong, S. HDAC2-MiR183-5p Epigenetic Circuit Contributes to the Growth of Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive B Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia via PTEN/AKT and c-MYC Signaling Pathway. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2025, 117, qiae200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, T.; Li, X.; Tang, J. Targeting the LncRNA DUXAP8/MiR-29a/PIK3CA Network Restores Doxorubicin Chemosensitivity via PI3K-AKT-MTOR Signaling and Synergizes With Inotuzumab Ozogamicin in Chemotherapy-Resistant B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 773601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longjohn, M.N.; Hudson, J.A.B.J.; Peña-Castillo, L.; Cormier, R.P.J.; Hannay, B.; Chacko, S.; Lewis, S.M.; Moorehead, P.C.; Christian, S.L. Extracellular Vesicle Small RNA Cargo Discriminates Non-Cancer Donors from Pediatric B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1272883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poncelet, L.; Richer, C.; Gutierrez-Camino, A.; Veres, T.; Sinnett, D. Long Circulating RNAs Packaged in Extracellular Vesicles: Prospects for Improved Risk Assessment in Childhood B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
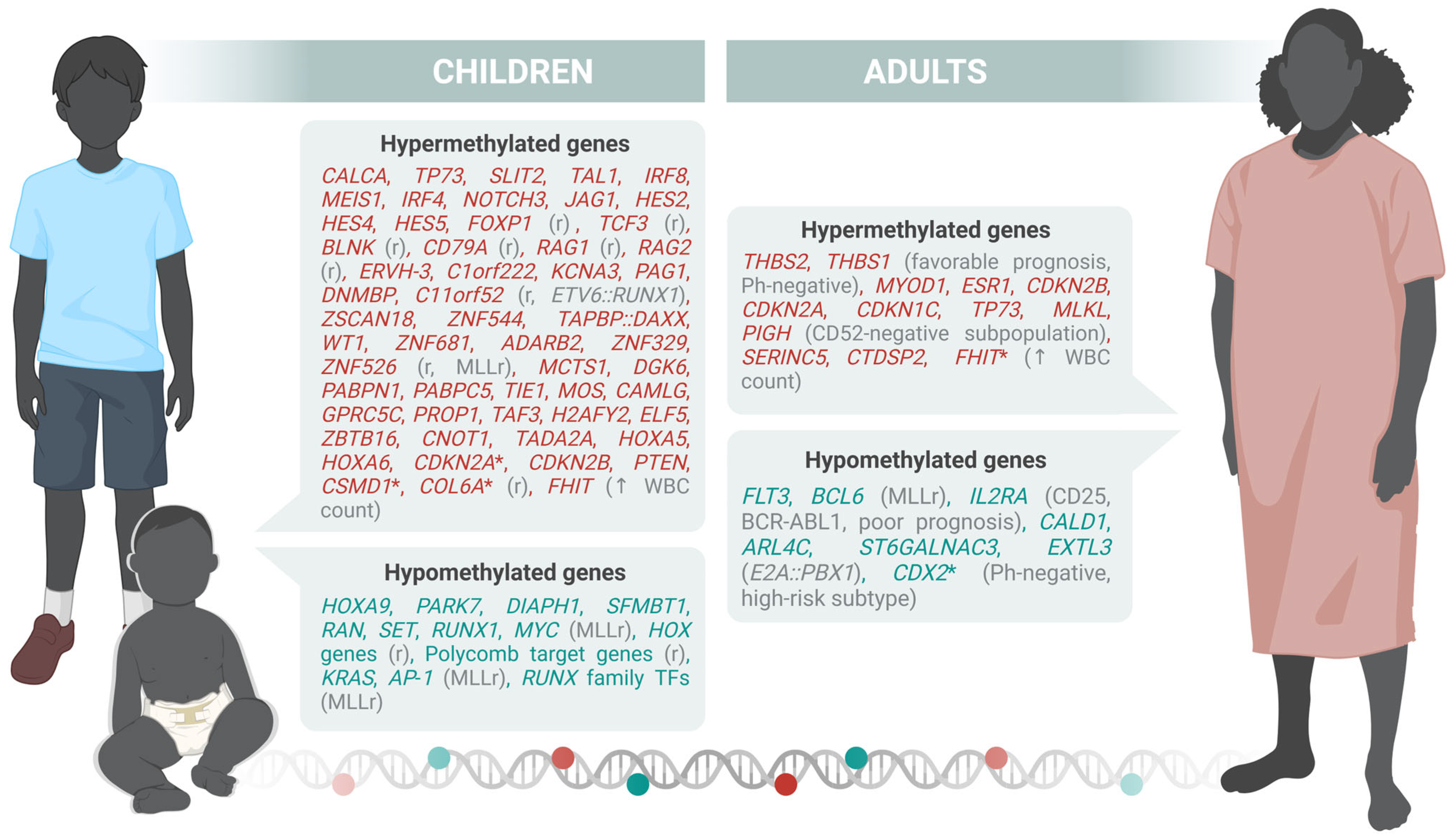
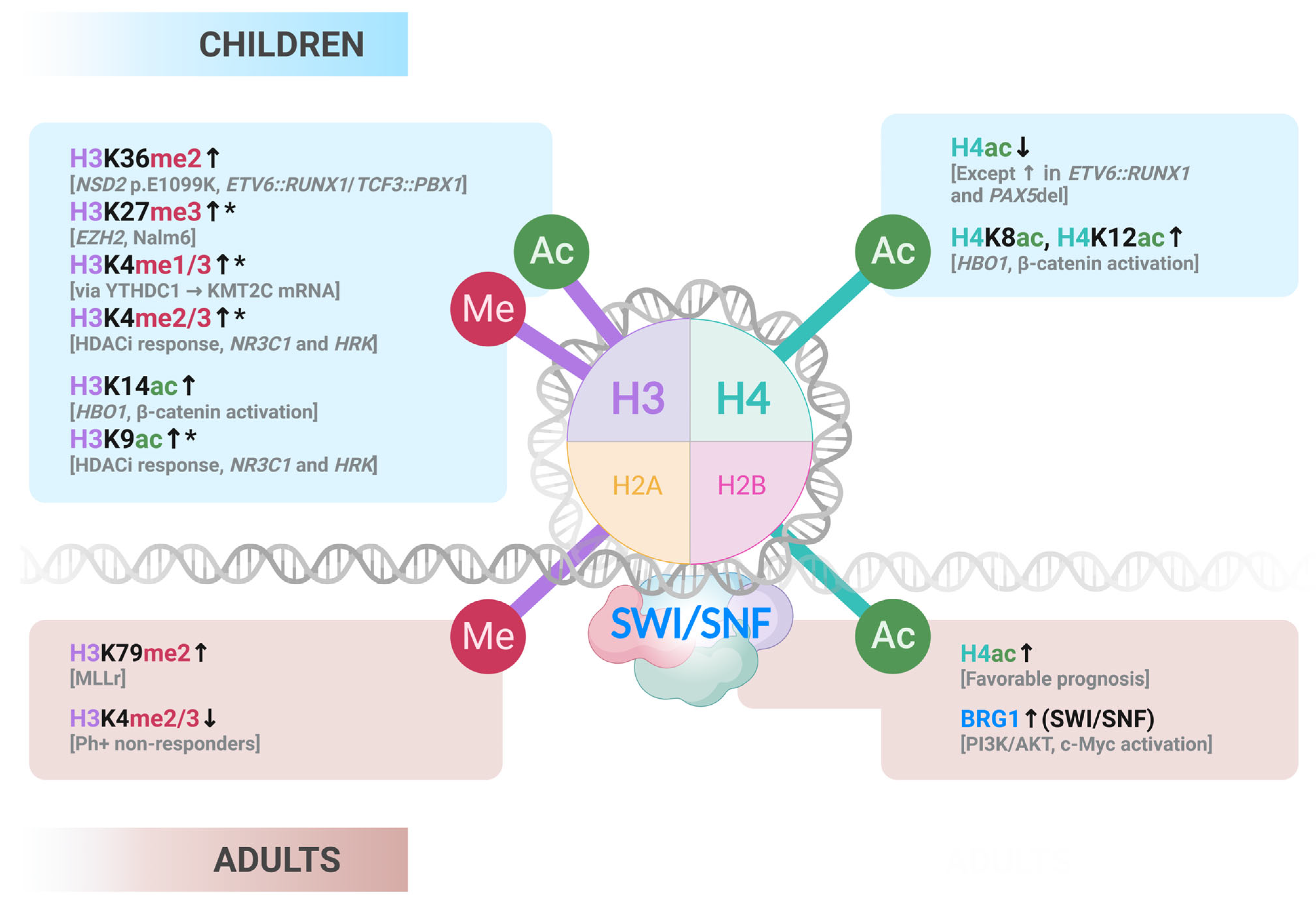
| Category | Subtype | Pediatric Frequency | Adult Frequency | Definition/Characteristics | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chromosomal Aneuploidy | High hyperdiploidy | ~30% | <10% | Gain of ≥5 chromosomes; nonrandom gains (e.g., 4, 10, 14, 21, X). Often RAS and epigenetic mutations. | Good in children, favorable in adults. |
| Low hypodiploidy | <1% | 5–15% | 32–39 chromosomes. TP53 mutations, germline in children, somatic in adults. | Poor, increasing with age. | |
| Near haploidy | ∼2% | <1% | 24–31 chromosomes. RAS mutations, IKZF3 deletions. | Very poor prognosis. | |
| Chromosomal Abnormalities | BCR::ABL1 (Ph+) | 2–5% | 20–40% | t(9;22). Common in older adults. IKZF1 deletions frequent. | Historically poor; better with TKIs. |
| KMT2A-rearranged (MLLr) | ∼80% in infants | 5–15% | t(v;11q23), often AFF1. High WBC, therapy-related. | Poor; needs intensive or novel treatment. | |
| ETV6::RUNX1 | ∼25% | 1–2% | t(12;21). Frequent in pediatric B-ALL. | Good in children; favorable in AYA. | |
| TCF3::PBX1 | 2–6% | 2–6% | t(1;19). CNS involvement common. | Prognosis variable; CNS-directed therapy important. | |
| iAMP21 | ∼3% | <2% | RUNX1 amplification. Rare in adults. | Poor unless intensively treated. | |
| HLF-rearranged | <1% | <1% | t(17;19); t(17;18). Rare, associated with hypercalcemia. | Dismal prognosis. | |
| PAX5alt | ∼10% | 5–10% | Multiple alterations in PAX5; frequent CDKN2A, IKZF1 deletions. | Intermediate to poor prognosis. | |
| DUX4-rearranged | ∼8% | 2–10% | t(4;14). CD371+, IGH rearranged, IKZF1 and ERG deletions. | Favorable prognosis. | |
| Point Mutations | PAX5 P80R | <2% | 3–6% | Missense mutation in PAX5; JAK-STAT/RAS pathway mutations common. | Favorable to intermediate. |
| IKZF1 N159Y | <1% | <1% | Rare point mutation with Chr 21 gain. | Unknown significance. | |
| IDH1/2 | ND | 1–2% | Metabolic gene mutations. | Poor prognosis. | |
| Transcriptional Signatures | BCR::ABL1-like (Ph-like) | 10–15% | 15–30% | CRLF2 rearranged or kinase-activated; resembles Ph+ without BCR::ABL1 fusion. | Poor; may respond to TKIs and targeted therapies. |
| ETV6::RUNX1-like | ∼3% | <1% | Similar expression to ETV6::RUNX1; ARPP21, IKZF1 deletions. | Likely favorable. | |
| KMT2A-like | <1% | <1% | Poor prognosis. | ||
| ZNF384-like | ∼5% | 2–8% | Mimics ZNF384-r with kinase and epigenetic pathway alterations. | Intermediate prognosis. |
| Reference | Population | Lineage | Altered Genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sandoval et al., 2012 [49] | 29 pediatric B-ALL (normal karyotype, hyperdiploid, pseudodiploid, others; relapse vs. non-relapse) | B | Hypermethylated (relapse group): FOXP1, TCF3, BLNK, CD79A, RAG1, RAG2. Hypomethylated: HOXA cluster (HOXA5/6/9), Polycomb target genes |
| Nordlund et al., 2013 [50] | 764 pediatric ALL (663 B, 101 T) + 27 relapse samples | B + T | Core hypermethylated (9406 CpGs): CDKN2A, CDKN2B, PTEN, TP73, DAPK1, WIF1, SFRP2/5, APC, HOXA5/6/9, TIE1, MOS, PCDH loci. Subtypes: HeH (hypomethylated: DDIT4L, PTPRG, FHIT); MLL-r (hypermethylated: BNIP3, ZAP70, XYLT2, HLA-B, EDEM1); Relapse (hypermethylated: CDH3, TBX2, ERCC1, NPR2, DAPK1, CCR6, HRK, LIFR1, DLX3) |
| Nordlund et al., 2015 [51] | 546 pediatric ALL (7 B-ALL subtypes, T-ALL) | B + T | ETV6-RUNX1: Hypermethylated promoters: CDKN2A/B, PTEN, DAPK1. MLL-r: HOXA cluster (HOXA9-11) hypomethylated; PcG targets hypermethylated. Classifier CpGs included EPOR, ASNS, TCF3, PBX1, and EBF1 regulatory regions |
| Gabriel et al., 2015 [52] | 52 pediatric B-ALL (ETV6-RUNX1, HeH, TCF3-PBX1, dic(9;20)) | B | ETV6-RUNX1 and dic(9;20): mostly hypermethylated (E2F6, DCC, NKX6-1, PTPN6). HeH and TCF3-PBX1: broad hypomethylation (ZNF clusters, intergenic). No consistent relapse-specific DMCs |
| Figueroa et al., 2013 [53] | 167 pediatric ALL (137 B, 30 T) | B + T | Hypermethylated (66 genes): TIE1, MOS, CAMLG, GPRC5C, MCTS1, DGKG, PABPN1, PABPC5, PROP1, TAF3, H2AFY2, ELF5, ZBTB16, CNOT1, TADA2A, HOXA5/6, CDKN2A/B, PTEN, BNIP3, DAPK1, SYK, BRINP1, WIF1. Hypomethylated: KRAS, FUT9, ADCY2, CETN3, ELF5, DNTT |
| Lee et al., 2015 [54] | 227 pediatric B-ALL (ETV6-RUNX1, HeH, others) | B | ETV6-RUNX1: hypermethylated ASNS, EPOR, PDK4, SYT family. HeH: global intergenic demethylation. PcG targets (GATA4, HLF, PAX5/6, HOXD1) hypermethylated |
| Tejedor et al., 2021 [55] | 69 infant B-ALL (37 MLL-AF4+, 12 MLL-AF9+, 20 non-MLLr) | B | Hypomethylated: FOS, JUN, RUNX1 (AP-1 network). Hypermethylated: developmental PcG targets (SOX2, OCT4, NANOG genes, DAPK1, CCR6, HRK, LIFR1, FHIT) |
| Geng et al., 2012 [36] | 215 adult B-ALL patients enrolled in a phase III clinical trial (ECOG E2993). | B | Hypomethylated: FLT3 and BCL6, IL2RA(CD25). |
| Song et al., 2025 [56] | 88 adult B-ALL patients (69 newly diagnosed and 19 relapsed/refractory). | B | Hypomethylated: MYC |
| Age Group | Type | Affection in B-ALL | ncRNAs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pediatric | miRNA | Upregulation | miR-155, miR-181a, miR-128, miR-130b, miR-210, miR-222, miR-708, miR-363 |
| Downregulation | miR-125b, miR-143, miR-148a, miR-223, miR-145, let-7e, miR-100, miR-340, miR-335 | ||
| lncRNA | Upregulation | AWPPH, BALR-2, CRNDE, MALAT1, LINC00958, RP11-252C15.1, ZEB1-AS1, DUXAP8 | |
| Downregulation | LINC00926, AC009495.3, CECR7, RP11-624C23.1, AC083949.1, SNHG16 | ||
| circRNA | Upregulation | circAF4 | |
| EV-associated ncRNA | Disease discrimination | let-7f-5p, miR-26b-5p, miR-335-5p (down in B-ALL); miR-4645 (up in B-ALL EVs) | |
| Adult | miRNA | Downregulation | miR-183-5p (in Ph+ B-ALL); miR-29a (drug resistance context); miR-125b (mixed data, often lower in adults) |
| lncRNA | Upregulation | DUXAP8 (chemoresistance), ZEB1-AS1 (STAT3 activation, functional data appear in adults as well as pediatric) | |
| Both | miRNA | Both | miR-29a (drug resistance), miR-125b (over/under expressed by subgroup), miR-146a (often up, subtype- and context-specific) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Veselinova, Y.; Esteller, M.; Ferrer, G. Age-Driven Genetic and Epigenetic Heterogeneity in B-ALL. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188774
Veselinova Y, Esteller M, Ferrer G. Age-Driven Genetic and Epigenetic Heterogeneity in B-ALL. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):8774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188774
Chicago/Turabian StyleVeselinova, Yoana, Manel Esteller, and Gerardo Ferrer. 2025. "Age-Driven Genetic and Epigenetic Heterogeneity in B-ALL" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 8774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188774
APA StyleVeselinova, Y., Esteller, M., & Ferrer, G. (2025). Age-Driven Genetic and Epigenetic Heterogeneity in B-ALL. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 8774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188774







