Establishment of Multiplex Digital PCR Assay for Detection of Four Porcine Enteric Coronaviruses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Result
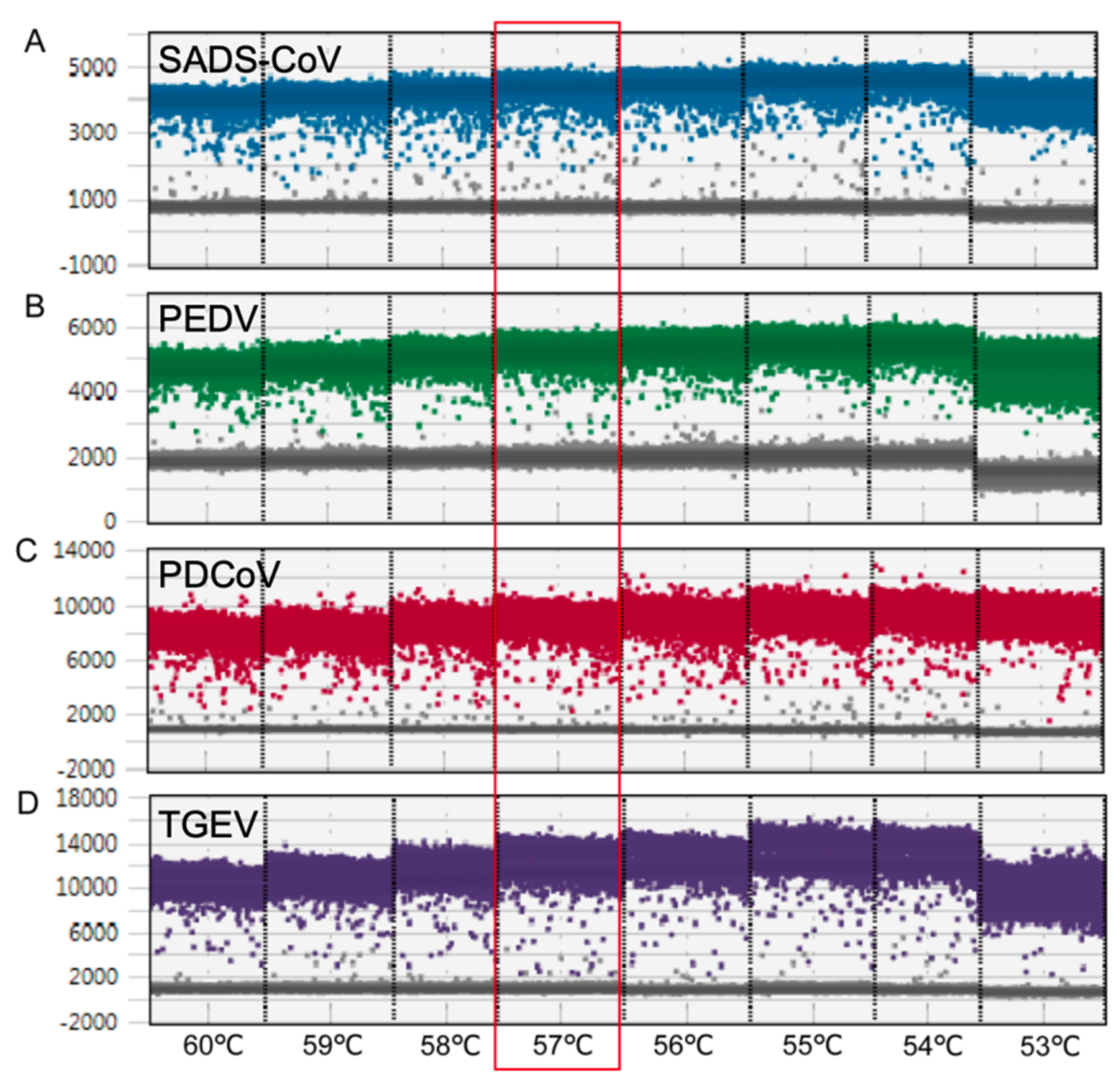
2.1. PCR Reaction Optimization
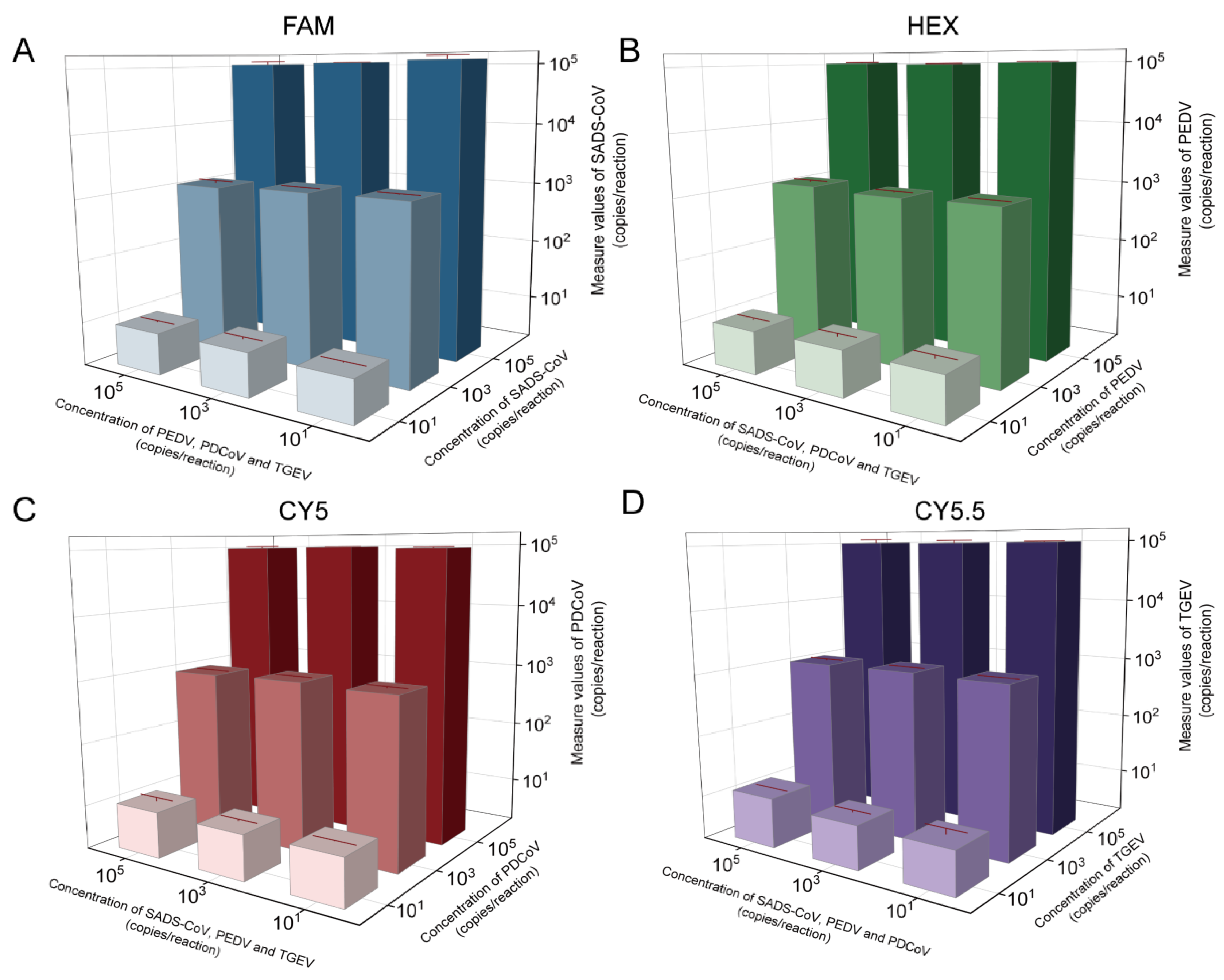
2.2. Anti-Interference
2.3. Specificity of the Multiplex dPCR
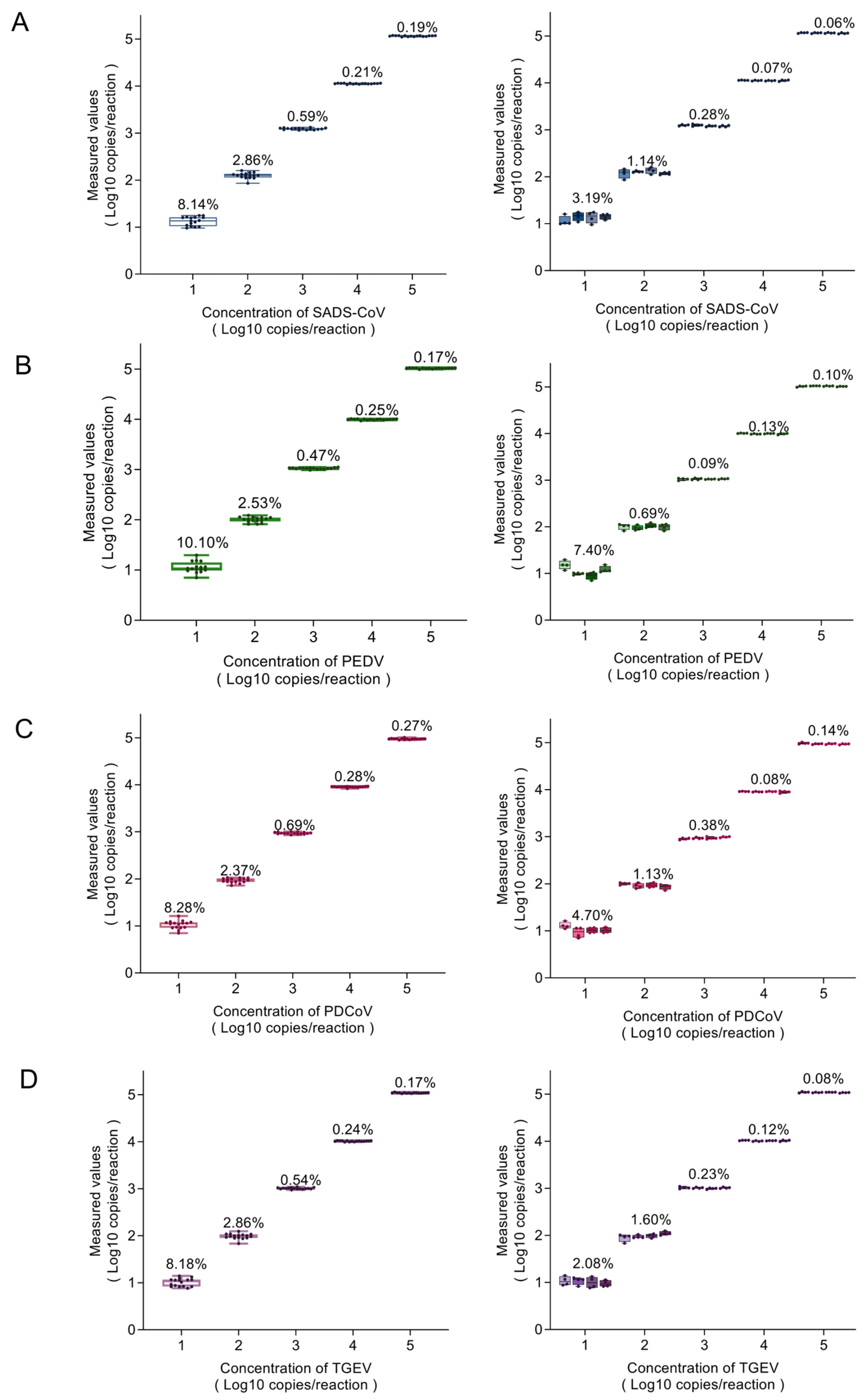
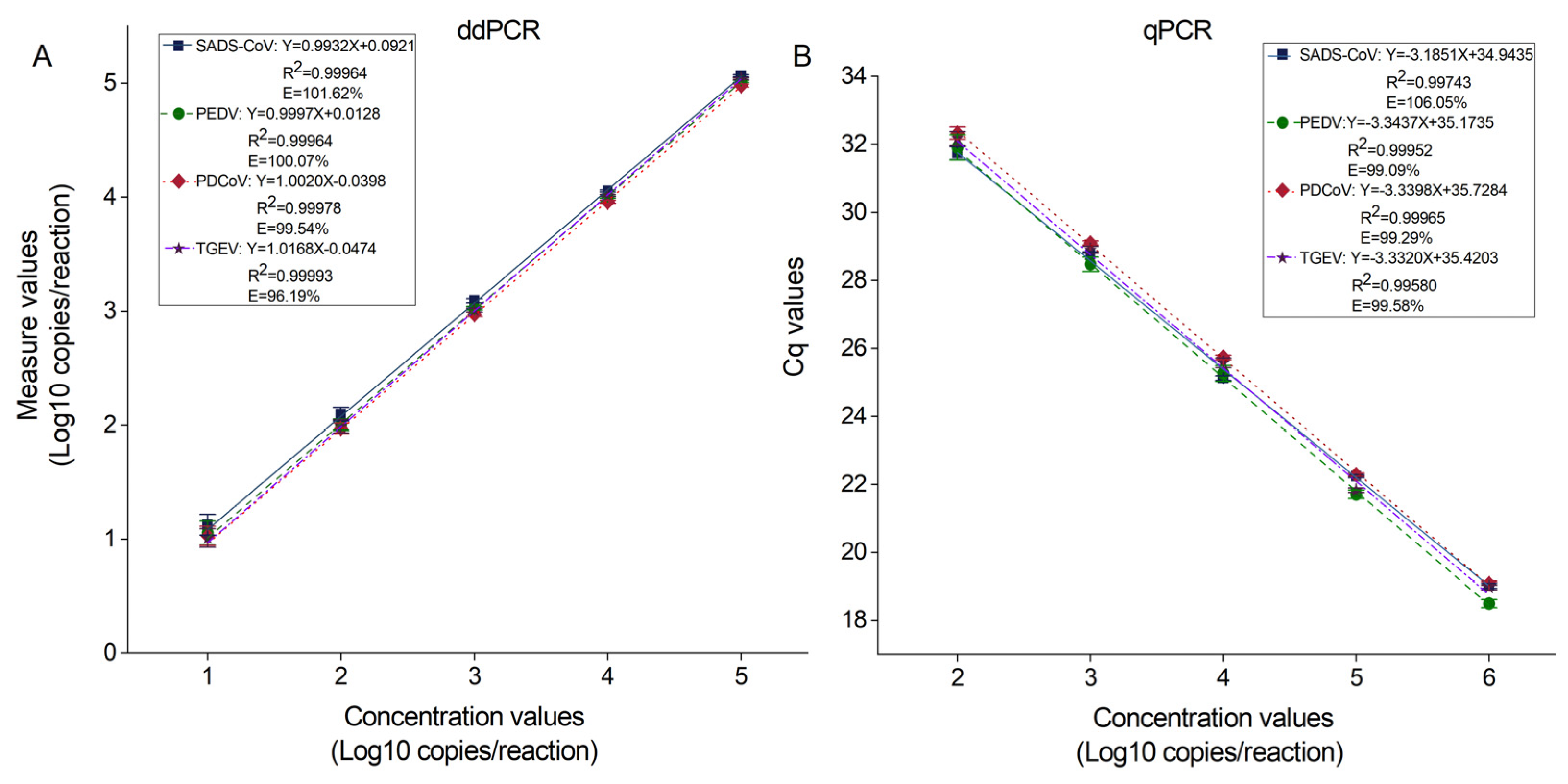
2.4. Repeatability and the Standard Curve
2.5. Sensitivity of the Multiplex dPCR
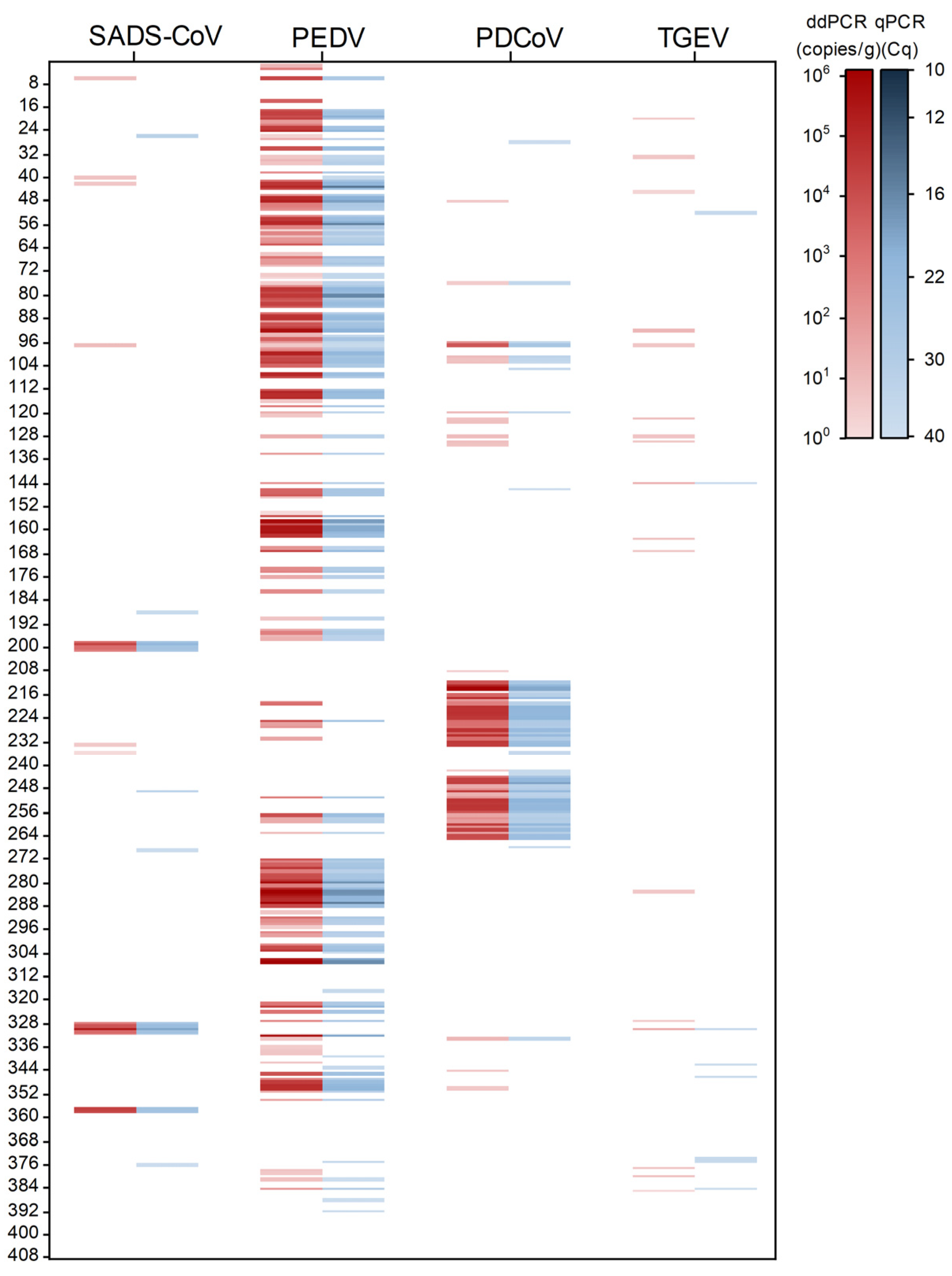
2.6. Sample Detection of dPCR and qPCR
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Virus
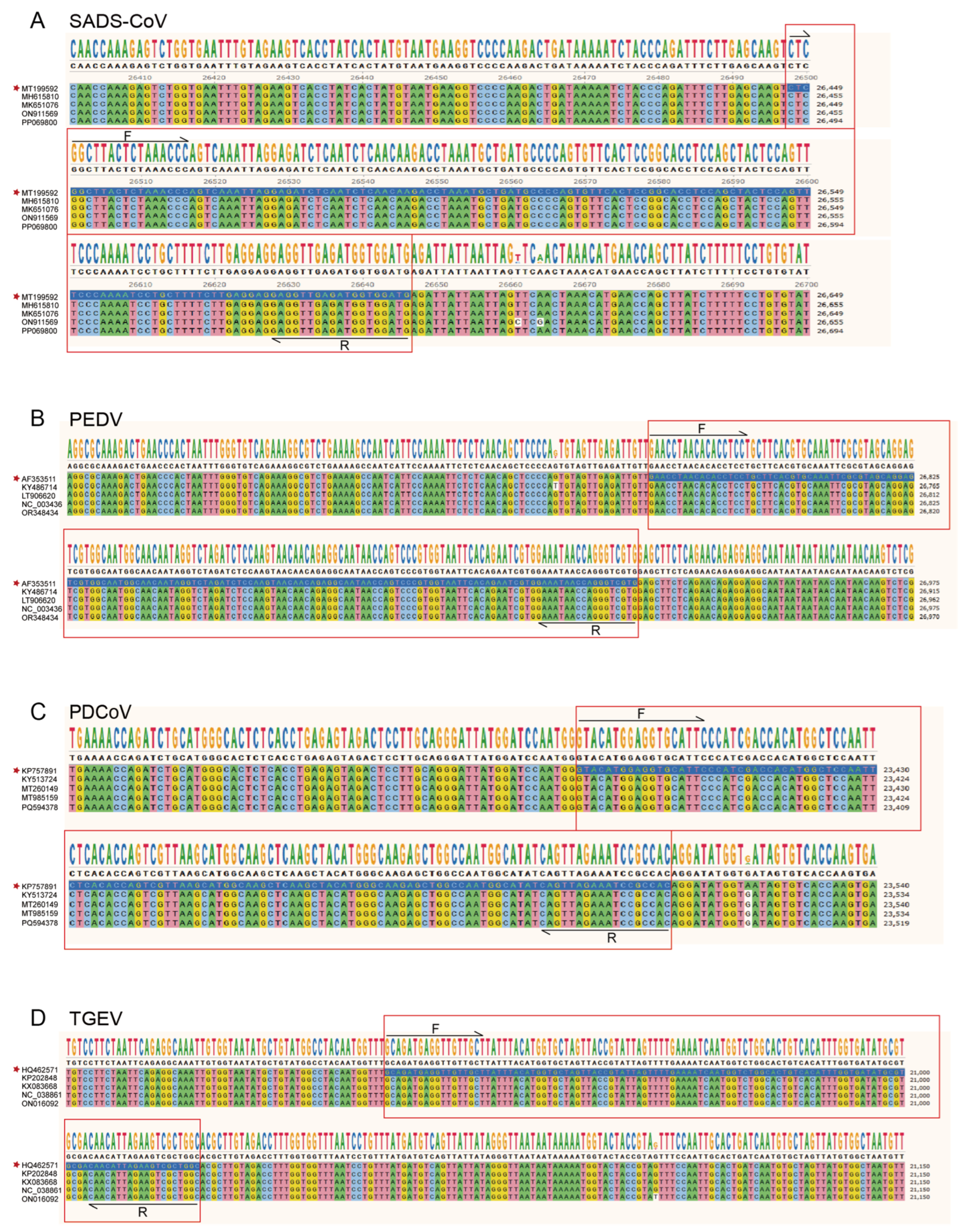
4.2. Primers and Probes
4.3. Standard Plasmid Construction and Concentration Determination
4.4. Nucleic Acid Extraction and Reverse Transcription
4.5. Optimization of the Multiplex dPCR Assay
4.6. Anti-Interference Analysis
4.7. Specificity, Repeatability, and Sensitivity of the Multiplex dPCR
4.8. Sample Detection
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lai, M.; Cavanagh, D. The Molecular Biology of Coronaviruses. In Advances in Virus Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; Volume 48, pp. 1–100. [Google Scholar]
- Su, S.; Wong, G.; Shi, W.; Liu, J.; Lai, A.C.K.; Zhou, J.; Liu, W.; Bi, Y.; Gao, G.F. Epidemiology, Genetic Recombination, and Pathogenesis of Coronaviruses. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.; Navas-Martín, S. Coronavirus Pathogenesis and the Emerging Pathogen Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 635–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Fang, L.; Hong, Y.; Liu, X.; Dong, N.; Ma, P.; Bi, J.; Wang, D.; Xiao, S. Discovery of a novel accessory protein NS7a encoded by porcine deltacoronavirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Fang, B.; Liu, Y.; Cai, M.; Jun, J.; Ma, J.; Bu, D.; Wang, L.; Zhou, P.; Wang, H.; et al. Newly emerged porcine enteric alphacoronavirus in southern China: Identification, origin and evolutionary history analysis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 62, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, C.; Wen, Z.; Cao, Y. A New Bat-HKU2–like Coronavirus in Swine, China, 2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1607–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Tian, X.; Qin, P.; Wang, B.; Zhao, P.; Yang, Y.-L.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Discovery of a novel swine enteric alphacoronavirus (SeACoV) in southern China. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 211, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-M.; Saif, L.J.; Marthaler, D.; Wang, Q. Evolution, antigenicity and pathogenicity of global porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strains. Virus Res. 2016, 226, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, C. Genomic and antigenic characterization of porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus strains isolated from South Korea, 2017. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Z.-L. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, R.; Goodbourn, S. Interferons and viruses: An interplay between induction, signalling, antiviral responses and virus countermeasures. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; Li, R.; Ma, X.; Qiu, G.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; et al. Epidemiology, pathogenesis, immune evasion mechanism and vaccine development of porcine Deltacoronavirus. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2024, 24, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Si, J.; Hao, Z.; Wang, J. Antiviral effects of ergosterol peroxide in a pig model of porcine deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) infection involves modulation of apoptosis and tight junction in the small intestine. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laude, H.; Rasschaert, D.; Delmas, B.; Godet, M.; Gelfi, J.; Charley, B. Molecular biology of transmissible gastroenteritis virus. Vet. Microbiol. 1990, 23, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.C.P.; Li, X.; Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y. Global Epidemiology of Bat Coronaviruses. Viruses 2019, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.-Y.; Shin, D.-L.; Li, G.; Wu, N.-H.; Herrler, G. Time-dependent viral interference between influenza virus and coronavirus in the infection of differentiated porcine airway epithelial cells. Virulence 2021, 12, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Shi, K.; Long, F.; Zhao, K.; Feng, S.; Yin, Y.; Xiong, C.; Qu, S.; Lu, W.; Li, Z. A Quadruplex qRT-PCR for Differential Detection of Four Porcine Enteric Coronaviruses. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Fan, H.; Lan, T.; Yang, X.-L.; Shi, W.-F.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Xie, Q.-M.; Mani, S.; et al. Fatal swine acute diarrhoea syndrome caused by an HKU2-related coronavirus of bat origin. Nature 2018, 556, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Vlasova, A.N.; Kenney, S.P.; Saif, L.J. Emerging and re-emerging coronaviruses in pigs. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Q.; Xu, Z.; Shen, H.; Chen, F. Characterization and pathogenicity of Vero cell-attenuated porcine epidemic diarrhea virus CT strain. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, N.; Qin, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.-m. The global prevalence of parasites in non-biting flies as vectors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antas, M.; Woźniakowski, G. Current Status of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhoea (PED) in European Pigs. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 63, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Okada, K.; Ohshima, K.-I. An outbreak of swine diarrhea of a new-type associated with coronavirus-like particles in Japan. Jpn. J. Vet. Sci. 1983, 45, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mole, B. Deadly pig virus slips through US borders. Nature 2013, 499, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, G.W.; Hoang, H.; Schwartz, K.J.; Burrough, E.R.; Sun, D.; Madson, D.; Cooper, V.L.; Pillatzki, A.; Gauger, P.; Schmitt, B.J.; et al. Emergence of Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in the United States: Clinical signs, lesions, and viral genomic sequences. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2013, 25, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Li, N.; Tian, Z.; Yin, X.; Qu, L.; Qu, J. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of transmissible gastroenteritis virus HX strain isolated from China. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, M.C.; Lam, H.C.; Rovira, A.; Marthaler, D.G. Complete Genome Sequence of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Strain COL/Cundinamarca/2014 from Colombia. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00239-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.; Lau, S.; Lam, C.S.F.; Lau, C.; Tsang, A.K.L.; Lau, J.H.N.; Bai, R.; Teng, J.L.; Tsang, C.C.C.; Wang, M.; et al. Discovery of Seven Novel Mammalian and Avian Coronaviruses in the Genus Deltacoronavirus Supports Bat Coronaviruses as the Gene Source of Alphacoronavirus and Betacoronavirus and Avian Coronaviruses as the Gene Source of Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3995–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Byrum, B.; Zhang, Y. Porcine coronavirus HKU15 detected in 9 US states, 2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1594–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Byrum, B.; Zhang, Y. Detection and genetic characterization of deltacoronavirus in pigs, Ohio, USA, 2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Hu, H.; Saif, L. Calves are susceptible to infection with the newly emerged porcine deltacoronavirus, but not with the swine enteric alphacoronavirus, porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 2357–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ding, Q.; Yuan, J.; Han, F.; Wei, Z.; Hu, H. Susceptibility to mice and potential evolutionary characteristics of porcine deltacoronavirus. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 5723–5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñeyro, P.E.; Lozada, M.I.; Alarcón, L.V.; Sanguinetti, R.; Cappuccio, J.A.; Pérez, E.M.; Vannucci, F.; Armocida, A.; Madson, D.M.; Perfumo, C.J.; et al. First retrospective studies with etiological confirmation of porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus infection in Argentina. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Niu, J.; Zhou, X.; Chu, P.; Zhang, K.; Gou, H.; Yang, D.-X.; Zhang, J.-F.; Li, C.-l.; Liao, M.; et al. Development of a multiplex qRT-PCR assay for the detection of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus and porcine Deltacoronavirus. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1158585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Ma, L.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Ouyang, H.; Yuan, H.; Pang, D. Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus: An Update Review and Perspective. Viruses 2023, 15, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Contreras, E.A.; Carrasco-González, J.A.; Linhares, D.C.L.; Corzo, C.A.; Campos-Villalobos, J.I.; Henao-Díaz, A.; Melchor-Martínez, E.M.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; González-González, R.B.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; et al. Emergent Molecular Techniques Applied to the Detection of Porcine Viruses. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.W.; Li, J.H.; Guan, J.L.; Deng, K.H.; Wang, X.W.; Li, G.; Zhou, X.; Xu, M.S.; Chen, R.A.; Zhai, S.L.; et al. Development of a multiplex RT-PCR method for the detection of four porcine enteric coronaviruses. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1033864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Lu, J.; Wang, N.; He, W.T.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, W.; Su, S. Development of a TaqMan-probe-based multiplex real-time PCR for the simultaneous detection of emerging and reemerging swine coronaviruses. Virulence 2020, 11, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.H.; Rawal, G.; Aljets, E.; Yim-Im, W.; Yang, Y.L.; Huang, Y.W.; Krueger, K.; Gauger, P.; Main, R.; Zhang, J. Development and clinical applications of a 5-plex real-time RT-PCR for swine enteric coronaviruses. Viruses 2022, 14, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, H.-Y. Porcine enteric coronaviruses: An updated overview of the pathogenesis, prevalence, and diagnosis. Vet. Res. Commun. 2021, 45, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Q.; Cheng, J.; Lan, X.; Li, X.R.; Li, W.; Yin, X.P.; Li, B.Y.; Yang, B.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Complete genomic sequence of transmissible gastroenteritis virus TS and 3’ end sequence characterization following cell culture. Virol. Sin. 2010, 25, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Yu, Q.; Liqi, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhao, S.; Qi, G.; He, K.; Qian, Y. Complete genomic sequence of the coronavirus transmissible gastroenteritis virus SHXB isolated in China. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 2295–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.; Yan, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Su, M.; Sun, D. Isolation and Characterization of a Porcine Transmissible Gastroenteritis Coronavirus in Northeast China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 611721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J. Epidemiology of porcine deltacoronavirus among Chinese pig populations in China: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1198593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Huang, W.; He, X.; Feng, Z.; Chen, Q. Research Advances on Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome Coronavirus. Animals 2024, 14, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeng-chuto, K.; Madapong, A.; Kaeoket, K.; Piñeyro, P.E.; Tantituvanont, A.; Nilubol, D. Co-infection of porcine deltacoronavirus and porcine epidemic diarrhea virus induces early TRAF6-mediated NF-κB and IRF7 signaling pathways through TLRs. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W. The Significance and Importance of dPCR, qPCR, and SYBR Green PCR Kit in the Detection of Numerous Diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2024, 30, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, J.J.; Kobayashi, D.T.; Lynes, M.M.; Naryshkin, N.N.; Tiziano, F.D.; Zaworski, P.G.; Rubin, L.L.; Jarecki, J. Assays for the identification and prioritization of drug candidates for spinal muscular atrophy. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2014, 12, 315–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuypers, J.; Jerome, K.R. Applications of Digital PCR for Clinical Microbiology. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, R.T.; Gu, Z.; Ingersoll, J.; Abdul-Ali, D.; Shi, L.; Pounds, S.; Caliendo, A.M. Comparison of Droplet Digital PCR to Real-Time PCR for Quantitative Detection of Cytomegalovirus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 51, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Positive Plasmid * | dPCR (n = 40) | qPCR (n = 40) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD * | Positive | RSD † | Mean Ct ± SD * | Positive | RSD † | ||
| SADS-CoV | 103 | 1235.38 ± 51.82 | 40 | 0.56% | 28.76 ± 0.08 | 40 | 0.27% |
| 102 | 126.25 ± 16.64 | 40 | 2.23% | 31.74 ± 0.20 | 40 | 0.62% | |
| 101 | 13.02 ± 4.74 | 40 | 8.14% | / | 39 | / | |
| 7.5 | 9.75 ± 3.69 | 40 | 18.55% | / | 35 | / | |
| 5 | 7.70 ± 3.5 | 40 | 31.40% | / | 19 | / | |
| 2.5 | 4.59 ± 2.35 | 40 | 40.67% | / | 4 | / | |
| 1 | / | 32 | / | / | 0 | / | |
| PEDV | 103 | 1059.63 ± 34.58 | 40 | 0.47% | 28.47 ± 0.21 | 40 | 0.75% |
| 102 | 101.48 ± 1.57 | 40 | 2.53% | 31.91 ± 0.37 | 40 | 1.16% | |
| 101 | 12.65 ± 4.81 | 40 | 10.10% | / | 38 | / | |
| 7.5 | 8.58 ± 3.43 | 40 | 21.48% | / | 31 | / | |
| 5 | 5.66 ± 2.16 | 40 | 27.20% | / | 16 | / | |
| 2.5 | / | 37 | / | / | 10 | / | |
| 1 | / | 29 | / | / | 0 | / | |
| PDCoV | 103 | 939.25 ± 44.18 | 40 | 0.69% | 29.10 ± 0.07 | 40 | 0.22% |
| 102 | 93.89 ± 9.81 | 40 | 2.37% | 32.33 ± 0.18 | 40 | 0.57% | |
| 101 | 9.75 ± 3.56 | 40 | 8.28% | / | 34 | / | |
| 7.5 | 6.881 ± 2.22 | 40 | 19.16% | / | 32 | / | |
| 5 | 4.66 ± 2.37 | 40 | 46.33% | / | 20 | / | |
| 2.5 | / | 34 | / | / | 3 | / | |
| 1 | / | 27 | / | / | 0 | / | |
| TGEV | 103 | 1020.88 ± 38.27 | 40 | 0.54% | 28.90 ± 0.10 | 40 | 0.36% |
| 102 | 98.40 ± 12.34 | 40 | 2.86% | 32.17 ± 0.21 | 40 | 0.65% | |
| 101 | 11.39 ± 2.77 | 40 | 11.35% | / | 39 | / | |
| 7.5 | 7.41 ± 2.57 | 40 | 18.19% | / | 34 | / | |
| 5 | 4.96 ± 1.54 | 40 | 20.80% | / | 13 | / | |
| 2.5 | / | 36 | / | / | 6 | / | |
| 1 | / | 29 | / | / | 0 | / | |
| Sample Type | Target Virus | dPCR | qPCR | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SADS-CoV | PEDV | PDCoV | TGEV | Positive | Multiple-Pathogen Detection Rate | Positive | Multiple-Pathogen Detection Rate | |
| Intestinal tissue (n = 201) | + | − | − | − | 5 | 15.00% (18/120) | 4 | 6.73% (7/104) |
| − | + | − | − | 94 | 92 | |||
| − | − | + | − | 2 | / | |||
| − | − | − | + | 1 | 1 | |||
| + | + | − | − | 2 | / | |||
| − | + | + | − | 7 | 7 | |||
| − | + | − | + | 5 | / | |||
| − | − | + | + | 2 | / | |||
| − | + | + | + | 1 | / | |||
| + | + | + | + | 1 | / | |||
| Feces (n = 130) | + | − | − | − | 3 | 17.28% (14/81) | 4 | 8.86% (7/79) |
| − | + | − | − | 31 | 31 | |||
| − | − | + | − | 33 | 37 | |||
| + | − | + | − | 1 | / | |||
| + | − | − | + | 1 | 1 | |||
| − | + | + | − | 10 | 6 | |||
| − | + | − | + | 2 | / | |||
| Serum (n = 41) | + | − | − | − | 2 | 12.50% (2/16) | 2 | 0% (0/11) |
| − | + | − | − | 11 | 8 | |||
| − | − | + | − | 1 | 1 | |||
| − | + | + | − | 2 | / | |||
| Feed (n = 36) | − | + | − | − | 4 | 0% (0/6) | 2 | 0% (0/2) |
| − | − | − | + | 2 | / | |||
| Total (n = 408) | 223 | 15.25% (34/223) | 196 | 7.14% (14/196) | ||||
| Target Virus: | Sample Number (n = 408) | Number of Positive Detections | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dPCR | qPCR | ||||||||||||
| SADS-CoV | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| PEDV | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| PDCoV | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| TGEV | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| Tissue | Positive | 8 | 110 | 14 | 10 | 8 | 110 | 13 | 10 | 4 | 99 | 7 | 1 |
| Feces | 5 | 44 | 45 | 3 | 5 | 43 | 44 | 3 | 4 | 37 | 43 | 1 | |
| Serum | 2 | 13 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 13 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 0 | |
| Feed | 0 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 15 | 172 | 62 | 15 | 15 | 170 | 60 | 15 | 10 | 146 | 51 | 2 | |
| Tissue | Negative | 193 | 91 | 187 | 191 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| Feces | 125 | 86 | 85 | 127 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0 | |
| Serum | 39 | 28 | 38 | 41 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| Feed | 36 | 31 | 36 | 34 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | |
| Total | 393 | 236 | 346 | 393 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 8 | 6 | |
| DSp * (%) | 100 | 99 | 100 | 99 | 99 | 97 | 98 | 98 | |||||
| DSe † (%) | 100 | 99 | 97 | 100 | 67 | 85 | 82 | 13 | |||||
| Primer/Probe | Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Position | Product (bp) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SADS-CoV | F 1 | CTCGGCTTACTCTAAACCC | 26,447–26,465 | 148 |
| R 2 | CATCCACCATCTCAACCTC | 26,577–26,595 | ||
| P 3 | FAM-AGTGTTCACTCCGGCACCTC-BHQ1 | 26,516–26,535 | ||
| PEDV | F | GAACCTAACACACCTCCT | 26,779–26,796 | 147 |
| R | CACGACCCTGGTTATTTC | 26,909–26,926 | ||
| P | HEX-CAGAGGCAATAACCAGTCCCGT-BHQ1 | 26,868–26,889 | ||
| PDCoV | F | GTACATGGAGGTGCATTC | 23,390–23,407 | 122 |
| R | GTGGCGGATTTCTAACTG | 23,495–23,512 | ||
| P | CY5-GGCTCCAATTCTCACACCAGTC-BHQ3 | 23,421–23,442 | ||
| TGEV | F | GCAGATGAGGTTGTTGCT | 20,908–20,925 | 116 |
| R | GCCAGCGACTTCTAATGTTG | 21,005–21,024 | ||
| P | CY5.5-TGGTCTGGCACTGTCACATTTGGT-BHQ3 | 20,968–20,991 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, X.; Chen, K.; Qiu, H.; Kong, P.; Li, X.; Fu, L.; Li, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Shuai, J. Establishment of Multiplex Digital PCR Assay for Detection of Four Porcine Enteric Coronaviruses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178731
Han X, Chen K, Qiu H, Kong P, Li X, Fu L, Li H, Zhou J, Zhang X, Shuai J. Establishment of Multiplex Digital PCR Assay for Detection of Four Porcine Enteric Coronaviruses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178731
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Xiao, Kexin Chen, Hui Qiu, Pengli Kong, Xiaoliang Li, Linglin Fu, Huan Li, Jinru Zhou, Xiaofeng Zhang, and Jiangbing Shuai. 2025. "Establishment of Multiplex Digital PCR Assay for Detection of Four Porcine Enteric Coronaviruses" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178731
APA StyleHan, X., Chen, K., Qiu, H., Kong, P., Li, X., Fu, L., Li, H., Zhou, J., Zhang, X., & Shuai, J. (2025). Establishment of Multiplex Digital PCR Assay for Detection of Four Porcine Enteric Coronaviruses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178731






