Sequencing Anti-CD19 Therapies in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: From Mechanistic Insights to Clinical Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. CD19 as Therapeutic Target
3. CD19-Directed Therapies in Relapsed/Refractory DLBCL
3.1. Tafasitamab in Combination with Lenalidomide
3.2. Loncastuximab Tesirine
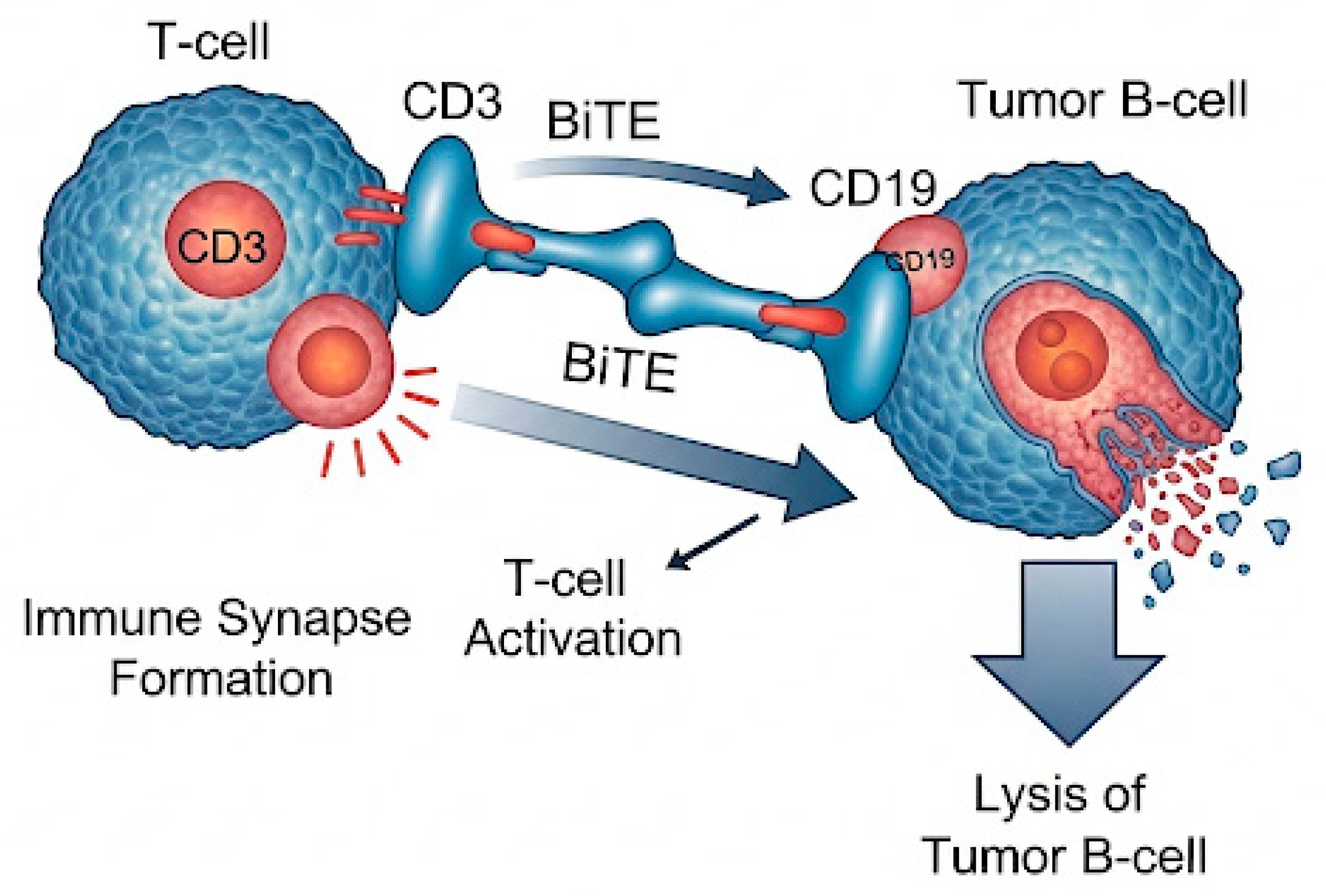
3.3. Anti-CD19 CAR-T Cell Therapies
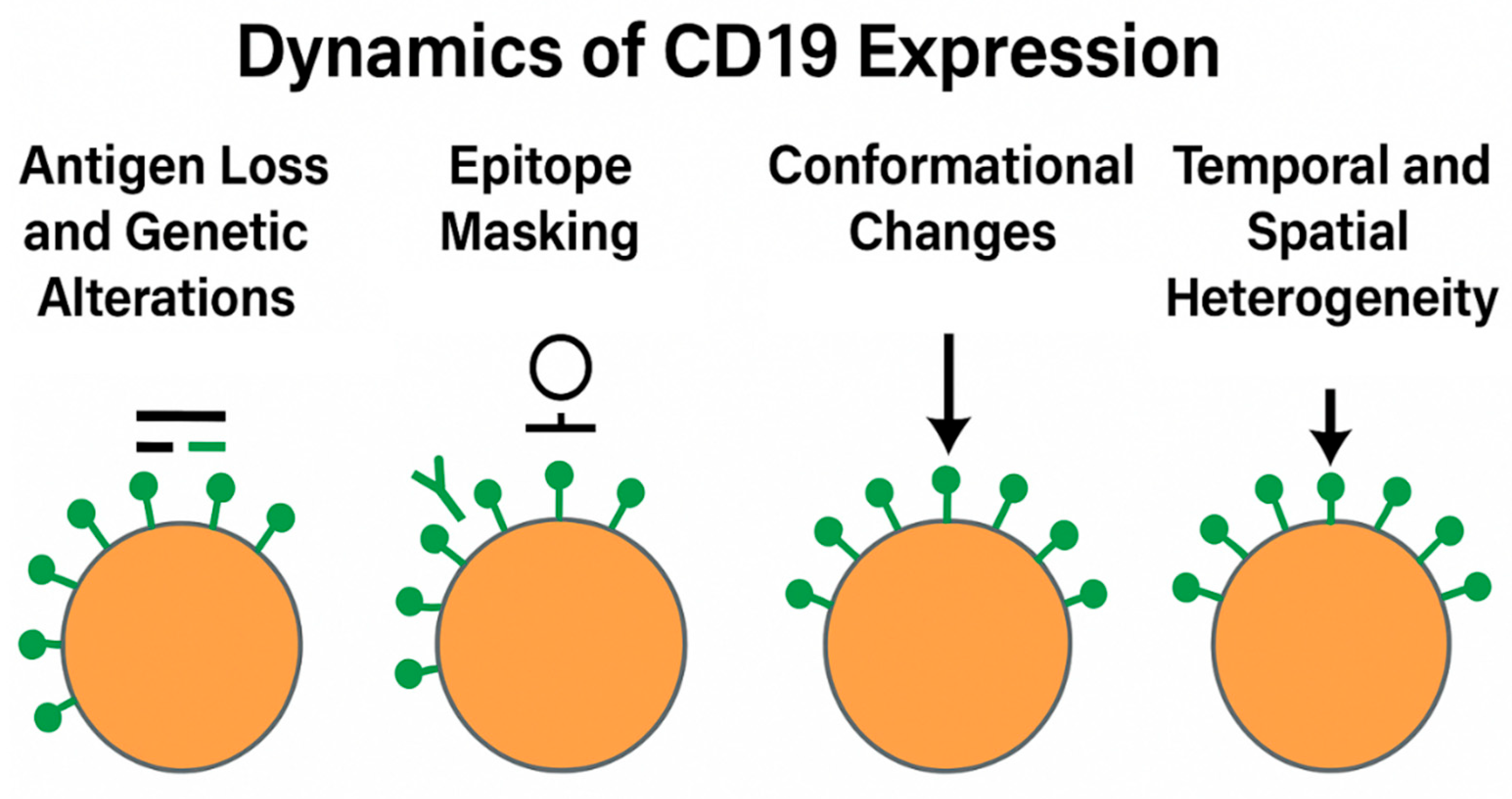
4. Dynamics of CD19 Expression
4.1. Antigen Loss and Genetic Alterations
- Genetic mutations, such as insertions, deletions, and point mutations in the CD19 gene, particularly affecting exon 2, which encodes the scFv-binding region of CAR constructs;
- Alternative splicing events, generating truncated isoforms lacking extracellular epitopes, as initially reported in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia and more recently observed in high-grade B-cell lymphomas;
- Transcriptional downregulation or epigenetic silencing, such as promoter hypermethylation, although the latter appears to be a less prevalent mechanism in DLBCL.
4.2. Epitope Masking and Conformational Changes
- Epitope masking, wherein prior therapeutic antibodies occupy key binding sites required for subsequent agents (e.g., tafasitamab pre-treatment, impairing CAR-T binding);
- Steric hindrance or receptor internalization induced by antibody engagement;
- Altered glycosylation patterns, which can modulate antigen structure and impair immune recognition.
4.3. Temporal and Spatial Heterogeneity
4.4. Implications for Sequential Therapy
5. Sequential Use of CD19 Therapies
5.1. Preclinical and Real-World Evidence
5.2. Post-CAR-T CD19 Re-Targeting
5.3. The Role of Epitope Accessibility and Washout
6. Alternative Approaches Beyond T-Cells
6.1. CD19-Directed CAR-NK Cells
- A lower risk of CRS and immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS),
- Intrinsic cytotoxicity independent of CAR activation, enabling recognition of CD19-low or CD19-negative targets via natural killer receptors,
- Minimal risk of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), enabling use in heavily pretreated or immunocompromised populations.
6.2. Bispecific and Trispecific CD19-Directed Antibodies
- Reduce the risk of immune evasion through multi-antigen targeting,
- Promote more robust and sustained T-cell activation,
- Maintain therapeutic activity in the setting of prior CAR-T failure or antigen heterogeneity.
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
- CD19 antigen status, encompassing expression level, isoform integrity, and epitope accessibility;
- Tumor microenvironment (TME) characteristics, such as immunosuppressive infiltrates and cytokine profiles;
- Treatment history, particularly prior exposure to CD19-directed agents and their immunologic sequelae;
- Host-related factors, including immune competence and eligibility for cellular therapy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guidolin, D.; Tamma, R.; Annese, T.; Tortorella, C.; Ingravallo, G.; Gaudio, F.; Perrone, T.; Musto, P.; Specchia, G.; Ribatti, D. Different spatial distribution of inflammatory cells in the tumor microenvironment of ABC and GBC subgroups of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 21, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinaccio, C.; Ingravallo, G.; Gaudio, F.; Perrone, T.; Nico, B.; Maoirano, E.; Specchia, G.; Ribatti, D. Microvascular density, CD68 and tryptase expression in human Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Leuk. Res. 2014, 38, 1374–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laddaga, F.E.; Ingravallo, G.; Mestice, A.; Tamma, R.; Perrone, T.; Maiorano, E.; Ribatti, D.; Specchia, G.; Gaudio, F. Correlation between circulating blood and microenvironment T lymphocytes in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 75, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamma, R.; Ingravallo, G.; Gaudio, F.; Annese, T.; Albano, F.; Ruggieri, S.; Dicataldo, M.; Maiorano, E.; Specchia, G.; Ribatti, D. STAT3, tumor microenvironment, and microvessel density in diffuse large B cell lymphomas. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 61, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudio, F.; Giordano, A.; Perrone, T.; Pastore, D.; Curci, P.; Delia, M.; Napoli, A.; Risi, C.D.; Spina, A.; Ricco, R.; et al. High Ki67 Index and Bulky Disease Remain Significant Adverse Prognostic Factors in Patients with Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma before and after the Introduction of Rituximab. Acta Haematol. 2011, 126, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangon, M.; Stefoni, V.; Castellino, A.; Visco, C.; Tani, M.; Cox, M.C.; Marasca, R.; Tecchio, C.; Devizzi, L.; Monaco, F.; et al. Lenalidomide Combination Therapy in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma: The Italian Real-Life Experience. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019, 19, e321–e323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broccoli, A.; Casadei, B.; Chiappella, A.; Visco, C.; Tani, M.; Cascavilla, N.; Conconi, A.; Balzarotti, M.; Cox, M.C.; Marino, D.; et al. Lenalidomide in Pretreated Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: An Italian Observational Multicenter Retrospective Study in Daily Clinical Practice. Oncologist 2019, 24, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duell, J.; Abrisqueta, P.; Andre, M.; Gaidano, G.; Gonzales-Barca, E.; Jurczak, W.; Kalakonda, N.; Liberati, A.M.; Maddocks, K.J.; Menne, T.; et al. Tafasitamab for patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Final 5-year efficacy and safety findings in the phase II L-MIND study. Haematologica 2023, 109, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderuccio, J.P.; Alencar, A.J.; Schatz, J.H.; Kuker, R.A.; Pongas, G.; Reis, I.M.; Lekakis, L.J.; Spiegel, J.Y.; Sandoval-Sus, J.; Beitinjaneh, A.; et al. Loncastuximab tesirine with rituximab in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma: A single-centre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2025, 12, e23–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, F.L.; Oluwole, O.O.; Kuruvilla, J.; Thieblemont, C.; Morschhauser, F.; Salles, G.A.; Rowe, S.P.; Vardhanabhuti, S.; Winters, J.; Filosto, S.; et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel vs standard of care in second-line large B-cell lymphoma: Outcomes by metabolic tumor volume. Blood 2024, 143, 2464–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesques, P.; Ferrant, E.; Safar, V.; Wallet, F.; Tordo, J.; Dhomps, A.; Karlin, L.; Brisou, G.; Vercasson, M.; Hospital-Gustem, C.; et al. Commercial anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy for patients with relapsed/refractory aggressive B cell lymphoma in a European center. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 1324–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, N.; Sehgal, A.; Liu, F.F.; Kostic, A.; Crotta, A.; De Benedetti, M.; Faccone, J.; Peng, L.; Gordon, L.I. Comparative efficacy of lisocabtagene maraleucel in the PILOT study versus second-line chemotherapy regimens in the real world. Haematologica 2024, 110, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duell, J.; Leipold, A.M.; Appenzeller, S.; Fuhr, V.; Rauert-Wunderlich, H.; Da Vià, M.C.; Dietrich, O.; Toussaint, C.; Imdahl, F.; Eisele, F.; et al. Sequential antigen loss and branching evolution in lymphoma after CD19- and CD20-targeted T-cell–redirecting therapy. Blood 2024, 143, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotillo, E.; Barrett, D.M.; Black, K.L.; Bagashev, A.; Oldridge, D.; Wu, G.; Sussman, R.; LaNauze, C.; Ruella, M.; Gazzara, M.R.; et al. Convergence of Acquired Mutations and Alternative Splicing of CD19 Enables Resistance to CART-19 Immunotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, K.N.; Quesada, A.E.; von Keudell, G.; Raj, S.; Lewis, N.E.; Dogan, A.; Salles, G.; Palomba, M.L. CD19 epitope masking by tafasitamab leads to delays in subsequent use of CD19 CAR T-cell therapy in two patients with aggressive mature B-cell lymphomas. Leuk. Lymphoma 2021, 63, 751–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, J.; Toppeta, F.; Trubert, A.; Danhof, S.; Hudecek, M.; Däullary, T. Multi-Targeting CAR-T Cell Strategies to Overcome Immune Evasion in Lymphoid and Myeloid Malignancies. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2025, 48, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wei, G.; Liu, D. CD19: A biomarker for B cell development, lymphoma diagnosis and therapy. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2012, 1, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrington, R.A.; Schneider, T.J.; Pitcher, L.A.; Mempel, T.R.; Ma, M.; Barteneva, N.S.; Carroll, M.C. Uncoupling CD21 and CD19 of the B-cell coreceptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14490–14495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J. Basic immunohistochemistry for lymphoma diagnosis. BLOOD Res. 2022, 57, S55–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, O. CD19 as an attractive target for antibody-based therapy. mAbs 2012, 4, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majzner, R.G.; Rietberg, S.P.; Sotillo, E.; Dong, R.; Vachharajani, V.T.; Labanieh, L.; Myklebust, J.H.; Kadapakkam, M.; Weber, E.W.; Tousley, A.M.; et al. Tuning the Antigen Density Requirement for CAR T-cell Activity. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 702–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilieva, K.; Eberl, M.; Jaehrling, J.; Blair, D.; Patra-Kneuer, M.; Boxhammer, R.; Arias, D.A.; Heitmüller, C. Preclinical study of CD19 detection methods post tafasitamab treatment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1274556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schanda, N.; Sauer, T.; Kunz, A.; Hückelhoven-Krauss, A.; Neuber, B.; Wang, L.; Hinkelbein, M.; Sedloev, D.; He, B.; Schubert, M.-L.; et al. Sensitivity and Specificity of CD19.CAR-T Cell Detection by Flow Cytometry and PCR. Cells 2021, 10, 3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sermer, D.; Elavalakanar, P.; Abramson, J.S.; Palomba, M.L.; Salles, G.; Arnason, J. Targeting CD19 for diffuse large B cell lymphoma in the era of CARs: Other modes of transportation. Blood Rev. 2023, 57, 101002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, A.M.; Epperla, N. Therapeutic landscape of primary refractory and relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Recent advances and emerging therapies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2025, 18, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’alò, F.; Bellesi, S.; Maiolo, E.; Alma, E.; Bellisario, F.; Malafronte, R.; Viscovo, M.; Campana, F.; Hohaus, S. Novel Targets and Advanced Therapies in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphomas. Cancers 2024, 16, 2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadiloo, K.; Taremi, S.; Safa, S.H.; Amidifar, S.; Esmaeilzadeh, A. The new era of immunological treatment, last updated and future consideration of CAR T cell-based drugs. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 203, 107158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, G.; Duell, J.; Barca, E.G.; Tournilhac, O.; Jurczak, W.; Liberati, A.M.; Nagy, Z.; Obr, A.; Gaidano, G.; André, M.; et al. Tafasitamab plus lenalidomide in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (L-MIND): A multicentre, prospective, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirosa, M.C.; Stathis, A.; Zucca, E. Tafasitamab for the treatment of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2024, 20, 2309701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, G.; Długosz-Danecka, M.; Ghesquières, H.; Jurczak, W. Tafasitamab for the treatment of relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2021, 21, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belada, D.; Kopeckova, K.; Burgues, J.M.B.; Stevens, D.; André, M.; Persona, E.P.; Pichler, P.; Staber, P.B.; Trneny, M.; Duell, J.; et al. Safety and efficacy of tafasitamab with or without lenalidomide added to first-line R-CHOP for DLBCL: The phase 1b First-MIND study. Blood 2023, 142, 1348–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Her, J.H.; Pretscher, D.; Patra-Kneuer, M.; Schanzer, J.; Cho, S.Y.; Hwang, Y.K.; Hoeres, T.; Boxhammer, R.; Heitmueller, C.; Wilhelm, M.; et al. Tafasitamab mediates killing of B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in combination with γδ T cell or allogeneic NK cell therapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 71, 2829–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Stock, W.; Zeidan, A.; Atallah, E.; McCloskey, J.; Heffner, L.; Tomlinson, B.; Bhatnagar, B.; Feingold, J.; Ungar, D.; et al. Loncastuximab tesirine, an anti-CD19 antibody-drug conjugate, in relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goparaju, K.; Winter, A.; Caimi, P.F.; Center, C.C.C.C. The Anti-CD19 Antibody-Drug Conjugate Loncastuximab Tesirine. Oncol. Haematol. 2021, 17, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B. Loncastuximab tesirine: An effective therapy for relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 78, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caimi, P.F.; Ai, W.; Alderuccio, J.P.; Ardeshna, K.M.; Hamadani, M.; Hess, B.; Kahl, B.S.; Radford, J.; Solh, M.; Stathis, A.; et al. Loncastuximab tesirine in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (LOTIS-2): A multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hu, B.; Pan, Z.; Mo, C.; Zhao, X.; Liu, G.; Hou, P.; Cui, Q.; Xu, Z.; Wang, W.; et al. Antibody–Drug Conjugates (ADCs): Current and future biopharmaceuticals. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2025, 18, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derenzini, E.; Gibb, A.; Kwiatek, M.; Strati, P. Loncastuximab tesirine in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Drug profile and expert opinion on the prevention and management of adverse events. Leuk. Lymphoma 2025. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Lopes-Garcia, L.R.; Viñal, D.; Bachmeier, C.; Shah, B.D.; Nishihori, T.; Khimani, F.; Davila, M.L.; Lazaryan, A.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; et al. Outcomes of CD19-Directed Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy for Transformed Nonfollicular Lymphoma. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2023, 29, 349.e1–349.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, F.L.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Perales, M.-A.; Kersten, M.-J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Ghobadi, A.; Rapoport, A.P.; McGuirk, J.; Pagel, J.M.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel as Second-Line Therapy for Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamdar, M.; Solomon, S.R.; Arnason, J.; Johnston, P.B.; Glass, B.; Bachanova, V.; Ibrahimi, S.; Mielke, S.; Mutsaers, P.; Hernandez-Ilizaliturri, F.; et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel versus standard of care with salvage chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation as second-line treatment in patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma (TRANSFORM): Results from an interim analysis of an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2022, 399, 2294–2308, Erratum in Lancet 2022, 400, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshalek, J.P.; Qing, X.; Dragan, M.; Tomassetti, S. Retrospective Study of CD20 Expression Loss in Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Hematol. 2024, 13, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atilla, P.A.; Atilla, E. Resistance against anti-CD19 and anti-BCMA CAR T cells: Recent advances and coping strategies. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 22, 101459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Chen, P.; Zhao, N.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Tang, Y. Unraveling resistance mechanisms in anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor-T therapy for B-ALL: A novel in vitro model and insights into target antigen dynamics. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakemura, R.L.; Roman, C.M.; Horvei, P.; Siegler, E.L.; Girsch, J.H.; Sirpilla, O.L.; Stewart, C.M.; Yun, K.; Can, I.; Ogbodo, E.J.; et al. CD19 occupancy with tafasitamab increases therapeutic index of CART19 cell therapy and diminishes severity of CRS. Blood 2024, 143, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duell, J.; Arias, D.A.; Rauert-Wunderlich, H.; Eisele, F.; Volgina, A.; Rumberger, B.; Larsen, T.S.; Rosenwald, A. Maintenance of CD19 Expression after Tafasitamab Treatment in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (R/R DLBCL) from Clinical Trial and Real-World Settings. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2025, 31, S394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshalek, J.P.; Qing, X.; Tomassetti, S. CD19 Expression in B-Cell Lymphomas and Clinical Considerations in the Evolving Landscape of CD19-Targeted Therapy. World J. Oncol. 2025, 16, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lownik, J.; Boiarsky, J.; Birhiray, R.; Merchant, A.; Mead, M. Sequencing of Anti-CD19 Therapies in the Management of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 2895–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, I.Y.; Tran, D.; Saibil, S.; Laister, R.C.; Kuruvilla, J. Biomarkers of outcome in patients undergoing CD19 CAR-T therapy for large B cell lymphoma. HemaSphere 2024, 8, e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio-Pérez, C.; Carmona, M.; Benabdellah, K.; Herrera, C. Failure of ALL recognition by CAR T cells: A review of CD 19-negative relapses after anti-CD 19 CAR-T treatment in B-ALL. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1165870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labrie, M.; Brugge, J.S.; Mills, G.B.; Zervantonakis, I.K. Therapy resistance: Opportunities created by adaptive responses to targeted therapies in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epperla, N.; Nastoupil, L.J.; Feinberg, B.; Galvin, J.; Pathak, P.; Amoloja, T.; Gentile, D.; Saverno, K. Real-world use of tafasitamab preceding CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Biomark. Res. 2025, 13, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalabi, H.; Kraft, I.L.; Wang, H.-W.; Yuan, C.M.; Yates, B.; Delbrook, C.; Zimbelman, J.D.; Giller, R.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; Jaffe, E.S.; et al. Sequential loss of tumor surface antigens following chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapies in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2018, 103, e215–e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epperla, N.; Nastoupil, L.; Feinberg, B.; Galvin, J.; Pathak, P.; Amoloja, T.; Gentile, D.; Saverno, K. Real-World Sequential Use of CD19-Directed Therapies for Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Tafasitamab Preceding Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy. Hematol. Transfus. Cell Ther. 2024, 46, S226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Yang, X.; Ye, S.; Huang, L.; Mu, W. Antigen escape in CAR-T cell therapy: Mechanisms and overcoming strategies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.J.; Bishop, M.R.; Tam, C.S.; Waller, E.K.; Borchmann, P.; McGuirk, J.P.; Jäger, U.; Jaglowski, S.; Andreadis, C.; Westin, J.R.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, B.; Caimi, P.F.; Ardeshna, K.M.; Solh, M.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Kahl, B.S.; Hamadani, M. CD19 antibody-drug conjugate therapy in DLBCL does not preclude subsequent responses to CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapy. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 3850–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caimi, P.F.; Ai, W.Z.; Alderuccio, J.P.; Ardeshna, K.M.; Hamadani, M.; Hess, B.; Kahl, B.S.; Radford, J.; Solh, M.; Stathis, A.; et al. Loncastuximab tesirine in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Long-term efficacy and safety from the phase 2 LOTIS-2 study. Haematologica 2023, 109, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.; Liu, F.; Zou, D.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, B.; Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Liu, K.; Guo, Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of CD19 CAR T constructed with a new anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor in relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crochet, G.; Iacoboni, G.; Couturier, A.; Bachy, E.; Iraola-Truchuelo, J.; Gastinne, T.; Cartron, G.; Fradon, T.; Lesne, B.; Kwon, M.; et al. Efficacy of CAR T-cell therapy is not impaired by previous bispecific antibody treatment in large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2024, 144, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, H.; Bollard, C.M.; Toner, K. CD19 CAR-T cell therapy for relapsed or refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma: Why does it fail? Semin. Hematol. 2023, 60, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perales, M.-A.; Anderson, L.D.; Jain, T.; Kenderian, S.S.; Oluwole, O.O.; Shah, G.L.; Svoboda, J.; Hamadani, M. Role of CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells in Second-Line Large B Cell Lymphoma: Lessons from Phase 3 Trials. An Expert Panel Opinion from the American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2022, 28, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, L.; Ye, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xiu, B.; Liang, A.; Li, P.; et al. CD19 CAR-T treatment shows limited efficacy in r/r DLBCL with double expression and TP53 alterations. Cytotherapy 2024, 26, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Yuan, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. Chimeric antigen receptor-engineered NK cells: New weapons of cancer immunotherapy with great potential. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbah, M.; Jondreville, L.; Lacan, C.; Norol, F.; Vieillard, V.; Roos-Weil, D.; Nguyen, S. CAR-NK Cells: A Chimeric Hope or a Promising Therapy? Cancers 2022, 14, 3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, K.; Rouce, R.; Liu, E.; Shpall, E. Engineering Natural Killer Cells for Cancer Immunotherapy. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 1769–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghobadi, A.; Bachanova, V.; Patel, K.; Park, J.H.; Flinn, I.; Riedell, P.A.; Bachier, C.; Diefenbach, C.S.; Wong, C.; Bickers, C.; et al. Induced pluripotent stem-cell-derived CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor natural killer cells in B-cell lymphoma: A phase 1, first-in-human trial. Lancet 2025, 405, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Marin, D.; Banerjee, P.; Macapinlac, H.A.; Thompson, P.; Basar, R.; Kerbauy, L.N.; Overman, B.; Thall, P.; Kaplan, M.; et al. Use of CAR-Transduced Natural Killer Cells in CD19-Positive Lymphoid Tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Liu, J. Emerging roles of CAR-NK cell therapies in tumor immunotherapy: Current status and future directions. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, U.; Castelli, G.; Pelosi, E. Emerging Role of Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Natural Killer Cells for the Treatment of Hematologic Malignancies. Cancers 2025, 17, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, L.V.; Christensen, E.B.; Barnkob, M.B.; Barington, T. The clinical landscape of CAR NK cells. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2025, 14, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Galisteo, A.; Álvarez-Vallina, L.; Sanz, L. Bi- and trispecific immune cell engagers for immunotherapy of hematological malignancies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 16, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Ning, W.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Luo, W.; Xia, N. Stepping forward: T-cell redirecting bispecific antibodies in cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 2361–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Bispecific T cell engagers: An emerging therapy for management of hematologic malignancies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Wu, Z.; Jia, H.; Tong, C.; Guo, Y.; Ti, D.; Han, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; et al. Bispecific CAR-T cells targeting both CD19 and CD22 for therapy of adults with relapsed or refractory B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoozgar, B.; Bangolo, A.; Habibi, M.; Cho, C.; Goy, A. From Molecular Precision to Clinical Practice: A Comprehensive Review of Bispecific and Trispecific Antibodies in Hematologic Malignancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Galisteo, A.; Compte, M.; Álvarez-Vallina, L.; Sanz, L. When three is not a crowd: Trispecific antibodies for enhanced cancer immunotherapy. Theranostics 2023, 13, 1028–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Therapy | Mechanism of Action | Effect on CD19 Expression | Implications for Sequential Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tafasitamab | Fc-enhanced monoclonal antibody inducing ADCC and phagocytosis | Epitope masking without significant internalization | CD19 often preserved; suitable for re-targeting |
| Loncastuximab Tesirine | Antibody–drug conjugate with internalization and DNA cross-linking | Internalization and degradation of CD19 | Reduced antigen density may affect subsequent targeting |
| CAR-T Cell Therapies | Autologous T-cells engineered to target CD19 | Antigen loss via mutation, splicing, or downregulation | Loss of CD19 may preclude further CD19-directed therapy |
| Therapy | ORR (%) | CR Rate (%) | Median OS (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tafasitamab + Lenalidomide | 57.5 | 40 | Not reached |
| Loncastuximab Tesirine | 48.3 | 24.1 | 9.5 |
| Axi-cel | 83 | 65 | 24.4 |
| Tisa-cel | 52 | 39 | 11.1 |
| Liso-cel | 73 | 53 | 18.1 |
| CD19 BiTEs | 43 | 19 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laddaga, F.E.; Della Mura, M.; Sorino, J.; Caruso, A.; Martinotti, S.; Ingravallo, G.; Gaudio, F. Sequencing Anti-CD19 Therapies in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: From Mechanistic Insights to Clinical Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178662
Laddaga FE, Della Mura M, Sorino J, Caruso A, Martinotti S, Ingravallo G, Gaudio F. Sequencing Anti-CD19 Therapies in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: From Mechanistic Insights to Clinical Strategies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178662
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaddaga, Filomena Emanuela, Mario Della Mura, Joana Sorino, Amanda Caruso, Stefano Martinotti, Giuseppe Ingravallo, and Francesco Gaudio. 2025. "Sequencing Anti-CD19 Therapies in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: From Mechanistic Insights to Clinical Strategies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178662
APA StyleLaddaga, F. E., Della Mura, M., Sorino, J., Caruso, A., Martinotti, S., Ingravallo, G., & Gaudio, F. (2025). Sequencing Anti-CD19 Therapies in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: From Mechanistic Insights to Clinical Strategies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178662









