The Presence of Risk and Protective HLA-DQ Haplotype Combinations and PLA2R1 Risk SNP in Hungarian Patients with Membranous Nephropathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. PLA2R1 Immunostaining, Serum Anti-PLA2R Antibody Level
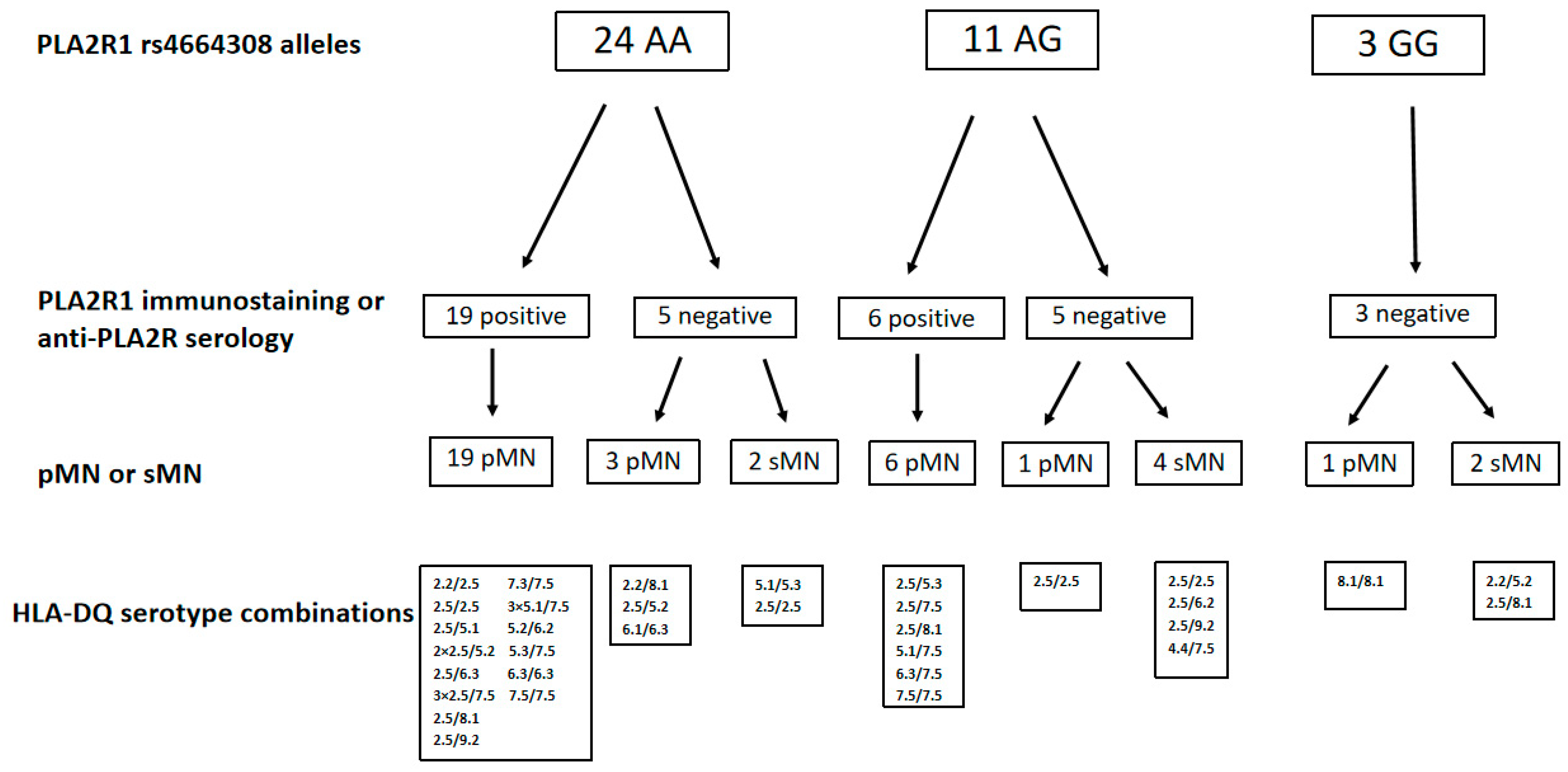
2.2. PLA2R1 Immunostaining, Anti-PLA2R Antibody Serology for Risk PLA2R1 rs4664308 Alleles
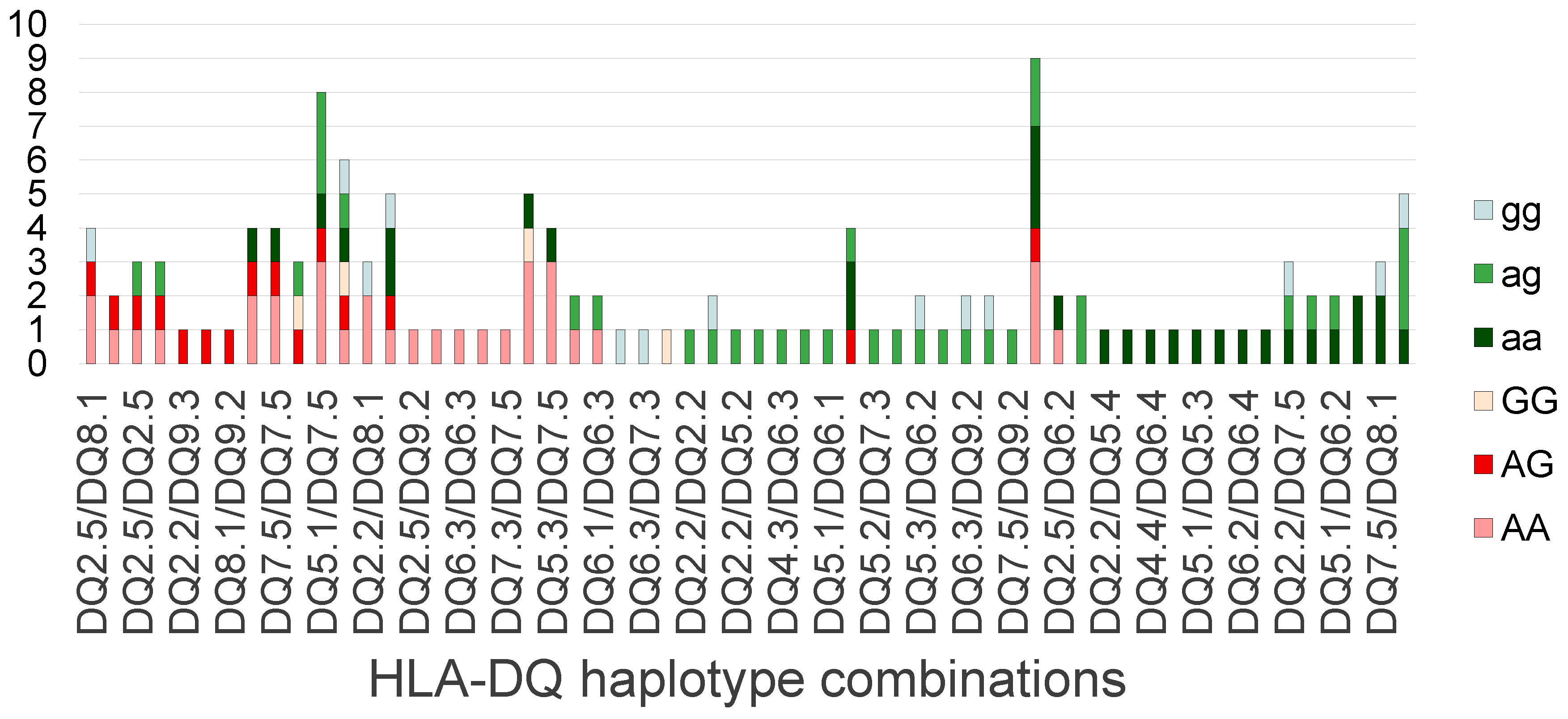
2.3. Allele Counts of PLA2R1 rs4664308 SNP and HLA-DQ 2.5 Haplotype
2.4. Scoring Procedure Used for Assessing the HLA-DQ Serotype Combinations in pMN
3. Discussion
4. Patients and Methods
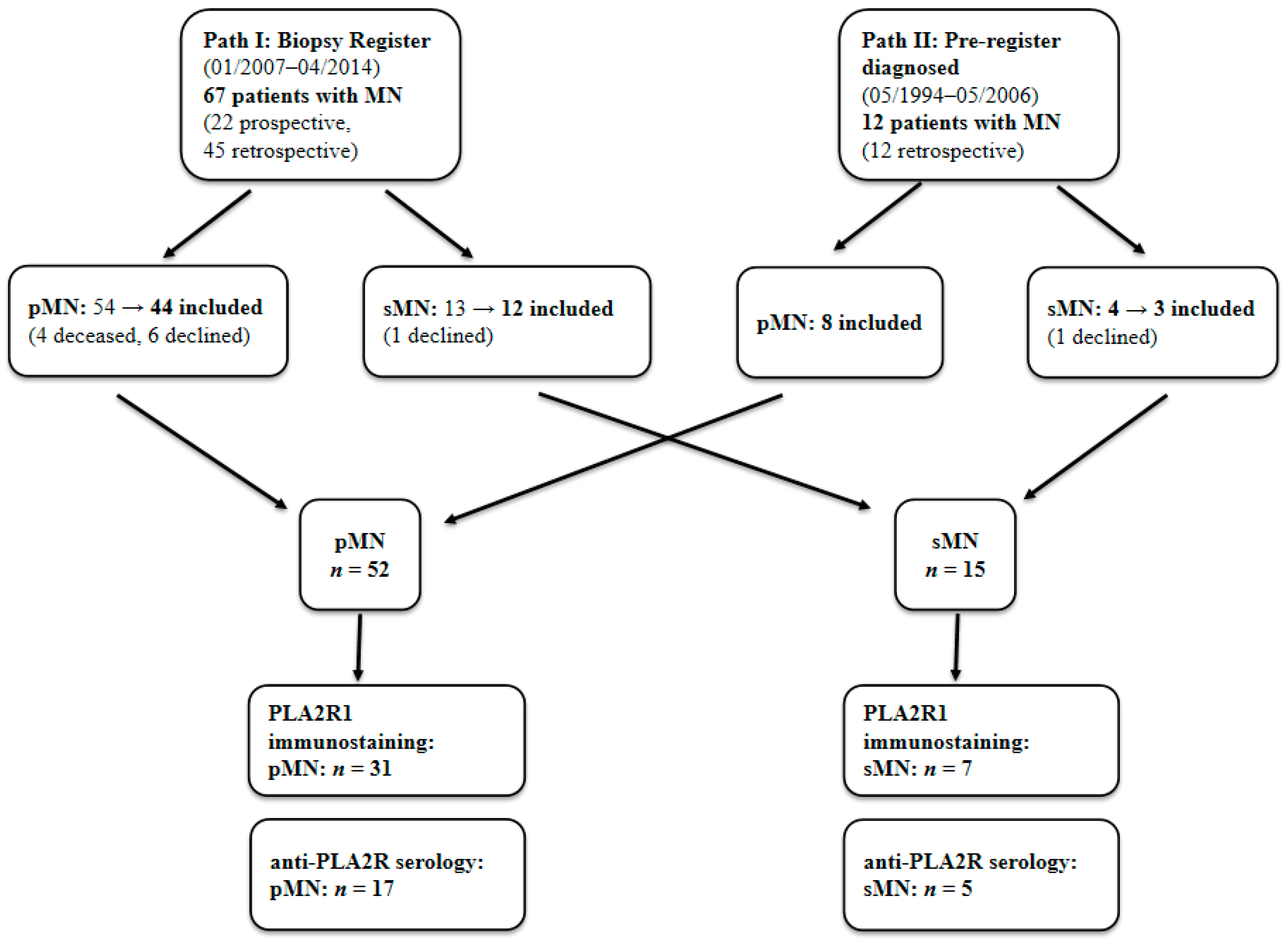
4.1. Patients
4.2. Histological Evaluation
4.3. Anti-PLA2R Serology
4.4. Genetic Evaluation
4.5. Scoring of the Risk Property of HLA-DQ Serotype Combinations in pMN
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGrogan, A.; Franssen, C.F.M.; De Vries, C.S. The Incidence of Primary Glomerulonephritis Worldwide: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQuarrie, E.P.; MacKinnon, B.; Stewart, G.A.; Geddes, C.C. Membranous Nephropathy Remains the Commonest Primary Cause of Nephrotic Syndrome in a Northern European Caucasian Population. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ronco, P.; Beck, L.; Debiec, H.; Fervenza, F.C.; Hou, F.F.; Jha, V.; Sethi, S.; Tong, A.; Vivarelli, M.; Wetzels, J. Membranous Nephropathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajcsi, D.; Bitó, L.; Turkevi-Nagy, S.; Nyári, T.; Kemény, É.; Légrády, P.; Ábrahám, G.; Iványi, B. The Value of PLA2R Antigen and IgG Subclass Staining Relative to Anti-PLA2R Seropositivity in the Differential Diagnosis of Membranous Nephropathy. BMC Nephrol. 2023, 24, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Beck, L.H.; Glassock, R.J.; Haas, M.; De Vriese, A.S.; Caza, T.N.; Hoxha, E.; Lambeau, G.; Tomas, N.M.; Madden, B.; et al. Mayo Clinic Consensus Report on Membranous Nephropathy: Proposal for a Novel Classification. Kidney Int. 2023, 104, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Ogawa, A.; Takahashi, K.; Uchiyama, M. HLA-DQB1 allele associates with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in Japanese children. Pediatr. Int. 1995, 37, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, R.W.; Tighe, M.R.; Boki, K.; Alexoupolos, S.; Papadakis, J.; Lanchbury, J.S.; Welsh, K.I.; Williams, D.G. An analysis of HLA class II gene polymorphism in British and Greek idiopathic membranous nephropathy patients. Eur. J. Immunogenet. 1995, 22, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanescu, H.C.; Arcos-Burgos, M.; Medlar, A.; Bockenhauer, D.; Kottgen, A.; Dragomirescu, L.; Voinescu, C.; Patel, N.; Pearce, K.; Hubank, M.; et al. Risk HLA-DQA1 and PLA(2)R1 Alleles in Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Hou, W.; Zhou, X.; Liu, G.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, N.; Hou, P.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, H. Interaction between PLA2R1 and HLA-DQA1 Variants Associates with Anti-PLA2R Antibodies and Membranous Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, W.B.; Shi, J.S.; Zhang, T.; Liu, L.; Qin, H.Z.; Liang, S.; Zhang, Y.W.; Zheng, C.X.; Jiang, S.; Qin, W.S.; et al. HLA-DRB1∗15:01 and HLA-DRB3∗02:02 in PLA2R-Related Membranous Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Xie, L.J.; Chen, F.J.; Pei, Z.Y.; Zhang, L.J.; Qu, Z.; Huang, J.; Gu, Q.H.; Zhang, Y.M.; Wang, X.; et al. MHC Class II Risk Alleles and Amino Acid Residues in Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1651–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiri, M.; Honda, K.; Kashiwase, K.; Mabuchi, A.; Suzuki, H.; Watanabe, K.; Nakayama, M.; Watanabe, T.; Doi, K.; Tokunaga, K.; et al. High-Density Association Mapping and Interaction Analysis of PLA2R1 and HLA Regions with Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy in Japanese. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Liu, L.; Mladkova, N.; Li, Y.; Ren, H.; Wang, W.; Cui, Z.; Lin, L.; Hu, X.; Yu, X.; et al. The Genetic Architecture of Membranous Nephropathy and Its Potential to Improve Non-Invasive Diagnosis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coenen, M.J.H.; Hofstra, J.M.; Debiec, H.; Stanescu, H.C.; Medlar, A.J.; Stengel, B.; Boland-Augé, A.; Groothuismink, J.M.; Bockenhauer, D.; Powis, S.H.; et al. Phospholipase A2 Receptor (PLA2R1) Sequence Variants in Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofstra, J.M.; Debiec, H.; Short, C.D.; Pellé, T.; Kleta, R.; Mathieson, P.W.; Ronco, P.; Brenchley, P.E.; Wetzels, J.F. Antiphospholipase A2 Receptor Antibody Titer and Subclass in Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.H.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Lin, Y.J.; Liao, W.L.; Tsai, C.H.; Wan, L. Association of Phospholipase A2 Receptor 1 Polymorphisms with Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy in Chinese Patients in Taiwan. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Chin, H.J.; Na, K.Y.; Kim, S.; Oh, J.; Chung, W.; Noh, J.W.; Lee, Y.K.; Cho, J.T.; Lee, E.K.; et al. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the Phospholipase A 2 Receptor Gene Are Associated with Genetic Susceptibility to Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2011, 117, c253–c258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, A.K.; Nada, R.; Kumar, H.; Kumar, V.; Rathi, M.; Kohli, H.S.; Gupta, K.L.; et al. PLA2R Antibodies, Glomerular PLA2R Deposits and Variations in PLA2R1 and HLA-DQA1 Genes in Primary Membranous Nephropathy in South Asians. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 1486–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Zhang, H.; He, Y. Diagnostic Accuracy of PLA2R Autoantibodies and Glomerular Staining for the Differentiation of Idiopathic and Secondary Membranous Nephropathy: An Updated Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Arora, S.; Lal, S.; Strand, T.A.; Makharia, G.K. Risk of Celiac Disease in the First- and Second-Degree Relatives of Patients with Celiac Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollid, L.M.; Thorsby, E. HLA Susceptibility Genes in Celiac Disease: Genetic Mapping and Role in Pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 1993, 105, 910–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Bang, S.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Okada, Y.; Han, B.; Saw, W.Y.; Teo, Y.Y.; Bae, S.C. The HLA-DRβ1 Amino Acid Positions 11-13-26 Explain the Majority of SLE-MHC Associations. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, M.M.A.; Stevens, C.R.; Sabeti, P.C.; Walsh, E.C.; McWhinnie, A.J.M.; Shah, A.; Green, T.; Rioux, J.D.; Vyse, T.J. Identification of Two Independent Risk Factors for Lupus within the MHC in United Kingdom Families. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, 2109–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.L.; Taylor, K.E.; Fernando, M.M.A.; Nititham, J.; Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E.; Barcellos, L.F.; Behrens, T.W.; Cotsapas, C.; Gaffney, P.M.; Graham, R.R.; et al. Unraveling Multiple MHC Gene Associations with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Model Choice Indicates a Role for HLA Alleles and Non-HLA Genes in Europeans. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 91, 778–793, Erratum in Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 97, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Molineros, J.E.; Looger, L.L.; Zhou, X.J.; Kim, K.; Okada, Y.; Ma, J.; Qi, Y.Y.; Kim-Howard, X.; Motghare, P.; et al. High-Density Genotyping of Immune-Related Loci Identifies New SLE Risk Variants in Individuals with Asian Ancestry. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moutsianas, L.; Jostins, L.; Beecham, A.H.; Dilthey, A.T.; Xifara, D.K.; Ban, M.; Shah, T.S.; Patsopoulos, N.A.; Alfredsson, L.; Anderson, C.A.; et al. Class II HLA Interactions Modulate Genetic Risk for Multiple Sclerosis. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsopoulos, N.A.; Barcellos, L.F.; Hintzen, R.Q.; Schaefer, C.; van Duijn, C.M.; Noble, J.A.; Raj, T.; Gourraud, P.A.; Stranger, B.E.; Oksenberg, J.; et al. Fine-Mapping the Genetic Association of the Major Histocompatibility Complex in Multiple Sclerosis: HLA and Non-HLA Effects. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, J.A.; Erlich, H.A. Genetics of Type 1 Diabetes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a007732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejentsev, S.; Howson, J.M.M.; Walker, N.M.; Szeszko, J.; Field, S.F.; Stevens, H.E.; Reynolds, P.; Hardy, M.; King, E.; Masters, J.; et al. Localization of Type 1 Diabetes Susceptibility to the MHC Class I Genes HLA-B and HLA-A. Nature 2007, 450, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D. Autoimmune Hepatitis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneghan, M.A.; Yeoman, A.D.; Verma, S.; Smith, A.D.; Longhi, M.S. Autoimmune Hepatitis. Lancet 2013, 382, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sárdy, M.; Tietze, J. Dermatitis Herpetiformis. Der Hautarzt 2009, 60, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychaudhuri, S. Recent Advances in the Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2010, 22, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGregor, A.J.; Snieder, H.; Rigby, A.S.; Koskenvuo, M.; Kaprio, J.; Aho, K.; Silman, A.J. Characterizing the Quantitative Genetic Contribution to Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Data from Twins. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, R.R.; Hom, G.; Ortmann, W.; Behrens, T.W. Review of Recent Genome-wide Association Scans in Lupus. J. Intern. Med. 2009, 265, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Allele Counts | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| pMN | sMN | Control | |
| HLA-DQ 2.5 | 27 + | 11 ++ | 18 |
| Other HLA-DQ haplotypes | 77 | 19 | 136 |
| PLA2R1 risk SNP (rs4664308) | 81 * | 17 | 94 |
| PLA2R1 non risk SNP | 23 | 13 | 60 |
| Membranous Nephropathy | Controls | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of cases | 68 (63 Caucasians, 4 Romas) | 77 Caucasians |
| Age at the time of genetic examinations (years) | 50.1 ± 14.7 | 46.8 ± 8.6 |
| Age at the time of kidney biopsy (years) | 46.0 ± 15.6 | NA |
| Female/Male (%) | 56/44 | 65/35 |
| 1. Exclusion of underlying autoimmune disorder (clinical signs, laboratory parameters, autoimmune serological tests) |
| 2. Exclusion of viral hepatitis (HbsAg, anti-HCV) |
| 3. Exclusion of malignancy (laboratory parameters, chest X-ray, abdominal and pelvic ultrasound, gynecological and urological examinations, fecal occult blood test; in patients over 60 years of age: gastroscopy, colonoscopy) |
| 4. Exploration of medications potentially causing drug-induced MN (NSAIDs, gold, penicillamine) |
| 5. No manifestation of autoimmune disorders or malignancy within two years after the kidney biopsy evaluation |
| Types of sMN | Number of Cases |
|---|---|
| Systemic autoimmune diseases | |
| Membranous lupus nephritis | 8 |
| Mixed tissue connective disease | 1 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis (+ in 1 case: gold exposure) | 2 |
| Organ-specific autoimmune diseases | |
| Hashimoto thyroiditis | 1 |
| Autoimmune hepatitis | 1 |
| Viral hepatitis | |
| Hepatitis B (+ Graves-Basedow disease) | 1 |
| Hepatitis C (+ lupus nephritis) | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bajcsi, D.; Maróti, Z.; Endreffy, E.; Légrády, P.; Ábrahám, G.; Iványi, B. The Presence of Risk and Protective HLA-DQ Haplotype Combinations and PLA2R1 Risk SNP in Hungarian Patients with Membranous Nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178621
Bajcsi D, Maróti Z, Endreffy E, Légrády P, Ábrahám G, Iványi B. The Presence of Risk and Protective HLA-DQ Haplotype Combinations and PLA2R1 Risk SNP in Hungarian Patients with Membranous Nephropathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178621
Chicago/Turabian StyleBajcsi, Dóra, Zoltán Maróti, Emőke Endreffy, Péter Légrády, György Ábrahám, and Béla Iványi. 2025. "The Presence of Risk and Protective HLA-DQ Haplotype Combinations and PLA2R1 Risk SNP in Hungarian Patients with Membranous Nephropathy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178621
APA StyleBajcsi, D., Maróti, Z., Endreffy, E., Légrády, P., Ábrahám, G., & Iványi, B. (2025). The Presence of Risk and Protective HLA-DQ Haplotype Combinations and PLA2R1 Risk SNP in Hungarian Patients with Membranous Nephropathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178621






