Interleukin Networks in GVHD: Mechanistic Crosstalk, Therapeutic Targeting, and Emerging Paradigms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Interleukins Promoting the Progression of GVHD
2.1. IL-1 Family
IL-1α and IL-1β
2.2. IL-2 Family
2.2.1. IL-7
2.2.2. IL-15
2.2.3. IL-21
2.3. IL-6 Family
IL-6
2.4. IL-10 Family
IL-26
2.5. IL-12 Family
2.5.1. IL-12
2.5.2. IL-23
2.5.3. IL-39
3. Interleukins Inhibit the Progression of GVHD
3.1. IL-2 Family
3.1.1. IL-2
3.1.2. IL-9
3.2. IL-4 Family
IL-13
3.3. IL-6 Family
3.3.1. IL-11
3.3.2. LIF
3.4. IL-10 Family
IFN-γ
3.5. IL-12 Family
IL-35
3.6. IL-17 Family
IL-25
4. Interleukins with Dual Effects on GVHD Progression
4.1. IL-1 Family
4.1.1. IL-33
4.1.2. IL-18
4.2. IL-4 Family
IL-4
4.3. IL-10 Family
4.3.1. IL-10
4.3.2. IL-22
4.4. IL-12 Family
IL-27
4.5. IL-17 Family
IL-17
5. Role of Interleukins in Clinical Trials of GVHD
6. Prospects and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aGVHD | Acute graft-versus-host disease |
| Allo-HCT | Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation |
| Allo-HSCT | Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| AML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| APCs | Antigen-presenting cells |
| ASC | Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD |
| ATG | Anti-thymocyte globulin |
| BCAP | B cell adaptor for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| BM | Bone marrow |
| BMT | Bone marrow transplantation |
| cGVHD | Chronic graft versus host disease |
| CTL | Cytotoxic T lymphocyte |
| DCs | Dendritic cells |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| FasL | Fas ligand |
| GI-GVHD | Gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease |
| GLUT1 | Facilitative glucose transporter |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| GVHD | Graft-versus-host disease |
| GVL | Graft-versus-leukemia |
| hIL-26Tg | IL-26 transgenic |
| hPMSCs | Human mesenchymal stem cells |
| HSCT | Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| IFN | Interferon |
| ILC2 | Type 2 innate lymphoid cells |
| ILs | Interleukins |
| ISCs | Intestinal stem cells |
| iTreg | Induced regulatory T |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| LIF | Leukemia inhibitory factor |
| LPSs | Lipopolysaccharides |
| MDSCs | Myeloid-derived suppressor cells |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| MSC-exo | Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| NK | Natural killer |
| NKT | Natural killer T cells |
| Nlrp3 | NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 |
| NRM | Non-relapse mortality |
| nTreg | Natural regulatory T |
| oIL-2 | Orthogonal IL-2 |
| PBMC | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| PD-L1 | Programmed Death-Ligand 1 |
| PEG-rIL-29 | Polyethylene glycolated recombinant IL-29 |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase |
| rLIF | Recombinant leukemia inhibitory factor |
| ROCK1 | Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1 |
| RORγt | Retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor gamma-t |
| SLE | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| SR-aGVHD | Steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease |
| sST2 | Soluble ST2 |
| ST2 | Growth stimulation expressed gene 2 |
| Teffs | Effector T cells |
| TGF | Transforming growth factor |
| Th | T helper |
| TLRs | Toll-like receptors |
| TMAO | Trimethylamine N-oxide |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| Treg | Regulatory T cell |
| URDs | Unrelated donors |
| VNTR | Variable number of tandem repeats |
References
- Demosthenous, C.; Sakellari, I.; Douka, V.; Papayanni, P.G.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Gavriilaki, E. The Role of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSCs) in Graft-Versus-Host Disease (GVHD). J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, J.L.; Reddy, P. Pathophysiology of graft-versus-host disease. Semin. Hematol. 2006, 43, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiser, R.; Blazar, B.R. Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease—Biologic Process, Prevention, and Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2167–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A.; Conti, P.; Mier, J.W. Effects of human interleukin-1 on natural killer cell activity: Is fever a host defense mechanism for tumor killing? Yale J. Biol. Med. 1986, 59, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Maurer, K.; Soiffer, R.J. The delicate balance of graft versus leukemia and graft versus host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Expert. Rev. Hematol. 2023, 16, 943–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Sacirbegovic, F.; Zhao, K.; Rosenberger, S.; Shlomchik, W.D. T cell exhaustion and a failure in antigen presentation drive resistance to the graft-versus-leukemia effect. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.Y.; Chou, T.Y.; Tzeng, C.H.; Lee, O.K. Cytokine profiles in various graft-versus-host disease target organs following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Cell Transpl. 2012, 21, 2033–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lighvani, A.A.; Frucht, D.M.; Jankovic, D.; Yamane, H.; Aliberti, J.; Hissong, B.D.; Nguyen, B.V.; Gadina, M.; Sher, A.; Paul, W.E.; et al. T-bet is rapidly induced by interferon-gamma in lymphoid and myeloid cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 15137–15142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.C.; Hwang, Y.S.; Chen, Y.Y.; Liu, C.L.; Shen, C.N.; Hong, W.H.; Lo, S.M.; Shen, C.R. Interleukin-4 Supports the Suppressive Immune Responses Elicited by Regulatory T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Bris, R.; Saez, A.; Herrero-Fernandez, B.; Rius, C.; Sanchez-Martinez, H.; Gonzalez-Granado, J.M. CD4 T-Cell Subsets and the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campe, J.; Ullrich, E. T Helper Cell Lineage-Defining Transcription Factors: Potent Targets for Specific GVHD Therapy? Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 806529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesmer, L.A.; Lundy, S.K.; Sarkar, S.; Fox, D.A. Th17 cells in human disease. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 223, 87–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lochner, M.; Wang, Z.; Sparwasser, T. The Special Relationship in the Development and Function of T Helper 17 and Regulatory T Cells. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2015, 136, 99–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Pan, S.; Zhang, Q.P.; Jamal, M.; Chen, L.H.; Yin, Q.; Wu, Y.J.; Xiong, J.; Xiao, R.J.; Kwong, Y.L.; et al. An Essential Role of Innate Lymphoid Cells in the Pathophysiology of Graft-vs.-Host Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetta, F.; Alvarez, M.; Negrin, R.S. Natural Killer Cells in Graft-Versus-Host-Disease after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.Q.; Wan, B.; Li, X.F. Macrophage regulation of graft-vs-host disease. World J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 1793–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.M.; Barreda, D.R. Acute Inflammation in Tissue Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mineishi, S.; Zhang, Y. Dendritic Cell Regulation of Graft-Vs.-Host Disease: Immunostimulation and Tolerance. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.F.; Lind, E.F.; Gondek, D.C.; Bennett, K.A.; Gleeson, M.W.; Pino-Lagos, K.; Scott, Z.A.; Coyle, A.J.; Reed, J.L.; Van Snick, J.; et al. Mast cells are essential intermediaries in regulatory T-cell tolerance. Nature 2006, 442, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.; Arend, W.; Sims, J.; Smith, D.; Blumberg, H.; O’Neill, L.; Goldbach-Mansky, R.; Pizarro, T.; Hoffman, H.; Bufler, P.; et al. IL-1 family nomenclature. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilal, J.; Berlinberg, A.; Riaz, I.B.; Faridi, W.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Ortega, G.; Murad, M.H.; Wang, Z.; Prokop, L.J.; Alhifany, A.A.; et al. Risk of Infections and Cancer in Patients with Rheumatologic Diseases Receiving Interleukin Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e1913102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jones, G.W.; Choy, E.H.; Jones, S.A. The biology behind interleukin-6 targeted interventions. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2016, 28, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J.M.; Moran, B.; Petrasca, A.; Smith, C.M. IL-17 in inflammatory skin diseases psoriasis and hidradenitis suppurativa. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 201, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, L.; Wittig, S.; Gruhn, B. Association of recipient and donor interleukin 6 polymorphisms 174 and 597 with outcome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 148, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, G.R.; Ferrara, J.L. The primacy of the gastrointestinal tract as a target organ of acute graft-versus-host disease: Rationale for the use of cytokine shields in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood 2000, 95, 2754–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, A.; Mancini, G. Current Approaches for the Prevention and Treatment of Acute and Chronic GVHD. Cells 2024, 13, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, D.; Ganesan, J.; Bscheider, M.; Stickel, N.; Weber, F.C.; Guarda, G.; Follo, M.; Pfeifer, D.; Tardivel, A.; Ludigs, K.; et al. The Nlrp3 inflammasome regulates acute graft-versus-host disease. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deason, K.; Troutman, T.D.; Jain, A.; Challa, D.K.; Mandraju, R.; Brewer, T.; Ward, E.S.; Pasare, C. BCAP links IL-1R to the PI3K-mTOR pathway and regulates pathogenic Th17 cell differentiation. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 2413–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Meng, R.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wu, J.; Xue, Q.; Yu, S.; Duan, M.; Shan, D.; et al. Caspase-11 signaling enhances graft-versus-host disease. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullup, H.; Dickinson, A.M.; Jackson, G.H.; Taylor, P.R.; Cavet, J.; Middleton, P.G. Donor interleukin 1 receptor antagonist genotype associated with acute graft-versus-host disease in human leucocyte antigen-matched sibling allogeneic transplants. Br. J. Haematol. 2001, 113, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiant, S.; Labalette, M.; Trauet, J.; Coiteux, V.; de Berranger, E.; Dessaint, J.P.; Yakoub-Agha, I. Plasma levels of IL-7 and IL-15 after reduced intensity conditioned allo-SCT and relationship to acute GVHD. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2011, 46, 1374–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpdogan, O.; Muriglan, S.J.; Eng, J.M.; Willis, L.M.; Greenberg, A.S.; Kappel, B.J.; van den Brink, M.R. IL-7 enhances peripheral T cell reconstitution after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, X.G.; Bolton, E.M.; Ruchatz, H.; Wei, X.; Liew, F.Y.; Bradley, J.A. Selective blockade of IL-15 by soluble IL-15 receptor alpha-chain enhances cardiac allograft survival. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 3444–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schluns, K.S.; Klonowski, K.D.; Lefrançois, L. Transregulation of memory CD8 T-cell proliferation by IL-15Ralpha+ bone marrow-derived cells. Blood 2004, 103, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurieva, R.; Yang, X.O.; Martinez, G.; Zhang, Y.; Panopoulos, A.D.; Ma, L.; Schluns, K.; Tian, Q.; Watowich, S.S.; Jetten, A.M.; et al. Essential autocrine regulation by IL-21 in the generation of inflammatory T cells. Nature 2007, 448, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, R.; Watanabe, T.; Kawakami, E.; Iwasaki, M.; Tomizawa-Murasawa, M.; Matsuda, M.; Najima, Y.; Takagi, S.; Fujiki, S.; Sato, R.; et al. Co-activation of macrophages and T cells contribute to chronic GVHD in human IL-6 transgenic humanised mouse model. EBioMedicine 2019, 41, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas-Bauer, K.; Stell, A.V.; Yan, K.L.; de Vega, E.; Vinnakota, J.M.; Unger, S.; Núñez, N.; Norona, J.; Talvard-Balland, N.; Koßmann, S.; et al. ROCK1/2 signaling contributes to corticosteroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnuma, K.; Hatano, R.; Aune, T.M.; Otsuka, H.; Iwata, S.; Dang, N.H.; Yamada, T.; Morimoto, C. Regulation of pulmonary graft-versus-host disease by IL-26+CD26+CD4 T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 3697–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, R.; Itoh, T.; Otsuka, H.; Saeki, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Song, D.; Shirakawa, Y.; Iyama, S.; Sato, T.; Iwao, N.; et al. Humanized anti-IL-26 monoclonal antibody as a novel targeted therapy for chronic graft-versus-host disease. Am. J. Transpl. 2022, 22, 2804–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sornasse, T.; Larenas, P.V.; Davis, K.A.; de Vries, J.E.; Yssel, H. Differentiation and stability of T helper 1 and 2 cells derived from naive human neonatal CD4+ T cells, analyzed at the single-cell level. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 184, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Chen, X.; Komorowski, R.; Hessner, M.J.; Drobyski, W.R. Interleukin-23 secretion by donor antigen-presenting cells is critical for organ-specific pathology in graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2009, 113, 2352–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.S.; Chu, Y.; Glass, J.F.; Brown, S.A. Absence of IL-23p19 in donor allogeneic cells reduces mortality from acute GVHD. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2010, 45, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, K.; Hu, B.; Xu, M.; Wan, L.; Jin, Z.; Xu, M.; Du, Y.; Ma, K.; Lv, Q.; Xu, Y.; et al. IL-39 promotes chronic graft-versus-host disease by increasing T and B Cell pathogenicity. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, G.R.; Teshima, T.; Gerbitz, A.; Pan, L.; Cooke, K.R.; Brinson, Y.S.; Crawford, J.M.; Ferrara, J.L. Differential roles of IL-1 and TNF-alpha on graft-versus-host disease and graft versus leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, E.K.; Choi, J.Y.; Cho, M.L. IL-1 Receptor Blockade Alleviates Graft-Versus-Host Disease Through Downregulation of an Interleukin-1β-Dependent Glycolytic Pathway in Th17 Cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 631384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, I.; Rider, P.; Carmi, Y.; Braiman, A.; Dotan, S.; White, M.R.; Voronov, E.; Martin, M.U.; Dinarello, C.A.; Apte, R.N. Differential release of chromatin-bound IL-1alpha discriminates between necrotic and apoptotic cell death by the ability to induce sterile inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2574–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Hodge, G. Intracellular cytokine production and cytokine receptor interaction of cord mononuclear cells: Relevance to cord blood transplantation. Br. J. Haematol. 1999, 107, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, D.H.; Foley, J.; Whit-Shan Hou, J.; Odom, J.; Castro, K.; Steinberg, S.M.; Gea-Banacloche, J.; Kasten-Sportes, C.; Gress, R.E.; Bishop, M.R. Clinical “cytokine storm” as revealed by monocyte intracellular flow cytometry: Correlation of tumor necrosis factor alpha with severe gut graft-versus-host disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2004, 2, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, D.F.; Cid, J. Graft-versus-host disease. Med. Clin. 2019, 152, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, L.; Núñez, G. Immunology. Orchestrating inflammasomes. Science 2012, 337, 1299–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Hu, B.; Li, P.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wu, D. Roles of the intestinal microbiota and microbial metabolites in acute GVHD. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wu, H. Structural Mechanisms of NLRP3 Inflammasome Assembly and Activation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 41, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.H.; Staudt, L.M. Toll-like receptor signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a011247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, H.; Dai, X.; Wang, S.; Sun, Z.; Wang, F.; Fei, H.; Lin, Q.; Jiang, H.; et al. The gut microbial metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide aggravates GVHD by inducing M1 macrophage polarization in mice. Blood 2020, 136, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, K.; Koreth, J.; Kim, H.T.; Bascug, G.; McDonough, S.; Kawano, Y.; Murase, K.; Cutler, C.; Ho, V.T.; Alyea, E.P.; et al. Low-dose interleukin-2 therapy restores regulatory T cell homeostasis in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 179ra143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, T.J.; Mackall, C.L. Interleukin-7: From bench to clinic. Blood 2002, 99, 3892–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, B.; Barbara-Burnham, L.; Barsky, L.; Weinberg, K. Radiosensitivity of thymic interleukin-7 production and thymopoiesis after bone marrow transplantation. Blood 2001, 98, 1601–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vudattu, N.K.; Kuhlmann-Berenzon, S.; Khademi, M.; Seyfert, V.; Olsson, T.; Maeurer, M.J. Increased numbers of IL-7 receptor molecules on CD4+CD25-CD107a+ T-cells in patients with autoimmune diseases affecting the central nervous system. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, B.; Dudl, E.P.; Min, D.; Barsky, L.; Smiley, N.; Weinberg, K.I. Prevention of graft-versus-host disease by anti IL-7Ralpha antibody. Blood 2007, 110, 2803–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, A.M.; Faucher, S.; Angel, J.B. Soluble IL-7R alpha (sCD127) inhibits IL-7 activity and is increased in HIV infection. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 4679–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamim, Z.; Spellman, S.; Haagenson, M.; Wang, T.; Lee, S.J.; Ryder, L.P.; Müller, K. Polymorphism in the interleukin-7 receptor-alpha and outcome after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with matched unrelated donor. Scand. J. Immunol. 2013, 78, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagaraine, C.; Lemoine, R.; Baron, C.; Nivet, H.; Velge-Roussel, F.; Lebranchu, Y. Induction of human CD4+ regulatory T cells by mycophenolic acid-treated dendritic cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 84, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, N.; Patel, H.J.; Waldmann, T.A.; Tagaya, Y. The IL-15/IL-15Ralpha on cell surfaces enables sustained IL-15 activity and contributes to the long survival of CD8 memory T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spolski, R.; Leonard, W.J. Interleukin-21: Basic biology and implications for cancer and autoimmunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Bhandoola, A. Decoding HSC heterogeneity. Blood 2012, 119, 4819–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ozaki, K.; Spolski, R.; Ettinger, R.; Kim, H.P.; Wang, G.; Qi, C.F.; Hwu, P.; Shaffer, D.J.; Akilesh, S.; Roopenian, D.C.; et al. Regulation of B cell differentiation and plasma cell generation by IL-21, a novel inducer of Blimp-1 and Bcl-6. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 5361–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippen, K.L.; Bucher, C.; Schirm, D.K.; Bearl, A.M.; Brender, T.; Mink, K.A.; Waggie, K.S.; Peffault de Latour, R.; Janin, A.; Curtsinger, J.M.; et al. Blocking IL-21 signaling ameliorates xenogeneic GVHD induced by human lymphocytes. Blood 2012, 119, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawa, R.S.; Anillo, S.; Huntoon, K.; Baumann, H.; Kulaylat, M. Analytic review: Interleukin-6 in surgery, trauma, and critical care: Part I: Basic science. J. Intensive Care Med. 2011, 26, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, N.R. Coordination of Immune-Stroma Crosstalk by IL-6 Family Cytokines. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T. IL-6 in inflammation, autoimmunity and cancer. Int. Immunol. 2021, 33, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tvedt, T.H.A.; Rose-John, S.; Tsykunova, G.; Ahmed, A.B.; Gedde-Dahl, T.; Ersvær, E.; Bruserud, Ø. IL-6 Responsiveness of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T Cells after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Differs between Patients and Is Associated with Previous Acute Graft versus Host Disease and Pretransplant Antithymocyte Globulin Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; He, C.; Lai, P.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Lin, X.; Ni, B.; Ju, R.; Yi, W.; et al. miR-204-containing exosomes ameliorate GVHD-associated dry eye disease. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabj9617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Bian, Y. Fibroblast-derived interleukin-6 exacerbates adverse cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2024, 28, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaro, L.; Passafaro, M.; Sala, D.; Etxaniz, U.; Lugarini, F.; Proietti, D.; Alfonsi, M.V.; Nicoletti, C.; Gatto, S.; De Bardi, M.; et al. Denervation-activated STAT3-IL-6 signalling in fibro-adipogenic progenitors promotes myofibres atrophy and fibrosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalla, A.E.; Lambert, N.; Duan, X.; Xie, J. Interleukin-10 Family and Tuberculosis: An Old Story Renewed. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekera, D.C.; Ma, J.; Vacharathit, V.; Shah, P.; Ramakrishnan, A.; Uprety, P.; Shen, Z.; Sheh, A.; Brayton, C.F.; Whary, M.T.; et al. The development of colitis in Il10−/− mice is dependent on IL-22. Mucosal Immunol. 2020, 13, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Hatano, R.; Horimoto, Y.; Yamada, T.; Song, D.; Otsuka, H.; Shirakawa, Y.; Mastuoka, S.; Iwao, N.; Aune, T.M.; et al. IL-26 mediates epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance through endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartziokas, K.; Fouka, E.; Loukides, S.; Steiropoulos, P.; Bakakos, P.; Papaioannou, A.I. IL-26 in the Lung and Its Role in COPD Inflammation. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y. Immunoregulatory Functions of the IL-12 Family of Cytokines in Antiviral Systems. Viruses 2019, 11, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamza, T.; Barnett, J.B.; Li, B. Interleukin 12 a key immunoregulatory cytokine in infection applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 789–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, K.M.; Szeto, C.C.; Betin, V.M.; Mathieson, P.W. Role of beta1 and beta2 subunits of the interleukin-12 receptor in determining T helper 1/T helper 2 responses in vivo in the rat. Immunology 2000, 99, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, E.; Garside, P.; Bradley, J.A.; Mowat, A.M. IL-12 is a central mediator of acute graft-versus-host disease in mice. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Hu, B.; Liu, Y.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, D.; Zhu, Y.; Lei, L.; Gong, H.; Mei, Y.; et al. IL-12/IL-18-preactivated donor NK cells enhance GVL effects and mitigate GvHD after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 48, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüber, C.M.; Doisne, J.M.; Colucci, F. IL-12/15/18-preactivated NK cells suppress GvHD in a mouse model of mismatched hematopoietic cell transplantation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, J.A.; Clear, A.; Aries, J.; Charrot, S.; Besley, C.; Mee, M.; Stagg, A.; Lindsay, J.O.; Cavenagh, J.; Calaminci, M.; et al. Retinoic acid-responsive CD8 effector T cells are selectively increased in IL-23-rich tissue in gastrointestinal GVHD. Blood 2021, 137, 702–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, S.; Fujiwara, H.; Nishimori, H.; Matsuoka, K.; Fujii, N.; Kondo, E.; Tanaka, T.; Yoshimura, A.; Tanimoto, M.; Maeda, Y. Anti-IL-12/23 p40 antibody attenuates experimental chronic graft-versus-host disease via suppression of IFN-γ/IL-17-producing cells. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Q.; Shi, Y. Biologic and Small-Molecule Therapies for Moderate-to-Severe Psoriasis: Focus on Psoriasis Comorbidities. BioDrugs 2023, 37, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shono, Y.; Docampo, M.D.; Peled, J.U.; Perobelli, S.M.; Velardi, E.; Tsai, J.J.; Slingerland, A.E.; Smith, O.M.; Young, L.F.; Gupta, J.; et al. Increased GVHD-related mortality with broad-spectrum antibiotic use after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in human patients and mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 339ra371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wei, Y.; Xiao, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, G.; Chen, G.; Hou, C.; Ma, N.; Shen, B.; et al. A novel IL-23p19/Ebi3 (IL-39) cytokine mediates inflammation in Lupus-like mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, S.; Rudensky, A.Y. Therapeutic use of regulatory T cells for graft-versus-host disease. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 187, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Qin, H.; Li, Y.; Riggs, A.D.; Martin, P.J.; Chen, Y.Z.; Zeng, D. Tolerogenic anti-IL-2 mAb prevents graft-versus-host disease while preserving strong graft-versus-leukemia activity. Blood 2021, 137, 2243–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, T.L.; Bolivar-Wagers, S.; Jin, S.; Thangavelu, G.; Simonetta, F.; Lin, P.Y.; Hirai, T.; Saha, A.; Koehn, B.; Su, L.L.; et al. Prevention of acute GVHD using an orthogonal IL-2/IL-2Rβ system to selectively expand regulatory T cells in vivo. Blood 2023, 141, 1337–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadan, A.; Griesenauer, B.; Adom, D.; Kapur, R.; Hanenberg, H.; Liu, C.; Kaplan, M.H.; Paczesny, S. Specifically differentiated T cell subset promotes tumor immunity over fatal immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 3577–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highfill, S.L.; Rodriguez, P.C.; Zhou, Q.; Goetz, C.A.; Koehn, B.H.; Veenstra, R.; Taylor, P.A.; Panoskaltsis-Mortari, A.; Serody, J.S.; Munn, D.H.; et al. Bone marrow myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) inhibit graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) via an arginase-1-dependent mechanism that is up-regulated by interleukin-13. Blood 2010, 116, 5738–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi, K.; Guilliams, M.; Van den Bossche, J.; Van den Bergh, R.; Gysemans, C.; Beschin, A.; De Baetselier, P.; Van Ginderachter, J.A. Identification of discrete tumor-induced myeloid-derived suppressor cell subpopulations with distinct T cell-suppressive activity. Blood 2008, 111, 4233–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.G.; Homer, R.J.; Zhu, Z.; Lanone, S.; Wang, X.; Koteliansky, V.; Shipley, J.M.; Gotwals, P.; Noble, P.; Chen, Q.; et al. Interleukin-13 induces tissue fibrosis by selectively stimulating and activating transforming growth factor beta(1). J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Verma, A.K.; Das, M.; Dwivedi, P.D. Molecular mechanisms of IgE mediated food allergy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 13, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshima, T.; Hill, G.R.; Pan, L.; Brinson, Y.S.; van den Brink, M.R.; Cooke, K.R.; Ferrara, J.L. IL-11 separates graft-versus-leukemia effects from graft-versus-host disease after bone marrow transplantation. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, G.R.; Cooke, K.R.; Teshima, T.; Crawford, J.M.; Keith, J.C., Jr.; Brinson, Y.S.; Bungard, D.; Ferrara, J.L. Interleukin-11 promotes T cell polarization and prevents acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chang, C.Y.; Yang, X.; Zhou, F.; Liu, J.; Zhu, S.; Yu, X.Z.; Liu, C.; O’Sullivan, T.E.; Xie, P.; et al. Leukemia inhibitory factor protects against graft-versus-host disease while preserving graft-versus-leukemia activity. Blood 2022, 140, 2076–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, K.; Van den Haute, C.; Baekelandt, V.; Lucas, S.; van Horssen, J.; Somers, V.; Van Wijmeersch, B.; Stinissen, P.; Hendriks, J.J.; Slaets, H.; et al. Leukemia inhibitory factor tips the immune balance towards regulatory T cells in multiple sclerosis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 45, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henden, A.S.; Koyama, M.; Robb, R.J.; Forero, A.; Kuns, R.D.; Chang, K.; Ensbey, K.S.; Varelias, A.; Kazakoff, S.H.; Waddell, N.; et al. IFN-λ therapy prevents severe gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2021, 138, 722–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, D.; Wu, Y.; Betts, B.C.; Yu, X.Z. The IL-12 Cytokine and Receptor Family in Graft-vs.-Host Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ara, T.; Hashimoto, D.; Hayase, E.; Noizat, C.; Kikuchi, R.; Hasegawa, Y.; Matsuda, K.; Ono, S.; Matsuno, Y.; Ebata, K.; et al. Intestinal goblet cells protect against GVHD after allogeneic stem cell transplantation via Lypd8. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaw0720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspuria, P.J.; Vivona, S.; Bauer, M.; Semana, M.; Ratti, N.; McCauley, S.; Riener, R.; de Waal Malefyt, R.; Rokkam, D.; Emmerich, J.; et al. An orthogonal IL-2 and IL-2Rβ system drives persistence and activation of CAR T cells and clearance of bulky lymphoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabg7565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, J.; Yuan, Y.; Ji, D.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhu, X.; Wu, X.; Hu, J.; et al. Proximity-enabled covalent binding of IL-2 to IL-2Rα selectively activates regulatory T cells and suppresses autoimmunity. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldhoen, M.; Uyttenhove, C.; van Snick, J.; Helmby, H.; Westendorf, A.; Buer, J.; Martin, B.; Wilhelm, C.; Stockinger, B. Transforming growth factor-beta ‘reprograms’ the differentiation of T helper 2 cells and promotes an interleukin 9-producing subset. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, N.; Xu, J.; Qu, J.; Duan, X.; Yuan, H.; Chen, G.; Jiang, M.; Ding, J. Peripheral blood Th9 cells reconstitution and its relationship with acute graft-versus-host disease after matched-sibling peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 3623–3632. [Google Scholar]
- Mangus, C.W.; Massey, P.R.; Fowler, D.H.; Amarnath, S. Rapamycin resistant murine th9 cells have a stable in vivo phenotype and inhibit graft-versus-host reactivity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mohammadpour, H.; Cao, X. Targeting Cytokines in GVHD Therapy. J. Immunol. Res. Ther. 2017, 2, 90–99. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, K.; Amakawa, R.; Takebayashi, M.; Son, Y.; Miyaji, M.; Tajima, K.; Nakai, K.; Ito, T.; Matsumoto, N.; Zen, K.; et al. IL-4-producing CD8(+) T cells may be an immunological hallmark of chronic GVHD. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2005, 36, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bruce, D.W.; Kolupaev, O.; Laurie, S.J.; Bommiasamy, H.; Stefanski, H.; Blazar, B.R.; Coghill, J.M.; Serody, J.S. Third-party type 2 innate lymphoid cells prevent and treat GI tract GvHD. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 4578–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, W.J.; Brookes, P.A.; Szydlo, R.M.; Goldman, J.M.; Lechler, R.I.; Ritter, M.A. IL-13 production by donor T cells is prognostic of acute graft-versus-host disease following unrelated donor stem cell transplantation. Blood 2004, 103, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawara, I.; Maeda, Y.; Sun, Y.; Lowler, K.P.; Liu, C.; Toubai, T.; McKenzie, A.N.; Reddy, P. Combined Th2 cytokine deficiency in donor T cells aggravates experimental acute graft-vs-host disease. Exp. Hematol. 2008, 36, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Williams, D.A. Interleukin-11: Review of molecular, cell biology, and clinical use. Blood 1997, 89, 3897–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.S.; Pfeiffer, C.J.; Keith, J.C., Jr. Protection by recombinant human interleukin-11 against experimental TNB-induced colitis in rats. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1996, 41, 1625–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepler, I.; Elias, L.; Smith, J.W., 2nd; Hussein, M.; Rosen, G.; Chang, A.Y.; Moore, J.O.; Gordon, M.S.; Kuca, B.; Beach, K.J.; et al. A randomized placebo-controlled trial of recombinant human interleukin-11 in cancer patients with severe thrombocytopenia due to chemotherapy. Blood 1996, 87, 3607–3614. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, B.A. Ultrastructural study of cervical gonorrhea. J. Infect. Dis. 1977, 136, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kong, D.; Yu, Q.; Si, X.; Yang, L.; Zeng, X.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Qian, P.; Huang, H.; et al. Cyclosporine A regulates PMN-MDSCs viability and function through MPTP in acute GVHD: Old medication, new target. Transpl. Cell. Ther. 2022, 28, 411.e1–411.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hematopoietic Stem Cell Application Group of the Hematology Branch of the Chinese Medical Association; Hematologic Diseases Translational Committee of the Chinese Anti-Cancer Association. Chinese consensus on the diagnosis and management of chronic graft-versus-host disease (2021). Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2021, 42, 265–275. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Haffty, B.; Verzi, M.; Zhang, L.; Gao, N.; et al. LIF is essential for ISC function and protects against radiation-induced gastrointestinal syndrome. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chang, C.Y.; Yang, X.; Zhou, F.; Liu, J.; Feng, Z.; Hu, W. Leukemia inhibitory factor, a double-edged sword with therapeutic implications in human diseases. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotenko, S.V.; Gallagher, G.; Baurin, V.V.; Lewis-Antes, A.; Shen, M.; Shah, N.K.; Langer, J.A.; Sheikh, F.; Dickensheets, H.; Donnelly, R.P. IFN-lambdas mediate antiviral protection through a distinct class II cytokine receptor complex. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syedbasha, M.; Egli, A. Interferon Lambda: Modulating Immunity in Infectious Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egwuagu, C.E.; Yu, C.R.; Sun, L.; Wang, R. Interleukin 35: Critical regulator of immunity and lymphocyte-mediated diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2015, 26, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.C.; Liu, X.Y.; Huang, A.F.; Xu, W.D. Emerging role of IL-35 in inflammatory autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lei, L. Interleukin-35 regulates the balance of Th17 and Treg responses during the pathogenesis of connective tissue diseases. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 24, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normanton, M.; Marti, L.C. Current data on IL-17 and Th17 cells and implications for graft versus host disease. Einstein 2013, 11, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yu, X.Z. IL-17A ≠ Th17 in GvHD. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 282–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappu, B.P.; Angkasekwinai, P.; Dong, C. Regulatory mechanisms of helper T cell differentiation: New lessons learned from interleukin 17 family cytokines. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 117, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, J.L. Pathogenesis of acute graft-versus-host disease: Cytokines and cellular effectors. J. Hematother. Stem Cell Res. 2000, 9, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichenbach, D.K.; Schwarze, V.; Matta, B.M.; Tkachev, V.; Lieberknecht, E.; Liu, Q.; Koehn, B.H.; Pfeifer, D.; Taylor, P.A.; Prinz, G.; et al. The IL-33/ST2 axis augments effector T-cell responses during acute GVHD. Blood 2015, 125, 3183–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, B.M.; Reichenbach, D.K.; Zhang, X.; Mathews, L.; Koehn, B.H.; Dwyer, G.K.; Lott, J.M.; Uhl, F.M.; Pfeifer, D.; Feser, C.J.; et al. Peri-alloHCT IL-33 administration expands recipient T-regulatory cells that protect mice against acute GVHD. Blood 2016, 128, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Ramadan, A.; Reichenbach, D.K.; Loschi, M.; Zhang, J.; Griesenauer, B.; Liu, H.; Hippen, K.L.; Blazar, B.R.; Paczesny, S. Rorc restrains the potency of ST2+ regulatory T cells in ameliorating intestinal graft-versus-host disease. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e122014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, J.; Prado-Acosta, M. Graft-versus-host disease: Establishing IL-33 as an important costimulatory molecule. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e160692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, R.G.; Carpenito, C.; Shan, X.; Danet-Desnoyers, G.; Liu, R.; Jiang, S.; Albelda, S.M.; Golovina, T.; Coukos, G.; Riley, J.L.; et al. Distinct effects of IL-18 on the engraftment and function of human effector CD8 T cells and regulatory T cells. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, I.; Kohno, K.; Tanimoto, T.; Iwaki, K.; Ishihara, T.; Akamatsu, S.; Ikegami, H.; Kurimoto, M. IL-18 prevents the development of chronic graft-versus-host disease in mice. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 6067–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, F.J.; Rodriguez Gomez, M.; Doser, K.; Edinger, M.; Hoffmann, P.; Schiechl, G.; Talke, Y.; Göbel, N.; Schmidbauer, K.; Syed, S.N.; et al. Basophils inhibit proliferation of CD4+ T cells in autologous and allogeneic mixed lymphocyte reactions and limit disease activity in a murine model of graft versus host disease. Immunology 2015, 145, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, S.; Guo, H.; Choi, J.G.; Ye, C.; Thomas, M.B.; Ortega, N.; Dwivedi, A.; Manjunath, N.; Yi, G.; Shankar, P. Combination of IL-10 and IL-2 induces oligoclonal human CD4 T cell expansion during xenogeneic and allogeneic GVHD in humanized mice. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhao, D.; Kim, Y.H.; Jeong, S.; Greenson, J.K.; Chaudhry, M.S.; Hoepting, M.; Anderson, E.R.; van den Brink, M.R.; Peled, J.U.; Gomes, A.L.; et al. Survival signal REG3α prevents crypt apoptosis to control acute gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4970–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartlan, K.H.; Bommiasamy, H.; Paz, K.; Wilkinson, A.N.; Owen, M.; Reichenbach, D.K.; Banovic, T.; Wehner, K.; Buchanan, F.; Varelias, A.; et al. A critical role for donor-derived IL-22 in cutaneous chronic GVHD. Am. J. Transpl. 2018, 18, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, M.A.; Marsden, M.; Pham, N.T.; Clare, S.; Dolton, G.; Stack, G.; Jones, E.; Klenerman, P.; Gallimore, A.M.; Taylor, P.R.; et al. Neutrophils recruited by IL-22 in peripheral tissues function as TRAIL-dependent antiviral effectors against MCMV. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belle, L.; Agle, K.; Zhou, V.; Yin-Yuan, C.; Komorowski, R.; Eastwood, D.; Logan, B.; Sun, J.; Ghilardi, N.; Cua, D.; et al. Blockade of interleukin-27 signaling reduces GVHD in mice by augmenting Treg reconstitution and stabilizing Foxp3 expression. Blood 2016, 128, 2068–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.; Chen, Z.; Xu, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, A.; Liu, T.; Zhao, N.; Xiong, Y.; Jiang, G.; Ma, J.; et al. IL-27 Promotes Human Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Ability To Induce the Generation of CD4+IL-10+IFN-γ+ T Cells via the JAK/STAT Pathway in the Treatment of Experimental Graft-versus-Host Disease. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, S.; Jin, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, L.; Qi, G.; Yang, J. The role of IL-33/ST2 signaling in the tumor microenvironment and Treg immunotherapy. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022, 247, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiering, C.; Krausgruber, T.; Chomka, A.; Fröhlich, A.; Adelmann, K.; Wohlfert, E.A.; Pott, J.; Griseri, T.; Bollrath, J.; Hegazy, A.N.; et al. The alarmin IL-33 promotes regulatory T-cell function in the intestine. Nature 2014, 513, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, L.; Poulsen, L.K. IL-1 family members IL-18 and IL-33 upregulate the inflammatory potential of differentiated human Th1 and Th2 cultures. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 4331–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesenauer, B.; Jiang, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Ramadan, A.M.; Egbosiuba, J.; Campa, K.; Paczesny, S. ST2/MyD88 Deficiency Protects Mice Against Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease and Spares Regulatory T Cells. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 3053–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, U.K.; Engelhardt, B.G. Predicting Immuno-Metabolic Complications After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplant with the Cytokine Interleukin-33 (IL-33) and its Receptor Serum-Stimulation 2 (ST2). Clin. Hematol. Int. 2020, 2, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, M.I.; Ramzi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Ebrahimi, N.; Owjfard, M.; Abdolyousefi, E.N.; Hesami, Z.; Valibeigi, B.; Zareei, N.; Tavasolian, F.; et al. Expression Levels of Il-6 and Il-18 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Its Relation with Response to Therapy and Acute GvHD After Bone Marrow Transplantation. Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 12, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.; Wasem, C.; Juillard, P.; Graber, P.; Cima, I.; Frutschi, C.; Herren, S.; Jakob, S.; Alouani, S.; Mueller, C.; et al. IL-18-independent cytotoxic T lymphocyte activation and IFN-gamma production during experimental acute graft-versus-host disease. Int. Immunol. 2002, 14, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Silva-Filho, J.L.; Caruso-Neves, C.; Pinheiro, A.A.S. IL-4: An important cytokine in determining the fate of T cells. Biophys. Rev. 2014, 6, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takabayashi, M.; Kanamori, H.; Takasaki, H.; Yamaji, S.; Koharazawa, H.; Taguchi, J.; Tomita, N.; Fujimaki, K.; Fujisawa, S.; Maruta, A.; et al. A possible association between the presence of interleukin-4-secreting cells and a reduction in the risk of acute graft-versus-host disease. Exp. Hematol. 2005, 33, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, S.; Tang, Y.W.; Graham, B.S. Interleukin-4 diminishes CD8+ respiratory syncytial virus-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activity in vivo. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 8944–8949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guan, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, H.L.; Truscott, J.; Beyatli, S.; Metwali, A.; Weiner, G.J.; Zavazava, N.; Blumberg, R.S.; et al. Helminth-Induced Production of TGF-β and Suppression of Graft-versus-Host Disease Is Dependent on IL-4 Production by Host Cells. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 2910–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, E.Y.; Chung, D.H. Donor bone marrow type II (non-Valpha14Jalpha18 CD1d-restricted) NKT cells suppress graft-versus-host disease by producing IFN-gamma and IL-4. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 6579–6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaki, R.; Toyoda, H.; Iwamoto, S.; Morimoto, M.; Nakato, D.; Ito, T.; Niwa, K.; Amano, K.; Hashizume, R.; Tawara, I.; et al. Donor-derived M2 macrophages attenuate GVHD after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2021, 9, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, S.; Choi, J.G.; Ye, C.; Manjunath, N.; Shankar, P. IL-10 exacerbates xenogeneic GVHD by inducing massive human T cell expansion. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 156, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Tan, Z.; Thomas, E.K.; Liang, P. Conservation of the genomic structure and receptor-mediated signaling between human and rat IL-24. Genes. Immun. 2004, 5, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zai, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, H.; Ju, D. Therapeutic Opportunities of IL-22 in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Applications. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanash, A.M.; Dudakov, J.A.; Hua, G.; O’Connor, M.H.; Young, L.F.; Singer, N.V.; West, M.L.; Jenq, R.R.; Holland, A.M.; Kappel, L.W.; et al. Interleukin-22 protects intestinal stem cells from immune-mediated tissue damage and regulates sensitivity to graft versus host disease. Immunity 2012, 37, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemans, C.A.; Calafiore, M.; Mertelsmann, A.M.; O’Connor, M.H.; Dudakov, J.A.; Jenq, R.R.; Velardi, E.; Young, L.F.; Smith, O.M.; Lawrence, G.; et al. Interleukin-22 promotes intestinal-stem-cell-mediated epithelial regeneration. Nature 2015, 528, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudakov, J.A.; Mertelsmann, A.M.; O’Connor, M.H.; Jenq, R.R.; Velardi, E.; Young, L.F.; Smith, O.M.; Boyd, R.L.; van den Brink, M.R.M.; Hanash, A.M. Loss of thymic innate lymphoid cells leads to impaired thymopoiesis in experimental graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2017, 130, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarthée, B.; Malard, F.; Gamonet, C.; Bossard, C.; Couturier, M.; Renauld, J.C.; Mohty, M.; Saas, P.; Gaugler, B. Donor interleukin-22 and host type I interferon signaling pathway participate in intestinal graft-versus-host disease via STAT1 activation and CXCL10. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Cao, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Mi, J.; Zhang, J.Z.; Jin, M.; Ge, H.; Emerson, S.G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. A new approach to the blocking of alloreactive T cell-mediated graft-versus-host disease by in vivo administration of anti-CXCR3 neutralizing antibody. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 7581–7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, L.; Goroncy, L.; Palaniyandi, S.; Gautam, S.; Triantafyllopoulou, A.; Mocsai, A.; Reichardt, W.; Karlsson, F.J.; Radhakrishnan, S.V.; Hanke, K.; et al. Neutrophil granulocytes recruited upon translocation of intestinal bacteria enhance graft-versus-host disease via tissue damage. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Nakaya, M.; Miyazaki, Y. Interleukin 27: A double-edged sword for offense and defense. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meka, R.R.; Venkatesha, S.H.; Dudics, S.; Acharya, B.; Moudgil, K.D. IL-27-induced modulation of autoimmunity and its therapeutic potential. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.T.; Keslar, K.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Blazar, B.R.; Hamilton, B.K.; Min, B. Interleukin-27 Enforces Regulatory T Cell Functions to Prevent Graft-versus-Host Disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, M.J.; West, M.L.; Coghill, J.M.; Panoskaltsis-Mortari, A.; Blazar, B.R.; Serody, J.S. In vitro-differentiated TH17 cells mediate lethal acute graft-versus-host disease with severe cutaneous and pulmonary pathologic manifestations. Blood 2009, 113, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varelias, A.; Ormerod, K.L.; Bunting, M.D.; Koyama, M.; Gartlan, K.H.; Kuns, R.D.; Lachner, N.; Locke, K.R.; Lim, C.Y.; Henden, A.S.; et al. Acute graft-versus-host disease is regulated by an IL-17-sensitive microbiome. Blood 2017, 129, 2172–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.; Zhao, D.; Lin, C.L.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; Todorov, I.; LeBon, T.; Kandeel, F.; Forman, S.; Zeng, D. Absence of donor Th17 leads to augmented Th1 differentiation and exacerbated acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2008, 112, 2101–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappel, L.W.; Goldberg, G.L.; King, C.G.; Suh, D.Y.; Smith, O.M.; Ligh, C.; Holland, A.M.; Grubin, J.; Mark, N.M.; Liu, C.; et al. IL-17 contributes to CD4-mediated graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2009, 113, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ma, S.; Liu, Y.; Gong, H.; Cheng, Q.; Hu, B.; Wu, Y.; Yu, X.; Dong, C.; Sun, K.; et al. Adoptively transferred donor IL-17-producing CD4(+) T cells augment, but IL-17 alleviates, acute graft-versus-host disease. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marwaha, A.K.; Leung, N.J.; McMurchy, A.N.; Levings, M.K. TH17 Cells in Autoimmunity and Immunodeficiency: Protective or Pathogenic? Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, A.C.; Ferrara, J.L.; Levine, J.E. Advances in predicting acute GVHD. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 160, 288–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, S.; Braun, S.; Deichmann, K.A. Distinct signal transduction processes by IL-4 and IL-13 and influences from the Q551R variant of the human IL-4 receptor alpha chain. Respir. Res. 2002, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatmaitan, J.G.; Lee, J.H. Challenges and Future Trends in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.Y.; Lickliter, J.; Huang, Z.H.; Xian, Z.S.; Chen, H.Y.; Huang, C.; Xiao, C.; Wang, Y.P.; Tan, Y.; Xu, L.F.; et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and biomarkers of F-652, a recombinant human interleukin-22 dimer, in healthy subjects. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünig, G.; Ford, J.G.; Donaldson, D.D.; Venkayya, R.; McArthur, C.; Hansell, E.; Kurup, V.A.; Warnock, M.; Rennick, D. Roles of interleukin-13 and interferon-gamma in lung inflammation. Chest 2002, 121 (Suppl. S3), 88s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, P.M.; Pavel, A.B.; Khattri, S.; Leonard, A.; Malik, K.; Rose, S.; Jim On, S.; Vekaria, A.S.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Singer, G.K.; et al. Baseline IL-22 expression in patients with atopic dermatitis stratifies tissue responses to fezakinumab. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonis, S.T.; Peterson, R.L.; Edwards, L.J.; Lucey, C.A.; Wang, L.; Mason, L.; Login, G.; Ymamkawa, M.; Moses, G.; Bouchard, P.; et al. Defining mechanisms of action of interleukin-11 on the progression of radiation-induced oral mucositis in hamsters. Oral Oncol. 2000, 36, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antin, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Neuberg, D.; Alyea, E.; Soiffer, R.J.; Sonis, S.; Ferrara, J.L. A phase I/II double-blind, placebo-controlled study of recombinant human interleukin-11 for mucositis and acute GVHD prevention in allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2002, 29, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidala, J.; Beato, F.; Kim, J.; Betts, B.; Jim, H.; Sagatys, E.; Levine, J.E.; Ferrara, J.L.M.; Ozbek, U.; Ayala, E.; et al. In vivo IL-12/IL-23p40 neutralization blocks Th1/Th17 response after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Haematologica 2018, 103, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysoy, A.; Bai, Z.; Satija, R.; Fan, R. The technological landscape and applications of single-cell multi-omics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 695–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.T. Single-cell Proteomics: Progress and Prospects. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2020, 19, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, L.; Alousi, A.; Kebriaei, P.; Mehta, R.; Rezvani, K.; Shpall, E. New and emerging therapies for acute and chronic graft versus host disease. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2018, 9, 21–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
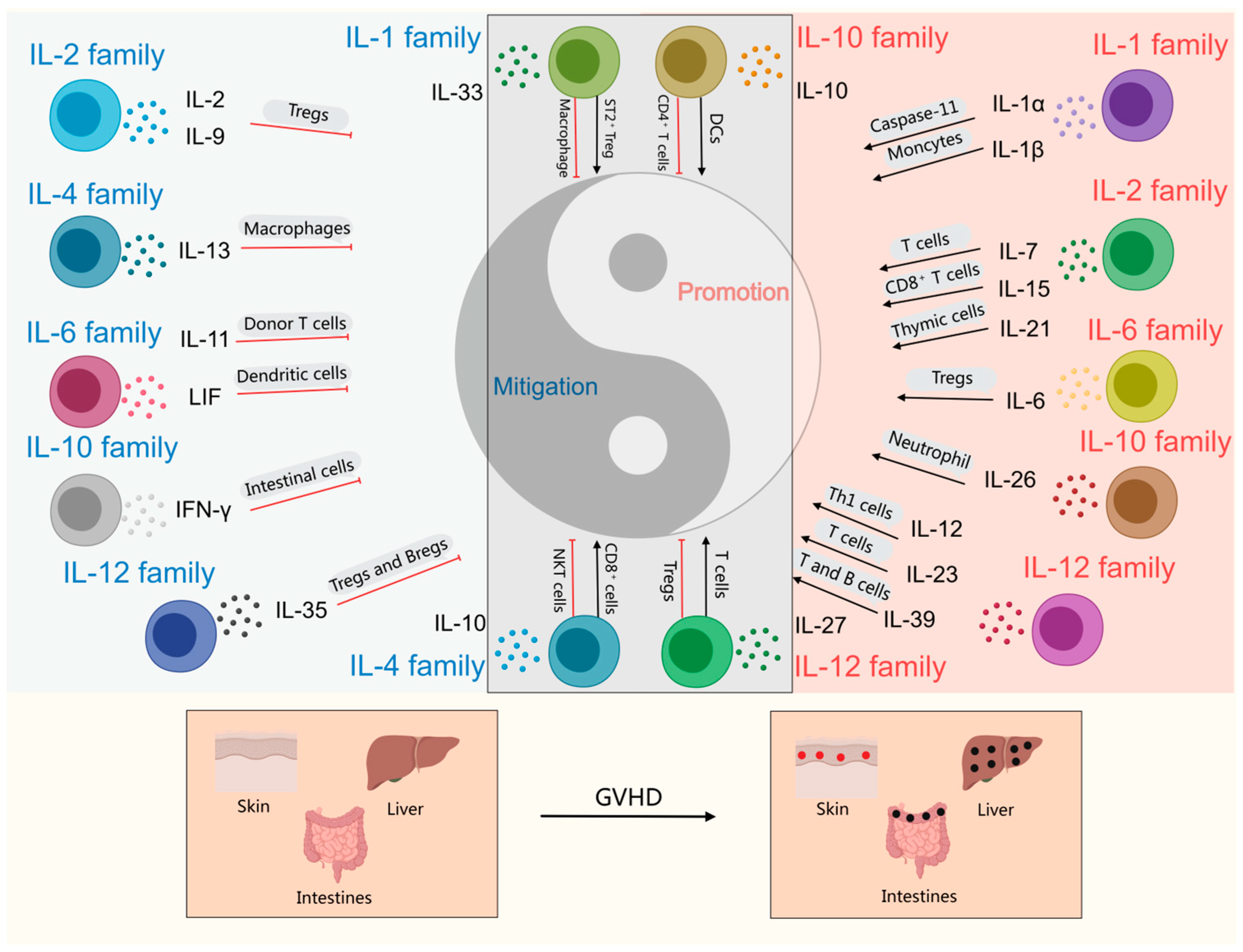
| Interleukin | Disease Promotion/Mitigation | Mode of Action | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1 family | IL-1α IL-1β | Promotion | 1. Caspase-11 signaling enhances GVHD via IL-1α. 2. IL-1β is produced by monocytes cells, affects DCs and T cells, and plays a key pro-inflammatory role in the early stages of GVHD, especially Th17 cells. | [27,28,29,30] |
| IL-2 family | IL-7 | Promotion | IL-7 also promotes the expansion of allogeneic reactive T cells that mediate GVHD. | [31,32] |
| IL-15 | Promotion | 1. IL-15 significantly increased tissue inflammation in the gut and liver as well as GVHD morbidity and mortality after BMT by promoting the expansion and activation of allogeneic reactive effector memory CD8+ T cells. | [33,34] | |
| IL-21 | Promotion | IL-21 directly stimulates the development of T cells in the thymus by increasing the number of thymic progenitor cells and promoting the recovery of TEC, IL-21 promotes Th17 differentiation in the presence of TGF and induces inflammation. | [35] | |
| IL-6 family | IL-6 | Promotion | 1. IL-6 facilitates the differentiation of Th17 cells in conjunction with TGF-β, while concurrently inhibiting the differentiation of Treg cells induced by TGF-β. 2. Abnormal expression of IL-6 drives the occurrence and progression of cGVHD by promoting macrophage differentiation and maturation, TGF-β production and tissue fibrosis. | [36,37,38]. |
| IL-10 family | IL-26 | Promotion | 1. IL-26 activates mouse fibroblasts, promotes collagen production, and aggravates GVHD pulmonary fibrosis. 2. IL-26 significantly increases neutrophil levels in GVHD target tissues and peripheral blood. The systemic symptoms of GVHD were exacerbated by significantly elevated levels of Th17 cytokine expression in donor CD4+ T cells, and significantly enhanced levels of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, IL-1β and IL-6. | [39,40] |
| IL-12 family | IL-12 | Promotion | IL-12 activates the STAT3 and STAT4 signaling pathways, facilitating the differentiation of naïve T cells into Th1 cells, while significantly enhancing the production of IFN-γ. Concurrently, it inhibits the synthesis of Th2 cytokines such as IL-4, thereby establishing a Th1-dominated immune response. | [41] |
| IL-23 | Promotion | 1. IL-23 plays a key role in the pathological damage of colonic GVHD mainly through T cell-dependent pathways, especially by inducing IFN-γ secretion. 2. IL-23 may affect aGVHD through IL-17-dependent and non-dependent pathways. | [42,43] | |
| IL-39 | Promotion | IL-39 promotes pro-inflammatory responses in T and B cells and plays an important role in the pathophysiology of cGVHD by activating the STAT pathway through interaction with IL-39 receptors on T cells. | [44] |
| Interleukin | Disease Promotion/Mitigation | Mode of Action | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-2 family | IL-2 | Mitigation | 1. IL-2, by pairing Tregs with oIL-2, is able to selectively expand Tregs in vivo while avoiding the activation of allogeneic reactive T cells, thereby reducing the severity of aGVHD and improving survival. 2. Increase the expression of PD-L1 in host tissues by blocking the binding of IL-2 to the IL-2 receptor on T cells using the anti-IL-2 monoclonal antibody JES6, and inhibit pathogenic T cell function by inhibiting the activation of the IL-2-Stat5 signaling pathway in donor T cells to promote T cell depletion or differentiation into Tr1 cells. | [92,93] |
| IL-9 | Mitigation | 1. IL-9 activates Treg cell recruitment and activates mast cell-mediated regional immunosuppression. 2. Th9 cells secreting IL-9 inhibit type I cytokine production by allogeneic-reactive T cells while maintaining IL-9 secretion capacity and suppressing IFN-γ-driven allogeneic responses. | [19,94] | |
| IL-4 family | IL-13 | Mitigation | 1. IL-13 Cultures produce MDSC-IL-13, which plays a protective role in GVHD by up-regulating the expression of arginase-1, which is more inhibitory to allogeneic T cell responses. 2. IL-13 can inhibit the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 in monocytes and macrophages, which contributes to reducing tissue damage. 3. IL-13 promotes the shift in Th1/Th2 balance to Th2 cells by inhibiting TNF-α and enhancing the secretion of IL-4 and IL-5, thus having a protective function in GVHD. | [95,96,97,98] |
| IL-6 family | IL-11 | Mitigation | IL-11 affects the activation of donor T cells by down-regulating IL-12, which directly inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IFN-γ by monocytes and macrophages, providing a new strategy for the treatment of GHVD. | [99,100] |
| LIF | Mitigation | rLIF activates the STAT1 signaling pathway, resulting in the downregulation of IL-12-p40 expression in irradiated recipient dendritic cells. This process leads to a decrease in MHC class II expression on intestinal epithelial cells, which subsequently reduces donor T cell activation and infiltration. | [101,102] | |
| IL-10 family | IFN-λ | Mitigation | IFN- λ limits the loss of intestinal stem cells and promotes the regeneration of intestinal epithelial cells, thereby protecting the mucosal barrier function. IFN- λ is a key protective factor in the immunopathology of GVHD in the gastrointestinal tract and plays an important role especially in the ISC compartment. | [103] |
| IL-12 family | IL-35 | Mitigation | IL-35 is mainly released by Treg and Breg and plays a role in suppressing inflammation and reducing the severity of autoimmune diseases. | [104] |
| IL-17 family | IL-25 | Mitigation | IL-25 protects cuprocytes from GVHD, prevents bacterial translocation, reduces IFN-γ and IL-6 plasma levels, and ameliorates GVHD. | [105] |
| Interleukin | Disease Promotion/Mitigation | Mode of Action | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1 family | IL-33 | Promotion/mitigation | 1. The IL-33/ST2 axis exacerbates the severity of GVHD by increasing IFN-g production, upregulating IL-18R expression and promoting cell proliferation. 2. IL-33’s can promote tissue repair by amplifying Tregs, especially the ST2+ Treg subpopulation, and by up-regulating the expression of bi-regulated proteins. 3. IL-33 functions by inhibiting M1-type macrophage activation and promoting granulocyte MDSC. | [133,134,135,136] |
| IL-18 | Promotion/mitigation | 1. In mouse model studies, IL-18 pre-activated NK cells were able to maintain Eomes and T-bet expression and inhibit acute GVHD. 2. IL-18 administration resulted in an increase in the number of CD8+ T cells and a significant decrease in the number of Treg cells, an effector that accelerated the onset and exacerbated the severity of GVHD. 3. IL-18 exerts its therapeutic effect on chronic GVHD through a triple mechanism of action by inducing donor-versus-host CD8+ CTLs, down-regulating host B cell MHC class II expression, and reducing the number of donor CD4+ T cells, etc. | [85,137,138] | |
| IL-4 family | IL-4 | Promotion/mitigation | 1. IL-4 derived from basophils, NKT cells, and conventional CD4+ T cells can effectively inhibit GVHD, and exogenous IL-4 treatment also demonstrates alleviating effects on acute GVHD. 2. The proportion of IL-4-producing CD8+ T cells in the peripheral blood of cGVHD patients was significantly higher than in non-cGVHD patients and healthy controls, suggesting these cells may serve as an immunological marker for cGVHD. | [95,112,139] |
| IL-10 family | IL-10 | Promotion/mitigation | 1. ROCK1/2 inhibitors reduce CD8+ cell proliferation by inhibiting DCs and increase the expression of IL-10 mRNA, which plays an anti-inflammatory role during aGVHD. 2. When co-administered with IL-2, IL-10 initially inhibits activation and expansion of responding T cells, but later modulates the response to induce massive oligoclonal expansion of CD4+ T cells, ultimately leading to GVHD lethality. | [37,140] |
| IL-22 | Promotion/mitigation | 1. IL-22 expressed in ILC3 cells from the intestine and thymus supports intestinal epithelial and thymic regeneration and barrier function during allografting, respectively. 2. IEC can secrete Reg3α and Reg3γ in response to IL-22 stimulation, and elevated serum Reg3α levels may reflect more severe intestinal barrier damage, predisposing patients to more severe intestinal GVHD. 3. The synergistic effect between IFN-α and IL-22 activates STAT1 in colonocytes, while prompting CXCL10 to recruit CXCR3-expressing effector T cells to the site of tissue damage, exacerbating GHVD. | [141,142,143] | |
| IL-12 family | IL-27 | Promotion/mitigation | 1. Inhibition of IL-27 selectively reduced IL-10 production in conventional T cells without affecting IL-10 production in Treg cells, thus preserving the ability of Treg to inhibit GVHD through this mechanistic pathway. 2. IL-27 in the inflammatory milieu in turn regulates the function of hPMSCs, upregulates PDL2 expression in hPMSCs via the JAK/STAT pathway, which in turn enhances the ability to induce CD4+ IL-10+ IFN-g+ T cell production and has therapeutic implications for the control of GVHD. | [144,145] |
| IL-17 family | IL-17 | Promotion/mitigation | 1. IL-17 can protect against GVHD by inhibiting IL-12 production by donor macrophages to downregulate the Th1 response. 2. IL-17A is a key part of the pathogenicity of these Th17 cells in GVHD. | [130] |
| Interleukin | Intervention Methods | Mechanisms of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-7/IL-5 | Prognostic biomarkers for acute GVHD | Within the first month after BMT, elevated IL-7 and IL-15 levels independently predicted the occurrence and severity of aGVHD. | [177] |
| IL-21 | Monoclonal antibody | The T cell response was regulated by increasing the number of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and reducing the number of T cells that produce interferon γ/granzyme B. | [68] |
| IL-13 | Prognostic molecules for aGVHD | IL-13 has a chemotactic effect on monocytes and eosinophils. | [178] |
| IL-26 | Monoclonal antibody | Reducing T cell/neutrophil infiltration and fibroblast proliferation shows potential for the treatment of chronic GVHD. | [40] |
| IL-22 | 1.Monoclonal antibody(fezakinumab) 2.Recombinant fusion protein(F-652) | 1.After neutralization of IL-22, the severity of inflammation, epidermal thickness and fibrosis were reduced 2.F-652 plays an important protective role in promoting tissue survival and regeneration under immune attack. | [179,180] |
| IL-11 | Recombinant protein | IL-11 alleviates inflammation by reducing the transformation of T cells to Th2 phenotype, downregulating IL-12 levels and promoting mucosal repair. | [100] |
| IL-2 | Recombinant protein | Low-dose IL-2 treatment has been shown to amplify Tregs and thus alleviate cGVHD. | [87] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, P.; Zhao, J.; Jin, J.; Yang, J. Interleukin Networks in GVHD: Mechanistic Crosstalk, Therapeutic Targeting, and Emerging Paradigms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178620
Niu Y, Liu C, Li P, Zhao J, Jin J, Yang J. Interleukin Networks in GVHD: Mechanistic Crosstalk, Therapeutic Targeting, and Emerging Paradigms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178620
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Yewei, Chen Liu, Peiyan Li, Jiawei Zhao, Jiamin Jin, and Jinfeng Yang. 2025. "Interleukin Networks in GVHD: Mechanistic Crosstalk, Therapeutic Targeting, and Emerging Paradigms" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178620
APA StyleNiu, Y., Liu, C., Li, P., Zhao, J., Jin, J., & Yang, J. (2025). Interleukin Networks in GVHD: Mechanistic Crosstalk, Therapeutic Targeting, and Emerging Paradigms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178620





