Micro RNA in Colorectal Cancer—Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers—An Updated Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Characteristics of MicroRNAs
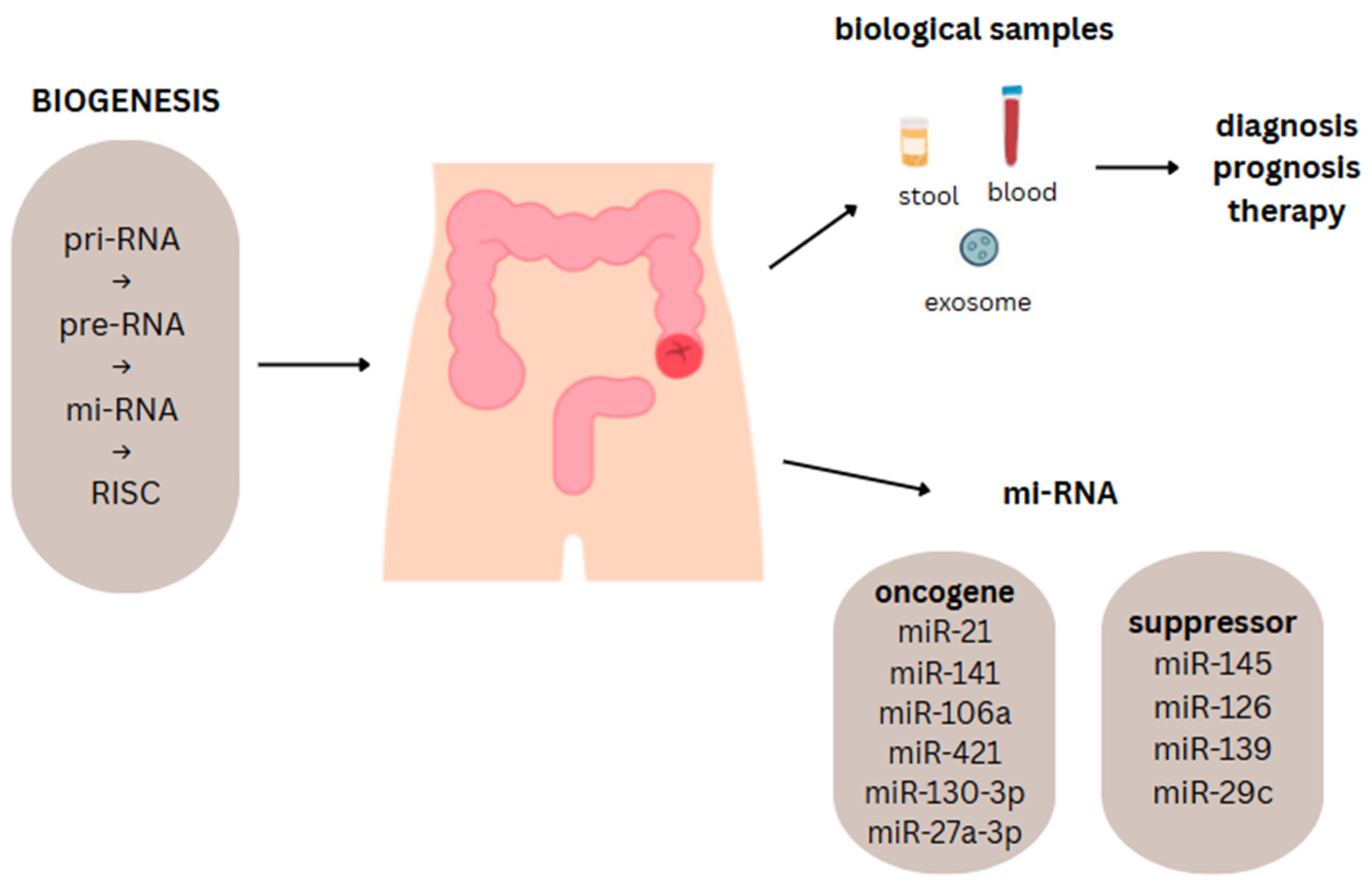
2.1. Biogenesis of MiRNAs
2.2. Mechanisms of Regulation of Gene Expression by MiRNAs
2.3. The Role of MiRNAs in Carcinogenesis
2.4. Ways to Detect and Analyze MiRNAs
3. MicroRNAs in Inflammatory Colorectal Cancer Genesis
4. MicroRNA Dysregulation in Colorectal Cancer
4.1. Role of MiRNAs in CRC Initiation, Progression, Angiogenesis, Invasion, and Metastasis
4.2. MiRNA Interactions with Epigenetics and Signaling in CRC
4.3. OncomiRNAs and Tumor-Suppressor MiRNAs in CRC
4.4. The Influence of MiRNAs on Cancer Cell Proliferation, Invasion, Angiogenesis, and Metastasis
4.5. The Application of MiRNA Panels in Diagnostics
5. MiRNAs as Diagnostic Biomarkers
5.1. MiRNAs with Diagnostic Potential
5.2. Application of MiRNAs in Non-Invasive Samples
5.3. Sensitivity and Specificity of Selected MiRNAs in CRC Diagnosis: A Comparative Analysis with Other Diagnostic Methods
6. MiRNAs as Prognostic and Predictive Biomarkers
6.1. MiRNA in Response to CRC Treatment
6.2. Prognostic Value of MiRNA and Its Association with Clinical Outcome
6.3. The Potential for Personalized Therapy
7. The Latest Advances and Research Trends
8. Limitations and Challenges
9. Summary
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3′-UTR | 3′-untranslated region |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| Ago2 | Argonaute 2 |
| BTG1 | B-cell translocation gene 1 |
| CASP3 | caspase 3 |
| CEA | carcinoembryonic antigen |
| CHD9 | chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 9 |
| CRC | colorectal cancer |
| DGCR8 | DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8 |
| EMT | epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| FC | fold change |
| FDR | false discovery rate |
| FIT | immunochemical test |
| GW182 | 182-kDa protein containing glycine and tryptophan residues |
| LFAs | lateral flow assays |
| OncomiRs | oncogenes miRNAs |
| PABPC | cytoplasmic poly(A) tail-binding protein |
| PTEN | phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| Pre-miRNA | primary microRNA |
| QRT-PCR | quantitative reverse transcription PCR |
| RISC | RNA-induced silencing complex |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| TME | tumor microenvironment |
| TS-miRs | tumor-suppressor miRNAs |
| UC | ulcerative colitis |
| iFOBT | immunochemical fecal occult blood test |
| mRNA | informational RNA |
| miRNAs | microRNAs |
| qPCR | quantitative PCR |
References
- Liu, S.C.; Zhang, H. Early diagnostic strategies for colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 3818–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Morris, V.K.; Bandey, I.N.; Hong, D.S.; Kopetz, S. Advancements in combining targeted therapy and immunotherapy for colorectal cancer. Trends Cancer 2024, 10, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biller, L.H.; Schrag, D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidoun, F.; Elshiwy, K.; Elkeraie, Y.; Merjaneh, Z.; Khoudari, G.; Sarmini, M.T.; Gad, M.; Al-Husseini, M.; Saad, A. Colorectal Cancer Epidemiology: Recent Trends and Impact on Outcomes. Curr. Drug Targets 2021, 22, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, N.O.; Senda, T. Circulating microRNA-92a-3p in colorectal cancer: A review. Med. Mol. Morphol. 2021, 54, 193–202, Erratum in Med. Mol. Morphol. 2021, 54, 302–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-021-00284-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.A.R.; Gaiteiro, C.; Santos, M.; Santos, L.; Dinis-Ribeiro, M.; Lima, L. MicroRNA Biomarkers as Promising Tools for Early Colorectal Cancer Screening-A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legras, A.; Pécuchet, N.; Imbeaud, S.; Pallier, K.; Didelot, A.; Roussel, H.; Gibault, L.; Fabre, E.; Le Pimpec-Barthes, F.; Laurent-Puig, P.; et al. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and MicroRNAs in Lung Cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godlewski, J.; Lenart, J.; Salinska, E. MicroRNA in Brain pathology: Neurodegeneration the Other Side of the Brain Cancer. Noncoding RNA 2019, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppino, G.; Riccardo, F.; Arigoni, M.; Bolli, E.; Barutello, G.; Cavallo, F.; Quaglino, E. Role and Involvement of TENM4 and miR-708 in Breast Cancer Development and Therapy. Cells 2022, 11, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidorova, E.A.; Zhernov, Y.V.; Antsupova, M.A.; Khadzhieva, K.R.; Izmailova, A.A.; Kraskevich, D.A.; Belova, E.V.; Simanovsky, A.A.; Shcherbakov, D.V.; Zabroda, N.N.; et al. The Role of Different Types of microRNA in the Pathogenesis of Breast and Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Cao, Y.; Sun, M.; Feng, H. Expression, regulation, and function of exosome-derived miRNAs in cancer progression and therapy. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xia, Z.; Deng, Y.N.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, H.; Xu, N.; Liang, S. Emerging microRNA biomarkers for colorectal cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Open Biol. 2019, 9, 180212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharudin, R.; Rus Bakarurraini, N.Q.; Ismail, I.; Lee, L.H.; Ab Mutalib, N.S. MicroRNA Methylome Signature and Their Functional Roles in Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Chemoresistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, G.; Contreras, H.R.; Marcelain, K.; Burotto, M.; González-Montero, J. Understanding microRNA-Mediated Chemoresistance in Colorectal Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.; Tran, N. miRNA interplay: Mechanisms and consequences in cancer. Dis. Model. Mech. 2021, 14, dmm047662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, A.; Abd-Aziz, N.; Khalid, K.; Poh, C.L.; Naidu, R. miRNA: APromising Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, D.; Rivera, B.; Fabian, M.R.; Foulkes, W.D. miRNA biogenesis and inherited disorders: Clinico-molecular insights. Trends Genet. 2023, 39, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X. The roles of microRNAs in epigenetic regulation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 51, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastian-delaCruz, M.; Gonzalez-Moro, I.; Olazagoitia-Garmendia, A.; Castellanos-Rubio, A.; Santin, I. The Role of lncRNAs in Gene Expression Regulation through mRNA Stabilization. Noncoding RNA 2021, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, M.; Chen, J.; Tao, Z.; Miao, L.; Qi, X.; Wang, Y.; Ren, J. Regulatory network of miRNA on its target: Coordination between transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bofill-De Ros, X.; Vang Ørom, U.A. Recent progress in miRNA biogenesis and decay. RNA Biol. 2024, 21, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perconti, G.; Rubino, P.; Contino, F.; Bivona, S.; Bertolazzi, G.; Tumminello, M.; Feo, S.; Giallongo, A.; Coronnello, C. RIP-Chip analysis supports different roles for AGO2 and GW182 proteins in recruiting and processing microRNA targets. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20 (Suppl. S4), 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zhao, Z.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Shi, S.; Xie, H.; Peng, X.; Yin, W.; Tao, Y.; et al. miRNA-based biomarkers, therapies, and resistance in Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2628–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Mukherjee, K.; Chakrabarty, Y.; Chatterjee, S.; Ghoshal, B.; Bhattacharyya, S.N. GW182 Proteins Restrict Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Export of MicroRNAs in Mammalian Cancer Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2021, 41, e00483-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Z.; Zhou, J.; Cao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, D.; Ruan, W.; Zhao, Q.; et al. A novel class of microRNA-recognition elements that function only within open reading frames. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, F.; Xi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ding, C.; Luo, H.; Li, Y.; et al. MicroRNAs activate gene transcription epigenetically as an enhancer trigger. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarshad, A.A.; Juan, A.H.; Muler, A.I.C.; Anastasakis, D.G.; Wang, X.; Genzor, P.; Feng, X.; Tsai, P.F.; Sun, H.W.; Haase, A.D.; et al. Argonaute-miRNA Complexes Silence Target mRNAs in the Nucleus of Mammalian Stem Cells. Mol. Cell. 2018, 71, 1040–1050.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavast, C.J.; Erkeland, S.J. The Non-Canonical Aspects of MicroRNAs: Many Roads to Gene Regulation. Cells 2019, 8, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billi, M.; De Marinis, E.; Gentile, M.; Nervi, C.; Grignani, F. Nuclear miRNAs: Gene Regulation Activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganju, A.; Khan, S.; Hafeez, B.B.; Behrman, S.W.; Yallapu, M.M.; Chauhan, S.C.; Jaggi, M. miRNA nanotherapeutics for cancer. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagoni, M.; Cava, C.; Sideris, D.C.; Avgeris, M.; Zoumpourlis, V.; Michalopoulos, I.; Drakoulis, N. miRNA-Based Technologies in Cancer Therapy. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell 2018, 173, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broughton, J.P.; Lovci, M.T.; Huang, J.L.; Yeo, G.W.; Pasquinelli, A.E. Pairing beyond the Seed Supports MicroRNA Targeting Specificity. Mol. Cell. 2016, 64, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balacescu, O.; Sur, D.; Cainap, C.; Visan, S.; Cruceriu, D.; Manzat-Saplacan, R.; Muresan, M.-S.; Balacescu, L.; Lisencu, C.; Irimie, A. The Impact of miRNA in Colorectal Cancer Progression and Its Liver Metastases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Xu, M.; Tian, X.; Cai, S.; Zeng, S. Research advances in the detection of miRNA. J. Pharm. Anal. 2019, 9, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z. Recent advances in microRNA detection. Analyst 2018, 143, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otmani, K.; Rouas, R.; Lewalle, P. OncomiRs as noncoding RNAs having functions in cancer: Their role in immune suppression and clinical implications. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 913951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, H.; Sun, G.; Zhang, X.; Ye, H.; Wang, P. Role of miR-21 in the diagnosis of colorectal cancer: Meta-analysis and bioinformatics. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2023, 248, 154670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otmani, K.; Lewalle, P. Tumor Suppressor miRNA in Cancer Cells and the Tumor Microenvironment: Mechanism of Deregulation and Clinical Implications. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 708765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jet, T.; Gines, G.; Rondelez, Y.; Taly, V. Advances in multiplexed techniques for the detection and quantification of microRNAs. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 4141–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, B.; Sun, X.; Xie, R.; Chen, A. Recent advances in the rapid detection of microRNA with lateral flow assays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 211, 114345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafari, N.B.; Zamani, M.; Mosayyebi, B. Recent advances in lateral flow assays for MicroRNA detection. Clin. Chim. Acta 2025, 567, 120096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M.; Greten, F.R. The inflammatory pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Long, T.; Huang, W.J.M. Noncoding RNAs in inflammation and colorectal cancer. RNA Biol. 2020, 17, 1628–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Gutierrez, A.; Carbajal-Lopez, B.; Bui, T.M.; Mendoza-Rodriguez, M.; Campos-Parra, A.D.; Calderillo-Ruiz, G.; Cantú-De Leon, D.; Madrigal-Santillán, E.O.; Sumagin, R.; Pérez-Plasencia, C.; et al. A microRNA panel that regulates proinflammatory cytokines as diagnostic and prognosis biomarkers in colon cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2022, 30, 101252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josse, C.; Bours, V. MicroRNAs and Inflammation in Colorectal Cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 937, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchetti, M.; Ferraro, M.G.; Ricciardiello, F.; Ottaiano, A.; Luce, A.; Cossu, A.M.; Scrima, M.; Leung, W.Y.; Abate, M.; Stiuso, P.; et al. The Role of microRNAs in Development of Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Zhou, D. MicroRNAs in colorectal carcinoma--from pathogenesis to therapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boros, É.; Hegedűs, Z.; Kellermayer, Z.; Balogh, P.; Nagy, I. Global alteration of colonic microRNAome landscape associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 991346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yi, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.L.; Miao, G.; Qi, R.M.; Zhao, Y.Y. MicroRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in colorectal cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2016, 8, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, T.; Liu, D.; Guan, S.; Dong, M. Diagnostic role of circulating MiR-21 in colorectal cancer: A update meta-analysis. Ann. Med. 2021, 53, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hussen, B.M.; Sulaiman, S.H.A.; Abdullah, S.R.; Hidayat, H.J.; Khudhur, Z.O.; Eslami, S.; Samsami, M.; Taheri, M. MiRNA-155: A double-edged sword in colorectal cancer progression and drug resistance mechanisms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 299, 140134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.L.; Wang, H.F.; Sun, Z.Q.; Tang, Y.; Han, X.N.; Yu, X.B.; Liu, K. Up-regulated miR-155-5p promotes cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis in colorectal carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 6988–6994. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pidíkova, P.; Reis, R.; Herichova, I. miRNA Clusters with Down-Regulated Expression in Human Colorectal Cancer and Their Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Kacimi, S.E.O.; Nguyen, T.L.; Suman, K.H.; Lemus-Martin, R.; Saleem, H.; Do, D.N. MiR-21 in the Cancers of the Digestive System and Its Potential Role as a Diagnostic, Predictive, and Therapeutic Biomarker. Biology 2021, 10, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrgou, A.; Ebadollahi, S.; Seidi, K.; Ayoubi-Joshaghani, M.H.; Ahmadieh Yazdi, A.; Zare, P.; Jaymand, M.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, R. Roles of miRNAs in Colorectal Cancer: Therapeutic Implications and Clinical Opportunities. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 11, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzad, S.; Eterafi, M.; Karimi, Z.; Barazesh, M. MicroRNAs involved in colorectal cancer, a rapid mini-systematic review. BMC Cancer 2025, 25, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.P.; Suman, K.H.; Nguyen, T.B.; Nguyen, H.T.; Do, D.N. The Role of miR-29s in Human Cancers-An Update. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, F.; Xuan, G.; Chen, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhao, M.; Wang, C.; Chen, E. MicroRNAs Are Key Molecules Involved in the Gene Regulation Network of Colorectal Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 828128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Oryani, M.A.; Al-Mosawi, A.K.M.; Javid, H.; Tajaldini, M.; Karimi-Shahri, M. A Bioligical Perspective on the role of miR-206 in Colorectal cancer. Gene 2025, 961, 149552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, Z.; Zaki-Dizaji, M. Epigenetically Regulating Non-coding RNAs in Colorectal Cancer: Promises and Potentials. Middle East J. Dig. Dis. 2025, 17, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fellizar, A.; Refuerzo, V.; Ramos, J.D.; Albano, P.M. Expression of specific microRNAs in tissue and plasma in colorectal cancer. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2023, 57, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Laowichuwakonnukul, K.; Soontornworajit, B.; Arunpanichlert, J.; Rotkrua, P. Simultaneous targeted delivery of doxorubicin and KRAS suppression by a hybrid molecule containingmiR-143 and AS1411 aptamer. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Ye, A.; Ye, W.; Liao, X.; Qin, G.; Xu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Luo, H.; Yi, M.; Xian, L.; et al. Cancer-secreted exosomal miR-21-5p induces angiogenesis and vascular permeability by targeting KRIT1. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Toiyama, Y.; Okugawa, Y.; Fleshman, J.; Richard Boland, C.; Goel, A. MicroRNAs as potential liquid biopsy biomarkers in colorectal cancer: A systematic review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2018, 1870, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xu, J.; Pan, L.; Wu, D.; Yao, L.; Jiang, W.; Min, J.; Xu, S.; Deng, Z. Comparison of the diagnostic value of various microRNAs in blood for colorectal cancer: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sado, A.I.; Batool, W.; Ahmed, A.; Zafar, S.; Patel, S.K.; Mohan, A.; Zia, U.; Aminpoor, H.; Kumar, V.; Tejwaney, U. Role of microRNA in colorectal carcinoma (CRC): A narrative review. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 86, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Shi, P.D.; Wan, B.S. MiR-410-3p activates the NF-κB pathway by targeting ZCCHC10 to promote migration, invasion and EMT of colorectal cancer. Cytokine 2021, 140, 155433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farasati Far, B.; Vakili, K.; Fathi, M.; Yaghoobpoor, S.; Bhia, M.; Naimi-Jamal, M.R. The role of microRNA-21 (miR-21) in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and prognosis of gastrointestinal cancers: A review. Life Sci. 2023, 316, 121340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattan Negi, R.; Rana, S.V.; Gupta, V.; Gupta, R.; Dhawan, D.K. Evaluation of the Plasma Expression Levels of miR-21 and miR-145 as Potential Non-Invasive Biomarkers for Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2024, 25, 2797–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanusova, V.; Matouskova, P.; Manethova, M.; Soukup, J.; John, S.; Zofka, M.; Vošmikova, H.; Krbal, L.; Rudolf, E. Comparative Analysis of miRNA and EMT Markers in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Investig. 2023, 41, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran-Sanchon, S.; Moreno, L.; Augé, J.M.; Serra-Burriel, M.; Cuatrecasas, M.; Moreira, L.; Martín, A.; Serradesanferm, A.; Pozo, À.; Costa, R.; et al. Identification and Validation of MicroRNA Profiles in Fecal Samples for Detection of Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 947–957.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, L.; Sun, X. MiR-130b-3p promotes colorectal cancer progression by targeting CHD9. Cell Cycle 2022, 21, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, P.; Huang, L.; Qiao, J.; Li, J. Bioinformatic analysis reveals an exosomal miRNA-mRNA network in colorectal cancer. BMC Med. Genom. 2021, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Jing, M.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Hua, H.; Pan, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; et al. ERp29 forms a feedback regulation loop with microRNA-135a-5p and promotes progression of colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, S.; Aazzane, O.; Guendaoui, S.; Tawfiq, N.; Sahraoui, S.; Guessous, F.; Karkouri, M. A miRNA Signature for Non-Invasive Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis in Morocco: miR-21, miR-29a and miR-92a. Noncoding RNA 2025, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhu, A.; Bhardwaj, M.; Schrotz-King, P.; Brenner, H. Fecal microRNAs, Fecal microRNA Panels, or Combinations of Fecal microRNAs with Fecal Hemoglobin for Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer and Its Precursors: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2021, 14, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Tang, J.; Shi, H.; Li, H.; Zhen, T.; Duan, J.; Kang, L.; Zhang, F.; Dong, Y.; Han, A. miR-27a-3p targeting RXRα promotes colorectal cancer progression by activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 82991–83008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, F.; Cheng, L.; Wu, X.; Ye, M.; Zhang, H. miR-141 Promotes Colon Cancer Cell Proliferation by Targeted PHLPP2 Expression Inhibitionn. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 11341–11350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, R.; Lv, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, Y. Functional mechanism and clinical implications of MicroRNA-423 in human cancers. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 9036–9051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasudome, R.; Seki, N.; Asai, S.; Goto, Y.; Kita, Y.; Hozaka, Y.; Wada, M.; Tanabe, K.; Idichi, T.; Mori, S.; et al. Molecular Pathogenesis of Colorectal Cancer: Impact of Oncogenic Targets Regulated by Tumor Suppressive miR-139-3p. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, S.; Tang, L. MicroRNA 320, an Anti-Oncogene Target miRNA for Cancer Therapy. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Tang, A.; Huang, S.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Shen, S.; Ma, J.; Wang, X. MiR-126 suppresses colon cancer cell proliferation and invasion via inhibiting RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2013, 380, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, F.; Cao, T.; Xie, H.; Li, T.; Sun, L.; Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Kim, T.; et al. KRAS Mutation-Responsive miR-139-5p inhibits Colorectal Cancer Progression and is repressed by Wnt Signaling. Theranostics 2020, 10, 7335–7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.X.; Mai, S.J.; Huang, X.X.; Wang, F.W.; Liao, Y.J.; Lin, M.C.; Kung, H.F.; Zeng, Y.X.; Xie, D. MiR-29c mediates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human colorectal carcinoma metastasis via PTP4A and GNA13 regulation of β-catenin signaling. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 2196–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, D.; Kuwada, S. miRNA as a Biomarker for the Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer. Genes 2024, 15, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Shi, W.J.; Xie, Y.B.; Zhang, Z.G. Diagnostic value of four serum exosome microRNAs panel for the detection of colorectal cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 13, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaukat, A.; Kaltenbach, T.; Dominitz, J.A.; Robertson, D.J.; Anderson, J.C.; Cruise, M.; Burke, C.A.; Gupta, S.; Lieberman, D.; Syngal, S.; et al. Endoscopic Recognition and Management Strategies for Malignant Colorectal Polyps: Recommendations of the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1916–1934.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.L.; Chun, H.; Lee, H.; Seo, W.; Lee, J.Y.; Yoon, J.H. Identification and Validation of Serum Biomarkers to Improve Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e70460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świtalski, J.; Tatara, T.; Wnuk, K.; Miazga, W.; Karauda, D.; Matera, A.; Jabłońska, M.; Jopek, S.; Religioni, U.; Gujski, M. Clinical Effectiveness of FaecalImmunochemical Test in the Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer—An Umbrella Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, F.H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Kong, D.; Ali, S. Implication of microRNAs in drug resistance for designing novel cancer therapy. Drug Resist. Updates 2010, 13, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugut, A.I.; Lin, A.; Raab, G.T.; Hillyer, G.C.; Keller, D.; O’Neil, D.S.; Accordino, M.K.; Kiran, R.P.; Wright, J.; Hershman, D.L. FOLFOX and FOLFIRI Use in Stage IV Colon Cancer: Analysis of SEER-Medicare Data. Clin. Colorectal. Cancer 2019, 18, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliakou, E.; Lampropoulou, D.I.; Dovrolis, N.; Chrysikos, D.; Filippou, D.; Papadimitriou, C.; Vezakis, A.; Aravantinos, G.; Gazouli, M. Circulating miRNA Expression Profiles and Machine Learning Models in Association with Response to Irinotecan-Based Treatment in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano-Fonseca, M.; Gómez-España, M.A.; Élez, E.; Grávalos, C.; García-Alfonso, P.; Rodríguez, R.; Losa, F.; Alés Díaz, I.; Graña, B.; Valladares-Ayerbes, M.; et al. Spanish Cooperative Group for the Treatment of Digestive Tumors (TTD). A signature of circulating microRNAs predicts the response to treatment with FOLFIRI plus aflibercept in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 159, 114272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, K.; Yuan, Y.; Bai, H.; Meng, L. Exosomal miRNA as biomarker in cancer diagnosis and prognosis: A review. Medicine 2024, 103, e40082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Sun, W.; Liu, R.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Ba, Y. Plasma Exosomal miRNA Expression Profile as Oxaliplatin-Based Chemoresistant Biomarkers in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bian, Z.; Yao, S.; Fei, B.; Zhou, L.; Yin, Y.; Huang, Z. A panel of serum exosomal microRNAs as predictive markers for chemoresistance in advanced colorectal cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2019, 84, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Pickard, K.; Jenei, V.; Bullock, M.D.; Bruce, A.; Mitter, R.; Kelly, G.; Paraskeva, C.; Strefford, J.; Primrose, J.; et al. miR-153 Supports Colorectal Cancer Progression via Pleiotropic Effects That Enhance Invasion and Chemotherapeutic Resistance. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 6435–6447, Erratum in Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Hu, J.; Jin, T.; Wang, J.; Yang, B.B. MicroRNA-17-5p promotes chemotherapeutic drug resistance and tumour metastasis of colorectal cancer by repressing PTEN expression. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2974–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Collins, G.; Wang, H.; Toh, J.W.T. Pathological Features and Prognostication in Colorectal Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 5356–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Z.; Rong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Peng, J.; Zou, B.; Zhou, N.; Pan, Z. Development of a Novel Six-miRNA-Based Model to Predict Overall Survival Among Colon Adenocarcinoma Patients. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.-T.; Wang, J.-L.; Du, W.; Hong, J.; Zhao, S.-L.; Wang, Y.-C.; Xiong, H.; Chen, H.-M.; Fang, J.-Y. MicroRNA 345, a methylation-sensitive microRNA is involved in cell proliferation and invasion in human colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezayi Soufiani, A.; Dolatkhah, R.; Raeisi, M.; Chavoshi, H.; Mohammadi, P.; Mehdinavaz Aghdam, A. Hypermethylation of MIR129-2 Regulates SOX4 Transcription and Associates with Metastasis in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2022, 53, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ress, A.L.; Stiegelbauer, V.; Winter, E.; Schwarzenbacher, D.; Kiesslich, T.; Lax, S.; Jahn, S.; Deutsch, A.; Bauernhofer, T.; Ling, H.; et al. MiR-96-5p influences cellular growth and is associated with poor survival in colorectal cancer patients. Mol. Carcinog. 2015, 54, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toiyama, Y.; Hur, K.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kusunoki, M.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Serum miR-200c Is a Novel Prognostic and Metastasis-Predictive Biomarker in Patients With Colorectal Cancer. Ann. Surg. 2014, 259, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcakaya, P.; Ekelund, S.; Kolosenko, I.; Caramuta, S.; Özata, D.M.; Xie, H.; Lindforss, U.; Olivecrona, H.; Lui, W.O. miR-185 and miR-133b deregulation is associated with overall survival and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 39, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schetter, A.J.; Leung, S.Y.; Sohn, J.J.; Zanetti, K.A.; Bowman, E.D.; Yanaihara, N.; Yuen, S.T.; Chan, T.L.; Kwong, D.L.; Au, G.K. MicroRNA Expression Profiles Associated With Prognosis and Therapeutic Outcome in Colon Adenocarcinoma. JAMA 2008, 299, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, B.S.; Jørgensen, S.; Fog, J.U.; Søkilde, R.; Christensen, I.J.; Hansen, U.; Brünner, N.; Baker, A.; Møller, S.; Nielsen, H.J. High levels of microRNA-21 in the stroma of colorectal cancers predict short disease-free survival in stage II colon cancer patients. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2011, 28, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-C.; Hsieh, Y.-Y.; Lo, H.-L.; Li, A.; Chou, C.-J.; Yang, P.-M. In Vitro and In Silico Mechanistic Insights into miR-21-5p-Mediated Topoisomerase Drug Resistance in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Jin, L.; Xu, Q.; Shen, B.; Jiao, X.; Huang, X. Expression of miR-21 and miR-138 in colon cancer and its effect on cell proliferation and prognosis. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 2271–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mjelle, R.; Kristensen, A.K.; Solheim, T.S.; Westvik, G.S.; Elvebakken, H.; Hofsli, E. Serum small RNAs in metastatic colorectal cancer predict response to chemotherapy and characterize high-risk patients. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suto, T.; Yokobori, T.; Yajima, R.; Morita, H.; Fujii, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Altan, B.; Tsutsumi, S.; Asao, T.; Kuwano, H. MicroRNA-7 expression in colorectal cancer is associated with poor prognosis and regulates cetuximab sensitivity via EGFR regulation. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapti, S.M.; Kontos, C.K.; Papadopoulos, I.N.; Scorilas, A. High miR-96 levels in colorectal adenocarcinoma predict poor prognosis, particularly in patients without distant metastasis at the time of initial diagnosis. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 11815–11824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, C.-G.; Liu, F.-J. Expression profiling of miR-96, miR-584 and miR-422a in colon cancer and their potential involvement in colon cancer pathogenesis. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. Dec. 2016, 15, 2535–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokutani, Y.; Uemura, M.; Munakata, K.; Okuzaki, D.; Haraguchi, N.; Takahashi, H.; Nishimura, J.; Hata, T.; Murata, K.; Takemasa, I.; et al. Down-Regulation of microRNA-132 is Associated with Poor Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23 (Suppl. S5), 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulivi, P.; Canale, M.; Passardi, A.; Marisi, G.; Valgiusti, M.; Frassineti, G.L.; Calistri, D.; Amadori, D.; Scarpi, E. Circulating Plasma Levels of miR-20b, miR-29b and miR-155 as Predictors of Bevacizumab Efficacy in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, X.; Li, H.; Yue, X.; Deng, L.; Cui, Y.; Lu, Y. MicroRNA-223 functions as an oncogene in human colorectal cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Sun, W.; Qin, S.; Qin, L.; Wang, X. miR-223 promotes colon cancer by directly targeting p120 catenin. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 63764–63779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Pang, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Xuan, B.; Wang, Y. MicroRNA-137 chemosensitizes colon cancer cells to the chemotherapeutic drug oxaliplatin (OXA) by targeting YBX1. Cancer Biomark. 2017, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, T.; Kandimalla, R.; Gao, F.; Nozawa, H.; Hata, K.; Nagata, H.; Okada, S.; Izumi, D.; Baba, H.; Fleshman, J.; et al. A MicroRNA Signature Associated With Metastasis of T1 Colorectal Cancers to Lymph Nodes. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 844–848.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.M.; Hutvagner, G. A comparative analysis of single cell small RNA sequencing data reveals heterogeneous isomiR expression and regulation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cai, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, N. A lateral flow assay for miRNA-21 based on CRISPR/Cas13a and MnO2 nanosheets-mediated recognition and signal amplification. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 3401–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Peng, C.; Du, R.; Hong, X.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Machine Learning-Aided Identification of Fecal Extracellular Vesicle microRNA Signatures for Noninvasive Detection of Colorectal Cancer. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 10013–10025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyszewski, J.; Malawski, M.; Lichołai, S. GraphTar: Applying word2vec and graph neural networks to miRNA target prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayat, S.; Cascione, L.; Cunningham, D.; Schirripa, M.; Lampis, A.; Hahne, J.C.; Tunariu, N.; Hong, S.P.; Marchetti, S.; Khan, K.; et al. Circulating microRNA Analysis in a Prospective Co-clinical Trial Identifies MIR652-3p as a Response Biomarker and Driver of Regorafenib Resistance Mechanisms in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 2140–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chioccioli, M.; Roy, S.; Newell, R.; Pestano, L.; Dickinson, B.; Rigby, K.; Herazo-Maya, J.; Jenkins, G.; Ian, S.; Saini, G.; et al. A lung targeted miR-29 mimic as a therapy for pulmonary fibrosis. EBioMedicine 2022, 85, 104304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, A.; Ly, B.; Cailleau, C.; Gao, F.; de Ponfilly-Sotier, M.P.; Pascaud, J.; Rivière, E.; Yang, L.; Nwosu, L.; Elmesmari, A.; et al. Liposomal AntagomiR-155-5p Restores Anti-Inflammatory Macrophages and Improves Arthritis in Preclinical Models of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; MacIntyre, D.A.; Sykes, L.; Arianoglou, M.; Bennett, P.R.; Terzidou, V. Whole Blood Holding Time Prior to Plasma Processing Alters microRNA Expression Profile. Front. Genet. 2022, 12, 818334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permuth, J.B.; Mesa, T.; Williams, S.L.; Cardentey, Y.; Zhang, D.; Pawlak, E.A.; Li, J.; Cameron, M.E.; Ali, K.N.; Jeong, D.; et al. A pilot study to troubleshoot quality control metrics when assessing circulating miRNA expression data reproducibility across study sites. Cancer Biomark. 2022, 33, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.S.; Kang, Y.K.; Borad, M.; Sachdev, J.; Ejadi, S.; Lim, H.Y.; Brenner, A.J.; Park, K.; Lee, J.L.; Kim, T.Y.; et al. Phase 1 study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekadir, K.; Frangi, A.F.; Porras, A.R.; Glocker, B.; Cintas, C.; Langlotz, C.P.; Weicken, E.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Prior, F.; Collins, G.S.; et al. FUTURE-AI Consortium. FUTURE-AI: International consensus guideline for trustworthy and deployable artificial intelligence in healthcare. BMJ 2025, 388, e081554, Erratum in BMJ 2025, 388, r340. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.r340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| miRNA | Molecular Mechanism and Clinical Relevance | Diagnostic Utility | Expression Pattern in CRC |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-21 | Promotes tumor growth and invasion by targeting PTEN, KRIT1, and other tumor suppressors; involved in angiogenesis and metastasis [55,64,65] | High sensitivity and specificity as a circulating biomarker; superior to CEA in early CRC detection [51,55,65,66] | Overexpressed in CRC tissues and plasma; upregulated in tumor and circulating exosomes [51,55,62,64] |
| miR-92a | Regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis; implicated in Wnt/β-catenin signaling; contributes to tumor progression [54,59] | Effective liquid biopsy marker with high diagnostic accuracy; improves detection when combined with other miRNAs [55,65,66] | Upregulated in CRC tissues and patient plasma; part of miR-17-92 cluster overexpressed in CRC [54,55,64] |
| miR-29a | Targets genes involved in extracellular matrix remodeling and DNA methylation; influences tumor microenvironment and metastasis [58,59] | Diagnostic potential as part of miRNA panels; useful for distinguishing CRC from benign lesions [58,62,66] | Dysregulated, often downregulated in CRC, but variable depending on subtype and stage [58,59,62] |
| miR-17-3p | Promotes proliferation and invasion by targeting tumor-suppressor genes and modulating key oncogenic pathways [54,59] | Included in diagnostic panels enhancing sensitivity and specificity in CRC detection [55,66] | Overexpressed in CRC; part of miR-17-92 cluster associated with oncogenic functions [54,59] |
| miR-223 | Modulates immune response and promotes tumor cell proliferation; targets genes involved in cell cycle and apoptosis regulation [49,62] | Potential diagnostic biomarker, particularly in combination with other miRNAs [62,66] | Overexpressed in CRC tissues and plasma; involved in inflammation and tumor progression [49,62] |
| miR-206 | Inhibits tumor proliferation, invasion and migration by targeting Notch3 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling; involved in EMT suppression and apoptosis induction [60] | Potential diagnostic and therapeutic biomarker, especially in combination with methylation status [60] | Frequently downregulated in CRC; low levels correlate with poor differentiation and metastasis [60] |
| miR-101 | Epigenetically silenced in CRC; targets EZH2 and COX-2; modulates histone methylation and inflammatory pathways [56] | Promising biomarker for early CRC detection and therapeutic response prediction [56] | Downregulated in CRC due to CpG island hypermethylation [56] |
| miR-34a | Induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by repressing SIRT1; acts downstream of p53; inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling [56] | Recognized diagnostic and prognostic marker; part of p53-related tumor suppressor network [56] | Downregulated in CRC; expression restored by p53 activation [56] |
| miR-375 | Acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting proliferation, invasion, and metastasis; targets oncogenic pathways (YAP1, IGF1R) and modulates EMT; low expression linked to advanced TNM stage and poor prognosis [57] | Independent prognostic biomarker; low serum levels correlate with shorter overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS); potential for non-invasive detection and monitoring [57] | Independent prognostic biomarker; low serum levels correlate with shorter overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS); potential for non-invasive detection and monitoring [57] |
| Type of MiRNA | AUC | Biological Sample | Molecular Function/Target | Biological Role |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-21 | 0.919 [12] | plasma, serum, saliva [12] | PTEN, SPRY2, RECK, PDCD4 [55] | oncogene |
| miR-135a-5p | 0.832 [12] | serum [12] | ERp29 [75] | |
| miR-29a | 0.898 [76] | plasma [76] | KLF4 [50] | |
| miR-27a-3p | 0.690 [77] | stool [77] | Wnt/β-catenin pathway [78] | |
| miR-141 | 1.000 [74] | exosomes isolated from blood [74] | PHLPP2 [79] | |
| miR-423 | 0.801 [74] | exosomes isolated from blood [74] | possible involvement in p53 pathway, LAMC1 [80] | possibly oncogene |
| miR-139-3p | 0.994 [12] | serum [12] | KRT80 [81] | suppressor |
| miR-320a | 0.886 [12] | serum [12] | Wnt/β-catenin pathway, FOXM1, TWIST1 [82] | |
| miR-126 | 1.000 [74] | exosomes isolated from blood [74] | RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway [83] | |
| miR-139 | 0.993 [74] | exosomes isolated from blood [74] | Wnt/β-catenin pathway [84] | |
| miR-29c | 0.987 [74] | exosomes isolated from blood [74] | GNA13, PTP4A [85] |
| MiRNA | Expression in Tumors | Role in CRC Prognosis | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-7 | low | poor survival | [112] |
| miR-21 | high | poor overall survival, poor therapeutic outcome | [107] |
| miR-21 | high | liver metastasis | [102] |
| miR-96 | high | advanced stages of CRC, poor prognosis in patients without distant metastasis at the time of initial diagnosis | [113] |
| miR-96 | low | increased tumor size | [114] |
| miR-96-5p | low | distant metastasis, independent prognostic factor with respect to cancer-specific survival | [104] |
| miR-126 | low | liver metastasis | [102] |
| miR-129-2 | low | lymph node and liver metastasis | [103] |
| miR-132 | low | progression, poor survival | [115] |
| miR-133b | low | poor survival and metastasis | [106] |
| miR-138 | low | shorter survival time | [110] |
| miR-141 | high | liver metastasis | [102] |
| miR-155-5p | high | shortened overall survival and progression-free survival | [116] |
| miR-185 | high | poor survival and metastasis | [106] |
| miR-200c | high | lymph node metastasis, tumor reoccurrence | [105] |
| miR-223 | high | high grade types of CRC | [117] |
| miR-345 | low | lymph node metastasis, worse histological type | [102] |
| miR-422a | low | increased tumor size | [114] |
| miR-584 | low | increased tumor size | [114] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pająk, W.; Kleinrok, J.; Pec, J.; Michno, K.; Wojtas, J.; Badach, M.; Teresińska, B.; Baj, J. Micro RNA in Colorectal Cancer—Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers—An Updated Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178615
Pająk W, Kleinrok J, Pec J, Michno K, Wojtas J, Badach M, Teresińska B, Baj J. Micro RNA in Colorectal Cancer—Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers—An Updated Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178615
Chicago/Turabian StylePająk, Weronika, Jakub Kleinrok, Joanna Pec, Karolina Michno, Jan Wojtas, Miłosz Badach, Barbara Teresińska, and Jacek Baj. 2025. "Micro RNA in Colorectal Cancer—Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers—An Updated Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178615
APA StylePająk, W., Kleinrok, J., Pec, J., Michno, K., Wojtas, J., Badach, M., Teresińska, B., & Baj, J. (2025). Micro RNA in Colorectal Cancer—Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers—An Updated Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178615







