Biomarkers of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Subtypes: A Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Distress Phenomena in OCD
2.2. Genetic Factors Associated with OCD
2.2.1. Serotonergic Transmission
2.2.2. Glutamatergic Transmission
2.2.3. The Dopaminergic System
2.2.4. Neurotrophic Factors
2.2.5. Conclusion of the Chapter
| No. | System/Neuromodulator | Year | Genes/Polymorphisms | Authors | Full Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [43] | Glutamatergic system | 2012 | Polymorphisms in GRIN2B | Alonso et al. | Association between the NMDA glutamate receptor GRIN2B gene and obsessive–compulsive disorder |
| [49] | 2018 | rs301430, rs2228622, rs3780413 (SLC1A1) | Abdolhosseinzadeh et al. | Genetic and pharmacogenetic study of glutamate transporter (SLC1A1) in Iranian patients with obsessive–compulsive disorder | |
| [50] | 2009 | rs3087879, rs301430, rs7858819 (SLC1A1) | Wendland et al. | A haplotype containing quantitative trait loci for SLC1A1 gene expression and its association with obsessive–compulsive disorder | |
| [36] | Serotoninergic system | 2017 | 5-HTTLPR, rs25531, rs25532, rs16965628 (SLC6A4) | Grünblatt et al. | Combining genetic and epigenetic parameters of the serotonin transporter gene in obsessive–compulsive disorder |
| [48] | 2006 | SLITRK1 and SLC6A4 (G56A) | Wendland et al. | Functional SLITRK1 var321, varCDfs and SLC6A4 G56A variants and susceptibility to obsessive–compulsive disorder | |
| [39] | 2012 | 5-HTTLPR, HTR2A, COMT, MAOA, DAT1, DRD3 | Taylor et al. | Molecular genetics of obsessive–compulsive disorder: a comprehensive meta-analysis of genetic association studies | |
| [38] | 2008 | STin2VNTR, 5-HTTLPR (SLC6A4), A1438G, T102C (HTR2A) | Saiz et al. | Association study between obsessive–compulsive disorder and serotonergic candidate genes | |
| [44] | Dopaminergic system | 2005 | COMT Val158Met (L/L genotype) | Lochner et al. | Hoarding in obsessive–compulsive disorder: clinical and genetic correlates |
| [45] | 2015 | COMT Val158Met; COMT−287A > G | Melo-Felippe et al. | Catechol-O-Methyltransferase gene polymorphisms in specific obsessive–compulsive disorder patients’ subgroups | |
| [41] | 2007 | OLIG2 (rs9653711, rs762178, rs1059004; rs6517137, rs13046814) | Stewart et al. | A genetic family-based association study of OLIG2 in obsessive–compulsive disorder | |
| [47] | Neurotrophic systems | 2009 | BDNF Val66Met | Katerberg et al. | The role of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) val66met variant in the phenotypic expression of obsessive–compulsive disorder |
2.3. Review of Literature on Individual Subtypes of OCD
2.3.1. The Contamination/Cleaning Subtype
Subtype Description
Neuroimaging Studies
Data from Molecular Genetic Studies
Psychological Research Data
Response to Therapy
2.3.2. The Obsession/Checking Subtype
Subtype Description
Neuroimaging Studies
Data from Molecular Genetic Studies
Psychological Research Data
Response to Therapy
2.3.3. The Symmetry/Ordering Subtype
Subtype Description
Neuroimaging Research
Data from Molecular Genetic Studies
Psychological Research Data
Response to Therapy
2.3.4. The Hoarding Subtype
Subtype Description
Neuroimaging Research
Data from Molecular Genetic Studies
Psychological Research Data
Response to Therapy
2.3.5. The Taboo Thoughts Subtype
Subtype Description
Neuroimaging Research
Data from Molecular Genetic Studies
Psychological Research Data
Response to Therapy
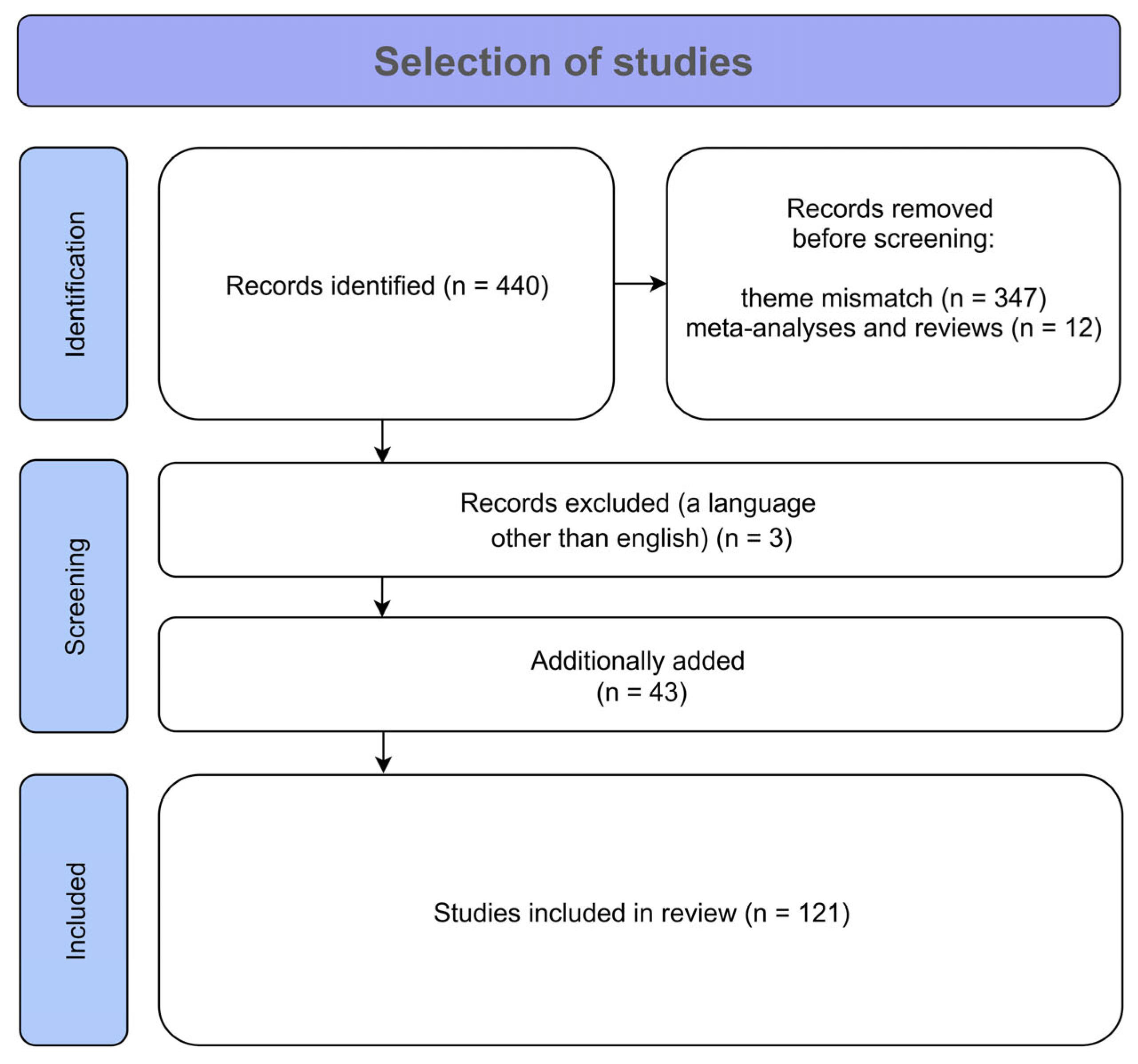
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OCD | Obsessive–compulsive disorder |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| fMRI | Functional magnetic resonance imaging |
| Y-BOCS | Yale-Brown Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder Scale |
| NJREs | Not just right experiences |
| SSRIs | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors |
| CSTC | Cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical |
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Venter, J.C. The Human Genome at 10: Successes and Challenges. Science 2011, 331, 546–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, W.; Korngiebel, D.M. Closing the Gap between Knowledge and Clinical Application: Challenges for Genomic Translation. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1004978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesman, I.I.; Shields, J. A Polygenic Theory of Schizophrenia. Int. J. Ment. Health 1972, 1, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesman, I.I.; Gould, T.D. The Endophenotype Concept in Psychiatry: Etymology and Strategic Intentions. Am. J. Psychiatry 2003, 160, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, T.D.; Keller, M.C. Endophenotypes in the Genetic Analyses of Mental Disorders. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2006, 2, 267–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.A.; Rockstroh, B. Endophenotypes in Psychopathology Research: Where Do We Stand? Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2013, 9, 177–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anokhin, A.P. Genetic Psychophysiology: Advances, Problems, and Future Directions. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2014, 93, 173–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, D.J.A.; Posthuma, D.; Boomsma, D.I.; De Geus, E.J.C. Heritability of Background EEG across the Power Spectrum. Psychophysiology 2005, 42, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.M.; Jahanshad, N.; Shukla, D.; Glahn, D.C.; Blangero, J.; Reynolds, R.C.; Cox, R.W.; Fieremans, E.; Veraart, J.; Novikov, D.S.; et al. Heritability Estimates on Resting State fMRI Data Using ENIGMA Analysis Pipeline. In Proceedings of the Biocomputing 2018, Kohala Coast, HI, USA, 3–7 January 2018; World Scientific: Singapore, 2018; pp. 307–318. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Lindenberg, A. The Future of fMRI and Genetics Research. NeuroImage 2012, 62, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravchik, A.; Goldman, D. Neurochemical Individuality: Genetic Diversity Among Human Dopamine and Serotonin Receptors and Transporters. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2000, 57, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabana-Domínguez, J.; Torrico, B.; Reif, A.; Fernàndez-Castillo, N.; Cormand, B. Comprehensive Exploration of the Genetic Contribution of the Dopaminergic and Serotonergic Pathways to Psychiatric Disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachman, S.; Hodgson, R.J. Obsessions and Compulsions; Century psychology series; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1980; ISBN 978-0-13-629139-8. [Google Scholar]
- Sanavio, E. Obsessions and Compulsions: The Padua Inventory. Behav. Res. Ther. 1988, 26, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, W.K. The Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale: I. Development, Use, and Reliability. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1989, 46, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baer, L. Factor Analysis of Symptom Subtypes of Obsessive Compulsive Disorder and Their Relation to Personality and Tic Disorders. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1994, 55, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Leckman, J.F.; Grice, D.E.; Boardman, J.; Zhang, H. Symptoms of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 1997, 154, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calamari, J.E.; Wiegartz, P.S.; Janeck, A.S. Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder Subgroups: A Symptom-Based Clustering Approach. Behav. Res. Ther. 1999, 37, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mataix-Cols, D.; Rauch, S.L.; Manzo, P.A.; Jenike, M.A.; Baer, L. Use of Factor-Analyzed Symptom Dimensions to Predict Outcome with Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Placebo in the Treatment of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 1999, 156, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowitz, J.S.; Franklin, M.E.; Schwartz, S.A.; Furr, J.M. Symptom Presentation and Outcome of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2003, 71, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mataix-Cols, D.; Do Rosario-Campos, M.C.; Leckman, J.F. A Multidimensional Model of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, E.; Guze, S.B. Establishment of Diagnostic Validity in Psychiatric Illness: Its Application to Schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 1970, 126, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowsell, M.; Francis, S.E. OCD Subtypes: Which, If Any, Are Valid? Clin. Psychol. Sci. Pract. 2015, 22, 414–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Li, B.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiong, B.; Li, D.; Wen, R.; et al. The Suitability of Different Subtypes and Dimensions of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder for Treatment with Anterior Capsulotomy: A Long-Term Follow-Up Study. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2019, 97, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, J.M. SSRI Antidepressant Medications: Adverse Effects and Tolerability. Prim. Care Companion CNS Disord. 2001, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starcevic, V.; Berle, D.; Brakoulias, V.; Sammut, P.; Moses, K.; Milicevic, D.; Hannan, A. Functions of Compulsions in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2011, 45, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, M.A.; Summerfeldt, L.J.; Joffe, R.T.; Swinson, R.P. The Tridimensional Personality Questionnaire in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Psychiatry Res. 1996, 65, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summerfeldt, L.J.; Huta, V.; Swinson, R.P. Personality and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. In Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Theory, Research, and Treatment; Guilford Publications, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 79–119. [Google Scholar]
- Summerfeldt, L.; Antony, M.; Swinson, R. Incompleteness: A Link between Perfectionistic Traits and OCD. Perfectionism and psychopathology: Linking personality and dysfunctional behavior. In Proceedings of the Symposium at the 34th Annual Meeting of the Association for the Advancement of Behaviour Therapy, New Orleans, LA, USA, 16–19 November 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pietrefesa, A.S.; Coles, M.E. Moving Beyond an Exclusive Focus on Harm Avoidance in Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: Considering the Role of Incompleteness. Behav. Ther. 2008, 39, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfeldt, L.J.; Kloosterman, P.H.; Antony, M.M.; Swinson, R.P. Examining an Obsessive-Compulsive Core Dimensions Model: Structural Validity of Harm Avoidance and Incompleteness. J. Obs. Compuls. Relat. Disord. 2014, 3, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, M.E.; Frost, R.O.; Heimberg, R.G.; Rhéaume, J. “Not Just Right Experiences”: Perfectionism, Obsessive–Compulsive Features and General Psychopathology. Behav. Res. Ther. 2003, 41, 681–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, M.E.; Heimberg, R.G.; Frost, R.O.; Steketee, G. Not Just Right Experiences and Obsessive–Compulsive Features: Experimental and Self-Monitoring Perspectives. Behav. Res. Ther. 2005, 43, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesch, K.-P.; Bengel, D.; Heils, A.; Sabol, S.Z.; Greenberg, B.D.; Petri, S.; Benjamin, J.; Müller, C.R.; Hamer, D.H.; Murphy, D.L. Association of Anxiety-Related Traits with a Polymorphism in the Serotonin Transporter Gene Regulatory Region. Science 1996, 274, 1527–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünblatt, E.; Marinova, Z.; Roth, A.; Gardini, E.; Ball, J.; Geissler, J.; Wojdacz, T.K.; Romanos, M.; Walitza, S. Combining Genetic and Epigenetic Parameters of the Serotonin Transporter Gene in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 96, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrez, S.; Neamatallah, M.A.; Gomaa, Z.; El-Gilany, A.H.; Shahda, M.; Elsaied, H.F. Association between Serotonin Transporter Gene Polymorphism and Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder in the Egyptian Population. Middle East Curr. Psychiatry 2024, 31, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz, P.A.; Garcia-Portilla, M.P.; Arango, C.; Morales, B.; Bascaran, M.T.; Martinez-Barrondo, S.; Florez, G.; Sotomayor, E.; Paredes, B.; Alvarez, C.; et al. Association Study between Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder and Serotonergic Candidate Genes. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 32, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S. Molecular Genetics of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Genetic Association Studies. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perani, D.; Garibotto, V.; Gorini, A.; Moresco, R.M.; Henin, M.; Panzacchi, A.; Matarrese, M.; Carpinelli, A.; Bellodi, L.; Fazio, F. In Vivo PET Study of 5HT2A Serotonin and D2 Dopamine Dysfunction in Drug-Naive Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. NeuroImage 2008, 42, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.E.; Platko, J.; Fagerness, J.; Birns, J.; Jenike, E.; Smoller, J.W.; Perlis, R.; Leboyer, M.; Delorme, R.; Chabane, N.; et al. A Genetic Family-Based Association Study of OLIG2 in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2007, 64, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milad, M.R.; Rauch, S.L. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Beyond Segregated Cortico-Striatal Pathways. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2012, 16, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, P.; Gratacós, M.; Segalàs, C.; Escaramís, G.; Real, E.; Bayés, M.; Labad, J.; López-Solà, C.; Estivill, X.; Menchón, J.M. Association between the NMDA Glutamate Receptor GRIN2B Gene and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2012, 37, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochner, C.; Kinnear, C.J.; Hemmings, S.M.J.; Seller, C.; Niehaus, D.J.H.; Knowles, J.A.; Daniels, W.; Moolman-Smook, J.C.; Seedat, S.; Stein, D.J. Hoarding in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Clinical and Genetic Correlates. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2005, 66, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo-Felippe, F.B.; De Salles Andrade, J.B.; Giori, I.G.; Vieira-Fonseca, T.; Fontenelle, L.F.; Kohlrausch, F.B. Catechol-O-Methyltransferase Gene Polymorphisms in Specific Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder Patients’ Subgroups. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 58, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmings, S.M.J.; Kinnear, C.J.; Lochner, C.; Niehaus, D.J.H.; Knowles, J.A.; Moolman-Smook, J.C.; Corfield, V.A.; Stein, D.J. Early- versus Late-Onset Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Investigating Genetic and Clinical Correlates. Psychiatry Res. 2004, 128, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katerberg, H.; Lochner, C.; Cath, D.C.; De Jonge, P.; Bochdanovits, Z.; Moolman-Smook, J.C.; Hemmings, S.M.J.; Carey, P.D.; Stein, D.J.; Sondervan, D.; et al. The Role of the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Val66met Variant in the Pheno-typic Expression of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD). Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2009, 150, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendland, J.R.; Kruse, M.R.; Murphy, D.L. Functional SLITRK1 Var321, varCDfs and SLC6A4 G56A Variants and Susceptibility to Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2006, 11, 802–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdolhosseinzadeh, S.; Alizadeh, N.; Shams, J.; Asadi, S.; Ahmadiani, A. BDNF Association Study with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder, its Clinical Characteristics, and Response to Fluvoxamine-Treatment in Iranian Patients. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 28, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendland, J.R.; Moya, P.R.; Timpano, K.R.; Anavitarte, A.P.; Kruse, M.R.; Wheaton, M.G.; Ren-Patterson, R.F.; Murphy, D.L. A Haplotype Containing Quantitative Trait Loci for SLC1A1 Gene Expression and Its Association with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, S.G.; Baer, L.; Otto, M.W. Symptom Subtypes of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder in Behavioral Treatment Studies: A Quantitative Review. Behav. Res. Ther. 1996, 34, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mathis, M.A.; de Alvarenga, P.; Funaro, G.; Torresan, R.C.; Moraes, I.; Torres, A.R.; Zilberman, M.L.; Hounie, A.G. Gender Differences in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: A Literature Review. Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2011, 33, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, S.L.; Dougherty, D.D.; Shin, L.M.; Alpert, N.M.; Manzo, P.; Leahy, L.; Fischman, A.J.; Jenike, M.A.; Baer, L. Neural Correlates of Factor-Analyzed OCD Symptom Dimensions: A PET Study. CNS Spectr. 1998, 3, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.L.; Marks, I.M.; Senior, C.; Lythgoe, D.; O’Dwyer, A.-M.; Meehan, O.; Williams, S.C.R.; Brammer, M.J.; Bullmore, E.T.; McGuire, P.K. A Differential Neural Response in Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder Patients with Washing Compared with Checking Symptoms to Disgust. Psychol. Med. 2000, 30, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mataix-Cols, D.; Wooderson, S.; Lawrence, N.; Brammer, M.J.; Speckens, A.; Phillips, M.L. Distinct Neural Correlates of Washing, Checking, and Hoarding Symptom Dimensions in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2004, 61, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, A.; Richter, M.; Jain, T.; Ravindran, L.; Rector, N.; Farb, N. Functional Connectivity in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder and Its Subtypes. Psychol. Med. 2020, 50, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, P.; Gratacòs, M.; Segalàs, C.; Escaramís, G.; Real, E.; Bayés, M.; Labad, J.; Pertusa, A.; Vallejo, J.; Estivill, X.; et al. Variants in Estrogen Receptor Alpha Gene Are Associated with Phenotypical Expression of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2011, 36, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taj, M.J.R.J.; Ganesh, S.; Shukla, T.; Deolankar, S.; Nadella, R.K.; Sen, S.; Purushottam, M.; Reddy, Y.C.J.; Jain, S.; Viswanath, B. BDNF Gene and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder Risk, Symptom Dimensions and Treatment Response. Asian J. Psychiatry 2018, 38, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saremi, A.A.; Shariat, S.V.; Nazari, M.A.; Dolatshahi, B. Research Paper: Neuropsychological Functioning in Obsessive-Compulsive Washers: Drug-Naive Without Depressive Symptoms. Basic Clin. Neurosci. J. 2017, 8, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leopold, R.; Backenstrass, M. Neuropsychological Differences between Obsessive-Compulsive Washers and Checkers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Anxiety Disord. 2015, 30, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoudi, M.; Pourshahbaz, A.; Dolatshahi, B.; Nazeriastaneh, A.; Poshtmashhadi, M. Network Analysis for Predicting Treatment Response in Patients with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Iran. J. Psychiatry Behav. Sci. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starcevic, V.; Brakoulias, V. Symptom Subtypes of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Are They Relevant for Treatment? Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2008, 42, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, V. Modification of Expectations in Cases with Obsessional Rituals. Behav. Res. Ther. 1966, 4, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaherirenani, R.; Mortazavi, S.S.; Shalbafan, M.; Ashouri, A.; Farani, A.R. Virtual Reality Exposure and Response Prevention in the Treatment of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder in Patients with Contamination Subtype in Comparison with in Vivo Exposure Therapy: A Randomized Clinical Controlled Trial. BMC Psychiatry 2022, 22, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krochmalik, A.; Jones, M.K.; Menzies, R.G.; Kirkby, K. The Superiority of Danger Ideation Reduction Therapy (DIRT) Over Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP) in Treating Compulsive Washing. Behav. Change 2004, 21, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.K.; Menzies, R.G. Danger Ideation Reduction Therapy (DIRT): Preliminary Findings with Three Obsessive-Compulsive Washers. Behav. Res. Ther. 1997, 35, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqbool, M.; Sengar, K.S.; Vikas; Kumar, M.; Uparikar, P.D. Efficacy of Danger Ideation Reduction Therapy in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Washer with Poor Insight: A Case Study and Literature Review. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2017, 39, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, P.; Yuan, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, N.; Li, C.-S.R.; Liu, N. Symptom Provocation in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: A Voxel-Based Meta-Analysis and Meta-Analytic Connectivity Modeling. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2022, 146, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsobrook II, J.P.; Leckman, J.F.; Goodman, W.K.; Rasmussen, S.A.; Pauls, D.L. Segregation Analysis of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Using Symptom-Based Factor Scores. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1999, 88, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biria, M.; Banca, P.; Keser, E.; Healy, M.P.; Sawiak, S.J.; Frota Lisbôa Pereira De Souza, A.M.; Marzuki, A.A.; Sule, A.; Rob-bins, T.W. Excessive Checking in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Neurochemical Correlates Revealed by 7T Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Biol. Psychiatry Glob. Open Sci. 2024, 4, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, I.M.; Murata, Y.; Yamanishi, T.; Nakaaki, S.; Akechi, T.; Mikuni, M.; Furukawa, T.A. The Differential Impact of Executive Attention Dysfunction on Episodic Memory in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Patients with Checking Symptoms vs. Those with Washing Symptoms. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2007, 41, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakoulias, V.; Elhindi, J.; Starcevic, V. A Network Analysis of Obsessive-Compulsive Symptoms and Their Comorbidity with Other Disorders. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2025, 183, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouche, J.-P.; Du Plessis, S.; Hattingh, C.; Roos, A.; Lochner, C.; Soriano-Mas, C.; Sato, J.R.; Nakamae, T.; Nishida, S.; Kwon, J.S.; et al. Cortical Thickness in Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder: Multisite Mega-Analysis of 780 Brain Scans from Six Centres. Br. J. Psychiatry 2017, 210, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, S.J.; Alonso, P.; Schweren, L.; Mataix-Cols, D.; Lochner, C.; Menchón, J.M.; Stein, D.J.; Fouche, J.-P.; Soriano-Mas, C.; Sato, J.R.; et al. Multicenter Voxel-Based Morphometry Mega-Analysis of Structural Brain Scans in Obsessive-Compulsive Dis-order. Am. J. Psychiatry 2014, 171, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazari, N.; Narayanaswamy, J.C.; Venkatasubramanian, G. Neuroimaging Findings in Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder: A Narrative Review to Elucidate Neurobiological Underpinnings. Indian J. Psychiatry 2019, 61, S9–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasler, G.; LaSalle-Ricci, V.H.; Ronquillo, J.G.; Crawley, S.A.; Cochran, L.W.; Kazuba, D.; Greenberg, B.D.; Murphy, D.L. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Symptom Dimensions Show Specific Relationships to Psychiatric Comorbidity. Psychiatry Res. 2005, 135, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taj, M.J.R.J.; Viswanath, B.; Purushottam, M.; Kandavel, T.; Janardhan Reddy, Y.C.; Jain, S. DRD4 Gene and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: Do Symptom Dimensions Have Specific Genetic Correlates? Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 41, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radomsky, A.S.; Rachman, S. Symmetry, Ordering and Arranging Compulsive Behaviour. Behav. Res. Ther. 2004, 42, 893–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfeldt, L.J. Understanding and Treating Incompleteness in Obsessive-compulsive Disorder. J. Clin. Psychol. 2004, 60, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rück, C.; Larsson, K.J.; Mataix-Cols, D. Predictors of Medium and Long-Term Outcome Following Capsulotomy for Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder: One Site May Not Fit All. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012, 22, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, L. Cingulotomy for Intractable Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Prospective Long-Term Follow-up of 18 Patients. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1995, 52, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, D.J.; Andersen, E.W.; Overo, K.F. Response of Symptom Dimensions in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder to Treatment with Citalopram or Placebo. Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2007, 29, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, R.O.; Gross, R.C. The Hoarding of Possessions. Behav. Res. Ther. 1993, 31, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, R.O.; Hartl, T.L.; Christian, R.; Williams, N. The Value of Possessions in Compulsive Hoarding: Patterns of Use and Attachment. Behav. Res. Ther. 1995, 33, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, R.O.; Hartl, T.L. A Cognitive-Behavioral Model of Compulsive Hoarding. Behav. Res. Ther. 1996, 34, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowitz, J.S.; Wheaton, M.G.; Storch, E.A. The Status of Hoarding as a Symptom of Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder. Behav. Res. Ther. 2008, 46, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelevich, V.D.; Gabutdinov, K.A.; Ruzhenkova, V.V. Hoarding: A New Diagnosis against the Traditional Interpretation. Case Artem L. Neurol. Bull. 2023, 55, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moheb, N.; Charuworn, K.; Ashla, M.M.; Desarzant, R.; Chavez, D.; Mendez, M.F. Repetitive Behaviors in Frontotemporal Dementia: Compulsions or Impulsions? J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 31, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mataix-Cols, D.; Marks, I.M.; Greist, J.H.; Kobak, K.A.; Baer, L. Obsessive-Compulsive Symptom Dimensions as Predictors of Compliance with and Response to Behaviour Therapy: Results from a Controlled Trial. Psychother. Psychosom. 2002, 71, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.K.; Mataix-Cols, D.; Lawrence, N.S.; Wooderson, S.; Giampietro, V.; Speckens, A.; Brammer, M.J.; Phillips, M.L. To Discard or Not to Discard: The Neural Basis of Hoarding Symptoms in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, S.; Brody, A.L.; Maidment, K.M.; Smith, E.C.; Zohrabi, N.; Katz, E.; Baker, S.K.; Baxter Jr, L.R. Cerebral Glucose Metabolism in Obsessive-Compulsive Hoarding. Am. J. Psychiatry 2004, 161, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolin, D.F.; Stevens, M.C.; Villavicencio, A.L.; Norberg, M.M.; Calhoun, V.D.; Frost, R.O.; Steketee, G.; Rauch, S.L.; Pearl-son, G.D. Neural Mechanisms of Decision Making in Hoarding Disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2012, 69, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cromer, K.R.; Schmidt, N.B.; Murphy, D.L. Do Traumatic Events Influence the Clinical Expression of Compulsive Hoarding? Behav. Res. Ther. 2007, 45, 2581–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tükel, R.; Ertekin, E.; Batmaz, S.; Alyanak, F.; Sözen, A.; Aslantaş, B.; Atlı, H.; Özyıldırım, İ. Influence of Age of Onset on Clinical Features in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Depress. Anxiety 2005, 21, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshier, S.J.; Wootton, B.M.; Bragdon, L.B.; Tolin, D.F.; Davis, E.; DiMauro, J.; Diefenbach, G.J. The Relationship between Self-Reported and Objective Neuropsychological Impairments in Patients with Hoarding Disorder. J. Obs. Compuls. Relat. Disord. 2016, 9, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaman, C.; Oldfield, V.B.; Gordon, O.; Forrester, E.; Salkovskis, P.M. The Impact of Symptomatic Hoarding in OCD and Its Treatment. Behav. Cogn. Psychother. 2010, 38, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentil, A.F.; Lopes, A.C.; Dougherty, D.D.; Rück, C.; Mataix-Cols, D.; Lukacs, T.L.; Canteras, M.M.; Eskandar, E.N.; Lars-son, K.J.; Hoexter, M.Q. Hoarding Symptoms and Prediction of Poor Response to Limbic System Surgery for Treatment-Refractory Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 121, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachman, S. A Cognitive Theory of Obsessions. In Behavior and Cognitive Therapy Today; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 209–222. [Google Scholar]
- Rachman, S. Obsessions, Responsibility and Guilt. Behav. Res. Ther. 1993, 31, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.T.; Farris, S.G.; Turkheimer, E.; Pinto, A.; Ozanick, K.; Franklin, M.E.; Liebowitz, M.; Simpson, H.B.; Foa, E.B. Myth of the Pure Obsessional Type in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Depress. Anxiety 2011, 28, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, G. How Does “Pure-O” Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Impact on a Patient’s Treatment Plan? Expert Rev. Neurother. 2023, 23, 1051–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J.; Kwon, S.-M. Two Different Types of Obsession: Autogenous Obsessions and Reactive Obsessions. Behav. Res. Ther. 2003, 41, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherian, A.V.; Narayanaswamy, J.C.; Viswanath, B.; Guru, N.; George, C.M.; Bada Math, S.; Kandavel, T.; Janardhan Reddy, Y.C. Gender Differences in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Findings from a Large Indian Sample. Asian J. Psychiatry 2014, 9, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labad, J.; Menchon, J.M.; Alonso, P.; Segalas, C.; Jimenez, S.; Jaurrieta, N.; Leckman, J.F.; Vallejo, J. Gender Differences in Obsessive-Compulsive Symptom Dimensions. Depress. Anxiety 2008, 25, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, B.J.; Pujol, J.; Soriano-Mas, C.; Hernández-Ribas, R.; López-Solà, M.; Ortiz, H.; Alonso, P.; Deus, J.; Menchon, J.M.; Real, E.; et al. Neural correlates of moral sensitivity in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2012, 69, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujol, J.; Soriano-Mas, C.; Alonso, P.; Cardoner, N.; Menchón, J.M.; Deus, J.; Vallejo, J. Mapping Structural Brain Alterations in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2004, 61, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Nakao, T.; Sanematsu, H.; Murayama, K.; Honda, S.; Tomita, M.; Togao, O.; Yoshiura, T.; Kanba, S. Biological Heterogeneity of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: A Voxel-Based Morphometric Study Based on Dimensional Assessment. Psychi-atry Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 69, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, P.G.; Do Rosário, M.C.; Batistuzzo, M.C.; Diniz, J.B.; Shavitt, R.G.; Duran, F.L.S.; Dougherty, D.D.; Bressan, R.A.; Miguel, E.C.; Hoexter, M.Q. Obsessive-Compulsive Symptom Dimensions Correlate to Specific Gray Matter Volumes in Treatment-Naïve Patients. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2012, 46, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siev, J.; Steketee, G.; Fama, J.M.; Wilhelm, S. Cognitive and Clinical Characteristics of Sexual and Religious Obsessions. J. Cogn. Psychother. 2011, 25, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glazier, K.; Wetterneck, C.; Singh, S.; Williams, M. Stigma and Shame as Barriers to Treatment for Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders. J. Depress. Anxiety 2015, 4, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, R.J.; Guzick, A.G.; Swan, L.K.; McNamara, J.P. Stigma and Recognition of Different Types of Symptoms in OCD. J. Obs. Compuls. Relat. Disord. 2017, 12, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, N.C.; Shaw, A.M.; Wilhelm, S. Emotion Regulation in Patients with Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: Unique Effects for Those with “Taboo Thoughts”. Cogn. Ther. Res. 2018, 42, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, G.; Mataix-Cols, D.; Rijsdijk, F.; Rück, C.; Lichtenstein, P.; Lundström, S.; Larsson, H.; Eley, T.C.; de la Cruz, L.F. Concurrent and Prospective Associations of Obsessive-Compulsive Symptoms with Suicidality in Young Adults: A Genetically-Informative Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 281, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravani, V.; Kamali, Z.; Ardakani, R.J.; Ardestani, M.S. The Relation of Childhood Trauma to Suicide Ideation in Patients Suffering from Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder with Lifetime Suicide Attempts. Psychiatry Res. 2017, 255, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.R.; Ramos-Cerqueira, A.T.A.; Ferrão, Y.A.; Fontenelle, L.F.; Do Rosário, M.C.; Miguel, E.C. Suicidality in Obses-sive-Compulsive Disorder: Prevalence and Relation to Symptom Dimensions and Comorbid Conditions. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2011, 72, 20314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervin, M.; Do Rosário, M.C.; Fontenelle, L.F.; Ferrão, Y.A.; Batistuzzo, M.C.; Torres, A.R.; Damiano, R.F.; Fernández De La Cruz, L.; Miguel, E.C.; Mataix-Cols, D. Taboo Obsessions and Their Association with Suicidality in Obsessive-Compulsive Disor-der. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2022, 154, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landeros-Weisenberger, A.; Bloch, M.H.; Kelmendi, B.; Wegner, R.; Nudel, J.; Dombrowski, P.; Pittenger, C.; Krystal, J.H.; Goodman, W.K.; Leckman, J.F. Dimensional Predictors of Response to SRI Pharmacotherapy in Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2010, 121, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, P.; Menchon, J.M.; Pifarre, J.; Mataix-Cols, D.; Torres, L.; Salgado, P.; Vallejo, J. Long-Term Follow-Up and Predictors of Clinical Outcome in Obsessive-Compulsive Patients Treated with Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Behavioral Therapy. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2001, 62, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufer, M.; Fricke, S.; Moritz, S.; Kloss, M.; Hand, I. Symptom Dimensions in Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder: Prediction of Cognitive-behavior Therapy Outcome. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2006, 113, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.T.; Farris, S.G.; Turkheimer, E.N.; Franklin, M.E.; Simpson, H.B.; Liebowitz, M.; Foa, E.B. The Impact of Symptom Dimensions on Outcome for Exposure and Ritual Prevention Therapy in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. J. Anxiety Disord. 2014, 28, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Database/Platform | Search Date | Search Query |
|---|---|---|
| PubMed | 17 October 2024 | ((obsessive–compulsive disorder OR OCD) AND (subtypes OR biotypes)) AND (EEG OR fMRI OR MRI OR brain OR cognitive OR genetics OR genes) |
| Springer Link | 20 November 2024 | (obsessive–compulsive disorder OR OCD) AND (subtype * OR biotype *) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Proshina, E.; Gaidareva, A.; Beskhizhko, M.; Kazaryan, G.; Bainbridge, E.; Khayrullina, G. Biomarkers of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Subtypes: A Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178578
Proshina E, Gaidareva A, Beskhizhko M, Kazaryan G, Bainbridge E, Khayrullina G. Biomarkers of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Subtypes: A Literature Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178578
Chicago/Turabian StyleProshina, Ekaterina, Anastasia Gaidareva, Margarita Beskhizhko, Grigor Kazaryan, Emily Bainbridge, and Guzal Khayrullina. 2025. "Biomarkers of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Subtypes: A Literature Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178578
APA StyleProshina, E., Gaidareva, A., Beskhizhko, M., Kazaryan, G., Bainbridge, E., & Khayrullina, G. (2025). Biomarkers of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Subtypes: A Literature Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178578






