Is Radiographic Aftercare Obsolete? How Testing Positive for ctDNA Can Be a Precedent for Late Relapse, Even in Low-Risk Hormone-Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
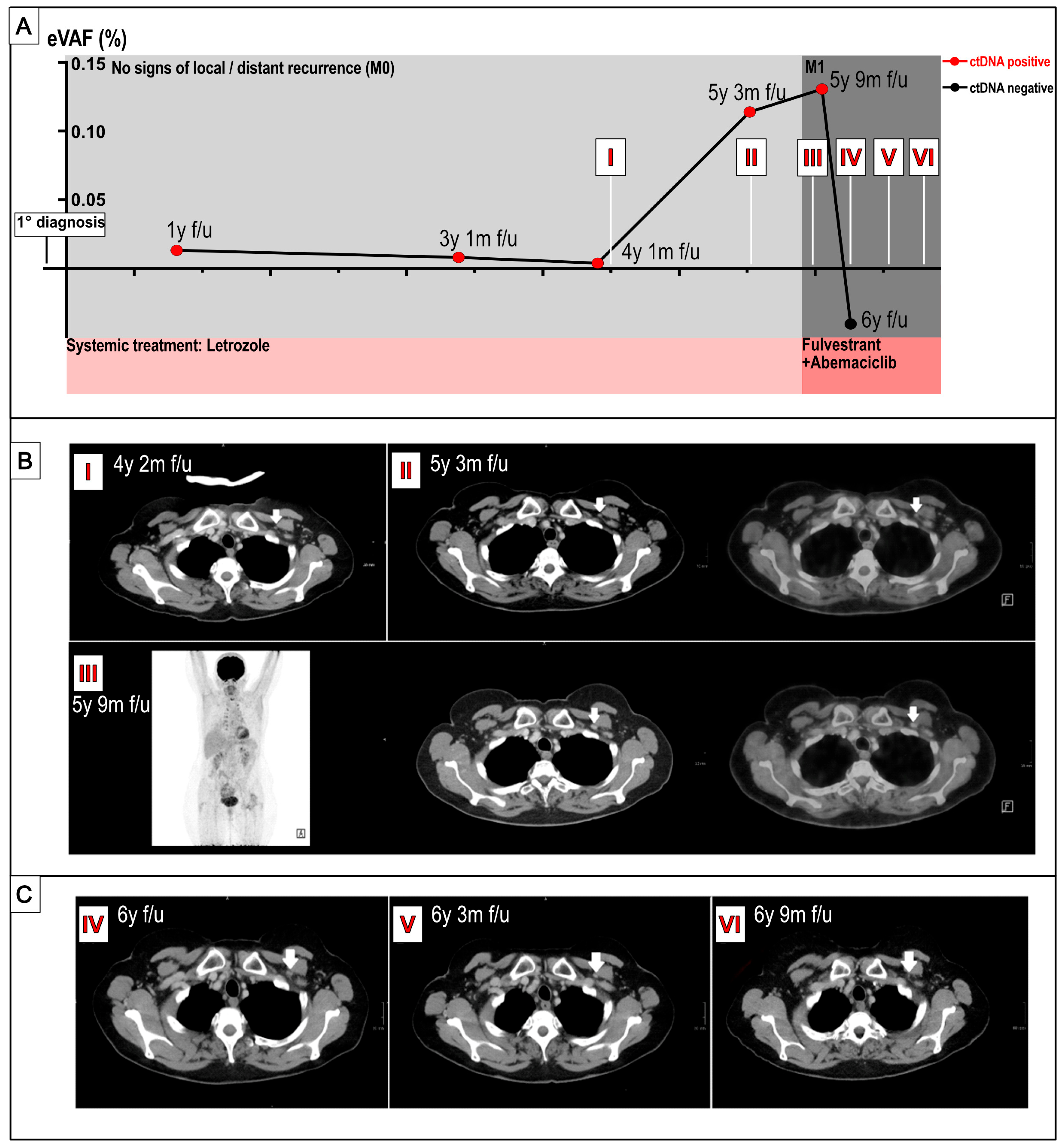
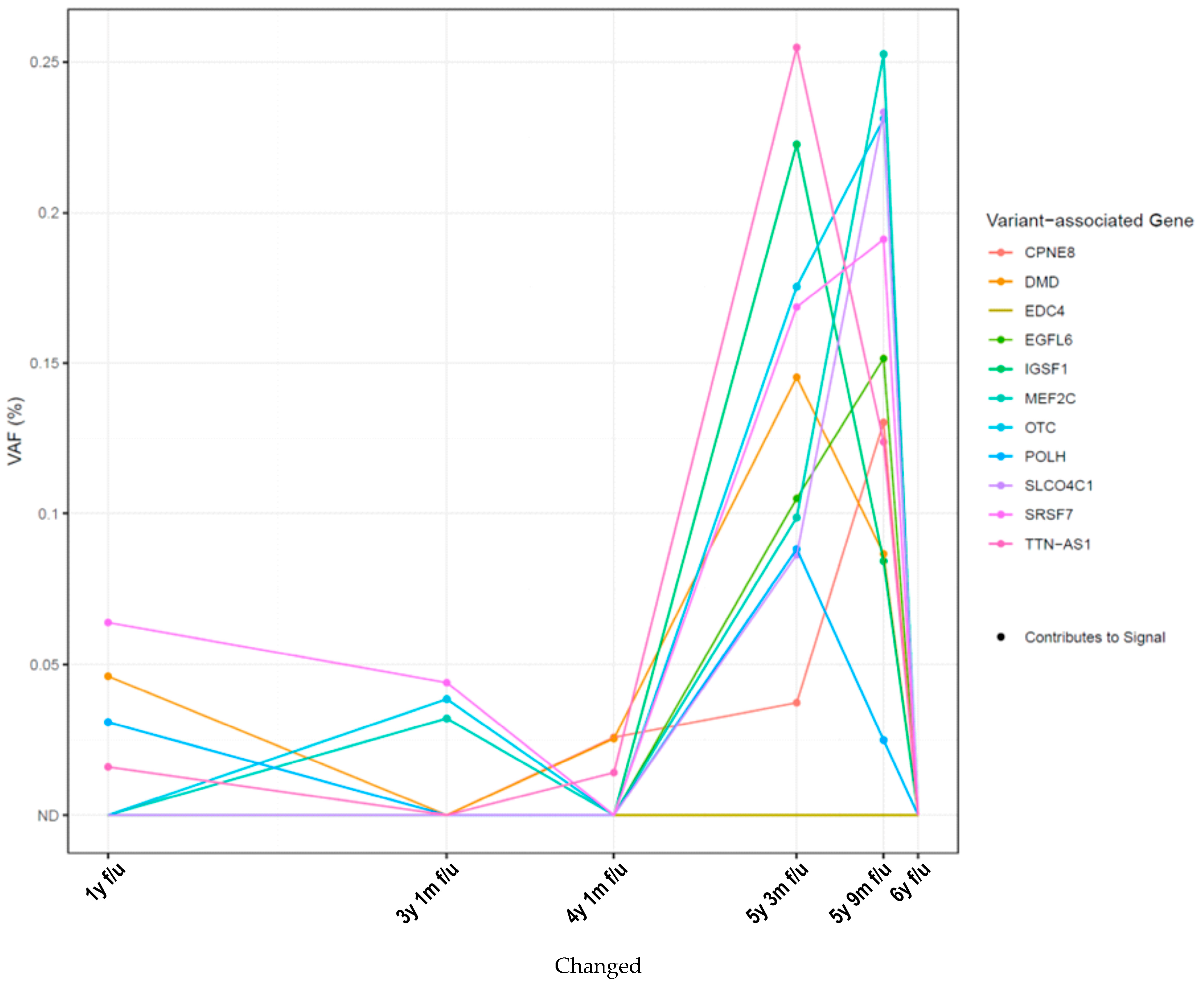
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
- RaDaR panel design
- b.
- Plasma ctDNA test
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Aromatase inhibitor |
| CTC | Circulating tumor cells |
| ctDNA | Circulating free tumor DNA |
| CT scan | Computer tomography scan |
| eBC | Early breast cancer |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| MRD | Molecular residual disease |
| PgR | Progesterone receptor |
References
- Robert Koch Institut. Zentrum für Krebsregisterdaten. Available online: https://www.krebsdaten.de/Krebs/EN/Content/Cancer_sites/Breast_cancer/breast_cancer_node.html (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Rosselli Del Turco, M.; Palli, D.; Cariddi, A.; Ciatto, S.; Pacini, P.; Distante, V. Intensive diagnostic follow-up after treatment of primary breast cancer. A randomized trial. National Research Council Project on Breast Cancer follow-up. JAMA 1994, 271, 1593–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The GIVIO Investigators. Impact of follow-up testing on survival and health-related quality of life in breast cancer patients. A multicenter randomized controlled trial. The GIVIO Investigators. JAMA 1994, 271, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, F.; Schmidt, K.; Choti, M.A.; Romans, K.; Goodman, S.; Li, M.; Thornton, K.; Agrawal, N.; Sokoll, L.; Szabo, S.A.; et al. Circulating mutant DNA to assess tumor dynamics. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, L.A., Jr.; Bardelli, A. Liquid biopsies: Genotyping circulating tumor DNA. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coombes, R.C.; Page, K.; Salari, R.; Hastings, R.K.; Armstrong, A.; Ahmed, S.; Ali, S.; Cleator, S.; Kenny, L.; Stebbing, J.; et al. Personalized Detection of Circulating Tumor DNA Antedates Breast Cancer Metastatic Recurrence. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4255–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Murillas, I.; Chopra, N.; Comino-Mendez, I.; Beaney, M.; Tovey, H.; Cutts, R.J.; Swift, C.; Kriplani, D.; Afentakis, M.; Hrebien, S.; et al. Assessment of Molecular Relapse Detection in Early-Stage Breast Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsyc-Sharf, M.; de Bruin, E.C.; Santos, K.; McEwen, R.; Stetson, D.; Patel, A.; Kirkner, G.J.; Hughes, M.E.; Tolaney, S.M.; Partridge, A.H.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA and Late Recurrence in High-Risk Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2408–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Du, Y.; Fan, X.; Wang, Y.; Ivan, C.; Zhang, X.G.; Sood, A.K.; An, Z.; Zhang, N. EGFL6 promotes breast cancer by simultaneously enhancing cancer cell metastasis and stimulating tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene 2019, 38, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Huang, C.; Ke, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Xue, H.; Chen, J. lncRNA TTN-AS1 facilitates proliferation, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells by regulating miR-139-5p/ZEB1 axis. J. Cell Biochem. 2020, 121, 4772–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AGO Komission Mamma AGO-Leitlinien Mammakarzinom. Available online: https://www.ago-online.de/fileadmin/ago-online/downloads/_leitlinien/kommission_mamma/2024/Einzeldateien/AGO_2024D_16_Nachsorge.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- Slamon, D.; Lipatov, O.; Nowecki, Z.; McAndrew, N.; Kukielka-Budny, B.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Yardley, D.A.; Huang, C.S.; Fasching, P.A.; Crown, J.; et al. Ribociclib plus Endocrine Therapy in Early Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1080–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nader-Marta, G.; Monteforte, M.; Agostinetto, E.; Cinquini, M.; Martins-Branco, D.; Langouo, M.; Llombart-Cusac, A.; Cortés, J.; Ignatiadis, M.; Torri, V.; et al. Circulating tumor DNA for predicting recurrence in patients with operable breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. ESMO Open 2024, 9, 102390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, K.; Huesmann, S.; Friedl, T.W.P.; Fink, A.; Mehmeti, F.; Mergel, F.; Schäffler, H.; Heublein, S.; Hartkopf, A.D.; Mueller, V.; et al. The SURVIVE study: Liquid biopsy guided surveillance after intermediate- to high-risk early breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, TPS620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flach, S.; Howarth, K.; Hackinger, S.; Pipinikas, C.; Ellis, P.; McLay, K.; Marsico, G.; Forshew, T.; Walz, C.; Reichel, C.A.; et al. Liquid BIOpsy for MiNimal RESidual DiSease Detection in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (LIONESS)-a personalised circulating tumour DNA analysis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dorp, J.; Pipinikas, C.; Suelmann, B.B.M.; Mehra, N.; van Dijk, N.; Marsico, G.; van Montfoort, M.L.; Hackinger, S.; Braaf, L.M.; Amarante, T.; et al. High- or low-dose preoperative ipilimumab plus nivolumab in stage III urothelial cancer: The phase 1B NABUCCO trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, T.; Ullius, A.; Schonborn, M.; Oelmuller, U. Sensitivity assessment of workflows detecting rare circulating cell-free DNA targets: A study design proposal. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://kersnikova.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/1.-Isolation-of-mononuclear-cells-_-basic-protocol_-GE-Healthcare.pdf. (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/DE/de/technical-documents/protocol/clinical-testing-and-diagnostics-manufacturing/hematology/recommended-standard-method (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Yang, J.; Gong, Y.; Lam, V.K.; Shi, Y.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qian, F.; et al. Deep sequencing of circulating tumor DNA detects molecular residual disease and predicts recurrence in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pfister, K.; Huesmann, S.; Fink, A.; Friedl, T.W.P.; Mergel, F.; Schäffler, H.P.; Hartkopf, A.; Lukac, S.; Veselinovic, K.; Mehmeti, F.; et al. Is Radiographic Aftercare Obsolete? How Testing Positive for ctDNA Can Be a Precedent for Late Relapse, Even in Low-Risk Hormone-Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178498
Pfister K, Huesmann S, Fink A, Friedl TWP, Mergel F, Schäffler HP, Hartkopf A, Lukac S, Veselinovic K, Mehmeti F, et al. Is Radiographic Aftercare Obsolete? How Testing Positive for ctDNA Can Be a Precedent for Late Relapse, Even in Low-Risk Hormone-Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178498
Chicago/Turabian StylePfister, Kerstin, Sophia Huesmann, Angelina Fink, Thomas W. P. Friedl, Franziska Mergel, Henning P. Schäffler, Andreas Hartkopf, Stefan Lukac, Kristina Veselinovic, Forca Mehmeti, and et al. 2025. "Is Radiographic Aftercare Obsolete? How Testing Positive for ctDNA Can Be a Precedent for Late Relapse, Even in Low-Risk Hormone-Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178498
APA StylePfister, K., Huesmann, S., Fink, A., Friedl, T. W. P., Mergel, F., Schäffler, H. P., Hartkopf, A., Lukac, S., Veselinovic, K., Mehmeti, F., Campbell, N., Pipinikas, C., Deininger, K., Beer, A., Lorenz, S., Beer, M., Wiesmüller, L., Janni, W., Heublein, S., & Rack, B. (2025). Is Radiographic Aftercare Obsolete? How Testing Positive for ctDNA Can Be a Precedent for Late Relapse, Even in Low-Risk Hormone-Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178498






