Computational Discovery of Selective Carbonic Anhydrase IX (CA IX) Inhibitors via Pharmacophore Modeling and Molecular Simulations for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
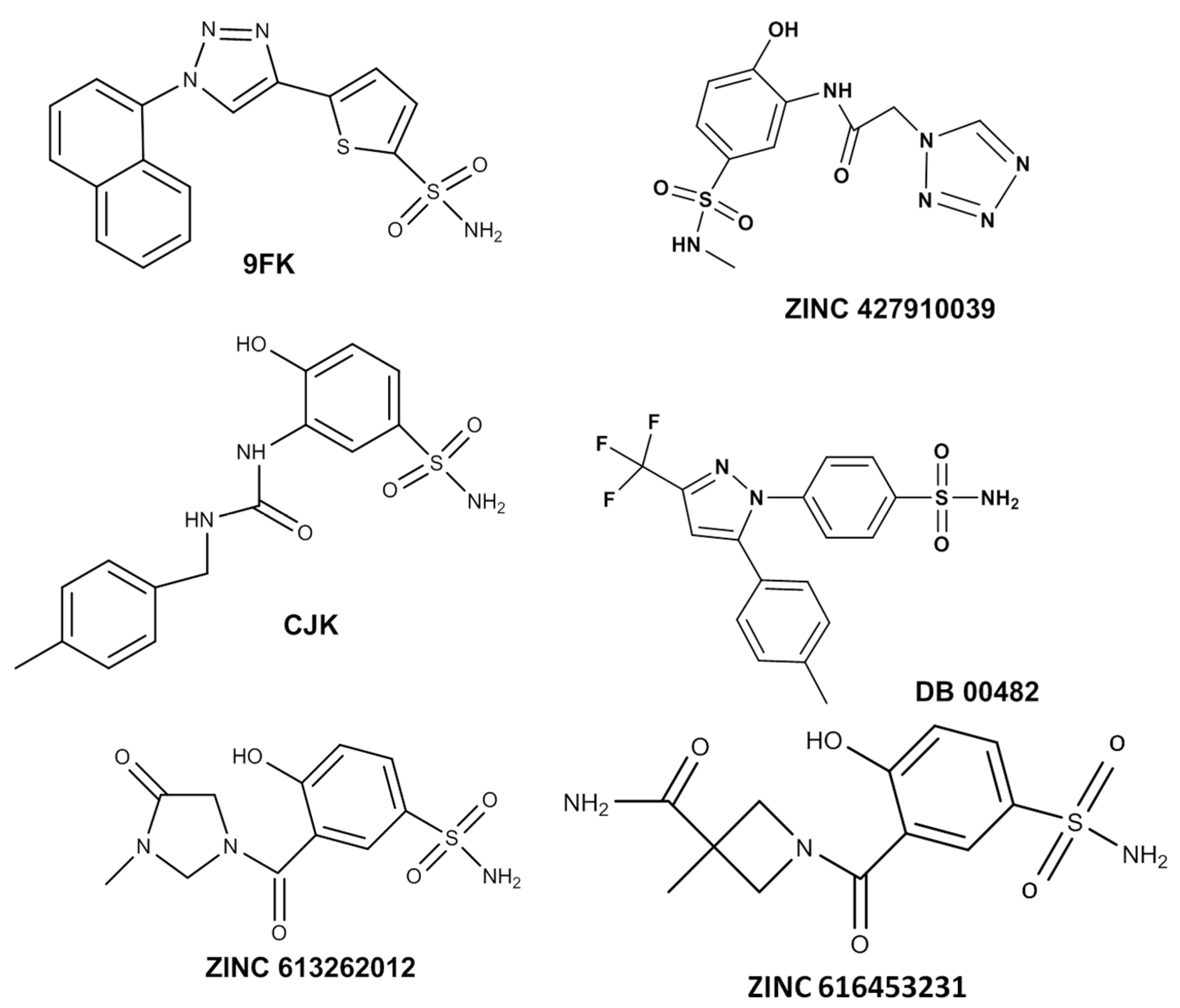
2.1. Pharmacophore Model-Based Screening
2.2. Molecular Docking
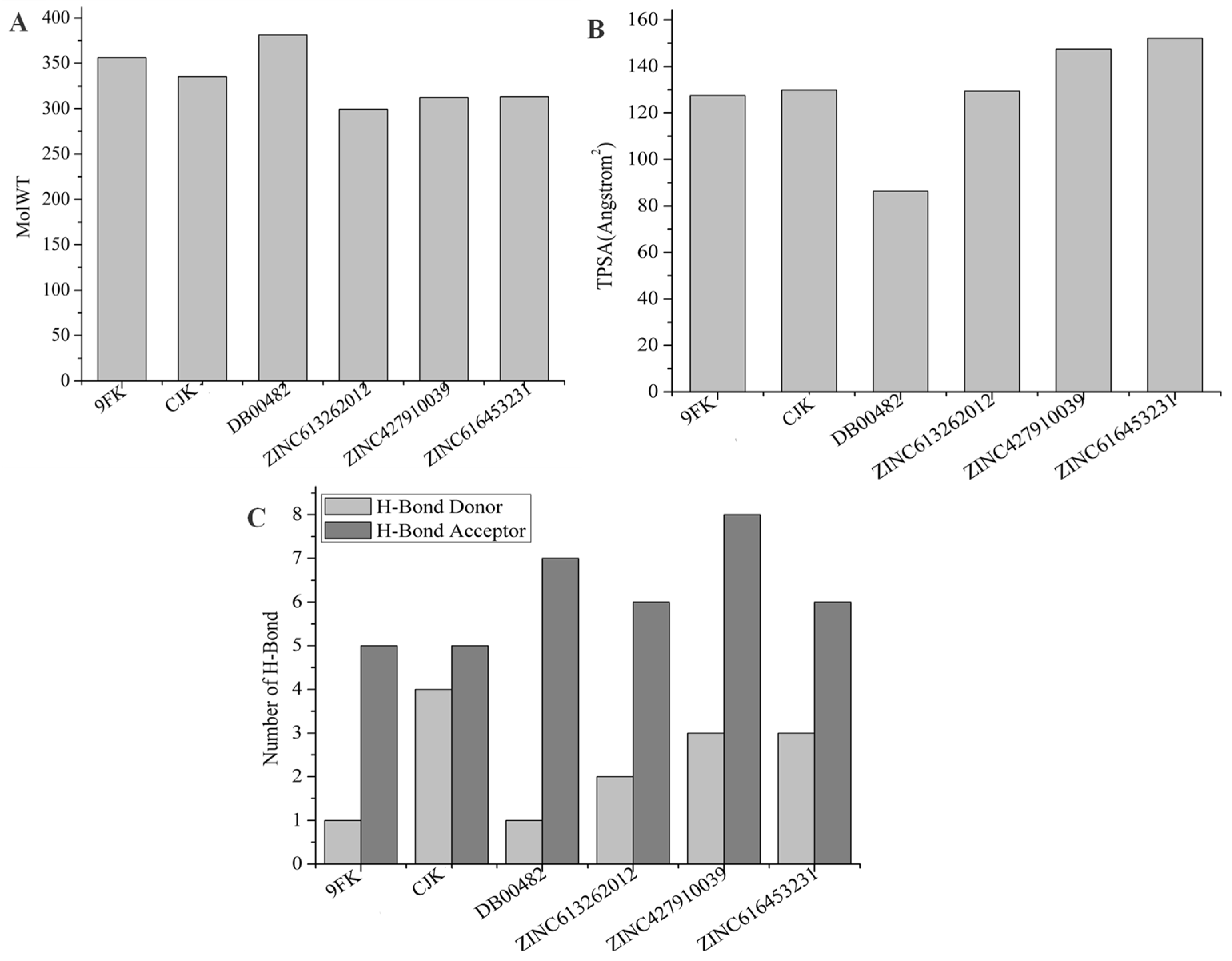
2.3. Physiochemical Characteristics
2.4. Toxicity Profile
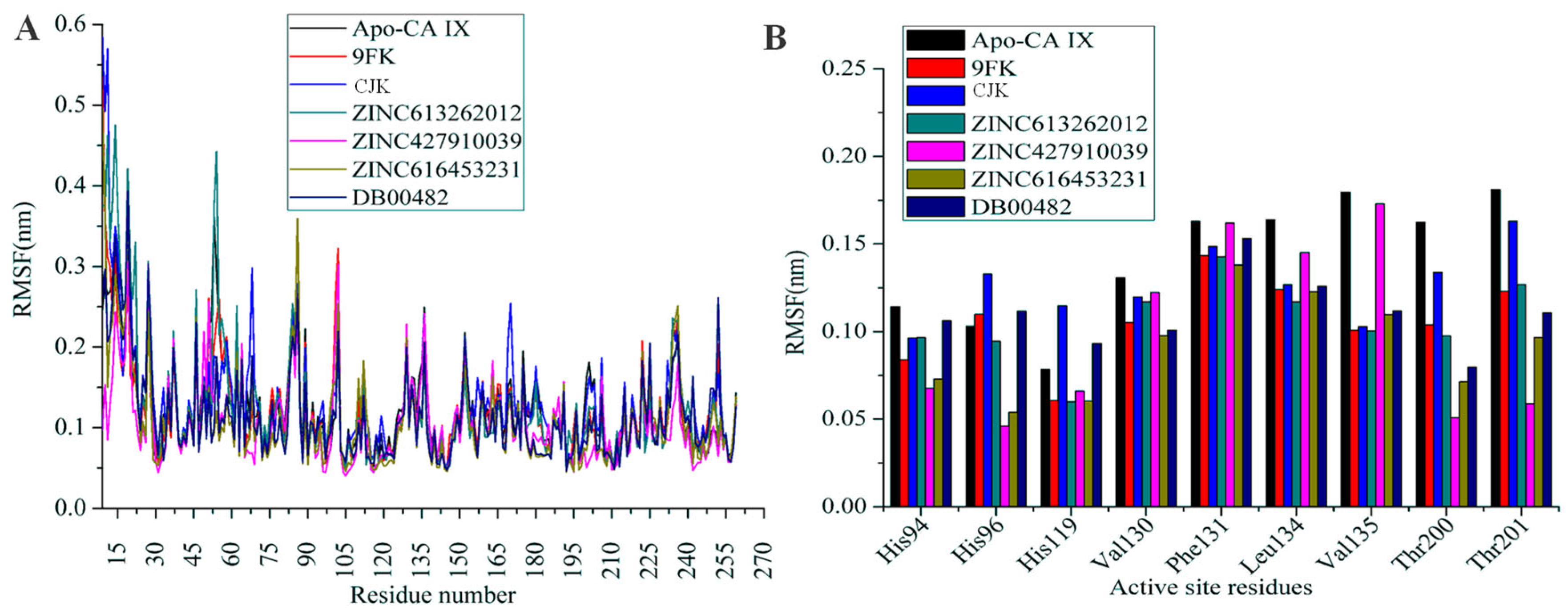
2.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
2.6. Intermolecular Interactions
2.7. MM-PBSA Analysis
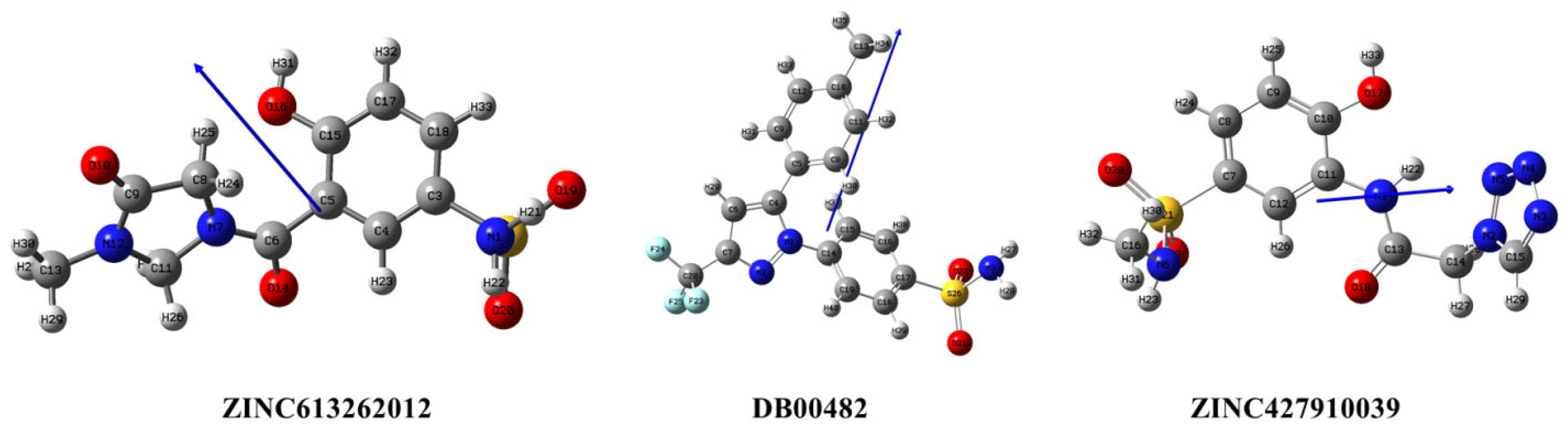
2.8. DFT Analysis of the Three Selected Candidate Compounds
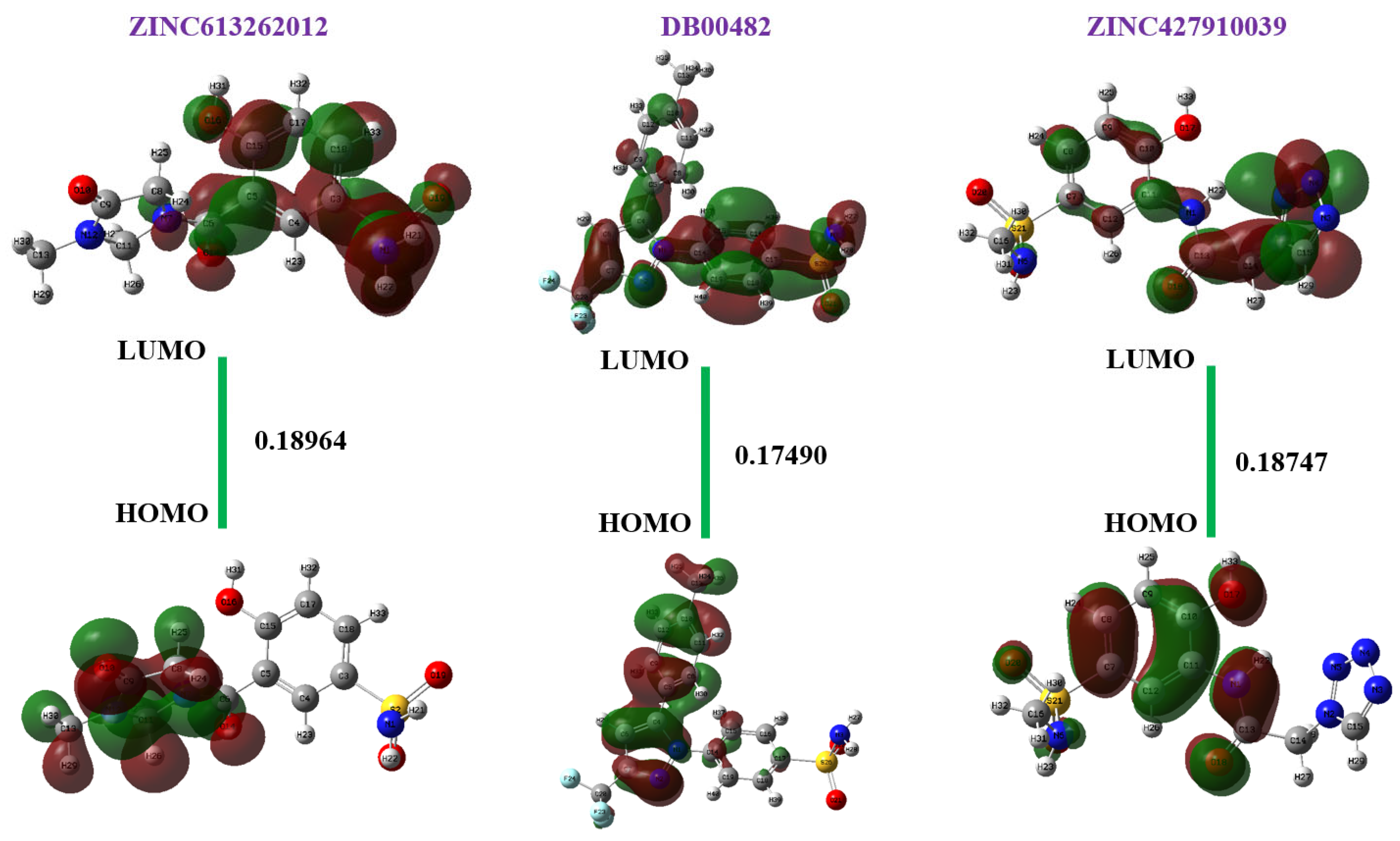
2.8.1. FMO Analysis
2.8.2. Dipole Moment and Electronic Energy
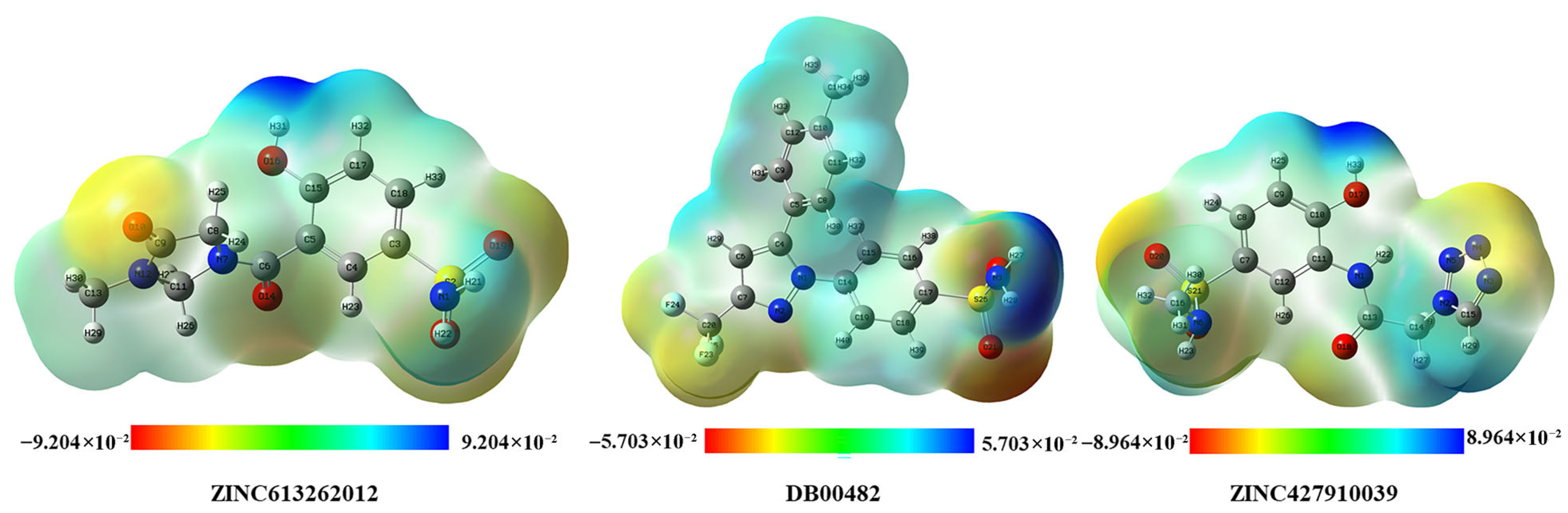
2.8.3. Molecular Electrostatic Potential (MEP)
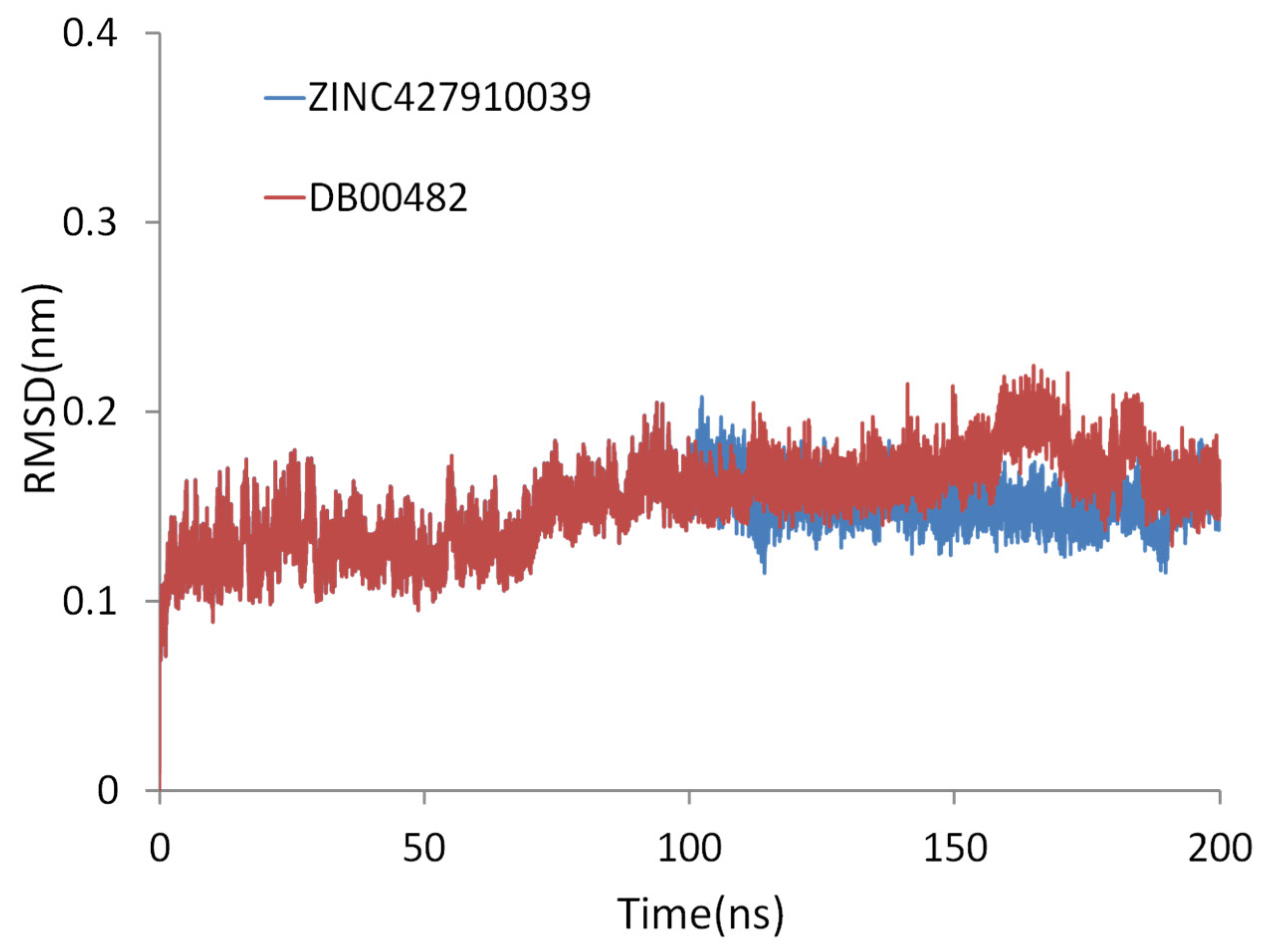
2.9. Extended Simulation of the ZINC427910039 and DB00482
2.10. Comparative Docking Analysis of CA IX and Off-Target Isoforms (CA I, CA II)
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Pharmacophore Model Building
4.2. Protein and Ligand Structure Optimization
4.3. Molecular Docking
4.4. Toxicity Measurement
4.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
4.6. Molecular Mechanics Poisson–Boltzmann Surface Area (MM-PBSA) Analysis
4.7. Density Functional Theory (DFT)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jing, X.; Yang, F.; Shao, C.; Wei, K.; Xie, M.; Shen, H.; Shu, Y. Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaupel, P. The role of hypoxia-induced factors in tumor progression. Oncologist 2004, 9, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.M. Exploiting the hypoxic cancer cell: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Mol. Med. Today 2000, 6, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami Nejad, A.; Najafgholian, S.; Rostami, A.; Sistani, A.; Shojaeifar, S.; Esparvarinha, M.; Nedaeinia, R.; Haghjooy Javanmard, S.; Taherian, M.; Ahmadlou, M.; et al. The role of hypoxia in the tumor microenvironment and development of cancer stem cell: A novel approach to developing treatment. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaini, G.; Sgarbi, G.; Baracca, A. Oxidative phosphorylation in cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Bioenerg. 2011, 1807, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, S.K.; Debnath, M.; Ghosh, A.; Srivastava, R.; Omri, A. Targeting Tumor Hypoxia with Nanoparticle-Based Therapies: Challenges, Opportunities, and Clinical Implications. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takacova, M.; Kajanova, I.; Kolarcikova, M.; Lapinova, J.; Zatovicova, M.; Pastorekova, S. Understanding metabolic alterations and heterogeneity in cancer progression through validated immunodetection of key molecular components: A case of carbonic anhydrase IX. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021, 40, 1035–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilie, M.I.; Hofman, V.; Ortholan, C.; Ammadi, R.E.; Bonnetaud, C.; Havet, K.; Venissac, N.; Mouroux, J.; Mazure, N.M.; Pouysségur, J. Overexpression of carbonic anhydrase XII in tissues from resectable non-small cell lung cancers is a biomarker of good prognosis. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 1614–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.-Y.; Lerman, M.I.; Stanbridge, E.J. Expression of transmembrane carbonic anhydrases, CAIX and CAXII, in human development. BMC Dev. Biol. 2009, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, R.; Zheng, X.; Luo, Y.; Yao, M.; Ke, F.; Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q. Cooperative Role of Carbonic Anhydrase IX/XII in Driving Tumor Invasion and Metastasis: A Novel Targeted Therapeutic Strategy. Cells 2025, 14, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Feng, K.; Li, G.; Chen, W.; Shao, Y.; Ding, J.; Zheng, M.; Yuan, K.; Sun, X.; Yang, P. Carbonic anhydrase IX-targeted SMDCs for cancer precision treatment. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2025, 111047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrosio, K.; Di Fiore, A.; Langella, E. Dual targeting carbonic anhydrase inhibitors as promising therapeutic approach: A structural overview. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2025, 12, 1511281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldera, A.P.; Govender, D. Carbonic anhydrase IX: A regulator of pH and participant in carcinogenesis. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 74, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Designing isozyme-specific inhibitors as therapeutic agents. In The Carbonic Anhydrases: Current and Emerging Therapeutic Targets; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 221–235. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, H.M. Carbonic anhydrase IX and acid transport in cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queen, A.; Bhutto, H.N.; Yousuf, M.; Syed, M.A.; Hassan, M.I. Carbonic anhydrase IX: A tumor acidification switch in heterogeneity and chemokine regulation. Semi. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86, 899–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspatwar, A.; Tolvanen, M.E.; Barker, H.; Syrjänen, L.; Valanne, S.; Purmonen, S.; Waheed, A.; Sly, W.S.; Parkkila, S. Carbonic anhydrases in metazoan model organisms: Molecules, mechanisms, and physiology. Physiol. Rev. 2022, 102, 1327–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, D.; Taraphder, S. Structure and non-reactive dynamics of the dimeric catalytic domain of human carbonic anhydrase IX. Chem. Phys. Impact 2024, 8, 100625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterio, V.; Hilvo, M.; Di Fiore, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Pan, P.; Parkkila, S.; Scaloni, A.; Pastorek, J.; Pastorekova, S.; Pedone, C.; et al. Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the tumor-associated human carbonic anhydrase IX. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16233–16238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazokaitė, J.; Aspatwar, A.; Parkkila, S.; Matulis, D. An update on anticancer drug development and delivery targeting carbonic anhydrase IX. PeerJ 2017, 5, e4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. How many carbonic anhydrase inhibition mechanisms exist? J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerella, S.G.; Thacker, P.S.; Arifuddin, M.; Supuran, C.T. Tumor associated carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Rational approaches, design strategies, structure activity relationship and mechanistic insights. Eur. J. Med. Chem. Rep. 2024, 10, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatiparti, K.; Rauf, M.A.; Sau, S.; Iyer, A.K. Carbonic anhydrase-IX guided albumin nanoparticles for hypoxia-mediated triple-negative breast cancer cell killing and imaging of patient-derived tumor. Molecules 2020, 25, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antal, I.; Koneracka, M.; Kubovcikova, M.; Zavisova, V.; Jurikova, A.; Khmara, I.; Omastova, M.; Micusik, M.; Barathova, M.; Jelenska, L.; et al. Targeting of carbonic anhydrase IX-positive cancer cells by glycine-coated superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 205, 111893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T.; Winum, J.-Y. Carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors in cancer therapy: An update. Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzozowski, Z.; Sławiński, J.; Sączewski, F.; Innocenti, A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Synthesis and inhibition of the human cytosolic isozymes I and II and transmembrane isozymes IX, XII (cancer-associated) and XIV with 4-substituted 3-pyridinesulfonamides. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 2396–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maresca, A.; Temperini, C.; Vu, H.; Pham, N.B.; Poulsen, S.-A.; Scozzafava, A.; Quinn, R.J.; Supuran, C.T. Non-zinc mediated inhibition of carbonic anhydrases: Coumarins are a new class of suicide inhibitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3057–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowski, Z.; Sławiński, J.; Innocenti, A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Regioselective synthesis of novel 1-substituted 1, 4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-pyridinesulfonamides and their inhibition of the human cytosolic isozymes I and II and transmembrane cancer-associated isozymes IX and XII. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 3656–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Başar, Ö.; Başar, N.; Tuna, Y.; Yüksel, H.; Çoban, Ş. Acetazolamide induced severe hepatotoxicity. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2013, 125, 223–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerzada, M.N.; Khan, P.; Ahmad, K.; Hassan, M.I.; Azam, A. Synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation of tertiary sulfonamide derivatives of pyridyl-indole based heteroaryl chalcone as potential carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors and anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 155, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniwa, N.; Saito, Y. Pharmacogenomics of severe cutaneous adverse reactions and drug-induced liver injury. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 58, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: An update on experimental agents for the treatment and imaging of hypoxic tumors. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2021, 30, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, P.C.; Chia, S.; Bedard, P.L.; Chu, Q.; Lyle, M.; Tang, L.; Singh, M.; Zhang, Z.; Supuran, C.T.; Renouf, D.J.; et al. A phase 1 study of SLC-0111, a novel inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase IX, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 43, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Latest advances in specific inhibition of tumor-associated carbonic anhydrases. Future Med. Chem. 2023, 15, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrant, J.D.; McCammon, J.A. Molecular dynamics simulations and drug discovery. BMC Biol. 2011, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salo-Ahen, O.M.; Alanko, I.; Bhadane, R.; Bonvin, A.M.; Honorato, R.V.; Hossain, S.; Juffer, A.H.; Kabedev, A.; Lahtela-Kakkonen, M.; Larsen, A.S.; et al. Molecular dynamics simulations in drug discovery and pharmaceutical development. Processes 2020, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhum, L.H. Geometry optimization of coupling allin-Metformin using DFT/B3LYP molecular modelling technique: Geometry optimization of coupling allin-metformin using DFT/B3LYP molecular modelling technique. Iraqi J. Mark. Res. Consum. Prot. 2021, 13, 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafa, M.A.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Badran, A.-S. Spectroscopic elucidation, quantum chemical computations (FMO, HOMO–LUMO, MEP, NLO), and biological activity on some novel heterocyclic compounds using 3-substituted-6, 8-dimethylchromones. Synth. Commun. 2024, 54, 1523–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Addali, A.; El Boukili, A.; Boudad, L.; Taibi, M.; Guedira, T. Theoretical study of the phosphate units stability by the DFT B3LYP/6-311G quantum method. J. Chem. Technol. 2023, 31, 477–485. [Google Scholar]
- Naeem, N.; Mughal, E.U. Comprehensive assessment of 3-benzyloxyflavones as β-glucosidase inhibitors: In vitro, in vivo, kinetic, SAR and computational studies. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 10484–10500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidj, M.; Djafri, A.; Rahmani, R.; Belkafouf, N.E.H.; Boukabcha, N.; Djafri, A.; Chouaih, A. Molecular structure, experimental and theoretical vibrational spectroscopy,(HOMO-LUMO, NBO) investigation,(RDG, AIM) analysis,(MEP, NLO) study and molecular docking of ethyl-2-[41] acetate. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2023, 43, 2152–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, N.; Shakoor, B.; Yaqoob, N.; Parveen, S.; Brogi, S.; Mohammad Salamatullah, A.; Rashid, M.; Bourhia, M. A virtual insight into mushroom secondary metabolites: 3D-QSAR, docking, pharmacophore-based analysis and molecular modeling to analyze their anti-breast cancer potential. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2025, 43, 4512–4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, C.; Harris, A.L. Hypoxia inducible carbonic anhydrase IX, marker of tumour: Hypoxia, survival pathway and therapy target. Cell Cycle 2004, 3, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatovicova, M.; Jelenska, L.; Hulikova, A.; Csaderova, L.; Ditte, Z.; Ditte, P.; Goliasova, T.; Pastorek, J.; Pastorekova, S. Carbonic anhydrase IX as an anticancer therapy target: Preclinical evaluation of internalizing monoclonal antibody directed to catalytic domain. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 3255–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadood, A.; Ahmed, N.; Shah, L.; Ahmad, A.; Hassan, H.; Shams, S. In-silico drug design: An approach which revolutionarised the drug discovery process. OA Drug Des Deliv. 2013, 1, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, L.; Costa, B.; Pereira, M.; Silva, A.; Santos, J.; Saldanha, L.; Silva, I.; Magalhães, P.; Schmidt, S.; Vale, N. Advancing precision medicine: A review of innovative In Silico approaches for drug development, clinical pharmacology and personalized healthcare. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitans, J.; Kazaks, A.; Balode, A.; Ivanova, J.; Zalubovskis, R.; Supuran, C.T.; Tars, K. Efficient expression and crystallization system of cancer-associated carbonic anhydrase isoform IX. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 9004–9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S. Safety of celecoxib versus traditional nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in older patients with arthritis. J. Pain Res. 2018, 11, 3211–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.-W.; Zhang, X.-M.; Zhou, J.-N.; Zhou, X.; Ma, G.-J.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Yu, J.; Feng, J.-F.; Chen, S.-Q. Analysis of small fragment deletions of the APC gene in Chinese patients with familial adenomatous polyposis, a precancerous condition. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 4915–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bozdag, M.; Carta, F.; Ceruso, M.; Ferraroni, M.; McDonald, P.C.; Dedhar, S.; Supuran, C.T. Discovery of 4-hydroxy-3-(3-(phenylureido) benzenesulfonamides as SLC-0111 analogues for the treatment of hypoxic tumors overexpressing carbonic anhydrase IX. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 6328–6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, A.B.; Hpc, L. Introduction to AutoDock and AutoDock Tools; Louisiana State University: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Tresanco, M.S.; Valdés-Tresanco, M.E.; Valiente, P.A.; Moreno, E. gmx_MMPBSA: A new tool to perform end-state free energy calculations with GROMACS. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 6281–6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juma, J.M.; Vuai, S.A. Computational studies of the thermodynamic properties, and global and reactivity descriptors of fluorescein dye derivatives in acetonitrile using density functional theory. J. Chem. Res. 2021, 45, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, D.; Arasu, M.A.; Girija, A.M. Spectroscopic (FTIR, UV-Vis, NMR) investigations, DFT predictions of global reactivity descriptors and efficient corrosion inhibitors of N-carbobenzoxy-L-ValineSuccinimidyl Ester. J. Indian. Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 100400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
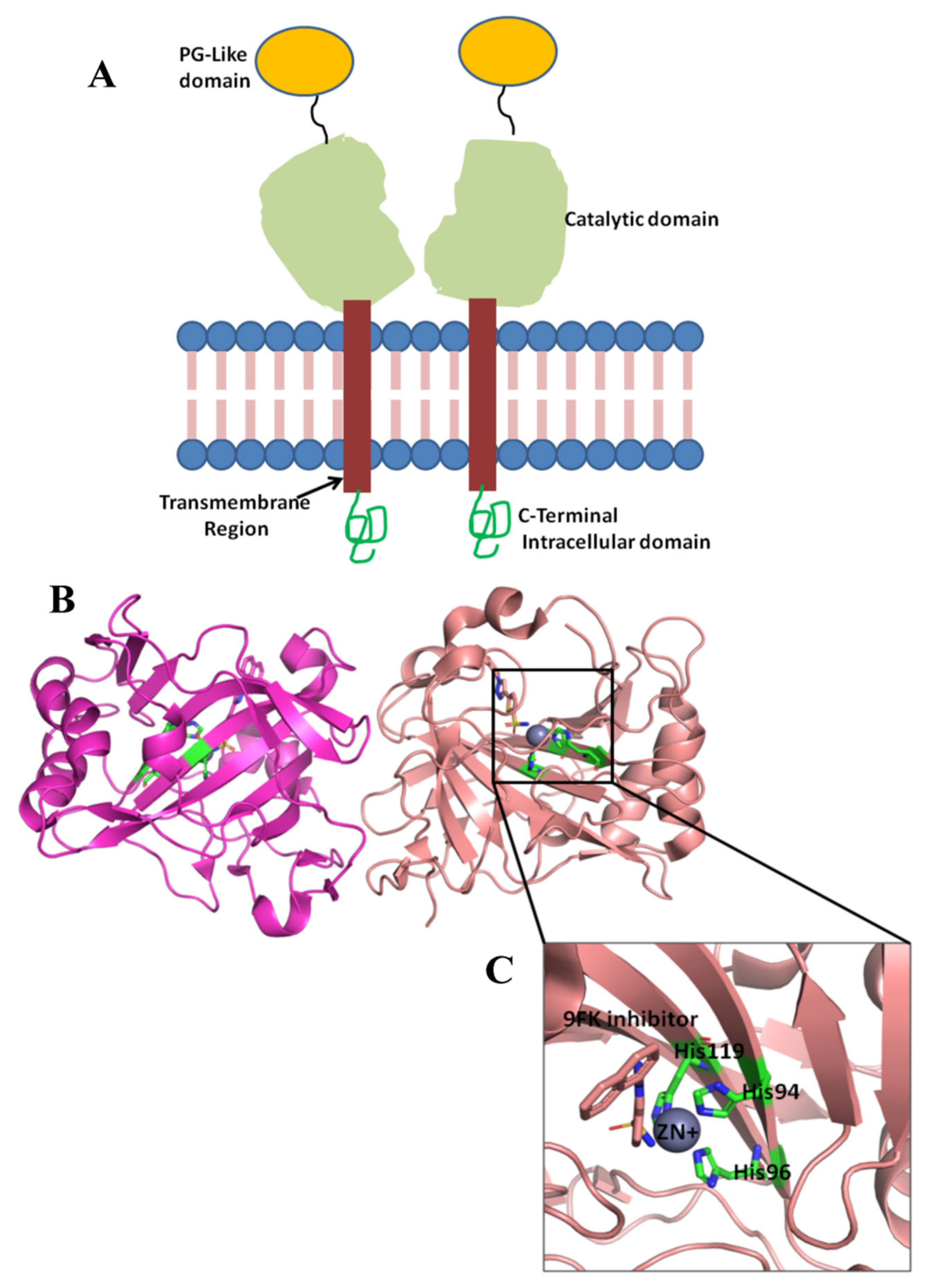
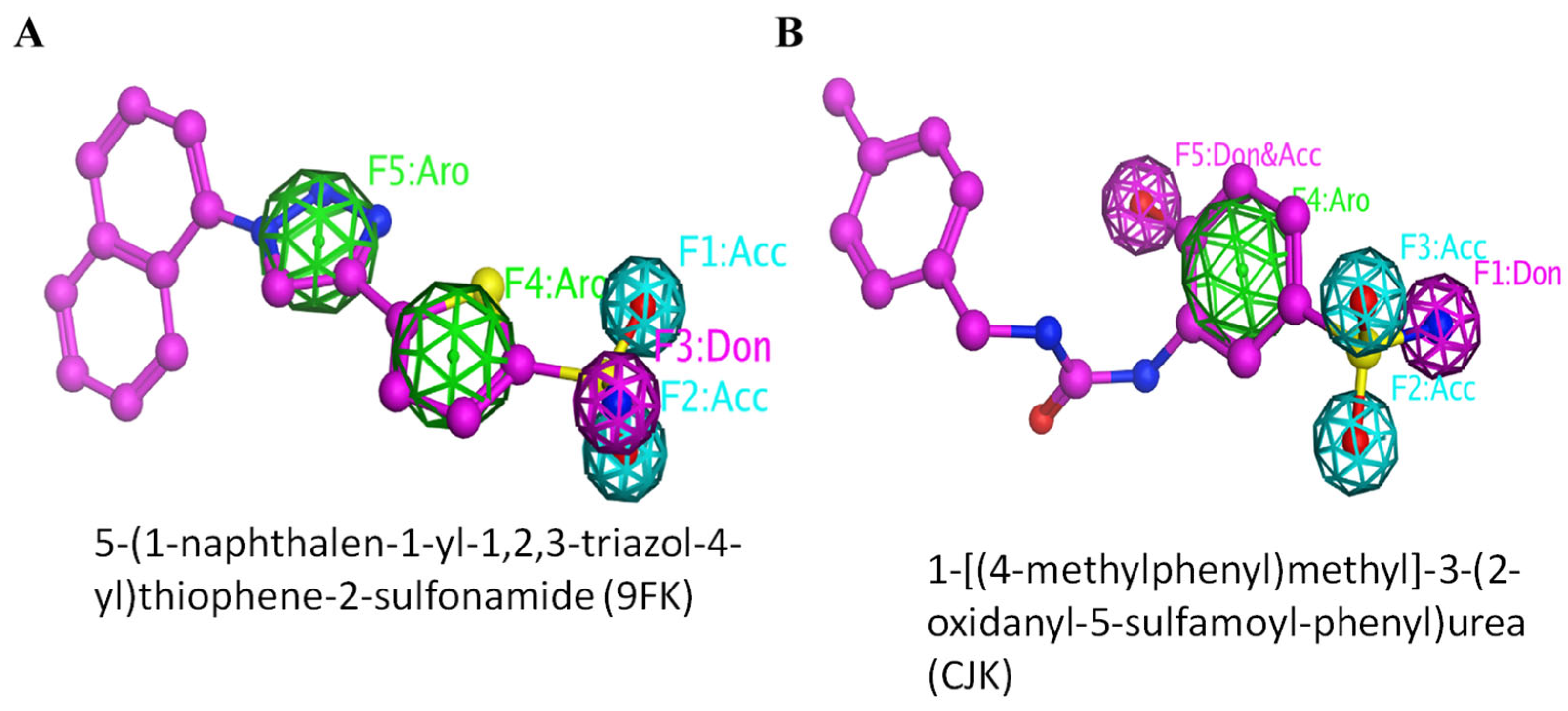

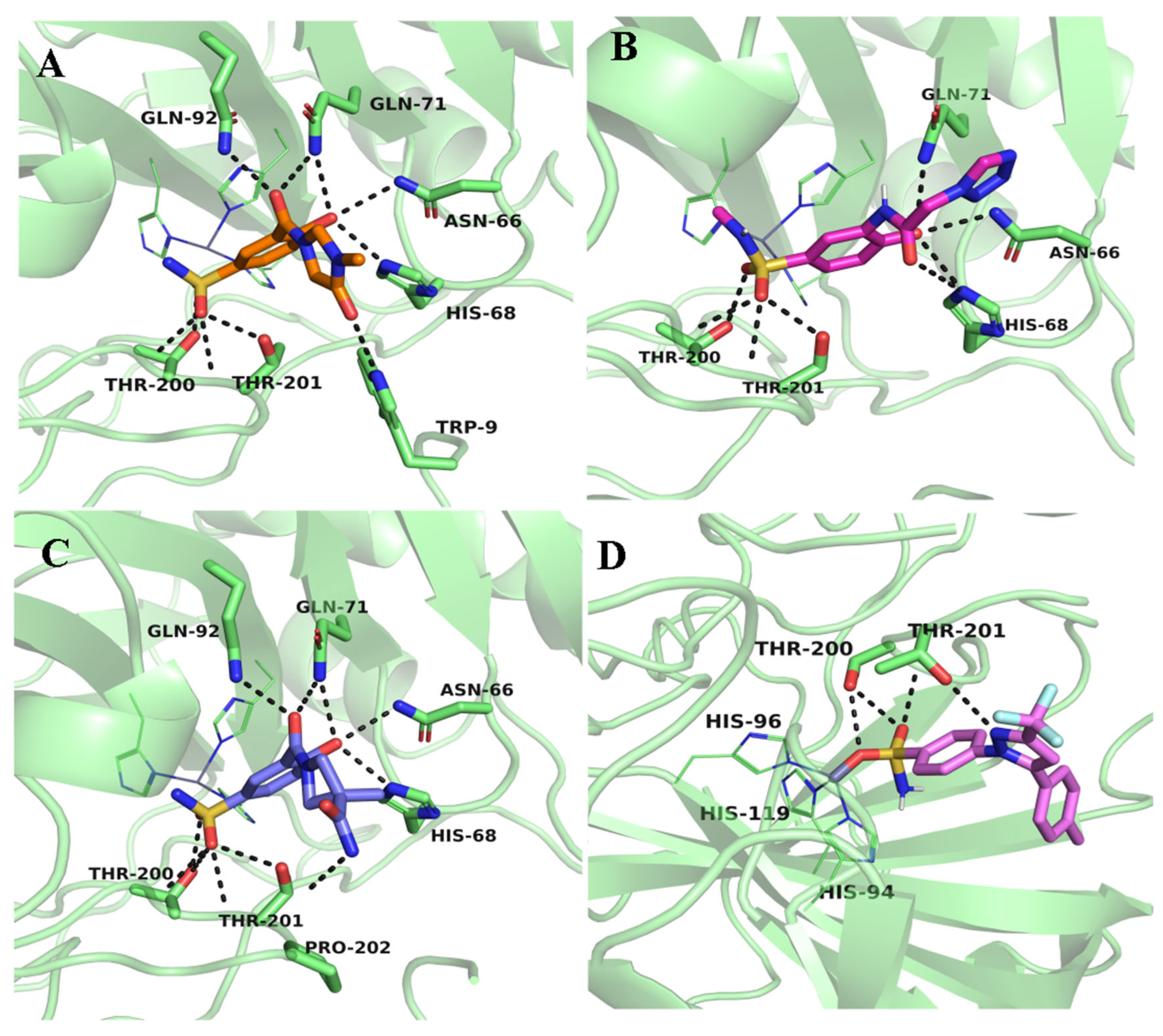
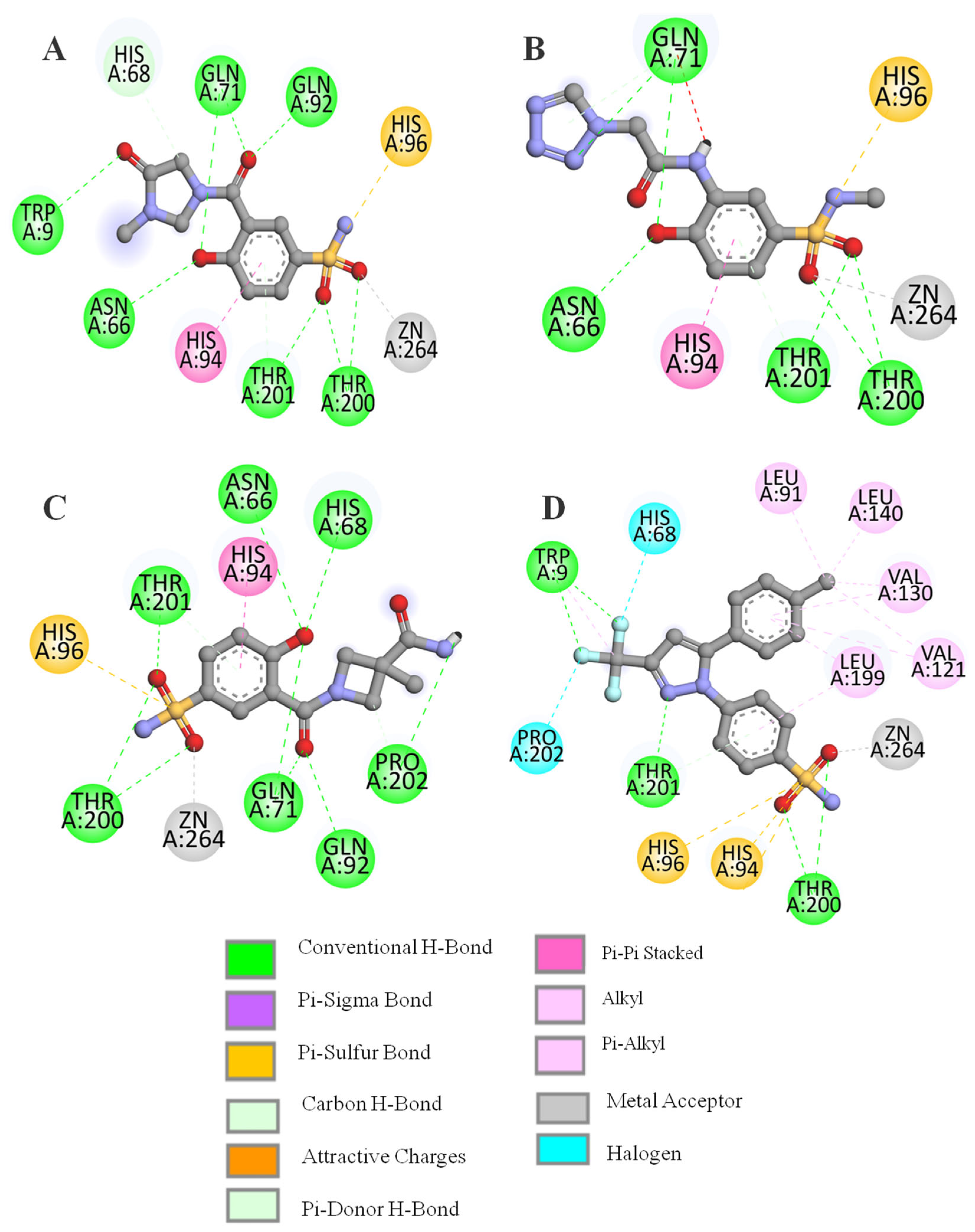

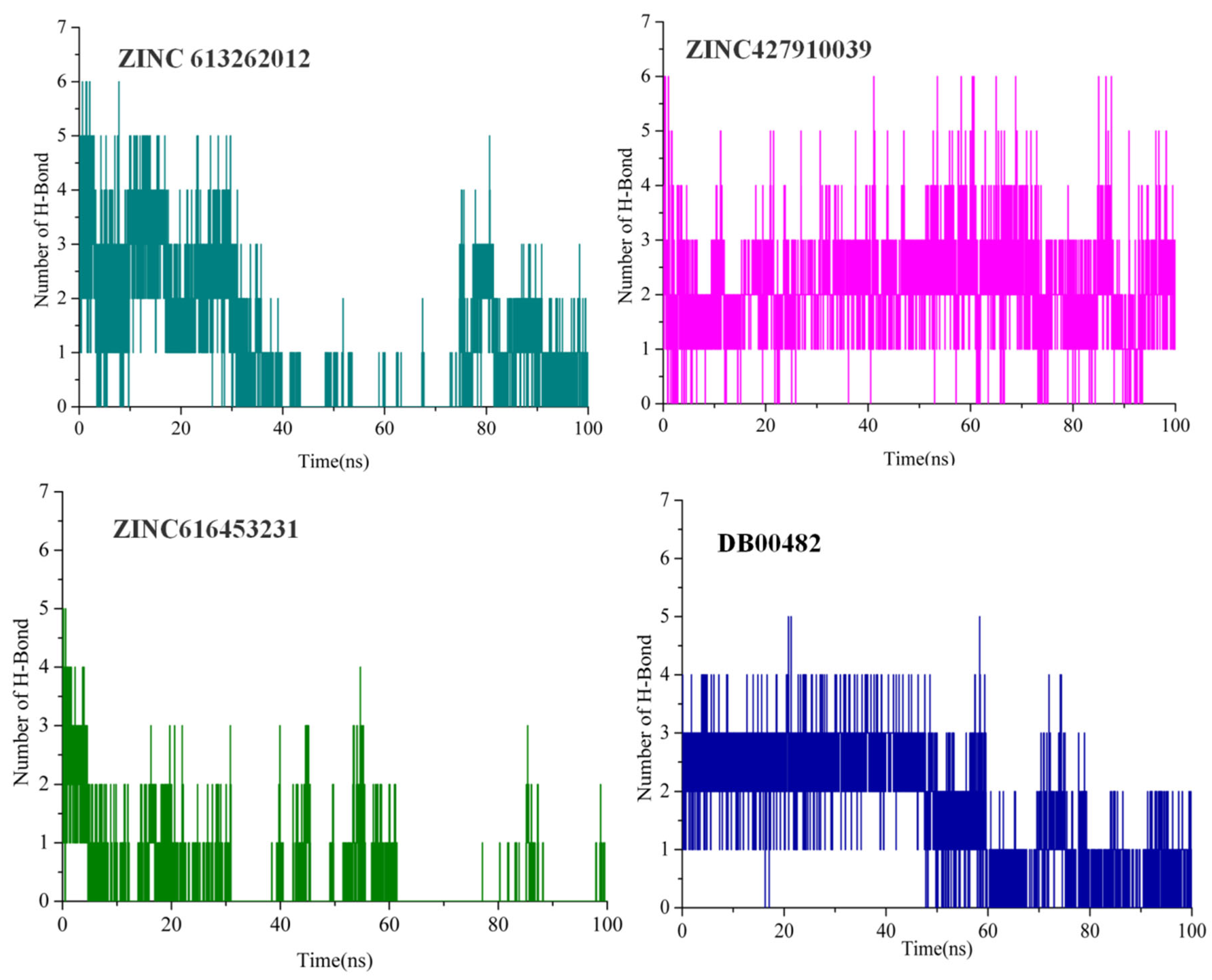
| Compound | Binding Score Kcal/mol | Residues Involved in H-Bonds | Total Number of H-Bonds Formed |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9FK | −8.2 | Thr200, Thr201 | 5 |
| CJK | −8.3 | Thr200 | 2 |
| ZINC613262012 | −8.0 | Trp9, Gln71, Asn66, His86, Gln92, Thr200, and Thr201 | 10 |
| ZINC427910039 | −8.0 | Gln71, Asn66, Thr200, and Thr201 | 8 |
| ZINC616453231 | −8.1 | Asn66, His68, Gln71, Gln92, Thr200, Thr201, and pro202 | 11 |
| DrugBank ID (DB00482) | −8.7 | Thr200, Thr201 | 4 |
| Compound | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | LogP | H-Bond Donors | H-Bond Acceptors | TPSA (Å2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9FK | 356.432 | 2.796 | 1 | 6 | 127 |
| CJK | 335.385 | 1.67 | 4 | 5 | 130 |
| ZINC613262012 | 299.308 | −1.089 | 1 | 5 | 123 |
| ZINC427910039 | 312.311 | −1.075 | 3 | 8 | 139 |
| ZINC616453231 | 313.335 | −1.013 | 2 | 5 | 146 |
| DB00482 | 381.379 | 3.514 | 1 | 4 | 77 |
| Toxicity | 9FK | CJK | ZINC 613262012 | ZINC 427910039 | ZINC 616453231 | DB00482 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatotoxicity | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Active (0.51) | Inactive | Inactive |
| Neurotoxicity | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive |
| Immogenicity | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive |
| Carcinogenicity | Active | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive |
| Cytotoxicity | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive |
| Mutagenicity | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive |
| Toxicity Class | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 4 |
| LD50 | 400 mg/kg | 5000 mg/kg | 1000 mg/kg | 3500 mg/kg | 1000 mg/kg | 1400 mg/kg |
| Compound | RMSD (nm) | RMSF (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| Apo CA IX | 0.174478 | 0.12 |
| 9FK | 0.147564 | 0.12 |
| CJK | 0.166459 | 0.12 |
| ZINC613262012 | 0.184293 | 0.12 |
| ZINC427910039 | 0.158802 | 0.10 |
| ZINC616453231 | 0.150055 | 0.10 |
| DB00482 | 0.136467 | 0.11 |
| Compounds | ΔEelec | ΔEvdw | ΔEGB | ΔESURF | ΔGSOLV | ΔGGAS | ΔTOTAL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9FK | −23.34 | −12.29 | 26.84 | −1.92 | 24.92 | −35.63 | −10.71 |
| CJK | −3.70 | −8.05 | 7.92 | −1.16 | 6.13 | −11.75 | −5.62 |
| ZINC613262012 | −18.94 | −15.36 | 25.83 | −2.45 | 23.38 | −34.30 | −10.92 |
| ZINC427910039 | −26.60 | −28.81 | 40.78 | −4.14 | 36.64 | −55.41 | −18.77 |
| ZINC616453231 | −1.88 | −2.85 | 3.81 | −0.36 | 3.44 | −4.72 | −1.28 |
| DB00482 | −5.37 | −23.01 | 19.92 | −3.83 | 16.09 | −28.38 | −12.29 |
| Formula | ZINC613262012 | DB00482 | ZINC427910039 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dipole moment | 5.009836 | 8.795973 | 3.979740 | |
| Electronic energy | −1365.331849 | −1668.442782 | −1415.560093 | |
| LUMO | −0.07229 | −0.08551 | −0.06934 | |
| HOMO | −0.26193 | −0.26041 | −0.25681 | |
| Energy gap (eV) | EHOMO − ELUMO | 0.18964 | 0.17490 | 0.18747 |
| Electron affinity (A) | A = −ELUMO | 0.07229 | 0.08551 | 0.06934 |
| Ionization potential (I) | I = −EHOMO | 0.26193 | 0.26041 | 0.25681 |
| Chemical potential (μ) | μ = 1/2 (I + A) | 0.16711 | 0.17296 | 0.16308 |
| Electronegativity (χ) | χ = −1/2 (I + A) | −0.16711 | −0.17296 | −0.16308 |
| Chemical hardness (η) | η = 1/2 (I − A) | 0.09482 | 0.08745 | 0.09374 |
| Chemical softness (S) | S = 1/ η | 10.5463 | 11.4351 | 10.6684 |
| Electrophilicity index (ω) | ω = 2 (μ2/η) | 0.14726 | 0.17104 | 0.14185 |
| Nucleophilicity index (N) | N = 1/ω | 6.7909 | 5.8465 | 7.0495 |
| Additional electronic charge | =−μ/η | −1.7624 | −1.9778 | −1.7397 |
| Isoforms | Compound |
Docking Score (Kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| CA II (Carbonic Anhydrase II) | Native ligand | −8.9 |
| ZINC613262012 | −8.1 | |
| ZINC427910039 | −7.8 | |
| DB00482 | −8.4 | |
| CA I (Carbonic Anhydrase I) | Native ligand | −6.5 |
| ZINC613262012 | −7.2 | |
| ZINC427910039 | −7.3 | |
| DB00482 | −7.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almansour, N.M. Computational Discovery of Selective Carbonic Anhydrase IX (CA IX) Inhibitors via Pharmacophore Modeling and Molecular Simulations for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178465
Almansour NM. Computational Discovery of Selective Carbonic Anhydrase IX (CA IX) Inhibitors via Pharmacophore Modeling and Molecular Simulations for Cancer Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178465
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmansour, Nahlah Makki. 2025. "Computational Discovery of Selective Carbonic Anhydrase IX (CA IX) Inhibitors via Pharmacophore Modeling and Molecular Simulations for Cancer Therapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178465
APA StyleAlmansour, N. M. (2025). Computational Discovery of Selective Carbonic Anhydrase IX (CA IX) Inhibitors via Pharmacophore Modeling and Molecular Simulations for Cancer Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178465







