Multi-Omics Platforms Reveal Synergistic Intestinal Toxicity in Tilapia from Acute Co-Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics, Sulfamethoxazole, and BDE153
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
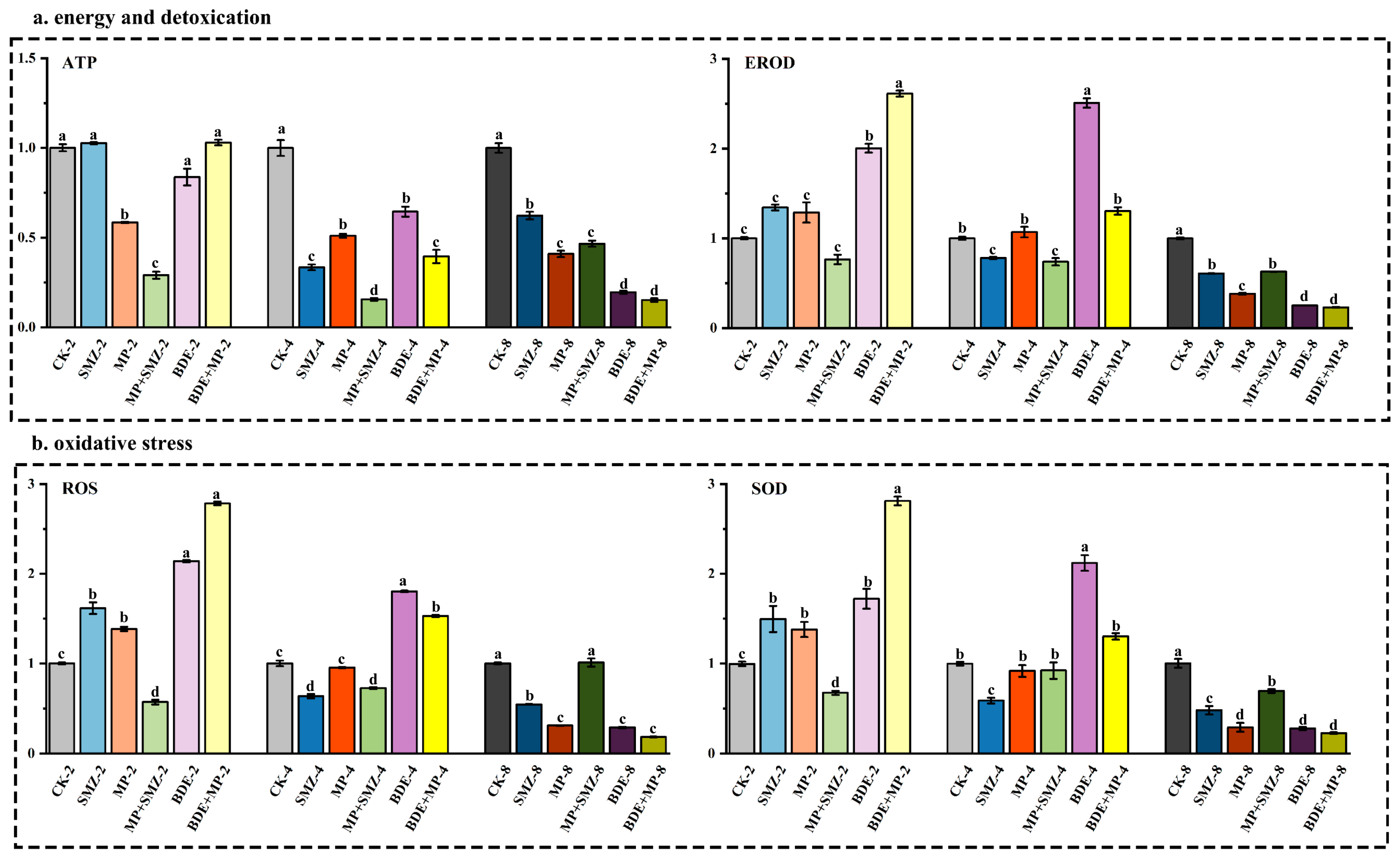
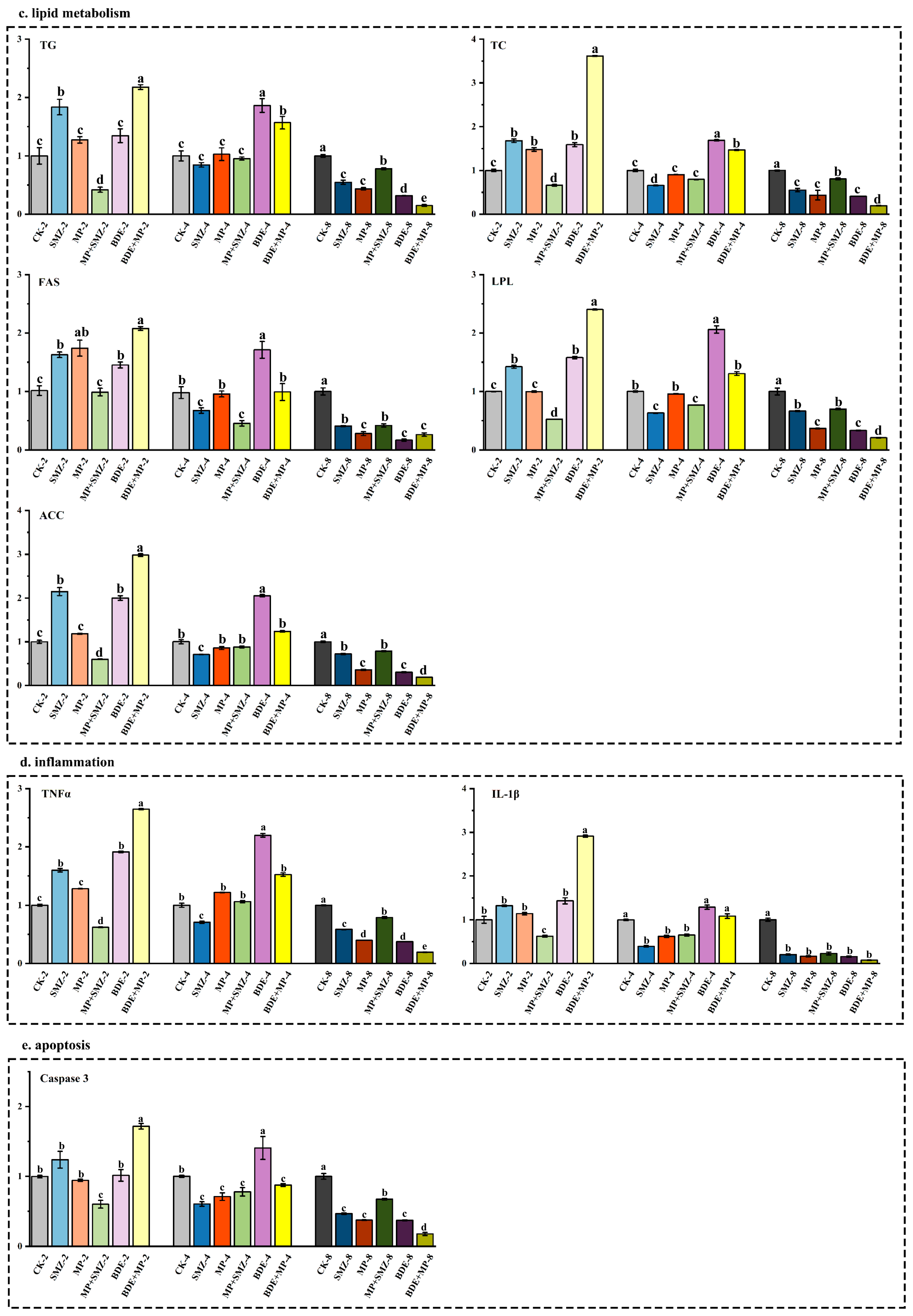
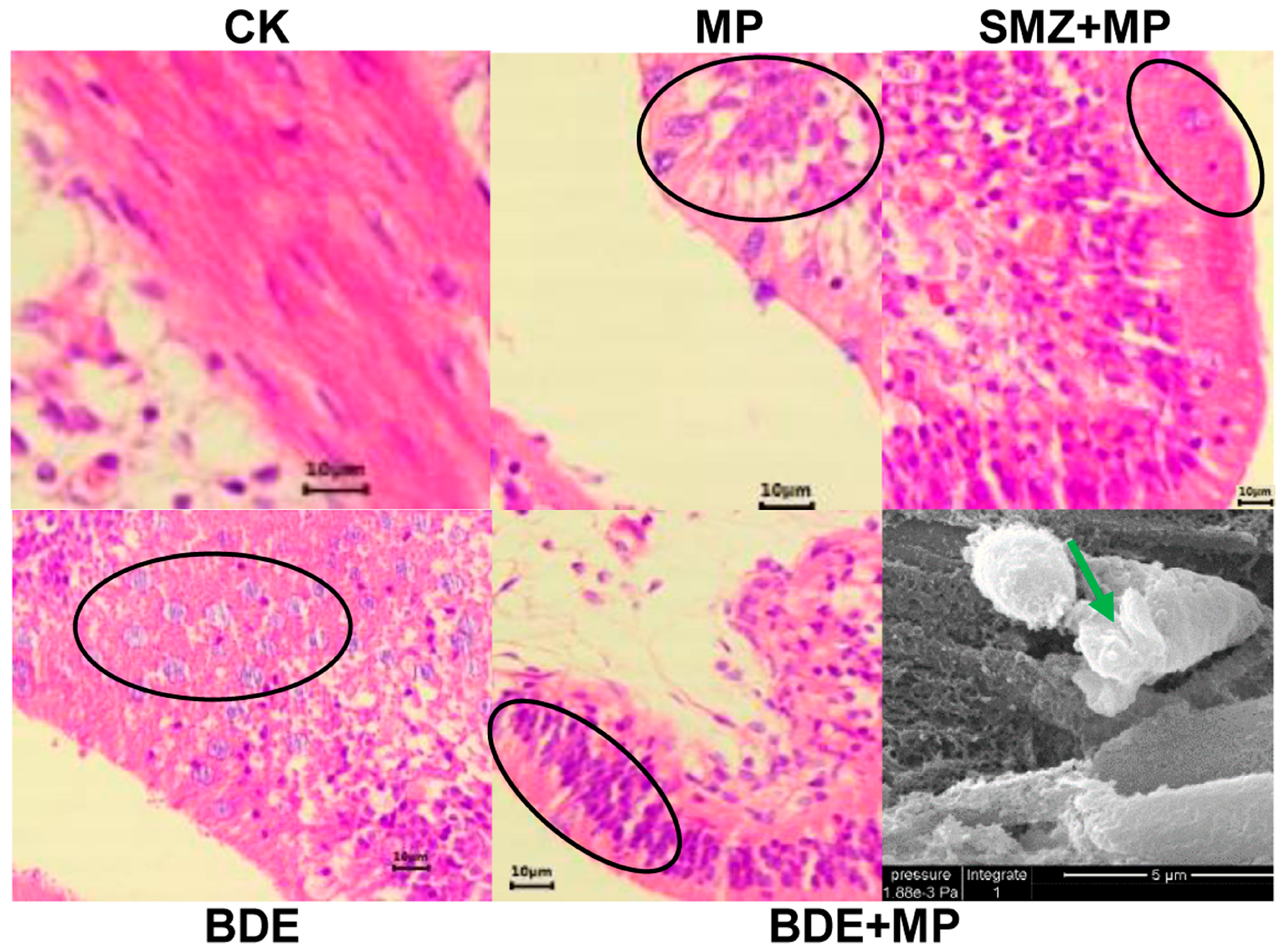
2.1. Biological Responses and Enzymatic Activity
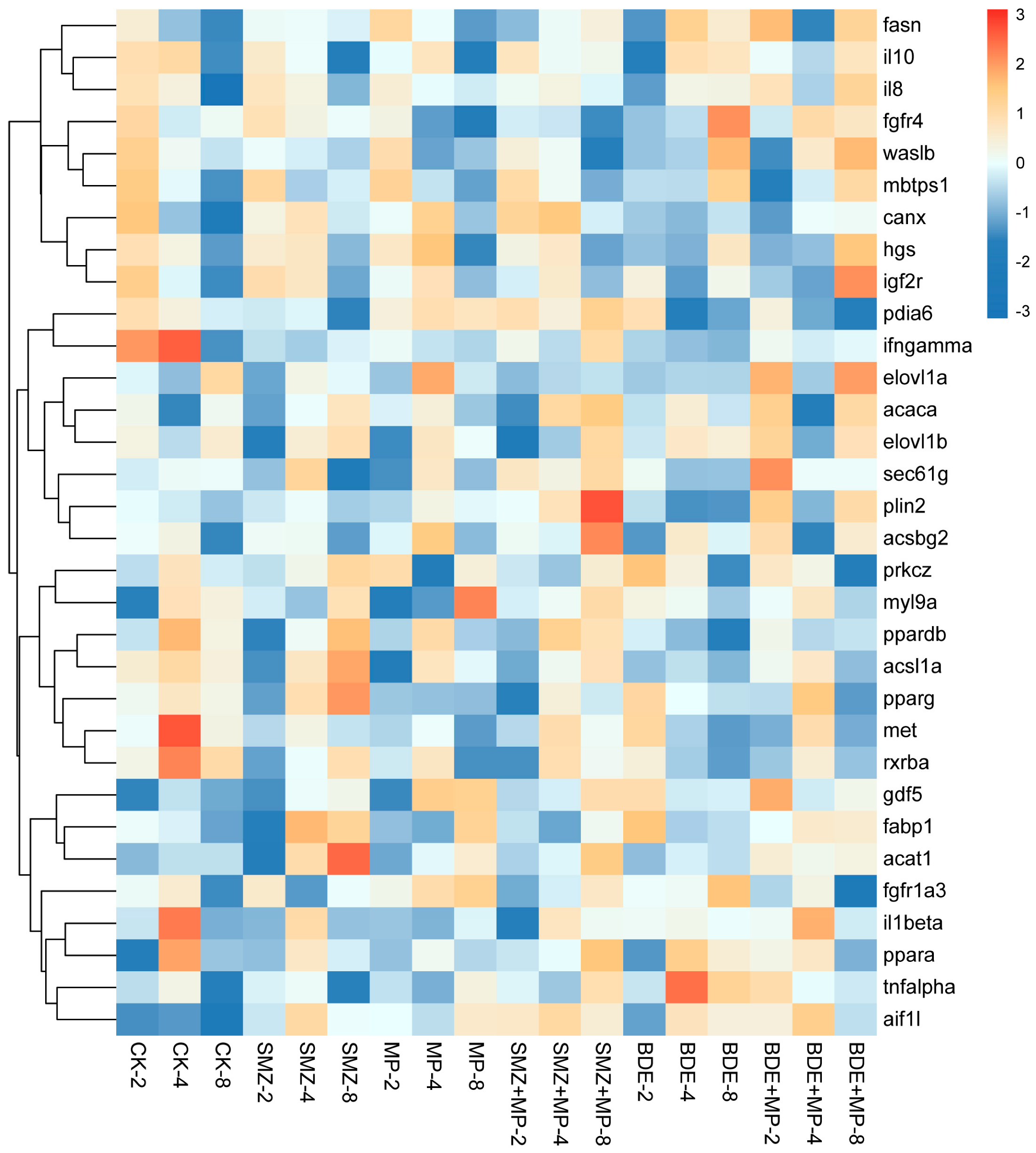
2.2. Transcriptomics
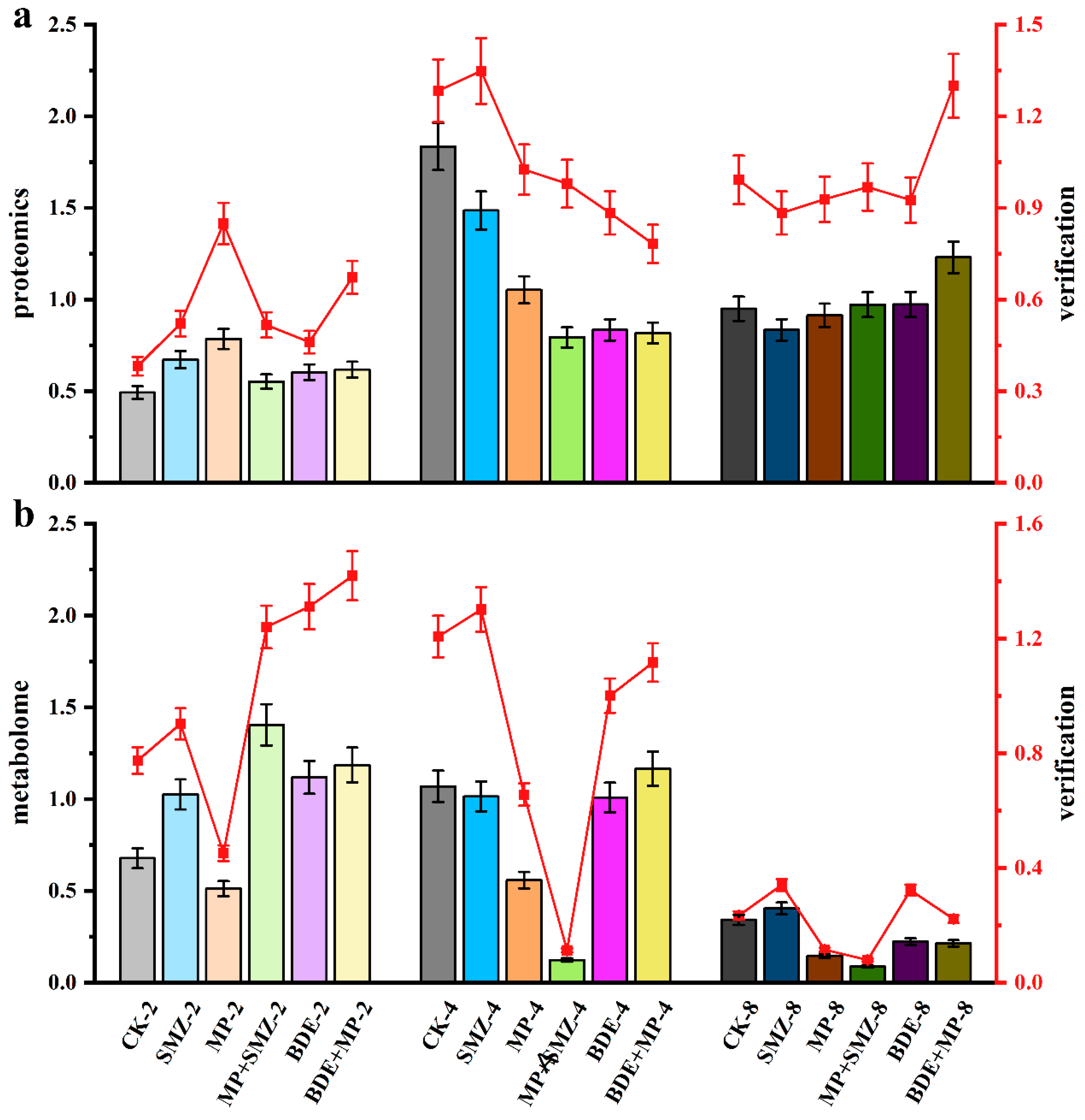
2.3. Proteomics
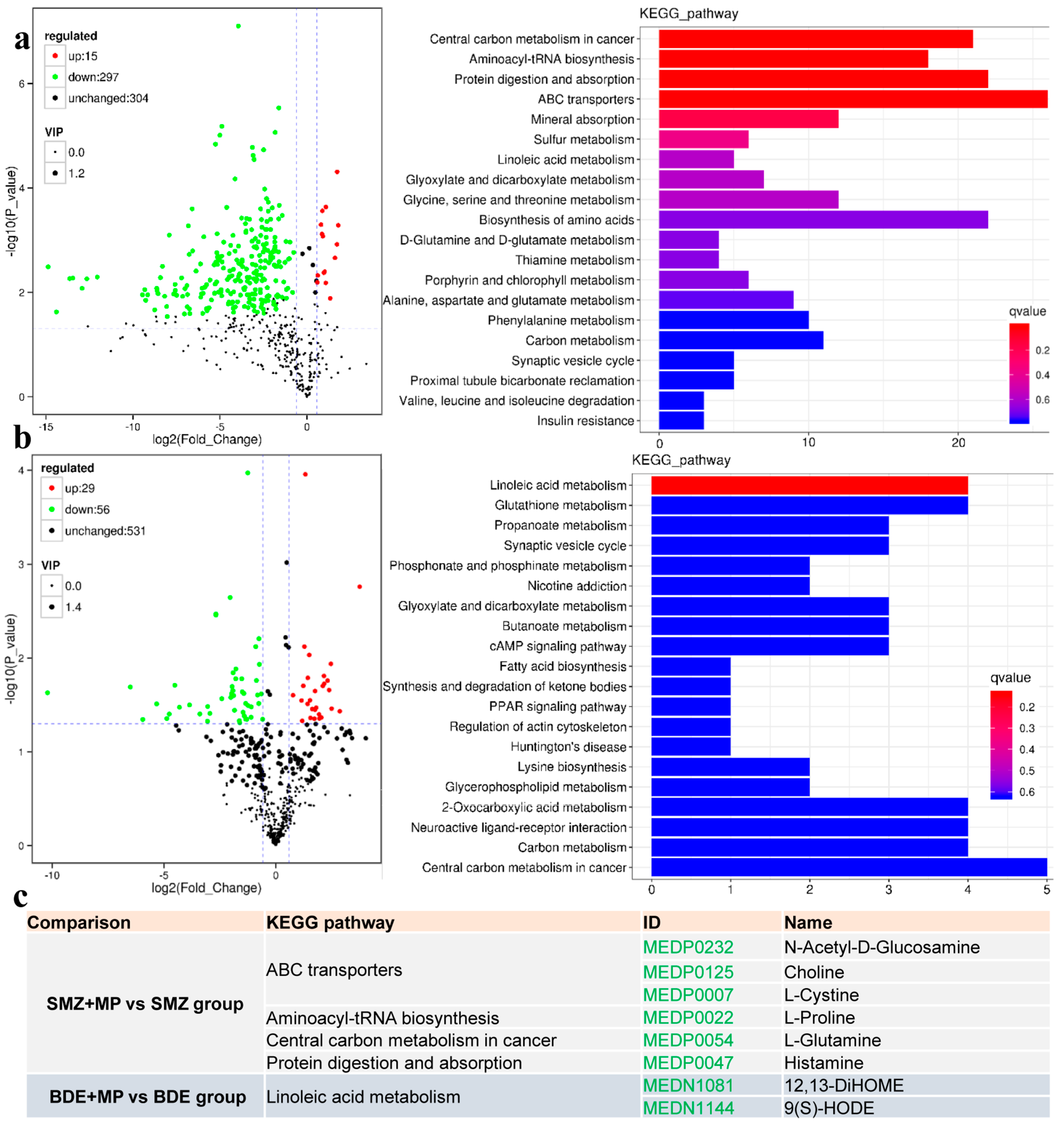
2.4. Metabolome
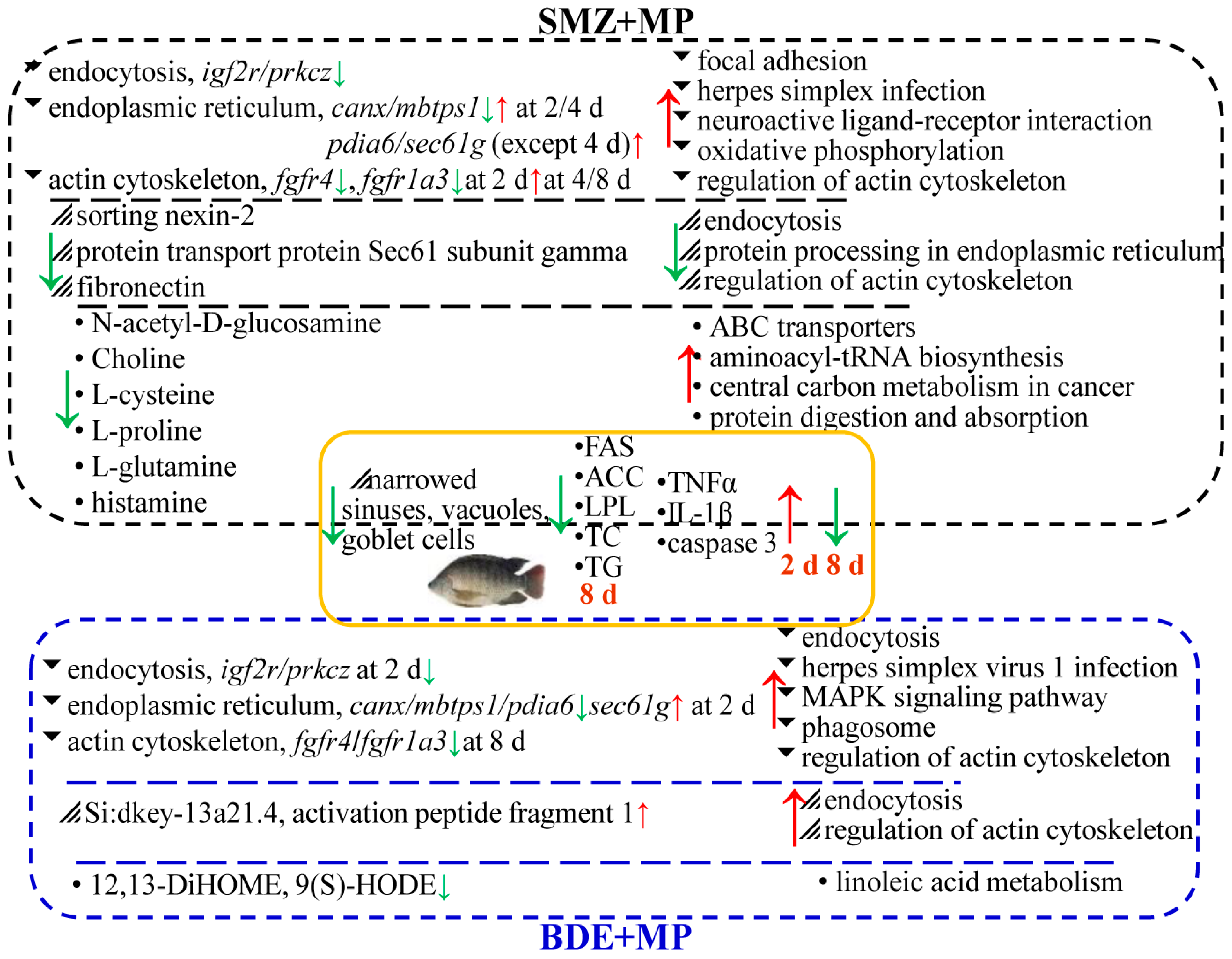
2.5. The Combined Analysis
3. Discussion
3.1. Transcriptomic and Proteomic Pathway Enrichment Highlights Metabolic and Inflammatory Disruptions
3.2. Lipid Metabolism Alterations Revealed by qPCR and Metabolomic Analysis
3.3. Distinct Roles of SMZ and BDE153 in Co-Exposure with Microplastics
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection and Experimental Setup
4.2. Histopathological and Biological Determination
4.3. Multi-Omics and the Combined Analysis
4.4. Data Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Appendix A
| Pathway | Gene | Primers | Product (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| reference gene | β-actin | F:GGTGGGTATGGGTCAGAAAGA R:GCTGTCGTGAAGGAGTAG | 124 |
| endocytosis | hgs | F:ATCCCAAAACCGATCCCACC R:CTTTCCACGGGCTGACTGAT | 241 |
| waslb | F:TTGTCATCTTCGGTCGTCGG R:ACTGGGAACGTGTGCTATGG | 179 | |
| igf2r | F:AAACGTGCACGCACTTCTTC R:ATTTCCACAGGTGGTCCGTC | 280 | |
| prkcz | F:ACCACACAACTGTGCAGTGA R:GCATAGCTGCCACGTCCTAT | 153 | |
| protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | canx | F:AAGCAGCGACGGGAAACTAA R:TCCTGCAGGTTCGAGTGTTC | 181 |
| mbtps1 | F:TGCTCCTCCTTTCTGCATGG R:ATGTACAGGCTGCGAGCTTT | 256 | |
| pdia6 | F:CATGAGAGACACCTGCGGTT R:GTCACATCAGGTGGGACGTT | 293 | |
| sec61g | F:GGGGTGATCTGTGTCGTAGC R:TCCCATGATCGCAAACCCAA | 226 | |
| regulation of actin cytoskeleton | myl9a | F:AATCCGAAACGCCTTCACCT R:TGGCTCCGTGCTTTAGGATG | 197 |
| fgfr1a3 | F:TTTTGAAGCACCCCCACACT R:AGGGACGGACTAGCATCACT | 257 | |
| fgfr4 | F:TCACCCACAGAAGATGACGC R:CACTGCCGTGGTGTTTTCAG | 160 | |
| inflammation | il10 | F:TTACCTGGACACGGTTCTGC R:GTGACTTAAAGCAGCGCGAG | 200 |
| ifnγ | F:CCAACAACTCAGGCTCGCTA R:TGCTCATGGTAGCGGTGTTT | 150 | |
| tnfα | F:CAGGATCTGGCGCTACTCAG R:TAGCTGGTTGGTTTCCGTCC | 184 | |
| il1β | F:CCTACACCCATCGCTGAGAC R:GGGTAGCGGACAGACATGAG | 224 | |
| il8 | F:GCACTGCCGCTGCATTAAG R:GCAGTGGGAGTTGGGAAGAA | 147 | |
| aif1l | F:TGGGTCTCAAGCGGATGATG R:CACTTAAGGAAGGCTGGCGA | 248 | |
| met | F:GTCCTGCTCAACACCACGTA R:CGAGTCTCATCCATCACCCG | 203 | |
| gdf5 | F:AAGAGATCAAAGCGCGGTCA R:CGATGATCCAGTCGTCCCAG | 228 | |
| lipid metabolism | fasn | F:CGCCATAGCGCTCAGTAAGA R:CTTTGCCTTGTGTGTGGAGC | 164 |
| acaca | F:GCCTGCATTAGCATTCCAGC R:TACCAGATCAGAGTGGCGGA | 178 | |
| fabp1 | F:TGACAATCACAACCGGCTCA R:CACCAGTTCCGTGACTGACA | 164 | |
| rxrba | F:ACAGCCGTTCTCCACTCTTG R:GGCGGACCCCAAAATTCAAC | 265 | |
| acat1 | F:ACGGAGGAGTGAGGATGGAA R:GCTCTGCTGCGGCTATAAGA | 163 | |
| ppara | F:CGGTGTTTACGAAGCCCTCT R:GCTCCAGAGAGTTGAAGCGT | 176 | |
| pparg | F:CCGCAGAGTGAAGAACACCT R:ACCTGATGGTGCGTCTGAAG | 268 | |
| ppardb | F:TGGTGTGCACGAGGCTATTT R:TTAGCCCAGGTCGATCTCCA | 242 | |
| acsl1a | F:GAGAGGTGTGCGTCAAAGGA R:GTTGCTGCGCACATAGATGG | 227 | |
| elovl1a | F:TGGTGATCTCTACCTGCCCA R:GTACGCCCAAGCAACAAAGG | 155 | |
| elovl1b | F:GGGTTACCAAAAACGGCACC R:GGAAGTCACTGACCGCATCA | 225 | |
| plin2 | F:CTCACAGGTGTACGCCAACT R:CGTAGGTGCTGCTGTCTTCA | 227 | |
| acsbg2 | F:CATCGTGGTGGAGAACCACA R:GGTTAGGTTGTCGTGGCTGA | 280 |
References
- Shi, J.; Dong, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yin, T.; He, W.; An, T.; Tang, Y.; Hou, X.; Chong, S.; Chen, D.; et al. Groundwater antibiotics and microplastics in a drinking-water source area, northern China: Occurrence, spatial distribution, risk assessment, and correlation. Environ. Res. 2022, 210, 112855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, A.; Nishil, B.; Thatikonda, S. Experimental and numerical elucidation of the fate and transport of antibiotics in aquatic environment: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Hou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, T.; Wang, Y.; Xing, M. Polystyrene microplastics mediate cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy in the G2/M phase through ROS in grass carp kidney cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2024, 39, 1923–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Cui, H.; Jia, X.; Huang, X. Occurrence and ecotoxicity of sulfonamides in the aquatic environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Gong, L.; Cheng, Y.; Yuan, Q.; He, Y. Combined toxicity of polystyrene microplastics and sulfamethoxazole on zebrafish embryos. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 19273–19282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, H.A.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Jia, D.; Liu, X.; Ding, C.; Guo, J.; Yao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Sun, J. Combined influence of the nanoplastics and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons exposure on microbial community in seawater environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 173772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Maryam, B.; Ji, Z.; Sun, J.; Liu, X. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers as hitchhikers on microplastics: Sorption behaviors and combined toxicities to Epinephelus moara. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 252, 106317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Lai, C.; Xu, F.; Huang, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, X.; Xu, M.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; et al. A review of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and novel brominated flame retardants in Chinese aquatic environment: Source, occurrence, distribution, and ecological risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, H.; Hu, J.; Sun, Y.; Xu, G. Endocytosis, endoplasmic reticulum, actin cytoskeleton affected in tilapia liver under microplastics and BDE153 co-exposure. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2025, 289, 110117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, N.; Takada, N.; Takahashi, M.; Yeo, B.G.; Oya, Y.; Watanabe, I.; Fujita, Y.; Takada, H.; Mizukawa, K. Bioaccumulation and metabolism of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in coenobitid hermit crabs from marine litter-polluted beaches in remote islands. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 190, 114812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhu, W.; Wu, S.; Hou, H.; Cheng, L.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Lin, X.; Xue, Z. Distribution and changes in microplastics in Taihu Lake and cyanobacterial blooms formed by the aggregation of Microcystis colonies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 107331–107340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Wen, H.; Liu, J.; Wu, C.; Mai, L.; Zeng, E. Hydrophobic organic contaminants affiliated with polymer-specific microplastics in urban river tributaries and estuaries. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 899, 166415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zhu, L.; Bian, J.; Fang, S. Bioaccumulation and metabolism of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in carp (Cyprinus carpio) in a water/sediment microcosm: Important role of particulate matter exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2951–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liao, J.; Fang, D.; Wang, L.; Zeng, R.; Xiong, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; et al. Exposure levels and determinants of placental polybrominated diphenyl ethers in Chinese pregnant women. Environ. Res. 2024, 241, 117615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Lu, G.; Liu, J.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Z. Bioaccumulation, distribution and metabolism of BDE-153 in the freshwater fish Carassius auratus after dietary exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 108, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Hale, R.C.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Wu, Y.; Liang, X.; Liu, Y.; Tan, H.; Chen, D. Sorption of representative organic contaminants on microplastics: Effects of chemical physicochemical properties, particle size, and biofilm presence. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 251, 114533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Lu, X.; Hu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xu, G. Chlorella alleviates the intestinal damage of tilapia caused by microplastics. Chemosphere 2024, 353, 141644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Guo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Hou, L.; Ma, C.; Xing, M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation as a novel mechanism of polystyrene microplastics (PS-MPs)-induced pulmonary inflammation in chickens. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2024, 25, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marana, M.H.; Poulsen, R.; Thormar, E.A.; Clausen, C.G.; Thit, A.; Mathiessen, H.; Jaafar, R.; Korbut, R.; Hansen, A.M.B.; Hansen, M.; et al. Plastic nanoparticles cause mild inflammation, disrupt metabolic pathways, change the gut microbiota and affect reproduction in zebrafish: A full generation multi-omics study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424 Pt D, 127705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohoro, C.R.; Adeniji, A.O.; Okoh, A.I.; Okoh, O.O. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the environmental systems: A review. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 1229–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Tang, N.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Chen, D. Dietary exposure to 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) induces oxidative damage promoting cell apoptosis primarily via mitochondrial pathway in the hepatopancreas of carp, Cyprinus carpio. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 274, 116192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Lu, G.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Yan, Z. Aged microplastics change the toxicological mechanism of roxithromycin on Carassius auratus: Size-dependent interaction and potential long-term effects. Environ. Int. 2022, 169, 107540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Booth, A.M.; Zhu, L.; Sui, Q.; Chen, B.; Qu, K.; Xia, B. New insights into the impact of polystyrene micro/nanoplastics on the nutritional quality of marine jacopever (Sebastes schlegelii). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Zhang, H.; Shi, H.; Peng, Y.; Han, M.; Hu, T.; Liao, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, G. Enhanced hepatotoxicity in zebrafish due to co-exposure of microplastics and sulfamethoxazole: Insights into ROS-mediated MAPK signaling pathway regulation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 278, 116415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Hu, Q.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, C.; Li, X. Multi-omics analysis of oxidative stress and apoptosis in hepatopancreas cells induced by Polyascus gregaria parasitizing the Eriocheir sinensis. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2023, 143, 109180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, J.; Jin, W.; Hu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xu, G. Apoptosis, MAPK signaling pathway affected in tilapia liver following microplastics and sulfamethoxazole co-exposure. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2025, 53, 101370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Cao, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D. Activation of FGF signal in germline mediates transgenerational toxicity of polystyrene nanoparticles at predicted environmental concentrations in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 451, 131174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Yang, K.; Cheng, X.; Guo, C.; Xing, X.; Sun, H.; Liu, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, D. Accumulation of polystyrene microplastics induces liver fibrosis by activating cGAS/STING pathway. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Tang, H.; Hu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xu, G. Integrated transcriptomics and proteomics analyses reveal the ameliorative effect of hepatic damage in tilapia caused by microplastics with chlorella addition. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 2024, 285, 117076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanpradit, P.; Byeon, E.; Lee, J.S.; Jeong, H.; Kim, H.S.; Peerakietkhajorn, S.; Lee, J.S. Combined effects of nanoplastics and elevated temperature in the freshwater water flea Daphnia magna. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.; Zhu, D.; Luo, Y.; He, D.; Zhang, H.; El-Naggar, A.; Palansooriya, K.N.; Chen, K.; Yan, Y.; Lu, X.; et al. Nanoplastics induce molecular toxicity in earthworm: Integrated multi-omics, morphological, and intestinal microorganism analyses. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 130034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, Y.; Xing, M. Dose-effect of polystyrene microplastics on digestive toxicity in chickens (Gallus gallus): Multi-omics reveals critical role of gut-liver axis. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 52, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Qiu, D.; Zhou, T.; Zeng, L.; Yan, C. Biofilm enhances the interactive effects of microplastics and oxytetracycline on zebrafish intestine. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 270, 106905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Shi, W.; Du, X.; Han, Y.; Tang, Y.; Ri, S.; Ju, K.; Kim, T.; Huang, L.; Zhang, W.; et al. Assessment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease symptoms and gut-liver axis status in zebrafish after exposure to polystyrene microplastics and oxytetracycline, alone and in combination. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 47006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Jin, C.; Liang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Song, F.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, J.; Luo, J. Microplastics weaken the digestion and absorption functions in the golden pompano (Trachinotus blochii) by affecting the intestinal structure, bacteria and metabolites. Chemosphere 2024, 362, 142415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Rao, C.; Yuan, R.; Sun, D.; Guo, S.; Li, L.; Yang, S.; Qian, D.; Lu, R.; Cao, X. Long-term exposure to polyethylene microplastics and glyphosate interferes with the behavior, intestinal microbial homeostasis, and metabolites of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, W.; Sun, S.; Hu, X. Microplastics trigger the Matthew effect on nitrogen assimilation in marine diatoms at an environmentally relevant concentration. Water Res. 2023, 233, 119762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, M.; Zhao, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, C.; White, J.C.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, L.; Duan, M.; Wu, F. Polystyrene nanoplastics toxicity to zebrafish: Dysregulation of the brain-intestine-microbiota axis. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 8190–8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Choi, D.; Han, S.; Choi, J.; Hong, J. An assessment of the toxicity of polypropylene microplastics in human derived cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Zhou, L.; Yu, D.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Lin, T. Effects of polystyrene microplastics on the metabolic level of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Yin, H.; Peng, H.; Lu, G.; Dang, Z. Proteomic mechanism of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) biodegradation by Microbacterium Y2 and its potential in remediation of BDE-209 contaminated water-sediment system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, H.; Wang, L.; Xia, X.; Dong, C.; Tan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Ding, J. Sulfamethoxazole stress endangers the gut health of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) and affects host metabolism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 273, 116099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ling, S.; Hu, S.; Shen, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W. Combined exposure to decabromodiphenyl ether and nano zero-valent iron aggravated oxidative stress and interfered with metabolism in earthworms. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 172033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, L.; Lu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, M. Effects of environmentally relevant cypermethrin and sulfamethoxazole on intestinal health, microbiome, and liver metabolism in grass carp. Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 265, 106760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurup, A.; Yakal, S.; Tarçın, G.; Şahinler Ayla, S.; Turan, H.; Toprak, M.S.; Gungor, Z.B.; Ercan, O. Effect of acute exercise on 12,13-dihydroxy-9Z-octadecenoic acid (12,13-diHOME) levels in obese male adolescents. Clin. Endocrinol. 2023, 99, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tong, M.; Li, L.; Hui, F.; Meng, F.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Guo, X.; Shi, B.; Yan, S. Rectal microbiomes and serum metabolomics reveal the improved effect of Artemisia ordosica crude polysaccharides on the lactation performance, antioxidant and immune responses of lactating donkeys. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 6696–6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lv, J.; Fu, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Liu, S.; Zheng, L.; Feng, W.; Zhang, L. Metabolome-wide association study of four groups of persistent organic pollutants and abnormal blood lipids. Environ. Int. 2023, 173, 107817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Jang, S.; Kim, S.S.; Bae, M.A.; Shin, J.; Lee, K.B.; Kim, K.T. Size-dependent seizurogenic effect of polystyrene microplastics in zebrafish embryos. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Lu, X.; Dong, L.X.; Tian, J.; Deng, J.; Wei, L.; Wen, H.; Zhong, S.; Jiang, M. Nano polystyrene microplastics could accumulate in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): Negatively impacts on the intestinal and liver health through water exposure. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 137, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Song, Y.; Wang, N.; Yu, X.; Sun, T.; Yu, H.; Ruan, Z.; Qiu, Y. Exposure of Danio rerio to environmental sulfamethoxazole may contribute to neurobehavioral abnormalities via gut microbiome disturbance. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 918, 170546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, T.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Q.; Hou, Y.; Yan, Z. BDE-209-induced genotoxicity, intestinal damage and intestinal microbiota dysbiosis in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Junaid, M.; Wang, J. Toxicological effects of polystyrene nanoplastics and perfluorooctanoic acid to Gambusia affinis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 127, 1100–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhu, H.; Xu, G. Transcriptome analysis of the response of four immune related organs of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) to the addition of resveratrol in feed. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 133, 108510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yang, X.; Gao, J.; Nie, Z.; Xu, G. Effects of resveratrol on lipid metabolism in liver of red tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 261, 109408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Shao, N.; Yang, X.; Shi, Y.; Xu, G. Resveratrol ameliorates intestinal lipid metabolism through the PPAR signaling pathway in high-fat diet-fed red tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 145, 109302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Khoso, P.A.; Xu, S.; Li, S. Unraveling the mechanism of quercetin alleviating perfluorooctane sulfonate-induced apoptosis in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) hepatocytes: AMPK/mTOR-mediated mitophagy. Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 265, 106769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, G. Resveratrol attenuated fatty acid synthesis through MAPK-PPAR pathway in red tilapia. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 2023, 268, 109598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Wang, G.; Zhao, H. Exposed to sulfamethoxazole induced hepatic lipid metabolism disorder and intestinal microbiota changes on zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 253, 109245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, S.; Chen, X.; Gyimah, E.; Xu, H.; Chen, J. Hepatic oxidative stress, DNA damage and apoptosis in adult zebrafish following sub-chronic exposure to BDE-47 and BDE-153. Environ. Toxicol. 2020, 35, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Xu, G. Multi-Omics Platforms Reveal Synergistic Intestinal Toxicity in Tilapia from Acute Co-Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics, Sulfamethoxazole, and BDE153. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178441
Zheng Y, Li J, Li L, Xu G. Multi-Omics Platforms Reveal Synergistic Intestinal Toxicity in Tilapia from Acute Co-Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics, Sulfamethoxazole, and BDE153. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178441
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yao, Jiajia Li, Lihong Li, and Gangchun Xu. 2025. "Multi-Omics Platforms Reveal Synergistic Intestinal Toxicity in Tilapia from Acute Co-Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics, Sulfamethoxazole, and BDE153" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178441
APA StyleZheng, Y., Li, J., Li, L., & Xu, G. (2025). Multi-Omics Platforms Reveal Synergistic Intestinal Toxicity in Tilapia from Acute Co-Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics, Sulfamethoxazole, and BDE153. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178441







