Investigating the Neuroprotective, Hepatoprotective, and Antimicrobial Effects of Mushroom Extracts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bioactive Components of Mushroom Extracts
2.1.1. Protein Content
2.1.2. Total Phenols and Total Flavonoids
2.1.3. Phenolic Components
2.2. In Vivo Investigation of Neuroprotective and Hepatoprotective Effects
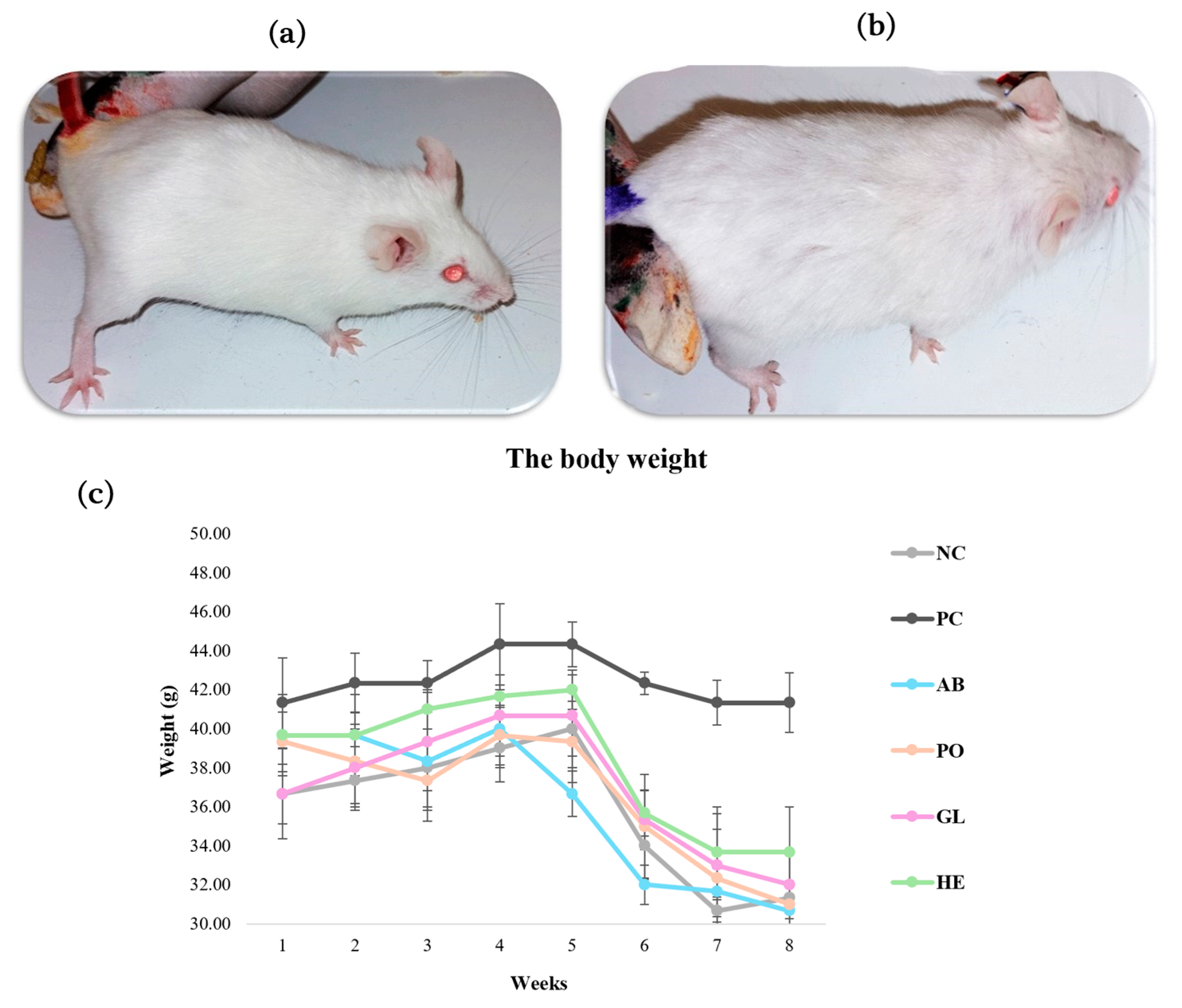
2.2.1. Evaluation of Body Weights
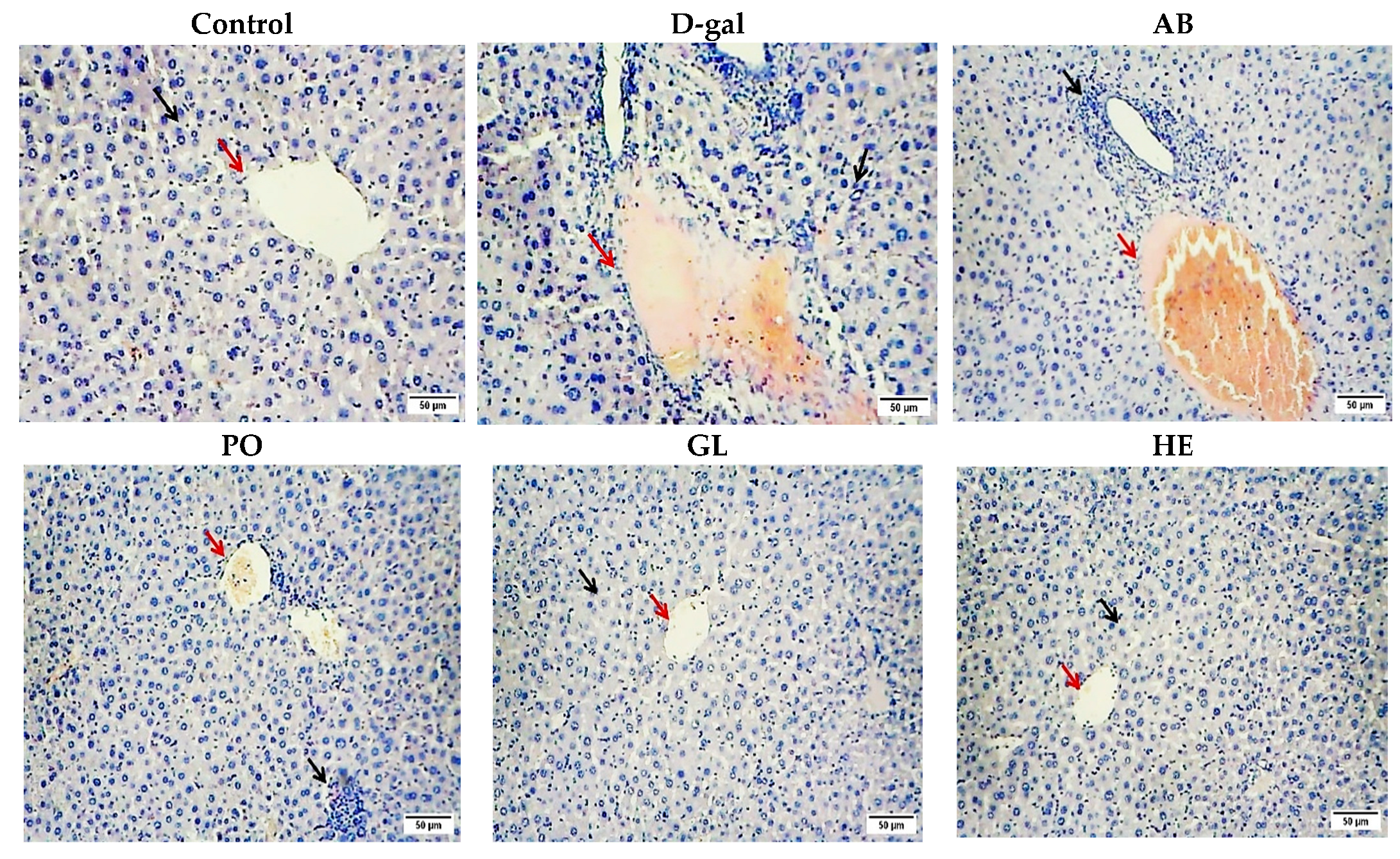
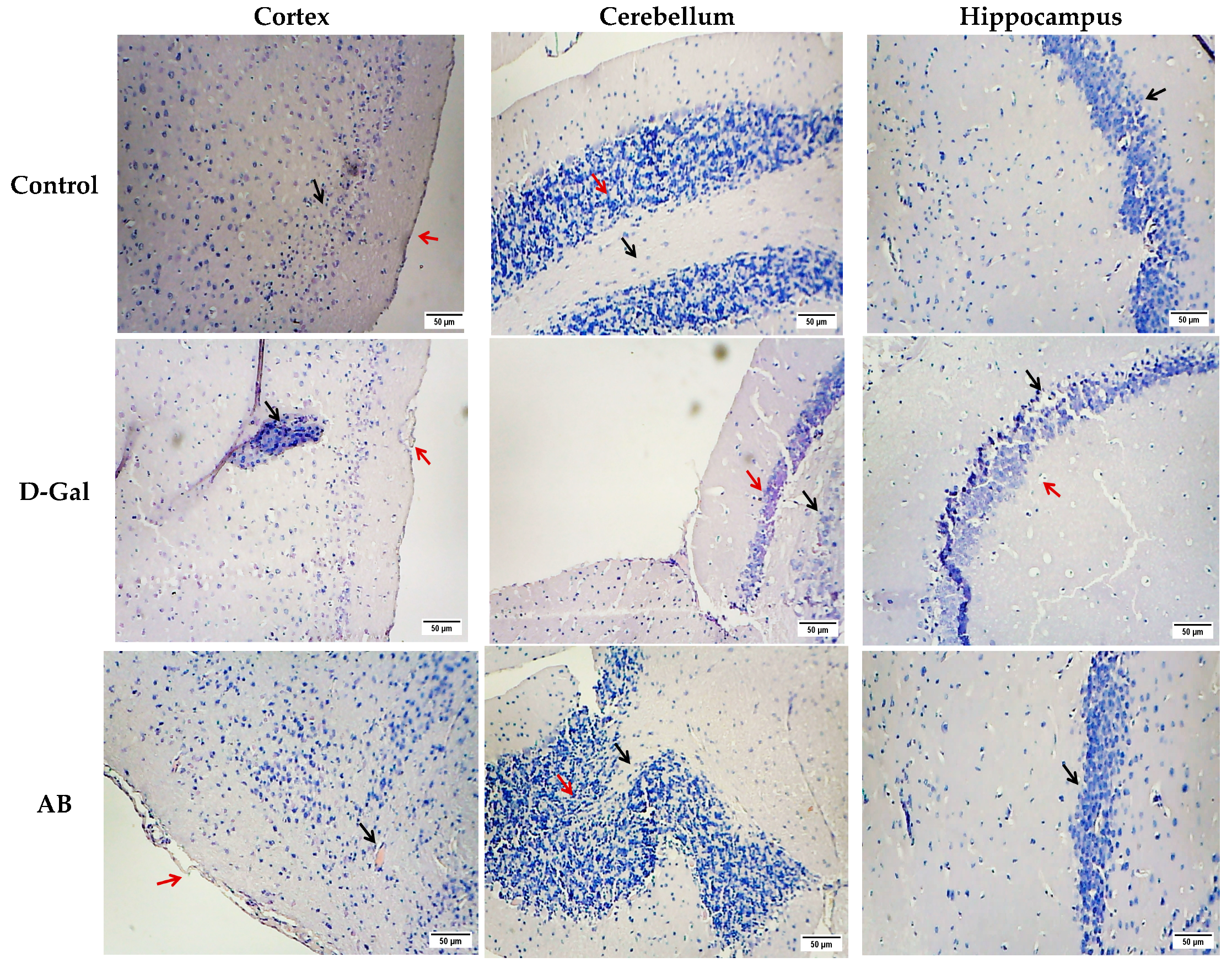
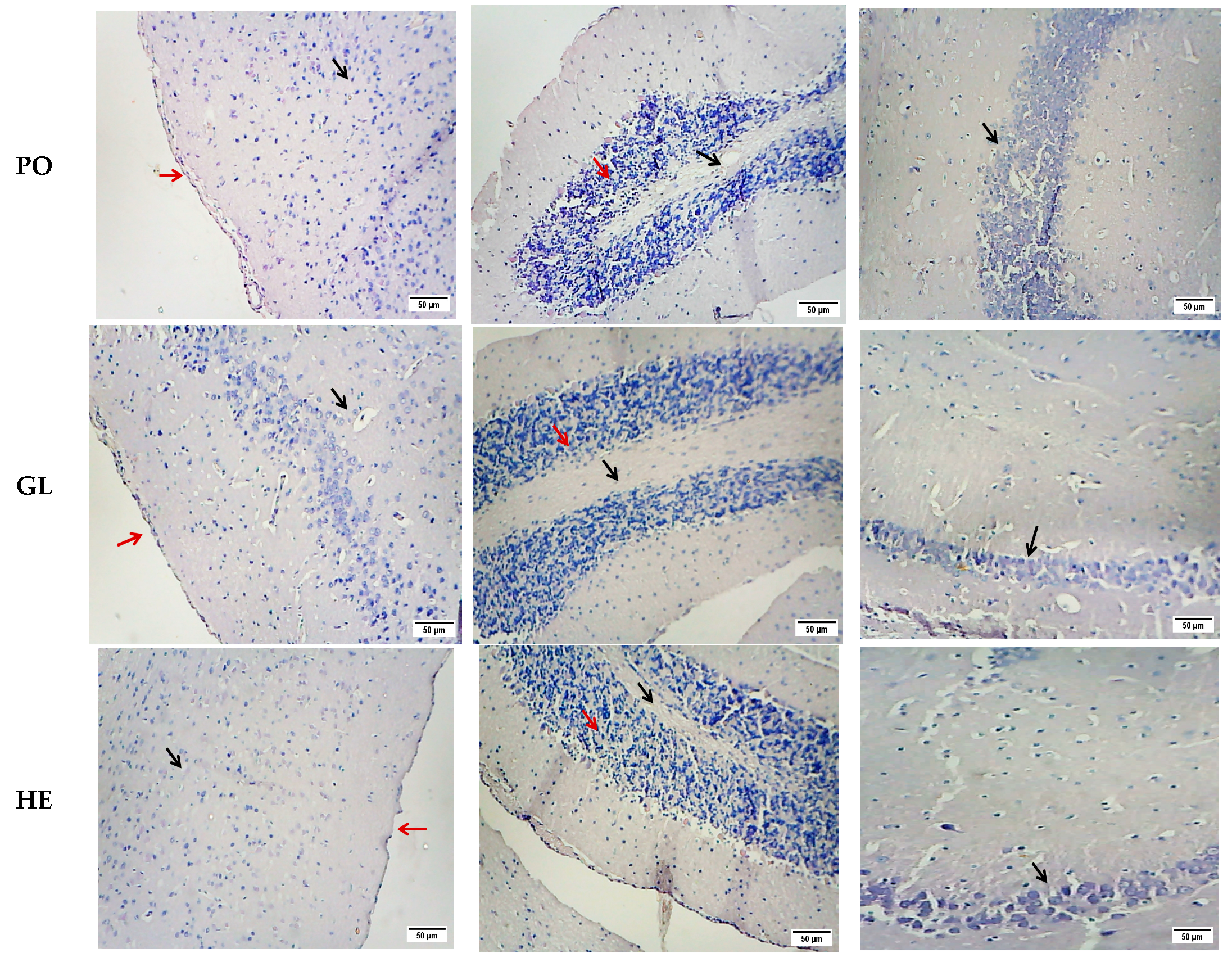
2.2.2. Histopathological Studies
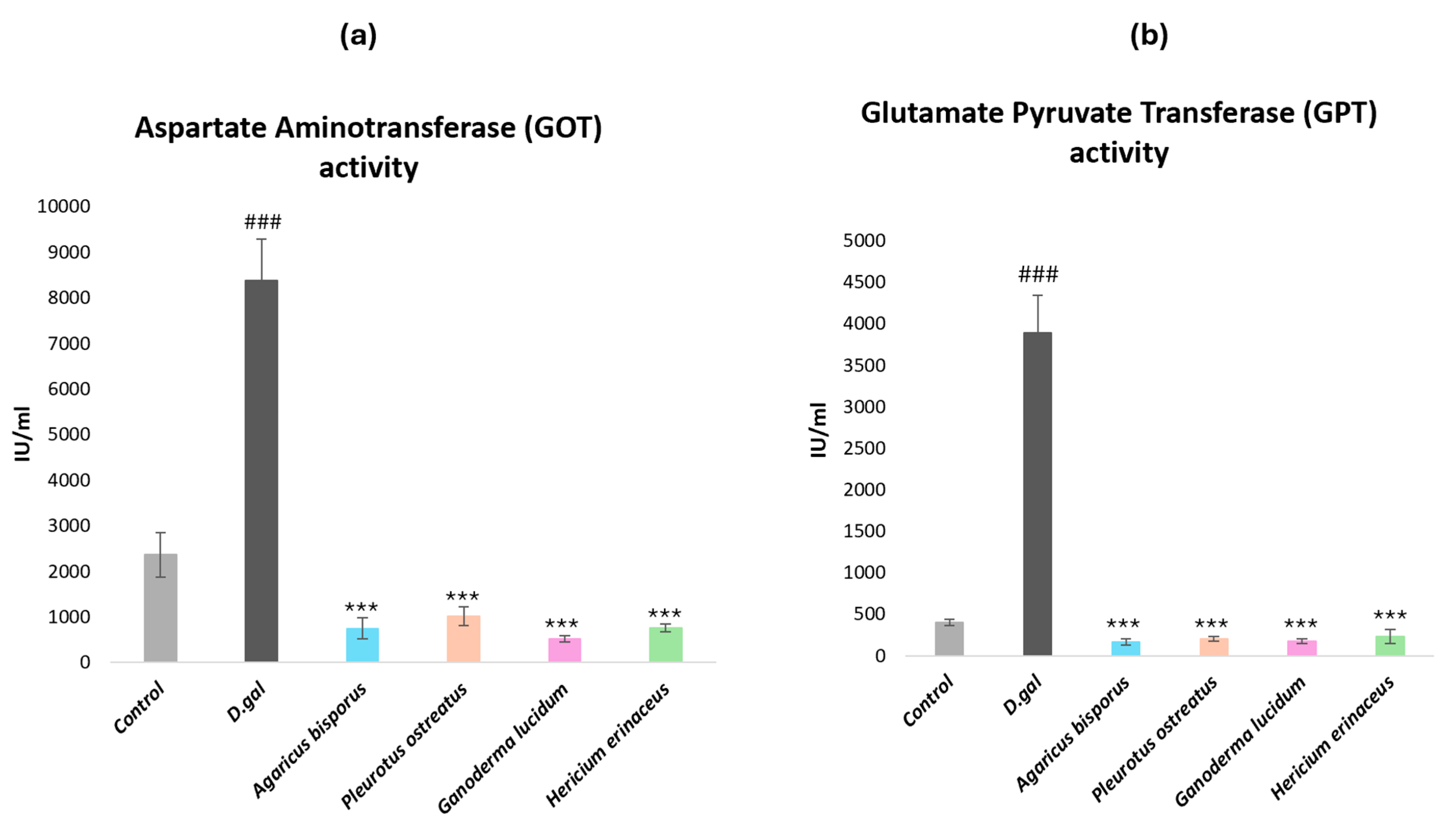
2.2.3. Biochemical Parameters of Liver Functions
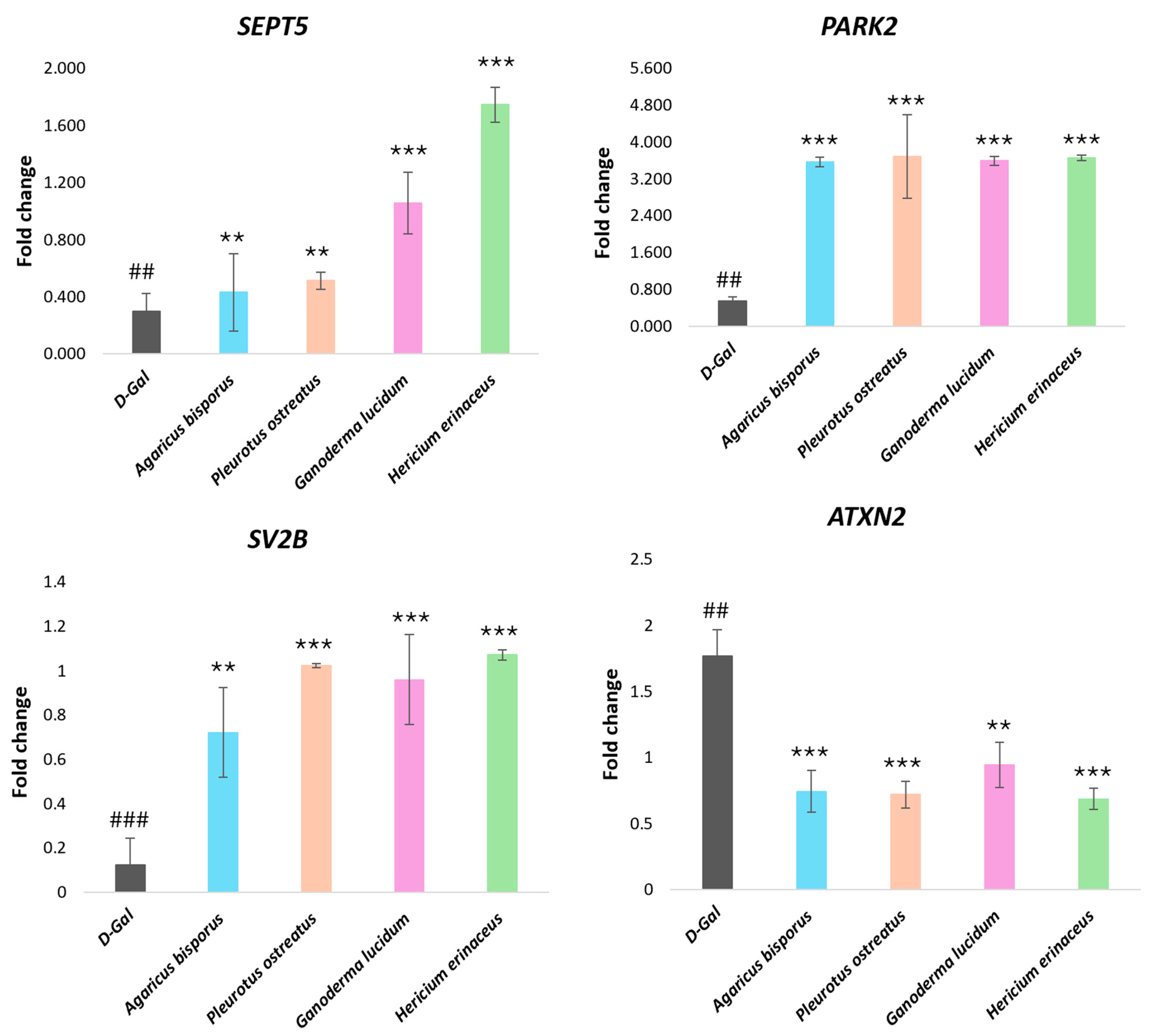
2.2.4. Molecular Analysis (qRT-PCR)
Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis of Immunomodulation and Inflammation-Regulation Genes
Real-Time PCR Analysis of Neurodegeneration-Related Genes
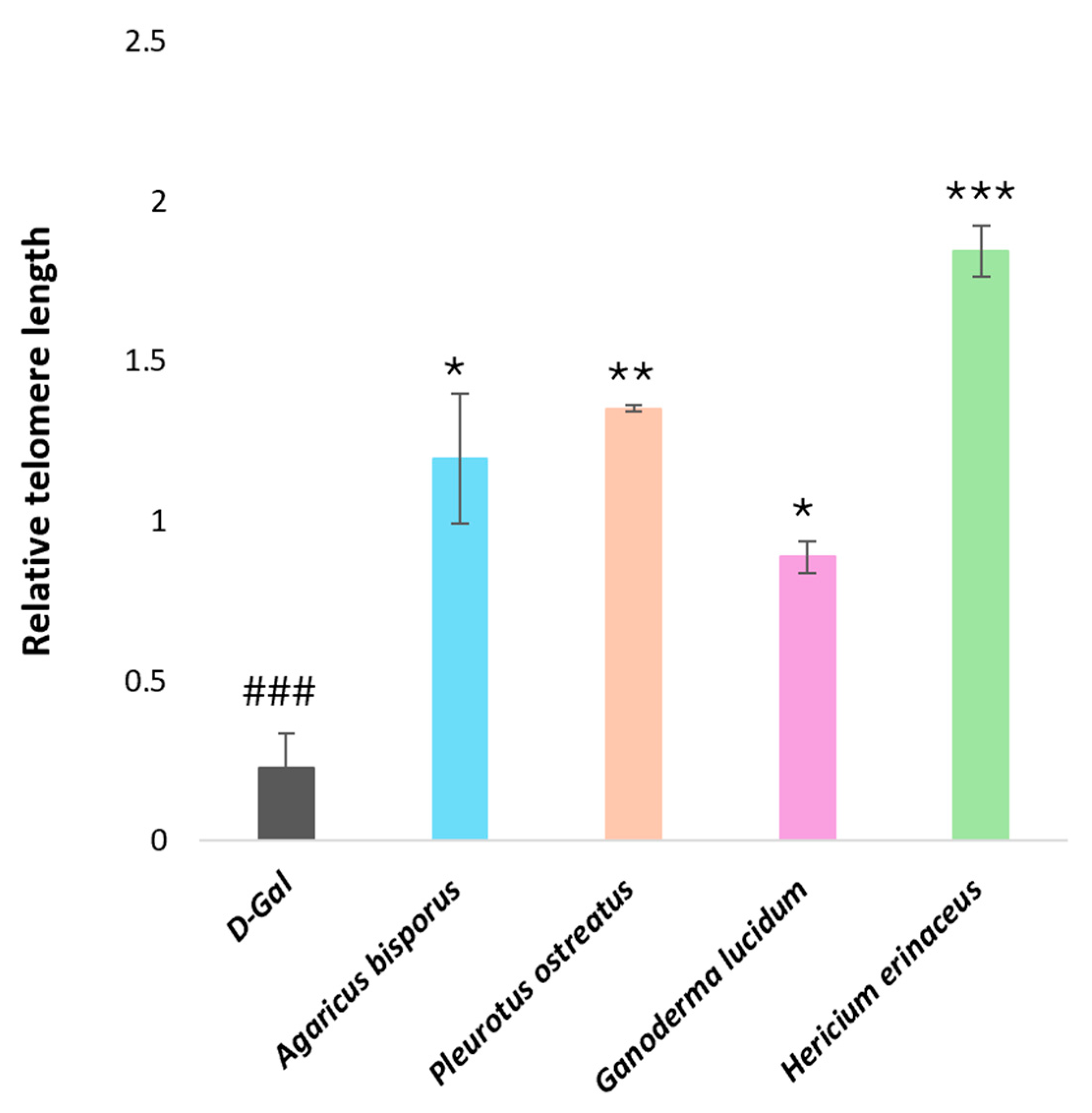
Real-Time PCR Analysis of Genes Encoding Functions Affecting Telomere Length
2.3. Antimicrobial Activity of Mushroom Extracts
2.3.1. Isolation and Activation of Bacteria
2.3.2. Antimicrobial Activity Measured by Agar Well Diffusion
2.3.3. Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MIC) by Microdilution Method
3. Discussion
3.1. Mushroom Bioactive Components
3.2. In Vivo Experimental (Hepatoprotective, Neuroprotection, Immune Modulation)
3.3. In Vitro Experimental (Antimicrobial Activity)
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Collection of Samples
4.2. Preparation of Aqueous Extract
4.3. Chemical Analysis of Mushroom Extracts
4.3.1. Determination of Protein Content
4.3.2. Determination of Total Flavonoid Content
4.3.3. Determination of Total Phenolic Content
4.3.4. Determination of Individual Phenolic Components
4.4. Neuroprotective and Hepatoprotective Effects: An In Vivo Study
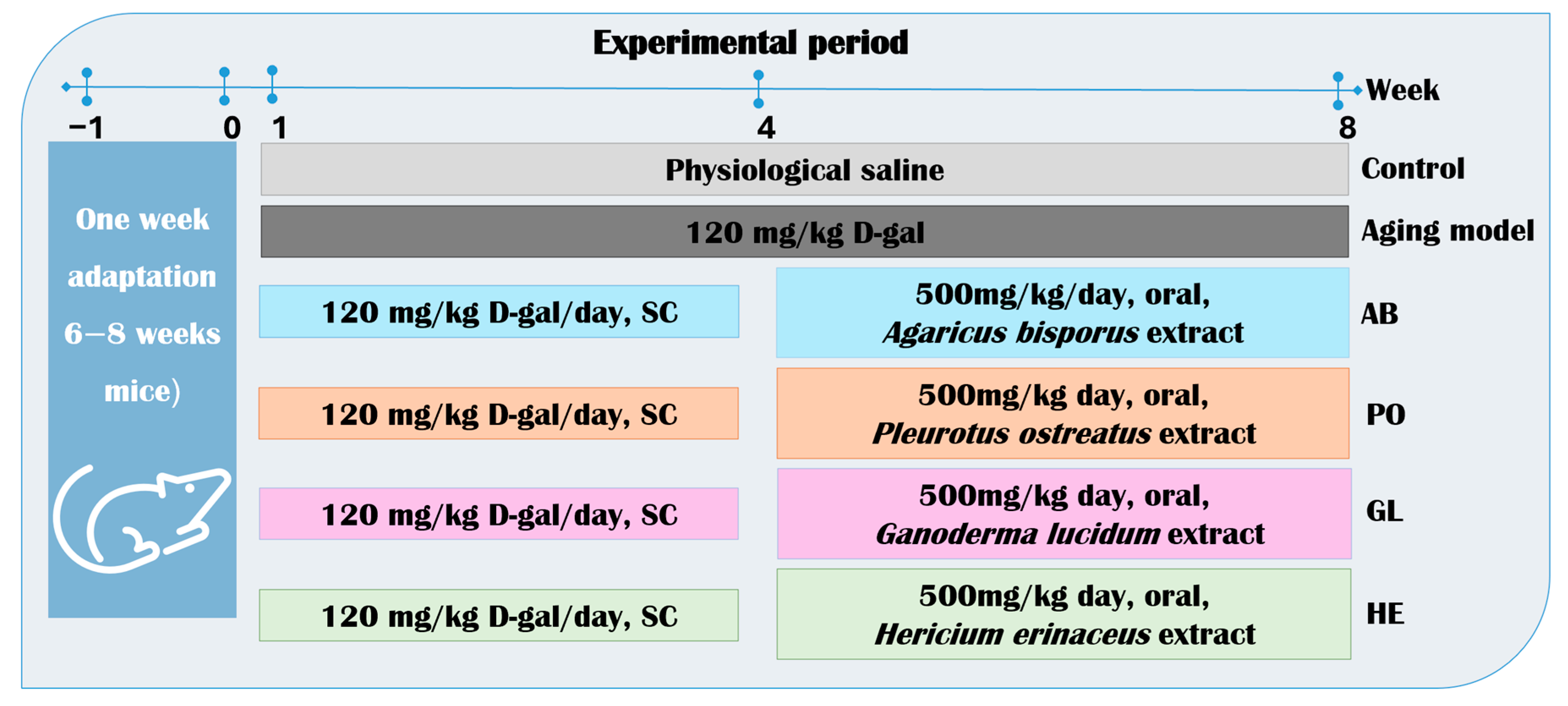
4.4.1. Animal Housing and Experimental Design
4.4.2. Blood and Tissue Collection
4.4.3. Pathological Examination of Tissues
4.4.4. RNA Isolation and Quantitative PCR
4.5. Determination of Antimicrobial Activity
4.5.1. Preparation of Bacterial Isolates and Inoculum
4.5.2. Agar Well Diffusion Method
4.5.3. Microdilution Method
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agrawal, D.; Chen, E.; Chang, H.; Tsay, H.; Chandra Agrawal, D.; Chin-Fun Chen, E.; Chang, H.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Kuo, C.-L.; Tsay, H.-S. Biotechnology of Medicinal Plants and Fungi in Taiwan: Production of Bioactive Secondary Metabolites in In Vitro Culture Systems. In Medicinal Plants and Fungi: Recent Advances in Research and Development; Medicinal and Aromatic Plants of the World; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 459–483. ISBN 978-981-10-5978-0. [Google Scholar]
- Sevindik, M.; Akgul, H.; Selamoglu, Z.; Braidy, N. Antioxidant and Antigenotoxic Potential of Infundibulicybe geotropa Mushroom Collected from Northwestern Turkey. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 5620484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Wang, H.; Zheng, W.; Gao, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Q. Characterization and Immunomodulatory Activities of Polysaccharide Isolated from Pleurotus eryngii. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturella, G.; Ferraro, V.; Cirlincione, F.; Gargano, M.L. Medicinal mushrooms: Bioactive compounds, use, and clinical trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Kadappa, H.S.; Meena, S.C. Recent molecular genetics and biotechnological approaches in mushroom research. In Microbial Biodiversity in Sustainable Agriculture; Daya Publishing House, Astral International (P) Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2014; pp. 323–343. [Google Scholar]
- Assemie, A.; Abaya, G. The Effect of Edible Mushroom on Health and Their Biochemistry. Int. J. Microbiol. 2022, 2022, 8744788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, T. Immunomodulatory Activities of Polysaccharides from Ganoderma on Immune Effector Cells. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshesha, F. Pharmacological Activities of Reishi (Ganoderma lucidum): Potent Medicinal Mushroom. Microb. J. 2023, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.L.; Wang, C.D.; Wang, T.; Ding, H.; Zhou, M.; Yang, N.; Liu, Y.Y.; Chan, P. Ganoderma lucidum Extract Ameliorates MPTP-Induced Parkinsonism and Protects Dopaminergic Neurons from Oxidative Stress via Regulating Mitochondrial Function, Autophagy, and Apoptosis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 40, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Tan, X.; Cao, Y.; Li, S.; Hong, H.D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Q. Ganoderma lucidum Rhodiola Compound Preparation Prevent D-Galactose-Induced Immune Impairment and Oxidative Stress in Aging Rat Model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Mao, J.; Ding, K.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, X.; Yang, W.; Wang, P.; Zhao, C.; Yao, J.; Xia, P.; et al. Polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum Promote Cognitive Function and Neural Progenitor Proliferation in Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 8, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.Z.; Yang, F.; Tan, W.; Li, X.; Jiao, C.; Huang, R.; Yang, B.B. The Anti-Cancer Components of Ganoderma lucidum Possesses Cardiovascular Protective Effect by Regulating Circular RNA Expression. Oncoscience 2016, 3, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Sun, Y.; Jia, Y.; Geng, X.; Chen, R.; Zhou, H.; Yang, B. Ganoderma triterpenes Protect against Hyperhomocysteinemia Induced Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition via TGF-β Signaling Inhibition. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 433195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mei, L.; Li, J.; Wang, A.; Luo, H.; Lin, Z. Effect of JUNCAO-Cultivated Ganoderma lucidum Spent Mushroom Substrate-Hot Water Extract on Immune Function in Mice. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 17, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Q.; Lian, C.L.; Hu, T.Y.; Wang, C.F.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, L.; Liu, Z.Q.; Qiu, S.Q.; Cheng, B.H. Two New Farnesyl Phenolic Compounds with Anti-Inflammatory Activities from Ganoderma duripora. Food Chem. 2018, 263, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celal, B. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Capacities of Ganoderma lucidum. MedCrave 2019, 7, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin, S.; Craciunescu, O.; Oancea, A.; Ilie, D.; Ciucan, T.; Antohi, L.S.; Toma, A.; Nicolescu, A.; Deleanu, C.; Oancea, F. Antioxidant, Cytotoxic and Antimicrobial Activity of Chitosan Preparations Extracted from Ganoderma lucidum Mushroom. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e2000175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Sivaprakasam, E.; Balakumar, R.; Kavitha, D. Evaluation of Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of Ganoderma lucidum (Curtis) P. Karst Fruit Bodies Extracts. World J. Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.C.; Yin, X.; Cao, C.Y.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, J.M. Chemical Constituents from Hericium erinaceus and Their Ability to Stimulate NGF-Mediated Neurite Out-growth on PC12 Cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5078–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, I.C.; Lee, L.Y.; Tzeng, T.T.; Chen, W.P.; Chen, Y.P.; Shiao, Y.J.; Chen, C.C. Neurohealth Properties of Hericium erinaceus Mycelia Enriched with Erinacines. Behav. Neurol. 2018, 2018, 5802634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limanaqi, F.; Biagioni, F.; Busceti, C.L.; Polzella, M.; Fabrizi, C.; Fornai, F. Potential Antidepressant Effects of Scutellaria baicalensis, Hericium erinaceus and Rhodiola rosea. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Mármol, R.; Chai, Y.J.; Conroy, J.N.; Khan, Z.; Hong, S.M.; Kim, S.B.; Gormal, R.S.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, J.K.; Coulson, E.J.; et al. Hericerin Derivatives Activates a Pan-Neurotrophic Pathway in Central Hippocampal Neurons Converging to ERK1/2 Signaling Enhancing Spatial Memory. J. Neurochem. 2023, 165, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, F.; Gao, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Zhang, C.; Xu, N.; Zhao, H.; Lin, L.; Zhou, M.; Jia, L. Protective Effects of Extracellular and Intracellular Polysaccharides on Hepatotoxicity by Hericium erinaceus SG-02. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 73, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Ouchi, K.; Hirasawa, N. The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Lion’s Mane Culinary-Medicinal Mushroom, Hericium erinaceus (Higher Basidiomycetes) in a Coculture System of 3T3-L1 Adipocytes and RAW264 Macrophages. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2015, 17, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Liu, H.; Wen, Y.; Chen, P.; Liu, Z. A Novel Polysaccharide from Hericium erinaceus: Preparation, Structural Characteristics, Thermal Stabilities, and Antioxidant Activities in Vitro. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongbai, B.; Rapior, S.; Hyde, K.D.; Wittstein, K.; Stadler, M. Hericium erinaceus, an Amazing Medicinal Mushroom. Mycol. Prog. 2015, 14, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, W.B.; Shehata, R.M.; Younis, A.M. In Vitro Assessment of Multipotential Therapeutic Importance of Hericium erinaceus Mushroom Extracts Using Different Solvents. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2022, 9, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalaf, M.; Shawkat, M.S. Antibacterial Activity of (Hericium erinaceus) Extract on Some Clinical Pathogenic Isolates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 54, 691–699. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.U.; Lee, E.H.; Jung, H.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Cho, Y.J. Inhibitory Activity against Biological Activities and Antimicrobial Activity against Pathogenic Bacteria of Extracts from Hericium erinaceus. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2019, 62, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomberg, M.; Krupodorova, T.; Krasinko, V.; Mykchaylova, O. The antibacterial activity of culture filtrates and mycelia of selected strains of macromycetes from the genus Hericium. Bot. Serb. 2023, 47, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibar, B.; Peksen, A. Modelling the Effects of Temperature and Light Intensity on the Development and Yield of Different Pleurotus Species. Agric. Trop. Subtrop. 2008, 41, 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Farhan, E.M.; Chechan, R.A. Evaluating the Ability of Pleurotus ostreatus Aqueous Extract to Modulate Genotoxicity Induced by Cyclophosphamide in Mice Bone Marrow Cells. Iraqi. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 51, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar]
- Sarma, D.; Saha, A.K.; Datta, B.K. Bioactive Compounds with Special References to Anticancer Property of Oyster Mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 2694–2698. [Google Scholar]
- Jayakumar, T.; Ramesh, E.; Geraldine, P. Antioxidant Activity of the Oyster Mushroom, Pleurotus ostreatus, on CCl4-Induced Liver Injury in Rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, T.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, G.; Yang, Y. Antidiabetic Effect of Polysaccharides from Pleurotus ostreatus in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 83, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakumar, T.; Aloysius Thomas, P.; Geraldine, P. Protective Effect of an Extract of the Oyster Mushroom, Pleurotus ostreatus, on Antioxidants of Major Organs of Aged Rats. Exp. Gerontol. 2007, 42, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, X.; Cui, L.; Ma, C. Extraction and Bioactivities of the Chemical Composition from Pleurotus ostreatus: A Review. J. Future Foods 2024, 4, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdal, M.; Gülmez, Ö.; Gür Özdal, Ö.; Algur, Ö.F. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activity of Mycelial Extracts of Different Pleurotus Species. Food Health 2019, 5, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Razek, A.; Amal, M.; Ibrahim, A.; Elattar, A.; Asker, D. Utilization of Agro-Wastes to Produce Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) with High Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities. Alex. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogidi, O.I.; Maureen, L.; Oguoma, O.; Adigwe, P.C.; Anthony, B.B. Phytochemical Properties and In-Vitro Antimicrobial Potency of Wild Edible Mushrooms (Pleurotus ostreatus) Obtained from Yenagoa, Nigeria. J. Phytopharm. 2021, 10, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, D.; El-Sayed, H.; Ahmed, W.; Sonbol, H.; Ramadan, M.A.H. GC-MS Analysis of Potentially Volatile Compounds of Pleurotus ostreatus Polar Extract: In Vitro Antimicrobial, Cytotoxic, Immunomodulatory, and Antioxidant Activities. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 834525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golak-Siwulska, I.; Kałuzewicz, A.; Spizewski, T.; Siwulski, M.; Sobieralski, K. Bioactive Compounds and Medicinal Properties of Oyster Mushrooms (Pleurotus sp.). Folia Hortic. 2018, 30, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.; Burgos, N.; Barnard, A.; Evans, G.; Preece, J.; Graz, M.; Ruthes, A.C.; Jiménez-Quero, A.; Martínez-Abad, A.; Vilaplana, F.; et al. Agaricus Bisporus and Its By-Products as a Source of Valuable Extracts and Bioactive Compounds. Food Chem. 2019, 292, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, B.; De, B.; Chetree, R.; Mandal, S.C. Medicinal Aspect of Mushrooms: A View Point. In Herbal Medicine in India: Indigenous Knowledge, Practice, Innovation and its Value; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 509–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszyńska, B.; Kała, K.; Rojowski, J.; Grzywacz, A.; Opoka, W. Composition and Biological Properties of Agaricus Bisporus Fruiting Bodies—A Review. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2017, 67, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Li, J.; Fan, L. Agaricus bisporus Polysaccharides Ameliorates Behavioral Deficits in D-Galactose-Induced Aging Mice: Mediated by Gut Microbiota. Foods 2023, 12, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sanmartín, J.; Bobadilla, M.; Mirpuri, E.; Grifoll, V.; Pérez-Clavijo, M.; Martínez, A. Agaricus Mushroom-Enriched Diets Modulate the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis and Reduce Brain Oxidative Stress in Mice. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneimy, E.A.; Wu, F.; Elkhawaga, A.; Alassar, M.M.; Abdelaziz, M.; Elbatrawy, E.N. Evaluation of Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Some Edible Mushrooms. Egypt. Acad. J. Biol. Sci. G Microb. 2014, 6, 69–82. [Google Scholar]
- Soltanian, H.; Rezaeian, S.; Shaker, I.; Abolfazl; Janpoor, J.; Pourianfar, H.R. Antibacterial Activity of Crude Extracts and Fractions from Iranian Wild-Grown and Cultivated Agaricus spp. Biomed. Res. 2015, 27, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, J.E.; Wilson, N.; Son, S.M.; Obrocki, P.; Wrobel, L.; Rob, M.; Takla, M.; Korolchuk, V.I.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Autophagy, Aging, and Age-Related Neurodegeneration. Neuron 2024, 113, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, P.; Chami, B.; Lim, J.; Middleton, T.; Sutherland, G.T.; Witting, P.K. Evidence Supporting Oxidative Stress in a Moderately Affected Area of the Brain in Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, E.; Sheng, Y.; Shi, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Qi, T.; Pan, M.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, X.; et al. Spatial Transcriptome Profiling of Mouse Hippocampal Single Cell Microzone in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, S.A.; Ko, M.Y.; Jang, S.; Lee, B.S.; Rho, J.; Kim, K.K.; Kim, W.Y.; Ka, M. Bisphenol-A Impairs Synaptic Formation and Function by RGS4-Mediated Regulation of BDNF Signaling in the Cerebral Cortex. DMM Dis. Models Mech. 2022, 15, dmm049177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Zglinicki, T. Oxidative Stress Shortens Telomeres. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabluchanskiy, A.; Ungvari, Z.; Csiszar, A.; Tarantini, S. Advances and Challenges in Geroscience Research: An Update. Physiol. Int. 2018, 105, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.; Ferreira, I.F.R.; Dias, J.; Teixeira, V.; Martins, A.; Pintado, M. A Review on Antimicrobial Activity of Mushroom (Basidiomycetes) Extracts and Isolated Compounds. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nellums, L.B.; Thompson, H.; Holmes, A.; Castro-Sánchez, E.; Otter, J.A.; Norredam, M.; Friedland, J.S.; Hargreaves, S. Antimicrobial Resistance among Migrants in Europe: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 796–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Dong, J.; Yin, Z.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X. Procyanidin B2 Protects against D-Galactose-Induced Mimetic Aging in Mice: Metabolites and Microbiome Analysis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 119, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibu, M.A.; Agrawal, D.C.; Huang, C.-Y. Mushrooms: A Pandora Box of Cardioprotective Phytochemicals. In Medicinal Plants and Fungi: Recent Advances in Research and Development; Springer: Singapore, 2017; ISBN 978-981-10-5978-0. [Google Scholar]
- Usman, M.; Murtaza, G.; Ditta, A. Nutritional, Medicinal, and Cosmetic Value of Bioactive Compounds in Button Mushroom (Agaricus bisporus): A Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 13, 5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirullah, N.A.; Abdullah, E.; Zainal Abidin, N.; Abdullah, N.; Manickam, S. Influence of Extraction Technologies on the Therapeutic Properties of Pleurotus spp. (Oyster mushrooms)—A Critical Review. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zuo, J.; Gong, X.; Yi, F.; Zhu, W.; Li, L. Advances in Research on the Active Constituents and Physiological Effects of Ganoderma lucidum. Biomed. Dermatol. 2019, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Lin, G.; Liu, W.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, A. Bioactive Substances in Hericium erinaceus and Their Biological Properties: A Review. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 1825–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, V.A.; Alvarez, A. Compositional and Nutritional Studies on Two Wild Edible Mushrooms from Northwest Spain. Food Chem. 2001, 75, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Protein Quality Evaluation: Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation; Food & Agriculture Organization: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1991; p. 51. [Google Scholar]
- Kalbarczyk, J.; Radzki, W. Cultivated Mushrooms as a Valuable Diet Constituent and a Source of Biologically Active Substances. Herba Pol. 2009, 55, 224–232. [Google Scholar]
- Braaksma, A.; Schaap, D.J. Protein Analysis of the Common Mushroom Agaricus bisporus. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 1996, 7, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszyńska, B.; Sułkowska-Ziaja, K.; Ekiert, H. Indole Compounds in Fruiting Bodies of Some Edible Basidiomycota Species. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 1306–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyüz, M.; Kirbaǧ, S. Nutritive Value of Edible Wild and Cultured Mushrooms. Turk. J. Biol. 2010, 34, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesa, K.N.; Khandaker, M.U.; Mohammad Rashed Iqbal, F.; Sharma, R.; Islam, F.; Mitra, S.; Emran, T.B. Nutritional Value, Medicinal Importance, and Health-Promoting Effects of Dietary Mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus). J. Food Qual. 2022, 2022, 2454180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claude, I.; Aimable, N.; Mediatrice, H.; Zhou, H.; Lin, D.; Liu, P.; Lin, Z. Evaluation of the Influence of Varied Juncao Grass Substrates on Physiological and Enzymatic Reactions of Pleurotus ostreatus. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 9493–9502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mau, J.L.; Lin, H.C.; Chen, C.C. Non-Volatile Components of Several Medicinal Mushrooms. Food Res. Int. 2001, 34, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. Chemistry, Nutrition, and Health-Promoting Properties of Hericium erinaceus (Lion’s Mane) Mushroom Fruiting Bodies and Mycelia and Their Bioactive Compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7108–7123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mircea, C.; Cioancă, O.; Iancu, C.; Tătărîngă, G.; Hăncianu, M. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Some Extracts Obtained from Agaricus bisporus Brown, Pleurotus ostreatus and Fomes fomentarius. Farmacia 2015, 63, 927–933. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimah, S.B.; Djunaedi, D.D.; Soeroto, A.Y.; Bisri, T. The Phytochemical Screening, Total Phenolic Contents and Antioxidant Activities in Vitro of White Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) Preparations. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Palma, I.; Escalona-Buendía, H.B.; Ponce-Alquicira, E.; Téllez-Téllez, M.; Gupta, V.K.; Díaz-Godínez, G.; Soriano-Santos, J. Evaluation of the Antioxidant Activity of Aqueous and Methanol Extracts of Pleurotus ostreatus in Different Growth Stages. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 206086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhusseiny, S.M.; El-Mahdy, T.S.; Awad, M.F.; Elleboudy, N.S.; Farag, M.M.S.; Yassein, M.A.; Aboshanab, K.M. Proteome Analysis and In Vitro Antiviral, Anticancer and Antioxidant Capacities of the Aqueous Extracts of Lentinula edodes and Pleurotus ostreatus Edible Mushrooms. Molecules 2021, 26, 4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthi, R.; Srinivash, M.; Mahalingam, P.U.; Malaikozhundan, B. Dietary Nutrients in Edible Mushroom, Agaricus bisporus and Their Radical Scavenging, Antibacterial, and Antifungal Effects. Process Biochem. 2022, 121, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, F.; Zielinski, A.A.F.; Helm, C.V.; Maciel, G.M.; Pedro, A.C.; Stafussa, A.P.; Ávila, S.; Haminiuk, C.W.I. Bio Compounds of Edible Mushrooms: In Vitro Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 107, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alispahić, A.; Šapčanin, A.; Salihović, M.; Ramić, E.; Dedić, A.; Pazalja, M. Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity of Mushroom Extracts from Bosnian Market. Bull. Chem. Technol. Bosnia Herzeg. 2015, 44, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nitthikan, N.; Leelapornpisid, P.; Naksuriya, O.; Intasai, N.; Kiattisin, K. Potential and Alternative Bioactive Compounds from Brown Agaricus bisporus Mushroom Extracts for Xerosis Treatment. Sci. Pharm. 2022, 90, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, S.; Wang, F.; Lu, M.; Wang, F.; Hu, R. Optimization of Flavonoid Compound Extraction from Ganoderma lucidum and Its Antioxidant Activity on PC12 Cells Exposed to H2O2. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, E.; Farragher-Gnadt, A.P.; Igbanugo, M.; Huber, T.; Michelotti, J.C.; Milenkowic, A.; Ludlam, S.; Walker, M.; Hanes, D.; Bradley, R.; et al. Comparison of Antioxidant Activity and Extraction Techniques for Commercially and Laboratory Prepared Extracts from Six Mushroom Species. J. Agric. Food Res. 2021, 4, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, N.; Ismail, S.M.; Aminudin, N.; Shuib, A.S.; Lau, B.F. Evaluation of Selected Culinary-Medicinal Mushrooms for Antioxidant and ACE Inhibitory Activities. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 464238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.H.; Sabaratnam, V.; Abdullah, N.; Kuppusamy, U.R.; Naidu, M. Effects of Cultivation Techniques and Processing on Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Hericium erinaceus (Bull.:Fr.) Pers. Extracts. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 47, 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lew, S.Y.; Yow, Y.Y.; Lim, L.W.; Wong, K.H. Antioxidant-Mediated Protective Role of Hericium Erinaceus (Bull.: Fr.) Pers. against Oxidative Damage in Fibroblasts from Friedreich’s Ataxia Patient. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 40, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, M.A.E.; Mediatrice, H.; Lin, D.; Lin, Z.; Aggag, S.A. Mitigating Oxidative Stress and Promoting Cellular Longevity with Mushroom Extracts. Foods 2024, 13, 4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Pan, J.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Z. Anti-Aging Effect of Brown Black Wolfberry on Drosophila Melanogaster and D-Galactose-Induced Aging Mice. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 65, 103724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, I.C.; Chen, W.P.; Chen, Y.P.; Lee, L.Y.; Tsai, Y.T.; Chen, C.C. Acute and Developmental Toxicity Assessment of Erincine A-Enriched Hericium erinaceus Mycelia in Sprague–Dawley Rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 41, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moukha, S.; Férandon, C.; Mobio, T.; Creppy, E.E.; Ferandon, C.; Mobio, T. Safety Evaluation of Agaricus subrufescens Varieties and Their Products of Therapeutic Interest or for Disease Prevention. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Mushroom Biology and Mushroom Products, Arcachon, France, 4–7 October 2011; pp. 285–297. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Tulsawani, R.; Agrawal, U. Pharmacological Effects of Ganoderma lucidum Extract against High-Altitude Stressors and Its Subchronic Toxicity Assessment. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e13081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimah, S.B.; Kharisma, Y.; Dewi, M.K.; Hartati, J.; Maharani, W. Acute Toxicity Test for the Ethanolic Extract of the White Oyster Mushroom. In Medical Technology and Environmental Health; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 41–43. ISBN 9781003016700. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Xu, J.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Guo, M.; Xu, W.; Luo, Y.; Huang, K.; He, X. Pleurotus ostreatus Ameliorates Obesity by Modulating the Gut Microbiota in Obese Mice Induced by High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Jeon, Y.-E.; Kim, S.-M.; Jung, J.-I.; Ko, D.; Kim, E.-J.; Kim, H.; Jeon, Y.-E.; Kim, S.-M.; Jung, J.-I.; et al. Agaricus bisporus Extract Exerts an Anti-Obesity Effect in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese C57BL/6N Mice by Inhibiting Pancreatic Lipase-Mediated Fat Absorption. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Jing, H.; Ren, Z.; Gao, Z.; Song, X.; et al. Antioxidant and Anti-Aging Effects of Acidic-Extractable Polysaccharides by Agaricus bisporus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llauradó, G.; Beltrán, Y.; Morris, H.J.; Marcos, E.; Díaz, U.; Marcos, J.; García, J.; Disotuar, D.; Cos, P. Restoration of Liver Function in Malnourished Mice Orally Administered with Pleurotus Ostreatus Fruiting Bodies Extract. J. Pharm. Pharmacogn. Res. 2020, 8, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulos, T.T.; Lippi, S.L.P.; Davila, J.F.; Barkey, R.E.; Doherty, E.N.; Flinn, J.M. White Button Mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) Supplementation Ameliorates Spatial Memory Deficits and Plaque Formation in an Amyloid Precursor Protein Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Tulsawani, R. Ganoderma lucidum Aqueous Extract Prevents Hypobaric Hypoxia Induced Memory Deficit by Modulating Neurotransmission, Neuroplasticity and Maintaining Redox Homeostasis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, E.; Priori, E.C.; Ratto, D.; De Luca, F.; Di Iorio, C.; Angelone, P.; Locatelli, C.A.; Desiderio, A.; Goppa, L.; Savino, E.; et al. Neuroprotective Metabolites of Hericium erinaceus Promote Neuro-Healthy Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Fan, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, W.; Cao, H.; Xiao, J.; Liu, B. Hepatoprotective activity of Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoids in alcohol-induced liver injury in mice, an iTRAQ-based proteomic analysis. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, H.; Yin, Y.; Guo, W.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shu, C.; Dong, L. Role of Interleukin-6 to Differentiate Sepsis from Non-Infectious Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome. Cytokine 2016, 88, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, I.; Tomassoni, D.; Roy, P.; Amenta, F.; Khosrow Tayebati, S.; Jin, K.; Su, H.; Yang, G.-Y. Altered Brain Cholinergic and Synaptic Markers in Obese Zucker Rats. Cells 2021, 10, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ageta-Ishihara, N.; Yamakado, H.; Morita, T.; Hattori, S.; Takao, K.; Miyakawa, T.; Takahashi, R.; Kinoshita, M. Chronic Overload of SEPT4, a Parkin Substrate That Aggregates in Parkinson’s Disease, Causes Behavioral Alterations but Not Neurodegeneration in Mice. Mol. Brain 2013, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Györffy, B.A.; Tóth, V.; Török, G.; Gulyássy, P.; Kovács, Á.; Vadászi, H.; Micsonai, A.; Tóth, M.E.; Sántha, M.; Homolya, L.; et al. Synaptic Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Septin Accumulation Are Linked to Complement-Mediated Synapse Loss in an Alzheimer’s Disease Animal Model. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 5243–5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuvanov, L.; Mota, D.M.D.; Araujo, A.P.U.; DeMarco, R. A Blueprint of Septin Expression in Human Tissues. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2019, 19, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, C.B.; Marttinen, M.; Coelho, J.E.; Paldanius, K.M.A.; Takalo, M.; Mäkinen, P.; Leppänen, L.; Miranda-Lourenço, C.; Fonseca-Gomes, J.; Tanqueiro, S.R.; et al. S327 Phosphorylation of the Presynaptic Protein SEPTIN5 Increases in the Early Stages of Neurofibrillary Pathology and Alters the Functionality of SEPTIN5. Neurobiol. Dis. 2022, 163, 105603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotta, M.M.; Ronca, R.; Carotenuto, R.; Porreca, I.; Turano, M.; Ambrosino, C.; Capriglione, T. Specific Effects of Chronic Dietary Exposure to Chlorpyrifos on Brain Gene Expression-A Mouse Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyama, B.H.; Hetzer, M.W. Protein Homeostasis: Live Long, Won’t Prosper; Nature Publishing Group: London, UK, 2013; Volume 14. [Google Scholar]
- Noda, S.; Sato, S.; Fukuda, T.; Tada, N.; Uchiyama, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Hattori, N. Loss of Parkin Contributes to Mitochondrial Turnover and Dopaminergic Neuronal Loss in Aged Mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 136, 104717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leduc-Gaudet, J.P.; Reynaud, O.; Hussain, S.N.; Gouspillou, G. Parkin Overexpression Protects from Ageing-Related Loss of Muscle Mass and Strength. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 1975–1991, Erratum in J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 5991; Corrigendum in J. Physiol. 2020, 598, 4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimmi, A.; Peluso, I.; Rajabi, A.; Hassanzadeh, K. MiR-185 and SEPT5 Genes May Contribute to Parkinson’s Disease Pathophysiology. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5019815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, V.K.; Huang, B.X.; Desai, A.; Kevala, K.; Kim, H.Y. Role of DHA in Aging-Related Changes in Mouse Brain Synaptic Plasma Membrane Proteome. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 41, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffita-Mesa, J.; Paucar, M.; Svenningsson, P. Are ATXN2 Variants Modifying Our Understanding about Neural Pathogenesis, Phenotypes, and Diagnostic? Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 2445–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, D.; Bigio, M.D.; Ho, D.H.; Pulst, S.M. Expression of Ataxin-2 in Brains from Normal Individuals and Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease and Spinocerebellar Ataxia 2. Ann. Neurol. Off. J. Am. Neurol. Assoc. Child Neurol. Soc. 1999, 45, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, O.A.; Rutherford, N.J.; Baker, M.; Soto-Ortolaza, A.I.; Carrasquillo, M.M.; Dejesus-Hernandez, M.; Adamson, J.; Li, M.; Volkening, K.; Finger, E.; et al. Ataxin-2 Repeat-Length Variation and Neurodegeneration. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 3207–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, L.A.; Huang, B.; Bieri, G.; Ma, R.; Knowles, D.A.; Jafar-Nejad, P.; Messing, J.; Kim, H.J.; Soriano, A.; Auburger, G.; et al. Therapeutic Reduction of Ataxin-2 Extends Lifespan and Reduces Pathology in TDP-43 Mice. Nature 2017, 544, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, M.; Pusceddu, I.; März, W.; Herrmann, W. Telomere Biology and Age-Related Diseases. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 56, 1210–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oskouei, Z.; Mehri, S.; Kalalinia, F.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Evaluation of the Effect of Thymoquinone in D-Galactose-Induced Memory Impairments in Rats: Role of MAPK, Oxidative Stress, and Neuroinflammation Pathways and Telomere Length. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 2252–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pang, N.; Huang, X.; Meng, W.; Meng, L.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yi, Z.; Luo, Z.; et al. Ultrasound Deep Brain Stimulation Decelerates Telomere Shortening in Alzheimer’s Disease and Aging Mice. Fundam. Res. 2023, 3, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, L.; Guo, Y. Cerebroprotein Hydrolysate-I Protects Senescence-Induced by D-Galactose in PC12 Cells and Mice. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 3722–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, M.; Qi, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, X.; Tang, X.; Yong, T.; Xie, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Chen, D. Long-Term Administration of Triterpenoids from Ganoderma lucidum Mitigates Age-Associated Brain Physiological Decline via Regulating Sphingolipid Metabolism and Enhancing Autophagy in Mice. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 628860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Far, A.H.; Elghaity, M.M.; Mohamed, S.A.; Noreldin, A.E.; Elewa, Y.H.A.; Al Jaouni, S.K.; Alsenosy, A.A. Diosgenin Alleviates D-Galactose-Induced Oxidative Stress in Rats’ Brain and Liver Targeting Aging and Apoptotic Marker Genes. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1303379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccardi, V.; Marano, L. Aging, Cancer, and Inflammation: The Telomerase Connection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Ganesan, K.; Xu, B. Unlocking the Power: New Insights into the Anti-Aging Properties of Mushrooms. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadish, L.K.; Krishnan, V.V.; Shenbhagaraman, R.; Kaviyarasan, V. Comparitive Study on the Antioxidant, Anticancer and Antimicrobial Property of Agaricus bisporus (JE Lange) Imbach before and after Boiling. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 654–661. [Google Scholar]
- Kalyoncu, F.; Oskay, M.; Saǧlam, H.; Erdoǧan, T.F.; Tamer, A.U. Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Mycelia of 10 Wild Mushroom Species. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Tang, W.; Gao, H.E.; Chan, E.; Lan, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, S. Antimicrobial Activity of the Medicinal Mushroom Ganoderma. Food Rev. Int. 2005, 21, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poniedziałek, B.; Siwulski, M.; Wiater, A.; Komaniecka, I.; Komosa, A.; Asecka, M.G.; Magdziak, Z.; Mleczek, M.; Niedzielski, P.; Edrzej Proch, J.; et al. The Effect of Mushroom Extracts on Human Platelet and Blood Coagulation: In Vitro Screening of Eight Edible Species. Nutrients 2019, 11, 3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, K.; Singh, N.; Jindal, S.; Kaur, R.; Goyal, A.; Awasthi, R. Kjeldahl Method. In Advanced Techniques of Analytical Chemistry; Kumar, H., Ed.; Bentham Science Publisher: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2022; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wei, D. Antioxidant Activity of a Flavonoid-Rich Extract of Hypericum perforatum L. in Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 5032–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Analysis of Total Phenols and Other Oxidation Substrates and Antioxidants by Means of Folin-Ciocalteu Reagent. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.E.; Raner, G.M.; Isaacs, G.D. High Performance Liquid Chromatography Separation of Epigenetic Cytosine Variants. Methods Protoc. 2018, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, J.; Song, D.; Zhuang, L.; Ma, Q.; Xu, X. Antioxidant capacity of phenolic compounds separated from tea seed oil in vitro and in vivo. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bancroft, J.D.; Gamble, M. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; p. 725. ISBN 0443102791. [Google Scholar]
- Aggag, S.A.; Abdelkader, M.A.E.; Yacout, M.M. Neomycin’s Immunomodulatory Effect on the Gene Expression, Some Hematologic Parameters, and Intestinal Histology in Two Rabbit Lines. Anim. Gene 2022, 25, 200130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espino, A.M.; Rivera, F. Quantitation of Cytokine mRNA by Real-Time RT-PCR during a Vaccination Trial in a Rabbit Model of Fascioliasis. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 169, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawthon, R.M. Telomere Measurement by Quantitative PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.M.; Makhlouf, A.A.; Abdelrrassoul, H.A.; Yacuot, M.M. Molecular Genetic Studies on Some Pathogenic Bacteria Isolated from Rabbit Stomach. In Proceedings of the 15th International Symposium on Biocontrol and Biotechnology (ISBB 2017), Hurghada, Egypt, 17–20 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Oli, A.N.; Edeh, P.A.; Al-Mosawi, R.M.; Mbachu, N.A.; Al-Dahmoshi, H.O.M.; Al-Khafaji, N.S.K.; Ekuma, U.O.; Okezie, U.M.; Saki, M. Evaluation of the Phytoconstituents of Auricularia Auricula-Judae Mushroom and Antimicrobial Activity of Its Protein Extract. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 38, 101176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuia, M.S.; Rahaman, M.M.; Islam, T.; Bappi, M.H.; Sikder, M.I.; Hossain, K.N.; Akter, F.; Al Shamsh Prottay, A.; Rokonuzzman, M.; Gürer, E.S.; et al. Neurobiological Effects of Gallic Acid: Current Perspectives. Chin. Med. 2023, 18, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, M.; Liñán-Atero, R.; Tarahi, M.; Christodoulou, M.C.; Aghababaei, F. The Potential Health Benefits of Gallic Acid: Therapeutic and Food Applications. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, L.; Jin, W.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y. The Specific Effect of Gallic Acid on Escherichia coli Biofilm Formation by Regulating PgaABCD Genes Expression. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranwal, A.; Aggarwal, P.; Rai, A.; Kumar, N. Pharmacological Actions and Underlying Mechanisms of Catechin: A Review. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2021, 22, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.; Taine, E.G.; Meng, D.; Cui, T.; Tan, W. Chlorogenic Acid: A Systematic Review on the Biological Functions, Mechanistic Actions, and Therapeutic Potentials. Nutrients 2024, 16, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekinci-Akdemir, F.N.; Gülçin, I.; Gürsul, C.; Alwasel, S.H.; Bayir, Y. Effect of P-Coumaric Acid against Oxidative Stress Induced by Cisplatin in Brain Tissue of Rats. JAPS J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2017, 27, 1560–1564. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Z.; Wang, H.; Rao, S.; Sun, J.; Ma, C.; Li, J. p-Coumaric Acid Kills Bacteria through Dual Damage Mechanisms. Food Control. 2012, 25, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kaushik, D.; Shubham, S.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, V.; Oz, E.; Brennan, C.; Zeng, M.; Proestos, C.; Çadırcı, K.; et al. Ferulic Acid: Extraction, Estimation, Bioactivity and Applications for Human Health and Food. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 4168–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Wang, T.; Fu, Y.; Yu, T.; Ding, Y.; Nie, H. Ferulic Acid: A Review of Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Therapeutic Effects on Pulmonary Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzan, M.; Abedi, B.; Bhia, I.; Madanipour, A.; Farzan, M.; Bhia, M.; Aghaei, A.; Kheirollahi, I.; Motallebi, M.; Amini-Khoei, H.; et al. Pharmacological Activities and Molecular Mechanisms of Sinapic Acid in Neurological Disorders. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2024, 15, 2966–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandi, A.; Kalappan, V.M. Pharmacological and Therapeutic Applications of Sinapic Acid—An Updated Review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 3733–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, R.; Sarkar, A.; Ghosh, P.; Ganguly, M.; Karmakar, B.C.; Saha, D.R.; Halder, A.; Chowdhury, A.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K. Antimicrobial Activity of Ellagic Acid against Helicobacter pylori Isolates from India and during Infections in Mice. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Yan, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, X. Ellagic Acid and Its Anti-Aging Effects on Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naraki, K.; Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar, M.; Ajiboye, B.O.; Hosseinzadeh, H. The Effect of Ellagic Acid on the Metabolic Syndrome: A Review Article. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, A.; Booth, B.W. Biomedical Applications of Tannic Acid. J. Biomater. Appl. 2022, 36, 1503–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Moghaddam, L.; Barner, L.; Cometta, S.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Medeiros Savi, F. The Multifaceted Role of Tannic Acid: From Its Extraction and Structure to Antibacterial Properties and Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2025, 160, 101908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruwizhi, N.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Cinnamic Acid Derivatives and Their Biological Efficacy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.C.; Deng, J.S.; Chiu, C.S.; Hou, W.C.; Huang, S.S.; Shie, P.H.; Huang, G.J. Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Cinnamomum Cassia Constituents In Vitro and In Vivo. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 429320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Mushroom Sample | Agaricus bisporus | Pleurotus ostreatus | Ganoderma lucidum | Hericium erinaceus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Phenols (mg GAE/g Extract) | 2.49 ± 0.08 | 5.19 ± 0.06 | 2.92 ± 0.04 | 2.01 ± 0.05 |
| Total Flavonoid (mg QE/g Extract) | 1.28 ± 0.02 | 0.95 ± 0.07 | 0.45 ± 0.04 | 0.38 ± 0.02 |
| Groups | Sinusoidal Dilatation | Vacuolar and Hydropic Degeneration | Hemorrhage | Mononuclear Cell Infiltration (Inflammation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | − | − | − | − |
| D-gal | − | ++ | +++ | ++ |
| AB | − | − | ++ | ++ |
| PO | − | − | + | + |
| GL | − | − | − | − |
| HE | − | − | − |
| Groups | Cerebral Cortex | Cerebellum | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaculation | Necrosis | Corrugation of the Meninges | Hemorrhage | Inflammation | Vaculation | Necrosis | Hemorrhage | |
| Control | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| D-gal | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | − |
| AB | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | − | − | − |
| PO | + | + | + | − | + | ++ | ++ | − |
| GL | + | + | − | − | + | − | − | − |
| HE | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − |
| Diameter of Inhibition Zone (mm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microorganism | Mushroom Extract (500 mg/mL) | Ampicillin (AMP) (10 μg/disk) | |||
| Agaricus bisporus | Pleurotus ostreatus | Ganoderma lucidum | Hericium erinaceus | ||
| Gram-negative bacteria | |||||
| Escherichia coli | 20.00 ± 0.15 | 18.00 ± 0.06 | 16.00 ± 0.10 | 22.00 ± 0.06 | 24 |
| Klebsiella oxytoca | 15.00 ± 0.10 | 14.00 ± 0.10 | 15.00 ± 0.10 | - | 24 |
| Gram-positive bacteria | |||||
| Lysinibacillus odyssey | 22.00 ± 0.06 | 21.00 ± 0.06 | 14.00 ± 0.06 | - | 23 |
| Lysinibacillus fusiformis | 11.00 ± 0.06 | 13.00 ± 0.06 | 10.00 ± 0.06 | - | 25 |
| Microorganism | MIC Value (mg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agaricus bisporus | Pleurotus ostreatus | Ganoderma lucidum | Hericium erinaceus | |
| Gram-negative bacteria | ||||
| Escherichia coli | 3.90 ± 0.33 | 3.90 ± 0.52 | 31.25 ± 0.23 | 3.90 ± 0.4 |
| Klebsiella oxytoca | 7.81 ± 0.38 | 7.81 ± 0.46 | 3.90 ± 0.16 | - |
| Gram-positive bacteria | ||||
| Lysinibacillus odyssey | 1.95 ± 0.24 | 3.90 ± 0.27 | 125.00 ± 0.19 | - |
| Lysinibacillus fusiformis | 125.00 ± 0.57 | 15.62 ± 0.55 | 125.00 ± 0.28 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelkader, M.-A.E.; Mediatrice, H.; Lin, Z.; Rensing, C.; Yacout, M.M.; Lin, D.; Aggag, S.A. Investigating the Neuroprotective, Hepatoprotective, and Antimicrobial Effects of Mushroom Extracts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178440
Abdelkader M-AE, Mediatrice H, Lin Z, Rensing C, Yacout MM, Lin D, Aggag SA. Investigating the Neuroprotective, Hepatoprotective, and Antimicrobial Effects of Mushroom Extracts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178440
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelkader, Menna-Allah E., Hatungimana Mediatrice, Zhanxi Lin, Christopher Rensing, Mohamed M. Yacout, Dongmei Lin, and Sarah A. Aggag. 2025. "Investigating the Neuroprotective, Hepatoprotective, and Antimicrobial Effects of Mushroom Extracts" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178440
APA StyleAbdelkader, M.-A. E., Mediatrice, H., Lin, Z., Rensing, C., Yacout, M. M., Lin, D., & Aggag, S. A. (2025). Investigating the Neuroprotective, Hepatoprotective, and Antimicrobial Effects of Mushroom Extracts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178440








