Lymphoid and Myeloid Proliferations After Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Therapy: The Pathologist’s Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cases
2.2. Histologic Evaluation
2.3. Flow Cytometric Analysis
2.4. Conventional Cytogenetic and Interphase Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Studies
2.5. Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) for Hematologic Cancer
3. Cases and Discussion
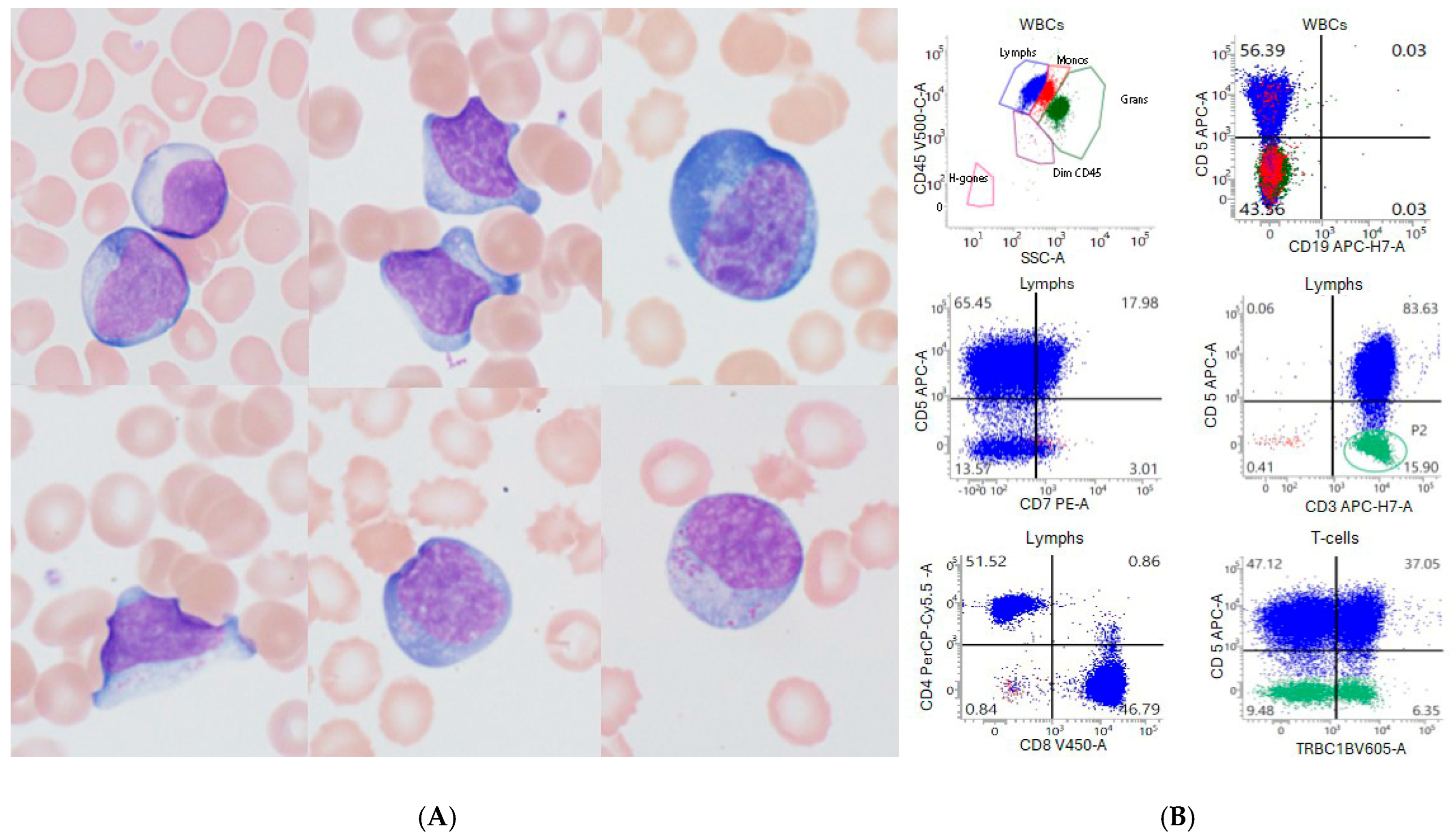
3.1. Absolute Lymphocytosis After CAR-T-Cell Infusion
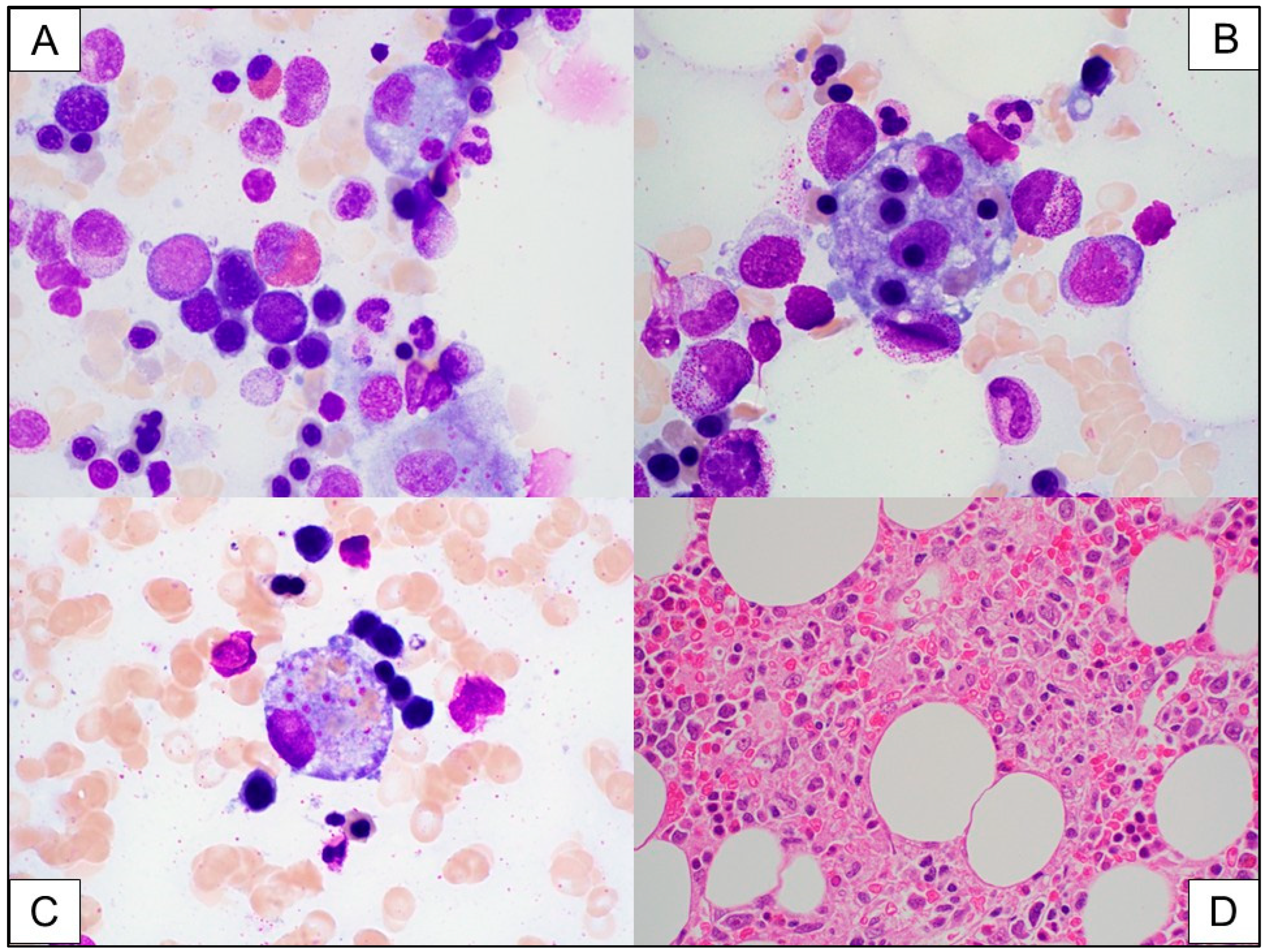
3.2. Immune Effector Cell (IEC)-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis-like Syndrome
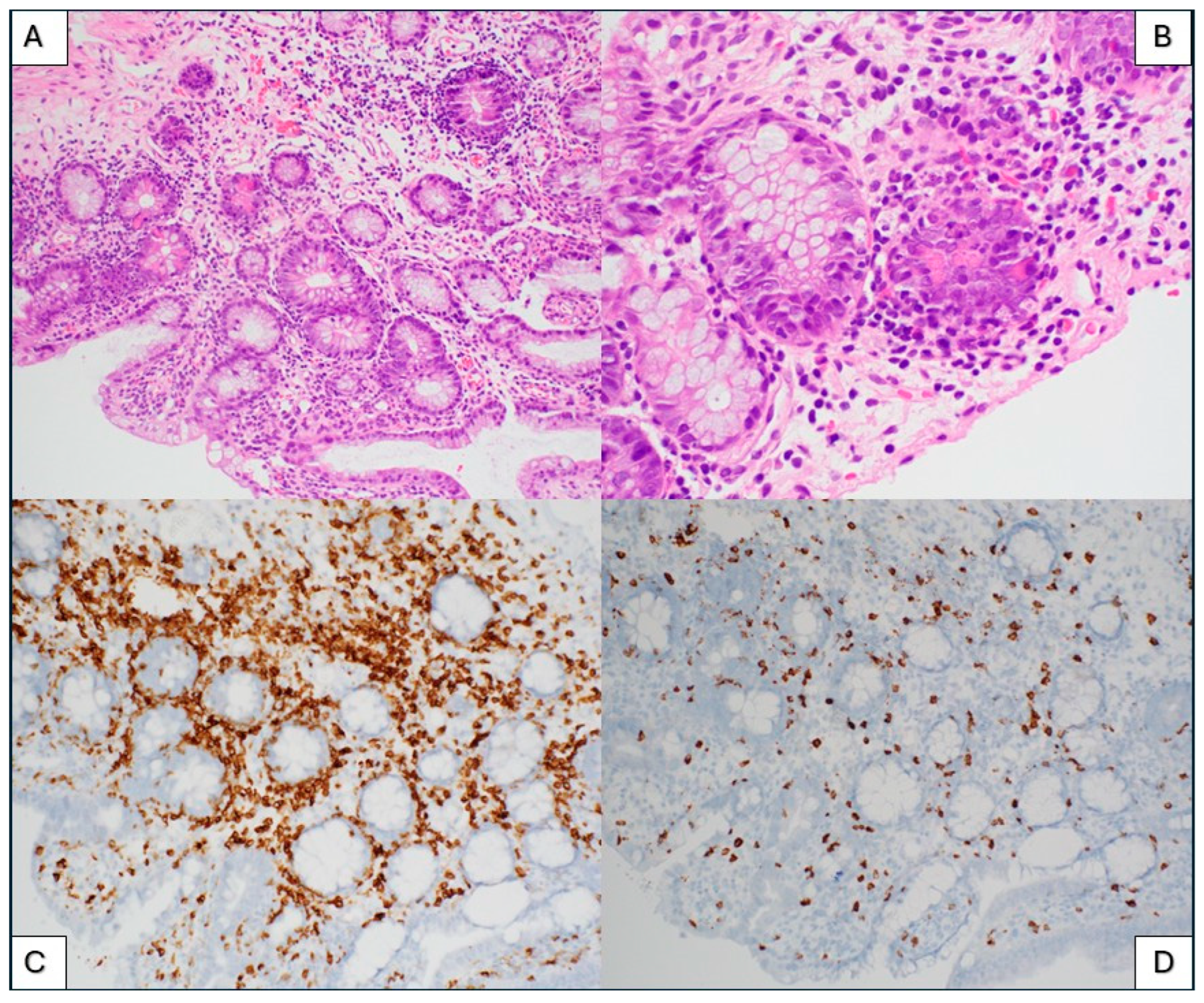
3.3. Immune Effector Cell (IEC)-Associated Enteropathy
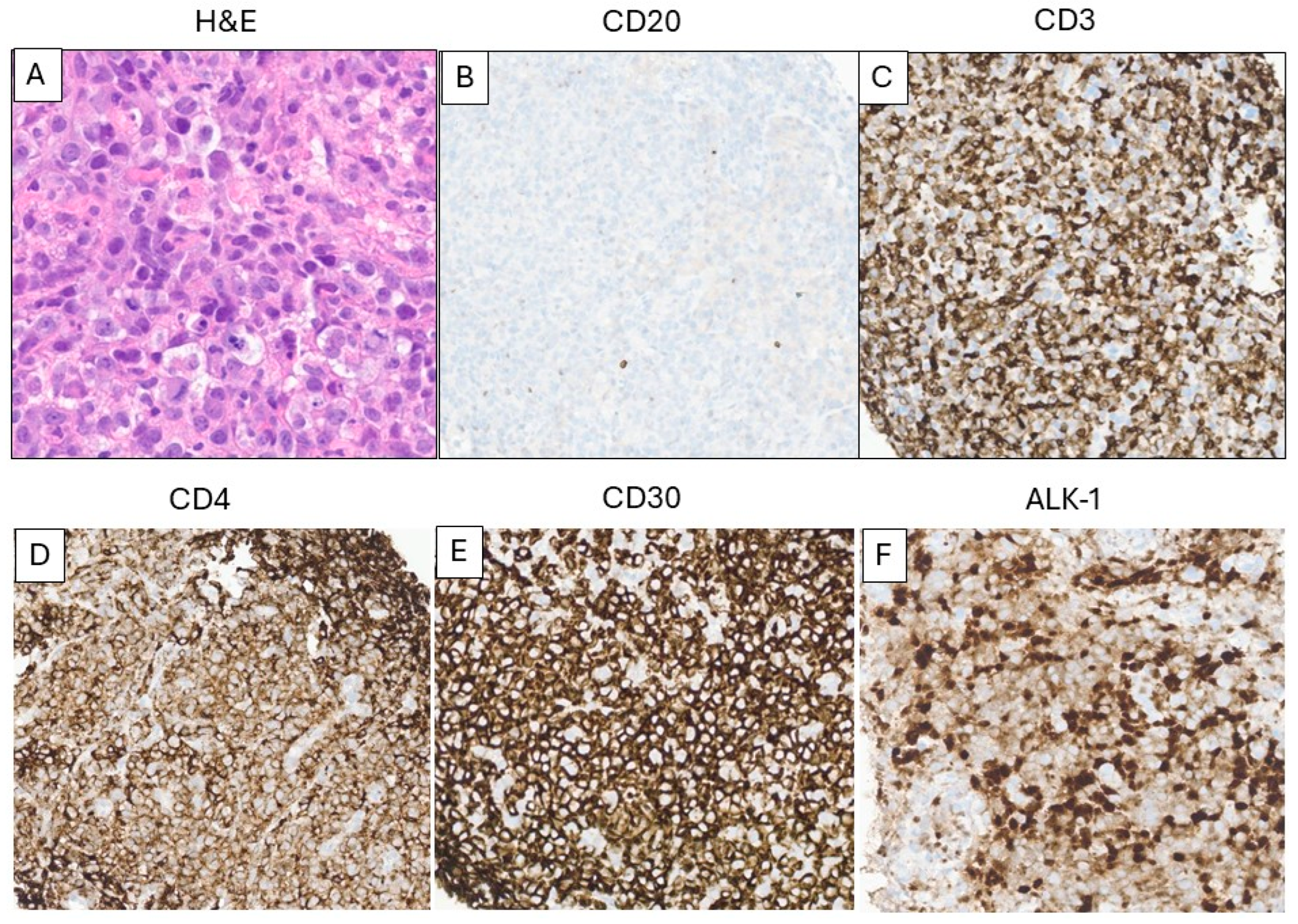
3.4. T-Cell Lymphoma After CAR T-Cell Therapy
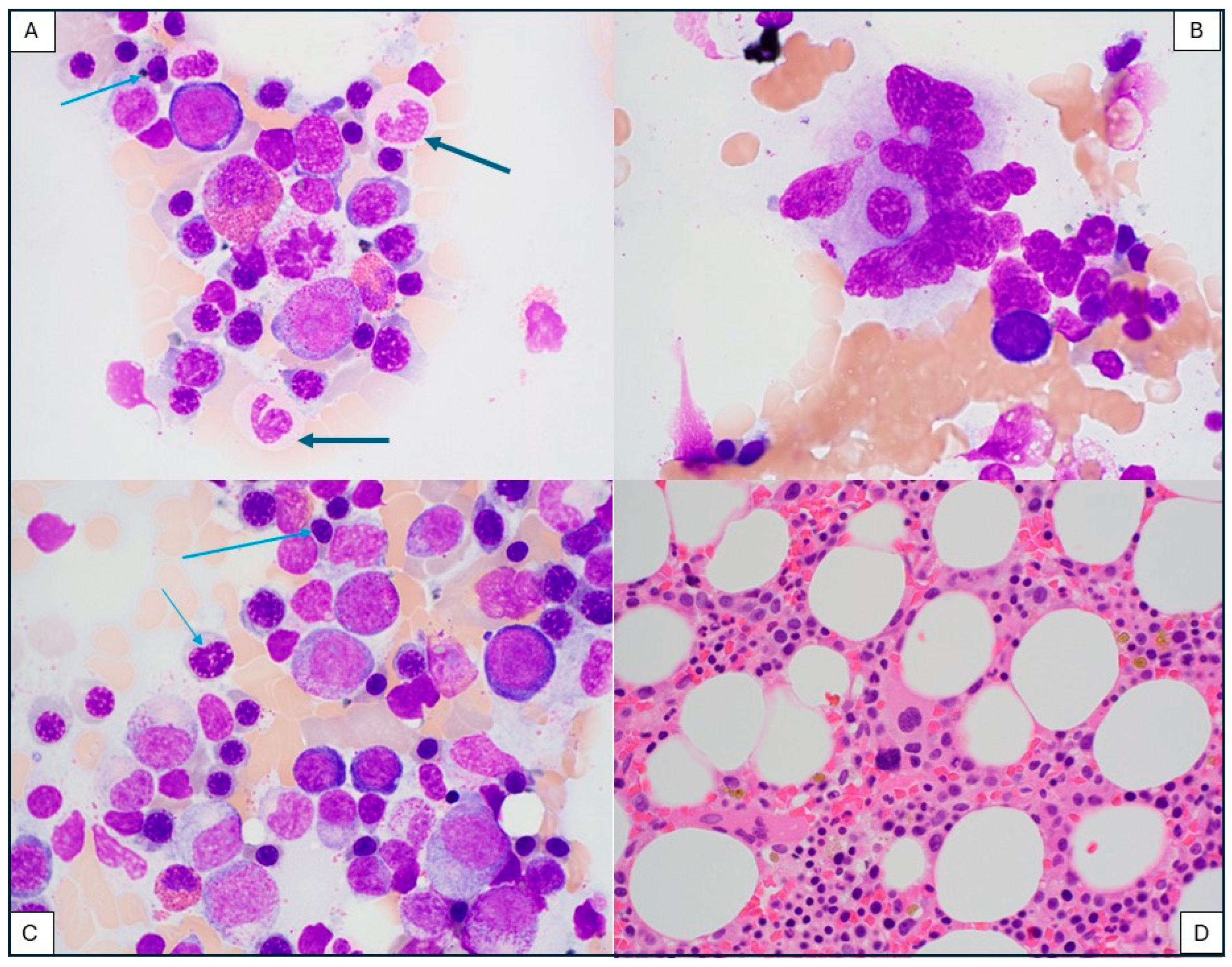
3.5. Secondary Myeloid Neoplasm After CAR-T-Cell Therapy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ong, M.Z.; Kimberly, S.A.; Lee, W.H.; Ling, M.; Lee, M.; Tan, K.W.; Foo, J.B.; Yow, H.Y.; Sellappans, R.; Hamzah, S. FDA-approved CAR T-cell Therapy: A Decade of Progress and Challenges. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2024, 25, 1377–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffin, D.H.M.; Muhsen, I.N.; Hill, L.C.; Ramos, C.A.; Ahmed, N.; Hegde, M.; Wang, T.; Wu, M.; Gottschalk, S.; Whittle, S.B.; et al. Long-term follow-up for the development of subsequent malignancies in patients treated with genetically modified IECs. Blood 2022, 140, 16–24, Erratum in Blood 2023, 141, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens-Kroef, M.; Simons, A.; Rack, K.; Hastings, R.J. Cytogenetic Nomenclature and Reporting. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1541, 303–309. [Google Scholar]
- Mejia Saldarriaga, M.; Pan, D.; Unkenholz, C.; Mouhieddine, T.H.; Velez-Hernandez, J.E.; Engles, K.; Fein, J.A.; Monge, J.; Rosenbaum, C.; Pearse, R.; et al. Absolute lymphocyte count after BCMA CAR-T therapy is a predictor of response and outcomes in relapsed multiple myeloma. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 3859–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faude, S.; Wei, J.; Muralidharan, K.; Xu, X.; Wertheim, G.; Paessler, M.; Bhoj, V.G.; Grupp, S.A.; Maude, S.L.; Rheingold, S.R.; et al. Absolute lymphocyte count proliferation kinetics after CAR T-cell infusion impact response and relapse. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 2128–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santurio, D.S.; Barros, L.R.C.; Glauche, I.; Fassoni, A.C. Mathematical modeling unveils the timeline of CAR-T cell therapy and macrophage-mediated cytokine release syndrome. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2025, 21, e1012908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, A.G.; Minson, A.; Blombery, P.; Dickinson, M.; Harrison, S.J.; Anderson, M.A. CAR-T cell therapy: Practical guide to routine laboratory monitoring. Pathology 2021, 53, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixao, E.A.; Barros, L.R.C.; Fassoni, A.C.; Almeida, R.C. Modeling Patient-Specific CAR-T Cell Dynamics: Multiphasic Kinetics via Phenotypic Differentiation. Cancers 2022, 14, 5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ayyar, V.S.; Zheng, X.; Chen, W.; Zheng, S.; Mody, H.; Wang, W.; Heald, D.; Singh, A.P.; Cao, Y. Model-Based Cellular Kinetic Analysis of Chimeric Antigen Receptor-T Cells in Humans. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 109, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittibschlager, V.; Bacher, U.; Seipel, K.; Porret, N.; Wiedemann, G.; Haslebacher, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Daskalakis, M.; Akhoundova, D.; Pabst, T. CAR T-Cell Persistence Correlates with Improved Outcome in Patients with B-Cell Lymphoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trottestam, H.; Horne, A.; Arico, M.; Egeler, R.M.; Filipovich, A.H.; Gadner, H.; Imashuku, S.; Ladisch, S.; Webb, D.; Janka, G.; et al. Chemoimmunotherapy for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: Long-term results of the HLH-94 treatment protocol. Blood 2011, 118, 4577–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canna, S.W.; Marsh, R.A. Pediatric hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 2020, 135, 1332–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henter, J.I.; Horne, A.; Arico, M.; Egeler, R.M.; Filipovich, A.H.; Imashuku, S.; Ladisch, S.; McClain, K.; Webb, D.; Winiarski, J.; et al. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2007, 48, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, V.E.; Wong, C.; Huang, C.Y.; Thiruvengadam, S.K.; Wolf, J.; Martin, T.G.; Shah, N.; Wong, S.W. Macrophage activation syndrome-like (MAS-L) manifestations following BCMA-directed CAR T cells in multiple myeloma. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 5344–5348, Erratum in: Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lichtenstein, D.A.; Schischlik, F.; Shao, L.; Steinberg, S.M.; Yates, B.; Wang, H.W.; Wang, Y.; Inglefield, J.; Dulau-Florea, A.; Ceppi, F.; et al. Characterization of HLH-like manifestations as a CRS variant in patients receiving CD22 CAR T cells. Blood 2021, 138, 2469–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, M.R.; Keenan, C.; Maron Alfaro, G.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, Y.; Sharma, A.; Hurley, C.; Nichols, K.E.; Gottschalk, S.; Triplett, B.M.; et al. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis-like toxicity (carHLH) after CD19-specific CAR T-cell therapy. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 194, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, T.J.; Lazarevic, A.; Ziggas, J.E.; Fuchs, E.; Kim, K.; Byrnes, H.; Luznik, L.; Bolanos-Meade, J.; Ali, S.A.; Shah, N.N.; et al. Hyperinflammatory syndrome resembling haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis following axicabtagene ciloleucel and brexucabtagene autoleucel. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 199, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, H.; Bachmeier, C.; Chavez, J.C.; Song, J.; Hussaini, M.; Krivenko, G.; Nishihori, T.; Kotani, H.; Davila, M.L.; Locke, F.L.; et al. Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis has variable time to onset following CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 187, e35–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Santomasso, B.D.; Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Turtle, C.J.; Brudno, J.N.; Maus, M.V.; Park, J.H.; Mead, E.; Pavletic, S.; et al. ASTCT Consensus Grading for Cytokine Release Syndrome and Neurologic Toxicity Associated with Immune Effector Cells. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, M.R.; Knight, T.E.; McNerney, K.O.; Leick, M.B.; Jain, T.; Ahmed, S.; Frigault, M.J.; Hill, J.A.; Jain, M.D.; Johnson, W.T.; et al. Immune Effector Cell-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis-Like Syndrome. Transplant. Cell Ther. 2023, 29, 438.e1–438.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvelli, J.; Piperoglou, C.; Farnarier, C.; Vely, F.; Mazodier, K.; Audonnet, S.; Nitschke, P.; Bole-Feysot, C.; Boucekine, M.; Cambon, A.; et al. Functional and genetic testing in adults with HLH reveals an inflammatory profile rather than a cytotoxicity defect. Blood 2020, 136, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Sbeih, H.; Tang, T.; Ali, F.S.; Luo, W.; Neelapu, S.S.; Westin, J.R.; Okhuysen, P.C.; Foo, W.C.; Curry, J.L.; Richards, D.M.; et al. Gastrointestinal Adverse Events Observed After Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 42, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuna, G.G.; Banerjee, R.; Savid-Frontera, C.; Song, J.; Moran-Segura, C.M.; Nguyen, J.V.; Lekakis, L.; Fernandez-Pol, S.; Samraj, A.N.; Naresh, K.N.; et al. Immune effector cell-associated enterocolitis following chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy in multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2024, 14, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, A.; Patten, P.E.M.; Kuhnl, A.; Ooft, M.L.; Hayee, B.; Sanderson, R. Colitis After CAR T-Cell Therapy for Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma Responds to Anti-Integrin Therapy. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2021, 27, e45–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zundler, S.; Vitali, F.; Kharboutli, S.; Volkl, S.; Polifka, I.; Mackensen, A.; Atreya, R.; Neurath, M.F.; Mougiakakos, D. Case Report: IBD-like colitis following CAR T cell therapy for diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1149450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.J.L.; Chhabra, S.; De Menezes Silva Corraes, A.; Parrondo, R.D.; Gertz, M.; Hwa, L.; Stephens, H.; Bansal, R.; Jankowski, M.; Kapoor, P.; et al. Risk Factors for Immune Effector Cell-Associated Enterocolitis (IEC-colitis) in Patients with Relapsed Myeloma Treated with Ciltacabtagene Autoleucel (cilta-cel). Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2025, 31, S234–S235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemirli, M.; Loughney, T.M.; Deniz, E.; Chahine, J.J.; Albitar, M.; Pittaluga, S.; Sadigh, S.; Armand, P.; Uren, A.; Anderson, K.C. Indolent CD4+ CAR T-Cell Lymphoma after Cilta-cel CAR T-Cell Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 2074–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsallab, M.; Ellithi, M.; Lunning, M.A.; D’Angelo, C.; Ma, J.; Perales, M.A.; Frigault, M.; Maus, M.V. Second primary malignancies after commercial CAR T-cell therapy: Analysis of the FDA Adverse Events Reporting System. Blood 2024, 143, 2099–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulery, R.; Guiraud, V.; Choquet, S.; Thieblemont, C.; Bachy, E.; Barete, S.; Todesco, E.; Arnulf, B.; Boissel, N.; Baruchel, A.; et al. T cell malignancies after CAR T cell therapy in the DESCAR-T registry. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 1130–1133, Erratum in Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tix, T.; Alhomoud, M.; Shouval, R.; Cliff, E.R.S.; Perales, M.A.; Cordas Dos Santos, D.M.; Rejeski, K. Second Primary Malignancies after CAR T-Cell Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of 5517 Lymphoma and Myeloma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 4690–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, M.P.; Sugio, T.; Noordenbos, T.; Shi, S.; Bulterys, P.L.; Liu, C.L.; Kang, X.; Olsen, M.N.; Good, Z.; Dahiya, S.; et al. Risk of Second Tumors and T-Cell Lymphoma after CAR T-Cell Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 2047–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghilardi, G.; Fraietta, J.A.; Gerson, J.N.; Van Deerlin, V.M.; Morrissette, J.J.D.; Caponetti, G.C.; Paruzzo, L.; Harris, J.C.; Chong, E.A.; Susanibar Adaniya, S.P.; et al. T cell lymphoma and secondary primary malignancy risk after commercial CAR T cell therapy. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micklethwaite, K.P.; Gowrishankar, K.; Gloss, B.S.; Li, Z.; Street, J.A.; Moezzi, L.; Mach, M.A.; Sutrave, G.; Clancy, L.E.; Bishop, D.C.; et al. Investigation of product-derived lymphoma following infusion of piggyBac-modified CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T cells. Blood 2021, 138, 1391–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobbe, G.; Bruggemann, M.; Baermann, B.N.; Wiegand, L.; Trautmann, H.; Yousefian, S.; Libertini, S.; Menssen, H.D.; Maier, H.J.; Ulrich, P.; et al. Aggressive Lymphoma after CD19 CAR T-Cell Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, B.L.; Pasquini, M.C.; Connolly, J.E.; Porter, D.L.; Gustafson, M.P.; Boelens, J.J.; Horwitz, E.M.; Grupp, S.A.; Maus, M.V.; Locke, F.L.; et al. Unanswered questions following reports of secondary malignancies after CAR-T cell therapy. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.J.; Touzeau, C.; Kint, N.; Li, K.; Nguyen, T.; Mayeur-Rousse, C.; Rahman, M.; Le Bris, Y.; Er, J.; Eugene-Lamer, J.; et al. CAR+ T-Cell Lymphoma after Cilta-cel Therapy for Relapsed or Refractory Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Jacobson, C.A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lekakis, L.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Lin, Y.; Braunschweig, I.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; et al. Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): A single-arm, multicentre, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.J.; Bishop, M.R.; Tam, C.S.; Waller, E.K.; Borchmann, P.; McGuirk, J.P.; Jager, U.; Jaglowski, S.; Andreadis, C.; Westin, J.R.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, A.; Bezerra, E.D.; Hirayama, A.V.; Hill, J.A.; Wu, Q.V.; Voutsinas, J.; Sorror, M.L.; Turtle, C.J.; Maloney, D.G.; Bar, M. Late Events after Treatment with CD19-Targeted Chimeric Antigen Receptor Modified T Cells. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020, 26, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; Bejar, R.; Germing, U.; Haferlach, C.; Ogawa, S.; Padron, E.; Patkar, N.V.; Xiao, W. Haematolymphoid Tumours Part A. In Myeloid Neoplasm Post Cytotoxic Therapy; Board TWCoTE, Ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC): Lyon, France, 2024; pp. 170–172. [Google Scholar]
- Falini, L.; Venanzi, A.; Tini, V.; Innocente, A.; Ballanti, S.; Saldi, S.; Sivolella, S.; Pierini, A.; Aristei, C.; Tiacci, E.; et al. Acute myeloid leukemia development soon after anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell infusion in a patient with refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and pre-existing clonal hematopoiesis. Haematologica 2023, 108, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accorsi Buttini, E.; Farina, M.; Lorenzi, L.; Polverelli, N.; Radici, V.; Morello, E.; Colnaghi, F.; Almici, C.; Ferrari, E.; Bianchetti, A.; et al. High risk-myelodysplastic syndrome following CAR T-cell therapy in a patient with relapsed diffuse large B cell lymphoma: A case report and literature review. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1036455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhateeb, H.B.; Mohty, R.; Greipp, P.; Bansal, R.; Hathcock, M.; Rosenthal, A.; Murthy, H.; Kharfan-Dabaja, M.; Bisneto Villasboas, J.C.; Bennani, N.; et al. Therapy-related myeloid neoplasms following chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainstein, V.; Avni, B.; Grisariu, S.; Kfir-Erenfeld, S.; Asherie, N.; Nachmias, B.; Auman, S.; Saban, R.; Zimran, E.; Assayag, M.; et al. Clonal Myeloid Dysplasia Following CAR T-Cell Therapy: Chicken or the Egg? Cancers 2023, 15, 3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| CAR T-Cell Therapy | Target | Approved Use |
|---|---|---|
| Abecma (ide-cel) | BCMA | Multiple myeloma |
| Carvytki (cilta-cel) | BCMA | Multiple myeloma |
| Aucatzyl (obe-cel) | CD19 | B-cell ALL (adult) |
| Kymriah (tisa-cel) | CD19 | B-cell ALL (pediatric/young adult) Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma Follicular lymphoma |
| Tecartus (brexu-cel) | CD19 | B-cell ALL (adult) Mantle cell lymphoma |
| Yescarta (axi-cel) | CD19 | Large B-cell lymphoma Follicular lymphoma |
| Breyanzi (liso-cel) | CD19 | Follicular lymphoma Large B-cell lymphoma Mantle cell lymphoma Chronic lymphocytic leukemia |
| Case# | Original Disease | CAR-T Type | Post-CAR-T Abnormality | Timing After CAR-T Infusion | CAR-T-Cell Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Multiple Myeloma | Celta-cel | Atypical lymphocytosis | 12–14 days | Expansion |
| 2 | DLBCL | Axi-cel | IEC-associated HLH | 14–30 days | Expansion/Contraction |
| 3 | Multiple Myeloma | Ide-cel | IEC-associated enterocolitis | 5 months | Persistence |
| 4 | Follicular Lymphoma | Axi-cel | ALCL, ALK+ | 7 months | Persistence |
| 5 | DLBCL | Axi-cel | MDS | 24 months | Persistence |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Kelemen, K. Lymphoid and Myeloid Proliferations After Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Therapy: The Pathologist’s Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178388
Zhou J, Kelemen K. Lymphoid and Myeloid Proliferations After Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Therapy: The Pathologist’s Perspective. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178388
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jiehao, and Katalin Kelemen. 2025. "Lymphoid and Myeloid Proliferations After Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Therapy: The Pathologist’s Perspective" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178388
APA StyleZhou, J., & Kelemen, K. (2025). Lymphoid and Myeloid Proliferations After Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Therapy: The Pathologist’s Perspective. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178388





