Erythropoietin Attenuates Insulin Resistance and Renal Inflammation in High-Sucrose-Treated Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. EPO Improved Insulin Sensitivity in High-Sucrose-Induced Insulin Resistance Model Rats
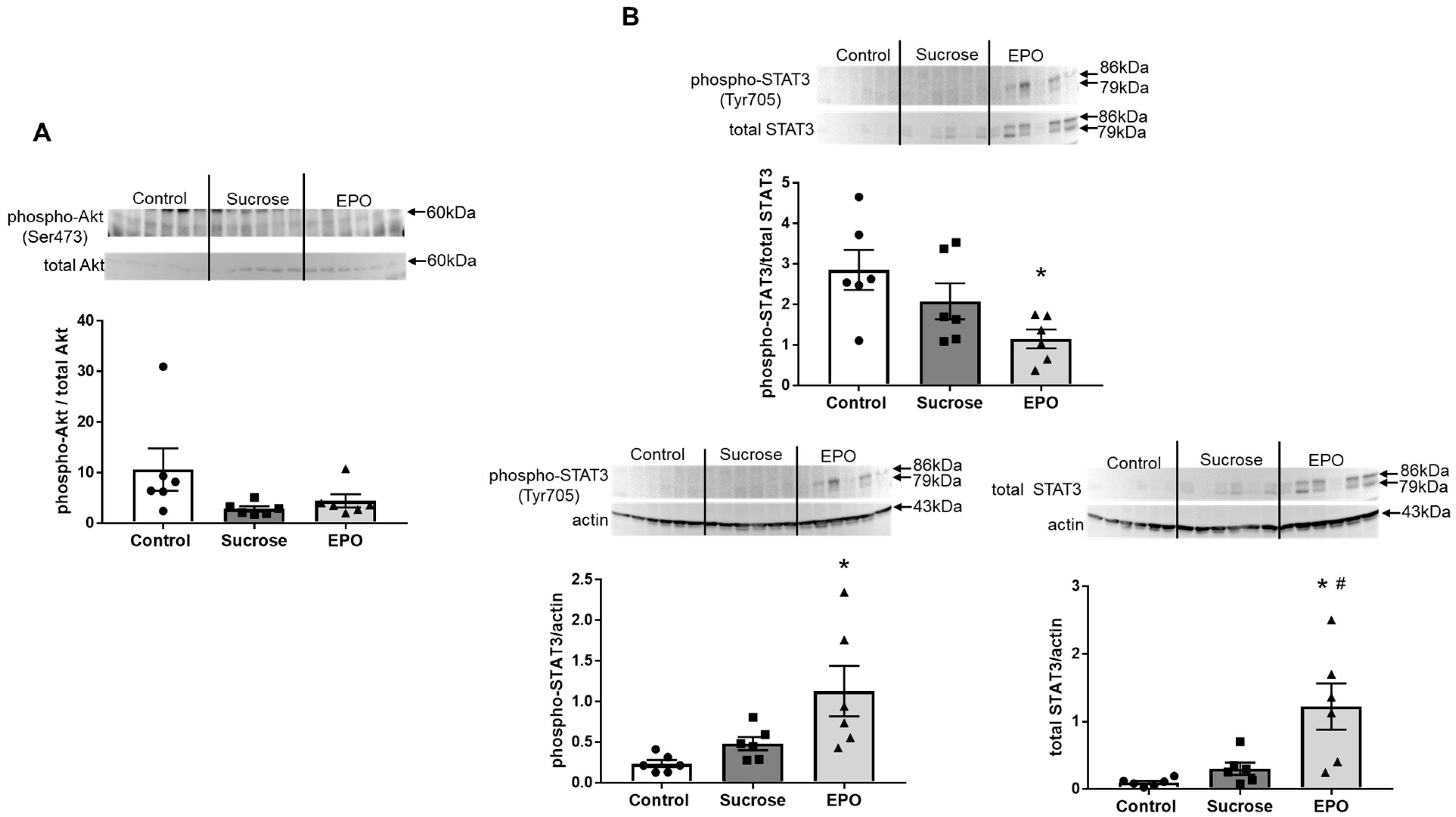
2.2. EPO Had No Effects on the Akt Pathway, but Activated the Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription (STAT)3 Pathway in the Insulin Resistant Rat Liver
2.3. Vascular Inflammation in the Insulin-Resistant Model Rat Was Suppressed in the EPO-Treated Group
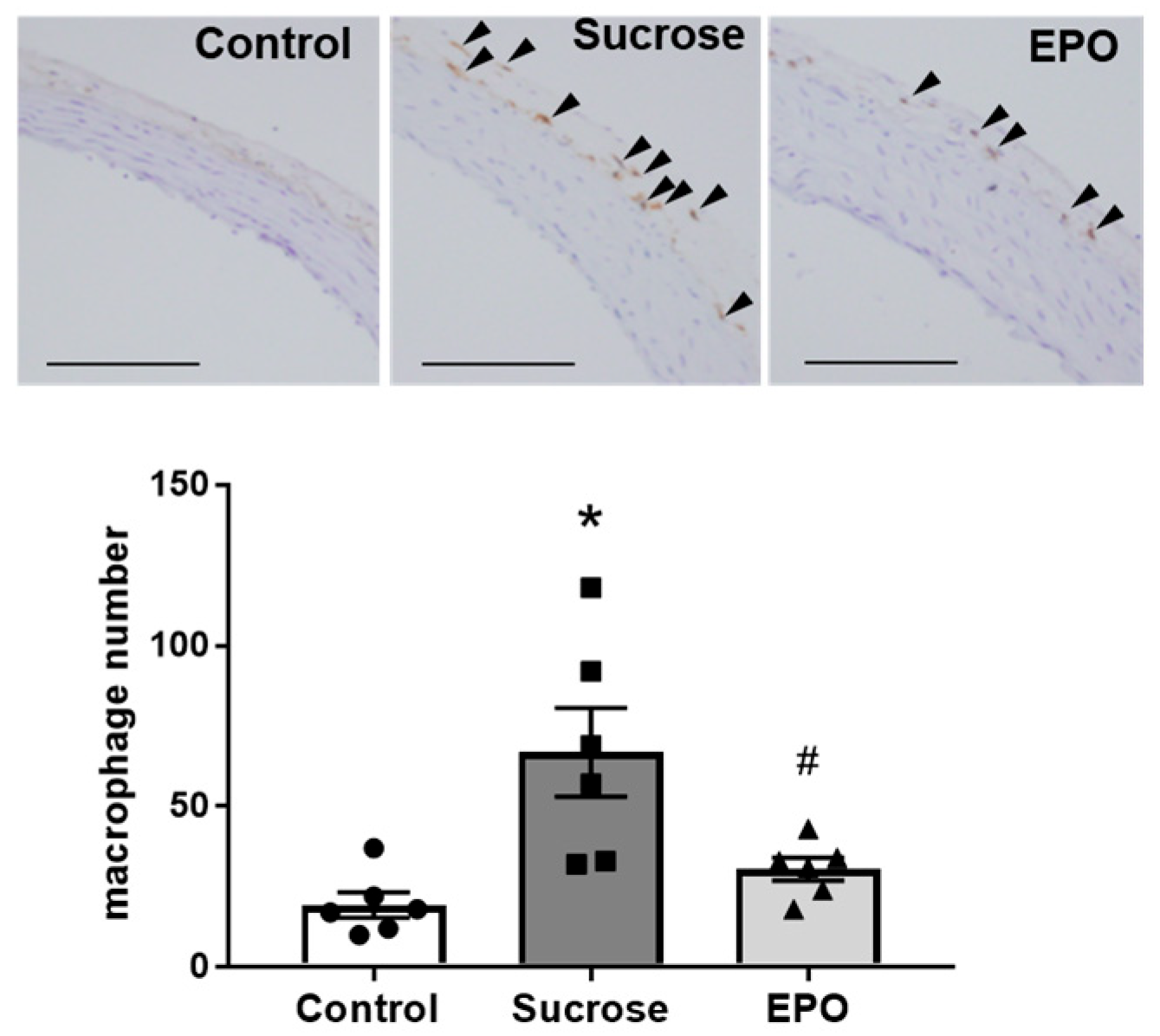
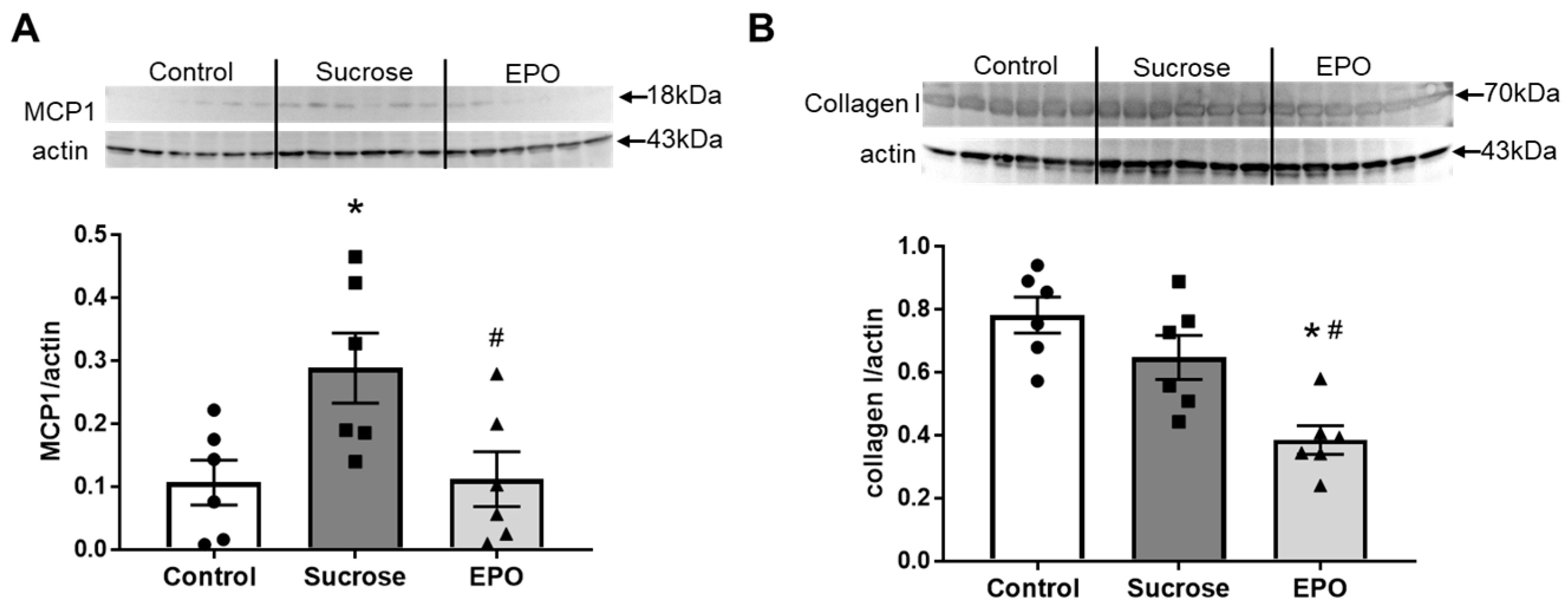
2.4. EPO Treatment Attenuated Renal Inflammation and Reduced Collagen Content in Insulin-Resistant Model Rats
2.5. EPO Promoted Macrophage M1 < M2 Polarization in the Kidney of Sucrose-Treated Insulin-Resistant Model Rats
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Insulin Resistance Model and EPO Treatment
4.3. Functional Studies
4.4. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
4.5. Immunoblotting
4.6. Histology
4.7. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.8. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Means, R.T., Jr.; Krantz, S.B. Progress in understanding the pathogenesis of the anemia of chronic disease. Blood 1992, 80, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, T.; Kung, C.K.; Goldwasser, E. Purification of human erythropoietin. J. Biol. Chem. 1977, 252, 5558–5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.W. Erythropoietin: Physiology and pharmacology update. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2003, 228, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, P.K. Pleiotropic renal actions of erythropoietin. Lancet 2005, 365, 1890–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschos, N.; Lykissas, M.G.; Beris, A.E. The role of erythropoietin as an inhibitor of tissue ischemia. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 4, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshdel, A.; Carney, S.; Gillies, A.; Mourad, A.; Jones, B.; Nanra, R.; Trevillian, P. Potential roles of erythropoietin in the management of anaemia and other complications diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2008, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Toba, H.; Morita, Y.; Nakashima, K.; Noda, K.; Tian, W.; Kobara, M.; Nakata, T. Endothelial dysfunction, macrophage infiltration and NADPH oxidase-dependent superoxide production were attenuated by erythropoietin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat aorta. Pharmacology 2013, 91, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toba, H.; Sawai, N.; Morishita, M.; Murata, S.; Yoshida, M.; Nakashima, K.; Morita, Y.; Kobara, M.; Nakata, T. Chronic treatment with recombinant human erythropoietin exerts renoprotective effects beyond hematopoiesis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 612, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toba, H.; Kojima, Y.; Wang, J.; Noda, K.; Tian, W.; Kobara, M.; Nakata, T. Erythropoietin attenuated vascular dysfunction and inflammation by inhibiting NADPH oxidase-derived superoxide production in nitric oxide synthase-inhibited hypertensive rat aorta. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 691, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toba, H.; Morishita, M.; Tojo, C.; Nakano, A.; Oshima, Y.; Kojima, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Nakashima, K.; Wang, J.; Kobara, M.; et al. Recombinant human erythropoietin ameliorated endothelial dysfunction and macrophage infiltration by increasing nitric oxide in hypertensive 5/6 nephrectomized rat aorta. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 656, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toba, H.; Nakashima, K.; Oshima, Y.; Kojima, Y.; Tojo, C.; Nakano, A.; Wang, J.; Kobara, M.; Nakata, T. Erythropoietin prevents vascular inflammation and oxidative stress in subtotal nephrectomized rat aorta beyond haematopoiesis. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2010, 37, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, P.H.; Brunn, G.J.; Kohn, A.D.; Roth, R.A.; Lawrence, J.C., Jr. Evidence of insulin-stimulated phosphorylation and activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin mediated by a protein kinase B signaling pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7772–7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaven, G.M. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 1988, 37, 1595–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, Y.; Hirata, A.; Murakami, H.; Fukuoka, M.; Agata, J.; Higashiura, K.; Masuda, A.; Ura, N.; Shimamoto, K. Effects of aging on the insulin actions for the glucose metabolism and renal function in normotensives and essential hypertensives. Am. J. Hypertens. 1998, 11, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- King, G.L.; Wakasaki, H. Theoretical mechanisms by which hyperglycemia and insulin resistance could cause cardiovascular diseases in diabetes. Diabetes Care 1999, 22 (Suppl. 3), C31–C37. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Shimamoto, K.; Hirata, A.; Fukuoka, M.; Higashiura, K.; Miyazaki, Y.; Shiiki, M.; Masuda, A.; Nakagawa, M.; Iimura, O. Insulin sensitivity and the effects of insulin on renal sodium handling and pressor systems in essential hypertensive patients. Hypertension 1994, 23, I29–I33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iimura, O.; Shimamoto, K.; Masuda, A.; Higashiura, K.; Miyazaki, Y.; Hirata, A.; Fukuoka, M.; Murakami, H. Effects of a calcium channel blocker, manidipine, on insulin sensitivity in essential hypertensives. J. Diabetes Complicat. 1995, 9, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamide, K.; Hori, M.T.; Zhu, J.H.; Barrett, J.D.; Eggena, P.; Tuck, M.L. Insulin-mediated growth in aortic smooth muscle and the vascular renin-angiotensin system. Hypertension 1998, 32, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ormazabal, V.; Nair, S.; Elfeky, O.; Aguayo, C.; Salomon, C.; Zuniga, F.A. Association between insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnaeeli, M.; Raaka, B.M.; Gavrilova, O.; Teng, R.; Chanturiya, T.; Noguchi, C.T. Erythropoietin signaling: A novel regulator of white adipose tissue inflammation during diet-induced obesity. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2415–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, B.; Shi, R.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z. Nonerythropoietic Erythropoietin-Derived Peptide Suppresses Adipogenesis, Inflammation, Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuma, Y.; Mori, J.; Ota, T.; Kawabe, Y.; Morimoto, H.; Fukuhara, S.; Kodo, K.; Umemura, A.; Nakajima, H.; Hosoi, H. Erythropoietin and long-acting erythropoiesis stimulating agent ameliorate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by increasing lipolysis and decreasing lipogenesis via EPOR/STAT pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 509, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster, J.J.; Ouchi, N.; Gokce, N.; Walsh, K. Obesity-Induced Changes in Adipose Tissue Microenvironment and Their Impact on Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1786–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.H.; Yeh, W.T.; Weng, L.C. Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome in Asia. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 17 (Suppl. 1), 37–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.S.; Ho, H.; Hoffman, B.B.; Reaven, G.M. Fructose-induced insulin resistance and hypertension in rats. Hypertension 1987, 10, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaven, G.M.; Ho, H.; Hoffman, B.B. Attenuation of fructose-induced hypertension in rats by exercise training. Hypertension 1988, 12, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorburn, A.W.; Storlien, L.H.; Jenkins, A.B.; Khouri, S.; Kraegen, E.W. Fructose-induced in vivo insulin resistance and elevated plasma triglyceride levels in rats. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1989, 49, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basciano, H.; Federico, L.; Adeli, K. Fructose, insulin resistance, and metabolic dyslipidemia. Nutr. Metab. 2005, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahed, M.; Abou Jaoudeh, M.G.; Merhi, S.; Mosleh, J.M.B.; Ghadieh, R.; Al Hayek, S.; El Hayek Fares, J.E. Evaluation of risk factors for insulin resistance: A cross sectional study among employees at a private university in Lebanon. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2020, 20, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armato, J.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Abdul-Ghani, M.; Ruby, R. Pre-Prediabetes: Insulin Resistance Is Associated with Cardiometabolic Risk in Nonobese Patients (STOP DIABETES). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 110, e1481–e1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, A.; Virbasius, J.V.; Puri, V.; Czech, M.P. Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in underweight and obesity from 1990 to 2022: A pooled analysis of 3663 population-representative studies with 222 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2024, 403, 1027–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubanyi, G.M. The role of endothelium in cardiovascular homeostasis and diseases. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1993, 22 (Suppl. 4), S1–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R. Atherosclerosis--an inflammatory disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Palmieri, M.R. The endothelium in health and in cardiovascular disease. P. R. Health Sci. J. 1997, 16, 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanta, S.K.; Peng, L.; Li, Y.; Lu, S.; Sun, T.; Carnevale, L.; Perrotta, M.; Ma, Z.; Forstera, B.; Stanic, K.; et al. Neuroimmune cardiovascular interfaces control atherosclerosis. Nature 2022, 605, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazihan, N.; Karakurt, O.; Ataoglu, H. Erythropoietin reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced cell Damage and midkine secretion in U937 human histiocytic lymphoma cells. Adv. Ther. 2008, 25, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafidis, P.A.; Ruilope, L.M. Insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, and renal injury: Mechanisms and implications. Am. J. Nephrol. 2006, 26, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Semenza, G.L. Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signaling is required for erythropoietin-mediated acute protection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circulation 2004, 109, 2050–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, Z.Z.; Kang, J.Q.; Maiese, K. Erythropoietin is a novel vascular protectant through activation of Akt1 and mitochondrial modulation of cysteine proteases. Circulation 2002, 106, 2973–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharples, E.J.; Patel, N.; Brown, P.; Stewart, K.; Mota-Philipe, H.; Sheaff, M.; Kieswich, J.; Allen, D.; Harwood, S.; Raftery, M.; et al. Erythropoietin protects the kidney against the injury and dysfunction caused by ischemia-reperfusion. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 2115–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Sica, A.; Sozzani, S.; Allavena, P.; Vecchi, A.; Locati, M. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentworth, J.M.; Naselli, G.; Brown, W.A.; Doyle, L.; Phipson, B.; Smyth, G.K.; Wabitsch, M.; O’Brien, P.E.; Harrison, L.C. Pro-inflammatory CD11c+CD206+ adipose tissue macrophages are associated with insulin resistance in human obesity. Diabetes 2010, 59, 1648–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsouris, D.; Li, P.P.; Thapar, D.; Chapman, J.; Olefsky, J.M.; Neels, J.G. Ablation of CD11c-positive cells normalizes insulin sensitivity in obese insulin resistant animals. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R. Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J. Clin. Investig.. 2007, 117, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNelis, J.C.; Olefsky, J.M. Macrophages, immunity, and metabolic disease. Immunity 2014, 41, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cildir, G.; Akincilar, S.C.; Tergaonkar, V. Chronic adipose tissue inflammation: All immune cells on the stage. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantley, L.C. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 2002, 296, 1655–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncada, S.; Palmer, R.M.; Higgs, E.A. Nitric oxide: Physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 1991, 43, 109–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000410. [Google Scholar]
- Takeno, K.; Tamura, Y.; Kawaguchi, M.; Kakehi, S.; Watanabe, T.; Funayama, T.; Furukawa, Y.; Kaga, H.; Yamamoto, R.; Kim, M.; et al. Relation Between Insulin Sensitivity and Metabolic Abnormalities in Japanese Men with BMI of 23–25 kg/m2. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 3676–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Control | Sucrose | EPO | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (g) | 459 ± 6 | 453 ± 2 | 461 ± 7 |
| Food intake (g) | 15.5 ± 1.2 | 4.4 ± 0.4 * | 5.8 ± 0.8 * |
| Water intake (mL) | 38 ± 1.2 | 124 ± 2.1 * | 116 ± 2.5 *# |
| Urinary volume (mL) | 21 ± 1.0 | 89 ± 1.3 * | 90 ± 2.3 * |
| Hematocrit (%) | 48 ± 0.8 | 48 ± 0.6 | 68 ± 0.3 *# |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toba, H.; Jin, D.; Kobara, M.; Takai, S.; Nakata, T. Erythropoietin Attenuates Insulin Resistance and Renal Inflammation in High-Sucrose-Treated Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178321
Toba H, Jin D, Kobara M, Takai S, Nakata T. Erythropoietin Attenuates Insulin Resistance and Renal Inflammation in High-Sucrose-Treated Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178321
Chicago/Turabian StyleToba, Hiroe, Denan Jin, Miyuki Kobara, Shinji Takai, and Tetsuo Nakata. 2025. "Erythropoietin Attenuates Insulin Resistance and Renal Inflammation in High-Sucrose-Treated Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178321
APA StyleToba, H., Jin, D., Kobara, M., Takai, S., & Nakata, T. (2025). Erythropoietin Attenuates Insulin Resistance and Renal Inflammation in High-Sucrose-Treated Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178321






