Neuroprotective Potential of Major Alkaloids from Nelumbo nucifera (Lotus): Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method and Materials
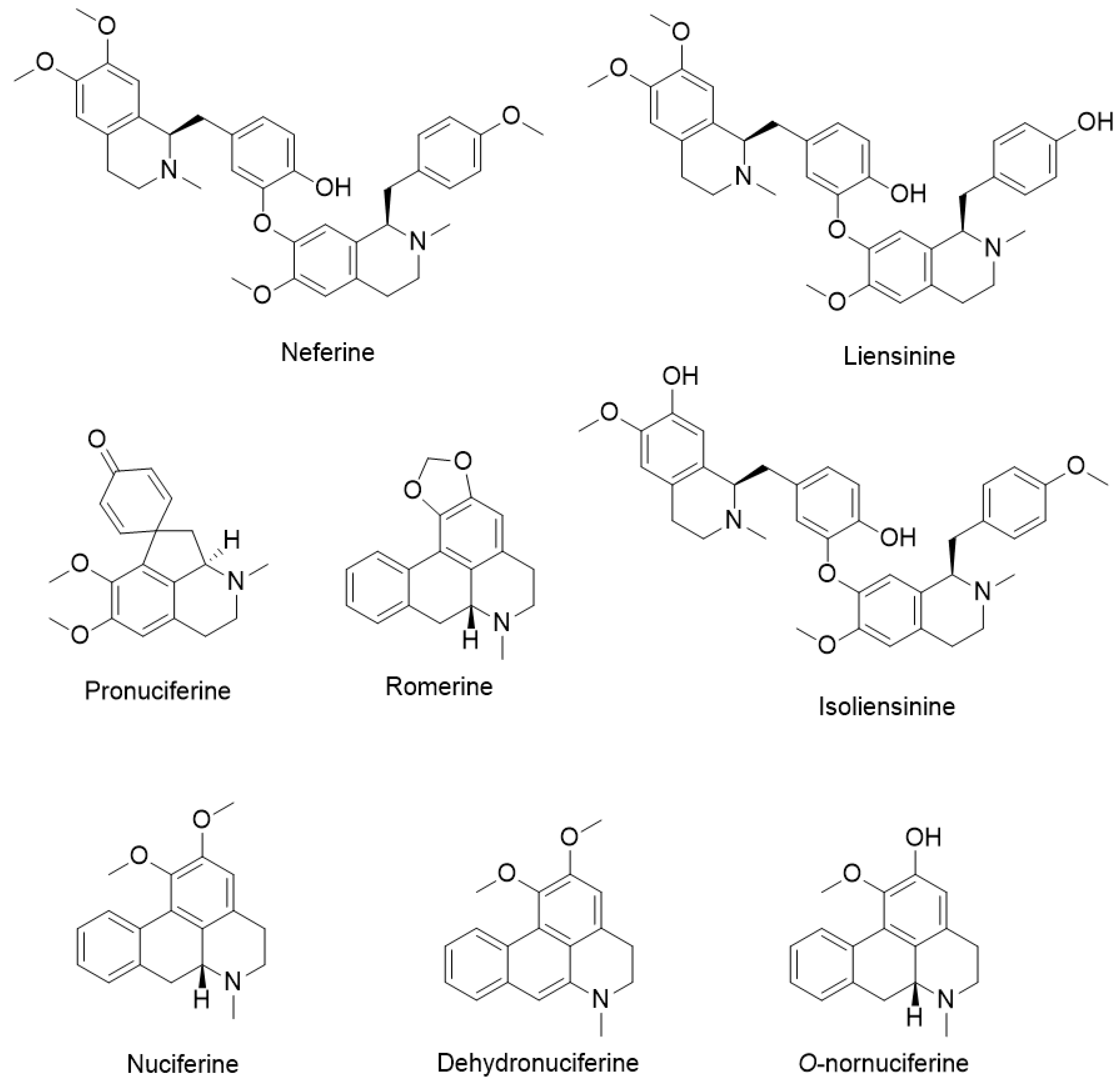
3. Chemical Constituents of Lotus Alkaloids
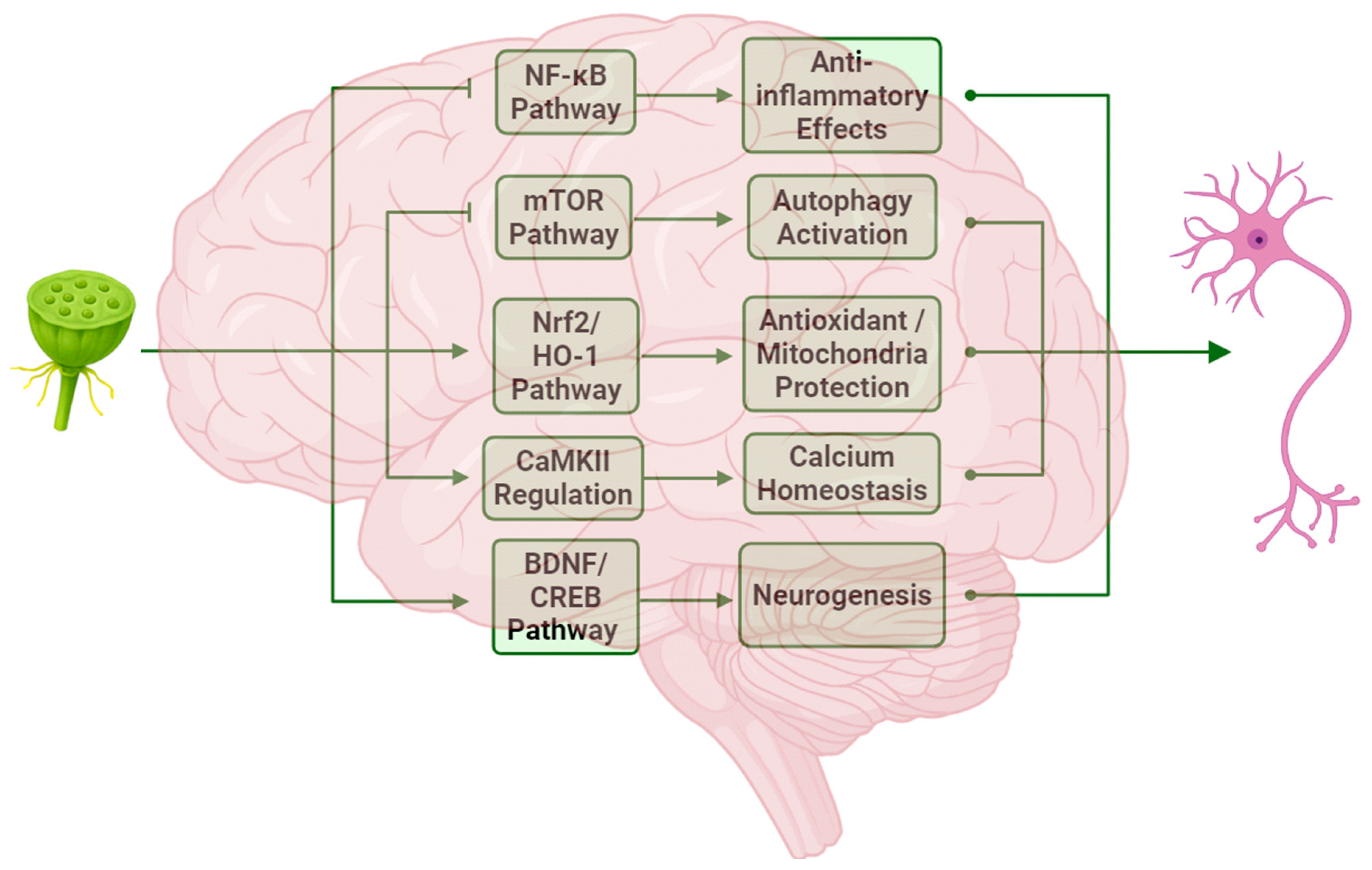
4. Mechanism of Neuroprotection
4.1. Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Autophagy Regulation
| Compound | Dose | Model | Mechanism | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neferine | 10 µM | LPS-treated BV-2 cells | ↓ INOS ↓ interleukin-6 ↓ TNFα | [40,44] |
| Nuciferine | 5–20 μM | LPS-stimulated BV2 microglia cells | ↓ IL-1β ↓ PGE2 ↓ TNFα ↓ NO secretion ↓ NF-κB | [45] |
| Liensinine | 20 and 40 mg/kg | Sepsis-associated encephalopathy mice cerebrum | ↓ iNOS activities ↓ inflammatory responses | [43,46] |
| Liensinine, neferine, and isoliensinine | 5.02 μM, 4.13 μM and 4.36 µM (IC50 values) | Mouse macrophage cell line | ↓ NO production ↓ NF-κB ↓ IL-1β ↓ PGE2 ↓ TNFα | [47] |
| Compound | Dose | Model | Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neferine | 12.8 µM | PC-12 cells | ↓ 50% level of Huntingtin Protein | [60] |
| Liensinine | 100 µM | Aβ transgenic GMC101 nematodes | ↑ autophagy-related genes ↑ autophagosome formation | [61] |
| Total alkaloids of lotus embryo | 200 mg kg−1 20 μM | LPS-treated mice BV2 microglial cell | ↑ autophagy ↑ LC3B-II and Beclin-1 ↓ depression | [58] |
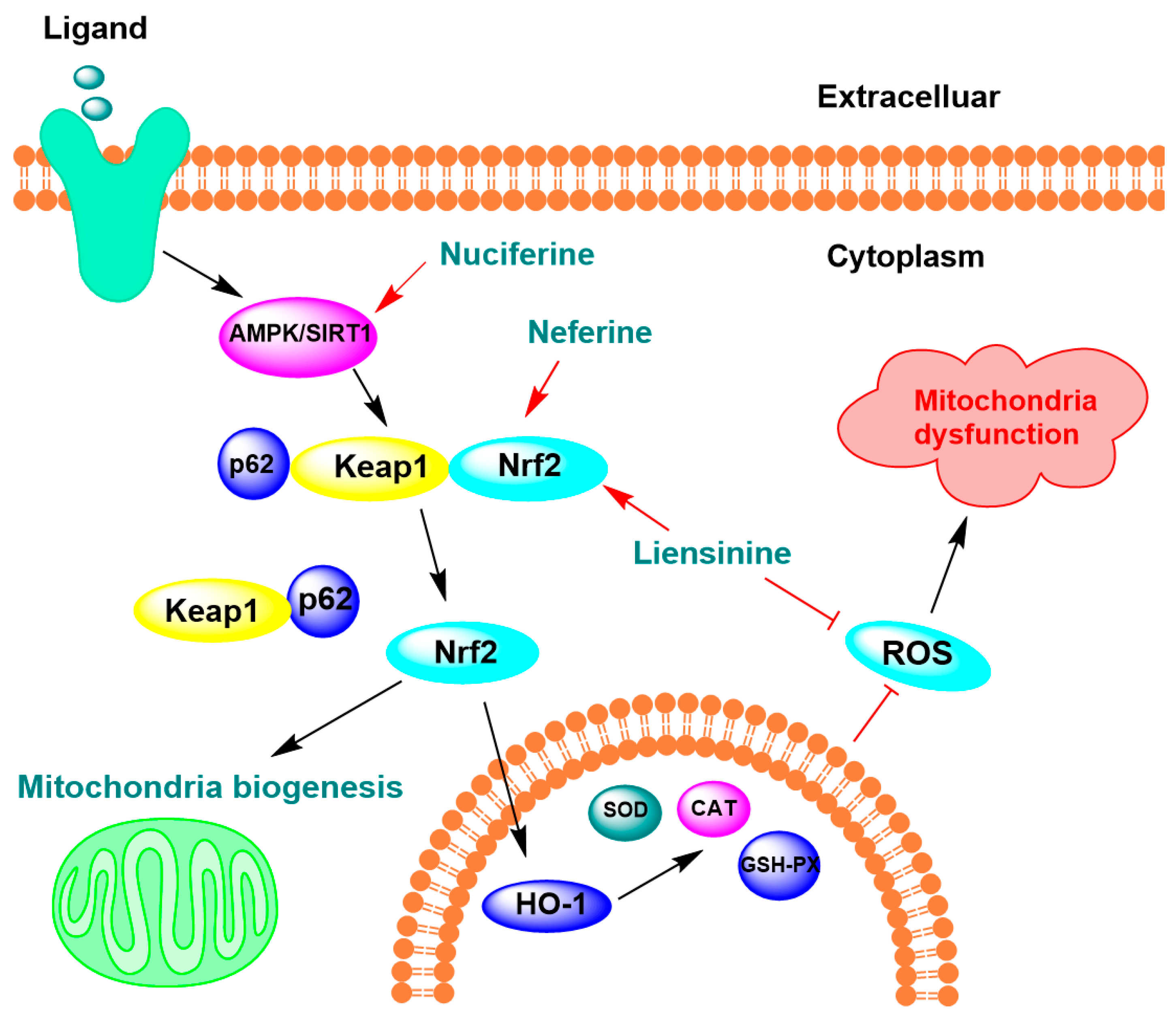
4.2. Oxidative Stress Protection and Mitochondrial Function Regulation
| Compound | Dose | Model | Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronuciferine | 5 µM | SH-SY5Y cells | ↓ neuronal death caused by H2O2, ↑ cell proliferation by 45% | [86] |
| Liensinine, neferine, and isoliensinine | 5.4, 6.9, and 6.6 μM | LPS-activated microglial cells | ↓ 50% ·OH | [44] |
| 10.5, 7.8, and 10.3 μM | ↓ 50% ONOO− | |||
| Liensinine and neferine | 10 µM | APP695swe SH-SY5Y cells | ↑ 15.31% oxidative stress resistance ↓ 20.37% ROS levels | [61] |
| Nuciferine | 40 mg/kg | High-fat diets obese mice | ↓ 69.55% GSH, ↓ 60.05% SOD ↓ 3.59% CAT | [89] |
| Compound | Dose | Model | Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liensinine | 40 mg/kg | Sepsis-associated encephalopathy mice | ↓ cerebrum mitochondria apoptosis | [43] |
| Neferine | 50 mg/kg | Rats with induced cerebral ischaemia | ↑ mitochondrial structures ↑ mitochondrial respiration | [100] |
| 10 µM | PC12 cells | ↑ mitochondrial membrane potentials ↓ mitochondrial ROS |
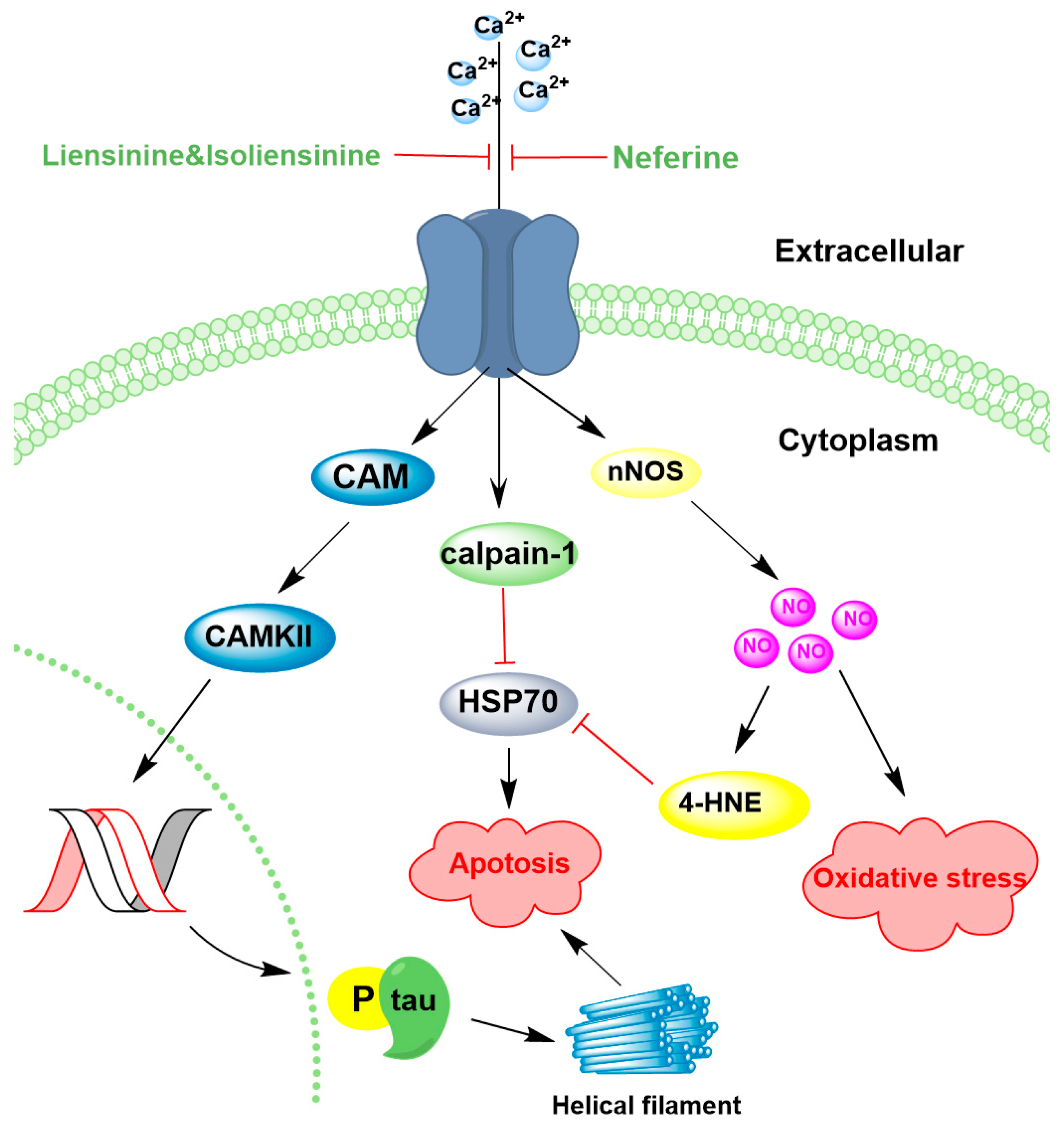
4.3. Regulation of Ion Channels
| Compound | Dose | Model | Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neferine, Liensinine, Isoliensinine | 10 μM | PC12 cells damaged by Aβ25–35 | ↓ Ca2+ level 72.8% and 46.9% | [115] |
| Neferine | 50 mg/kg | Permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (pMCAO) rats | ↓ Ca2+ ↑ Hsp70 ↓ NO | [119] |
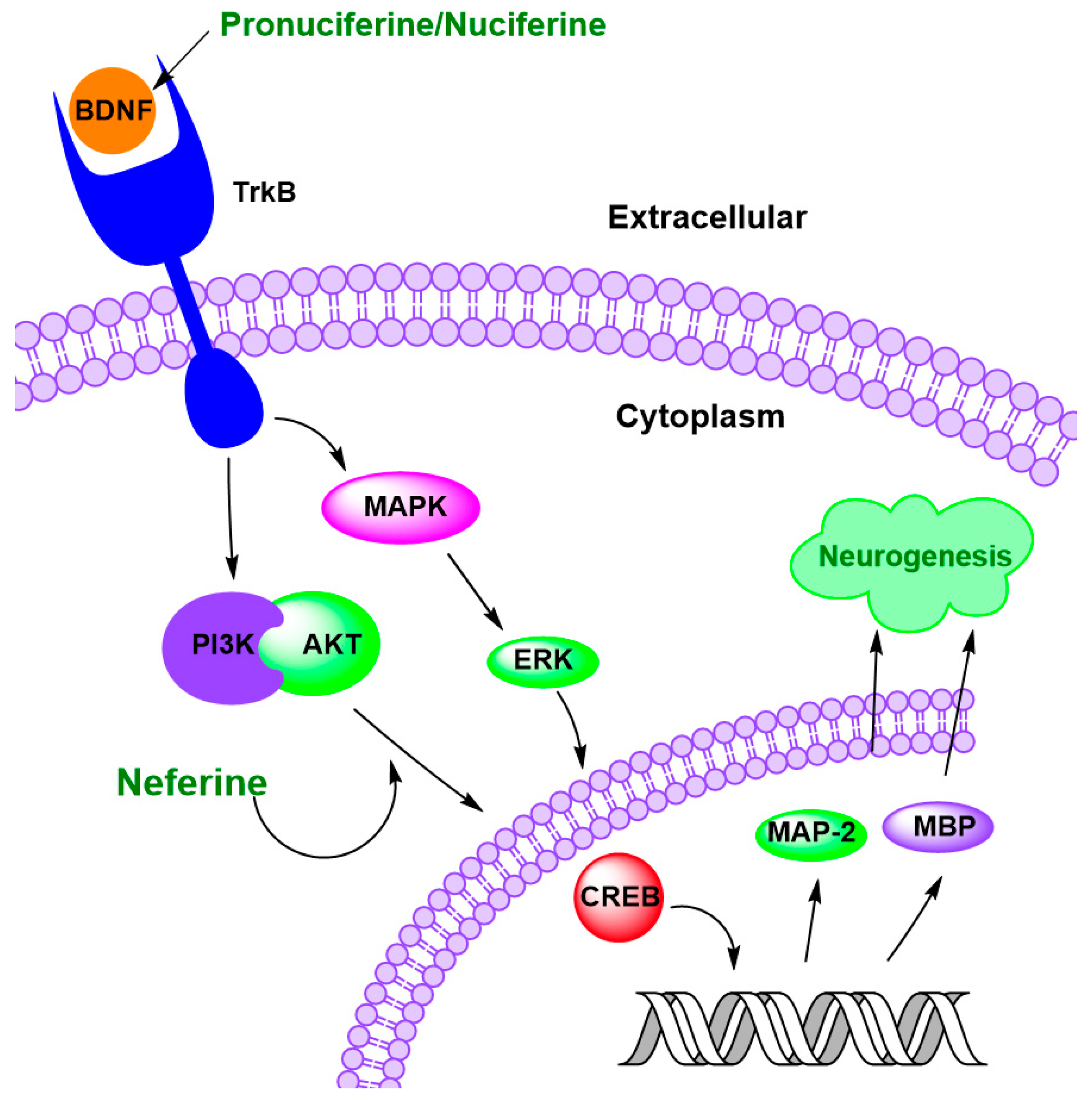
4.4. Regulation of Neurogenesis
| Compound | Dose | Model | Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neferine | 50 mg/kg | Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic-injured rats | ↓ neuronal loss, ↑ morphological recovery of the brain ↑ MAP-2 and MBP ↑ myelination | [135] |
| N. nucifera leaf water extracts | 10 to 20 μg/mL | Scopolamine-treated mice | ↑ hippocampus neurogenesis | [136] |
| Pronuciferine | 0.1 to 10 μM | SH-SY5Y cells | ↑ 17% to 20% BDNF level | [86] |
| Roemerine | 20 mM and 10 mM | SH-SY5Y cells | ↑ 73% and 36% BDNF expression | [137] |
4.5. Multimodal Actions of Lotus Alkaloids on Neurotransmitter Systems: Possible Neuroprotective Effects
5. Conclusions and Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Aβ | Amyloid beta |
| AChE | Acetylcholinesterase |
| AChEI | Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| Ca2+ | Calcium ion |
| CaMKII | Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II |
| CAT | Catalase |
| CREB | cAMP response element-binding protein |
| D1 | Dopamine freceptor D1 |
| D2 | Dopamine receptor D2 |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| GABA | Gamma-aminobutyric acid |
| GSH-Px | Glutathione peroxidase |
| Hsp70 | Heat shock protein 70 kDa |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase-1 |
| IC50 | Half maximal inhibitory concentration |
| INOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IκBα | Inhibitor of kappa B alpha |
| MAP-2 | Microtubule-associated protein 2 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MBP | Myelin basic protein |
| MPTP | 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine |
| nNOS | Neuronal nitric oxide synthase |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 |
| pMCAO | Permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SH-SY5Y | Human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| TrkB | Tropomyosin receptor kinase B |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| 4-HNE | 4-Hydroxynonenal |
References
- Marshall, A.C. Traditional Chinese medicine and clinical pharmacology. In Drug Discovery and Evaluation: Methods in Clinical Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 455–482. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Mukherjee, D.; Maji, A.K.; Rai, S.; Heinrich, M. The sacred lotus (Nelumbo nucifera)—Phytochemical and therapeutic profile. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 407–422. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Balasubramanian, R.; Saha, K.; Saha, B.P.; Pal, M. A review on nelumbo nucifera gaertn. Anc. Sci. Life 1996, 15, 268–276. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Xiao, M.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Y. Plumula Nelumbinis: A review of traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and safety. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 266, 113429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Zeng, S.; Huang, X.; Guo, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, B. Nutritional composition, physiological functions and processing of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) seeds: A review. Phytochem. Rev. 2015, 14, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhu, M.; Guo, M. Research advances in traditional and modern use of Nelumbo nucifera: Phytochemicals, health promoting activities and beyond. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59 (Suppl. S1), S189–S209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, C.; Cao, D.; Damaris, R.N.; Yang, P. The Latest Studies on Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera)—An Emerging Horticultural Model Plant. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubbendieck, J.; Milby, J.L. Legumes of the Great Plains: An Illustrated Guide; University of Nebraska Press: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, I.; Dey, P. A review on lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) seed. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2015, 4, 1659–1665. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; He, S.; Feng, Q.; Liu, Z.; Xia, S.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera): A multidisciplinary review of its cultural, ecological, and nutraceutical significance. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2024, 11, 18, Correction in Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2024, 11, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.Y.; Zhang, S.D.; Liu, S.; He, B.M. Protective effect of neferine on endothelial cell nitric oxide production induced by lysophosphatidylcholine: The role of the DDAH-ADMA pathway. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2011, 89, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, K.; Bhat, R. Lotus-A potential nutraceutical source. J. Agric. Technol. 2007, 3, 143–155. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Mu, Y.; Yang, M. A simple multi-residue method for determination of plant growth retardants in Ophiopogon japonicus and soil using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Shahrajabian, M.H.; Cheng, Q. Exploring Notable Functional Foods in East of Asia, Health Benefits and Ideal Nutrition. Res. Crop Ecophysiol. 2019, 14, 10–27. [Google Scholar]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W.; Cheng, Q.; Khoshkharam, M. Exploring the quality of foods from ancient China based on traditional Chinese medicine. Res. Crop Ecophysiol. 2022, 14, 10–27. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, W.; Luo, S.; Hao, L.; Zhang, F. Lotus Seedpod Oligomeric Procyanidin Nanoliposomes Targeting TLR4/NF-κB Reduce Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2023, 19, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Lee, J.J.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Hsiao, G.; Chou, D.S.; Sheu, J.R. Inhibitory effects of ketamine on lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial activation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2009, 2009, 705379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangar, S.P.; Dunno, K.; Kumar, M.; Mostafa, H.; Maqsood, S. A comprehensive review on lotus seeds (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.): Nutritional composition, health-related bioactive properties, and industrial applications. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 89, 104937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-F.; Shen, Z.-C.; Li, J.; Liang, T.; Lin, X.-F.; Li, Y.-P.; Zeng, W.; Zou, Q.; Shen, J.-L.; Wang, X.-Y. Phytochemicals, biological activity, and industrial application of lotus seedpod (Receptaculum Nelumbinis): A review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1022794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Han, L.; Shi, W.; Fang, X.; Hong, Y.; Cao, Y. Research advances in lotus leaf as Chinese dietary herbal medicine. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2022, 50, 1423–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Qiu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, L.; Shi, X.; Yang, J.; Lin, Q.; Lin, J. Lotus leaf Nuciferine improves sleep and reduces the low neuronal activity and brain tissue abnormalities associated with insomnia. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temviriyanukul, P.; Sritalahareuthai, V.; Promyos, N.; Thangsiri, S.; Pruesapan, K.; Srinuanchai, W.; Nuchuchua, O.; Siriwan, D.; On-Nom, N.; Suttisansanee, U. The effect of sacred lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) and its mixtures on phenolic profiles, antioxidant activities, and inhibitions of the key enzymes relevant to Alzheimer’s disease. Molecules 2020, 25, 3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, F. Phytochemical Properties and Nutritional Benefits of Lotus Rhizome (Nelumbo nucifera): A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Aquac. 2024, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandin, V.S.; Sebastian, J.K.; Dalavi, J.V.; Nagella, P.; Madhav, N.A.; Khot, V.V. Bioactive Compounds and Biological Activities of Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.). In Bioactive Compounds in the Storage Organs of Plants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Lin, H.; Jin, F.; Luo, Y.; Yang, P.; Song, J.; Yao, W.; Lin, W.; Yuan, D.; Zuo, A. Jia Wei Qingxin Lotus Seed Drink ameliorates epithelial mesenchymal transition injury in diabetic kidney disease via inhibition of JMJD1C/SP1/ZEB1 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 135, 156142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, C.-C.; Tung, C.-W.; Chang, C.-W.; Tsai, C.-C.; Hsu, M.-C.; Wu, Y.-T. Potential risk of higenamine misuse in sports: Evaluation of lotus plumule extract products and a human study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arooj, M.; Imran, S.; Inam-Ur-Raheem, M.; Rajoka, M.S.R.; Sameen, A.; Siddique, R.; Sahar, A.; Tariq, S.; Riaz, A.; Hussain, A.; et al. Lotus seeds (Nelumbinis semen) as an emerging therapeutic seed: A comprehensive review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 3971–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Yin, W.; Cai, H. Alkaloids of plumula Nelumbinis. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 1991, 16, 673–675, 703. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Zhu, L.; Fang, T.; Vimolmangkang, S.; Yang, D.; Ogutu, C.; Liu, Y.; Han, Y. Analysis of Isoquinoline Alkaloid Composition and Wound-Induced Variation in Nelumbo Using HPLC-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, K.; Raihan, M.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Rouf, R.; Reza, H.M.; Uddin, S.J.; Muhammad, I. Therapeutic Potential of Nelumbo nucifera (Sacred Lotus) in CNS Disorders. Dhaka Univ. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 20, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manogaran, P.; Beeraka, N.M.; Padma, V.V. The cytoprotective and anti-cancer potential of bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids from Nelumbo nucifera. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 2940–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.-Z.; Chang, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Xiao, B.-X.; Feng, L.; Cao, F.-R.; Pan, R.-L.; Zhang, Z.-S.; Liao, Y.-H.; Liu, X.-M. Lotus leaf alkaloid extract displays sedative–hypnotic and anxiolytic effects through GABAA receptor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9277–9285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Hou, T.; Gao, Z.; Guo, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liang, X. Discovery of eight alkaloids with D1 and D2 antagonist activity in leaves of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. Using FLIPR assays. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 278, 114335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, C.; Pan, H. Advances in the pharmacological effects and mechanisms of Nelumbo nucifera gaertn. Extract nuciferine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 331, 118262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Ma, D.; Zeng, M.; Wang, Z.; Qin, F.; Chen, J.; Christian, M.; He, Z. Alkaloids from lotus (Nelumbo nucifera): Recent advances in biosynthesis, pharmacokinetics, bioactivity, safety, and industrial applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 4867–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Teka, T.; Lv, C.; Han, L.; Huang, Y.; Pan, G. Thirteen bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids in five Chinese medicinal plants: Botany, traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacokinetic and toxicity studies. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 268, 113566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Dong, S.; Yu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xiang, B.; Li, Q. Research progress on neuroprotective effects of isoquinoline alkaloids. Molecules 2023, 28, 4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Hawkins, K.E.; Doré, S.; Candelario-Jalil, E. Neuroinflammatory mechanisms of blood-brain barrier damage in ischemic stroke. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2019, 316, C135–C153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempuraj, D.; Thangavel, R.; Natteru, P.; Selvakumar, G.; Saeed, D.; Zahoor, H.; Zaheer, S.; Iyer, S.; Zaheer, A. Neuroinflammation induces neurodegeneration. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Spine 2016, 1, 1003. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Zhai, Y.X.; Zheng, T.; Xu, B. Neferine exerts anti-inflammatory activity in BV-2 microglial cells and protects mice with MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease by inhibiting NF-kappaB activation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2023, 28, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, C.K.; Saijo, K.; Winner, B.; Marchetto, M.C.; Gage, F.H. Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell 2010, 140, 918–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.N.; Al-Omran, A.; Parvathy, S.S. Role of nitric oxide in inflammatory diseases. Inflammopharmacology 2007, 15, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Q.; Dai, D.; Zhang, L.; Fan, H.; Zhang, W.; Dong, J.; Zhao, P. Liensinine, a alkaloid from lotus plumule, mitigates lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis-associated encephalopathy through modulation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor-mediated inflammatory biomarkers and mitochondria apoptosis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 177, 113813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-L.; Zheng, L.-C.; Liu, J.; Gao, C.-C.; Qiu, M.-C.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, D.; Chen, C.-L. Inhibitory effects of three bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids on lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial activation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 18347–18357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, J.; Tang, P.; Chong, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Hou, C. Nuciferine inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response in BV2 cells by activating PPAR-gamma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 63, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dong, S.; Quan, S.; Ding, S.; Zhou, X.; Yu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Huang, W.; Shi, Q.; Li, Q. Nuciferine reduces inflammation induced by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 125, 155312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Sha, T.; Tian, W.; Wu, L.; Chen, J.; Huang, J.; Xia, Z.; Liu, K.; Sun, P.; Fan, H.; et al. Anti-inflammatory Activity of Total Alkaloids in Nelumbo nucifera and Simultaneous Determination of Major Bisbenzylisoquinolines. Rev. Bras. De Farmacogn. 2023, 33, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeuerle, P.A.; Baltimore, D. IκB: A specific inhibitor of the NF-κB transcription factor. Science 1988, 242, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.A.; Mills, K.H.; Harris, J. Autophagy and inflammatory diseases. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2013, 91, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-Y.; Lu, J.-H. Autophagy and macrophage functions: Inflammatory response and phagocytosis. Cells 2019, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, F.; Liu, B.; Huang, C.; Wei, Y. Deconvoluting the role of reactive oxygen species and autophagy in human diseases. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Zhu, M.; Che, X.; Wang, H.; Liang, X.-J.; Wu, C.; Xue, X.; Yang, J. Lipopolysaccharide induces neuroinflammation in microglia by activating the MTOR pathway and downregulating Vps34 to inhibit autophagosome formation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Zhao, F.; Cao, Z.; Aschner, M.; Luo, W. The role of autophagy in modulation of neuroinflammation in microglia. Neuroscience 2016, 319, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Zhou, X.; Lu, J.-H.; Yue, Z. Autophagy deficiency in neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Wu, M.; Yin, X.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Bai, M.; Wang, B.; Xu, E. Modified Xiaoyao San reverses lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behavior through suppressing microglia M1 polarization via enhancing autophagy involved in PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 315, 116659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petibone, D.M.; Majeed, W.; Casciano, D.A. Autophagy function and its relationship to pathology, clinical applications, drug metabolism and toxicity. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 37, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Guo, W.; Qi, X.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Y. Natural alkaloids from lotus plumule ameliorate lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behavior: Integrating network pharmacology and molecular mechanism evaluation. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6062–6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, P.W.; Licinio, J.; Pavlatou, M. Pathological parainflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress in depression: Potential translational targets through the CNS insulin, klotho and PPAR-γ systems. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, V.K.; Wu, A.G.; Wang, J.R.; Liu, L.; Law, B.Y. Neferine attenuates the protein level and toxicity of mutant huntingtin in PC-12 cells via induction of autophagy. Molecules 2015, 20, 3496–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.C.; Gao, Y.H.; Zhang, C.; Ma, B.T.; Lin, H.R.; Jiang, J.Y.; Xue, M.F.; Li, S.; Wang, H.B. Liensinine and neferine exert neuroprotective effects via the autophagy pathway in transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Autophagy in autoimmune disease. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 93, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, H.K. The role of autophagy in the function of CD4+ T cells and the development of chronic inflammatory diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 860146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapaquette, P.; Guzzo, J.; Bretillon, L.; Bringer, M.-A. Cellular and molecular connections between autophagy and inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 398483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netea-Maier, R.T.; Plantinga, T.S.; van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Smit, J.W.; Netea, M.G. Modulation of inflammation by autophagy: Consequences for human disease. Autophagy 2016, 12, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindle, J.V. Ageing, neurodegeneration and Parkinson’s disease. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y. AMPK and autophagy. In Autophagy: Biology and Diseases: Basic Science; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 85–108. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, L.; Wang, X. AMPK and mTOR coordinate the regulation of Ulk1 and mammalian autophagy initiation. Autophagy 2011, 7, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.M. Regulation and function of AMPK in physiology and diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhang, H. You are what you eat: Multifaceted functions of autophagy during C. elegans development. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, K.; Levine, B. Autophagy and longevity: Lessons from C. elegans. In Protein Metabolism and Homeostasis in Aging; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 47–60. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, F.; Li, K.; Shang, S.; Wang, F.; Hu, Z. Immune signaling and autophagy regulation. In Autophagy: Biology and Diseases: Basic Science; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 551–593. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, M.; Fang, X.; Wang, X. Autophagy and inflammation. Clin. Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, P.I.; Smith, M.A.; Zhu, X.; Nunomura, A.; Castellani, R.J.; Perry, G. Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1043, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and disease. In Oxidative Stress and Biomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 35–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ahdab-Barmada, M.; Moossy, J.; Nemoto, E.M.; Lin, M.R. Hyperoxia produces neuronal necrosis in the rat. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1986, 45, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terraneo, L.; Paroni, R.; Bianciardi, P.; Giallongo, T.; Carelli, S.; Gorio, A.; Samaja, M. Brain adaptation to hypoxia and hyperoxia in mice. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.; Abramov, A.Y. Mechanism of oxidative stress in neurodegeneration. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 428010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottenberg, H.; Hoek, J.B. The path from mitochondrial ROS to aging runs through the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Aging Cell 2017, 16, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magistretti, P.J.; Allaman, I. Brain energy and metabolism. In Neuroscience in the 21st Century: From Basic to Clinical; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 2197–2227. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.T.; Beal, M.F. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 2006, 443, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfawy, H.A.; Das, B. Crosstalk between mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and age related neurodegenerative disease: Etiologies and therapeutic strategies. Life Sci. 2019, 218, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, S.C.; Mead, R.J.; Shaw, P.J. Oxidative stress in ALS: A mechanism of neurodegeneration and a therapeutic target. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2006, 1762, 1051–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenaz, G.; Bovina, C.; D’aurelio, M.; Fato, R.; Formiggini, G.; Genova, M.L.; Giuliano, G.; Pich, M.M.; Paolucci, U.; Castelli, G.P. Role of mitochondria in oxidative stress and aging. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 959, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckman, J.S.; Koppenol, W.H. Nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite: The good, the bad, and ugly. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 1996, 271, C1424–C1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayazeid, O.; Nemutlu, E.; Eylem, C.C.; Yalcin, F.N. Neuroactivity of naturally occurring proaporphine alkaloid, pronuciferine. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2020, 34, e22601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limón-Pacheco, J.; Gonsebatt, M.E. The role of antioxidants and antioxidant-related enzymes in protective responses to environmentally induced oxidative stress. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2009, 674, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goc, Z.; Szaroma, W.; Kapusta, E.; Dziubek, K. Protective effects of melatonin on the activity of SOD, CAT, GSH-Px and GSH content in organs of mice after administration of SNP. Chin. J. Physiol. 2017, 60, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Hao, R.; Lv, X.; Su, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, C. Neuroprotective effects of nuciferine on high-fat diet-induced cognitive dysfunction in obese mice: Role of insulin resistance, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress. Food Front. 2024, 5, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Cruzat, V.F.; Newsholme, P.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y. Regulation of SIRT1 in aging: Roles in mitochondrial function and biogenesis. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2016, 155, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadenbach, B. Introduction to mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. In Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation: Nuclear-Encoded Genes, Enzyme Regulation, and Pathophysiology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Tauffenberger, A.; Magistretti, P.J. Reactive oxygen species: Beyond their reactive behavior. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, S.; Wang, F.; Cui, H. The role of mitochondria in reactive oxygen species generation and its implications for neurodegenerative diseases. Cells 2018, 7, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanatos, R.; Sanz, A. The role of mitochondrial ROS in the aging brain. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 743–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.J.; Chandrasekaran, K.; Morgan, W.F. Mitochondrial dysfunction, persistently elevated levels of reactive oxygen species and radiation-induced genomic instability: A review. Mutagenesis 2006, 21, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.H.; Dar, K.B.; Anees, S.; Zargar, M.A.; Masood, A.; Sofi, M.A.; Ganie, S.A. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases; a mechanistic insight. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 74, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, T.; Deore, S.L.; Kide, A.A.; Shende, B.A.; Sharma, R.; Chakole, R.D.; Nemade, L.S.; Kale, N.K.; Borah, S.; Deokar, S.S. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-an updated review. Mitochondrion 2023, 71, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, P.; Gursahani, H.I.; Pang, Z.; Bondada, V.; Lee, J.; Hadley, R.W.; Geddes, J.W. Influence of cytosolic and mitochondrial Ca2+, ATP, mitochondrial membrane potential, and calpain activity on the mechanism of neuron death induced by 3-nitropropionic acid. Neurochem. Int. 2003, 43, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schon, E.A.; Manfredi, G. Neuronal degeneration and mitochondrial dysfunction. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Chen, J.; Yang, R.; Duan, F.; Li, S.; Chen, X. Mitochondrial protective effect of neferine through the modulation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 signalling in ischaemic stroke. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 400–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Wei, Z.; Yang, W.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J. The role of BCL-2 family proteins in regulating apoptosis and cancer therapy. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 985363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, K.S.; Elkelawy, A.M.M.H.; Abd-Allah, S.; Helmy, N.A. Involvement of Mfn2, Bcl2/Bax signaling and mitochondrial viability in the potential protective effect of Royal jelly against mitochondria-mediated ovarian apoptosis by cisplatin in rats. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 515. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Duan, H.; Li, R.; Peng, W.; Wu, C. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling: An important molecular mechanism of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis via the protection of vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 34, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorov, D.B.; Juhaszova, M.; Sollott, S.J. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS release. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 909–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfali, R.; Alwatban, A.Z.; Orfali, R.S.; Lau, L.; Chea, N.; Alotaibi, A.M.; Nam, Y.-W.; Zhang, M. Oxidative stress and ion channels in neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1320086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordaro, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R. Ion channels and neurodegenerative disease aging related. In Ion Transporters-From Basic Properties to Medical Treatment; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, M.L.; Khakh, B.S.; Skatchkov, S.N.; Zhou, M.; Lee, C.J.; Rouach, N. New insights on astrocyte ion channels: Critical for homeostasis and neuron-glia signaling. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 13827–13835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arundine, M.; Tymianski, M. Molecular mechanisms of calcium-dependent neurodegeneration in excitotoxicity. Cell Calcium 2003, 34, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cojocaru, A.; Burada, E.; Bălșeanu, A.-T.; Deftu, A.-F.; Cătălin, B.; Popa-Wagner, A.; Osiac, E. Roles of microglial ion channel in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia, J.; Arrizabalaga-Iriondo, A.; Sanchez-del-Rey, A.; Martinez-Ibargüen, A.; Gallego, M.; Casis, O.; Revuelta, M. Therapeutic role of voltage-gated potassium channels in age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1406709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zündorf, G.; Reiser, G. Calcium dysregulation and homeostasis of neural calcium in the molecular mechanisms of neurodegenerative diseases provide multiple targets for neuroprotection. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Wills, Z.; Chu, C.T. Excitatory dendritic mitochondrial calcium toxicity: Implications for Parkinson’s and other neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P. Oxidative stress, perturbed calcium homeostasis, and immune dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurovirology 2002, 8, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunkova, M.; Alwasel, S.H.; Alhazza, I.M.; Jomova, K.; Kollar, V.; Rusko, M.; Valko, M. Management of oxidative stress and other pathologies in Alzheimer’s disease. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 2491–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.L.; Liu, S.Y.; Xue, J.S.; Gou, J.M.; Wang, D.; Liu, H.S.; Chen, C.L.; Xu, C.B. Protective effects of Liensinine, Isoliensinine, and Neferine on PC12 cells injured by amyloid-beta. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurt, M.; Davies, D.; Kidd, M.; Duff, K.; Howlett, D. Hyperphosphorylated tau and paired helical filament-like structures in the brains of mice carrying mutant amyloid precursor protein and mutant presenilin-1 transgenes. Neurobiol. Dis. 2003, 14, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Yang, J.; Yang, H.; Xu, B.; Yang, T.; Liu, W. Research advances on CaMKs-mediated neurodevelopmental injury. Arch. Toxicol. 2024, 98, 3933–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsky, J.; Pichlerova, K.; Hanes, J. Tau Protein Interaction Partners and Their Roles in Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Tauopathies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengking, J.; Oka, C.; Yawoot, N.; Tocharus, J.; Chaichompoo, W.; Suksamrarn, A.; Tocharus, C. Protective effect of Neferine in permanent cerebral ischemic rats via anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic mechanisms. Neurotox. Res. 2022, 40, 1348–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, L.; Basova, N.; Shpakov, A. Neuronal NO Synthase in the Pathogenesis of Metabolic Syndrome. Cell Tissue Biol. 2023, 17, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellios, V. The Role of Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase in Regulating Cerebellar Network Formation Across Murine Development. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Western Ontario (Canada), London, ON, Canada, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, F. Modification of HSP proteins and Ca2+ are responsible for the NO-derived peroxynitrite mediated neurological damage in PC12 cell. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 4492. [Google Scholar]
- Albakova, Z.; Mangasarova, Y.; Albakov, A.; Gorenkova, L. HSP70 and HSP90 in cancer: Cytosolic, endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial chaperones of tumorigenesis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 829520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.K. Calpain and caspase: Can you tell the difference? Trends Neurosci. 2000, 23, 20–26, Erratum in Trends Neurosci. 2000, 23, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayre, L.M.; Zelasko, D.A.; Harris, P.L.; Perry, G.; Salomon, R.G.; Smith, M.A. 4-Hydroxynonenal-derived advanced lipid peroxidation end products are increased in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 1997, 68, 2092–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culig, L.; Chu, X.; Bohr, V.A. Neurogenesis in aging and age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 78, 101636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polis, B.; Samson, A.O. Neurogenesis versus neurodegeneration: The broken balance in Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 496–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdipranoto, A.; Wu, S.; Stayte, S.; Vissel, B. The role of neurogenesis in neurodegenerative diseases and its implications for therapeutic development. CNS Neurol. Disord.-Drug Targets (Former. Curr. Drug Targets—CNS Neurol. Disord.) 2008, 7, 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horgusluoglu, E.; Nudelman, K.; Nho, K.; Saykin, A.J. Adult neurogenesis and neurodegenerative diseases: A systems biology perspective. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2017, 174, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davinelli, S.; Medoro, A.; Ali, S.; Passarella, D.; Intrieri, M.; Scapagnini, G. Dietary flavonoids and adult neurogenesis: Potential implications for brain aging. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2023, 21, 651–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.; Jope, R. The role of microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP-2) in neuronal growth, plasticity, and degeneration. J. Neurosci. Res. 1992, 33, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matus, A. Microtubule-associated proteins and neuronal morphogenesis. J. Cell Sci. 1991, 1991 (Suppl. S15), 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandr, S.; Alexey, G. Role of the MBP protein in myelin formation and degradation in the brain. Biol. Commun. 2022, 67, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kister, A.; Kister, I. Overview of myelin, major myelin lipids, and myelin-associated proteins. Front. Chem. 2023, 10, 1041961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.J.; Yu, B.Y.; Huang, X.K.; He, M.Z.; Chen, B.W.; Chen, T.T.; Fang, H.Y.; Chen, S.Q.; Fu, X.Q.; Li, P.J.; et al. Neferine Protects against Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage in Neonatal Rats by Suppressing NLRP3-Mediated Inflammasome Activation. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6654954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Lin, C.M.; Chang, Y.C.; Yang, M.Y.; Wang, C.J.; Hsu, L.S. Nelumbo nucifera leaves extract ameliorated scopolamine-induced cognition impairment via enhanced adult hippocampus neurogenesis. Environ. Toxicol. 2024, 39, 3198–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayazeid, O.; Nemutlu, E.; Eylem, C.C.; Ilhan, M.; Kupeli-Akkol, E.; Karahan, H.; Kelicen-Ugur, P.; Ersoz, T.; Yalcin, F.N. Neuroactivity of the naturally occurring aporphine alkaloid, roemerine. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 6147–6152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Nie, Z.; Shu, H.; Kuang, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J.; Yu, S.; Liu, H. The role of BDNF on neural plasticity in depression. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, N.K.; Ilchibaeva, T.V.; Naumenko, V.S. Neurotrophic Factors (BDNF and GDNF) and the Serotonergic System of the Brain. Biochemistry 2017, 82, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azman, K.F.; Zakaria, R. Recent advances on the role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci-D’Amato, L.; Speranza, L.; Volpicelli, F. Neurotrophic factor BDNF, physiological functions and therapeutic potential in depression, neurodegeneration and brain cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworkin, S.; Mantamadiotis, T. Targeting CREB signalling in neurogenesis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2010, 14, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Martínez, S. A new perspective on the role of the CREB family of transcription factors in memory consolidation via adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldessarini, R.J.; Tarazi, F.I. Brain dopamine receptors: A primer on their current status, basic and clinical. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 1996, 3, 301–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahata, I.; Finkelstein, D.I.; Fukunaga, K. Dopamine D1–D5 receptors in brain nuclei: Implications for Health and Disease. Receptors 2024, 3, 155–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Arachchige, A.S.P.M. Depletion of dopamine in Parkinson’s disease and relevant therapeutic options: A review of the literature. AIMS Neurosci. 2023, 10, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisahara, S.; Shimohama, S. Dopamine Receptors and Parkinson′ s Disease. Int. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 2011, 403039. [Google Scholar]
- Anzalone, A.; Lizardi-Ortiz, J.E.; Ramos, M.; De Mei, C.; Hopf, F.W.; Iaccarino, C.; Halbout, B.; Jacobsen, J.; Kinoshita, C.; Welter, M. Dual control of dopamine synthesis and release by presynaptic and postsynaptic dopamine D2 receptors. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 9023–9034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacson, S.H.; Hauser, R.A.; Pahwa, R.; Gray, D.; Duvvuri, S. Dopamine agonists in Parkinson’s disease: Impact of D1-like or D2-like dopamine receptor subtype selectivity and avenues for future treatment. Clin. Park. Relat. Disord. 2023, 9, 100212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Huang, R. Neuroprotective effect of neferine, an alkaloid against the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine induced Parkinson’s disease mouse model. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2021, 17, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D.J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 2002, 297, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Song, Z.; Xue, W.; Sheng, J.; Shu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Liang, J.; Yao, X. Synthesis and structure–activity relationship of nuciferine derivatives as potential acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Med. Chem. Res. 2014, 23, 3178–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.A.; Karki, S.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, J.S. BACE1 and cholinesterase inhibitory activities of Nelumbo nucifera embryos. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2015, 38, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, B.; Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Elekhnawy, E.; Alharbi, H.; Alexiou, A.; Papadakis, M.; Batiha, G.E.-S. Role of GABA pathway in motor and non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease: A bidirectional circuit. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, D.; Wen, L.; Wu, Z.; Shen, Y. GABAergic dysfunction in excitatory and inhibitory (E/I) imbalance drives the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2020, 16, 1312–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez-Perdomo, I.M.; Facchini, P.J. Benzylisoquinoline Alkaloids Biosynthesis in Sacred Lotus. Molecules 2018, 23, 2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.R.; Thompson, M.L.; Shepherd, S.A.; Dunstan, M.S.; Herbert, A.J.; Smith, D.R.M.; Cronin, V.A.; Menon, B.R.K.; Levy, C.; Micklefield, J. Structure and Biocatalytic Scope of Coclaurine N-Methyltransferase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 10600–10604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, T.; Shen, C.; Chiu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Huang, Y. Effects of armepavine against hepatic fibrosis induced by thioacetamide in rats. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, M.; Ogutu, C.; Li, J.; Deng, X. Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) benzylisoquinoline alkaloids: Advances in chemical profiling, extraction methods, pharmacological activities, and biosynthetic elucidation. Veg. Res. 2024, 4, e005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhu, L.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Feng, J.; Liu, Y. Digital gene expression analysis provides insight into the transcript profile of the genes involved in aporphine alkaloid biosynthesis in lotus (Nelumbo nucifera). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempster, P.; Ma, A. Parkinson’s disease, dopaminergic drugs and the plant world. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 970714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.-H.; He, X.-X.; You, C.; Tao, X.; Wang, L.-S.; Zhang, M.-D.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Chang, Q. Pharmacokinetics of nuciferine and N-nornuciferine, two major alkaloids from Nelumbo nucifera leaves, in rat plasma and the brain. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilgun-Sherki, Y.; Melamed, E.; Offen, D. Oxidative stress induced-neurodegenerative diseases: The need for antioxidants that penetrate the blood brain barrier. Neuropharmacology 2001, 40, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhambhani, S.; Kondhare, K.R.; Giri, A.P. Diversity in chemical structures and biological properties of plant alkaloids. Molecules 2021, 26, 3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, H.-L.; Zhou, Z.-W.; Long, H.-Z.; Luo, H.-Y.; Wen, D.-D.; Cheng, L.; Gao, L.-C. Isoliensinine: A Natural Compound with “Drug-Like” Potential. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 630385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poornima, P.; Weng, C.F.; Padma, V.V. Neferine, an alkaloid from lotus seed embryo, inhibits human lung cancer cell growth by MAPK activation and cell cycle arrest. Biofactors 2014, 40, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabedo, N.; Berenguer, I.; Figadere, B.; Cortes, D. An overview on benzylisoquinoline derivatives with dopaminergic and serotonergic activities. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 2441–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plazas, E.; Muñoz, D.R. Natural isoquinoline alkaloids: Pharmacological features and multi-target potential for complex diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 177, 106126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portoghese, P.S. Relationships between stereostructure and pharmacological activities. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. 1970, 10, 51–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.-M.; Sun, J.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, J.-L.; Xiao, M.; Zhu, M.-S. Isolation and identification of a tribenzylisoquinoline alkaloid from Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn, a novel potential smooth muscle relaxant. Fitoterapia 2018, 124, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.A.; Jin, S.E.; Choi, R.J.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Ryu, J.H.; Son, Y.K.; Park, J.J.; Choi, J.S. Anti-amnesic activity of neferine with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities, as well as inhibition of ChEs and BACE1. Life Sci. 2010, 87, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Sun, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Lan, F.; Li, S.; Liu, C. Liensinine- and Neferine-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Primary Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes and Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, Y.; Ding, J.; et al. Isoliensinine suppresses bone loss by targeted inhibition of RANKL-RANK binding. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 210, 115463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrell, S.N.; Li, Y.-C.; Yamaguchi, H.; Chen, H.-F.; Hung, M.-C. Herbal Compounds Dauricine and Isoliensinine Impede SARS-CoV-2 Viral Entry. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wang, J.; Chu, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, G. Purification and characterization of aporphine alkaloids from leaves of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn and their effects on glucose consumption in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 3481–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-M.; Park, E.-J.; Lee, H.-J. Nuciferine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inflammatory responses by inhibiting p38 MAPK/ATF2 signaling pathways. Inflammopharmacology 2022, 30, 2373–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, D.; Ma, L.; Brownlie, J.; Tonissen, K.; Pan, Y.; Feng, Y. Neuroprotective Potential of Major Alkaloids from Nelumbo nucifera (Lotus): Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178280
Zhao D, Ma L, Brownlie J, Tonissen K, Pan Y, Feng Y. Neuroprotective Potential of Major Alkaloids from Nelumbo nucifera (Lotus): Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178280
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Douyang, Linlin Ma, Jeremy Brownlie, Kathryn Tonissen, Yang Pan, and Yunjiang Feng. 2025. "Neuroprotective Potential of Major Alkaloids from Nelumbo nucifera (Lotus): Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178280
APA StyleZhao, D., Ma, L., Brownlie, J., Tonissen, K., Pan, Y., & Feng, Y. (2025). Neuroprotective Potential of Major Alkaloids from Nelumbo nucifera (Lotus): Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178280






