Bisphenol A and Its Analogue Bisphenol S Inhibit Cholinergic Neurotransmission at the Tripartite Colonic Myenteric Synapse of CD1 Mice by Targeting Interstitial Cells of Cajal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. BPA and BPS Decrease the Release of [3H]ACh from Stimulated Myenteric Neurons Without Affecting Smooth Muscle Performance in Isolated LM-MP Preparations of CD1 Mice Mid Colon
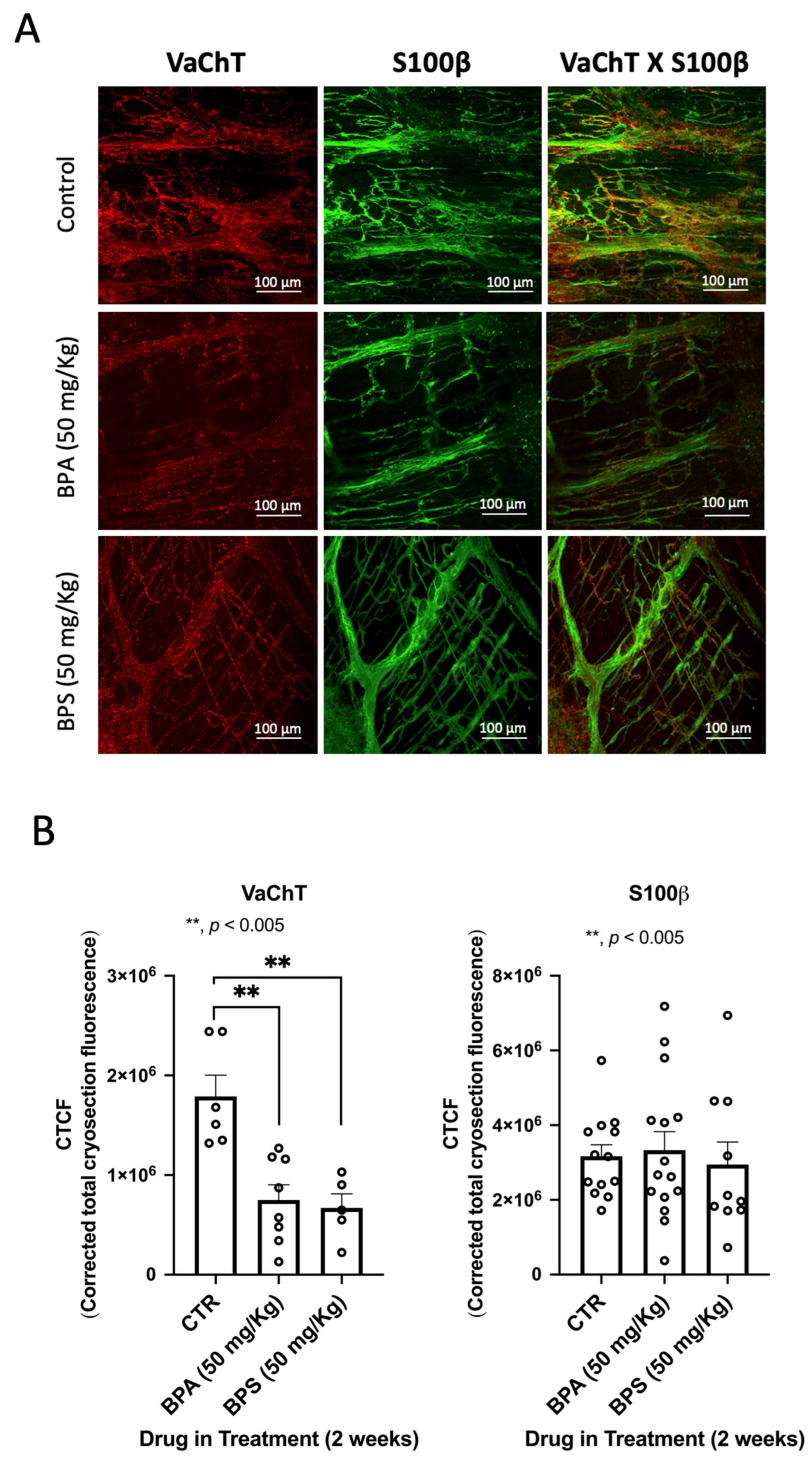
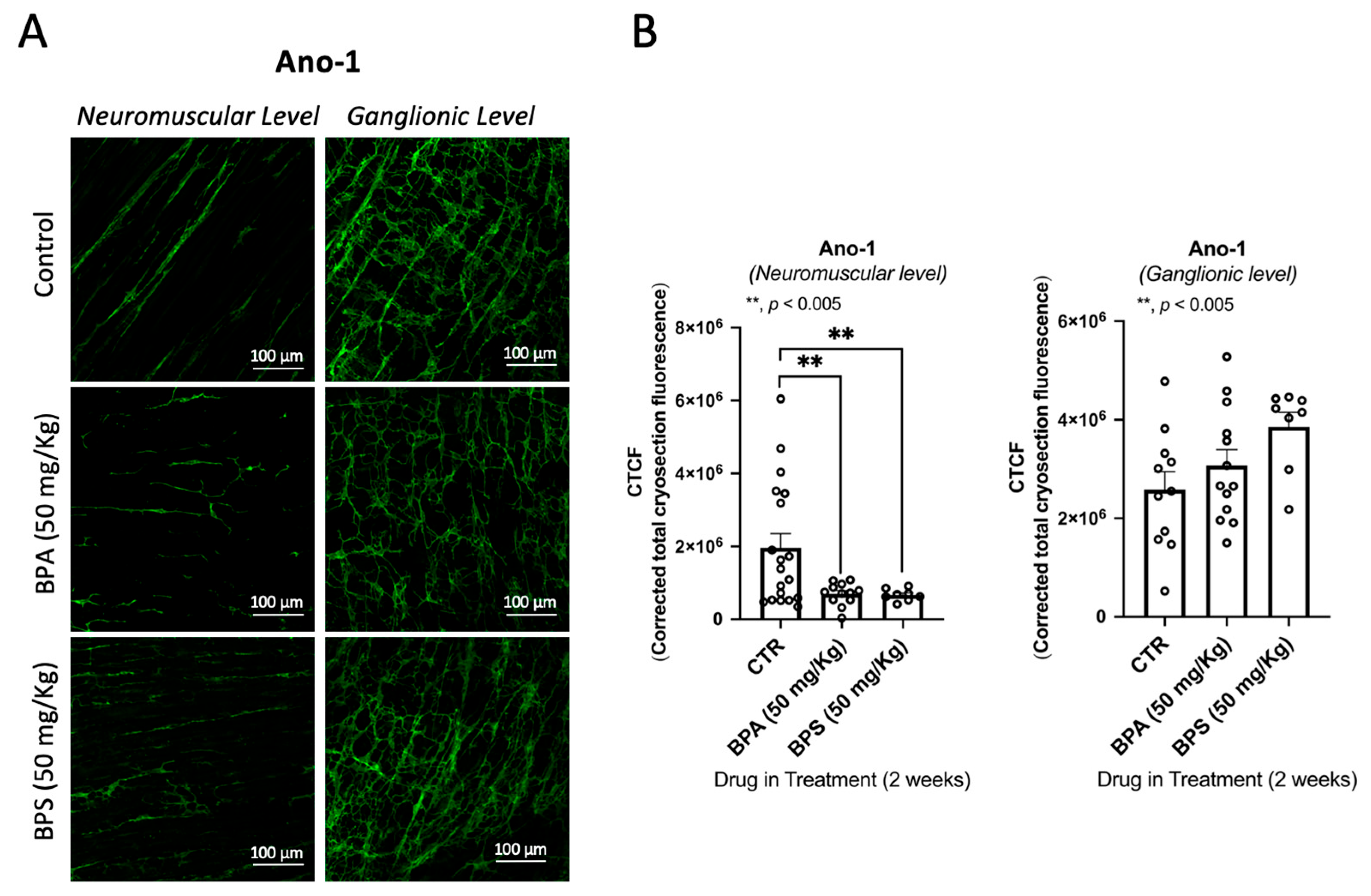
2.2. Oral Administration of BPA and BPS Causes a Partial Loss of Myenteric Cholinergic Neurons and Interstitial Cells of Cajal (ICCs), Without Affecting Enteric Glial Cells Immunoreactivity in CD1 Mice Colon
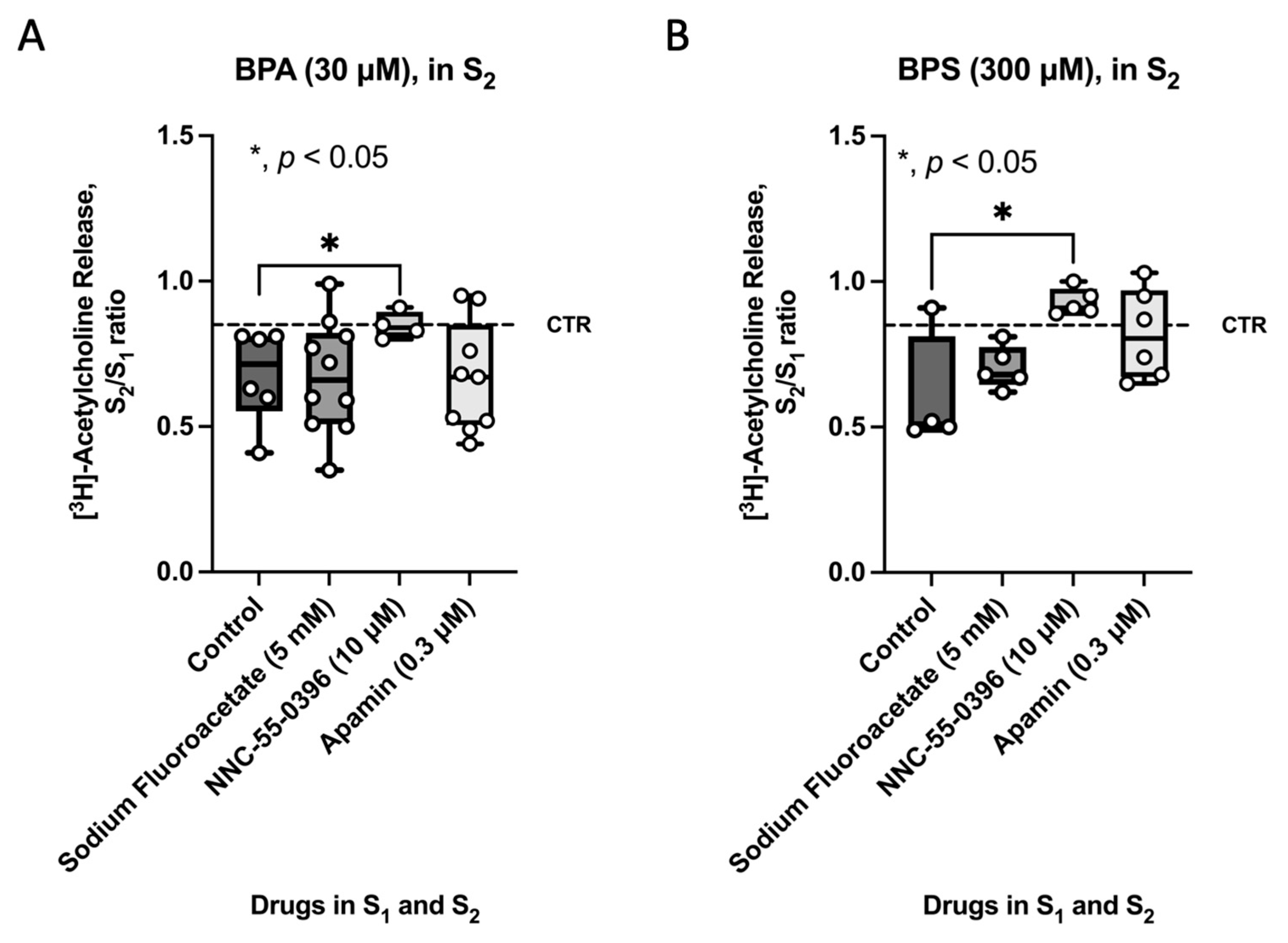
2.3. Selective Blockage of ICCs Activity Prevents the Inhibitory Effect of BPA and BPS on [3H]ACh Release from Stimulated Myenteric Neurons of CD1 Mice Mid Colon
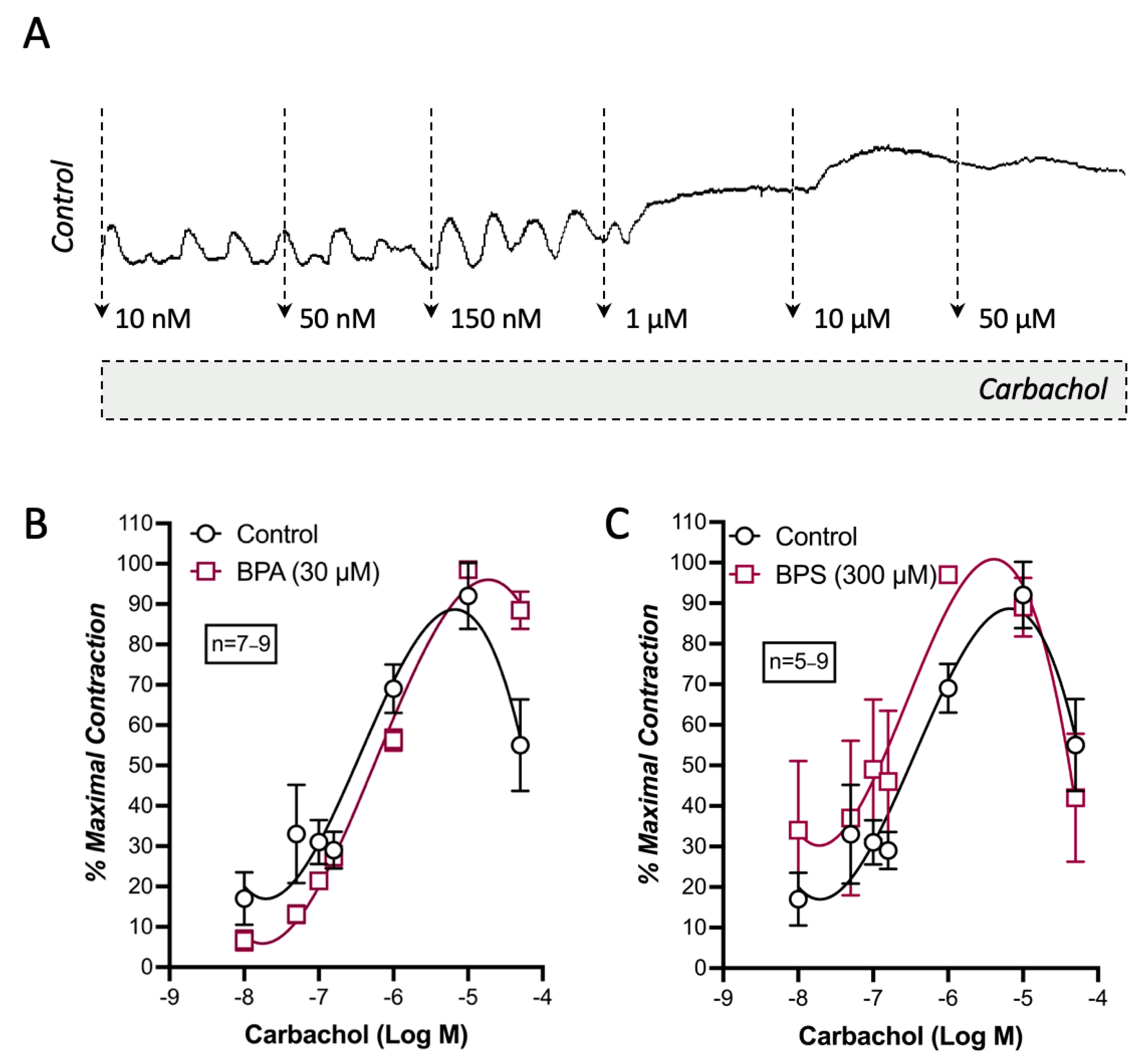
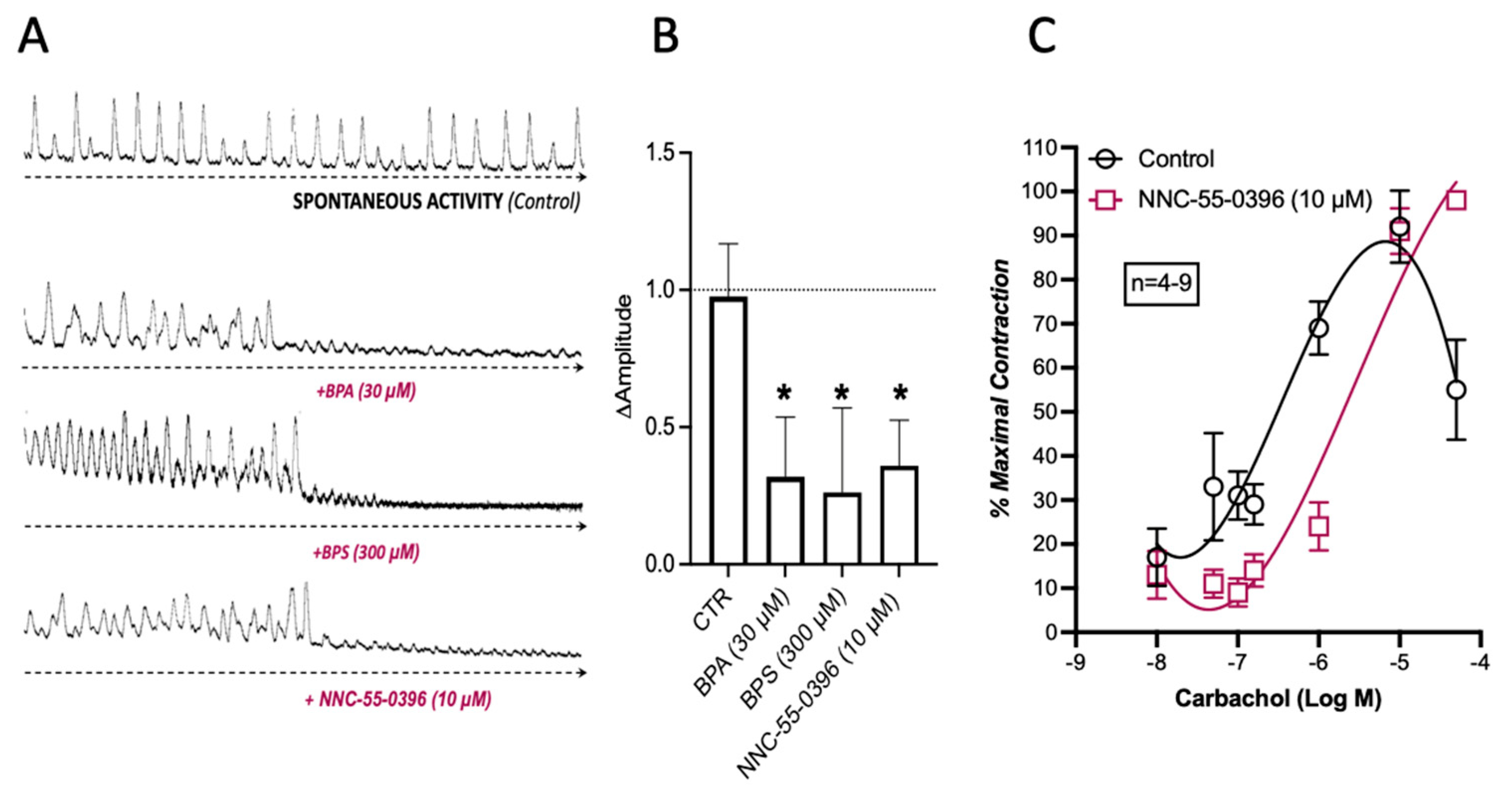
2.4. BPA and BPS Decrease the Spontaneous Myographic Activity of CD1 Mice Mid Colon in a Similar Manner to That Caused by Blockage of Voltage-Sensitive Cav3 (T-Type) Channels in ICCs with NNC-55-936
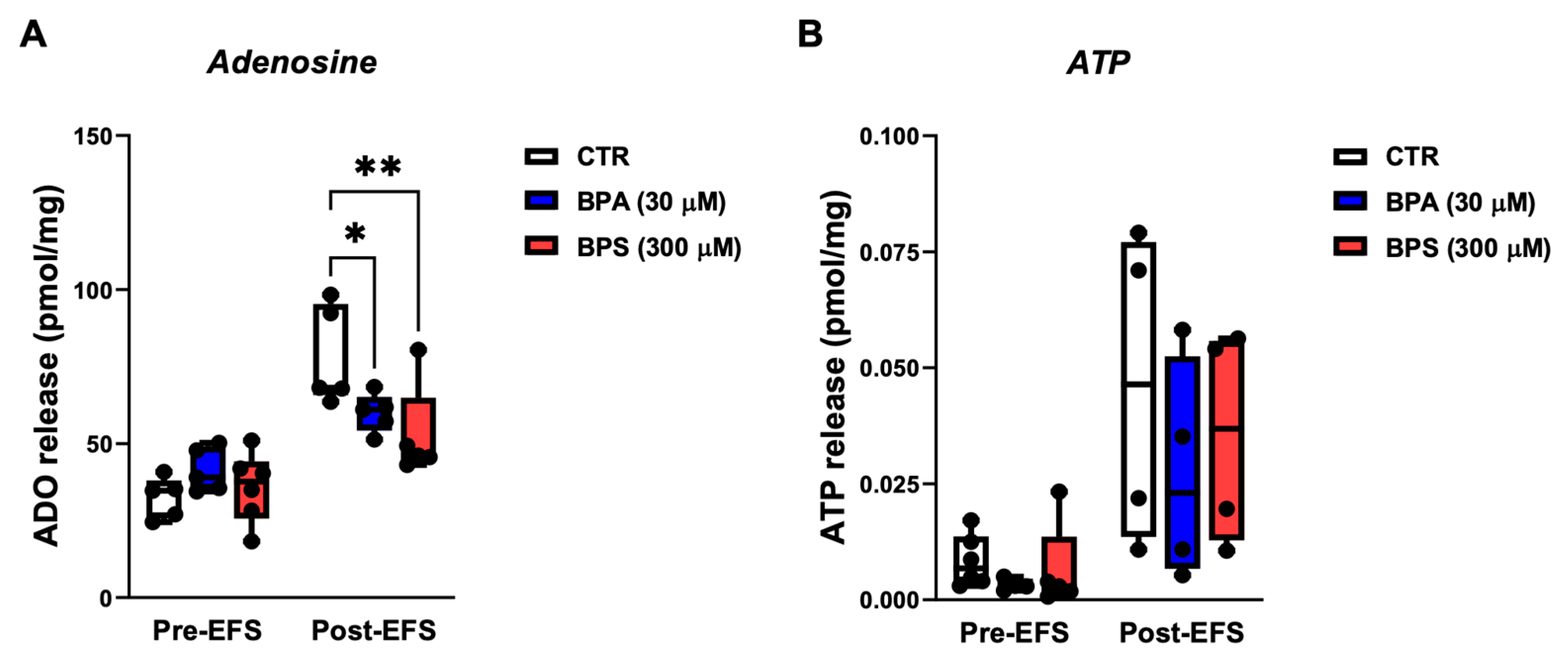
2.5. BPA and BPS Reduce the Release of Adenosine, but Not of ATP, from Stimulated LM-MP Preparations of the CD1 Mice Mid Colon
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Tissue Collection
4.2. [3H]Acetylcholine Release
4.3. ATP and Adenosine Release
4.4. Myographic Recordings
4.5. Immunofluorescence Staining—Confocal Microscopy Observation
4.6. Materials and Solutions
4.7. Presentation of Data and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Becerra, V.; Odermatt, J. Detection and quantification of traces of bisphenol A and bisphenol S in paper samples using analytical pyrolysis-GC/MS. Analyst 2012, 137, 2250–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Liu, F.; Kannan, K. Bisphenol s, a new bisphenol analogue, in paper products and currency bills and its association with bisphenol a residues. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6515–6522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Ishikawa, K.; Sugiyama, K.; Furuta, H.; Nishimura, F. Content and release of bisphenol A from polycarbonate dental products. Dent. Mater. J. 2000, 19, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Hauser, R.; Marcus, M.; Olea, N.; Welshons, W.V. Human exposure to bisphenol A (BPA). Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 139–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, M.S.; Mok-Lin, E.; Fujimoto, V.Y. Bisphenol A and ovarian steroidogenesis. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Mandal, M.B.; Katiyar, R.; Singh, S.P.; Birla, H. A Comparative Study of Effects of 28-Day Exposure of Bisphenol A and Bisphenol S on Body Weight Changes, Organ Histology, and Relative Organ Weight. Int. J. Appl. Basic. Med. Res. 2021, 11, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloisi, A.M.; Della Seta, D.; Rendo, C.; Ceccarelli, I.; Scaramuzzino, A.; Farabollini, F. Exposure to the estrogenic pollutant bisphenol A affects pain behavior induced by subcutaneous formalin injection in male and female rats. Brain Res. 2002, 937, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braniste, V.; Jouault, A.; Gaultier, E.; Polizzi, A.; Buisson-Brenac, C.; Leveque, M.; Martin, P.G.; Theodorou, V.; Fioramonti, J.; Houdeau, E. Impact of oral bisphenol A at reference doses on intestinal barrier function and sex differences after perinatal exposure in rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporossi, L.; Papaleo, B. Bisphenol A and Metabolic Diseases: Challenges for Occupational Medicine. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramec Skledar, D.; Mašič, L.P. Bisphenol A and its analogs: Do their metabolites have endocrine activity? Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 47, 182–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, A.; Ahmad, M. From BPA to its analogues: Is it a safe journey? Chemosphere 2016, 158, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, C.S. Neuroendocrine disruption in animal models due to exposure to bisphenol A analogues. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2017, 47, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, K.; Tarafder, P.; Paul, G. Bisphenol A inhibits duodenal movement ex vivo of rat through nitric oxide-mediated soluble guanylyl cyclase and α-adrenergic signaling pathways. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2016, 36, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhao, Z.; Ji, W. Bisphenol A induces apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammatory response in colon and liver of mice in a mitochondria-dependent manner. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, K.; Makowska, K.; Całka, J.; Gonkowski, S. The Endocrine Disruptor Bisphenol A (BPA) Affects the Enteric Neurons Immunoreactive to Neuregulin 1 (NRG1) in the Enteric Nervous System of the Porcine Large Intestine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymańska, K.; Całka, J.; Gonkowski, S. Nitric oxide as an active substance in the enteric neurons of the porcine digestive tract in physiological conditions and under intoxication with bisphenol A (BPA). Nitric Oxide 2018, 80, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymańska, K.; Makowska, K.; Gonkowski, S. The Influence of High and Low Doses of Bisphenol A (BPA) on the Enteric Nervous System of the Porcine Ileum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makowska, K.; Gonkowski, S. Bisphenol A (BPA) Affects the Enteric Nervous System in the Porcine Stomach. Animals 2020, 10, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowska, K.; Gonkowski, S. Changes Caused by Low Doses of Bisphenol A (BPA) in the Neuro-Chemistry of Nerves Located in the Porcine Heart. Animals 2021, 11, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowska, K.; Całka, J.; Gonkowski, S. Effects of the long-term influence of bisphenol A and bisphenol S on the population of nitrergic neurons in the enteric nervous system of the mouse stomach. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowska, K.; Lepiarczyk, E.; Gonkowski, S. The comparison of the influence of bisphenol A (BPA) and its analogue bisphenol S (BPS) on the enteric nervous system of the distal colon in mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, J.P.; Scheuermann, D.W.; Stach, W.; Adriaensen, D.; De Groodt-Lasseel, M.H. Functional morphology of the enteric nervous system with special reference to large mammals. Eur. J. Morphol. 1992, 30, 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- Balemba, O.B.; Grøndahl, M.L.; Mbassa, G.K.; Semuguruka, W.D.; Hay-Smith, A.; Skadhauge, E.; Dantzer, V. The organization of the enteric nervous system in the sub-mucous and mucous layers of the small intestine of the pig studied by VIP and neurofilament protein immunohistochemistry. J. Anat. 1998, 192, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, J.B. The enteric nervous system and neurogastroenterology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, C.; Magalhães-Cardoso, M.T.; Ferreirinha, F.; Silva, I.; Dias, A.S.; Pelletier, J.; Sévigny, J.; Correia-de-Sá, P. Feed-forward inhibition of CD73 and upregulation of adenosine deaminase contribute to the loss of adenosine neuromodulation in postinflammatory ileitis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 254640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, C.; Ferreirinha, F.; Magalhães-Cardoso, M.T.; Silva, I.; Marques, P.; Correia-de-Sá, P. Post-inflammatory Ileitis Induces Non-neuronal Purinergic Signaling Adjustments of Cholinergic Neurotransmission in the Myenteric Plexus. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furness, J.B. The Enteric Nervous System; Blackwell Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.; Brookes, S.J.; Steele, P.A.; Gibbins, I.; Burcher, E.; Kandiah, C.J. Neurochemical classification of myenteric neurons in the guinea-pig ileum. Neuroscience 1996, 75, 949–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaleczyc, J.; Klimczuk, M.; Franke-Radowiecka, A.; Sienkiewicz, W.; Majewski, M.; Łakomy, M. The distribution and chemical coding of intramural neurons supplying the porcine stomach—The study on normal pigs and on animals suffering from swine dysentery. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2007, 36, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowska, K.; Obremski, K.; Zielonka, L.; Gonkowski, S. The Influence of Low Doses of Zearalenone and T-2 Toxin on Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide-Like Immunoreactive (CGRP-LI) Neurons in the ENS of the Porcine Descending Colon. Toxins 2017, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EU) 2016/2235 Adds Bisphenol A (BPA) to REACH Annex XVII Restricted Substances List. Available online: http://www.chemsafetypro.com/Topics/EU/REACH_annex_xvii_REACH_restricted_substance_list.html (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Cimmino, I.; Fiory, F.; Perruolo, G.; Miele, C.; Beguinot, F.; Formisano, P.; Oriente, F. Potential Mechanisms of Bisphenol A (BPA) Contributing to Human Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geueke, B. Food Packaking Forum - Dossier: Bisphenol S. Zenodo 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Kramer, J.P.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X. Automated on-line column-switching high performance liquid chromatography isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry method for the quantification of bisphenol A, bisphenol F, bisphenol S, and 11 other phenols in urine. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 944, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andra, S.S.; Charisiadis, P.; Arora, M.; van Vliet-Ostaptchouk, J.V.; Makris, K.C. Biomonitoring of human exposures to chlorinated derivatives and structural analogs of bisphenol A. Environ. Int. 2015, 85, 352–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochester, J.R.; Bolden, A.L. Bisphenol S and F: A Systematic Review and Comparison of the Hormonal Activity of Bisphenol A Substitutes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, K.; Noda, S.; Imatanaka, N.; Yakabe, Y. Comparative study of the uterotrophic potency of 14 chemicals in a uterotrophic assay and their receptor-binding affinity. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 146, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Sekulovski, N.; MacLean, J.A.; Hayashi, K. Effects of bisphenol A analogues on reproductive functions in mice. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 73, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.M. Effects of bisphenol S on the structures and activities of trypsin and pepsin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 11303–11311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokra, K.; Kocia, M.; Michałowicz, J. Bisphenol A and its analogs exhibit different apoptotic potential in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (in vitro study). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 84, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maćczak, A.; Cyrkler, M.; Bukowska, B.; Michałowicz, J. Bisphenol A, bisphenol S, bisphenol F and bisphenol AF induce different oxidative stress and damage in human red blood cells (in vitro study). Toxicol. In Vitr. 2017, 41, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinch, C.D.; Ibhazehiebo, K.; Jeong, J.H.; Habibi, H.R.; Kurrasch, D.M. Low-dose exposure to bisphenol A and replacement bisphenol S induces precocious hypothalamic neurogenesis in embryonic zebrafish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catanese, M.C.; Vandenberg, L.N. Bisphenol S (BPS) Alters Maternal Behavior and Brain in Mice Exposed During Pregnancy/Lactation and Their Daughters. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 516–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fic, A.; Žegura, B.; Sollner Dolenc, M.; Filipič, M.; Mašič, L.P. Mutagenicity and DNA damage of bisphenol A and its structural analogues in HepG2 cells. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2013, 64, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Chen, S.; Zhang, L.; Qu, W.; Chen, Z. Bisphenol A increases intestinal permeability through disrupting intestinal barrier function in mice. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.G.; Correia, J.; Adiga, D.; Rai, P.S.; Dsouza, H.S.; Chakrabarty, S.; Kabekkodu, S.P. A comprehensive review on the carcinogenic potential of bisphenol A: Clues and evidence. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 19643–19663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Choi, J.W.; Ahn, Y.A.; Kim, S. Pharmacokinetics of bisphenol S in humans after single oral administration. Environ. Int. 2018, 112, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, C.W.; Jeong, J.; Hwang, M.S.; Jung, K.K.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, H.M. Establishment of the korean tolerable daily intake of bisphenol a based on risk assessments by an expert committee. Toxicol. Res. 2010, 26, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyl, R.W.; Myers, C.B.; Marr, M.C.; Thomas, B.F.; Keimowitz, A.R.; Brine, D.R.; Veselica, M.M.; Fail, P.A.; Chang, T.Y.; Seely, J.C.; et al. Three-generation reproductive toxicity study of dietary bisphenol A in CD Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2002, 68, 121–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- vom Saal, F.S.; Akingbemi, B.T.; Belcher, S.M.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Crain, D.A.; Eriksen, M.; Farabollini, F.; Guillette, L.J., Jr.; Hauser, R.; Heindel, J.J.; et al. Chapel Hill bisphenol A expert panel consensus statement: Integration of mechanisms, effects in animals and potential to impact human health at current levels of exposure. Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA J. Scientific opinion on the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs: Executive summary. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 3978–4599. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Ma, W.; Gao, Y.; Long, C.; Yu, Y. Derivation of the oral reference dose (RfD) for bisphenol S and bisphenol F based on epidemiological and experimental studies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 293, 118045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liliana, R.; Slawomir, G.; Tomasz, J.; Joanna, W.; Andrzej, P. The Neurochemical Characterization of Parasympathetic Nerve Fibers in the Porcine Uterine Wall Under Physiological Conditions and After Exposure to Bisphenol A (BPA). Neurotox. Res. 2019, 35, 867–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.; Deshpande, S.B. Bisphenol A decreases the spontaneous contractions of rat uterus in vitro through a nitrergic mechanism. J. Basic. Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 29, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsenzadeh, M.S.; Razavi, B.M.; Imenshahidi, M.; Mohajeri, S.A.; Rameshrad, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Evaluation of green tea extract and epigallocatechin gallate effects on bisphenol A-induced vascular toxicity in isolated rat aorta and cytotoxicity in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 996–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zygmuntowicz, A.; Markiewicz, W.; Grabowski, T.; Jaroszewski, J. Effects of Bisphenol A and Bisphenol F on Porcine Uterus Contractility. J. Vet. Res. 2022, 66, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, N.; Marcelino, H.; Azevedo, R.; Verde, I. Effects of bisphenol A on human umbilical arteries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 27670–27681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feiteiro, J.; Mariana, M.; Glória, S.; Cairrao, E. Inhibition of L-type calcium channels by Bisphenol A in rat aorta smooth muscle. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 43, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wu, W.; Huan, F.; Xiao, H. Bisphenol A modulates calcium currents and intracellular calcium concentration in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J. Membr. Biol. 2013, 246, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, B.S.; Ahn, H.J.; Kang, H.S.; Jung, E.M.; Yang, H.; Hong, E.J.; Jeung, E.B. Effects of estrogen and estrogenic compounds, 4-tert-octylphenol, and bisphenol A on the uterine contraction and contraction-associated proteins in rats. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 375, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowska, K.; Gonkowski, S. Comparison of the Influence of Bisphenol A and Bisphenol S on the Enteric Nervous System of the Mouse Jejunum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mañé, N.; Viais, R.; Martínez-Cutillas, M.; Gallego, D.; Correia-de-Sá, P.; Jiménez, M. Inverse gradient of nitrergic and purinergic inhibitory cotransmission in the mouse colon. Acta Physiol. 2016, 216, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mañé, N.; Gil, V.; Martínez-Cutillas, M.; Clavé, P.; Gallego, D.; Jiménez, M. Differential functional role of purinergic and nitrergic inhibitory cotransmitters in human colonic relaxation. Acta Physiol. 2014, 212, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durnin, L.; Lees, A.; Manzoor, S.; Sasse, K.C.; Sanders, K.M.; Mutafova-Yambolieva, V.N. Loss of nitric oxide-mediated inhibition of purine neurotransmitter release in the colon in the absence of interstitial cells of Cajal. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 313, G419–G433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.K.; Deshpande, S.B. Bisphenol A depresses compound action potential of frog sciatic nerve in vitro involving Ca(2+)-dependent mechanisms. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 517, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Ward, S.M.; Gerthoffer, W.T.; Sanders, K.M. PKC-epsilon translocation in enteric neurons and interstitial cells of Cajal in response to muscarinic stimulation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2003, 285, G593–G601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziganshin, A.U.; Khairullin, A.E.; Hoyle, C.H.V.; Grishin, S.N. Modulatory Roles of ATP and Adenosine in Cholinergic Neuromuscular Transmission. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, C.; Ferreirinha, F.; Silva, I.; Duarte-Araújo, M.; Correia-de-Sá, P. Localization and function of adenosine receptor subtypes at the longitudinal muscle—Myenteric plexus of the rat ileum. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 59, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Araújo, M.; Nascimento, C.; Alexandrina Timóteo, M.; Magalhães-Cardoso, T.; Correia-de-Sá, P. Dual effects of adenosine on acetylcholine release from myenteric motoneurons are mediated by junctional facilitatory A2A and extrajunctional inhibitory A1 receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 141, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Colucci, R.; Awwad, O.; Ghisu, N.; Tuccori, M.; Del Tacca, M.; Blandizzi, C. Differential recruitment of high affinity A1 and A2A adenosine receptors in the control of colonic neuromuscular function in experimental colitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 650, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, C.; Duarte-Araújo, M.; Adães, S.; Magalhães-Cardoso, T.; Correia-de-Sá, P. Muscarinic M3 facilitation of acetylcholine release from rat myenteric neurons depends on adenosine outflow leading to activation of excitatory A2A receptors. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2009, 21, 1118-e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Araújo, M.; Timóteo, M.A.; Correia-de-Sá, P. Adenosine activating A2A-receptors coupled to adenylate cyclase/cyclic AMP pathway downregulates nicotinic autoreceptor function at the rat myenteric nerve terminals. Neurochem. Int. 2004, 45, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.; Yang, M.; Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Luo, S.; Wong, M.; Zheng, C. Bisphenol S-induced chronic inflammatory stress in liver via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ using fish in vivo and in vitro models. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaji, N.; Hori, M. Interstitial cells of Cajal in gastrointestinal inflammatory diseases. J. Smooth Muscle Res. 2023, 59, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.P.; Liu, Z.H.; Yuan, S.F.; Yin, H.; Dang, Z.; Wu, P.X. Worldwide human daily intakes of bisphenol A (BPA) estimated from global urinary concentration data (2000-2016) and its risk analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; Emerson, M.; et al. Reporting animal research: Explanation and elaboration for the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia-de-Sá, P.; Adães, S.; Timóteo, M.A.; Vieira, C.; Magalhães-Cardoso, T.; Nascimento, C.; Duarte-Araújo, M. Fine-tuning modulation of myenteric motoneurons by endogenous adenosine: On the role of secreted adenosine deaminase. Auton. Neurosci. 2006, 126–127, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primary Antibodies | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antigen | Code | Species | Working Dilution | Supplier |
| S100β | Ab868 | Rabbit (rb) | 1:400 | ABCAM |
| Ano-1 | Ab53212 | Rabbit (rb) | 1:100 | ABCAM |
| VaChT | AB1588 | Guineapig (gp) | 1:500 | Chemicon |
| Secondary antibodies | ||||
| Reagents | Working Dilution | Supplier | ||
| Alexa Fluor 488, anti-rb | 1:1000 | Molecular probes | ||
| TRITC 568, anti-gp | 1:150 | Jackson Immuno Res. | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makowska, K.; Vieira, C.; Silva, I.; Aprianto, Y.; Silva, D.; Bessa-Andrês, C.; Lopes, A.; Gonkowski, S.; Correia-de-Sá, P. Bisphenol A and Its Analogue Bisphenol S Inhibit Cholinergic Neurotransmission at the Tripartite Colonic Myenteric Synapse of CD1 Mice by Targeting Interstitial Cells of Cajal. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178279
Makowska K, Vieira C, Silva I, Aprianto Y, Silva D, Bessa-Andrês C, Lopes A, Gonkowski S, Correia-de-Sá P. Bisphenol A and Its Analogue Bisphenol S Inhibit Cholinergic Neurotransmission at the Tripartite Colonic Myenteric Synapse of CD1 Mice by Targeting Interstitial Cells of Cajal. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178279
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakowska, Krystyna, Cátia Vieira, Isabel Silva, Yoce Aprianto, Diogo Silva, Catarina Bessa-Andrês, Ana Lopes, Sławomir Gonkowski, and Paulo Correia-de-Sá. 2025. "Bisphenol A and Its Analogue Bisphenol S Inhibit Cholinergic Neurotransmission at the Tripartite Colonic Myenteric Synapse of CD1 Mice by Targeting Interstitial Cells of Cajal" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178279
APA StyleMakowska, K., Vieira, C., Silva, I., Aprianto, Y., Silva, D., Bessa-Andrês, C., Lopes, A., Gonkowski, S., & Correia-de-Sá, P. (2025). Bisphenol A and Its Analogue Bisphenol S Inhibit Cholinergic Neurotransmission at the Tripartite Colonic Myenteric Synapse of CD1 Mice by Targeting Interstitial Cells of Cajal. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178279







