A Microfluidic Approach for Profiling Total Nitrogen Content in Age-Specific Nutritional Formulas Using Microchip Gel Electrophoresis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Total Nitrogen Content Comparison
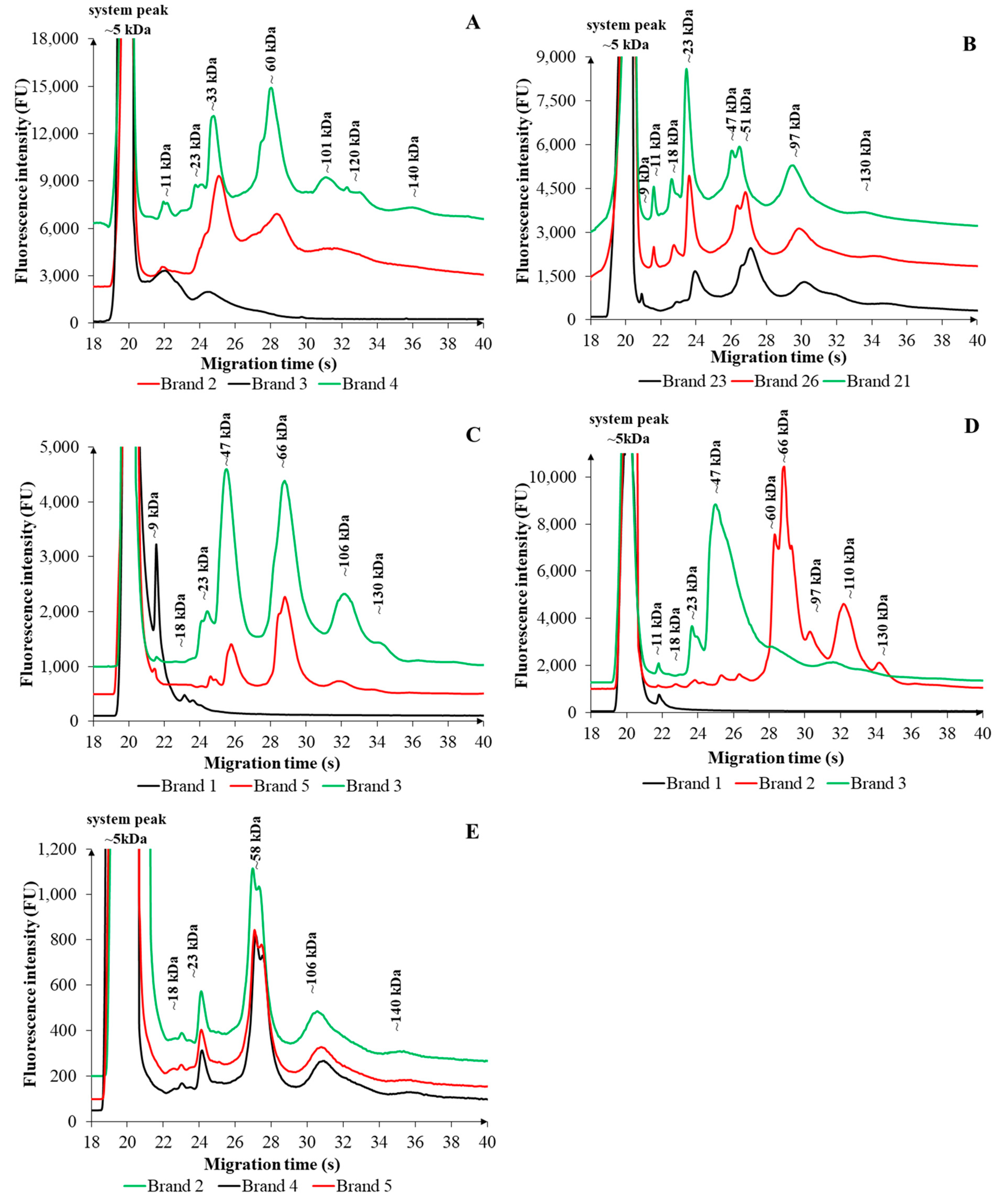
2.2. Comparison of FSMP Brands Within the Same Category
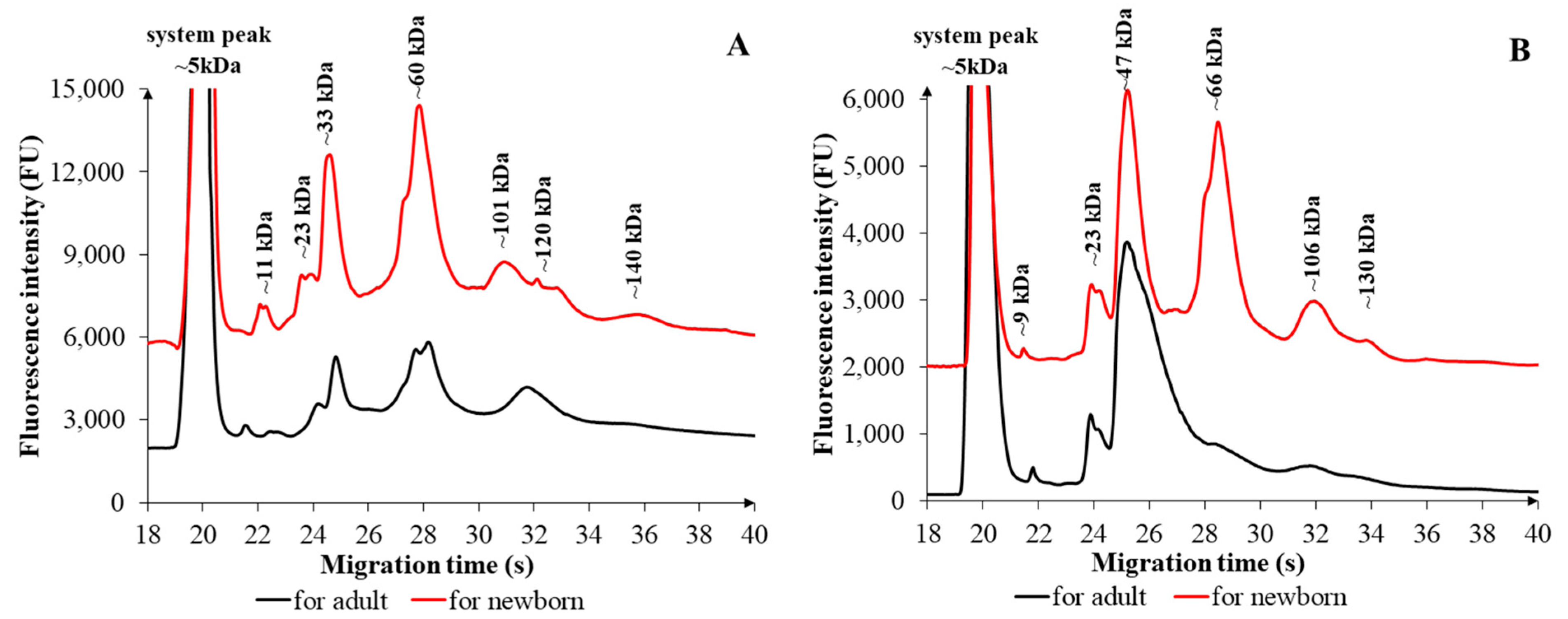
2.3. Comparison of FSMPs of the Same Consistency for Newborns and Adults
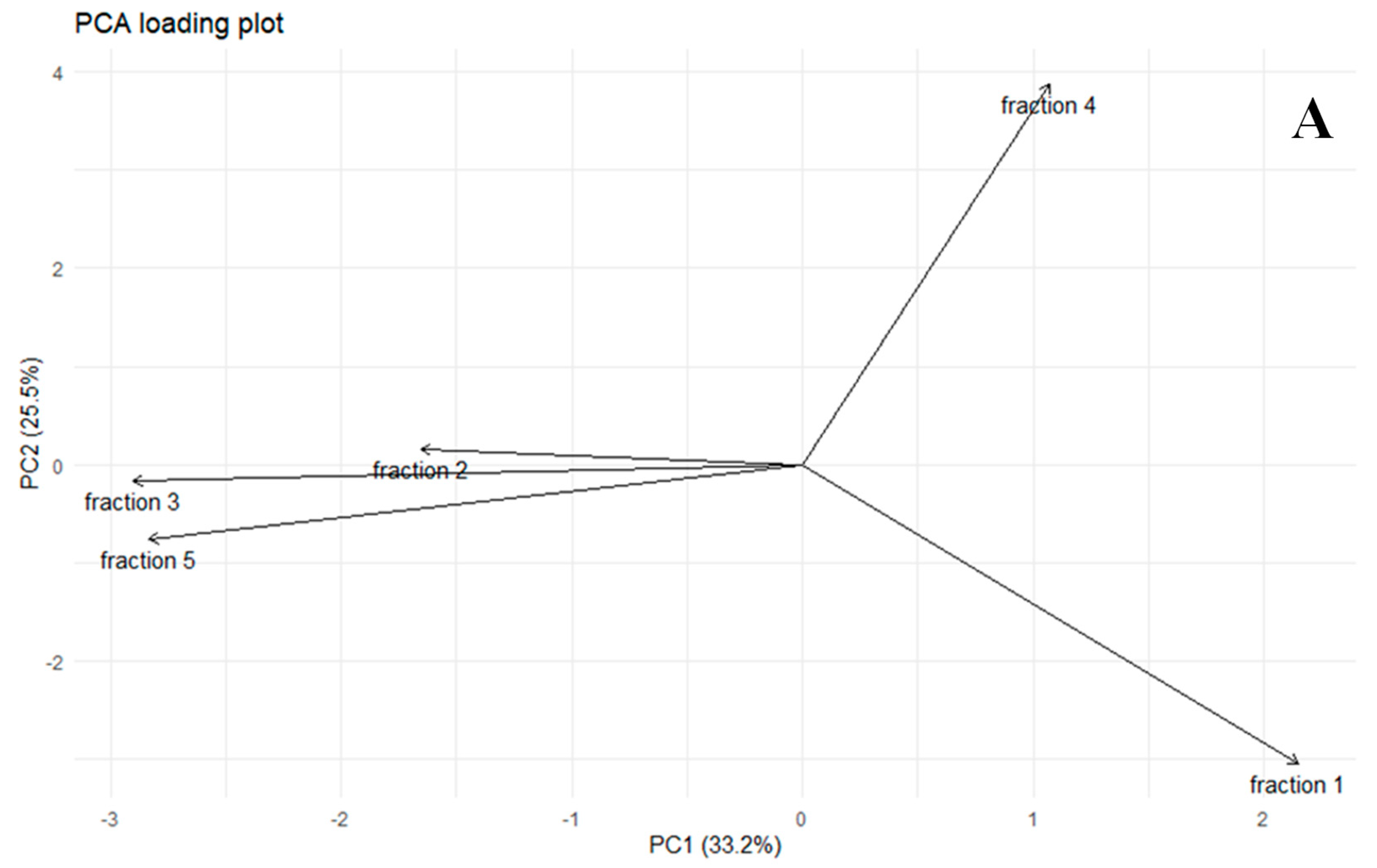
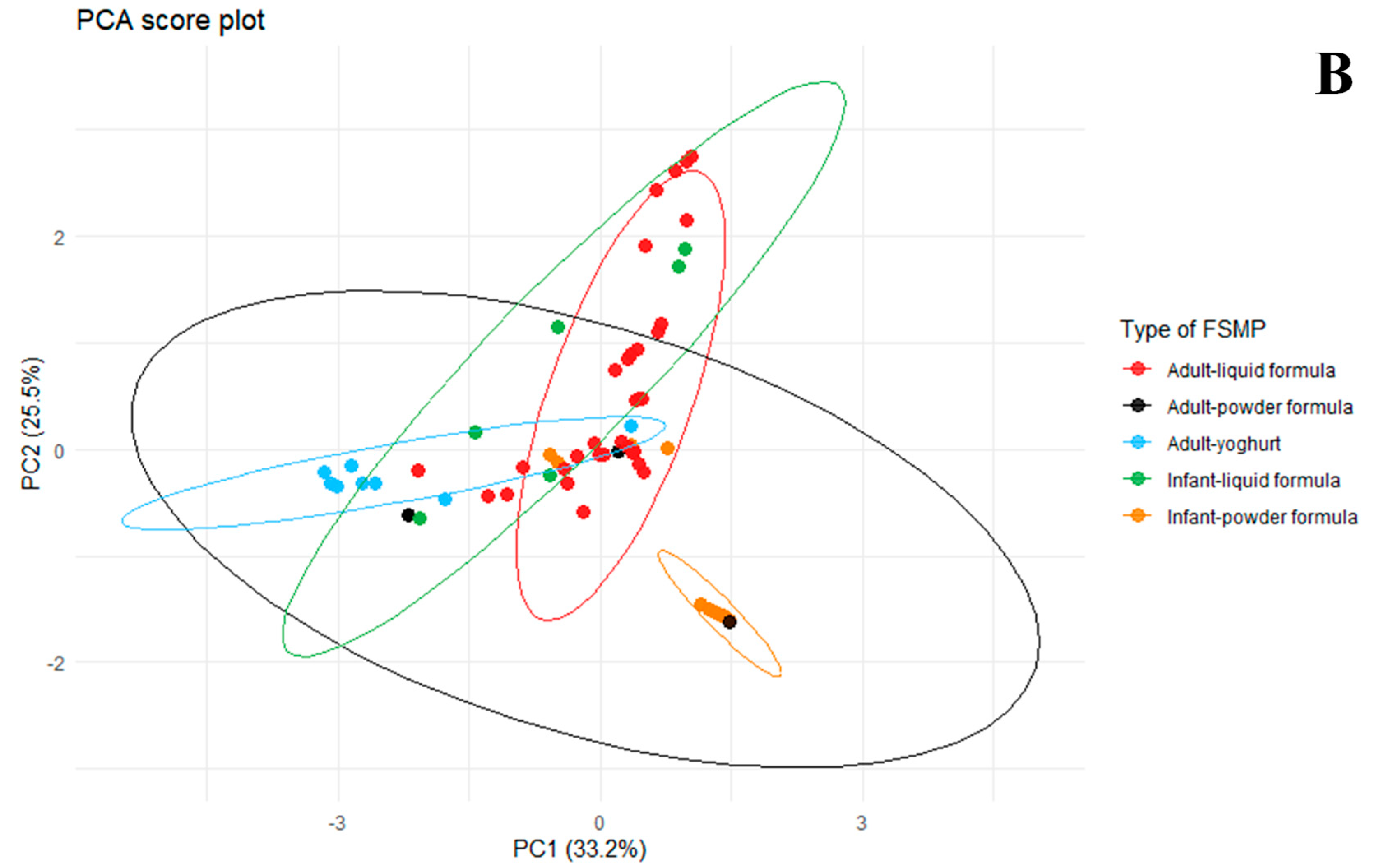
2.4. Statistical Diversity in FSMPs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Nutritional Formulas
3.2. Microchip Gel Electrophoresis for Electrophoretic Profiling and Total Nitrogen Determination
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- European Commission. Information from European Union Institutions, Bodies, Offices and Agencies Commission Notice on the Classification of Food for Special Medical Purposes; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2017; Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:52017XC1125(01) (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- European Parliament. Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 October 2011 on the Provision of Food Information to Consumers; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2011; Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A02011R1169-20180101 (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Auer, F.; Jarvas, G.; Guttman, A. Recent advances in the analysis of human milk oligosaccharides by liquid phase separation methods. J. Chromatogr. B 2021, 1162, 122497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, S.; Paswan, V.K.; Yadav, S.P.; Bhinchhar, B.K.; Kharkwal, S.; Rose, H.; Kanetkar, P.; Kumar, V.; Al-Zamani, Z.A.S.; Bunkar, D.S. A comprehensive review on infant formula: Nutritional and functional constituents, recent trends in processing and its impact on infants’ gut microbiota. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1194679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatchatee, P.; Nowak-Wegrzyn, A.; Lange, L.; Benjaponpitak, S.; Chong, K.W.; Sangsupawanich, P.; van Ampting, M.T.J.; Oude Nijhuis, M.M.; Harthoorn, L.F.; Langford, J.E.; et al. Tolerance development in cow’s milk–allergic infants receiving amino acid–based formula: A randomized controlled trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouwenhoven, S.M.P.; Muts, J.; Finken, M.J.J.; van Goudoever, J.B. Low-Protein Infant Formula and Obesity Risk. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinghäll Nilsson, U.; Lönnerdal, B.; Hernell, O.; Kvistgaard, A.S.; Jacobsen, L.N.; Karlsland Åkeson, P. Low-Protein Infant Formula Enriched with Alpha-Lactalbumin during Early Infancy May Reduce Insulin Resistance at 12 Months: A Follow-Up of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotto, N.; Orsi, A.; Menis, C.; Piemontese, P.; Morlacchi, L.; Condello, C.C.; Giannì, M.L.; Roggero, P.; Mosca, F. Clinical evaluation of two different protein content formulas fed to full-term healthy infants: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 59, Erratum in BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, S. The Protective Effects of 2’-Fucosyllactose Against E. coli O157 Infection Are Mediated by the Regulation of Gut Microbiota and the Inhibition of Pathogen Adhesion. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Fuerer, C.; McMahon, A.; Arendse, K.; Chanady, A.; Chen, H.; Chen, W.; Ding, X.; Gao, T.; Huang, K.; et al. Quantification of Whey Protein Content in Milk-Based Infant Formula Powders by Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate–Capillary Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-CGE): Multilaboratory Testing Study, Final Action 2016.15. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 1566–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, Y.; Omura, T.; Toyoshima, K.; Araki, A. Nutrition Management in Older Adults with Diabetes: A Review on the Importance of Shifting Prevention Strategies from Metabolic Syndrome to Frailty. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrino, L.; Hogenboom, J.A.; Rosi, V.; Sindaco, M.; Gerna, S.; D’Incecco, P. Focus on the Protein Fraction of Sports Nutrition Supplements. Molecules 2022, 27, 3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaytán-González, A.; Ocampo-Alfaro, M.D.J.; Torres-Naranjo, F.; González-Mendoza, R.G.; Gil-Barreiro, M.; Arroniz-Rivera, M.; López-Taylor, J.R. Dietary Protein Intake Patterns and Inadequate Protein Intake in Older Adults from Four Countries. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, J. The Application and Mechanism Analysis of Enteral Nutrition in Clinical Management of Chronic Diseases. Nutrients 2025, 17, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, S.M.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.G. Comparison of Early Enteral Nutrition Versus Early Parenteral Nutrition in Critically Ill Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balogh-Hartmann, F.; Páger, C.; Bufa, A.; Sipos, Z.; Dávidovics, A.; Verzár, Z.; Marosvölgyi, T.; Makszin, L. Comprehensive Study of Total Nitrogen Content and Microfluidic Profiles in Additive-Enriched Plant-Based Drinks. Foods 2024, 13, 2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazek, V.; Caldwell, R.A. Comparison of SDS gel capillary electrophoresis with microfluidic lab-on-a-chip technology to quantify relative amounts of 7S and 11S proteins from 20 soybean cultivars. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 2127–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleakley, S.; Hayes, M. Algal Proteins: Extraction, Application, and Challenges Concerning Production. Foods 2017, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallo, G.; Lorini, C.; Garamella, G.; Bonaccorsi, G. Seaweeds as a “Palatable” Challenge between Innovation and Sustainability: A Systematic Review of Food Safety. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravel, A.; Dubois-Laurin, F.; Turgeon, S.L.; Doyen, A. The role of the 7S/11S globulin ratio in the gelling properties of mixed β-lactoglobulin/pea proteins systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 156, 110273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, H.; Nunes, M.C.; Prista, C.; Raymundo, A. Innovative and Healthier Dairy Products through the Addition of Microalgae: A Review. Foods 2022, 11, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.A.; Singh, T.K.; Stockmann, R.; Jegasothy, H.; Buckow, R. Quality Attributes of Ultra-High Temperature-Treated Model Beverages Prepared with Faba Bean Protein Concentrates. Foods 2021, 10, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, U.; Benjakul, S. Coconut Milk and Coconut Oil: Their Manufacture Associated with Protein Functionality. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 2019–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roland, I.S.; Aguilera-Toro, M.; Nielsen, S.D.-H.; Poulsen, N.A.; Larsen, L.B. Processing-Induced Markers in Proteins of Commercial Plant-Based Drinks in Relation to Compositional Aspects. Foods 2023, 12, 3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, A.K.; Dhuli, K.; Donato, K.; Aquilanti, B.; Velluti, V.; Matera, G.; Iaconelli, A.; Connelly, S.T.; Bellinato, F.; Gisondi, P.; et al. Main nutritional deficiencies. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2022, 63, E93–E101. [Google Scholar]
- Castanys-Muñoz, E.; Martin, M.J.; Prieto, P.A. 2’-fucosyllactose: An abundant, genetically determined soluble glycan present in human milk. Nutr. Rev. 2013, 71, 773–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turck, D.; Bohn, T.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; Pelaez, C.; et al. Safety of 2’-fucosyllactose (2’-FL) produced by a derivative strain (APC199) of Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07647. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Fan, L.; Zheng, N.; Blecker, C.; Delcenserie, V.; Li, H.; Wang, J. 2’-Fucosyllactose Ameliorates Inflammatory Bowel Disease by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Promoting MUC2 Expression. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 822020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsatto, J.V.B.; Maciel, E.V.S.; Cifuentes, A.; Lanças, F.M. Online Extraction Followed by LC–MS/MS Analysis of Lipids in Natural Samples: A Proof-of-Concept Profiling Lecithin in Seeds. Foods 2023, 12, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada, C.; Urra, M.; Mella, C.; Zúñiga, R.N.; Troncoso, E. Plant-Based Oil-in-Water Food Emulsions: Exploring the Influence of Different Formulations on Their Physicochemical Properties. Foods 2024, 13, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltodextrin. Available online: https://www.acs.org/molecule-of-the-week/archive/m/maltodextrin.html (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Cecchi, S.; Di Stante, S.; Belcastro, S.; Bertuzzi, V.; Cardillo, A.; Diotallevi, L.; Grabocka, X.; Kulurianu, H.; Martello, M.; Nastasi, V.; et al. Supplemented Very Low Protein Diet (sVLPD) in Patients with Advanced Chronic Renal Failure: Clinical and Economic Benefits. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, P.; Lozano, P.; Solano, F. Unraveling the Metabolic Hallmarks for the Optimization of Protein Intake in Pre-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garneata, L.; Mocanu, C.-A.; Simionescu, T.P.; Mocanu, A.E.; Dragomir, D.R.; Mircescu, G. Low Protein Diet Reduces Proteinuria and Decline in Glomerular Filtration Rate in Advanced, Heavy Proteinuric Diabetic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofoulaki, E.; Tzanakakis, V.A.; Giannopoulos, G.; Kapellakis, I.; Kabourakis, E.; Chatzistathis, T.; Monokrousos, N. Different Contribution of Olive Groves and Citrus Orchards to Soil Organic Carbon Sequestration: A Field Study in Four Sites in Crete, Greece. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mæhre, H.; Dalheim, L.; Edvinsen, G.; Elvevoll, E.; Jensen, I.-J. Protein Determination—Method Matters. Foods 2018, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agilent Technologies, Inc. Quantification Strategies Using the High Sensitivity Protein 250 Assay for the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer Technical Note 5989-8941EN; 5989-8941EN; Agilent Technologies, Inc.: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2016; Available online: https://www.agilent.com/cs/library/technicaloverviews/public/5989-8941EN.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Agilent Technologies, Inc. Protein Analysis with the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer System An Overview of the Protein Assay Portfolio; Technical Overview 5990-5283EN; Agilent Technologies, Inc.: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Balogh-Hartmann, F.; Páger, C.; Bufa, A.; Madarászné Horváth, I.; Verzár, Z.; Marosvölgyi, T.; Makszin, L. Microfluidic Analysis for the Determination of Protein Content in Different Types of Plant-Based Drinks. Molecules 2023, 28, 6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agilent Technologies, Inc. Agilent High Sensitivity Protein 250 Kit Guide; Agilent Technologies, Inc.: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
| FSMP Type | Measured TN (g/100 mL) | Nominal TP * (g/100 mL) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid for newborns (n = 16) | 9.3 (4.1–23.4) | 1.9–2.9 | 0.011 |
| Liquid for adults (n = 116) | 21.2 (9.4–45.2) | 4.0–10.0 | <0.001 |
| Powder for newborns (n = 52) | 10.9 (7.3–54.8) | 1.3–15.3 | 0.001 |
| Powder for adults (n = 12) | 75.6 (38.8–81.4) | 0.0–7.5 | 0.026 |
| Yoghurt for adults (n = 24) | 3.9 (3.7–12.6) | 7.5–9.4 | 0.506 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balogh-Hartmann, F.; Páger, C.; Dávidovics, A.; Nagy, S.; Marosvölgyi, T.; Makszin, L. A Microfluidic Approach for Profiling Total Nitrogen Content in Age-Specific Nutritional Formulas Using Microchip Gel Electrophoresis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178233
Balogh-Hartmann F, Páger C, Dávidovics A, Nagy S, Marosvölgyi T, Makszin L. A Microfluidic Approach for Profiling Total Nitrogen Content in Age-Specific Nutritional Formulas Using Microchip Gel Electrophoresis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178233
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalogh-Hartmann, Fruzsina, Csilla Páger, Anna Dávidovics, Sára Nagy, Tamás Marosvölgyi, and Lilla Makszin. 2025. "A Microfluidic Approach for Profiling Total Nitrogen Content in Age-Specific Nutritional Formulas Using Microchip Gel Electrophoresis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178233
APA StyleBalogh-Hartmann, F., Páger, C., Dávidovics, A., Nagy, S., Marosvölgyi, T., & Makszin, L. (2025). A Microfluidic Approach for Profiling Total Nitrogen Content in Age-Specific Nutritional Formulas Using Microchip Gel Electrophoresis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178233








