Expression of CD44 and Its Spliced Variants: Innate and Inducible Roles in Nervous Tissue Cells and Their Environment
Abstract
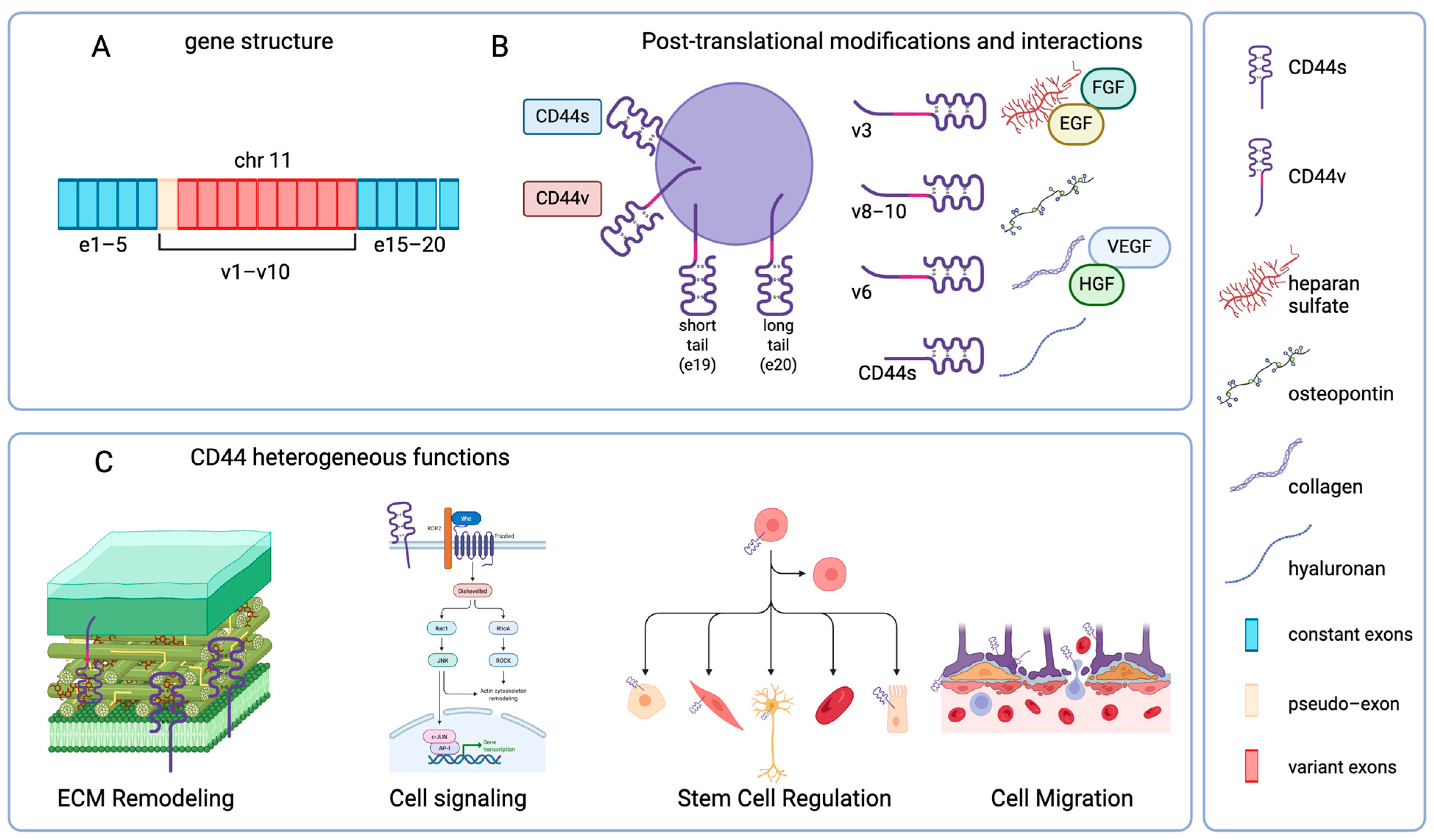
1. Introduction
2. The Role of CD44 in the Inflammatory Cells of the Central Nervous System
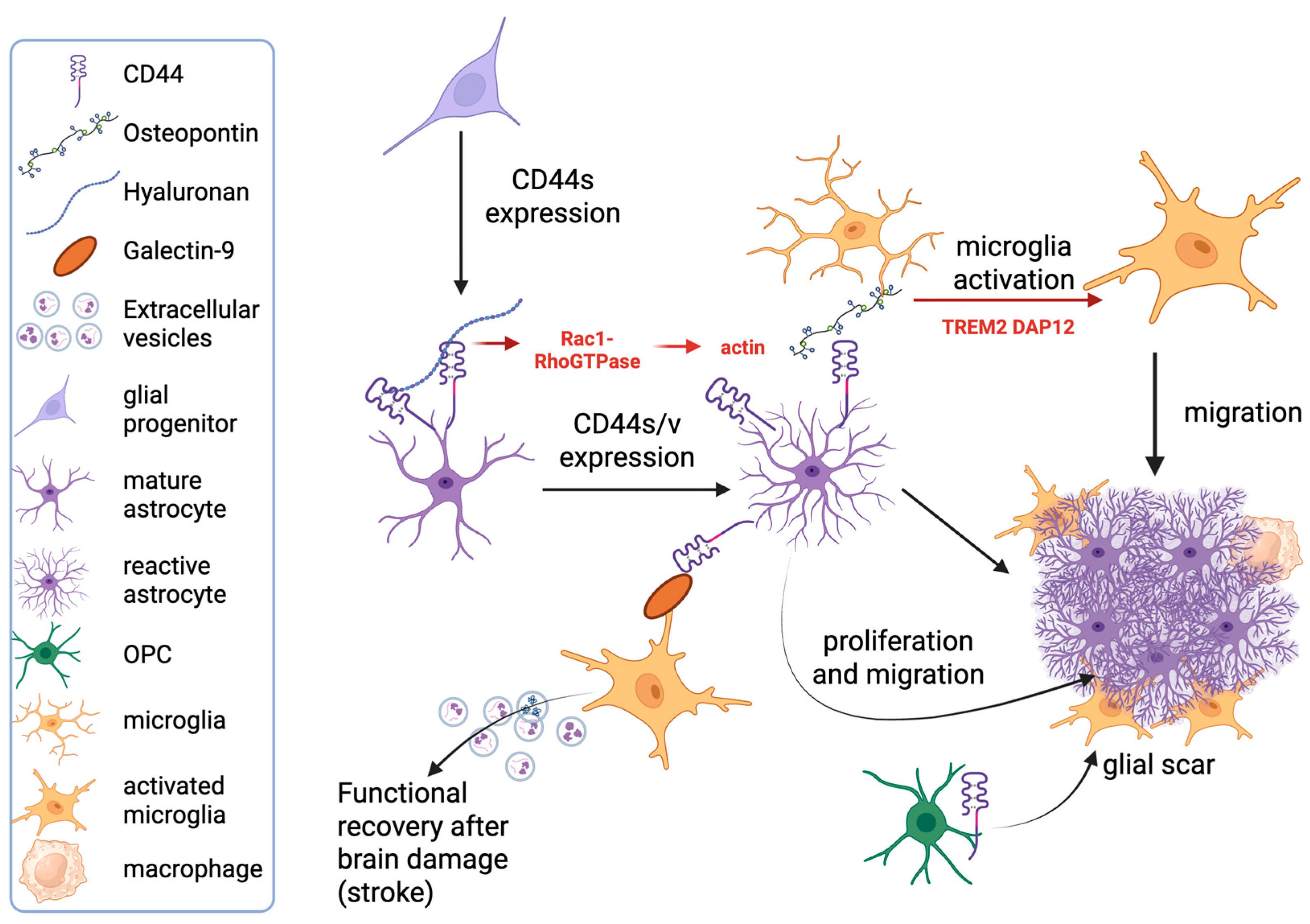
2.1. CD44 Expression in Microglia and Brain Macrophages
2.2. CD44 Expression in Astrocytes
3. CD44 Coregulates Myelination of Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems
3.1. CD44 and Oligodendrocytes
3.2. CD44 and Schwann Cells
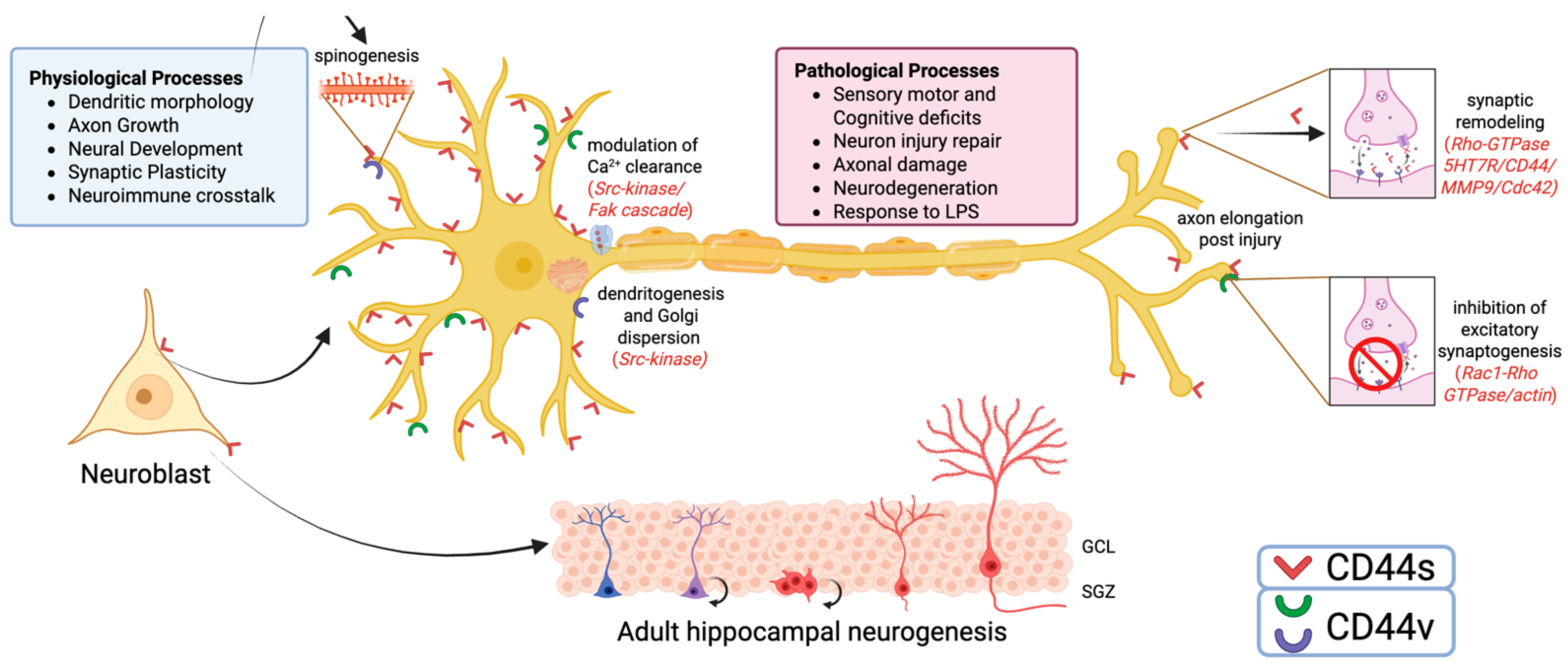
4. The Role of CD44 in Neuronal Functions
4.1. CD44 and Neural Development
4.2. CD44 in Synaptogenesis and Synaptic Plasticity
4.3. The Role of CD44 in Neurons in Pathological Conditions
4.4. CD44 Variants in Alzheimer’s Disease
5. CD44 in Central Nervous System Barriers
6. Therapeutic Perspectives
7. Conclusions—A Panoramic View of CD44 Roles in the Nervous System
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| Aβ | Amyloid beta |
| ALS | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| BAM | Border-associated macrophage |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| BCB | Blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier |
| CD | Cluster of differentiation |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| Dap12 | DNAX activation protein of 12 kDa |
| LGALS9 | Galectin-9 |
| HA | Hyaluronan |
| HMW | High molecular weight |
| HT7R | Hydroxytryptamine Receptor 7 |
| EAE | Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| EMT | Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition |
| EAAT | Excitatory amino-acid transporter |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| LTP | Long-term potentiation |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| MS | Multiple sclerosis |
| NMJ | Neuromuscular junction |
| NSC | Neural stem cell |
| OPN | Osteopontin |
| OPC | Oligodendrocyte progenitor cell |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| PI3K/AKT | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B |
| PK | Protein kinase |
| PMCA | Plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase |
| PNS | Peripheral nervous system |
| RNA-seq | RNA-sequencing |
| SLC7A11 | Cystine/glutamate antiporter xCT |
| SRGN | Serglycin |
| SLYM | Subarachnoid lymphatic-like membrane |
| TEER | Transepithelial electrical resistance |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| TREM | Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Goodison, S.; Urquidi, V.; Tarin, D. CD44 Cell Adhesion Molecules. Mol. Pathol. 1999, 52, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sante, G.; Migliara, G.; Valentini, M.; Delogu, G.; Ria, F. Regulation of and Regulation by CD 44: A Paradigm Complex Regulatory Network. Int. Trends Immun. 2013, 1, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Dyer, S.C.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov, A.G.; Barba, M.; Barnes, I.; Barrera-Enriquez, V.P.; Becker, A.; Bennett, R.; Beracochea, M.; Berry, A.; et al. Ensembl 2025. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D948–D957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tredicine, M.; Camponeschi, C.; Pirolli, D.; Lucchini, M.; Valentini, M.; Geloso, M.C.; Mirabella, M.; Fidaleo, M.; Righino, B.; Moliterni, C.; et al. A TLR/CD44 Axis Regulates T Cell Trafficking in Experimental and Human Multiple Sclerosis. iScience 2022, 25, 103763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidle, U.H.; Maisel, D.; Klostermann, S.; Weiss, E.H.; Schmitt, M. Differential Splicing Generates New Transmembrane Receptor and Extracellular Matrix-Related Targets for Antibody-Based Therapy of Cancer. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2011, 8, 211–226. [Google Scholar]
- Primeaux, M.; Gowrikumar, S.; Dhawan, P. Role of CD44 Isoforms in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity and Metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2022, 39, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, H.; Screaton, G.R.; Bell, M.V.; Jackson, D.G.; Bell, J.J.; Hodes, R.J. CD44 Isoform Expression Mediated by Alternative Splicing: Tissue-Specific Regulation in Mice. Int. Immunol. 1994, 6, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.; Motiani, K.; Giridhar, P.V.; Kasper, S. CD44 Integrates Signaling in Normal Stem Cell, Cancer Stem Cell and (Pre)Metastatic Niches. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013, 238, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camponeschi, C.; Righino, B.; Pirolli, D.; Semeraro, A.; Ria, F.; De Rosa, M.C. Prediction of CD44 Structure by Deep Learning-Based Protein Modeling. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrano-González, P.A.; Rivera-Ramírez, O.; Montaño, L.F.; Rendón-Huerta, E.P. Proteolytic Processing of CD44 and Its Implications in Cancer. Stem Cells Int. 2021, 2021, 6667735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zuo, X.; Wei, D. Concise Review: Emerging Role of CD44 in Cancer Stem Cells: A Promising Biomarker and Therapeutic Target. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatley, S.C.; Isacke, C.M.; Crossley, P.H. Restricted Expression of the Hyaluronan Receptor, CD44, during Postimplantation Mouse Embryogenesis Suggests Key Roles in Tissue Formation and Patterning. Development 1993, 119, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenderson, B.A.; Stamenkovic, I.; Aruffo, A. Localization of Hyaluronan in Mouse Embryos during Implantation, Gastrulation and Organogenesis. Differentiation 1993, 54, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesley, J.; Hyman, R.; Kincade, P.W. CD44 and Its Interaction with Extracellular Matrix. Adv. Immunol. 1993, 54, 271–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arch, R.; Wirth, K.; Hofmann, M.; Ponta, H.; Matzku, S.; Herrlich, P.; Zöller, M. Participation in Normal Immune Responses of a Metastasis-Inducing Splice Variant of CD44. Science 1992, 257, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltzman, J.S.; Carman, J.A.; Monroe, J.G. Role of EGR1 in Regulation of Stimulus-Dependent CD44 Transcription in B Lymphocytes. Mol. Cell Biol. 1996, 16, 2283–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuff, C.A.; Kothapalli, D.; Azonobi, I.; Chun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Belkin, R.; Yeh, C.; Secreto, A.; Assoian, R.K.; Rader, D.J.; et al. The Adhesion Receptor CD44 Promotes Atherosclerosis by Mediating Inflammatory Cell Recruitment and Vascular Cell Activation. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huebener, P.; Abou-Khamis, T.; Zymek, P.; Bujak, M.; Ying, X.; Chatila, K.; Haudek, S.; Thakker, G.; Frangogiannis, N.G. CD44 Is Critically Involved in Infarct Healing by Regulating the Inflammatory and Fibrotic Response. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 2625–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmits, R.; Filmus, J.; Gerwin, N.; Senaldi, G.; Kiefer, F.; Kundig, T.; Wakeham, A.; Shahinian, A.; Catzavelos, C.; Rak, J.; et al. CD44 Regulates Hematopoietic Progenitor Distribution, Granuloma Formation, and Tumorigenicity. Blood 1997, 90, 2217–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberth, S.; Schneider, B.; Rosenwald, A.; Hartmann, E.M.; Romani, J.; Zaborski, M.; Siebert, R.; Drexler, H.G.; Quentmeier, H. Epigenetic Regulation of CD44 in Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaro, M.; Gaggianesi, M.; Catalano, V.; Benfante, A.; Iovino, F.; Biffoni, M.; Apuzzo, T.; Sperduti, I.; Volpe, S.; Cocorullo, G.; et al. CD44v6 Is a Marker of Constitutive and Reprogrammed Cancer Stem Cells Driving Colon Cancer Metastasis. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Brown, R.L.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, P.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Deng, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Gao, X.D.; et al. CD44 Splice Isoform Switching Determines Breast Cancer Stem Cell State. Genes. Dev. 2019, 33, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonsa, A.M.; Na, T.-Y.; Gumbiner, B.M. E-Cadherin in Contact Inhibition and Cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 4769–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weg-Remers, S. Regulation of Alternative Pre-mRNA Splicing by the ERK MAP-Kinase Pathway. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 4194–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Yaffe, M.B.; Sharp, P.A. A Positive Feedback Loop Couples Ras Activation and CD44 Alternative Splicing. Genes. Dev. 2006, 20, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orian-Rousseau, V. CD44 Acts as a Signaling Platform Controlling Tumor Progression and Metastasis. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimoto, T.; Nagano, O.; Yae, T.; Tamada, M.; Motohara, T.; Oshima, H.; Oshima, M.; Ikeda, T.; Asaba, R.; Yagi, H.; et al. CD44 Variant Regulates Redox Status in Cancer Cells by Stabilizing the xCT Subunit of System Xc− and Thereby Promotes Tumor Growth. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, V.; Matos, P.; Jordan, P. The -Catenin/TCF4 Pathway Modifies Alternative Splicing through Modulation of SRp20 Expression. RNA 2008, 14, 2538–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Crossman, D.K.; Mitchell, E.H.; Sohn, P.; Crowley, M.R.; Serra, R. WNT5A Inhibits Metastasis and Alters Splicing of Cd44 in Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinner, E.; Gruper, Y.; Ben Zimra, M.; Kristt, D.; Laudon, M.; Naor, D.; Zisapel, N. CD44 Splice Variants as Potential Players in Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 58, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Kim, W.-K.; Huong Vu, G. Molecular Mechanisms Implicated in Protein Changes in the Alzheimer’s Disease Human Hippocampus. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2024, 219, 111930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditzen, C.; Tang, N.; Jastorff, A.M.; Teplytska, L.; Yassouridis, A.; Maccarrone, G.; Uhr, M.; Bronisch, T.; Miller, C.A.; Holsboer, F.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers for Major Depression Confirm Relevance of Associated Pathophysiology. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galfalvy, H.; Zalsman, G.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Murphy, L.; Rosoklija, G.; Dwork, A.J.; Haghighi, F.; Arango, V.; Mann, J.J. A Pilot Genome Wide Association and Gene Expression Array Study of Suicide with and without Major Depression. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 14, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiteri, A.G.; Wishart, C.L.; Pamphlett, R.; Locatelli, G.; King, N.J.C. Microglia and Monocytes in Inflammatory CNS Disease: Integrating Phenotype and Function. Acta Neuropathol. 2022, 143, 179–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Jiang, H. Border-Associated Macrophages in the Central Nervous System. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Jiang, J.; Tan, Y.; Chen, S. Microglia in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Mechanism and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, C.; Schlickeiser, S.; Sneeboer, M.A.M.; Kunkel, D.; Knop, A.; Paza, E.; Fidzinski, P.; Kraus, L.; Snijders, G.J.L.; Kahn, R.S.; et al. Human Microglia Regional Heterogeneity and Phenotypes Determined by Multiplexed Single-Cell Mass Cytometry. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrdjen, D.; Pavlovic, A.; Hartmann, F.J.; Schreiner, B.; Utz, S.G.; Leung, B.P.; Lelios, I.; Heppner, F.L.; Kipnis, J.; Merkler, D.; et al. High-Dimensional Single-Cell Mapping of Central Nervous System Immune Cells Reveals Distinct Myeloid Subsets in Health, Aging, and Disease. Immunity 2018, 48, 380–395.e6, Erratum in Immunity 2018, 48, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korin, B.; Ben-Shaanan, T.L.; Schiller, M.; Dubovik, T.; Azulay-Debby, H.; Boshnak, N.T.; Koren, T.; Rolls, A. High-Dimensional, Single-Cell Characterization of the Brain’s Immune Compartment. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordão, M.J.C.; Sankowski, R.; Brendecke, S.M.; Sagar; Locatelli, G.; Tai, Y.-H.; Tay, T.L.; Schramm, E.; Armbruster, S.; Hagemeyer, N.; et al. Single-Cell Profiling Identifies Myeloid Cell Subsets with Distinct Fates during Neuroinflammation. Science 2019, 363, eaat7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachon, E.; Martin, R.; Plumb, J.; Kwok, V.; Vandivier, R.W.; Glogauer, M.; Kapus, A.; Wang, X.; Chow, C.-W.; Grinstein, S.; et al. CD44 Is a Phagocytic Receptor. Blood 2006, 107, 4149–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puré, E.; Cuff, C.A. A Crucial Role for CD44 in Inflammation. Trends Mol. Med. 2001, 7, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, J.; Yamasaki, K.; Taylor, K.R.; Gallo, R.L. Engagement of CD44 by Hyaluronan Suppresses TLR4 Signaling and the Septic Response to LPS. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 47, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liang, J.; Gao, S.; Cai, X.; Yu, Y.; Qi, Z.; Li, J.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z. Association of Glioma CD44 Expression with Glial Dynamics in the Tumour Microenvironment and Patient Prognosis. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 5203–5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietras, A.; Katz, A.M.; Ekström, E.J.; Wee, B.; Halliday, J.J.; Pitter, K.L.; Werbeck, J.L.; Amankulor, N.M.; Huse, J.T.; Holland, E.C. Osteopontin-CD44 Signaling in the Glioma Perivascular Niche Enhances Cancer Stem Cell Phenotypes and Promotes Aggressive Tumor Growth. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi-Visser, L.; Laman, J.D.; Nagel, S.; van Meurs, M.; van Riel, D.; Tzankov, A.; Frank, S.; Adams, H.; Wolk, K.; Terracciano, L.; et al. CD44 Variant Isoforms Control Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Affecting the Lifespan of the Pathogenic T Cells. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 3683–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcondes, M.C.G.; Lanigan, C.M.S.; Burdo, T.H.; Watry, D.D.; Fox, H.S. Increased Expression of Monocyte CD44v6 Correlates with the Deveopment of Encephalitis in Rhesus Macaques Infected with Simian Immunodeficiency Virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, N.D.; Hill, J.D.; Juchem, K.W.; Stefanopoulos, D.E.; Modis, L.K. RNA Sequencing of Microglia and Monocyte-Derived Macrophages from Mice with Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Illustrates a Changing Phenotype with Disease Course. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 277, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi-Monfared, A.; Firouzi, M.; Bahrami, Z.; Zahednasab, H.; Harirchian, M.H. Minocycline Decreases CD36 and Increases CD44 in LPS-Induced Microglia. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 317, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, R.; Nakano-Doi, A.; Matsuyama, T.; Nakagomi, N.; Nakagomi, T. CD44 Expression in Stem Cells and Niche Microglia/Macrophages Following Ischemic Stroke. Stem Cell Investig. 2020, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Zhou, C.; Zong, N.; Geng, Y.; Xia, S.; Yang, H.; Bao, X.; Chen, Y.; et al. SRGN Amplifies Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation and Exacerbates Ischemic Brain Injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, T.; Imagama, S.; Hirano, K.; Ohgomori, T.; Natori, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Muramoto, A.; Ishiguro, N.; Kadomatsu, K. CD44 Expression in Astrocytes and Microglia Is Associated with ALS Progression in a Mouse Model. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 520, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, L.L.; Liu, Z.; Shen, J.; Werner, A.; Kreutzberg, G.W.; Raivich, G. Regulation of the Cell Adhesion Molecule CD44 after Nerve Transection and Direct Trauma to the Mouse Brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2000, 426, 468–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesämaa, I.; Müller, S.A.; Robinson, S.; Darcher, A.; Paquet, D.; Zetterberg, H.; Lichtenthaler, S.F.; Haass, C. A Microglial Activity State Biomarker Panel Differentiates FTD-Granulin and Alzheimer’s Disease Patients from Controls. Mol. Neurodegener. 2023, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolls, A.; Shechter, R.; London, A.; Segev, Y.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Amariglio, N.; Rechavi, G.; Schwartz, M. Two Faces of Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan in Spinal Cord Repair: A Role in Microglia/Macrophage Activation. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Butt, A.; Li, B.; Illes, P.; Zorec, R.; Semyanov, A.; Tang, Y.; Sofroniew, M.V. Astrocytes in Human Central Nervous System Diseases: A Frontier for New Therapies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzwonek, J.; Wilczynski, G.M. CD44: Molecular Interactions, Signaling and Functions in the Nervous System. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosunov, A.A.; Wu, X.; Tsankova, N.M.; Guilfoyle, E.; McKhann, G.M.; Goldman, J.E. Phenotypic Heterogeneity and Plasticity of Isocortical and Hippocampal Astrocytes in the Human Brain. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 2285–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, C.; Penna, E.; Hong, T.; Tarantal, A.F.; Hof, P.R.; Hopkins, W.D.; Sherwood, C.C.; Noctor, S.C.; Martínez-Cerdeño, V. Cortical Interlaminar Astrocytes Are Generated Prenatally, Mature Postnatally, and Express Unique Markers in Human and Nonhuman Primates. Cereb. Cortex 2021, 31, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dalahmah, O.; Sosunov, A.A.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Madden, N.; Connolly, E.S.; Troy, C.M.; McKhann, G.M.; Goldman, J.E. The Matrix Receptor CD44 Is Present in Astrocytes throughout the Human Central Nervous System and Accumulates in Hypoxia and Seizures. Cells 2024, 13, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, S.; Karus, M.; Faissner, A. Astrocytes as a Source for Extracellular Matrix Molecules and Cytokines. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, L.; Aita, M.; Caronti, B.; De Vita, R.; Margotta, V.; Medolago Albani, L.; Valente, A.M. Hyaluronate Receptor CD44 Is Expressed by Astrocytes in the Adult Chicken and in Astrocyte Cell Precursors in Early Development of the Chick Spinal Cord. Eur. J. Histochem. 1999, 43, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Moretto, G.; Xu, R.Y.; Kim, S.U. CD44 Expression in Human Astrocytes and Oligodendrocytes in Culture. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1993, 52, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Han, S.S.W.; Wu, Y.; Tuohy, T.M.F.; Xue, H.; Cai, J.; Back, S.A.; Sherman, L.S.; Fischer, I.; Rao, M.S. CD44 Expression Identifies Astrocyte-Restricted Precursor Cells. Dev. Biol. 2004, 276, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, N.; Kurachi, M.; Shibasaki, K.; Okano-Uchida, T.; Ishizaki, Y. CD44-Positive Cells Are Candidates for Astrocyte Precursor Cells in Developing Mouse Cerebellum. Cerebellum 2012, 11, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaltouki, A.; Peng, J.; Liu, Q.; Rao, M.S.; Zeng, X. Efficient Generation of Astrocytes from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells in Defined Conditions. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naruse, M.; Shibasaki, K.; Yokoyama, S.; Kurachi, M.; Ishizaki, Y. Dynamic Changes of CD44 Expression from Progenitors to Subpopulations of Astrocytes and Neurons in Developing Cerebellum. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulirsch, L.M.; Loeffler, K.U.; Holz, F.G.; Koinzer, S.; Nadal, J.; Müller, A.M.; Herwig-Carl, M.C. Spatial and Temporal Immunoreaction of Nestin, CD44, Collagen IX and GFAP in Human Retinal Müller Cells in the Developing Fetal Eye. Exp. Eye Res. 2022, 217, 108958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holländer, H.; Makarov, F.; Dreher, Z.; van Driel, D.; Chan-Ling, T.L.; Stone, J. Structure of the Macroglia of the Retina: Sharing and Division of Labour between Astrocytes and Müller Cells. J. Comp. Neurol. 1991, 313, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvier-Labit, C.; Liprandi, A.; Monti, G.; Pellissier, J.F.; Figarella-Branger, D. CD44H Is Expressed by Cells of the Oligodendrocyte Lineage and by Oligodendrogliomas in Humans. J. Neurooncol 2002, 60, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Niu, M.; Yuan, X.; Wu, K.; Liu, A. CD44 as a Tumor Biomarker and Therapeutic Target. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bormann, D.; Knoflach, M.; Poreba, E.; Riedl, C.J.; Testa, G.; Orset, C.; Levilly, A.; Cottereau, A.; Jauk, P.; Hametner, S.; et al. Single-Nucleus RNA Sequencing Reveals Glial Cell Type-Specific Responses to Ischemic Stroke in Male Rodents. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, P.K.; Nader, K.; Skupien-Jaroszek, A.; Wójtowicz, T.; Buszka, A.; Olech-Kochańczyk, G.; Wilczynski, G.M.; Worch, R.; Kalita, K.; Włodarczyk, J.; et al. Astrocytic CD44 Deficiency Reduces the Severity of Kainate-Induced Epilepsy. Cells 2023, 12, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa-Ishii, S.; Takei, S.; Inaba, M.; Umegaki, H.; Chiba, Y.; Furukawa, A.; Kawamura, N.; Hosokawa, M.; Shimada, A. Defects in Cytokine-Mediated Neuroprotective Glial Responses to Excitotoxic Hippocampal Injury in Senescence-Accelerated Mouse. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, K.; McDermott, D.L.; Dingledine, R. Reciprocal Changes of CD44 and GAP-43 Expression in the Dentate Gyrus Inner Molecular Layer after Status Epilepticus in Mice. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 188, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bausch, S.B. Potential Roles for Hyaluronan and CD44 in Kainic Acid-Induced Mossy Fiber Sprouting in Organotypic Hippocampal Slice Cultures. Neuroscience 2006, 143, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgrah, N.; Letarte, M.; Becker, L.E.; Cruz, T.F.; Theriault, E.; Moscarello, M.A. Localization of the CD44 Glycoprotein to Fibrous Astrocytes in Normal White Matter and to Reactive Astrocytes in Active Lesions in Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1991, 50, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Staugaitis, S.M.; Dutta, R.; Batt, C.E.; Easley, K.E.; Chomyk, A.M.; Yong, V.W.; Fox, R.J.; Kidd, G.J.; Trapp, B.D. Cortical Remyelination: A New Target for Repair Therapies in Multiple Sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinbach, C.; Stadler, M.-S.; Pröbstl, N.; Chrzanowski, U.; Schmitz, C.; Kipp, M.; Hochstrasser, T. CD44 Expression in the Cuprizone Model. Brain Res. 2020, 1745, 146950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.D.; Cho, H.J.; Shin, T. Expression of Osteopontin and Its Ligand, CD44, in the Spinal Cords of Lewis Rats with Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2004, 151, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, B.M.; Walmsley-Rowe, L.; Reynolds, J.; Verity, N.; Mabbott, N.A. Cell Adhesion Molecule CD44 Is Dispensable for Reactive Astrocyte Activation during Prion Disease. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, Y.; Takashima, S.; Becker, L.E. CD44 Expression in Tuberous Sclerosis. Pathobiology 2000, 68, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Tooyama, I.; Kawamata, T.; Ikeda, K.; McGeer, P.L. Morphological Diversities of CD44 Positive Astrocytes in the Cerebral Cortex of Normal Subjects and Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Res. 1993, 632, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viejo, L.; Noori, A.; Merrill, E.; Das, S.; Hyman, B.T.; Serrano-Pozo, A. Systematic Review of Human Post-Mortem Immunohistochemical Studies and Bioinformatics Analyses Unveil the Complexity of Astrocyte Reaction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2022, 48, e12753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Yoo, I.D.; Lim, J.; Moon, J.-S. Pathological Phenotypes of Astrocytes in Alzheimer’s Disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smajić, S.; Prada-Medina, C.A.; Landoulsi, Z.; Ghelfi, J.; Delcambre, S.; Dietrich, C.; Jarazo, J.; Henck, J.; Balachandran, S.; Pachchek, S.; et al. Single-Cell Sequencing of Human Midbrain Reveals Glial Activation and a Parkinson-Specific Neuronal State. Brain 2022, 145, 964–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofroniew, M.V. Astrocyte Reactivity: Subtypes, States, and Functions in CNS Innate Immunity. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopka, A.; Zeug, A.; Skupien, A.; Kaza, B.; Mueller, F.; Chwedorowicz, A.; Ponimaskin, E.; Wilczynski, G.M.; Dzwonek, J. Cleavage of Hyaluronan and CD44 Adhesion Molecule Regulate Astrocyte Morphology via Rac1 Signalling. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racchetti, G.; D’Alessandro, R.; Meldolesi, J. Astrocyte Stellation, a Process Dependent on Rac1 Is Sustained by the Regulated Exocytosis of Enlargeosomes. Glia 2012, 60, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguignon, L.Y.W.; Gilad, E.; Peyrollier, K.; Brightman, A.; Swanson, R.A. Hyaluronan-CD44 Interaction Stimulates Rac1 Signaling and PKN Gamma Kinase Activation Leading to Cytoskeleton Function and Cell Migration in Astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 2007, 101, 1002–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos-Cabré, R.; Burgos-Bravo, F.; Avalos, A.M.; Leyton, L. Connexins in Astrocyte Migration. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, P.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; O’Dea, M.R.; Munson, C.N.; Labib, D.; Fossati, V.; Neubert, T.A.; Liddelow, S.A. Proteomic Profiling of Interferon-Responsive Reactive Astrocytes in Rodent and Human. Glia 2024, 72, 625–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanian, J.L.; Xu, L.; Foo, L.C.; Nouri, N.; Zhou, L.; Giffard, R.G.; Barres, B.A. Genomic Analysis of Reactive Astrogliosis. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 6391–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yang, T.; Zhang, W.; Yu, K.; Xu, X.; Li, W.; Song, L.; Gu, X.; Cao, R.; Cui, S. Inhibition of CD44 Suppresses the Formation of Fibrotic Scar after Spinal Cord Injury via the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. iScience 2024, 27, 108935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, E.J.; Burnside, E.R. Moving beyond the Glial Scar for Spinal Cord Repair. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, S.A.; Tuohy, T.M.F.; Chen, H.; Wallingford, N.; Craig, A.; Struve, J.; Luo, N.L.; Banine, F.; Liu, Y.; Chang, A.; et al. Hyaluronan Accumulates in Demyelinated Lesions and Inhibits Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Maturation. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Lu, J.; Xu, W.; Xu, S.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Shao, A.; et al. Temporal Dynamics of Microglia-Astrocyte Interaction in Neuroprotective Glial Scar Formation after Intracerebral Hemorrhage. J. Pharm. Anal. 2023, 13, 862–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Xi, W.; Liu, C.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, M.; Yu, X.; Li, L.; et al. Integrating Spatial and Single-Cell Transcriptomics to Characterize the Molecular and Cellular Architecture of the Ischemic Mouse Brain. Sci. Transl. Med. 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struve, J.; Maher, P.C.; Li, Y.-Q.; Kinney, S.; Fehlings, M.G.; Kuntz, C.; Sherman, L.S. Disruption of the Hyaluronan-Based Extracellular Matrix in Spinal Cord Promotes Astrocyte Proliferation. Glia 2005, 52, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Sankowski, R.; Staszewski, O.; Böttcher, C.; Amann, L.; Sagar; Scheiwe, C.; Nessler, S.; Kunz, P.; van Loo, G.; et al. Spatial and Temporal Heterogeneity of Mouse and Human Microglia at Single-Cell Resolution. Nature 2019, 566, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallach, A.; Zielonka, M.; van Lieshout, V.; An, Y.; Khoo, J.H.; Vanheusden, M.; Chen, W.-T.; Moechars, D.; Arancibia-Carcamo, I.L.; Fiers, M.; et al. Microglia-Astrocyte Crosstalk in the Amyloid Plaque Niche of an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model, as Revealed by Spatial Transcriptomics. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaaijk, P.; Pals, S.T.; Morsink, F.; Bosch, D.A.; Troost, D. Differential Expression of CD44 Splice Variants in the Normal Human Central Nervous System. J. Neuroimmunol. 1997, 73, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haegel, H.; Tölg, C.; Hofmann, M.; Ceredig, R. Activated Mouse Astrocytes and T Cells Express Similar CD44 Variants. Role of CD44 in Astrocyte/T Cell Binding. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 122, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbaz, B.; Popko, B. Molecular Control of Oligodendrocyte Development. Trends Neurosci. 2019, 42, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccoliero, A.M.; Caldarella, A.; Arganini, L.; Mennonna, P.; Ammanati, F.; Taddei, A.; Taddei, G.L. Oligodendroglioma: CD44 as a Possible Prognostic Opportunity. Clin. Neuropathol. 2003, 22, 169–175. [Google Scholar]
- Tuohy, T.M.F.; Wallingford, N.; Liu, Y.; Chan, F.H.; Rizvi, T.; Xing, R.; Bebo, B.; Rao, M.S.; Sherman, L.S. CD44 Overexpression by Oligodendrocytes: A Novel Mouse Model of Inflammation-Independent Demyelination and Dysmyelination. Glia 2004, 47, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Blumberg, B.M.; Mock, D.J.; Goodman, A.D.; Moser, A.B.; Moser, H.W.; Smith, K.D.; Powers, J.M. Potential Environmental and Host Participants in the Early White Matter Lesion of Adreno-Leukodystrophy: Morphologic Evidence for CD8 Cytotoxic T Cells, Cytolysis of Oligodendrocytes, and CD1-Mediated Lipid Antigen Presentation. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 60, 1004–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugiani, M.; Postma, N.; Polder, E.; Dieleman, N.; Scheffer, P.G.; Sim, F.J.; van der Knaap, M.S.; Boor, I. Hyaluronan Accumulation and Arrested Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Maturation in Vanishing White Matter Disease. Brain 2013, 136, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloane, J.A.; Batt, C.; Ma, Y.; Harris, Z.M.; Trapp, B.; Vartanian, T. Hyaluronan Blocks Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Maturation and Remyelination through TLR2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11555–11560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Shirai, R.; Isogai, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Miyamoto, Y.; Yamauchi, J. Hyaluronic Acid and Its Receptor CD44, Acting through TMEM2, Inhibit Morphological Differentiation in Oligodendroglial Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 624, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, J.-H.; Wang, Y.; Duncan, I.D. CD44 Is Required for the Migration of Transplanted Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells to Focal Inflammatory Demyelinating Lesions in the Spinal Cord. Glia 2013, 61, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, L.S.; Rizvi, T.A.; Karyala, S.; Ratner, N. CD44 Enhances Neuregulin Signaling by Schwann Cells. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 150, 1071–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorlewicz, A.; Wlodarczyk, J.; Wilczek, E.; Gawlak, M.; Cabaj, A.; Majczynski, H.; Nestorowicz, K.; Herbik, M.A.; Grieb, P.; Slawinska, U.; et al. CD44 Is Expressed in Non-Myelinating Schwann Cells of the Adult Rat, and May Play a Role in Neurodegeneration-Induced Glial Plasticity at the Neuromuscular Junction. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 34, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, S.J.; Wiberg, M.; Terenghi, G.; Kingham, P.J. ECM Molecules Mediate Both Schwann Cell Proliferation and Activation to Enhance Neurite Outgrowth. Tissue Eng. 2007, 13, 2863–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouasti, S.; Faroni, A.; Kingham, P.J.; Ghibaudi, M.; Reid, A.J.; Tirelli, N. Hyaluronic Acid (HA) Receptors and the Motility of Schwann Cell(-Like) Phenotypes. Cells 2020, 9, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-B.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.-N.; Yang, T.; Du, S.; Cao, R.-J.; Cui, S.-S. SPP1 Promotes Schwann Cell Proliferation and Survival through PKCα by Binding with CD44 and Avβ3 after Peripheral Nerve Injury. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glezer, I.; Bittencourt, J.C.; Rivest, S. Neuronal Expression of Cd36, Cd44, and Cd83 Antigen Transcripts Maps to Distinct and Specific Murine Brain Circuits. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 517, 906–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Li, Y.; Thayer, S.A. Inhibition of the Plasma Membrane Ca2+ Pump by CD44 Receptor Activation of Tyrosine Kinases Increases the Action Potential Afterhyperpolarization in Sensory Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 2361–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, K.; Nakao, J.; Asou, H.; Toya, S.; Shinoda, J.; Uyemura, K. Expression of CD44H in the Cells of Neural Crest Origin in Peripheral Nervous System. Neuroreport 1996, 7, 1713–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skupien, A.; Konopka, A.; Trzaskoma, P.; Labus, J.; Gorlewicz, A.; Swiech, L.; Babraj, M.; Dolezyczek, H.; Figiel, I.; Ponimaskin, E.; et al. CD44 Regulates Dendrite Morphogenesis through Src Tyrosine Kinase-Dependent Positioning of the Golgi. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 5038–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, L.L.; Kreutzberg, G.W.; Raivich, G. Regulation of CD44 in the Regenerating Mouse Facial Motor Nucleus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1997, 9, 1854–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ailane, S.; Long, P.; Jenner, P.; Rose, S. Expression of Integrin and CD44 Receptors Recognising Osteopontin in the Normal and LPS-Lesioned Rat Substantia Nigra. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2013, 38, 2468–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raber, J.; Olsen, R.H.J.; Su, W.; Foster, S.; Xing, R.; Acevedo, S.F.; Sherman, L.S. CD44 Is Required for Spatial Memory Retention and Sensorimotor Functions. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 275, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sretavan, D.W.; Feng, L.; Puré, E.; Reichardt, L.F. Embryonic Neurons of the Developing Optic Chiasm Express L1 and CD44, Cell Surface Molecules with Opposing Effects on Retinal Axon Growth. Neuron 1994, 12, 957–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, K.; Ito-Dufros, Y. Angiogenic Potential of CD44+ CD90+ Multipotent CNS Stem Cells in Vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 349, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, A.; Goldberg, J.L.; Grimpe, B. A Novel Biological Function for CD44 in Axon Growth of Retinal Ganglion Cells Identified by a Bioinformatics Approach. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 1491–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Gan, W.; Peng, R.; Lu, L.; Lu, W.; Liu, J. Activation of the mTOR Pathway Promotes Neurite Growth through Upregulation of CD44 Expression. J. Int. Med. Res. 2023, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Foster, S.C.; Xing, R.; Feistel, K.; Olsen, R.H.J.; Acevedo, S.F.; Raber, J.; Sherman, L.S. CD44 Transmembrane Receptor and Hyaluronan Regulate Adult Hippocampal Neural Stem Cell Quiescence and Differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4434–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anacker, C.; Hen, R. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Cognitive Flexibility—Linking Memory and Mood. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, D.; Yuan, Y.; Qin, S.; Tan, Z.; Gu, Y.; Huang, X.; He, C.; Su, Z. Establishment and Characterization of Primary Astrocyte Culture from Adult Mouse Brain. Brain Res. Bull. 2017, 132, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochlamazashvili, G.; Henneberger, C.; Bukalo, O.; Dvoretskova, E.; Senkov, O.; Lievens, P.M.-J.; Westenbroek, R.; Engel, A.K.; Catterall, W.A.; Rusakov, D.A.; et al. The Extracellular Matrix Molecule Hyaluronic Acid Regulates Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity by Modulating Postsynaptic L-Type Ca(2+) Channels. Neuron 2010, 67, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, D.-M.; Huang, Y.-H.; Zhu, Y.-B.; Wang, Y. Both the Establishment and Maintenance of Neuronal Polarity Require the Activity of Protein Kinase D in the Golgi Apparatus. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 8832–8843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sann, S.; Wang, Z.; Brown, H.; Jin, Y. Roles of Endosomal Trafficking in Neurite Outgrowth and Guidance. Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, A.; Phillips, W.A.; Schulz, J.M.; Suzuki, M.; Larkum, M.E. Dysfunctions of Cellular Context-Sensitivity in Neurodevelopmental Learning Disabilities. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 161, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E.S.; Litwa, K. Synaptic Hyaluronan Synthesis and CD44-Mediated Signaling Coordinate Neural Circuit Development. Cells 2021, 10, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, R.F.; Legg, J.W.; Isacke, C.M. The Role of the CD44 Transmembrane and Cytoplasmic Domains in Co-Ordinating Adhesive and Signalling Events. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casini, P.; Nardi, I.; Ori, M. Hyaluronan Is Required for Cranial Neural Crest Cells Migration and Craniofacial Development. Dev. Dyn. 2012, 241, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, L.F.; Khomula, E.V.; Araldi, D.; Levine, J.D. CD44 Signaling Mediates High Molecular Weight Hyaluronan-Induced Antihyperalgesia. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roszkowska, M.; Skupien, A.; Wójtowicz, T.; Konopka, A.; Gorlewicz, A.; Kisiel, M.; Bekisz, M.; Ruszczycki, B.; Dolezyczek, H.; Rejmak, E.; et al. CD44: A Novel Synaptic Cell Adhesion Molecule Regulating Structural and Functional Plasticity of Dendritic Spines. MBoC 2016, 27, 4055–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpicelli, F.; Speranza, L.; di Porzio, U.; Crispino, M.; Perrone-Capano, C. The Serotonin Receptor 7 and the Structural Plasticity of Brain Circuits. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijata, M.; Labus, J.; Guseva, D.; Stawarski, M.; Butzlaff, M.; Dzwonek, J.; Schneeberg, J.; Böhm, K.; Michaluk, P.; Rusakov, D.A.; et al. Synaptic Remodeling Depends on Signaling between Serotonin Receptors and the Extracellular Matrix. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1767–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsdorf, S.; Zeug, A.; Wu, Y.; Mitroshina, E.; Vedunova, M.; Gaitonde, S.A.; Bouvier, M.; Wehr, M.C.; Labus, J.; Ponimaskin, E. The Cell Adhesion Molecule CD44 Acts as a Modulator of 5-HT7 Receptor Functions. Cell Commun. Signal 2024, 22, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, N.J.; Eroglu, C. Cell Biology of Astrocyte-Synapse Interactions. Neuron 2017, 96, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plantman, S. Osteopontin Is Upregulated after Mechanical Brain Injury and Stimulates Neurite Growth from Hippocampal Neurons through Β1 Integrin and CD44. Neuroreport 2012, 23, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinzel, R.T.; Higuchi-Sanabria, R.; Shalem, O.; Moehle, E.A.; Webster, B.M.; Joe, L.; Bar-Ziv, R.; Frankino, P.A.; Durieux, J.; Pender, C.; et al. The Hyaluronidase, TMEM2, Promotes ER Homeostasis and Longevity Independent of the UPRER. Cell 2019, 179, 1306–1318.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Wang, C.; Gong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, M.; Gao, R.; Dang, B. Potential Mechanism of TMEM2/CD44 in Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-induced Neuronal Apoptosis in a Rat Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2023, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, I.-M.; Wu, T.-T.; Hsu, C.-C.; Yang, C.-C.; Huang, J.-S.; Tu, Y.-K.; Lee, J.-S.; Su, F.-C.; Kuo, Y.-L. High Molecular Weight Form of Hyaluronic Acid Reduces Neuroinflammatory Response in Injured Sciatic Nerve via the Intracellular Domain of CD44. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2021, 109, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, V.A.; Tracey, K.J. The Vagus Nerve and the Inflammatory Reflex—Linking Immunity and Metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geloso, M.C.; Zupo, L.; Corvino, V. Crosstalk between Peripheral Inflammation and Brain: Focus on the Responses of Microglia and Astrocytes to Peripheral Challenge. Neurochem. Int. 2024, 180, 105872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennon, F.E.; Mirzapoiazova, T.; Mambetsariev, N.; Mambetsariev, B.; Salgia, R.; Singleton, P.A. Transactivation of the Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Ephrin Receptor A2 Is Required for the Low Molecular Weight Hyaluronan-Mediated Angiogenesis That Is Implicated in Tumor Progression. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 24043–24058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gou, D.; Ma, J.; Du, J.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Cui, H. Metabolic Reprogramming of Microglia Enhances Proinflammatory Cytokine Release through EphA2/P38 MAPK Pathway in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 88, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møllgård, K.; Beinlich, F.R.M.; Kusk, P.; Miyakoshi, L.M.; Delle, C.; Plá, V.; Hauglund, N.L.; Esmail, T.; Rasmussen, M.K.; Gomolka, R.S.; et al. A Mesothelium Divides the Subarachnoid Space into Functional Compartments. Science 2023, 379, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhuber, W. An “Outer Subarachnoid Space”: Fact or Artifact? A Commentary on “Structural Characterization of SLYM– a 4th Meningeal Membrane” Fluids and Barriers of the CNS (2023) 20:93 by V. Plá et al. Fluids Barriers CNS 2024, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solár, P.; Zamani, A.; Kubíčková, L.; Dubový, P.; Joukal, M. Choroid Plexus and the Blood–Cerebrospinal Fluid Barrier in Disease. Fluids Barriers CNS 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ahmad, A.J.; Patel, R.; Palecek, S.P.; Shusta, E.V. Hyaluronan Impairs the Barrier Integrity of Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells through a CD44-Dependent Pathway. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2019, 39, 1759–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventorp, F.; Barzilay, R.; Erhardt, S.; Samuelsson, M.; Träskman-Bendz, L.; Janelidze, S.; Weizman, A.; Offen, D.; Brundin, L. The CD44 Ligand Hyaluronic Acid Is Elevated in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Suicide Attempters and Is Associated with Increased Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 193, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, K.M.; Michaud, M.; Madri, J.A. CD44 Deficiency Contributes to Enhanced Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 1322–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.-S.; Klingbeil, P.; Schnölzer, M.; Zöller, M. CD44 Variant Isoforms Associate with Tetraspanins and EpCAM. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 297, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, S.; Koch, M.; Nübel, T.; Ladwein, M.; Antolovic, D.; Klingbeil, P.; Hildebrand, D.; Moldenhauer, G.; Langbein, L.; Franke, W.W.; et al. A Complex of EpCAM, Claudin-7, CD44 Variant Isoforms, and Tetraspanins Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression. Mol. Cancer Res. 2007, 5, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, W.A. Getting Leukocytes to the Site of Inflammation. Vet. Pathol. 2013, 50, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Nieves, J.; Gorfu, G.; Ley, K. Leukocyte Adhesion Molecules in Animal Models of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2008, 14, 1715–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Tsuchihashi, K.; Ishimoto, T.; Yae, T.; Motohara, T.; Sugihara, E.; Onishi, N.; Masuko, T.; Yoshizawa, K.; Kawashiri, S.; et al. xCT Inhibition Depletes CD44v-Expressing Tumor Cells That Are Resistant to EGFR-Targeted Therapy in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 1855–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, P.A.A.; Kaur, G.; Khan, R.; Zhu, G.; Ni, H.; Lazarus, A.H. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of CD44 Antibodies in Murine Immune Thrombocytopenia Is Mediated by Fcγ Receptor Inhibition. Blood 2021, 137, 2114–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogihara, K.; Kikuchi, E.; Okazaki, S.; Hagiwara, M.; Takeda, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Kosaka, T.; Mikami, S.; Saya, H.; Oya, M. Sulfasalazine Could Modulate the CD44v9-xCT System and Enhance Cisplatin-Induced Cytotoxic Effects in Metastatic Bladder Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyotsana, N.; Ta, K.T.; DelGiorno, K.E. The Role of Cystine/Glutamate Antiporter SLC7A11/xCT in the Pathophysiology of Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 858462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavousipour, S.; Mohammadi, S.; Eftekhar, E.; Barazesh, M.; Morowvat, M.H. In Silico Investigation of Signal Peptide Sequences to Enhance Secretion of CD44 Nanobodies Expressed in Escherichia Coli. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2021, 22, 1192–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, N.; Li, T.-Y.; Young, A.H.; Stokes, P.R. The 5-HT7 Receptor System as a Treatment Target for Mood and Anxiety Disorders: A Systematic Review. J. Psychopharmacol. 2023, 37, 1167–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedlund, P.B. The 5-HT7 Receptor and Disorders of the Nervous System: An Overview. Psychopharmacology 2009, 206, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Li, Y.; Zhong, F.; Deng, Z.; Wu, J.; Yu, W.; Lü, Y. Disease-Associated Neurotoxic Astrocyte Markers in Alzheimer Disease Based on Integrative Single-Nucleus RNA Sequencing. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 44, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeOre, B.J.; Partyka, P.P.; Fan, F.; Galie, P.A. CD44 Mediates Shear Stress Mechanotransduction in an in Vitro Blood-Brain Barrier Model through Small GTPases RhoA and Rac1. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremmel, M.; Matzke, A.; Albrecht, I.; Laib, A.M.; Olaku, V.; Ballmer-Hofer, K.; Christofori, G.; Héroult, M.; Augustin, H.G.; Ponta, H.; et al. A CD44v6 Peptide Reveals a Role of CD44 in VEGFR-2 Signaling and Angiogenesis. Blood 2009, 114, 5236–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Kim, M.-J.; Kumar, A.; Lee, H.-W.; Yang, Y.; Kim, Y. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Signaling in Health and Disease: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Perspectives. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, T.; Yamasaki, J.; Saya, H.; Nagano, O. CD44: A Key Regulator of Iron Metabolism, Redox Balance, and Therapeutic Resistance in Cancer Stem Cells. Stem Cells 2025, 43, sxaf024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Xu, S.; Deng, Y.; Xu, B.; Yang, T.; Liu, W. Ferroptosis and Neurodegenerative Diseases: Insights into the Regulatory Roles of SLC7A11. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 43, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geloso, M.C.; Ria, F.; Corvino, V.; Di Sante, G. Expression of CD44 and Its Spliced Variants: Innate and Inducible Roles in Nervous Tissue Cells and Their Environment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178223
Geloso MC, Ria F, Corvino V, Di Sante G. Expression of CD44 and Its Spliced Variants: Innate and Inducible Roles in Nervous Tissue Cells and Their Environment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178223
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeloso, Maria Concetta, Francesco Ria, Valentina Corvino, and Gabriele Di Sante. 2025. "Expression of CD44 and Its Spliced Variants: Innate and Inducible Roles in Nervous Tissue Cells and Their Environment" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178223
APA StyleGeloso, M. C., Ria, F., Corvino, V., & Di Sante, G. (2025). Expression of CD44 and Its Spliced Variants: Innate and Inducible Roles in Nervous Tissue Cells and Their Environment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178223







