Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Pathophysiology to Regression of Albuminuria and Kidney Damage: Is It Possible?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology of DN
3. Diagnosis of DN
4. Comprehensive Management of DN
5. Treatment of DN
6. RAAS Inhibition in DN
7. SGLT2i in DN
8. GLP1-RAs in DN
9. MRAs in DN
10. Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Activators and DN
11. Aldosterone Synthase Inhibitors and CKD
12. Combination Therapy in DN
13. Limitations for the Combination Treatment
14. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ElSayed, N.A.; McCoy, R.G.; Aleppo, G.; Balapattabi, K.; Beverly, E.A.; Briggs Early, K.; Bruemmer, D.; Ebekozien, O.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Ekhlaspour, L.; et al. 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48 (Suppl. S1), S27–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossing, P.; Caramori, M.L.; Chan, J.C.N.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Hurst, C.; Khunti, K.; Liew, A.; Michos, E.D.; Navaneethan, S.D.; Olowu, W.A.; et al. KDIGO 2022 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, S1–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N.A.; McCoy, R.G.; Aleppo, G.; Balapattabi, K.; Beverly, E.A.; Briggs Early, K.; Bruemmer, D.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Garg, R.; et al. 11. Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48 (Suppl. S1), S239–S251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chang, Y.H.; Yang, S.Y.; Wu, K.D.; Chu, T.S. Update of pathophysiology and management of diabetic kidney disease. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2018, 117, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Marco, L.; Guerra-Torres, X.; Viejo, I.; Lopez-Romero, L.; Yugueros, A.; Bermúdez, V. Non-albuminuric Diabetic Kidney Disease Phenotype: Beyond Albuminuria. Eur. Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, S.; Bhandari, U.; Habib, A. Efficacy of Dapagliflozin and Telmisartan Combination Therapy in Reducing Albuminuria and Inflammatory Markers in Diabetic Nephropathy: A Prospective Observational Study. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2025, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, I.H.; Khunti, K.; Sadusky, T.; Tuttle, K.R.; Neumiller, J.J.; Rhee, C.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Rossing, P.; Bakris, G. Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 3075–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicic, R.Z.; Rooney, M.T.; Tuttle, K.R. Diabetic Kidney Disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 2032–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Cai, G.; Chen, X. Clinical and pathological factors associated with progression of diabetic nephropathy. Nephrology 2017, 22 (Suppl. S4), 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umanath, K.; Lewis, J.B. Update on Diabetic Nephropathy: Core Curriculum 2018. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 71, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foundation, N.K. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes and CKD: 2012 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2012, 60, 850–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Bannuru, R.R.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Cusi, K.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Fleming, T.K.; Hilliard, M.E.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. 4. Comprehensive Medical Evaluation and Assessment of Comorbidities: Standards Care Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47 (Suppl. S1), S52–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tervaert, T.W.C.; Mooyaart, A.L.; Amann, K.; Cohen, A.H.; Cook, H.T.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Ferrario, F.; Fogo, A.B.; Haas, M.; de Heer, E.; et al. Pathologic Classification of Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natale, P.; Palmer, S.C.; Navaneethan, S.D.; Craig, J.C.; Strippoli, G.F. Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers for preventing the progression of diabetic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2024, 4, CD006257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The BErgamo NEphrologic DIabetes Complications Trial (BENEDICT): Design and baseline characteristics. Control. Clin. Trials. 2003, 24, 442–461. [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; Aroda, V.R.; Collins, B.S.; Gabbay, R.A.; Green, J.; Maruthur, N.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Del Prato, S.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2022. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1925–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakar, C.V. Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy: Changing Landscapes and New Horizons. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2021, 28, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parving, H.H.; Rossing, P. The History of Prevention and Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy. In Unveiling Diabetes-Historical Milestones in Diabetology; S. Karger AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscioni, S.S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; de Zeeuw, D. The effect of RAAS blockade on the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menne, J.; Ritz, E.; Ruilope, L.M.; Chatzikyrkou, C.; Viberti, G.; Haller, H. The Randomized Olmesartan and Diabetes Microalbuminuria Prevention (ROADMAP) Observational Follow-Up Study: Benefits of RAS Blockade with Olmesartan Treatment Are Sustained After Study Discontinuation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parving, H.H.; Lehnert, H.; Bröchner-Mortensen, J.; Gomis, R.; Andersen, S.; Arner, P. The Effect of Irbesartan on the Development of Diabetic Nephropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.J.; Hunsicker, L.G.; Clarke, W.R.; Berl, T.; Pohl, M.A.; Lewis, J.B.; Ritz, E.; Atkins, R.C.; Rohde, R.; Raz, I. Renoprotective Effect of the Angiotensin-Receptor Antagonist Irbesartan in Patients with Nephropathy Due to Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, B.M.; Cooper, M.E.; de Zeeuw, D.; Keane, W.F.; Mitch, W.E.; Parving, H.-H.; Remuzzi, G.; Snapinn, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Shahinfar, S. Effects of Losartan on Renal and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K. Treatment of diabetic kidney disease: Current and future targets. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2017, 32, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilakou, D.; Karagiannis, T.; Athanasiadou, E.; Mainou, M.; Liakos, A.; Bekiari, E.; Sarigianni, M.; Matthews, D.R.; Tsapas, A. Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors for Type 2 Diabetes. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 159, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, R.C. Sodium Glucose Transport 2 (SGLT2) Inhibition Decreases Glomerular Hyperfiltration. Circulation 2014, 129, 542–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, B.A.; Cherney, D.Z.I.; Partridge, H.; Soleymanlou, N.; Tschirhart, H.; Zinman, B.; Fagan, N.M.; Kaspers, S.; Woerle, H.-J.; Broedl, U.C.; et al. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition and Glycemic Control in Type 1 Diabetes: Results of an 8-Week Open-Label Proof-of-Concept Trial. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 1480–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherney, D.Z.; Perkins, B.A.; Soleymanlou, N.; Har, R.; Fagan, N.; Johansen, O.; Woerle, H.-J.; von Eynatten, M.; Broedl, U.C. The effect of empagliflozin on arterial stiffness and heart rate variability in subjects with uncomplicated type 1 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, D.Z.I.; Perkins, B.A. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition in Type 1 Diabetes: Simultaneous Glucose Lowering and Renal Protection? Can. J. Diabetes 2014, 38, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lee, T.; DeFronzo, R.A. Why Do SGLT2 Inhibitors Inhibit Only 30–50% of Renal Glucose Reabsorption in Humans? Diabetes 2012, 61, 2199–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmoune, H.; Thompson, P.W.; Ward, J.M.; Smith, C.D.; Hong, G.; Brown, J. Glucose Transporters in Human Renal Proximal Tubular Cells Isolated from the Urine of Patients with Non–Insulin-Dependent Diabetes. Diabetes 2005, 54, 3427–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; et al. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; de Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Law, G.; Desai, M.; Matthews, D.R. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.-F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallon, V.; Gerasimova, M.; Rose, M.A.; Masuda, T.; Satriano, J.; Mayoux, E.; Koepsell, H.; Thomson, S.C.; Rieg, T. SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin reduces renal growth and albuminuria in proportion to hyperglycemia and prevents glomerular hyperfiltration in diabetic Akita mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2014, 306, F194–F204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.M.; Bose, M.; Cooper, M.E. Glucose and Blood Pressure-Dependent Pathways–The Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.J.; Xie, S.H.; Liu, Y.N.; Kim, W.; Jin, H.Y.; Park, S.K.; Shao, Y.M.; Park, T.S. Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitor Attenuates Kidney Injury in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 340, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.W.; Kim, H.W.; Ko, S.H.; Lim, J.H.; Ryu, G.R.; Chung, H.W.; Han, S.W.; Shin, S.J.; Bang, B.K.; Breyer, M.D.; et al. Long-Term Treatment of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Analog Exendin-4 Ameliorates Diabetic Nephropathy through Improving Metabolic Anomalies in db/db Mice. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 1227–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.C. The potential and pitfalls of GLP-1 receptor agonists for renal protection in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2017, 43, 2S20–2S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonneijck, L.; Smits, M.M.; Muskiet, M.H.A.; Hoekstra, T.; Kramer, M.H.H.; Danser, A.H.J.; Diamant, M.; Joles, J.A.; van Raalte, D.H. Acute renal effects of the GLP-1 receptor agonist exenatide in overweight type 2 diabetes patients: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutzwiller, J.-P.; Tschopp, S.; Bock, A.; Zehnder, C.E.; Huber, A.R.; Kreyenbuehl, M.; Gutmann, H.; Drewe, J.; Henzen, C.; Goeke, B.; et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Induces Natriuresis in Healthy Subjects and in Insulin-Resistant Obese Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 3055–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, J.; Pedersen, M.; Holst, J.J.; Madsen, B.; Goetze, J.P.; Rittig, S.; Jonassen, T.; Frøkiær, J.; Dejgaard, A.; Christiansen, J.S. Short-term effects of liraglutide on kidney function and vasoactive hormones in type 2 diabetes: A randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, J.; Dejgaard, A.; Frøkiær, J.; Holst, J.J.; Jonassen, T.; Rittig, S.; Christiansen, J.S. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1): Effect on Kidney Hemodynamics and Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in Healthy Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E664–E671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Moreno, C.; Hoagland, K.M.; Dahly, A.; Ditter, K.; Mistry, M.; Roman, R.J. Antihypertensive effect of glucagon-like peptide 1 in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. J. Hypertens. 2003, 21, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muskiet, M.H.A.; Tonneijck, L.; Smits, M.M.; van Baar, M.J.B.; Kramer, M.H.H.; Hoorn, E.J.; Joles, J.A.; van Raalte, D.H. GLP-1 and the kidney: From physiology to pharmacology and outcomes in diabetes. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 605–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.J.; Bergenstal, R.; Bode, B.; Kushner, R.F.; Lewin, A.; Skjøth, T.V.; Andreasen, A.H.; Jensen, C.B.; DeFronzo, R.A. Correction in Efficacy of Liraglutide for Weight Loss Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. JAMA 2015, 314, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.F.E.; Ørsted, D.D.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Marso, S.P.; Poulter, N.R.; Rasmussen, S.; Tornøe, K.; Zinman, B.; Buse, J.B. Liraglutide and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muskiet, M.H.A.; Tonneijck, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, M.; Saremi, A.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; van Raalte, D.H. Lixisenatide and renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and acute coronary syndrome: An exploratory analysis of the ELIXA randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Hu, C.; Lu, W. Exenatide Reduces Urinary Transforming Growth Factor-β1 and Type IV Collagen Excretion in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Microalbuminuria. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2012, 35, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, R.R.; Bethel, M.A.; Mentz, R.J.; Thompson, V.P.; Lokhnygina, Y.; Buse, J.B.; Chan, J.C.; Choi, J.; Gustavson, S.M.; Iqbal, N.; et al. Effects of Once-Weekly Exenatide on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1228–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Lakshmanan, M.C.; Rayner, B.; Busch, R.S.; Zimmermann, A.G.; Woodward, D.B.; Botros, F.T. Dulaglutide versus insulin glargine in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate-to-severe chronic kidney disease (AWARD-7): A multicentre, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkovic, V.; Tuttle, K.R.; Rossing, P.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Mann, J.F.E.; Bakris, G.; Baeres, F.M.M.; Idorn, T.; Bosch-Traberg, H.; Lausvig, N.L.; et al. Effects of Semaglutide on Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Sattar, N.; Pavo, I.; Haupt, A.; Duffin, K.L.; Yang, Z.; Wiese, R.J.; Tuttle, K.R.; Cherney, D.Z.I. Effects of tirzepatide versus insulin glargine on kidney outcomes in type 2 diabetes in the SURPASS-4 trial: Post-hoc analysis of an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera-Chimal, J.; Estrela, G.R.; Lechner, S.M.; Giraud, S.; El Moghrabi, S.; Kaaki, S.; Kolkhof, P.; Hauet, T.; Jaisser, F. The myeloid mineralocorticoid receptor controls inflammatory and fibrotic responses after renal injury via macrophage interleukin-4 receptor signaling. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 1344–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutzmann, J.; Musmann, R.-J.; Haertlé, M.; Daniel, J.-M.; Sonnenschein, K.; Schäfer, A.; Kolkhof, P.; Bauersachs, J.; Sedding, D.G. The novel mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist finerenone attenuates neointima formation after vascular injury. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, R.; Xu, L.; Che, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Dong, B. Cardiovascular-renal protective effect and molecular mechanism of finerenone in type 2 diabetic mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1125693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.L.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Schloemer, P.; Joseph, A.; et al. Effect of Finerenone on Chronic Kidney Disease Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippatos, G.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; McGuire, D.K.; Rossing, P.; Ruilope, L.M.; Butler, J.; Jankowska, E.A.; Michos, E.D.; Farmakis, D.; et al. Finerenone Reduces Risk of Incident Heart Failure in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes: Analyses From the FIGARO-DKD Trial. Circulation 2022, 145, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossing, P.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Filippatos, G.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Amod, A.; Marre, M.; Joseph, A.; Lage, A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of finerenone in patients with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes by GLP-1RA treatment: A subgroup analysis from the FIDELIO-DKD trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.L.; Agarwal, R.; Chan, J.C.; Cooper, M.E.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Haller, H.; Remuzzi, G.; Rossing, P.; Schmieder, R.E.; Nowack, C.; et al. Effect of Finerenone on Albuminuria in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy. JAMA 2015, 314, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippatos, G.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; McGuire, D.K.; Rossing, P.; Ruilope, L.M.; Butler, J.; Jankowska, E.A.; Michos, E.D.; Farmakis, D.; et al. Finerenone efficacy in patients with chronic kidney disease, type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2022, 9, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.G.; Lampe, T.; El Sheikh, S.; Griebenow, N.; Woltering, E.; Schlemmer, K.-H.; Dietz, L.; Gerisch, M.; Wunder, F.; Becker-Pelster, E.-M.; et al. Discovery of the Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Activator Runcaciguat (BAY 1101042). J Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 5323–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasch, J.P.; Schlossmann, J.; Hocher, B. Renal effects of soluble guanylate cyclase stimulators and activators: A review of the preclinical evidence. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 21, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, S.; Kraehling, J.; Eitner, F.; Bénardeau, A.; Sandner, P. The Impact of the Nitric Oxide (NO)/Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase (sGC) Signaling Cascade on Kidney Health and Disease: A Preclinical Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, I.M.; Alter, M.L.; von Websky, K.; Kretschmer, A.; Tsuprykov, O.; Sharkovska, Y.; Krause-Relle, K.; Raila, J.; Henze, A.; Stasch, J.-P.; et al. Effects of Stimulation of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase on Diabetic Nephropathy in Diabetic eNOS Knockout Mice on Top of Angiotensin II Receptor Blockade. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehle, D.; Xu, M.Z.; Schomber, T.; Hahn, M.G.; Schweda, F.; Feil, S.; Kraehling, J.R.; Eitner, F.; Patzak, A.; Sandner, P.; et al. Novel soluble guanylyl cyclase activators increase glomerular cGMP, induce vasodilation and improve blood flow in the murine kidney. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 2476–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gansevoort, R.T.; Wheeler, D.C.; Debén, F.M.; Speeckaert, M.; Thomas, D.; Berger, M.; Klein, S.; Friedrichs, F.; Paraschin, K.; Schmieder, R.E. The soluble guanylate cyclase activator runcaciguat significantly improves albuminuria in patients with chronic kidney disease: A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2025, 40, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubin, R.F.; Shah, S.J. Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Stimulators: A Novel Treatment Option for Heart Failure Associated with Cardiorenal Syndromes? Curr. Heart Fail Rep. 2016, 13, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandner, P.; Stasch, J.P. Anti-fibrotic effects of soluble guanylate cyclase stimulators and activators: A review of the preclinical evidence. Respir. Med. 2017, 122, S1–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Costa, R.; Duran-Güell, M.; Casulleras, M.; López-Vicario, C.; Alcaraz-Quiles, J.; Diaz, A.; Lozano, J.J.; Titos, E.; Hall, K.; Sarno, R.; et al. Stimulation of soluble guanylate cyclase exerts antiinflammatory actions in the liver through a VASP/NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome circuit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 28263–28274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bénardeau, A.; Kahnert, A.; Schomber, T.; Meyer, J.; Pavkovic, M.; Kretschmer, A.; Lawrenz, B.; Hartmann, E.; Mathar, I.; Hueser, J.; et al. Runcaciguat, a novel soluble guanylate cyclase activator, shows renoprotection in hypertensive, diabetic, and metabolic preclinical models of chronic kidney disease. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 2363–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodošek Hojs, N.; Bevc, S.; Ekart, R.; Hojs, R. Oxidative Stress Markers in Chronic Kidney Disease with Emphasis on Diabetic Nephropathy. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandner, P.; Zimmer, D.P.; Milne, G.T.; Follmann, M.; Hobbs, A.; Stasch, J.P. Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Stimulators and Activators. In Reactive Oxygen Species: Network Pharmacology and Therapeutic Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 355–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boustany-Kari, C.M.; Harrison, P.C.; Chen, H.; Lincoln, K.A.; Qian, H.S.; Clifford, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Gueneva-Boucheva, K.; Bosanac, T.; et al. A Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Activator Inhibits the Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy in the ZSF1 Rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 356, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czirok, S.; Fang, L.; Radovits, T.; Szabó, G.; Szénási, G.; Rosivall, L.; Merkely, B.; Kökény, G. Cinaciguat ameliorates glomerular damage by reducing ERK1/2 activity and TGF-ß expression in type-1 diabetic rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harloff, M.; Prüschenk, S.; Seifert, R.; Schlossmann, J. Activation of soluble guanylyl cyclase signalling with cinaciguat improves impaired kidney function in diabetic mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 2460–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraehling, J.R.; Benardeau, A.; Schomber, T.; Popp, L.; Vienenkoetter, J.; Ellinger-Ziegelbauer, H.; Pavkovic, M.; Hartmann, E.; Siudak, K.; Freyberger, A.; et al. The sGC Activator Runcaciguat Has Kidney Protective Effects and Prevents a Decline of Kidney Function in ZSF1 Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, G.A.; Harrison, P.C.; Lincoln, K.; Chen, H.; Sun, P.; Hill, J.; Qian, H.S.; McHugh, M.C.; Clifford, H.; Ng, K.J.; et al. The Novel, Clinical-Stage Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Activator BI 685509 Protects from Disease Progression in Models of Renal Injury and Disease. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2023, 384, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Cherney, D.; Gafor, A.H.A.; Górriz, J.L.; Pergola, P.E.; Tang, S.C.W.; Desch, M.; Iliev, H.; Sun, Z.; Steubl, D.; et al. Effect of Avenciguat on Albuminuria in Patients with CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2024, 35, 1227–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Liu, W.; Tsai, X.-Q.E.; Wang, Z.; Outtrim, C.; Tang, A.; Pieper, M.P.; Reinhart, G.A.; Huang, Y. A novel soluble guanylate cyclase activator, avenciguat, in combination with empagliflozin, protects against renal and hepatic injury in diabetic db/db mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 328, E362–E376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Choi, J.; Sim, L.; Dey, A.; Mohan, M.; Kantharidis, P.; Dietz, L.; Sandner, P.; de Haan, J.B. Ameliorating diabetes-associated atherosclerosis and diabetic nephropathy through modulation of soluble guanylate cyclase. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1220095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzer, M.S.; Pavkovic, M.; Frederick, J.; Abedini, A.; Freyberger, A.; Vienenkötter, J.; Mathar, I.; Siudak, K.; Eitner, F.; Sandner, P.; et al. Treatment effects of soluble guanylate cyclase modulation on diabetic kidney disease at single-cell resolution. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 100992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Hoek, M.; Cox, J.; Lin, K.; Liu, Y.; Blumenschein, W.; Grein, J.; Swaminath, G. Effects of soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator on renal function in ZSF-1 model of diabetic nephropathy. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherney, D.Z.I.; de Zeeuw, D.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Cardona, J.; Desch, M.; Wenz, A.; Schulze, F.; Nangaku, M. Safety, tolerability, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of the soluble guanylyl cyclase activator BI 685509 in patients with diabetic kidney disease: A randomized trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 2218–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruno, S.; Tanaka, T.; Nangaku, M. Exploring molecular targets in diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 41, S33–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornstein, S.R.; de Zeeuw, D.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Schulze, F.; Cronin, L.; Wenz, A.; Tuttle, K.R.; Hadjadj, S.; Rossing, P. Aldosterone synthase inhibitor (BI 690517) therapy for people with diabetes and albuminuric chronic kidney disease: A multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase I trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 2128–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namsolleck, P.; Unger, T. Aldosterone synthase inhibitors in cardiovascular and renal diseases. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29 (Suppl. S1), i62–i68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Agarwal, R.; Alpers, C.E.; Bakris, G.L.; Brosius, F.C.; Kolkhof, P.; Uribarri, J. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Che, R.C.; Zhang, A.H. Role of Aldosterone in Renal Fibrosis. In Renal Fibrosis: Mechanisms and Therapies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.W.; Halvorsen, Y.; Bond, M.; Murphy, B.; Isaacsohn, J. Results from a Phase 1 Study Assessing the Pharmacokinetics of the Aldosterone Synthase Inhibitor Baxdrostat in Participants with Varying Degrees of Renal Function. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2024, 13, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Hauske, S.J.; Canziani, M.E.; Caramori, M.L.; Cherney, D.; Cronin, L.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Hugo, C.; Nangaku, M.; Rotter, R.C.; et al. Efficacy and safety of aldosterone synthase inhibition with and without empagliflozin for chronic kidney disease: A randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2024, 403, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Green, J.B.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Mann, J.F.E.; McGill, J.B.; Mottl, A.K.; Rosenstock, J.; Rossing, P.; Vaduganathan, M.; Brinker, M.; et al. Finerenone with Empagliflozin in Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 393, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangaku, M.; Kanda, H.; Takama, H.; Ichikawa, T.; Hase, H.; Akizawa, T. Randomized Clinical Trial on the Effect of Bardoxolone Methyl on GFR in Diabetic Kidney Disease Patients (TSUBAKI Study). Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Díaz, I.; Martos, N.; Llorens-Cebrià, C.; Álvarez, F.J.; Bedard, P.W.; Vergara, A.; Jacobs-Cachá, C.; Soler, M.J. Endothelin Receptor Antagonists in Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugahara, M.; Tanaka, S.; Tanaka, T.; Saito, H.; Ishimoto, Y.; Wakashima, T.; Ueda, M.; Fukui, K.; Shimizu, A.; Inagi, R.; et al. Prolyl Hydroxylase Domain Inhibitor Protects against Metabolic Disorders and Associated Kidney Disease in Obese Type 2 Diabetic Mice. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 560–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, S.; Tanaka, T.; Saito, T.; Fukui, K.; Wakashima, T.; Susaki, E.A.; Ueda, H.R.; Nangaku, M. The oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor enarodustat counteracts alterations in renal energy metabolism in the early stages of diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 934–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuen, B.L.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Vart, P.; Claggett, B.L.; Fletcher, R.A.; Arnott, C.; de Oliveira Costa, J.; Falster, M.O.; Pearson, S.-A.; Mahaffey, K.W.; et al. Estimated Lifetime Cardiovascular, Kidney, and Mortality Benefits of Combination Treatment with SGLT2 Inhibitors, GLP-1 Receptor Agonists, and Nonsteroidal MRA Compared with Conventional Care in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Albuminuria. Circulation 2024, 149, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
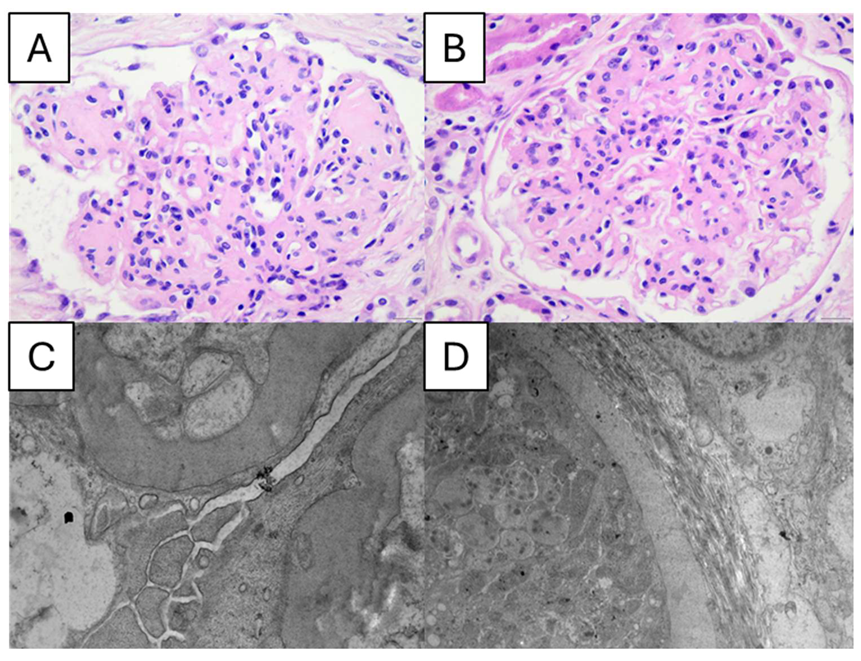

| Glomerular | Interstitial and Vascular | ||||||||
 |  | ||||||||
| I | IIa | IIb | III | IV | Interstitial lesions. | Interstitial inflammation. | Vascular lesions arteriolar hyalinosis. | Presence of large vessels. | Arteriosclerosis (score worst artery). |
 |  | ||||||||
| Mild or nonspecific LM changes and EM-proven GBM thickening. | Mild mesangial expansion. | Severe mesangial expansion. | Nodular sclerosis (Kimmelstiel– Wilson lesion). | Advanced diabetic glomerulosclerosis. | No IFTA 25% 25% to 50% 50% | Absent 0. Infiltration only in relation to IFTA 1. Infiltration in areas without IFTA 2. | Absent 0. At least one area of arteriolar hyalinosis 1. More than one area of arteriolar hyalinosis 2. | Yes/no | No intimal thickening 0. Intimal thickening less than thickness of media 1. Intimal thickening greater than thickness of media 2. |
| Biopsy does not meet any of the criteria mentioned below for class II, III, or IV. GBM 395 nm in female and 430 nm in male individuals 9 years of age and older. | Biopsy does not meet criteria for class III or IV. Mild mesangial expansion in 25% of the observed mesangium. | Biopsy does not meet criteria for class III or IV. Severe mesangial expansion in 25% of the observed mesangium. | Biopsy does not meet criteria for class IV. At least one convincing Kimmelstiel– Wilson lesion. | Global glomerular sclerosis in 50% of glomeruli. Lesions from classes I through III. | |||||
| Study | Subjects in the Study | Treatment | Outcome | Results | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAASi | IDNT | 1715 hypertensive patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. | Irbesartan (300 mg daily), amlodipine (10 mg daily) vs. placebo. | Doubling of baseline serum creatinine concentration, the development of ESRD, or death from any cause. | Doubling of serum creatinine concentration was 33 percent lower in the irbesartan group than in the placebo group (p = 0.003) and 37 percent lower in the irbesartan group compared to amlodipine (p < 0.001). |
| RENAAL | 1513 hypertensive patients. | Losartan (50 to 100 mg once daily) vs. placebo, both taken in addition to conventional antihypertensive treatment. | Doubling of the baseline serum creatinine concentration, ESRD, or death. | Losartan reduced the incidence of a doubling of the serum creatinine concentration (risk reduction, 25% p = 0.006) and ESRD (risk reduction, 28% p = 0.002) but had no effect on mortality. | |
| SGLT2 i | EMPA-REG | 7020 patients with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular (CV) risk. | Empagliflozin (10 mg or 25 mg) vs. placebo. | Death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke. | Lower risk of cardiovascular death (3.7% vs. 5.9% in the placebo group; 38% relative risk reduction), hospitalization for HF (2.7% and 4.1%, respectively; 35% relative risk reduction), and all-cause mortality in empagliflozin-treated patients. |
| CANVAS | 10,142 participants with type 2 DM and high CV risk. | Canagliflozin vs. placebo. | Death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke. | The rate of the primary outcome was lower with canagliflozin than with placebo (hazard ratio, 0.86; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.75 to 0.97; p < 0.001 for noninferiority; p = 0.02 for superiority). The results showed a possible benefit of canagliflozin with respect to the progression of albuminuria (hazard ratio, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.67 to 0.79) and the composite (hazard ratio, 0.60; 95% CI, 0.47 to 0.77). | |
| DAPA –CKD | 4304 participants with and without DM and high CV risk. | Dapagliflozin vs. placebo. | Rate of kidney function deterioration. | Lower decline in the eGFR of at least 50%, ESRD, or mortality. | |
| GLP1-RAs | LEADER | 9340 patients of high CV risk. | Liraglutide vs. placebo. | Rate of kidney function deterioration. | 26% reduction of the de novo macroalbuminuria; 19% reduction of UACR. |
| SUSTAIN-6 | 3297 patients with T2DM and CVD or with CV risk factors. | Semaglutide vs. placebo. | Rate of kidney function deterioration. | New or worsening nephropathy occurred less frequently; HR = 0.64 (0.46–0.88), p = 0.005. | |
| ELIXA | 6068 patients with T2DM and acute coronary syndrome. | Lixisenatide vs. placebo. | Progression of albuminuria. | Lixenatide reduces progression of UACR in macroalbuminuric patients. | |
| EXSCEL | 14,752 patients (73% had CVD). | Extended-release exenatide vs. placebo. | Rate of kidney function deterioration. | Reduction of eGFR with 40% decline, RRT or new macroalbumiuria; HR = 0.85 (0.73–0.98, p = 0.027). | |
| AWARD-7 | 577 patients with T2DM and advanced CKD. | Dulaglutide vs. insulin glargine. | eGFR and UACR change from baseline. | Dulaglutide reduced eGFR decline compared to insulin glargine. | |
| FLOW | 3533 patients with T2DM and CKD. | Semaglutide vs. placebo. | Major kidney disease events, a composite of the onset of kidney failure, at least a 50% reduction in eGFR from baseline or death from renal or CV causes. | 24% lower risk of a primary-outcome event in the Semaglutide group. The results for all confirmatory secondary outcomes favored Semaglutide: mean annual eGFR slope was less steep, the risk of major CV events was 18% lower (HR = 0.82, 0.68–0.98; p = 0.029), and the risk of all-cause mortality was 20% lower (HR = 0.80; 0.67–0.95, p = 0.01). | |
| Ns-MRAs | FIGARO-DKD | 7437 patients with CKD and type 2 DM | Finerenone vs. placebo. | Death from CV causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or hospitalization for heart failure. The first secondary outcome was a composite of renal failure, a sustained decrease from baseline of at least 40% in eGFR, or renal death. | A primary outcome event occurred in 12.4% of the finerenone group and in 14.2% of the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.87; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.76 to 0.98; p = 0.03), with the benefit driven primarily by a lower incidence of hospitalization for heart failure (hazard ratio, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.56 to 0.90). The secondary composite outcome occurred in 9.5% of the finerenone and in 10.8% of the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.76 to 1.01). |
| FIDELIO-DKD | 5734 patients with CKD and type 2 DM. | Finerenone vs. placebo. | Kidney failure, a sustained decrease of at least 40% in the eGFR from baseline, or death from renal causes. | A primary outcome occurred in 17.8% of the finerenone and 21.1% of the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.82; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.73 to 0.93; p = 0.001). | |
| FIDELITY | 13,026 patients combining data from FIGARO-DKD and FIDELIO-DKD. | Finerenone vs. placebo. | A composite of CV death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or hospitalization for heart failure, and a composite of kidney failure, a sustained ≥57% decrease in estimated glomerular filtration rate from baseline over ≥4 weeks, or renal death. | The composite cardiovascular outcome occurred in 825 (12.7%) patients receiving finerenone and 939 (14.4%) receiving placebo (hazard ratio (HR), 0.86; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.78–0.95; p = 0.0018). The composite kidney outcome occurred in 5.5% of patients receiving finerenone and 7.1% of patients receiving placebo (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.67–0.88; p = 0.0002). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doumani, G.; Theofilis, P.; Vordoni, A.; Thymis, V.; Liapis, G.; Smirloglou, D.; Kalaitzidis, R.G. Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Pathophysiology to Regression of Albuminuria and Kidney Damage: Is It Possible? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178224
Doumani G, Theofilis P, Vordoni A, Thymis V, Liapis G, Smirloglou D, Kalaitzidis RG. Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Pathophysiology to Regression of Albuminuria and Kidney Damage: Is It Possible? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178224
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoumani, Georgia, Panagiotis Theofilis, Aikaterini Vordoni, Vasileios Thymis, George Liapis, Despina Smirloglou, and Rigas G. Kalaitzidis. 2025. "Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Pathophysiology to Regression of Albuminuria and Kidney Damage: Is It Possible?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178224
APA StyleDoumani, G., Theofilis, P., Vordoni, A., Thymis, V., Liapis, G., Smirloglou, D., & Kalaitzidis, R. G. (2025). Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Pathophysiology to Regression of Albuminuria and Kidney Damage: Is It Possible? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178224






