Brucella-Induced Impairment of Decidualization and Its Impact on Trophoblast Function and Inflammatory Profile
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
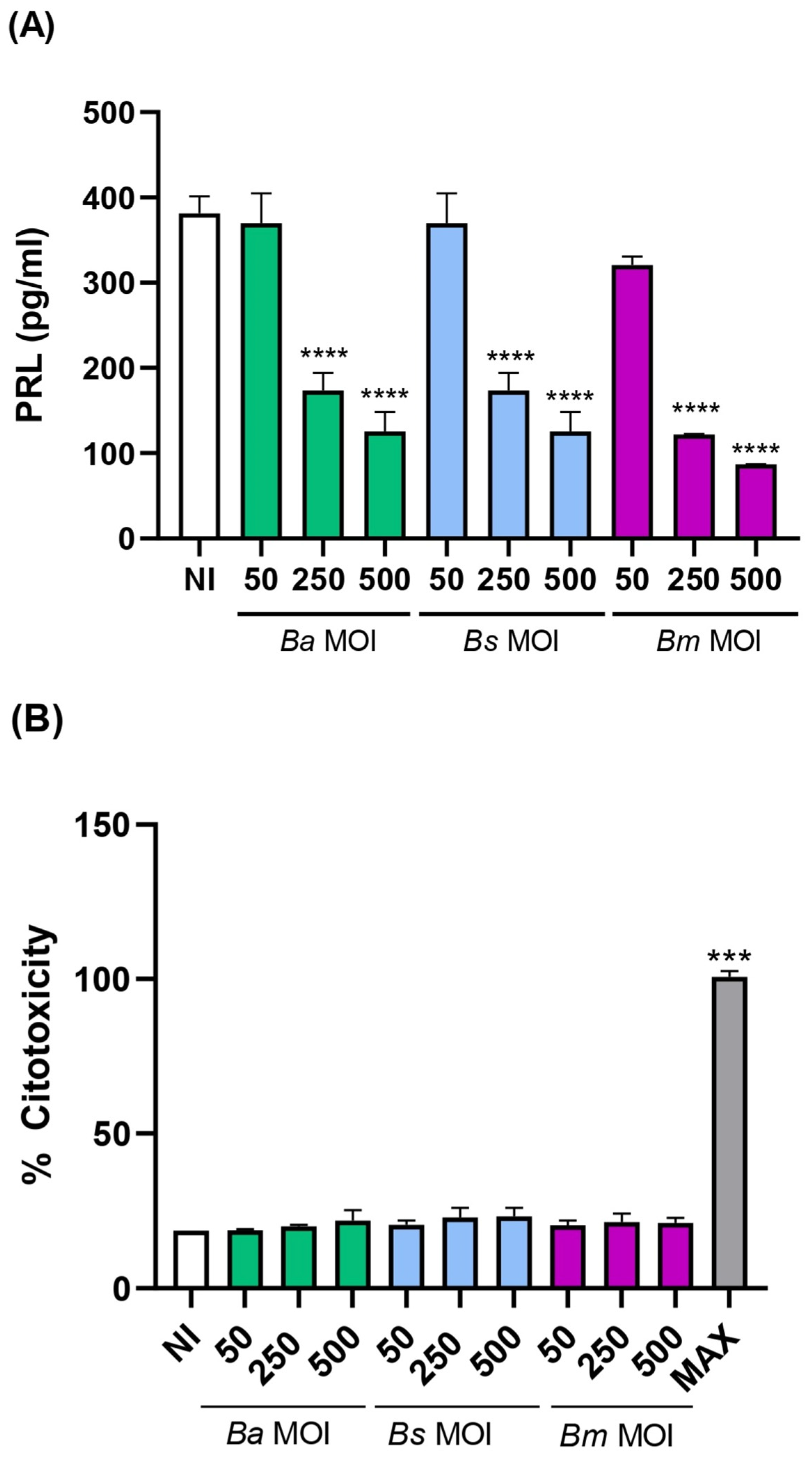
2.1. Brucella spp. Infection of Human Endometrial Stromal Cells Results in Deficient Decidualization
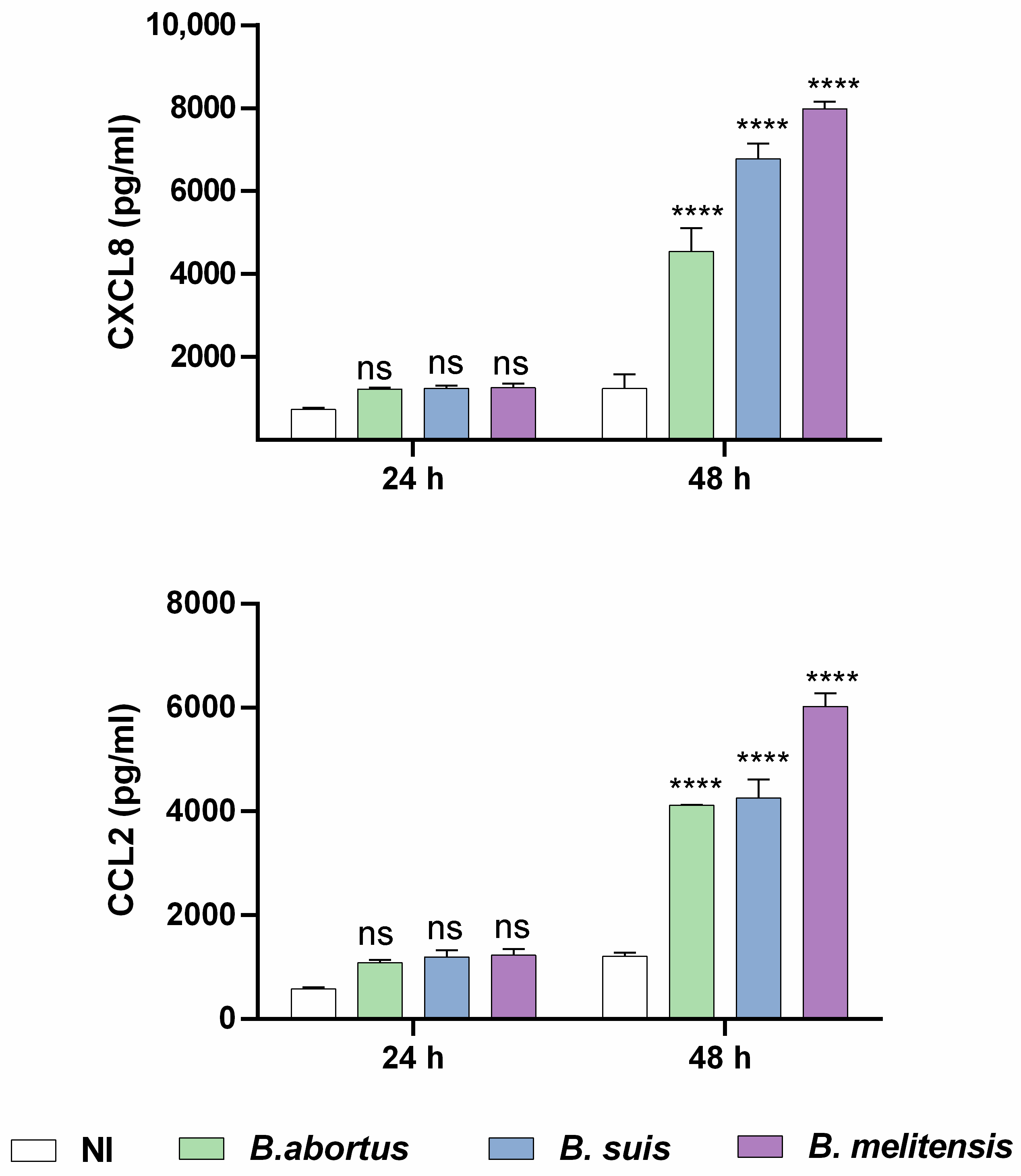
2.2. Brucella spp. Infection of Human Endometrial Stromal Cells Induces a Proinflammatory Chemokine Response
2.3. Factors Released by Infected Decidualized Stromal Cells Induce an Inflammatory Response in Trophoblasts
2.4. Brucella Infection Reduces the Ability of Decidualized T-HESC Cells to Stimulate Progesterone Production in Trophoblasts
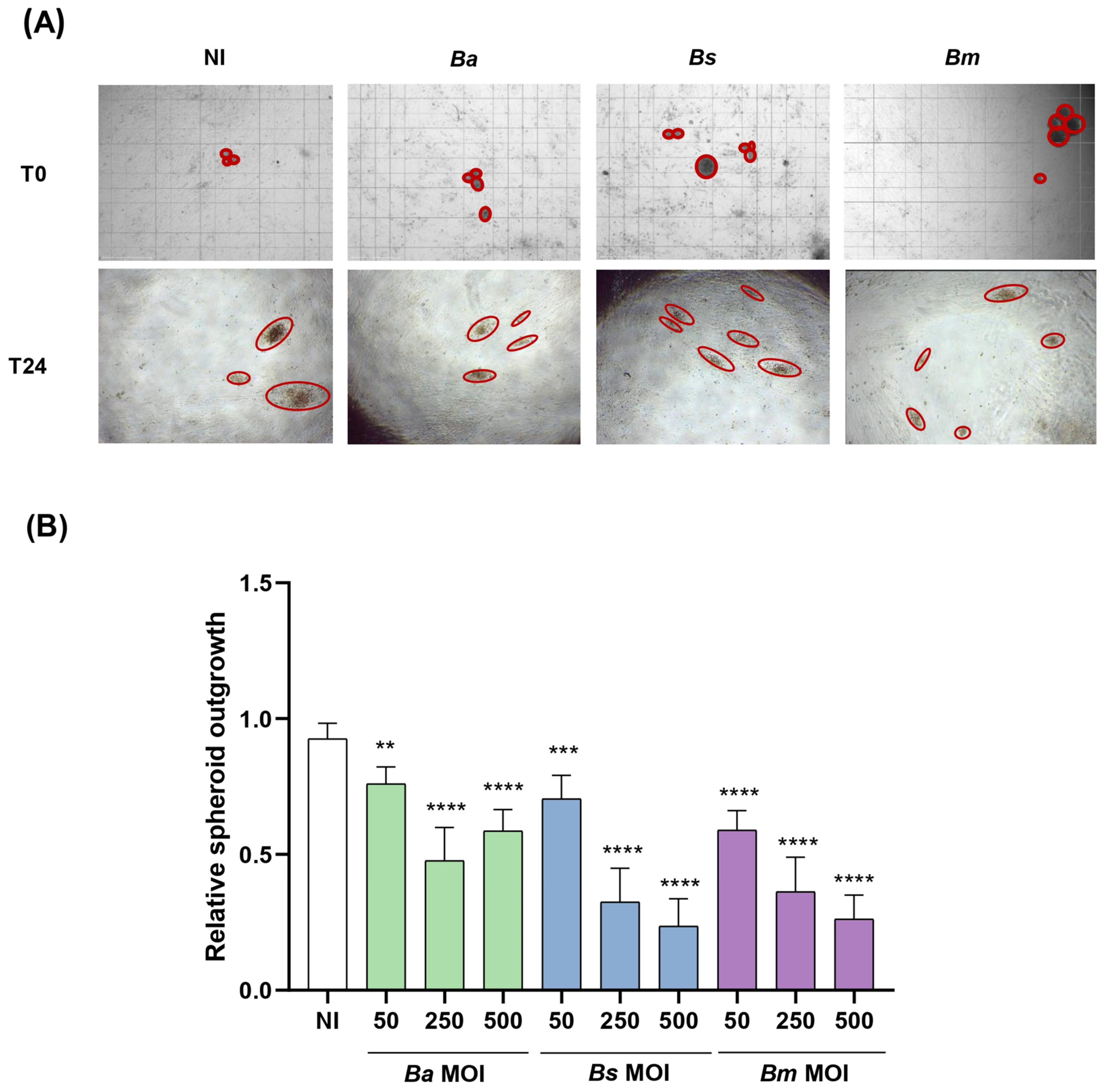
2.5. Brucella Infection of Decidualized Stromal Cells Impairs Outgrowth of Trophoblast Spheroid in Co-Culture Models
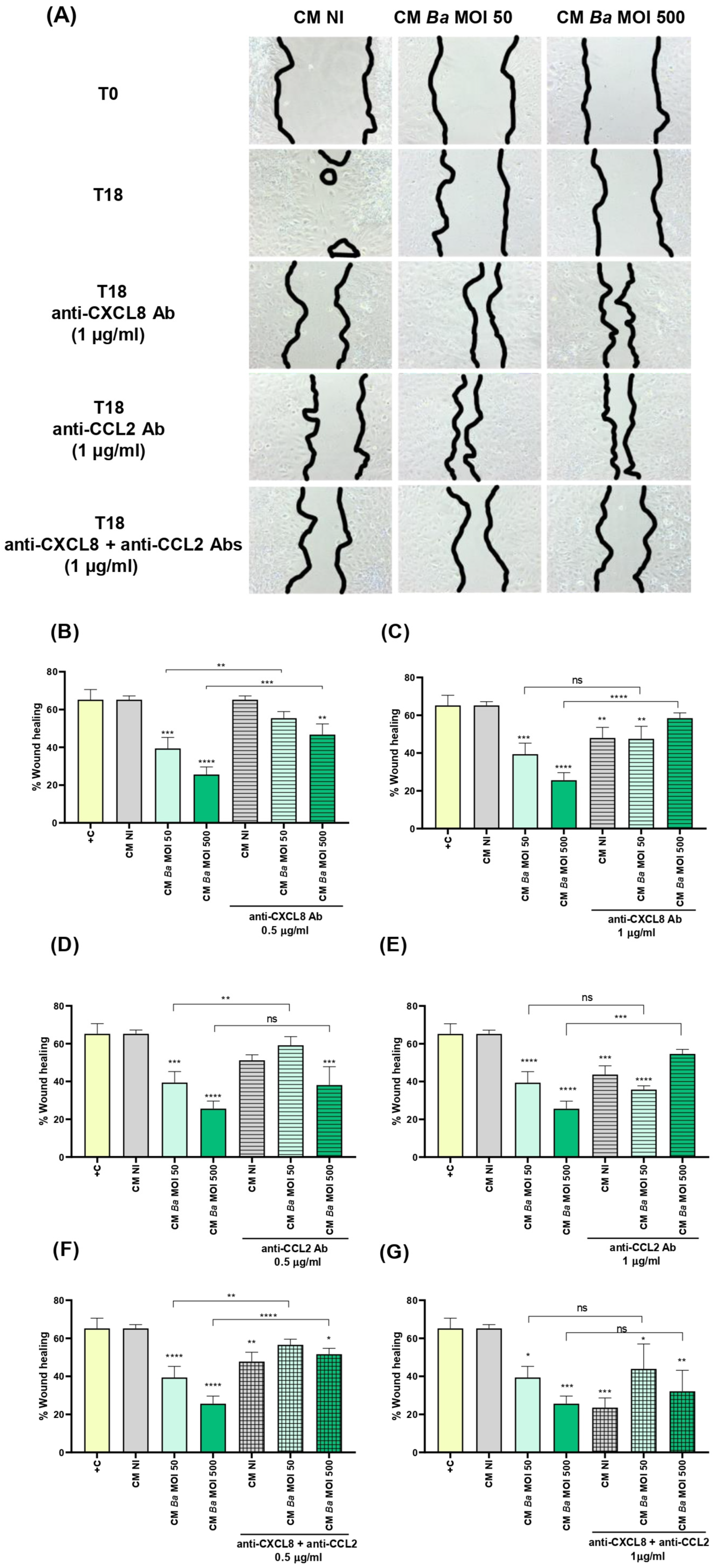
2.6. Conditioned Medium from Infected Decidualized Stromal Cells Affects the Migration of Trophoblast
2.7. Conditioned Medium from Infected Decidualized Stromal Cells Impairs Trophoblast Invasion
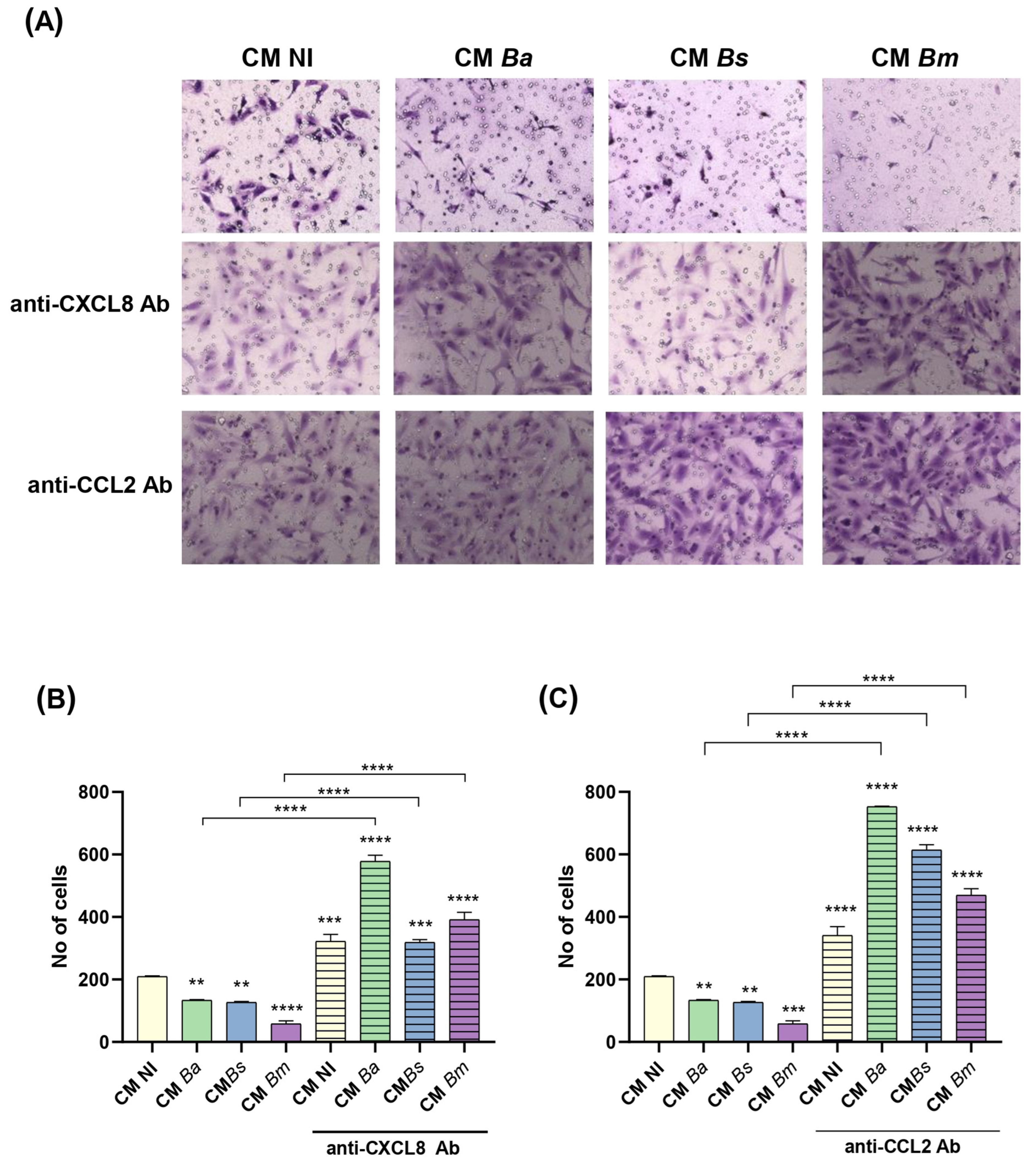
2.8. Brucella Infection of Decidualized Stromal Cells Impairs Their Chemotactic Capacity for Trophoblasts
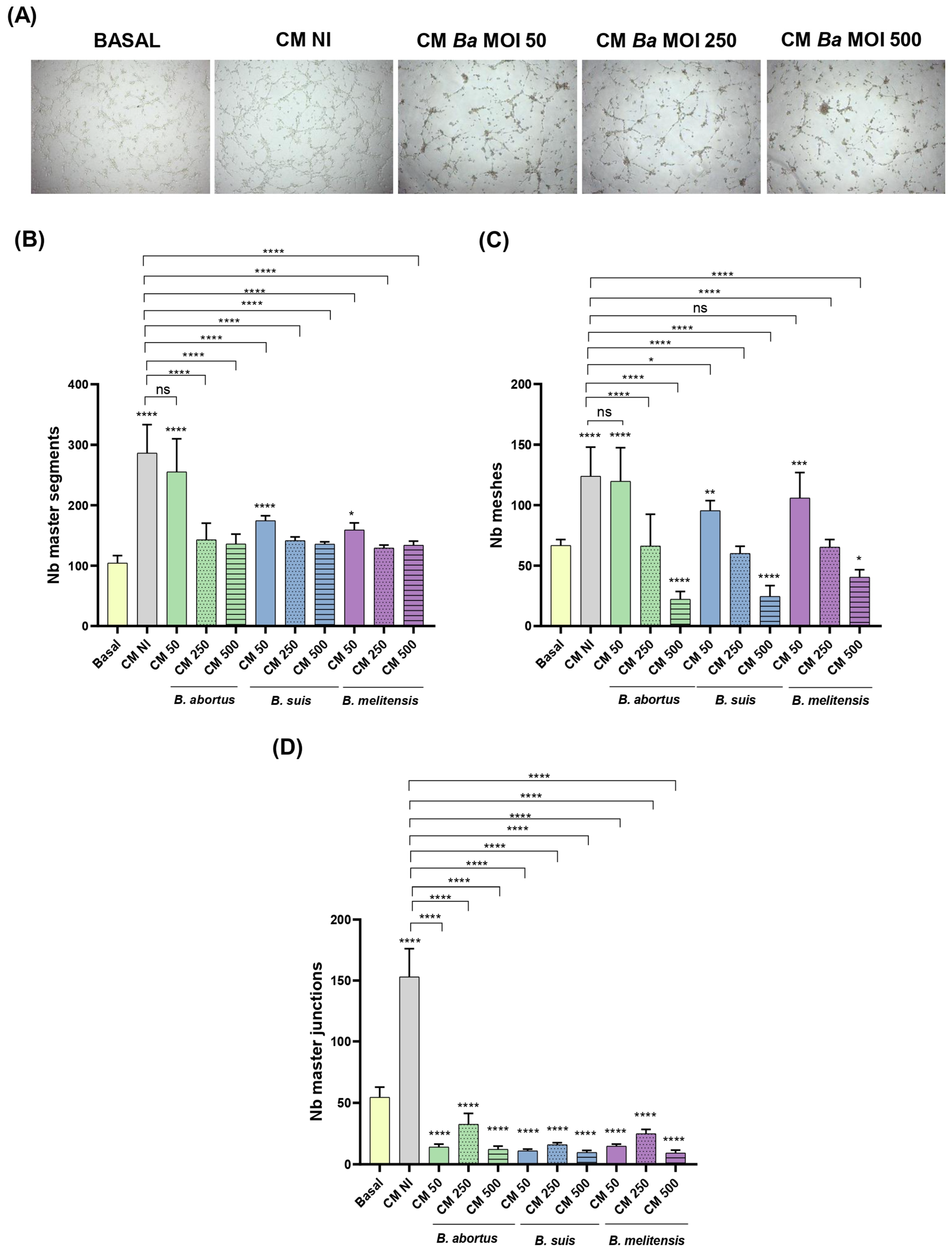
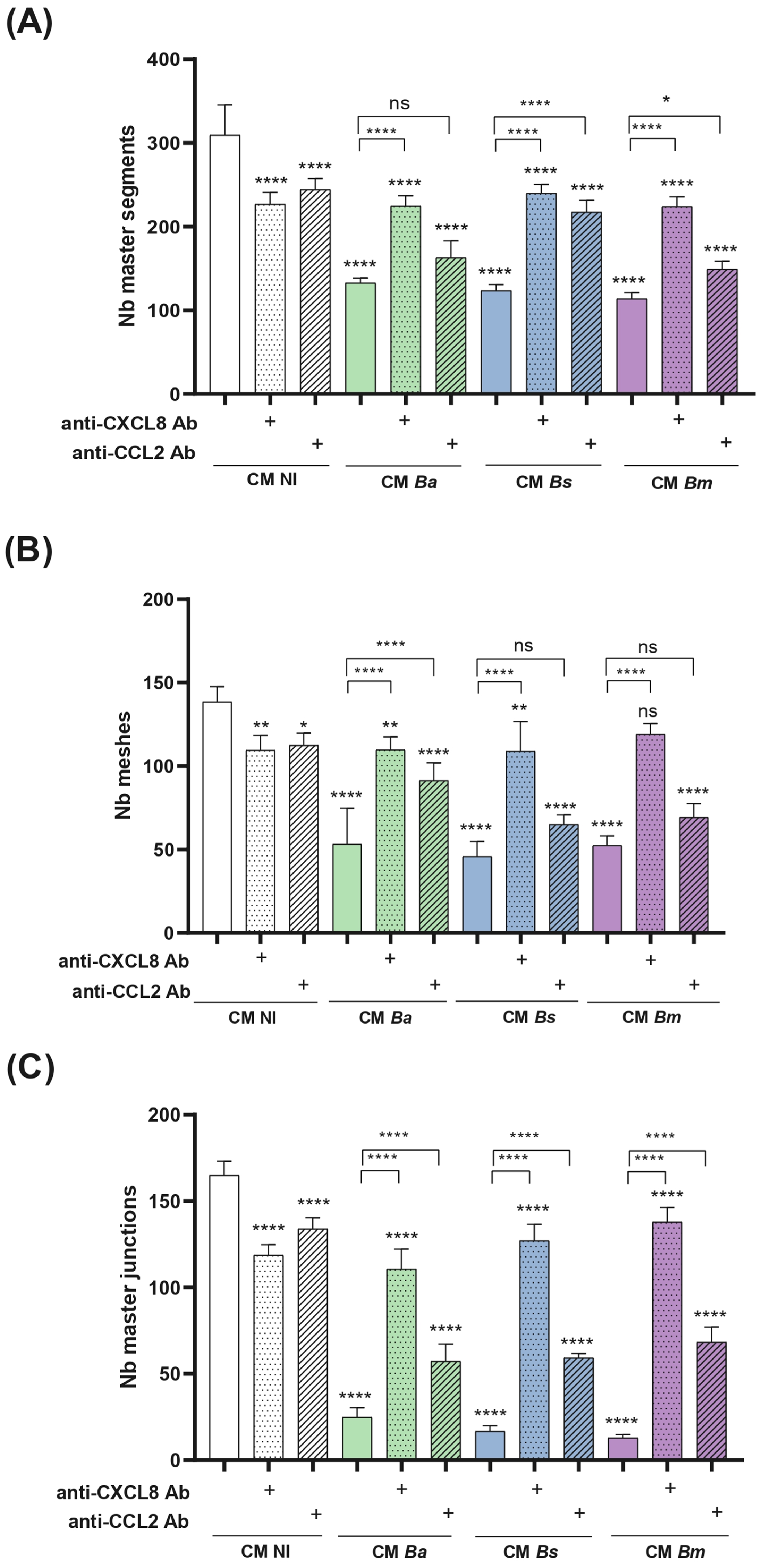
2.9. Conditioned Medium from Infected Decidualized Stromal Cells Impairs Trophoblast Tubulogenesis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Brucella spp. Growth Conditions
4.2. Cell Lines
4.3. Cellular Infections
4.4. Decidualization of T-HESC Endometrial Cells
4.5. Citotoxicity
4.6. Preparation of CM from Infected and Decidualized T-HESC
4.7. Cytokine Response of Trophoblasts Stimulated with T-HESC CM
4.8. Progesterone Response of Trophoblasts Stimulated with T-HESC CM
4.9. Functional Response of Trophoblasts Stimulated with T-HESC CM
- (a)
- Migration. The effect of CM from infected and non-infected decidualized stromal cells on the migration ability of trophoblasts was evaluated using the scratch test essentially as described by Rattila et al. [73]. Swan-71 cells were plated at 5 × 104 cells/well in culture medium without antibiotics to allow the formation of a confluent layer. The following day, the culture medium was carefully removed and cells were gently washed with DMEM-F12. A vertical scratch was performed through the monolayer using a pipette tip, and cells were cultured in the presence of CM from infected and non-infected decidualized stromal cells. Swan-71 cells cultured in DMEM/F-12 supplemented with 10% FBS were used as a positive control of migration. Pictures were taken at time 0 and later on the same microscopic field at 18 h post-stimulation. Each wound area in duplicate wells was measured with ImageJ software. The degree of wound closure was calculated as: [(area time 0 h − area time = 18 h)/area time = 0 h] × 100. The independent experiments were repeated three times.
- (b)
- Invasion. Trophoblast invasive capacity was evaluated as described by Rattila et al. [74]. A Geltrex matrix (0.6 mg/mL in DMEM-F12) was applied to Transwell inserts (8 µm pore size) in 24-well plates to simulate the basal membrane. Swan-71 cells (3 × 104) were pre-treated for 1 h with CM (1:2 dilution) from non-infected or Brucella-infected decidualized stromal cells (MOI 250), then seeded in the upper chamber on top of the Geltrex matrix. CM was maintained throughout the assay in the upper chamber.
- (c)
- Tubulogenesis. This assay was performed essentially as described by Rattila et al. [73]. A Geltrex matrix (9 mg/mL in DMEM-F12) was dispensed in a 96-well plate. When gelification was complete, Swan-71 cells (2 × 104/well) previously stimulated for 1 h with CM Ba, Bs, or Bm MOI 50, 250, or 500) or NI stromal decidualized cells were dispensed. After 6 h the wells were imaged using an EVOS microscope (Thermo Fisher) to evaluate the number of master junctions, master segments, and meshes using ImageJ software and the Angiogenesis Analyser plugin. CM were kept during the whole assay.
4.10. Evaluation of the Chemotactic Effect of CM from Decidualized Stromal Cells on Trophoblasts
4.11. Neutralization of CXCL8 and CCL2 in CM
4.12. Spheroids Adhesion to the Infected Decidua
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pappas, G.; Papadimitriou, P.; Akritidis, N.; Christou, L.; Tsianos, E.V. The New Global Map of Human Brucellosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, G.; Akritidis, N.; Bosilkovski, M.; Tsianos, E. Brucellosis. New Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 2325–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, M.P.; Mulder, M.; Gilman, R.H.; Smits, H.L. Human Brucellosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, K.A.; Parvez, A.; Fahmy, N.A.; Abdel Hady, B.H.; Kumar, S.; Ganguly, A.; Atiya, A.; Elhassan, G.O.; Alfadly, S.O.; Parkkila, S.; et al. Brucellosis: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Treatment—A Comprehensive Review. Ann. Med. 2023, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.N.; Da Silva, M.T.T.; Lima, M.A. Neurobrucellosis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 36, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colmenero, J.D.; Muñoz-Roca, N.L.; Bermudez, P.; Plata, A.; Villalobos, A.; Reguera, J.M. Clinical Findings, Diagnostic Approach, and Outcome of Brucella melitensis Epididymo-Orchitis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 57, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narimisa, N.; Razavi, S.; Khoshbayan, A.; Jazi, F.M. Prevalence of Brucella Endocarditis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Health Sci. Rep. 2023, 6, e1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosilkovski, M.; Arapović, J.; Keramat, F. Human Brucellosis in Pregnancy—An Overview. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 20, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshamy, M.; Ahmed, A.I. The Effects of Maternal Brucellosis on Pregnancy Outcome. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2008, 2, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdoglu, M.; Adali, E.; Kurdoglu, Z.; Karahocagil, M.K.; Kolusari, A.; Yildizhan, R.; Kucukaydin, Z.; Sahin, H.G.; Kamaci, M.; Akdeniz, H. Brucellosis in Pregnancy: A 6-Year Clinical Analysis. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2010, 281, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makala, R.; Majigo, M.V.; Bwire, G.M.; Kibwana, U.; Mirambo, M.M.; Joachim, A. Seroprevalence of Brucella Infection and Associated Factors among Pregnant Women Receiving Antenatal Care around Human, Wildlife and Livestock Interface in Ngorongoro Ecosystem, Northern Tanzania. A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Akhter, S.; Neubauer, H.; Scherag, A.; Kesselmeier, M.; Melzer, F.; Khan, I.; El-Adawy, H.; Azam, A.; Qadeer, S.; et al. Brucellosis in Pregnant Women from Pakistan: An Observational Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kledmanee, K.; Liabsuetrakul, T.; Sretrirutchai, S. Seropositivities against Brucellosis, Coxiellosis, and Toxoplasmosis and Associated Factors in Pregnant Women with Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes: A Cross-Sectional Study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.Y.; Mah, M.W.; Memish, Z.A. Brucellosis in Pregnant Women. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 1172–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Tawfiq, J.A.; Memish, Z.A. Pregnancy Associated Brucellosis. Recent Pat. Anti-Infect. Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannacopoulos, I.; Eliopoulou, M.I.; Ziambaras, T.; Papanastasiou, D.A. Transplacentally Transmitted Congenital Brucellosis Due to Brucella abortus. J. Infect. 2002, 45, 209–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaif, M.; Dabelah, K.; Girim, H.; Featherstone, R.; Robinson, J.L. Congenital Brucellosis: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2018, 18, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benirschke, P.; Kaufmann, K. Pathology of the Human Placenta, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Gellersen, B.; Brosens, J.J. Cyclic Decidualization of the Human Endometrium in Reproductive Health and Failure. Endocr. Rev. 2014, 35, 851–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancy, P.; Tagliani, E.; Tay, C.S.; Asp, P.; Levy, D.E.; Erlebacher, A. Chemokine Gene Silencing in Decidual Stromal Cells Limits T Cell Access to the Maternal-Fetal Interface. Science 2012, 336, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.R.; Wang, S.C.; Li, D.J. The Integrative Roles of Chemokines at the Maternal-Fetal Interface in Early Pregnancy. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 11, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, J.R.; Bakardjiev, A.I. Pathogens and the Placental Fortress. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelletti, M.; Presicce, P.; Feiyang, M.; Senthamaraikannan, P.; Miller, L.A.; Pellegrini, M.; Sim, M.S.; Jobe, A.H.; Divanovic, S.; Way, S.S.; et al. The Induction of Preterm Labor in Rhesus Macaques Is Determined by the Strength of Immune Response to Intrauterine Infection. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3001385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumelou, S.; Wheelhouse, N.; Cuschieri, K.; Entrican, G.; Howie, S.E.M.; Horne, A.W. The Role of Infection in Miscarriage. Hum. Reprod. Updat. 2016, 22, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, C.; Tibaldi, C.; Marozio, L.; Marini, S.; Masuelli, G.; Pelissetto, S.; Sozzani, P.; Latino, M.A. Cervicovaginal Infections during Pregnancy: Epidemiological and Microbiological Aspects. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2004, 16 (Suppl. 2), 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aflatoonian, R.; Tuckerman, E.; Elliott, S.L.; Bruce, C.; Aflatoonian, A.; Li, T.C.; Fazeli, A. Menstrual Cycle-Dependent Changes of Toll-like Receptors in Endometrium. Hum. Reprod. 2007, 22, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, T.; Osuga, Y.; Hamasaki, K.; Hirota, Y.; Nose, E.; Morimoto, C.; Harada, M.; Takemura, Y.; Koga, K.; Yoshino, O.; et al. Expression of Toll-like Receptors 2, 3, 4, and 9 Genes in the Human Endometrium during the Menstrual Cycle. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2007, 74, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salker, M.; Teklenburg, G.; Molokhia, M.; Lavery, S.; Trew, G.; Aojanepong, T.; Mardon, H.J.; Lokugamage, A.U.; Rai, R.; Landles, C.; et al. Natural Selection of Human Embryos: Impaired Decidualization of Endometrium Disables Embryo-Maternal Interactions and Causes Recurrent Pregnancy Loss. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Tessier, C.; Prigent-Tessier, A.; Li, F.; Buzzio, O.L.; Callegari, E.A.; Horseman, N.D.; Gibori, G. Decidual Prolactin Silences the Expression of Genes Detrimental to Pregnancy. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 2326–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durairaj, R.R.P.; Aberkane, A.; Polanski, L.; Maruyama, Y.; Baumgarten, M.; Lucas, E.S.; Quenby, S.; Chan, J.K.Y.; Raine-Fenning, N.; Brosens, J.J.; et al. Deregulation of the Endometrial Stromal Cell Secretome Precedes Embryo Implantation Failure. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2017, 23, 478–487, Erratum in Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2017, 23, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giakoumelou, S.; Wheelhouse, N.; Brown, J.; Wade, J.; Simitsidellis, I.; Gibson, D.; Saunders, P.T.K.; Horner, P.; Entrican, G.; Howie, S.E.M.; et al. Chlamydia Trachomatis Infection of Human Endometrial Stromal Cells Induces Defective Decidualisation and Chemokine Release. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavattieri, L.; Ferrero, M.C.; Paiva, I.M.A.; Sotelo, A.D.; Canellada, A.M.; Baldi, P.C. Brucella abortus Proliferates in Decidualized and Non-Decidualized Human Endometrial Cells Inducing a Proinflammatory Response. Pathogens 2020, 9, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yin, J.; Xu, Q.; Wang, T.; Jin, Y.; Wang, A. Lipopolysaccharides of Brucella suis S2 Impaired the Process of Decidualization in Early Pregnancy in Mice. Toxins 2023, 15, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, S.A.; Faustman, D.L.; Adams, L.G.; Garcia-Gonzalez, D.G.; Hensel, M.E.; Khalaf, O.H.; Arenas-Gamboa, A.M. Brucella abortus and Pregnancy in Mice: Impact of Chronic Infection on Fertility and the Role of Regulatory T Cells in Tissue Colonization. Infect. Immun. 2020, 88, e00257-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, G.; Jahans, K.L.; Reid, R.J.; Ross, H.M. Isolation of Brucella Species from Cetaceans, Seals and an Otter. Vet. Rec. 1996, 138, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smither, S.J.; Perkins, S.D.; Davies, C.; Stagg, A.J.; Nelson, M.; Atkins, H.S. Development and Characterization of Mouse Models of Infection with Aerosolized Brucella melitensis and Brucella suis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2009, 16, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Renzo, G.C.; Giardina, I.; Clerici, G.; Brillo, E.; Gerli, S. Progesterone in Normal and Pathological Pregnancy. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2016, 27, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreshkova, T.; Dimitrov, R.; Mourdjeva, M. A Cross-Talk of Decidual Stromal Cells, Trophoblast, and Immune Cells: A Prerequisite for the Success of Pregnancy. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2012, 68, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Sang, Y.; Li, D.J.; Du, M. Crosstalk Between Trophoblasts and Decidual Immune Cells: The Cornerstone of Maternal-Fetal Immunotolerance. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.L.; Lam, K.K.W.; Koistinen, H.; Seppala, M.; Kurpisz, M.; Fernandez, N.; Pang, R.T.K.; Yeung, W.S.B.; Chiu, P.C.N. Glycodelin-A as a Paracrine Regulator in Early Pregnancy. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2011, 90, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellersen, B.; Reimann, K.; Samalecos, A.; Aupers, S.; Bamberger, A.M. Invasiveness of Human Endometrial Stromal Cells Is Promoted by Decidualization and by Trophoblast-Derived Signals. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 25, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMaster, M.T.; Zhou, Y.; Fisher, S.J. Abnormal Placentation and the Syndrome of Preeclampsia. Semin. Nephrol. 2004, 24, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Godbole, G.; Modi, D. Decidual Control of Trophoblast Invasion. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2016, 75, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, A.P.; Gaddy, J.A.; Doster, R.S.; Aronoff, D.M. Current Concepts in Maternal-Fetal Immunology: Recognition and Response to Microbial Pathogens by Decidual Stromal Cells. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2017, 77, e12623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramhorst, R.; Grasso, E.; Paparini, D.; Hauk, V.; Gallino, L.; Calo, G.; Vota, D.; Leirós, C.P. Decoding the Chemokine Network That Links Leukocytes with Decidual Cells and the Trophoblast during Early Implantation. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2016, 10, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viganò, P.; Mangioni, S.; Pompei, F.; Chiodo, I. Maternal-Conceptus Cross Talk—A Review. Placenta 2003, 24, S56–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, L.G.; Lash, G.E.; Murray-Dunning, C.; Bulmer, J.N.; Innes, B.A.; Searle, R.F.; Sass, N.; Robson, S.C. Role of Interleukin 8 in Uterine Natural Killer Cell Regulation of Extravillous Trophoblast Cell Invasion. Placenta 2010, 31, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitman, H.; Innes, B.A.; Robson, S.C.; Bulmer, J.N.; Lash, G.E. Altered Expression of Interleukin-6, Interleukin-8 and Their Receptors in Decidua of Women with Sporadic Miscarriage. Hum. Reprod. 2013, 28, 2075–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchi, R.; Sotelo, A.D.; Parrado, A.C.; Salaverry, L.S.; Blanco, G.A.; Castro, M.S.; Rey-Roldán, E.B.; Canellada, A.M. Losartan Impairs HTR-8/SVneo Trophoblast Migration through Inhibition of Angiotensin II-Induced pro-Inflammatory Profile in Human Endometrial Stromal Cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2023, 461, 116383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, M.; Stefanoska, I.; Radojčić, L.; Vićovac, L. Interleukin-8 (CXCL8) Stimulates Trophoblast Cell Migration and Invasion by Increasing Levels of Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)2 and MMP9 and Integrins A5 and B1. Reproduction 2010, 139, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, B.J.; Han, J.W.; Kim, R.H.; Yun, S.; Kim, T.H.; Hur, S.E.; Kim, C.J.; Lee, S.K. Activation of NOD-1/JNK/IL-8 Signal Axis in Decidual Stromal Cells Facilitates Trophoblast Invasion. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2017, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.Y.; Du, M.R.; Guo, P.F.; He, X.J.; Zhou, W.H.; Zhu, X.Y.; Li, D.J. Regulation of C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2 and Its Receptor in Human Decidual Stromal Cells by Pregnancy-Associated Hormones in Early Gestation. Hum. Reprod. 2007, 22, 2733–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.X.; Jin, L.P.; Xu, B.; Liang, S.S.; Li, D.J. Decidual Stromal Cells Recruit Th17 Cells into Decidua to Promote Proliferation and Invasion of Human Trophoblast Cells by Secreting IL-17. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 11, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Shi, J.L.; Chen, M.; Zheng, Z.M.; Li, M.Q.; Shao, J. CCL2: An Important Cytokine in Normal and Pathological Pregnancies: A Review. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1053457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, N.; Weng, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, L.; Iqbal, F.; Yin, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, Y. TLRs Induce Th1/Th2 Responses by Affecting the Secretion of CCL2 at the Maternal-Foetal Interface. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 100, 108070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakumoto, R.; Hayashi, K.G.; Fujii, S.; Kanahara, H.; Hosoe, M.; Furusawa, T.; Kizaki, K. Possible Roles of CC- and CXC-Chemokines in Regulating Bovine Endometrial Function during Early Pregnancy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Li, W.; Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Deng, M.; Zhang, S.; Ren, X.; Wu, T.; Xia, J.; Cheng, B.; et al. Targeting CCL2-CCR4 Axis Suppress Cell Migration of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.M.; Hou, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.Y. CCL17 Induces Trophoblast Migration and Invasion by Regulating Matrix Metalloproteinase and Integrin Expression in Human First-Trimester Placenta. Reprod. Sci. 2014, 193371911351917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Guo, D.; Yin, T.; Yang, J. M2 Macrophage-Derived G-CSF Promotes Trophoblasts EMT, Invasion and Migration via Activating PI3K/Akt/Erk1/2 Pathway to Mediate Normal Pregnancy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 2136–2147, Erratum in J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 4742–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, M.; Vićovac, L. Interleukin-6 Stimulates Cell Migration, Invasion and Integrin Expression in HTR-8/SVneo Cell Line. Placenta 2009, 30, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo, R.; Ponce, M.L.; Young, H.A.; Wasserman, K.; Ward, J.M.; Kleinman, H.K.; Oppenheim, J.J.; Murphy, W.J. Human Endothelial Cells Express CCR2 and Respond to MCP-1: Direct Role of MCP-1 in Angiogenesis and Tumor Progression. Blood 2000, 96, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brünnert, D.; Kumar, V.; Kaushik, V.; Ehrhardt, J.; Chahar, K.R.; Sharma, P.K.; Zygmunt, M.; Goyal, P. Thrombin Impairs the Angiogenic Activity of Extravillous Trophoblast Cells via Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1 (MCP-1): A Possible Link with Preeclampsia. Reprod. Biol. 2021, 21, 100516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Dubey, S.; Varney, M.L.; Dave, B.J.; Singh, R.K. IL-8 Directly Enhanced Endothelial Cell Survival, Proliferation, and Matrix Metalloproteinases Production and Regulated Angiogenesis. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 3369–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, M.K.; Basak, S.; Ahmed, M.S.; Attramadal, H.; Duttaroy, A.K. Connective Tissue Growth Factor Induces Tube Formation and IL-8 Production in First Trimester Human Placental Trophoblast Cells. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2014, 181, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavarna, T.; Wolfe, B.; Wu, X.J.; Reyes, L. Porphyromonas Gingivalis-Mediated Disruption in Spiral Artery Remodeling Is Associated with Altered Uterine NK Cell Populations and Dysregulated IL-18 and Htra1. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grewal, S.; Carver, J.G.; Ridley, A.J.; Mardon, H.J. Implantation of the Human Embryo Requires Rac1-Dependent Endometrial Stromal Cell Migration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16189–16194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboussahoud, W.; Bruce, C.; Elliott, S.; Fazeli, A. Activation of Toll-like Receptor 5 Decreases the Attachment of Human Trophoblast Cells to Endometrial Cells in Vitro. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 25, 2217–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Lopez, J.A.; Caballero, I.; Montazeri, M.; Maslehat, N.; Elliott, S.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, R.; Calle, A.; Gutierrez-Adan, A.; Fazeli, A. Local Activation of Uterine Toll-like Receptor 2 and 2/6 Decreases Embryo Implantation and Affects Uterine Receptivity in Mice. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 90, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeschke, U.; Richter, D.U.; Möbius, B.M.; Briese, V.; Mylonas, I.; Friese, K. Stimulation of Progesterone, Estradiol and Cortisol in Trophoblast Tumor BeWo Cells by Glycodelin A N-Glycans. Anticancer. Res. 2007, 27, 2101–2108. [Google Scholar]
- Krikun, G.; Mor, G.; Alvero, A.; Guller, S.; Schatz, F.; Sapi, E.; Rahman, M.; Caze, R.; Qumsiyeh, M.; Lockwood, C.J. A Novel Immortalized Human Endometrial Stromal Cell Line with Normal Progestational Response. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 2291–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straszewski-Chavez, S.L.; Abrahams, V.M.; Alvero, A.B.; Aldo, P.B.; Ma, Y.; Guller, S.; Romero, R.; Mor, G. The Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Telomerase Immortalized First Trimester Trophoblast Cell Line, Swan 71. Placenta 2009, 30, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, E.; Gori, S.; Paparini, D.; Soczewski, E.; Fernández, L.; Gallino, L.; Salamone, G.; Martinez, G.; Irigoyen, M.; Ruhlmann, C.; et al. VIP Induces the Decidualization Program and Conditions the Immunoregulation of the Implantation Process. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 460, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattila, S.; Kleefeldt, F.; Ballesteros, A.; Beltrame, J.S.; Ribeiro, M.L.; Ergün, S.; Dveksler, G. Pro-Angiogenic Effects of Pregnancy-Specific Glycoproteins in Endothelial and Extravillous Trophoblast Cells. Reproduction 2020, 160, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattila, S.; Dunk, C.E.; Im, M.; Grichenko, O.; Zhou, Y.; Cohen, M.; Yanez-Mo, M.; Blois, S.M.; Yamada, K.M.; Erez, O.; et al. Interaction of Pregnancy-Specific Glycoprotein 1 with Integrin A5β1 Is a Modulator of Extravillous Trophoblast Functions. Cells 2019, 8, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmberg, J.C.; Haddad, S.; Wünsche, V.; Yang, Y.; Aldo, P.B.; Gnainsky, Y.; Granot, I.; Dekel, N.; Mor, G. An in Vitro Model for the Study of Human Implantation. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2012, 67, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zavattieri, L.; Macchi, R.; Canellada, A.M.; Pibuel, M.A.; Poodts, D.; Ferrero, M.C.; Baldi, P.C. Brucella-Induced Impairment of Decidualization and Its Impact on Trophoblast Function and Inflammatory Profile. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178189
Zavattieri L, Macchi R, Canellada AM, Pibuel MA, Poodts D, Ferrero MC, Baldi PC. Brucella-Induced Impairment of Decidualization and Its Impact on Trophoblast Function and Inflammatory Profile. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178189
Chicago/Turabian StyleZavattieri, Lucía, Rosario Macchi, Andrea Mercedes Canellada, Matías Arturo Pibuel, Daniela Poodts, Mariana Cristina Ferrero, and Pablo Cesar Baldi. 2025. "Brucella-Induced Impairment of Decidualization and Its Impact on Trophoblast Function and Inflammatory Profile" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178189
APA StyleZavattieri, L., Macchi, R., Canellada, A. M., Pibuel, M. A., Poodts, D., Ferrero, M. C., & Baldi, P. C. (2025). Brucella-Induced Impairment of Decidualization and Its Impact on Trophoblast Function and Inflammatory Profile. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178189







