Shared Risk Factors and Molecular Mechanisms Between Aortic Stenosis and Atherosclerosis: A Rationale for Therapeutic Repositioning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Risk Factors
4. Mechanisms
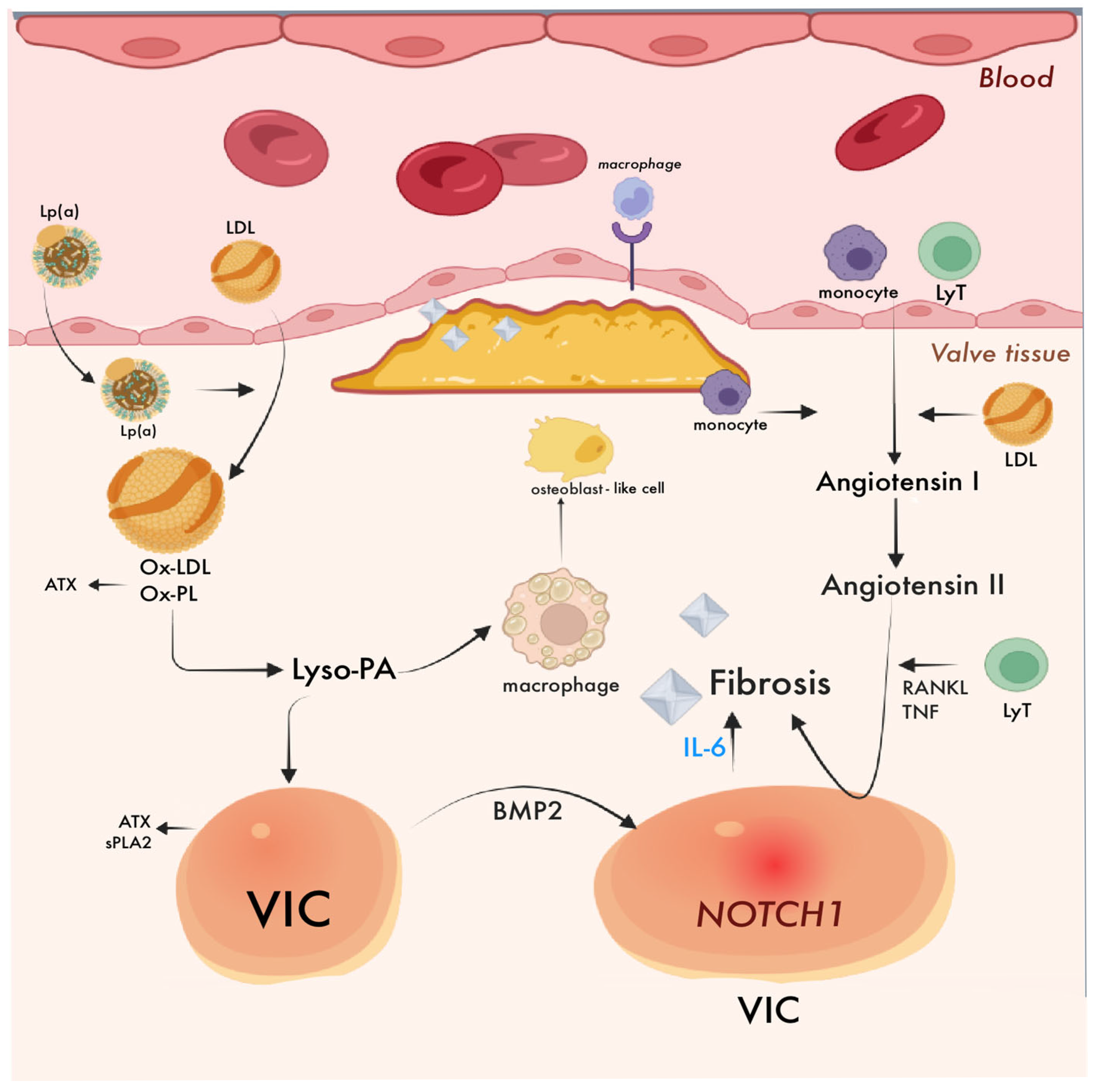
4.1. Aortic Stenosis and Atherosclerosis
4.1.1. Shared Pathological Features
4.1.2. Differentiating Mechanisms from Atherosclerosis
4.2. Aortic Stenosis: Pathogenesis
4.2.1. Endothelial Dysfunction
4.2.2. Oxidative Stress and Lipid Deposits
4.2.3. Inflammation and Fibrosis
4.2.4. Differentiation and Osteogenic Calcification
4.2.5. Angiogenesis and Hemorrhage
4.2.6. Shear Stress
4.2.7. Genetic Predisposition and Visceral Obesity
4.3. The Role of Plasma Biomarkers in Moderate-to-Severe Aortic Stenosis
5. Pharmaceutical Therapies Targeting Both Atherosclerosis and Aortic Stenosis
5.1. PCSK9 Inhibitors (Evolocumab, Alirocumab)
5.2. Lp(a)-Lowering RNA-Based Therapies
5.3. Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System (RAAS) Inhibitors
5.4. DPP-4 Inhibitors
5.5. Vitamin K Supplementation
5.6. Denosumab (Anti-RANKL Monoclonal Antibody)
5.7. Statins—A Cautionary Note
5.8. NOX2 Inhibition—Celastrol
5.9. Soluble Guanylate Cyclase (sGC) Activators—Ataciguat
5.10. Cadherin-11 Blockade—SYN0012
5.11. Notch1 Stabilizers—XCT790
5.12. P2Y2 Receptor Agonists
5.13. Conclusions and Translational Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| AGEs | advanced glycation end products |
| ANGII | angiotensin II |
| ARBs | angiotensin receptor blockers |
| Apo(a) | apolipoprotein(a) |
| ApoB | apolipoprotein B-100 |
| AS | aortic stenosis |
| ATP | adenosine triphosphate |
| BMP-2 | bone morphogenetic protein-2 |
| BP | blood pressure |
| CAVD | calcific aortic valve disease |
| CAVS | calcific aortic valve stenosis |
| CDH11 | cadherin-11 |
| cGMP | cyclic guanosine monophosphate |
| DPP-4 | dipeptidyl peptidase-4 |
| DRP1 | dynamin-related protein 1 |
| EndMT | mesenchymal cells |
| FGF2 | Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 |
| GIP | glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide |
| GLP-1 | glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| HDL | high-density lipoprotein |
| IGF-1 | insulin growth factor-1 |
| IL-1β | interleukin-1 beta |
| IMT | intima-media thickness |
| LDL | low-density lipoprotein |
| Lp(a) | lipoprotein(a) |
| Lp-PLA2 | lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 |
| Lrp5 | Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 5 |
| LRR | leucine-rich repeat |
| MACE | major adverse cardiovascular events |
| MGP | matrix Gla-protein |
| MMPs | matrix metalloproteinases |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NLRP3 | NOD-, LRR-, and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 |
| NADPH | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| NOD | nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain |
| NOX2 | NADPH oxidase 2 |
| OPG | osteoprotegerin |
| Ox-LDL | oxidized low-density lipoprotein |
| OxPL-apoB | oxidized phospholipids associated with apolipoprotein B |
| OxPL | oxidized phospholipids |
| PCSK9 | proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 |
| RAAS | renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system |
| RANK | receptor activator of nuclear factor kB |
| RANKL | receptor activator of nuclear factor kB ligand |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| RUNX2 | runt-related transcription factor 2 |
| sGC | soluble guanylate cyclase |
| TAVI | transcatheter aortic valve implantation |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| TZDs | thiazolidinediones |
| UTP | uridine triphosphate |
| VECs | endothelial valve cells |
| VICs | valvular interstitial cells |
| VKAs | vitamin K antagonists |
| VSMCs | vascular smooth muscle cells |
References
- Jayalath, R.W.; Mangan, S.H.; Golledge, J. Aortic Calcification. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2005, 30, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.T.; Koh, M.; Chan, K.K.; Guo, H.; Alter, D.A.; Austin, P.C.; Tu, J.V.; Wijeysundera, H.C.; Ko, D.T. Association Between Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Aortic Stenosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Engert, J.C.; Thanassoulis, G. Risk Factors for Valvular Calcification. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2019, 26, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggiano, P.; Antonini-Canterin, F.; Baldessin, F.; Lorusso, R.; D’Aloia, A.; Cas, L.D. Epidemiology and Cardiovascular Risk Factors of Aortic Stenosis. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2006, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.D. Pathogenesis of Calcific Aortic Valve Disease: A Disease Process Comes of Age (and a Good Deal More). ATVB 2006, 26, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Dina, C.; Small, A.M.; Shaffer, C.M.; Levinson, R.T.; Helgadóttir, A.; Capoulade, R.; Munter, H.M.; Martinsson, A.; Cairns, B.J.; et al. Dyslipidemia, Inflammation, Calcification, and Adiposity in Aortic Stenosis: A Genome-Wide Study. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 1927–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.H.; Younis, N.; Abdallah, R.; Shaer, F.; Dakroub, A.; Ayoub, M.A.; Iratni, R.; Yassine, H.M.; Zibara, K.; Orekhov, A.; et al. Lipid-Lowering Therapies for Atherosclerosis: Statins, Fibrates, Ezetimibe and PCSK9 Monoclonal Antibodies. CMC 2021, 28, 7427–7445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dweck, M.R.; Khaw, H.J.; Sng, G.K.Z.; Luo, E.L.C.; Baird, A.; Williams, M.C.; Makiello, P.; Mirsadraee, S.; Joshi, N.V.; Van Beek, E.J.R.; et al. Aortic Stenosis, Atherosclerosis, and Skeletal Bone: Is There a Common Link with Calcification and Inflammation? Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Nezet, E.; Marqueze-Pouey, C.; Guisle, I.; Clavel, M.-A. Molecular Features of Calcific Aortic Stenosis in Female and Male Patients. CJC Open 2024, 6, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tastet, L.; Capoulade, R.; Clavel, M.-A.; Larose, É.; Shen, M.; Dahou, A.; Arsenault, M.; Mathieu, P.; Bédard, É.; Dumesnil, J.G.; et al. Systolic Hypertension and Progression of Aortic Valve Calcification in Patients with Aortic Stenosis: Results from the PROGRESSA Study. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 18, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Wu, S.; Yang, Y.; Yue, X. Modified Effect of Active or Passive Smoking on the Association between Age and Abdominal Aortic Calcification: A Nationally Representative Cross-Sectional Study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e047645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gać, P.; Martuszewski, A.; Paluszkiewicz, P.; Poręba, M.; Mazur, G.; Poręba, R. Aortic Valve Calcification Score in Patients with Arterial Hypertension Environmentally Exposed to Tobacco Smoke. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2021, 21, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattazzi, M.; Bertacco, E.; Del Vecchio, A.; Puato, M.; Faggin, E.; Pauletto, P. Aortic Valve Calcification in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 2968–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, M.; Owada, T.; Yamauchi, H.; Misaka, T.; Machii, H.; Yamaki, T.; Sugimoto, K.; Kunii, H.; Nakazato, K.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Predominance of Abdominal Visceral Adipose Tissue Reflects the Presence of Aortic Valve Calcification. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2174657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anger, T.; Carson, W.; Weyand, M.; Daniel, W.G.; Hoeher, M.; Garlichs, C.D. Atherosclerotic Inflammation Triggers Osteogenic Bone Transformation in Calcified and Stenotic Human Aortic Valves: Still a Matter of Debate. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 86, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgorbini, L.; Scuteri, A.; Leggio, M.; Gianni, W.; Nevola, E.; Leggio, F. Carotid Intima–Media Thickness, Carotid Distensibility and Mitral, Aortic Valve Calcification: A Useful Diagnostic Parameter of Systemic Atherosclerotic Disease. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2007, 8, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.I.; Sakuma, I.; Sohn, I.S.; Jo, S.-H.; Koh, K.K. Inflammatory and Metabolic Mechanisms Underlying the Calcific Aortic Valve Disease. Atherosclerosis 2018, 277, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, F.E.C.M.; Meex, S.J.R.; Dweck, M.R.; Aikawa, E.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; Schurgers, L.J.; Kietselaer, B.L.J.H. Calcific Aortic Valve Stenosis: Hard Disease in the Heart. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 2618–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindman, B.R.; Sukul, D.; Dweck, M.R.; Madhavan, M.V.; Arsenault, B.J.; Coylewright, M.; Merryman, W.D.; Newby, D.E.; Lewis, J.; Harrell, F.E.; et al. Evaluating Medical Therapy for Calcific Aortic Stenosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 78, 2354–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.; Muth, A.N.; Ransom, J.F.; Schluterman, M.K.; Barnes, R.; King, I.N.; Grossfeld, P.D.; Srivastava, D. Mutations in NOTCH1 Cause Aortic Valve Disease. Nature 2005, 437, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-Y.; Kong, X.-Q.; Zhang, J.-J. Pathological Mechanism and Treatment of Calcified Aortic Stenosis. Cardiol. Rev. 2024, 32, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.; Kim, E.-Y.; Kim, J.-E.; Oh, S.; Park, S.-O.; Kim, S.-M.; Choi, H.; Song, J.-K.; Chang, E.-J. Evogliptin Suppresses Calcific Aortic Valve Disease by Attenuating Inflammation, Fibrosis, and Calcification. Cells 2021, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyamurthy, I.; Alex, S. Calcific Aortic Valve Disease: Is It Another Face of Atherosclerosis? Indian Heart J. 2015, 67, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.M.; Shah, J.; Lakey, S.M.; Garg, P.; Ripley, D.P. Pathophysiology, Emerging Techniques for the Assessment and Novel Treatment of Aortic Stenosis. Open Heart 2023, 10, e002244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, V.; Leosco, D.; Ferro, G.; Bevilacqua, A.; Pagano, G.; De Lucia, C.; Perrone Filardi, P.; Caruso, A.; Rengo, G.; Ferrara, N. The Lipid Theory in the Pathogenesis of Calcific Aortic Stenosis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, N.; Jha, K.; Razavi, A.C.; Boakye, E.; Anchouche, K.; Dzaye, O.; Budoff, M.J.; Tsai, M.Y.; Shah, S.J.; Rotter, J.I.; et al. Identifying People at High Risk for Severe Aortic Stenosis: Aortic Valve Calcium Versus Lipoprotein(a) and Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2024, 17, e016372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Eckardstein, A.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Remaley, A.T.; Catapano, A.L. High-Density Lipoprotein Revisited: Biological Functions and Clinical Relevance. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 1394–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, C.; Feng, D.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Niu, G.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ye, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. Association between Lipoprotein(a) and Long-Term Prognosis in Patients Receiving Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2025, 19, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, F.D.; Giugliano, R.P. Lipoprotein(a) and Its Significance in Cardiovascular Disease: A Review. JAMA Cardiol. 2022, 7, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Zahir, R.S.; Dominguez, A.C.; Romeo, F.J. Role of Lipoprotein (A) in Aortic Valve Stenosis: Novel Disease Mechanisms and Emerging Pharmacotherapeutic Approaches. IJC Heart Vasc. 2024, 55, 101543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Soffer, G.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Berglund, L.; Duell, P.B.; Heffron, S.P.; Kamstrup, P.R.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Marcovina, S.M.; Yeang, C.; Koschinsky, M.L. Lipoprotein(a): A genetically determined, causal, and prevalent risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2022, 42, E48–E60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronenberg, F.; Mora, S.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Ference, B.A.; Arsenault, B.J.; Berglund, L.; Dweck, M.R.; Koschinsky, M.; Lambert, G.; Mach, F.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease and Aortic Stenosis: A European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Statement. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3925–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phua, K.; Chew, N.W.; Kong, W.K.; Tan, R.-S.; Ye, L.; Poh, K.-K. The Mechanistic Pathways of Oxidative Stress in Aortic Stenosis and Clinical Implications. Theranostics 2022, 12, 5189–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Enriquez-Sarano, M.; Schaff, H.V.; Michelena, H.I.; Roos, C.M.; Hagler, M.A.; Zhang, H.; Casaclang-Verzosa, G.; Huang, R.; Bartoo, A.; et al. Reactivation of Oxidized Soluble Guanylate Cyclase as a Novel Treatment Strategy to Slow Progression of Calcific Aortic Valve Stenosis: Preclinical and Randomized Clinical Trials to Assess Safety and Efficacy. Circulation 2025, 151, 913–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Yao, D.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, T.; Shen, Q.; Tong, F.; Qian, X.; Xu, L.; Jiang, C.; Dong, N. Beyond VICs: Shedding Light on the Overlooked VECs in Calcific Aortic Valve Disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, G.; Su, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Hu, D.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Lin, Y.; Wen, L.; Lin, X.; et al. Activation of Piezo1 Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Aortic Valve Interstitial Cell through YAP-Dependent Glutaminolysis. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg0478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, S.-A.; Choi, B.; Kim, Y.-J.; Oh, S.J.; Choi, H.-M.; Kim, E.K.; Kim, D.-H.; Cho, G.-Y.; Song, J.-M.; et al. Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibition to Prevent Progression of Calcific Aortic Stenosis. Heart 2020, 106, 1824–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.-M.; Lee, E.-J.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, D.-H.; Jang, J.Y.; Kang, S.-W.; Lee, K.-U.; Chang, E.-J.; et al. Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Induces Aortic Valve Calcification by Inhibiting Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Signaling in Valvular Interstitial Cells. Circulation 2017, 135, 1935–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saku, K.; Tahara, N.; Takaseya, T.; Otsuka, H.; Takagi, K.; Shojima, T.; Shintani, Y.; Zaima, Y.; Kikusaki, S.; Fukuda, T.; et al. Pathological Role of Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products in Calcified Aortic Valve Stenosis. JAHA 2020, 9, e015261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banovic, M.; Athithan, L.; McCann, G.P. Aortic Stenosis and Diabetes Mellitus: An Ominous Combination. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2019, 16, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wal, P.; Rathore, S.; Aziz, N.; Singh, Y.K.; Gupta, A. Aortic Stenosis: A Review on Acquired Pathogenesis and Ominous Combination with Diabetes Mellitus. Egypt. Heart J. 2023, 75, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, C.; Fucile, I.; Lembo, M.; Manzi, M.V.; Ilardi, F.; Franzone, A.; Mancusi, C. Arterial Hypertension in Aortic Valve Stenosis: A Critical Update. JCM 2021, 10, 5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, S.; Scalise, F.; Chambers, J.B.; Mancia, G. Hypertension in Aortic Stenosis: A Focused Review and Recommendations for Clinical Practice. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelamegham, S.; Canty, J.M. Anemia, Increased Shear Stress, and the Progression of Aortic Stenosis. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2024, 9, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Dong, N.; Hui, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Xu, L.; Liu, M.; Rao, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Shang, Y.; et al. Endothelial Cell-Derived Tetrahydrobiopterin Prevents Aortic Valve Calcification. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 1652–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuruda, T.; Funamoto, T.; Suzuki, C.; Yamamura, Y.; Nakai, M.; Chosa, E.; Kaikita, K. Increasing Baseline Aortic Valve Peak Flow Velocity Is Associated with Progression of Aortic Valve Stenosis in Osteoporosis Patients—A Possible Link to Low Vitamin D Status. Arch. Osteoporos. 2023, 18, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrow, P.P. Aortic Stenosis: New Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Future Perspectives for Pharmacological Therapy. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2016, 126, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetkin, E.; Waltenberger, J. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Aortic Stenosis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2009, 135, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattazzi, M.; Faggin, E.; Bertacco, E.; Buso, R.; Puato, M.; Plebani, M.; Zaninotto, M.; Condotta, D.; Zoppellaro, G.; Pagliani, L.; et al. RANKL Expression Is Increased in Circulating Mononuclear Cells of Patients with Calcific Aortic Stenosis. J. Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. 2018, 11, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerman, D.A.; Prasad, S.; Alotti, N. Denosumab Could Be a Potential Inhibitor of Valvular Interstitial Cells Calcification In Vitro. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goody, P.R.; Hosen, M.R.; Christmann, D.; Niepmann, S.T.; Zietzer, A.; Adam, M.; Bönner, F.; Zimmer, S.; Nickenig, G.; Jansen, F. Aortic Valve Stenosis: From Basic Mechanisms to Novel Therapeutic Targets. ATVB 2020, 40, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, D.; Prendergast, B. Aortic Stenosis—Pathogenesis, Prediction of Progression, and Percutaneous Intervention. J. R. Coll. Physicians Edinb. 2017, 47, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokollari, A.; Sá, M.P.; Sicouri, S.; Ramlawi, B.; Torregrossa, G.; Bonacchi, M. Commentary: Osteogenic Metaplasia of the Aortic Valve. Do Bacteria, Diabetes, and Dyslipidemia Play a Role? Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2022, 34, 1178–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, C.J.; Dalgaard, F.; Bellinge, J.W.; Murray, K.; Sim, M.; Connolly, E.; Blekkenhorst, L.C.; Bondonno, C.P.; Lewis, J.R.; Gislason, G.H.; et al. Dietary Vitamin K1 Intake and Incident Aortic Valve Stenosis. ATVB 2024, 44, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilla, L.; Martín-Núñez, E.; Garaikoetxea, M.; Navarro, A.; Vico, J.A.; Arrieta, V.; García-Peña, A.; Fernández-Celis, A.; Gainza, A.; Álvarez, V.; et al. Characterization of the Sex-Specific Pattern of Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis in Aortic Stenosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 971802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronow, W.S. Hypertension, Aortic Stenosis, and Aortic Regurgitation. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutikhin, A.G.; Yuzhalin, A.E.; Brusina, E.B.; Ponasenko, A.V.; Golovkin, A.S.; Barbarash, O.L. Genetic Predisposition to Calcific Aortic Stenosis and Mitral Annular Calcification. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 5645–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakos, C.I.; Grassos, C.A.; Papadopoulos, D.P.; Dimitriadis, K.S.; Tsioufis, C.P.; Tousoulis, D. Arterial Hypertension and Aortic Valve Stenosis: Shedding Light on a Common "Liaison". Hell. J. Cardiol. 2017, 58, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurgens, S.; Ramo, J.T.; Kany, S.; Choi, S.H.; Wang, X.; Khurshid, S.; Ellinor, P.T.; Pirruccello, J.P. Rare Genetic Variants in LDLR, APOB, and PCSK9 Are Associated with Aortic Stenosis. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Kim, K.H.; Chun, K.J.; Lee, B.-K.; Cho, B.-R.; Ryu, D.R. Impact of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol on Progression of Aortic Valve Sclerosis and Stenosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1171703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Rodriguez, A.; Schroeder, M.E.; Grim, J.C.; Walker, C.J.; Speckl, K.F.; Weiss, R.M.; Anseth, K.S. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Promotes and Exacerbates Calcification in Heart Valve Myofibroblast Populations. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasipoularides, A. Calcific Aortic Valve Disease: Part 1—Molecular Pathogenetic Aspects, Hemodynamics, and Adaptive Feedbacks. J. Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. 2016, 9, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, P.N.; Kanhouche, G.; Rosa, V.E.E.; Campos, C.M.; Lopes, M.P.; Lopes, M.A.A.A.D.M.; Sampaio, R.O.; Brito Júnior, F.S.D.; Tarasoutchi, F.; Abizaid, A.A.C. B-Type Natriuretic Peptide and N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide in Severe Aortic Stenosis: A Comprehensive Literature Review. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1182530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphalen, J. Usefulness of Serial B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Assessment in Asymptomatic Aortic Stenosis. J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 47, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrot, N.; Thériault, S.; Rigade, S.; Chen, H.Y.; Dina, C.; Martinsson, A.; Boekholdt, S.M.; Capoulade, R.; Le Tourneau, T.; Messika-Zeitoun, D.; et al. Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A2 Activity, Genetics and Calcific Aortic Valve Stenosis in Humans. Heart 2020, 106, 1407–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oury, C.; Côté, N.; Clavel, M.-A. Biomarkers Associated with Aortic Stenosis and Structural Bioprosthesis Dysfunction. Cardiol. Clin. 2020, 38, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatine, M.S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Keech, A.C.; Honarpour, N.; Wiviott, S.D.; Murphy, S.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Wasserman, S.M.; et al. Evolocumab and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, G.G.; Szarek, M.; Bittner, V.A.; Diaz, R.; Goodman, S.G.; Jukema, J.W.; Landmesser, U.; López-Jaramillo, P.; Manvelian, G.; Pordy, R.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) and Benefit of PCSK9 Inhibition in Patients With Nominally Controlled LDL Cholesterol. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 78, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, J.; Stolarz, A.; Zhang, H.; Boerma, M.; Byrum, S.D.; Rusch, N.J.; Ding, Z. PCSK9 Attenuates Efferocytosis in Endothelial Cells and Promotes Vascular Aging. Theranostics 2023, 13, 2914–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capoulade, R.; Chan, K.L.; Yeang, C.; Mathieu, P.; Bossé, Y.; Dumesnil, J.G.; Tam, J.W.; Teo, K.K.; Mahmut, A.; Yang, X.; et al. Oxidized Phospholipids, Lipoprotein(a), and Progression of Calcific Aortic Valve Stenosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanassoulis, G.; Campbell, C.Y.; Owens, D.S.; Smith, J.G.; Smith, A.V.; Peloso, G.M.; Kerr, K.F.; Pechlivanis, S.; Budoff, M.J.; Harris, T.B.; et al. Genetic Associations with Valvular Calcification and Aortic Stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimikas, S.; Karwatowska-Prokopczuk, E.; Gouni-Berthold, I.; Tardif, J.-C.; Baum, S.J.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; Shapiro, M.D.; Stroes, E.S.; Moriarty, P.M.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) Reduction in Persons with Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viney, N.J.; Van Capelleveen, J.C.; Geary, R.S.; Xia, S.; Tami, J.A.; Yu, R.Z.; Marcovina, S.M.; Hughes, S.G.; Graham, M.J.; Crooke, R.M.; et al. Antisense Oligonucleotides Targeting Apolipoprotein(a) in People with Raised Lipoprotein(a): Two Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Ranging Trials. Lancet 2016, 388, 2239–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donoghue, M.L.; Rosenson, R.S.; Gencer, B.; López, J.A.G.; Lepor, N.E.; Baum, S.J.; Stout, E.; Gaudet, D.; Knusel, B.; Kuder, J.F.; et al. Small Interfering RNA to Reduce Lipoprotein(a) in Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmut, A.; Boulanger, M.-C.; El Husseini, D.; Fournier, D.; Bouchareb, R.; Després, J.-P.; Pibarot, P.; Bossé, Y.; Mathieu, P. Elevated Expression of Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A2 in Calcific Aortic Valve Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, M.A.; Aikawa, E. Cardiovascular Calcification: Artificial Intelligence and Big Data Accelerate Mechanistic Discovery. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghi, C.; Levy, B.I. Synergistic Actions between Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Statins in Atherosclerosis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznyak, A.V.; Bharadwaj, D.; Prasad, G.; Grechko, A.V.; Sazonova, M.A.; Orekhov, A.N. Renin-Angiotensin System in Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis and Treatment of CVD. IJMS 2021, 22, 6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillaert, M.A.; Lentjes, E.G.; Beygui, F.; Kemperman, H.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Nathoe, H.M.; Agostoni, P.; Voskuil, M.; Ivanes, F.; Jude, B.; et al. Measuring and Targeting Aldosterone and Renin in Atherosclerosis—A Review of Clinical Data. Am. Heart J. 2011, 162, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyunin, A.E.; Ovcharenko, E.A.; Barbarash, O.L. The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System as a Potential Target for Therapy in Patients with Calcific Aortic Stenosis: A Literature Review. Kardiologiia 2019, 59, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadir, M.A.; Wei, L.; Elder, D.H.J.; Libianto, R.; Lim, T.K.; Pauriah, M.; Pringle, S.D.; Doney, A.D.; Choy, A.-M.; Struthers, A.D.; et al. Impact of Renin-Angiotensin System Blockade Therapy on Outcome in Aortic Stenosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Shang, W. DPP-4 Inhibitor Linagliptin Ameliorates Oxidized LDL-Induced THP-1 Macrophage Foam Cell Formation and Inflammation. DDDT 2020, 14, 3929–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, E.M.; Tawfeek, W.M.; Hassanin, M.H.; Hassaballah, M.Y. Cardiovascular Protection by DPP-4 Inhibitors in Preclinical Studies: An Updated Review of Molecular Mechanisms. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2022, 395, 1357–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virta, J.; Hellberg, S.; Liljenbäck, H.; Ståhle, M.; Silvola, J.M.U.; Huusko, J.; Söderström, M.; Knuuti, J.; Nuutila, P.; Ylä-Herttuala, S.; et al. Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibition on Inflammation in Atherosclerosis: A 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Study of a Mouse Model of Atherosclerosis and Type 2 Diabetes. Atherosclerosis 2020, 305, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Luo, Y.R.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, S.H.; Chen, Y.D.; Tian, J.W.; Guo, Y. Sitagliptin, a Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor, Attenuates Apoptosis of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells and Reduces Atherosclerosis in Diabetic Apolipoprotein E–Deficient Mice. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2021, 140, 106854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diederichsen, A.C.P.; Lindholt, J.S.; Möller, S.; Øvrehus, K.A.; Auscher, S.; Lambrechtsen, J.; Hosbond, S.E.; Alan, D.H.; Urbonaviciene, G.; Becker, S.W.; et al. Vitamin K2 and D in Patients With Aortic Valve Calcification: A Randomized Double-Blinded Clinical Trial. Circulation 2022, 145, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meer, R.; Romero Prats, M.L.; Vervloet, M.G.; Van Der Schouw, Y.T.; De Jong, P.A.; Beulens, J.W.J. The Effect of Six-Month Oral Vitamin K Supplementation on Calcification Propensity Time in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Post Hoc Analysis of a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Atherosclerosis 2024, 394, 117307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasschaert, C.; Goss, C.J.; Pilkey, N.G.; McKeown, S.; Holden, R.M. Vitamin K Supplementation for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: Where Is the Evidence? A Systematic Review of Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geers, J.; Bing, R.; Pawade, T.A.; Doris, M.K.; Daghem, M.; Fletcher, A.J.; White, A.C.; Forsyth, L.; Evans, E.; Kwieciński, J.; et al. Effect of Denosumab or Alendronate on Vascular Calcification: Secondary Analysis of SALTIRE2 Randomized Controlled Trial. JAHA 2024, 13, e032571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawade, T.A.; Doris, M.K.; Bing, R.; White, A.C.; Forsyth, L.; Evans, E.; Graham, C.; Williams, M.C.; Van Beek, E.J.R.; Fletcher, A.; et al. Effect of Denosumab or Alendronic Acid on the Progression of Aortic Stenosis: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Circulation 2021, 143, 2418–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Y.; Chen, H.; Fei, S.; Chen, X.; Guo, L.; Pan, Q. Role of Denosumab in Lipid Metabolism Disorders: Clinical Significance and Potential Mechanisms. Arch. Osteoporos. 2025, 20, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Pan, Y.; Wang, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, C.; Shah, A.M.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, M. Celastrol Alleviates Aortic Valve Calcification Via Inhibition of NADPH Oxidase 2 in Valvular Interstitial Cells. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2020, 5, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, M.; Qu, M.; Zhou, S.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Luo, J.; Luo, Y.; et al. Effects of Celastrol-Enriched Peanuts on Metabolic Health and the Development of Atherosclerosis. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xue, X.; Yu, L.; Qian, J.; Li, X.; Tian, M.; Yang, J.; Deng, R.; Lu, C.; Xiao, C.; et al. Recombinant High-Density Lipoprotein Targeted Delivery of Celastrol to Promote Foam Cells Lipophagy against Early Atherosclerosis. J. Nanobiotechnology 2025, 23, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Bai, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Y.; Gu, Y.; Meng, G.; Xie, L.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Celastrol Prevents Atherosclerosis via Inhibiting LOX-1 and Oxidative Stress. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Li, C.; Jin, X.-P.; Weng, S.-X.; Fan, L.-L.; Zheng, Z.; Li, W.-L.; Wang, F.; Wang, W.-F.; Hu, X.-F.; et al. Celastrol May Have an Anti-Atherosclerosis Effect in a Rabbit Experimental Carotid Atherosclerosis Model. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 1684–1691. [Google Scholar]
- Yeang, C.; Tsimikas, S. Ancient Remedy for a Modern Disease. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2020, 5, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Sun, W.; Zhou, B.; Kong, X. Emodin Alleviates Aortic Valvular Calcification by Inhibiting the AKT/FOXO1 Pathway. Ann. Anat.-Anat. Anz. 2022, 240, 151885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauersberger, C.; Sager, H.B.; Wobst, J.; Dang, T.A.; Lambrecht, L.; Koplev, S.; Stroth, M.; Bettaga, N.; Schlossmann, J.; Wunder, F.; et al. Loss of Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase in Platelets Contributes to Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation and Vascular Inflammation. Nat. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 1, 1174–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.L.; Riley, L.; Bersi, M.; Linton, M.F.; Merryman, W.D. Impaired Macrophage Trafficking and Increased Helper T-Cell Recruitment with Loss of Cadherin-11 in Atherosclerotic Immune Response. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2021, 321, H756–H769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutcheson, J.D.; Chen, J.; Sewell-Loftin, M.K.; Ryzhova, L.M.; Fisher, C.I.; Su, Y.R.; Merryman, W.D. Cadherin-11 Regulates Cell–Cell Tension Necessary for Calcific Nodule Formation by Valvular Myofibroblasts. ATVB 2013, 33, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ryzhova, L.M.; Sewell-Loftin, M.K.; Brown, C.B.; Huppert, S.S.; Baldwin, H.S.; Merryman, W.D. Notch1 Mutation Leads to Valvular Calcification Through Enhanced Myofibroblast Mechanotransduction. ATVB 2015, 35, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lin, Y.; Sun, Z. Inhibition of miR-101-3p Prevents Human Aortic Valve Interstitial Cell Calcification through Regulation of CDH11/SOX9 Expression. Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, D.C.; Bowen, C.J.; Vaidya, K.A.; Zhou, J.; Chapurin, N.; Recknagel, A.; Zhou, B.; Chen, J.; Kotlikoff, M.; Butcher, J.T. Cadherin-11 Overexpression Induces Extracellular Matrix Remodeling and Calcification in Mature Aortic Valves. ATVB 2016, 36, 1627–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.R.; Bowler, M.A.; Snider, J.C.; Merryman, W.D. Targeting Cadherin-11 Prevents Notch1-Mediated Calcific Aortic Valve Disease. Circulation 2017, 135, 2448–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroer, A.K.; Bersi, M.R.; Clark, C.R.; Zhang, Q.; Sanders, L.H.; Hatzopoulos, A.K.; Force, T.L.; Majka, S.M.; Lal, H.; Merryman, W.D. Cadherin-11 Blockade Reduces Inflammation-Driven Fibrotic Remodeling and Improves Outcomes after Myocardial Infarction. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e131545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagawa, K.; Shi, M.; Chen, P.-I.; Hennigs, J.K.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, C.G.; Saito, T.; Taylor, S.; Sa, S.; et al. Smooth Muscle Contact Drives Endothelial Regeneration by BMPR2-Notch1–Mediated Metabolic and Epigenetic Changes. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.; Zheng, H.; Wei, G.; Li, M.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Guo, H.; Sun, J.; Li, C.; Zhong, S.; et al. circRNA Hipk3 Induces Cardiac Regeneration after Myocardial Infarction in Mice by Binding to Notch1 and miR-133a. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2020, 21, 636–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Zurita, L.; Prados, B.; Grego-Bessa, J.; Luxán, G.; Del Monte, G.; Benguría, A.; Adams, R.H.; Pérez-Pomares, J.M.; De La Pompa, J.L. Integration of a Notch-Dependent Mesenchymal Gene Program and Bmp2-Driven Cell Invasiveness Regulates Murine Cardiac Valve Formation. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3493–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGrogan, D.; Luna-Zurita, L.; De La Pompa, J.L. Notch Signaling in Cardiac Valve Development and Disease. Birth Defects Res. 2011, 91, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic Signalling: Therapeutic Developments. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Erb, L.; Shivaji, R.; Weisman, G.A.; Seye, C.I. Binding of the P2Y2 Nucleotide Receptor to Filamin A Regulates Migration of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Qian, S.; Hoggatt, A.; Tang, H.; Hacker, T.A.; Obukhov, A.G.; Herring, P.B.; Seye, C.I. Endothelial Cell–Specific Deletion of P2Y2 Receptor Promotes Plaque Stability in Atherosclerosis-Susceptible ApoE-Null Mice. ATVB 2017, 37, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschetta, D.; Di Maria, E.; Valerio, V.; Massaiu, I.; Bozzi, M.; Songia, P.; D’alessandra, Y.; Myasoedova, V.A.; Poggio, P. Purinergic Receptor P2Y2 Stimulation Averts Aortic Valve Interstitial Cell Calcification and Myofibroblastic Activation. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchareb, R.; Côté, N.; Marie-Chloé-Boulanger; Le Quang, K.; El Husseini, D.; Asselin, J.; Hadji, F.; Lachance, D.; Shayhidin, E.E.; Mahmut, A.; et al. Carbonic Anhydrase XII in Valve Interstitial Cells Promotes the Regression of Calcific Aortic Valve Stenosis. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2015, 82, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Therapeutic Class/Agent | Mechanism of Action | Targets | Translational Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCSK9 inhibitors/Lp(a)-targeted RNA therapies | Lower LDL-C and Lp(a) Reduce oxidized lipid-driven inflammation | Lipid metabolism, oxidized phospholipids | Effective in atherosclerosis Lp(a) lowering may delay CAVS progression |
| DPP-4 inhibitors (e.g., sitagliptin, evogliptin) | Anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative Suppress valvular calcification via IGF-1/BMP-2 modulation | VICs, macrophages, and endothelium | Clinical data suggest slower AS progression in diabetics |
| Vitamin K (K1, K2) | Activates matrix Gla protein (MGP) Inhibits calcification | VICs, vascular smooth muscle cells | Safe, widely available Ongoing trials in CKD and elderly populations |
| Denosumab (anti-RANKL mAb) | Blocks RANKL–RANK interaction Inhibits osteogenic signaling and calcification | Osteoclast-like VICs, macrophages | Evaluated in SALTIRE II trial-modest reduction in valvular and vascular calcification |
| NOX2 inhibitors (e.g., celastrol) | Reduces oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines Inhibits osteogenic markers (BMP-2, RUNX2) | VICs, VSMCs, macrophages | Dual benefit in atherosclerosis and CAVS in preclinical studies |
| sGC activators (e.g., ataciguat) | Restore cGMP signaling independent of NO Reduce fibrosis, calcification, and endothelial dysfunction | Endothelium, VICs, VSMCs | Phase II trial shows slowed AS calcification Benefits are also in arterial stiffness |
| Cadherin-11 inhibitors (e.g., SYN0012) | Blocks cell–cell adhesion and mechanotransduction Reduces VIC activation and fibrosis | Myofibroblasts, activated VICs | Experimental Prevents valvular and vascular fibrosis in preclinical models |
| Notch1 stabilizers (e.g., XCT790) | Maintains Notch1 signaling Inhibits the osteogenic transformation of VICs and VSMCs | VICs, VSMCs, developmental pathways | Promising in genetically predisposed models of early-onset CAVS |
| P2Y2 receptor agonists | Anti-inflammatory and anti-calcific Suppresses TNF-α, MMPs, and osteogenic transcription factors | VICs, VSMCs, endothelium | Emerging strategy Stabilizes plaques and reduces VIC calcification |
| RAAS inhibitors | Reduce fibrosis and inflammation Improve endothelial function | VSMCs, endothelium | Widely used May provide structural benefit beyond BP control |
| Statins (context-dependent) | Lower LDL-C, anti-inflammatory in atherosclerosis May increase Lp(a) and not benefit CAVS | Lipid metabolism, systemic inflammation | Strong role in CAD Not recommended for isolated AS without hyperlipidemia |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cinezan, C.; Magureanu, D.C.; Hiceag, M.L.; Rus, C.B.; Ilias, I.T.; Bogdan, I.D.; Buzle, A.M.; Cozma, A. Shared Risk Factors and Molecular Mechanisms Between Aortic Stenosis and Atherosclerosis: A Rationale for Therapeutic Repositioning. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8163. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178163
Cinezan C, Magureanu DC, Hiceag ML, Rus CB, Ilias IT, Bogdan ID, Buzle AM, Cozma A. Shared Risk Factors and Molecular Mechanisms Between Aortic Stenosis and Atherosclerosis: A Rationale for Therapeutic Repositioning. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8163. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178163
Chicago/Turabian StyleCinezan, Corina, Dan Claudiu Magureanu, Maria Luiza Hiceag, Camelia Bianca Rus, Ioana Tiberia Ilias, Iulia Denisa Bogdan, Alexandra Manuela Buzle, and Angela Cozma. 2025. "Shared Risk Factors and Molecular Mechanisms Between Aortic Stenosis and Atherosclerosis: A Rationale for Therapeutic Repositioning" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8163. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178163
APA StyleCinezan, C., Magureanu, D. C., Hiceag, M. L., Rus, C. B., Ilias, I. T., Bogdan, I. D., Buzle, A. M., & Cozma, A. (2025). Shared Risk Factors and Molecular Mechanisms Between Aortic Stenosis and Atherosclerosis: A Rationale for Therapeutic Repositioning. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8163. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178163






