Genome-Wide Expression Profile of SOD Gene Family in Isatis indigotica and the Key Role of IiSOD2 and IiSOD7 in Alkaline Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Physicochemical Propertiesof SOD Gene Family in I. indigotica
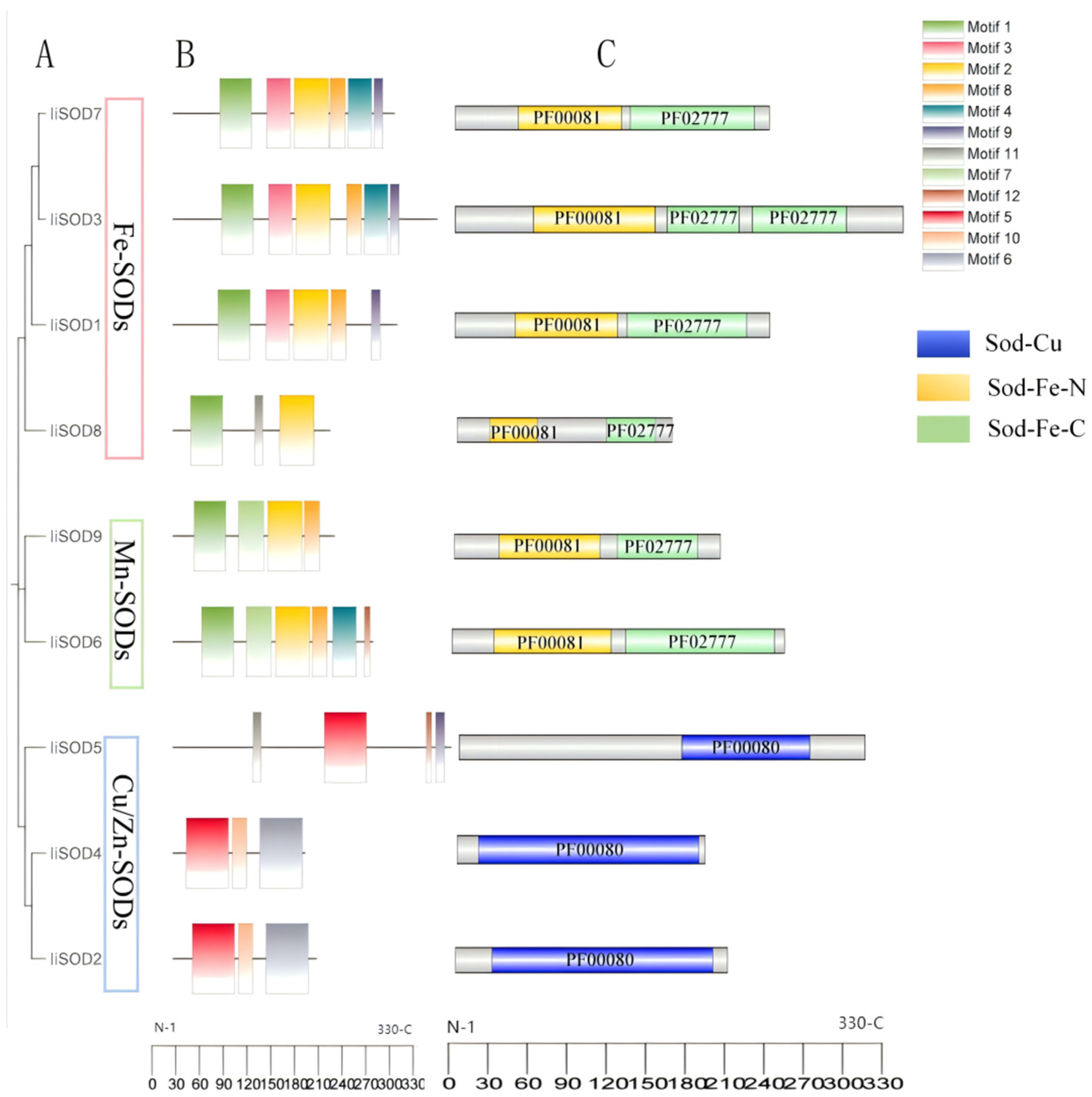
2.2. The Phylogenetic Relationship of IiSODs
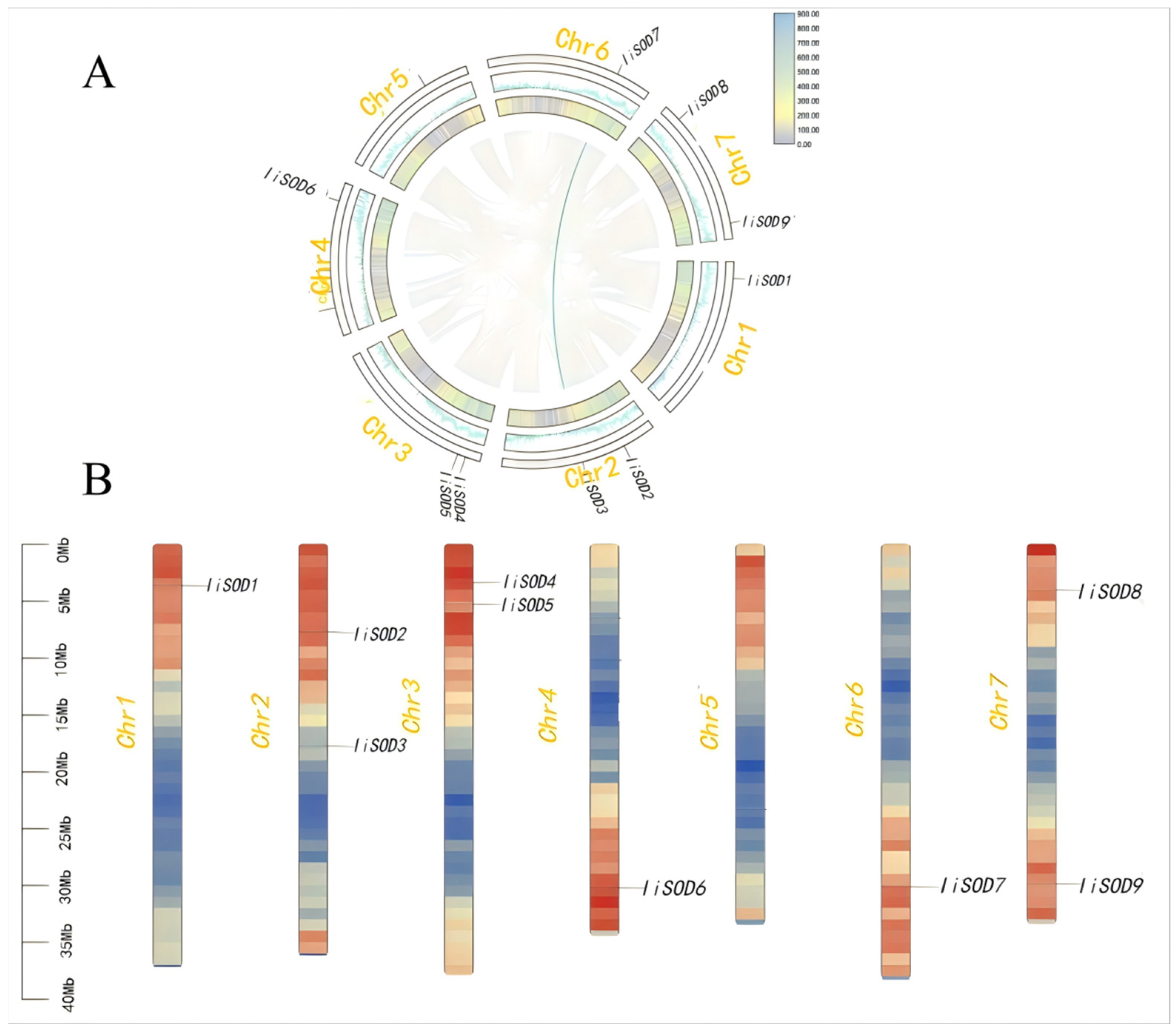
2.3. Chromosomal and Collinearity Analysis of IiSODs Gene
2.4. Conserved Motifs and Domains of IiSOD Proteins
2.5. Cis-Regulatory Elements in the Promoter Region of IiSODs Gene
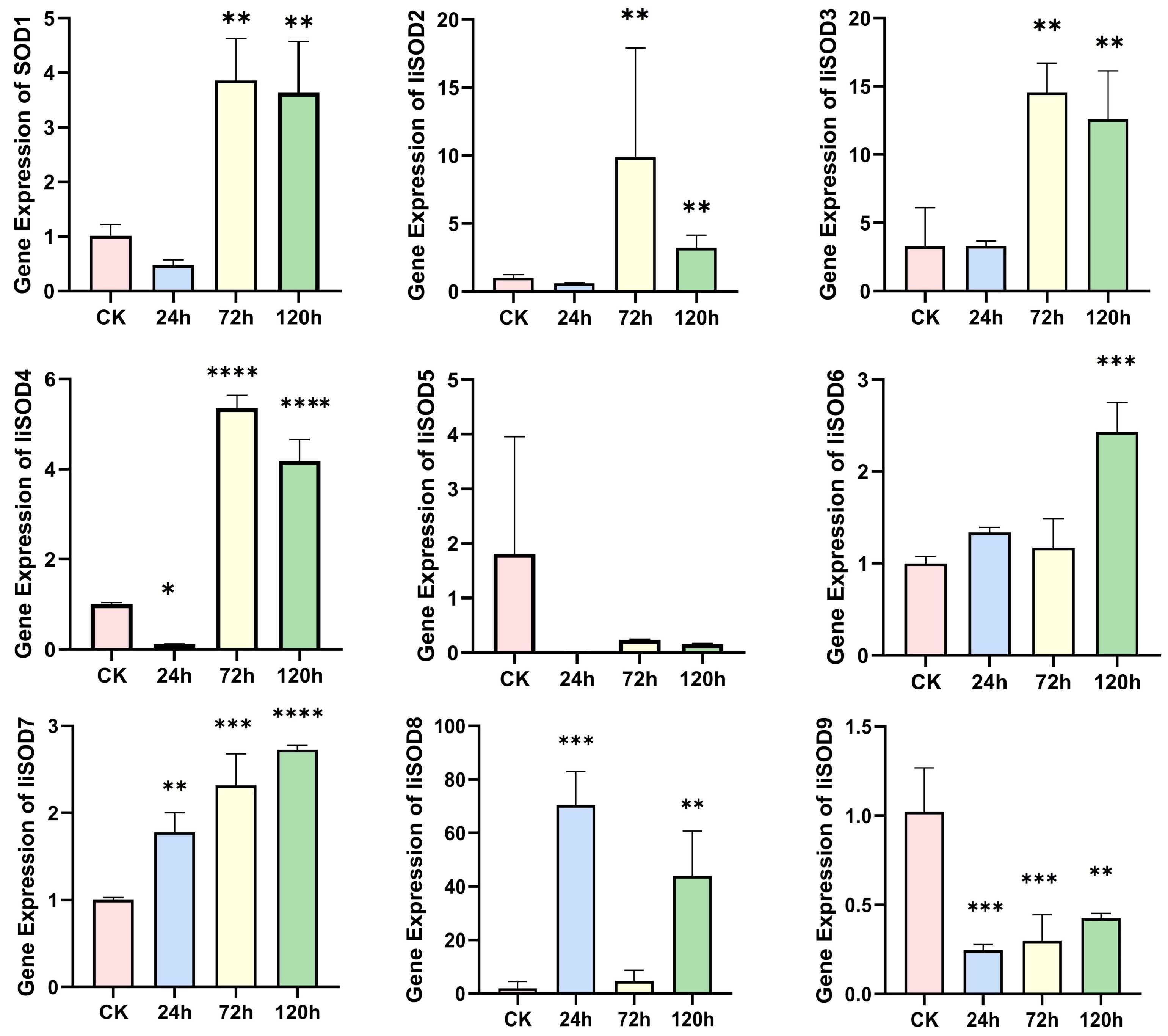
2.6. IiSOD Gene Expression Profile Under Alkaline Stress
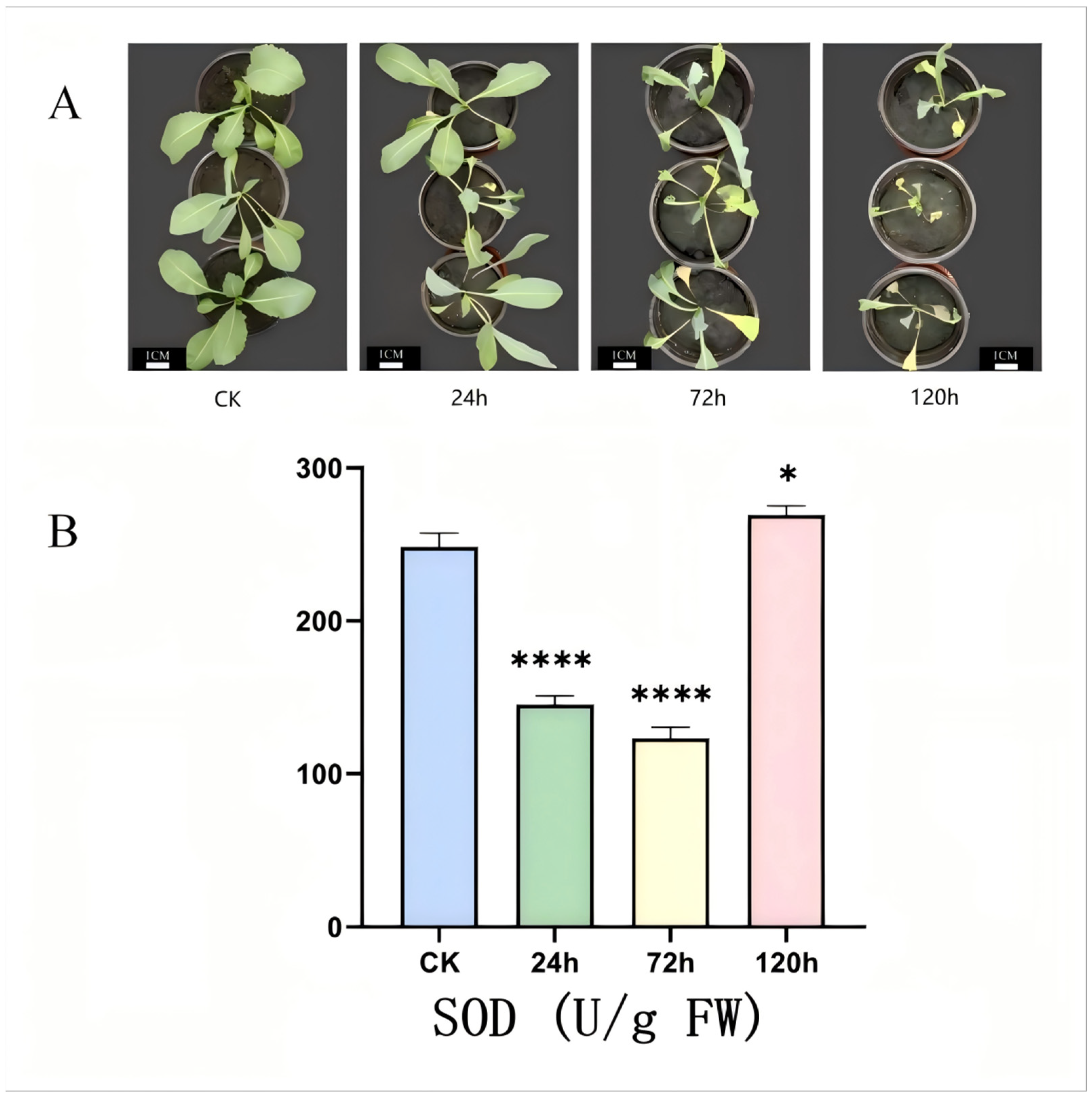
2.7. Determination of Phenotype and SOD Activity of I. indigotica Under Alkaline Stress
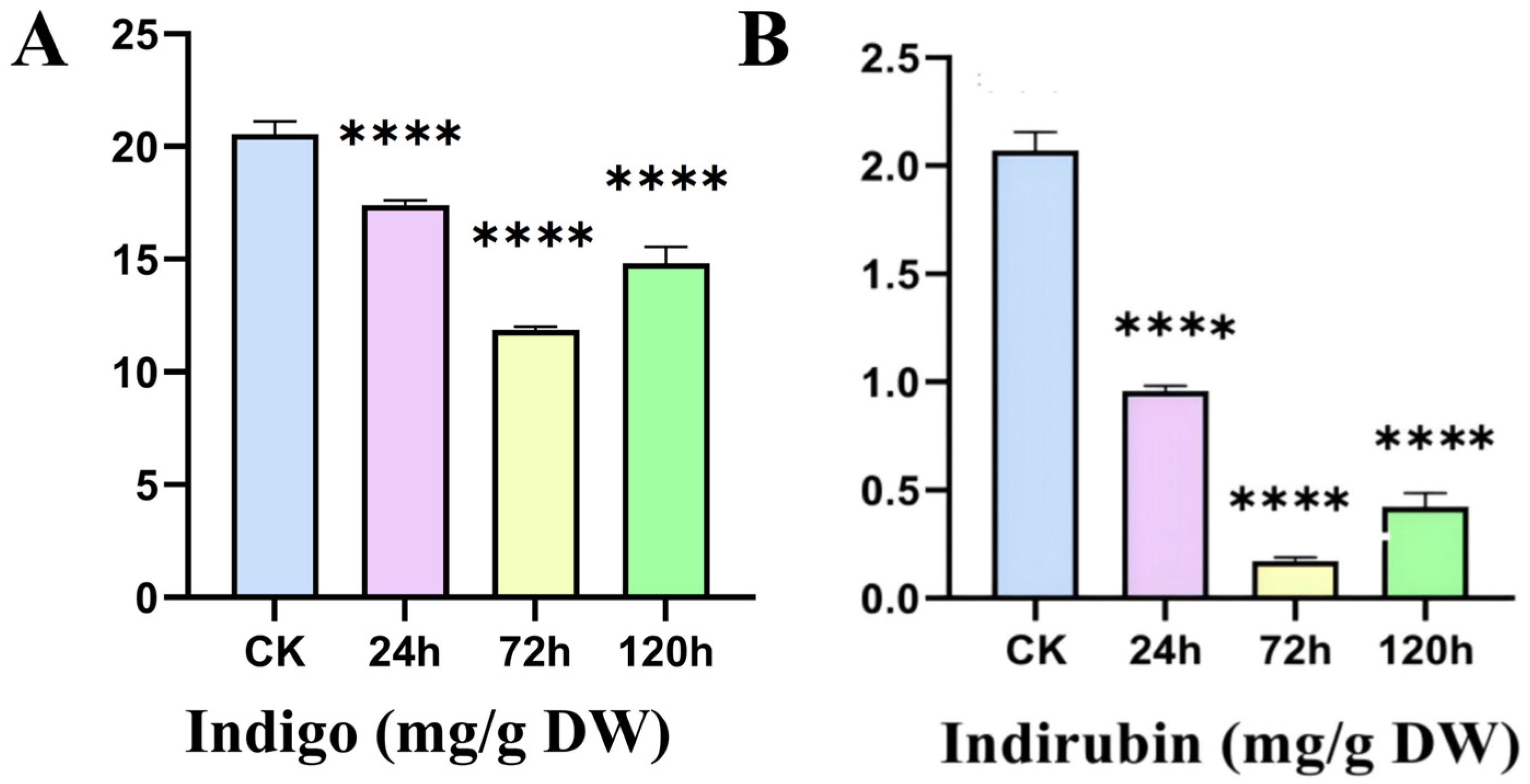
2.8. Content of Indole Alkaloids in Leaves of I. indigotica Under Alkaline Stress
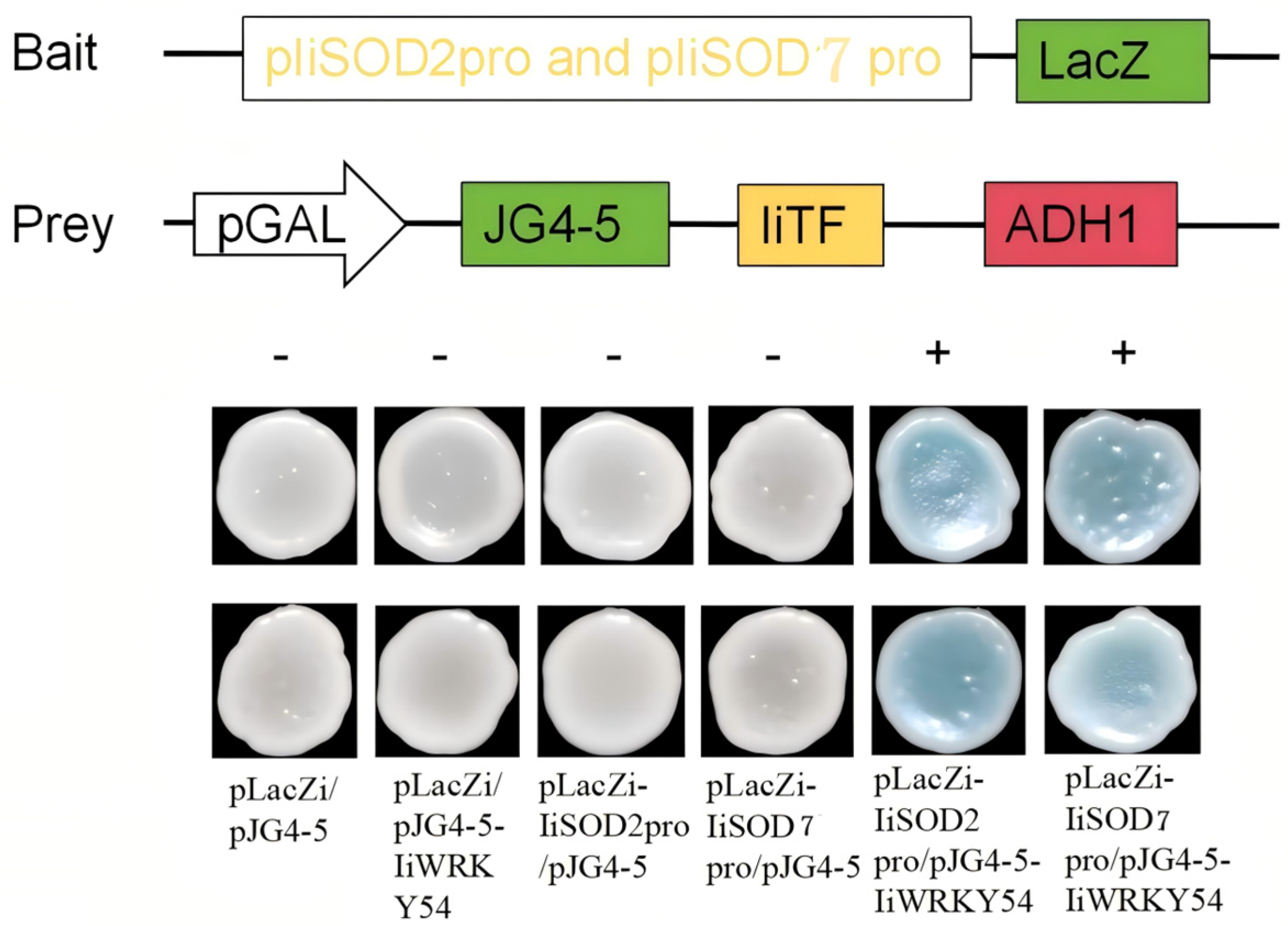
2.9. IiWRKY54 Binds to IiSOD2 and IiSOD7 Promoter Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Treatment Sampling
4.2. Identification and Physicochemical Properties of IiSOD Gene in I. indigotica
4.3. Phylogenetic and Collinearity Analysis of IiSOD Protein
4.4. Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements in IiSOD Promoter
4.5. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR Analysis of I. Indigotica
4.6. Phenotypes and Superoxide Dismutase Activity in Alkaline Stress
4.7. Effects of Alkaline Stress on the Accumulation of Indole Alkaloids in I. indigotica
4.8. Yeast One-Hybrid Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, L.W.; Goh, C.B.S.; Tan, J.B.L. A Systemic Review for Ethnopharmacological Studies on Isatis indigotica Fortune: Bioactive Compounds and their Therapeutic Insights. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2022, 50, 161–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Wang, Z.; Ren, W.; Yan, S.; Xing, N.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Ma, W. Identification of the bZIP gene family and regulation of metabolites under salt stress in isatis indigotica. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1011616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Huang, D.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Qiu, S.; Lv, Z.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Li, R.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Isatis indigotica: From (ethno) botany, biochemistry to synthetic biology. Mol. Hortic. 2021, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Jin, Y.; Chen, Z.Q.; Chen, S.B.; Zhan, Z.L. Textual research on medicinal blue herbs. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2020, 45, 5819–5828. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, A.F. Superoxide dismutases: Ancient enzymes and new insights. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Sheng, Y. Effect of various salt–alkaline mixed stress conditions on sunflower seedlings and analysis of their stress factors. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2005, 54, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, R.; XI, X.; Zhang, C.-y. Alkali stress tolerance analysis of four Rhododendron cultivars. J. Nanjing. For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 48, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Wei, J.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Yu, H. Growth, Fruit Yield, Photosynthetic Characteristics, and Leaf Microelement Concentration of Two Blueberry Cultivars under Different Long-Term Soil pH Treatments. Agronomy 2019, 9, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Han, J.; Zheng, W.; Yang, C. Comparison of ion balance and nitrogen metabolism in old and young leaves of alkali-stressed rice plants. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Duanmu, H.; Qiao, Y.; Jin, X.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.; Chen, C. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the soybean SOD family during alkaline stress. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Kong, G.; Chao, J.; Yin, T.; Tian, H.; Ya, H.; He, L.; Zhang, H. Genome-wide identification of the rubber tree superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family and analysis of its expression under abiotic stress. PeerJ 2022, 10, e14251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadarajah, K.K. ROS Homeostasis in Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knipfer, T.; Besse, M.; Verdeil, J.L.; Fricke, W. Aquaporin-facilitated water uptake in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) roots. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 4115–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorov, D.B.; Juhaszova, M.; Sollott, S.J. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS release. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 909–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelko, I.N.; Mariani, T.J.; Folz, R.J. Superoxide dismutase multigene family: A comparison of the CuZn-SOD (SOD1), Mn-SOD (SOD2), and EC-SOD (SOD3) gene structures, evolution, and expression. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 33, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, C.L.; Neupane, K.; Shearer, J.; Palenik, B. Diversity, function and evolution of genes coding for putative Ni-containing superoxide dismutases. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1831–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.S.; Tuteja, N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant. Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 909–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, G. Molecular mechanism of expression and regulation of SOD gene in plant. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2014, 36, 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.; Raza, A.; Gao, A.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hussain, M.A.; Mehmood, S.S.; Cheng, Y.; Lv, Y.; Zou, X. Genome-Wide Analysis and Expression Profile of Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Gene Family in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) under Different Hormones and Abiotic Stress Conditions. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zeng, L.; Chen, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y. In silico identification and expression analysis of superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family in Medicago truncatula. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.J.; Shin, D.S.; Getzoff, E.D.; Tainer, J.A. The structural biochemistry of the superoxide dismutases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1804, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Wu, H.; Yang, Q.; Huang, L.; Hu, Q.; Ma, T.; Li, Z.; Liu, J. A chromosome-scale genome assembly of Isatis indigotica, an important medicinal plant used in traditional Chinese medicine. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, W. Genome-wide identification of the Trihelix gene family and abiotic expression pattern analysis in Isatis indigotica Fort. of traditional Chinese medicine satidis radix and isatidis folium. China J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2023, 38, 2109–2115. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Ren, W.; Jiang, S.; Kong, L.; Ma, L.; He, J.; Wang, D.; Liu, W.; Ma, W.; Liu, X. Identification and expression analysis of the RBOH gene family of Isatis indigotica Fort. and the potential regulation mechanism of RBOH gene on H2O2 under salt stress. Plant Cell Rep. 2025, 44, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, H.; Hao, Z.; Zhu, L.; Lu, L.; Shi, J.; Chen, J. The Identification and Expression Analysis of the Liriodendron chinense (Hemsl.) Sarg. SOD Gene Family. Forests 2023, 14, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tounsi, S.; Jemli, S.; Feki, K.; Brini, F.; Najib Saidi, M. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) family in durum wheat: Promising candidates for improving crop resilience. Protoplasma. 2023, 260, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Assane Hamidou, A.; Zhao, X.; Ouyang, Z.; Lin, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Luo, K.; Chen, Y. Superoxide dismutase gene family in cassava revealed their involvement in environmental stress via genome-wide analysis. iScience 2023, 26, 107801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, J. Identification and characterization of the critical genes encoding Cd-induced enhancement of SOD isozymes activities in Zhe-Maidong (Ophiopogon japonicus). Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1355849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Yuanxin, D.; Anbo, W. Identification and Expression Pattern Analysis of Rosa roxburghii SOD Gene Family. Biotechnol. Bull. 2024, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Xue, B.; He, Y.; Liao, S.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Liang, Y.K. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Pattern Analysis of Dirigent Members in the Genus Oryza. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.M.; Hua, W.P.; Cao, X.Y.; Yan, J.A.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.Z. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Gene 2020, 742, 144603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Deng, F.; Yuan, R.; Shen, F. Genome-wide characterization and expression analyses of superoxide dismutase (SOD) genes in Gossypium hirsutum. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Y.; Hu, C.; Long, J.; Chen, Y. The superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family in perennial ryegrass: Characterization and roles in heat stress tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 226, 110061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, D.; Guo, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Shao, L.; Luo, C.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, J. Identification and Analysis of the Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Gene Family and Potential Roles in High-Temperature Stress Response of Herbaceous Peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.). Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Cao, Q.; Li, Y.; He, M.; Liu, X. Advances in cis-element- and natural variation-mediated transcriptional regulation and applications in gene editing of major crops. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 5441–5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, A.; Szabo, S.; Szabo, Z.; Hegedus, A.; Berenyi, D.; Holb, I.J. Temporal Patterns and Inter-Correlations among Physical and Antioxidant Attributes and Enzyme Activities of Apricot Fruit Inoculated with Monilinia laxa under Salicylic Acid and Methyl Jasmonate Treatments under Shelf-Life Conditions. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Yu, W.; Xu, J.; Lu, X.; Liu, Y. Anthocyanin Biosynthesis Induced by MYB Transcription Factors in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warzecha, H.; Frank, A.; Peer, M.; Gillam, E.M.J.; Guengerich, F.P.; Unger, M. Formation of the indigo precursor indican in genetically engineered tobacco plants and cell cultures. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2006, 5, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Liu, X.; Song, S.; Lv, W.; Yang, Y. Mechanisms of secondary metabolites regulating plant resistance to salinity and alkali stress. Plant. Physiol. J. 2023, 59, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, Y. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses. New. Phytol. 2017, 217, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Hou, X.; Liang, X. Response Mechanisms of Plants Under Saline-Alkali Stress. Front. Plant. Sci. 2021, 12, 667458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q. Comprehensive transcriptomic profiling of <italic>Isatis indigotica</italic> leaves reveals biosynthesis of indole active ingredients. Sci. Sin. Vitae 2018, 48, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.L.; Liu, L.Y.; Liu, H.X. Effect of NaHS on the expression of related genes in isatis indigotica alkaoid synthesis pathway. J. Shaanxi. Univ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 5, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, B.; Du, J.; Deng, T.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Fu, J.; Pang, J.; Yang, M.; et al. Transcriptomic and proteomic-based analysis of the mechanisms by which drought and salt stresses affect the quality of Isatidis Folium. BMC Plant. Biol. 2025, 25, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Liu, Y.; Han, M.; Wang, Z.; Lu, X.; Yang, C. Soil properties and enzyme activities varied with seasonal precipitation during vegetation succession in saline-alkali grassland in songnen plain. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2025, 56, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Study on the Distribution and Spatial Change of SALINE Alkali Land in Songnen Plain. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Normal University, Harbin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Wang, Z.; Mao, D.; Jia, M.; Chang, S.; Li, X. Spatiotemporal variations of soil salinization in China’s West Songnen Plain. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 2366–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Kong, L.; Wang, P.; He, L.; Cao, H.; Qin, C.; Ren, W.; Liu, X.; Ma, W. Identification and expression analysis of NAC family genes in Eleutherococcus senticosus under salt stress. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2025, 52, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Su, W.; Gao, A.; Mehmood, S.S.; Hussain, M.A.; Nie, W.; Lv, Y.; Zou, X.; Zhang, X. Catalase (CAT) Gene Family in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.): Genome-Wide Analysis, Identification, and Expression Pattern in Response to Multiple Hormones and Abiotic Stress Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, S.C.; Luciani, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Park, Y.; Lopez, R.; Finn, R.D. HMMER web server: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W200–W204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.C.; Shen, H.B. Cell-PLoc: A package of Web servers for predicting subcellular localization of proteins in various organisms. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescot, M.; Dehais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouze, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T.L. Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, K.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Bai, B.; Xia, X.; Geng, H. Identification of quantitative trait loci and candidate genes for grain superoxide dismutase activity in wheat. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Li, T.; Qu, X.; Zhang, N.; Lu, M.; Wang, J. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of indigo and indirubin from Isatis indigotica Fort. and their antioxidant capacities. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Xia, Y.; Cheng, P.; Fang, Y.; Da, G.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X. Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography was used to simultaneously determine the contents of indigo and indigo red in large green leaves. Her. Med. 2015, 34, 1506–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, C. Research progress on determination methods of plant indigo extract. BiomassChem. Eng. 2023, 57, 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Huang, Y. Genome-wide identification of the Pyrus R2R3-MYB gene family and PhMYB62 regulation analysis in Pyrus hopeiensis flowers at low temperature. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornson, M.; Pimprikar, P.; Nurnberger, T.; Zipfel, C. The transcriptional landscape of Arabidopsis thaliana pattern-triggered immunity. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Ma, S.; Ye, N.; Jiang, M.; Cao, J.; Zhang, J. WRKY transcription factors in plant responses to stresses. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2017, 59, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Xu, Y.; Du, Z.; Su, X.D.; Yu, J. Revealing atomic-scale molecular diffusion of a plant-transcription factor WRKY domain protein along DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2102621118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Luan, Y.; Meng, J.; Sun, J.; Tao, J.; Zhao, D. WRKY Transcription Factor Response to High-Temperature Stress. Plants 2021, 10, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, Z.; Huang, Y.; He, D.; Lu, L.; Wei, M.; Lin, S.; Luo, W.; Liao, X.; Jin, S.; et al. WRKY45 positively regulates salinity and osmotic stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 219, 109408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, R.; Cao, Y.; Tang, X.; Sun, L.; Wei, L.; Wang, K. Identification and expression analysis of the WRKY gene family in Isatis indigotica. Gene 2021, 783, 145561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, D.; Zhang, W.; Shu, H.; Sun, P.; Huang, C.; Deng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, S. Genome-Wide Identification of WRKY Gene Family and Functional Characterization of CcWRKY25 in Capsicum chinense. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene Name | Gene ID | Amino Acids | Chromosome Location | pI | Molecular Weight (Da) | Subcellular Location | Pfam Domain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IiSOD1 | Iin00748.t1 | 260 | Chr1 | 7.02 | 29,539.48 | mitochondrion | IMA, IMC |
| IiSOD2 | Iin05388.t1 | 167 | Chr2 | 6.48 | 17,057.09 | chloroplast | CZ |
| IiSOD3 | Iin06861.t1 | 307 | Chr2 | 4.85 | 34,597.74 | chloroplast | IMA, IMC |
| IiSOD4 | Iin08997.t1 | 153 | Chr3 | 5.45 | 15,163.77 | chloroplast | CZ |
| IiSOD5 | Iin09368.t1 | 323 | Chr3 | 7.64 | 34,325.95 | chloroplast | CZ |
| IiSOD6 | Iin15648.t1 | 232 | Chr4 | 8.74 | 25,463.07 | mitochondrion | IMA, IMC |
| IiSOD7 | Iin22527.t1 | 257 | Chr6 | 7.74 | 28,582.51 | chloroplast | IMA, IMC |
| IiSOD8 | Iin24760.t1 | 182 | Chr7 | 9.46 | 20,410.29 | mitochondrion | IMA, IMC |
| IiSOD9 | Iin27319.t1 | 187 | Chr7 | 6.79 | 20,318.94 | mitochondrion | IMA, IMC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, L.; Kong, L.; Jiang, S.; Ma, J.; He, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Ma, W.; Ren, W. Genome-Wide Expression Profile of SOD Gene Family in Isatis indigotica and the Key Role of IiSOD2 and IiSOD7 in Alkaline Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178131
Ma L, Kong L, Jiang S, Ma J, He L, Wu J, Zhang X, Wu W, Ma W, Ren W. Genome-Wide Expression Profile of SOD Gene Family in Isatis indigotica and the Key Role of IiSOD2 and IiSOD7 in Alkaline Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178131
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Lengleng, Lingyang Kong, Shan Jiang, Junbai Ma, Lianqing He, Jianhao Wu, Xiaozhuang Zhang, Wei Wu, Wei Ma, and Weichao Ren. 2025. "Genome-Wide Expression Profile of SOD Gene Family in Isatis indigotica and the Key Role of IiSOD2 and IiSOD7 in Alkaline Stress" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178131
APA StyleMa, L., Kong, L., Jiang, S., Ma, J., He, L., Wu, J., Zhang, X., Wu, W., Ma, W., & Ren, W. (2025). Genome-Wide Expression Profile of SOD Gene Family in Isatis indigotica and the Key Role of IiSOD2 and IiSOD7 in Alkaline Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178131






