Deciphering the Diagnostic Potential of Small Non-Coding RNAs for the Detection of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Through Liquid Biopsies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Enabling Non-Coding Profiling of the Cell-Free RNA Transcriptome
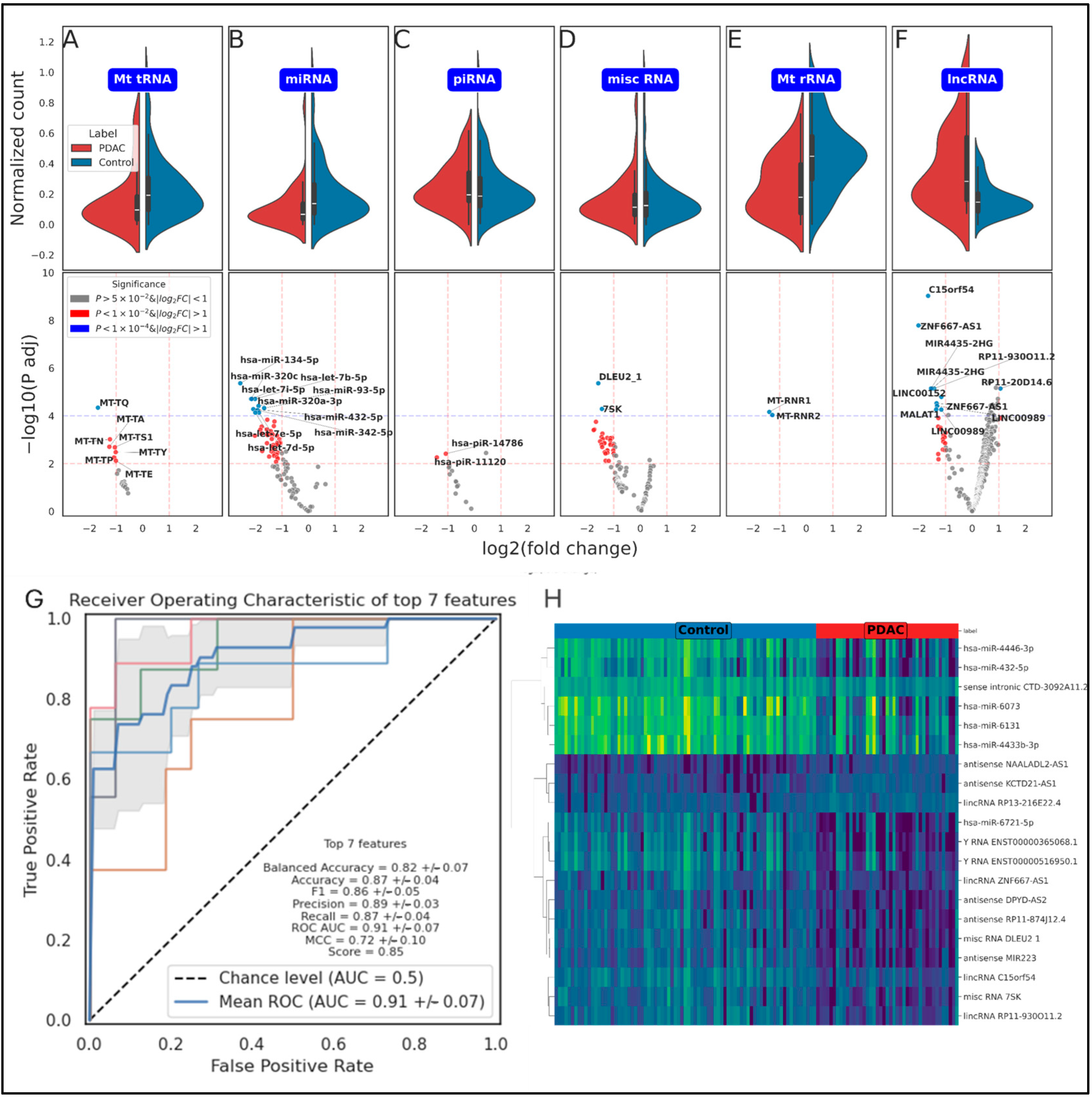
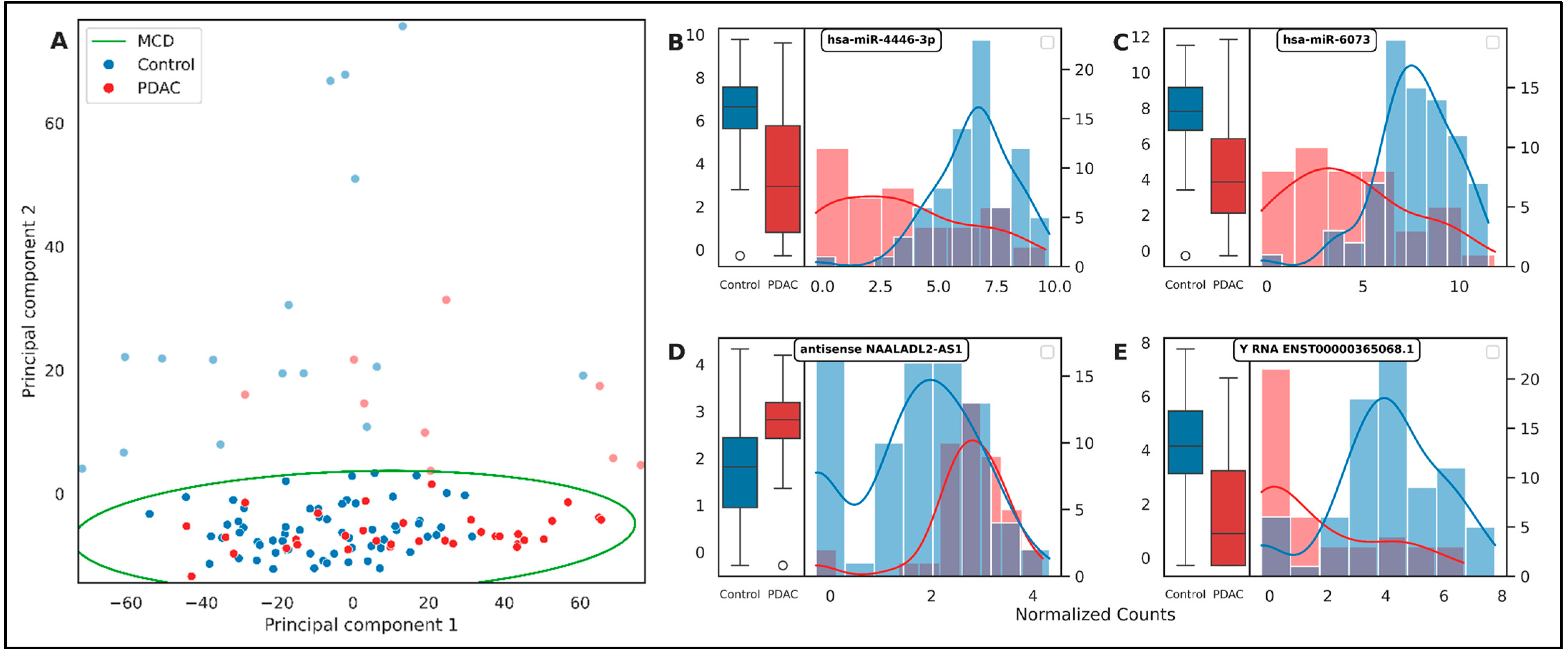
2.2. Differential Expression Analysis
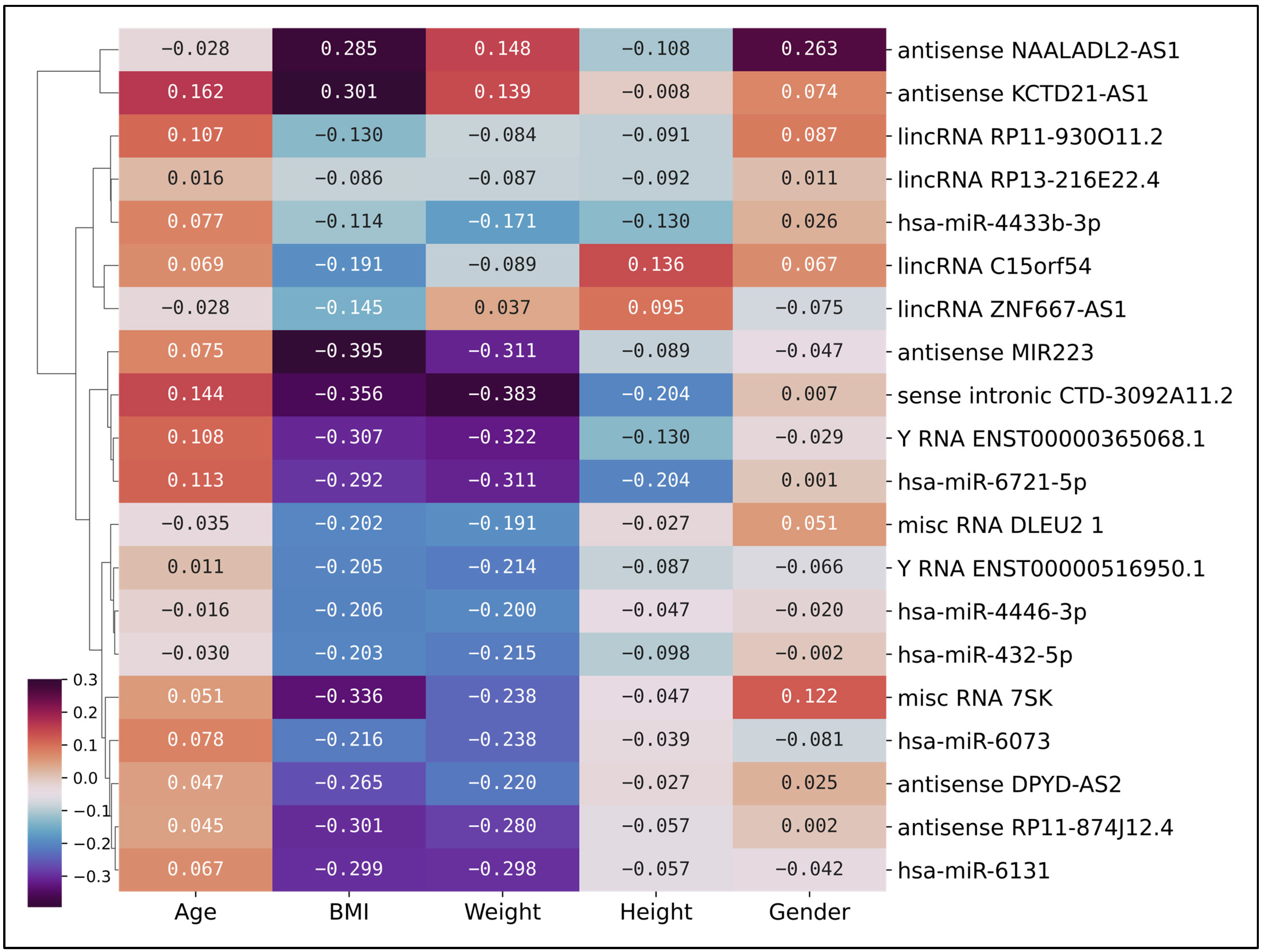
2.3. Correlation Analysis of Non-Coding Gene Expression and Clinical Features in PDAC Patients
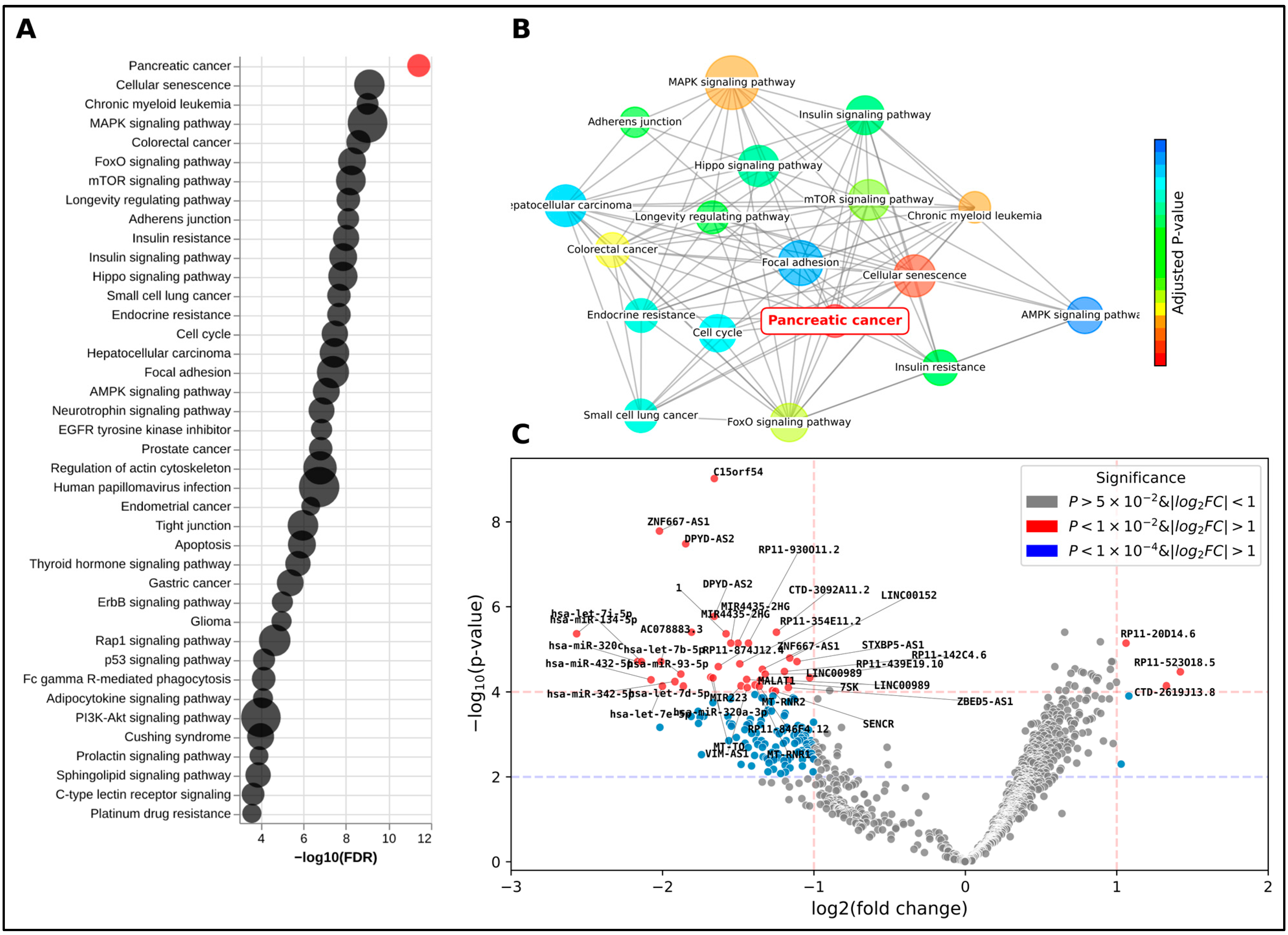
2.4. Investigation of Predicted miRNA Target Proteins
3. Discussion
Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cohort Aggregation and Sample Acquisition
4.2. Cell-Free Small RNA Isolation from Blood Plasma
4.3. Library Preparation for Cell-Free Small RNA-seq
4.4. RNA-seq Quality Control, Stepwise Alignment, and Quantification
4.5. Differential Expression Analysis and Count Normalization
4.6. Feature Importance and Ranking
4.7. Gene Set Enrichment and Pathway Analysis
4.8. Gradient Boosting Classification
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, K.D.; Siegel, R.L.; Lin, C.C.; Mariotto, A.B.; Kramer, J.L.; Rowland, J.H.; Stein, K.D.; Alteri, R.; Jemal, A. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sally, Á.; McGowan, R.; Finn, K.; Moran, B.M. Current and Future Therapies for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, M.; Metzger, P.; Gerum, S.; Belka, C.; Schnurr, M.; Lauber, K. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Biological hallmarks, current status, and future perspectives of combined modality treatment approaches. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrutkar, M.; Gladhaug, I.P. Pancreatic Cancer Chemoresistance to Gemcitabine. Cancers 2017, 9, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Ren, H. Precision treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2024, 585, 216636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.J.; Jaffee, E.M.; Zheng, L. The tumour microenvironment in pancreatic cancer—Clinical challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golan, T.; Atias, D.; Barshack, I.; Avivi, C.; Goldstein, R.S.; Berger, R. Ascites-derived pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma primary cell cultures as a platform for personalised medicine. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaoka, K.; Ohno, E.; Kawabe, N.; Kuzuya, T.; Funasaka, K.; Nakagawa, Y.; Nagasaka, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Watanabe, A.; Tochio, T.; et al. Current Status of the Diagnosis of Early-Stage Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, G.; Goh, S.K.; Christophi, C.; Muralidharan, V. Dilemmas and limitations interpreting carbohydrate antigen 19-9 elevation after curative pancreatic surgery: A case report. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2018, 54, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizian, A.; Rühlmann, F.; Krause, T.; Bernhardt, M.; Jo, P.; König, A.; Kleiß, M.; Leha, A.; Ghadimi, M.; Gaedcke, J. CA19-9 for detecting recurrence of pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Meng, Q.H.; Ramanathan, L.V. Chapter 1-Overview of traditional and nontraditional tumor markers. In Cancer Biomarkers; Ramanathan, L.V., Fleisher, M., Duffy, M.J., Eds.; Clinical Aspects and Laboratory Determination; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppaluri, K.R.; Challa, H.J.; Gaur, A.; Jain, R.; Vardhani, K.K.; Geddam, A.; Natya, K.; Aswini, K.; Palasamudram, K.; Sri Manjari, K. Unlocking the potential of non-coding RNAs in cancer research and therapy. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 35, 101730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reggiardo, R.E.; Maroli, S.V.; Peddu, V.; Davidson, A.E.; Hill, A.; LaMontagne, E.; Aaraj, Y.A.; Jain, M.; Chan, S.Y.; Kim, D.H. Profiling of repetitive RNA sequences in the blood plasma of patients with cancer. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 7, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Shi, L.; Luo, Z. Long Non-coding RNAs in Cancer: Implications for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapy. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 612393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimzadeh, M.; Wang, J.; Cavazos, T.B.; Schwartzberg, L.S.; Multhaup, M.; Ku, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Hanna, R.; et al. Detection of early-stage cancers using circulating orphan non-coding RNAs in blood. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41 (Suppl. 16). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Dragomir, G.A. Targeting non-coding RNAs to overcome cancer therapy resistance. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulìa, C.; Signore, F.; Gaffi, M.; Gigli, S.; Votino, R.; Nucciotti, R.; Bertacca, L.; Zaami, S.; Baffa, A.; Santini, E.; et al. Y RNA: An Overview of Their Role as Potential Biomarkers and Molecular Targets in Human Cancers. Cancers 2020, 12, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, K.; Fariha, A.; Hossain, M.S.; Tonmoy, M.I.Q.; Hami, I.; Roy, A.S.; Shakil, M.S.K.; Reza, H.A. Newaz Mohammed Bahadur c, Md Mizanur Rahaman d. Prediction of novel miRNA biomarker candidates for diagnostic and prognostic analysis of STAD and LIHC: An integrated in silico approach. Inform. Med. Unlocked. 2021, 24, 100581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, A.; Tsiatsianis, G.C.; Mouratidis, I.; Chan, C.S.Y.; Athanasiou, M.; Papanastasiou, A.D.; Kantere, V.; Syrigos, N.; Vathiotis, I.; Syrigos, K.; et al. Utilizing nullomers in cell-free RNA for early cancer detection. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024, 31, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, L. Mitochondrial DNA and MitomiR Variations in Pancreatic Cancer: Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilam, A.; Conde, J.; Weissglas-Volkov, D.; Oliva, N.; Friedman, E.; Artzi, N.; Shomron, N. Local microRNA delivery targets Palladin and prevents metastatic breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Navarro, E.; Duran-Sanchon, S.; Vila-Casadesús, M.; Moreira, L.; Ginès, À.; Cuatrecasas, M.; Lozano, J.; Bujanda, L.; Castells, A.; Gironella, M. Novel Circulating miRNA Signatures for Early Detection of Pancreatic Neoplasia. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aita, A.; Millino, C.; Sperti, C.; Pacchioni, B.; Plebani, M.; De Pittà, C.; Basso, D. Serum miRNA Profiling for Early PDAC Diagnosis and Prognosis: A Retrospective Study. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishibeppu, K.; Komatsu, S.; Imamura, T.; Kiuchi, J.; Kishimoto, T.; Arita, T.; Kosuga, T.; Konishi, H.; Kubota, T.; Shiozaki, A.; et al. Plasma microRNA profiles: Identification of miR-1229-3p as a novel chemoresistant and prognostic biomarker in gastric cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- miRNA and Gene Expression in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma-PMC. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6854437/ (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Yang, S.; Ji, J.; Wang, M.; Nie, J.; Wang, S. Construction of Ovarian Cancer Prognostic Model Based on the Investigation of Ferroptosis-Related lncRNA. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Jun, E.; Okugawa, Y.; Toiyama, Y.; Borazanci, E.; Bolton, J.; Taketomi, A.; Kim, S.C.; Shang, D.; Hoff, V.; et al. A circulating panel of circRNA biomarkers for the noninvasive and early detection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2023, 166, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overview of Cellular Senescence and Aging. Cell Signaling Technology. Available online: https://www.cellsignal.com/science-resources/overview-of-cellular-senescence (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- Xu, J.; Hu, S.; Chen, Q.; Shu, L.; Wang, P.; Wang, J. Integrated bioinformatics analysis of noncoding RNAs with tumor immune microenvironment in gastric cancer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Cao, T.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.; Xia, J.; Wang, Z.P. miR-223 Regulates Cell Proliferation and Invasion via Targeting PDS5B in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 14, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, F.; Chakraborty, A.; Khan, I.; Monts, J. Relevance of miR-223 as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers in Cancer. Biology 2022, 11, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keramati, F.; Seyedjafari, E.; Fallah, P.; Soleimani, M.; Ghanbarian, H. 7SK small nuclear RNA inhibits cancer cell proliferation through apoptosis induction. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 2809–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemberger, M.; Loewenstein, S.; Lubezky, N.; Nizri, E.; Pasmanik-Chor, M.; Barazovsky, E.; Klausner, J.M.; Lahat, G. MicroRNA profiling of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) reveals signature expression related to lymph node metastasis. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 2644–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girolimetti, G.; Pelisenco, I.A.; Eusebi, L.H.; Ricci, C.; Cavina, B.; Kurelac, I.; Verri, T.; Calcagnile, M.; Alifano, P.; Salvi, A.; et al. Dysregulation of a Subset of Circulating and Vesicle-Associated miRNA in Pancreatic Cancer. Non-Coding RNA 2024, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhayat, S.A.; Mardin, W.A.; Seggewiß, J.; Ströse, A.J.; Matuszcak, C.; Hummel, R.; Senninger, N.; Mees, S.Y.; Haier, J. MicroRNA Profiling Implies New Markers of Gemcitabine Chemoresistance in Mutant p53 Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, F.; Allen-Coyle, T.J.; Roche, S.; Meiller, J.; Conlon, N.T.; Swan, N.; Straubinger, R.M.; Geoghegan, J.; Straubinger, N.L.; Conlon, K. Alteration in Levels of Specific miRNAs and Their Potential Protein Targets between Human Pancreatic Cancer Samples, Adjacent Normal Tissue, and Xenografts Derived from These Tumors. Life 2023, 13, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.Y.; Lin, Y.C.D.; Cui, S.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xu, J.; Bao, J.; Li, Y.; Wen, J.; Zuo, H.; et al. miRTarBase update 2022: An informative resource for experimentally validated miRNA–target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 50, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yang, P.; Liu, B.; Tang, Y. Is there a CDKN2A-centric network in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma? OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 2551–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmers, C.; Sharma, N.; Opavsky, R.; Maiti, B.; Wu, L.; Wu, J.; Orringer, D.; Trikha, P.; Saavedra, H.I.; Leone, G. E2f1, E2f2, and E2f3 Control E2F Target Expression and Cellular Proliferation via a p53-Dependent Negative Feedback Loop. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Jin, M.; Jia, N.; Cui, X.; Hu, G.; Tang, T.; Yu, Q. Pan-cancer analysis on the role of PIK3R1 and PIK3R2 in human tumors. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, L.M.; Vaux, D.L. BCL2 and related prosurvival proteins require BAK1 and BAX to affect autophagy. Autophagy 2014, 10, 1474–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagathihalli, N.S.; Nagaraju, G. RAD51 as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Rev. Cancer 2011, 1816, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarantis, P.; Koustas, E.; Papadimitropoulou, A.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Karamouzis, M.V. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Treatment hurdles, tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 12, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakawa, M.; Kawahara, S.; Takahashi, D.; Kamioka, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Kobayashi, S.; Ueno, M.; Morimoto, M.; Sawazaki, S.; Tamagawa, H.; et al. Risk factors for early recurrence in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma who underwent curative resection. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 21, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Shi, K.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, G.; Song, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, W. Effect of exosomal miRNA on cancer biology and clinical applications. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, M.P.; Krude, T. Functional roles of non-coding Y RNAs. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2015, 66, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Cao, Y.; Xing, Y.-X.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.-J.; Yang, W.H.; Wang, B.-Q.; Han, S.-Y.; Wang, Y.-S. Deleted in lymphocytic leukemia 2 (DLEU2): A possible biomarker that holds promise for future diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 25, 2772–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, J.; Pu, Y.S.; Ma, Y.; Wu, M.; Wang, J.H. RP11-874J12.4, a novel lncRNA, confers chemoresistance in human gastric cancer cells by sponging miR-3972 and upregulating SSR2 expression. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 5892–5910. [Google Scholar]
- QIAamp Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit | ccfDNA/RNA | QIAGEN. Available online: https://www.qiagen.com/us/products/discovery-and-translational-research/dna-rna-purification/dna-purification/cell-free-dna/qiaamp-circulating-nucleic-acid-kit (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- QubitTM RNA High Sensitivity (HS), Broad Range (BR), and Extended Range (XR) Assay Kits. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/order/catalog/product/Q32855 (accessed on 10 September 2024).
- Small RNA Electrophoresis, MicroRNA, Bioanalyzer Small RNA | Agilent. Available online: https://www.agilent.com/en/product/automated-electrophoresis/bioanalyzer-systems/bioanalyzer-rna-kits-reagents/bioanalyzer-small-rna-analysis-228257 (accessed on 10 September 2024).
- SMARTer smRNA-Seq Kit for Illumina—Sequence Small RNAs with High Sensitivity and Minimal Bias. Available online: https://www.takarabio.com/products/next-generation-sequencing/rna-seq/small-rna-seq (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Chen, S. Ultrafast one-pass FASTQ data preprocessing, quality control, and deduplication using fastp. iMeta 2023, 2, e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babraham Bioinformatics-FastQC A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 29 August 2024).
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Käller, M. MultiQC: Summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.P.; Lowe, T.M. GtRNAdb 2.0: An expanded database of transfer RNA genes identified in complete and draft genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D184–D189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piuco, R.; Galante, P.A.F. PiRNAdb: A Piwi-Interacting RNA Database. Published online 24 September 2021:2021.09.21.461238. Available online: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.09.21.461238v1 (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Kozomara, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: Integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D152–D157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome. Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantano, L. miRTOP.github.io: Basic Structure for Home Page. Published online 1 February 2016. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/45385 (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M.; et al. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. GigaScience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Lun, A.T.L.; Baldoni, P.L.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR 4.0, Powerful Differential Analysis of Sequencing Data with Expanded Functionality and Improved Support for Small Counts and Larger Datasets. Published online 24 January 2024, 2024.01.21.576131. Available online: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.01.21.576131v2 (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Robinson, M.D.; Oshlack, A. A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome. Biol. 2010, 11, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, M.; Debruyne, M. Minimum covariance determinant. WIREs Comput Stat. 2010, 2, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ExtraTreesClassifier. Scikit-Learn. Available online: https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.ensemble.ExtraTreesClassifier.html#extratreesclassifier (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Mao, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Pian, C. NcPath: A novel platform for visualization and enrichment analysis of human non-coding RNA and KEGG signaling pathways. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btac812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.-Y. LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]

| Mean Importance | Std Importance | Count Importance | |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-4446-3p | 0.014894 | 0.005917 | 954 |
| hsa-miR-6073 | 0.014332 | 0.005727 | 954 |
| antisense NAALADL2-AS1 | 0.011694 | 0.004016 | 948 |
| Y_RNA ENST00000365068.1 | 0.012318 | 0.004933 | 891 |
| misc RNA DLEU2 | 0.011427 | 0.004455 | 835 |
| antisense RP11-874J12.4 | 0.011055 | 0.004207 | 830 |
| hsa-miR-432-5p | 0.010819 | 0.004178 | 827 |
| lncRNA C15orf54 | 0.009861 | 0.003446 | 813 |
| hsa-miR-6721-5p | 0.011645 | 0.004544 | 805 |
| sense intronic CTD-3092A11.2 | 0.011123 | 0.004365 | 801 |
| Y_RNA ENST00000516950.1 | 0.011071 | 0.004198 | 794 |
| antisense DPYD-AS2 | 0.009608 | 0.003261 | 769 |
| hsa-miR-6131 | 0.011233 | 0.004398 | 760 |
| misc RNA 7SK | 0.010671 | 0.004205 | 752 |
| antisense KCTD21-AS1 | 0.00875 | 0.00281 | 744 |
| lncRNA RP13-216E22.4 | 0.008391 | 0.002512 | 717 |
| antisense MIR223 | 0.010194 | 0.003838 | 712 |
| hsa-miR-4433b-3p | 0.010528 | 0.004083 | 702 |
| lncRNA RP11-930O11.2 | 0.009267 | 0.003152 | 698 |
| Total (n = 122) | Control (n = 79) | PDAC (n = 43) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Male | 55 (45.08%) | 27 (34.18%) | 28 (65.12%) |
| Female | 67 (54.92%) | 52 (65.82%) | 15 (34.88%) |
| Age (Mean ± SD) | 54.11 ± 16.05 | 48.60 ± 15.73 | 64.23 ± 10.98 |
| BMI (Mean ± SD) | 25.62 ± 5.00 | 26.01 ± 5.12 | 24.76 ± 4.64 |
| Hospital | |||
| Hadassah | 110 (90.16%) | 79 (100%) | 31 (72.09%) |
| Sheba | 12 (9.84%) | 0 (0%) | 12 (27.91%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Volkov, H.; Shlayem, R.; Shomron, N. Deciphering the Diagnostic Potential of Small Non-Coding RNAs for the Detection of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Through Liquid Biopsies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168108
Volkov H, Shlayem R, Shomron N. Deciphering the Diagnostic Potential of Small Non-Coding RNAs for the Detection of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Through Liquid Biopsies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):8108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168108
Chicago/Turabian StyleVolkov, Hadas, Rani Shlayem, and Noam Shomron. 2025. "Deciphering the Diagnostic Potential of Small Non-Coding RNAs for the Detection of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Through Liquid Biopsies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 8108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168108
APA StyleVolkov, H., Shlayem, R., & Shomron, N. (2025). Deciphering the Diagnostic Potential of Small Non-Coding RNAs for the Detection of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Through Liquid Biopsies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 8108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168108






