Exploring the Protective Effects of Taxifolin in Cardiovascular Health: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
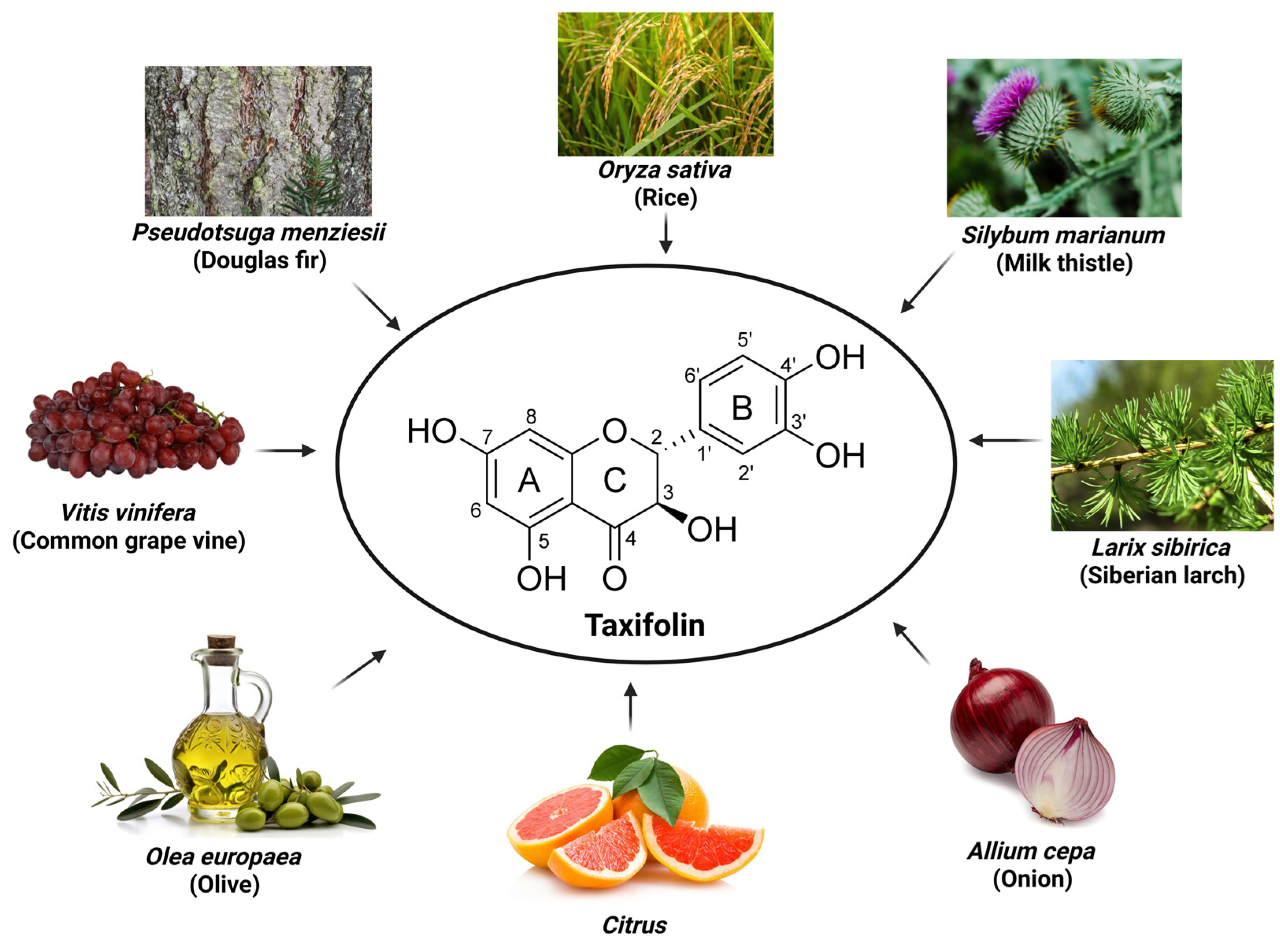
2. Taxifolin
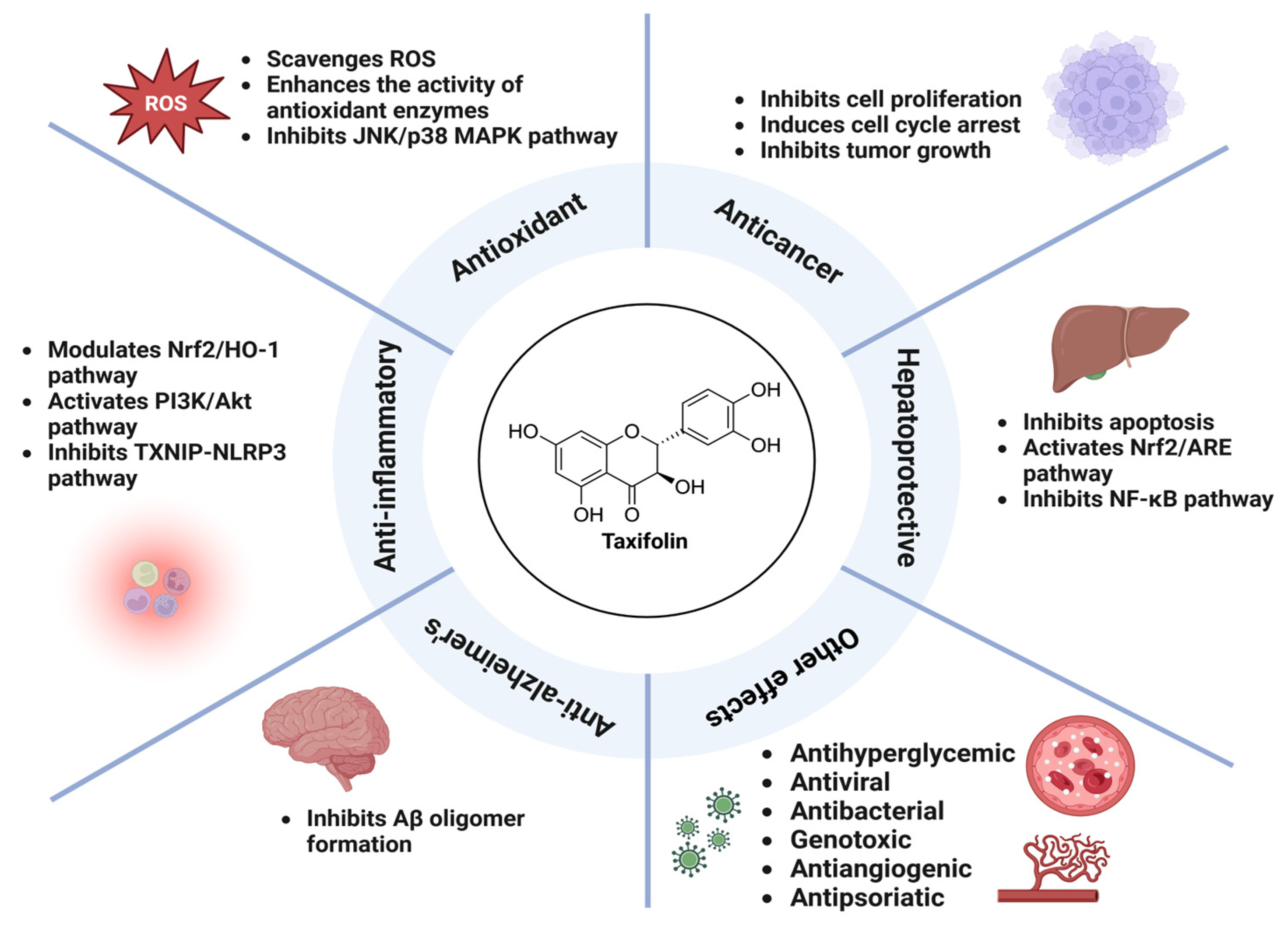
3. Pharmacological Activity of Taxifolin
3.1. Antioxidant Activity
3.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
3.3. Hepatoprotective Activity
3.4. Anticancer Activity
3.5. Anti-Alzheimer’s Activity
3.6. Other Pharmacological Activities
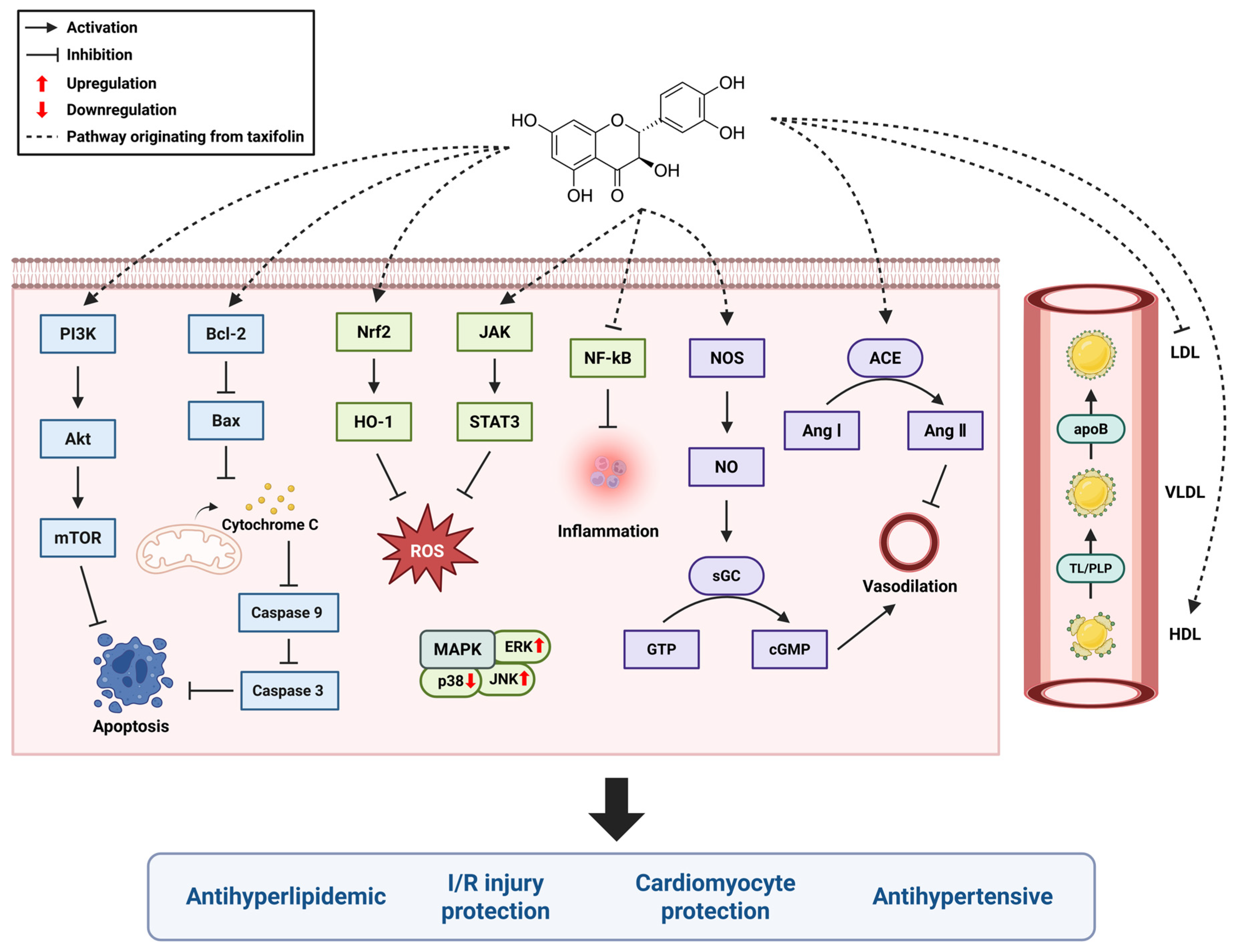
4. Taxifolin and the Cardiovascular System
4.1. Antihypertensive
4.2. Cardiomyocyte Protection
4.3. Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion (I/R) Injury Protection
4.4. Antihyperlipidemic
4.5. Clinical Studies
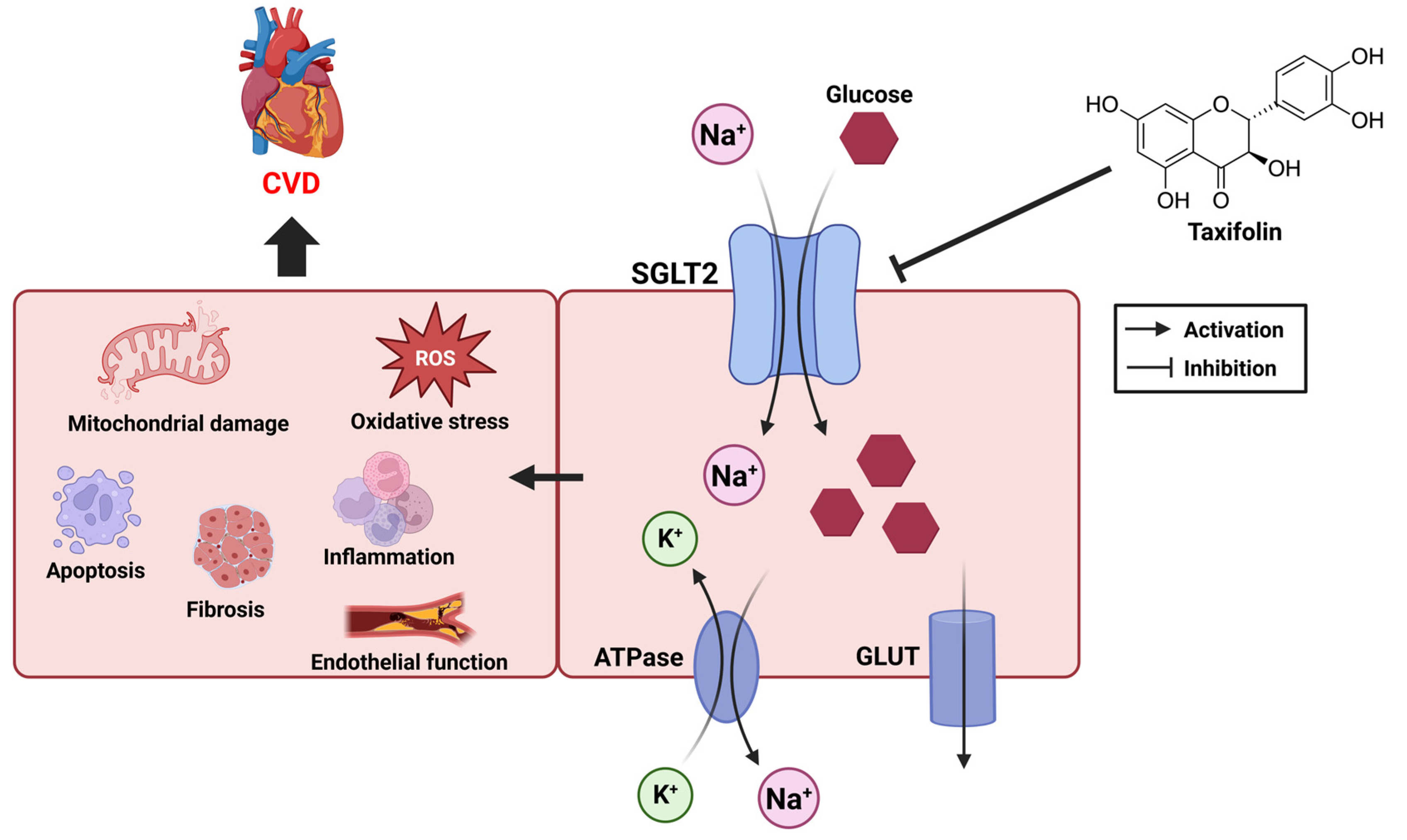
5. Future Research Directions
5.1. CVD and Sodium–Glucose Transporter
5.2. SGLT and Taxifolin
5.3. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thiriet, M. Cardiovascular disease: An introduction. In Vasculopathies: Behavioral, Chemical, Environmental, and Genetic Factors; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–90. [Google Scholar]
- Rader, D.J.; Daugherty, A. Translating molecular discoveries into new therapies for atherosclerosis. Nature 2008, 451, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgary, S.; Rastqar, A.; Keshvari, M. Functional food and cardiovascular disease prevention and treatment: A review. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2018, 37, 429–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, L.; Kroon, P.A.; Rimm, E.B.; Cohn, J.S.; Harvey, I.; Le Cornu, K.A.; Ryder, J.J.; Hall, W.L.; Cassidy, A. Flavonoids, flavonoid-rich foods, and cardiovascular risk: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Yang, C.; Zuo, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Taxifolin protects rat against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by modulating the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeidat, H.M.; Althunibat, O.Y.; Alfwuaires, M.A.; Aladaileh, S.H.; Algefare, A.I.; Almuqati, A.F.; Alasmari, F.; Aldal’in, H.K.; Alanezi, A.A.; Alsuwayt, B. Cardioprotective effect of taxifolin against isoproterenol-induced cardiac injury through decreasing oxidative stress, inflammation, and cell death, and activating Nrf2/HO-1 in mice. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Baidya, R.; Chakraborty, T.; Samanta, A.K.; Roy, S. Pharmacological basis and new insights of taxifolin: A comprehensive review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 112004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pew, J.C. A Flavonone from Douglas-Fir Heartwood2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1948, 70, 3031–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, C.; Xu, B. An insight into the health-promoting effects of taxifolin (dihydroquercetin). Phytochemistry 2019, 166, 112066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Luo, L.; Zong, D.; Li, H.; Zeng, Z.; Cui, Y.; Meng, W.; Chen, Y. Dihydroquercetin suppresses cigarette smoke induced ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by activating Nrf2-mediated pathway. Phytomedicine 2022, 96, 153894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilahur, G.; Casaní, L.; Peña, E.; Crespo, J.; Juan-Babot, O.; Ben-Aicha, S.; Mendieta, G.; Béjar, M.T.; Borrell, M.; Badimon, L. Silybum marianum provides cardioprotection and limits adverse remodeling post-myocardial infarction by mitigating oxidative stress and reactive fibrosis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 270, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendler, B.S. Garlic (Allium sativum) and onion (Allium cepa): A review of their relationship to cardiovascular disease. Prev. Med. 1987, 16, 670–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.K. Health benefits of onion bioactives on hypercholesterolemia, cardiovascular diseases, and bone mineral density. Food Front. 2020, 1, 107–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Tian, S.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, D.; Chen, Y.; Shi, Y.; Sun, Z. Determination of active component in silymarin by RP-LC and LC/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2001, 26, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Distylin (accessed on 17 August 2025).
- Beecher, G.R. Overview of dietary flavonoids: Nomenclature, occurrence and intake. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 3248S–3254S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice-Evans, C.A.; Miller, N.J.; Paganga, G. Structure-antioxidant activity relationships of flavonoids and phenolic acids. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 933–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trouillas, P.; Fagnère, C.; Lazzaroni, R.; Calliste, C.; Marfak, A.; Duroux, J.-L. A theoretical study of the conformational behavior and electronic structure of taxifolin correlated with the free radical-scavenging activity. Food Chem. 2004, 88, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topal, F.; Nar, M.; Gocer, H.; Kalin, P.; Kocyigit, U.M.; Gülçin, İ.; Alwasel, S.H. Antioxidant activity of taxifolin: An activity–structure relationship. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nifant’ev, E.; Koroteev, M.; Kaziev, G.; Uminskii, A.; Grachev, A.; Men’shov, V.; Tsvetkov, Y.; Nifant’ev, N.; Bel’skii, V.; Stash, A. On the problem of identification of the dihydroquercetin flavonoid. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2006, 76, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terekhov, R.P.; Melnikov, E.S.; Nikitin, I.D.; Tokareva, M.A.; Rodina, T.A.; Savina, A.D.; Pankov, D.I.; Zhevlakova, A.K.; Beloborodov, V.L.; Selivanova, I.A. Diastereomers of spheroidal form and commercially available taxifolin samples. Sci. Pharm. 2024, 92, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhai, S.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Chu, S. An insight into novel therapeutic potentials of taxifolin. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1173855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, S.S.; Khan, K.; Badshah, Y.; Rafiq, M.; Shabbir, M. Evaluation of pro-apoptotic potential of taxifolin against liver cancer. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Rahaman, S. Flavonoids: A vital resource in healthcare and medicine. Pharm. Pharmacol. Int. J. 2020, 8, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, B.; Yang, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. Advances in Flavonoid Research: Sources, Biological Activities, and Developmental Prospectives. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 2884–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhong, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X. Enhancement of solubility, antioxidant ability and bioavailability of taxifolin nanoparticles by liquid antisolvent precipitation technique. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 471, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolhir, V.; Bykov, V.; Baginskaja, A.; Sokolov, S.; Glazova, N.; Leskova, T.; Sakovich, G.; Tjukavkina, N.; Kolesnik, Y.A.; Rulenko, I. Antioxidant activity of a dihydroquercetin isolated from Larix gmelinii (Rupr.) Rupr. wood. Phytother. Res. 1996, 10, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teselkin, Y.O.; Babenkova, I.; Kolhir, V.; Baginskaya, A.; Tjukavkina, N.; Kolesnik, Y.A.; Selivanova, I.; Eichholz, A. Dihydroquercetin as a means of antioxidative defence in rats with tetrachloromethane hepatitis. Phytother. Res. 2000, 14, 160–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xie, H.; Jiang, Q.; Wei, G.; Lin, L.; Li, C.; Ou, X.; Yang, L.; Xie, Y.; Fu, Z. The mechanism of (+) taxifolin’s protective antioxidant effect for •OH-treated bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2017, 22, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanezi, A.A.; Almuqati, A.F.; Alfwuaires, M.A.; Alasmari, F.; Namazi, N.I.; Althunibat, O.Y.; Mahmoud, A.M. Taxifolin prevents cisplatin nephrotoxicity by modulating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and mitigating oxidative stress and inflammation in mice. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Yuan, P.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zheng, X.; Feng, W. Taxifolin improves disorders of glucose metabolism and water-salt metabolism in kidney via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in metabolic syndrome rats. Life Sci. 2020, 263, 118713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, M.; Kato, H.; Iwashita, K.; Yamakage, H.; Kato, S.; Saito, S.; Ihara, M.; Nishimura, H.; Kawamoto, A.; Suganami, T. Taxifolin Suppresses Inflammatory Responses of High-Glucose-Stimulated Mouse Microglia by Attenuating the TXNIP–NLRP3 Axis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-L.; Lin, Y.-S.; Liu, K.-F.; Peng, W.-H.; Hsu, C.-M. Hepatoprotective mechanisms of taxifolin on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Huang, D. Protective effects of dihydroquercetin on an APAP-induced acute liver injury mouse model. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2017, 10, 10223. [Google Scholar]
- Okkay, U.; Ferah Okkay, I.; Cicek, B.; Aydin, I.C.; Ozkaraca, M. Hepatoprotective and neuroprotective effect of taxifolin on hepatic encephalopathy in rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 2022, 37, 1541–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razak, S.; Afsar, T.; Ullah, A.; Almajwal, A.; Alkholief, M.; Alshamsan, A.; Jahan, S. Taxifolin, a natural flavonoid interacts with cell cycle regulators causes cell cycle arrest and causes tumor regression by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oi, N.; Chen, H.; Ok Kim, M.; Lubet, R.A.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z. Taxifolin suppresses UV-induced skin carcinogenesis by targeting EGFR and PI3K. Cancer Prev. Res. 2012, 5, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Maki, T.; Hattori, Y.; Ito, H.; Mizuno, K.; Harada-Shiba, M.; Kalaria, R.N.; Fukushima, M.; Takahashi, R. Taxifolin inhibits amyloid-β oligomer formation and fully restores vascular integrity and memory in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2017, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Bao, X.; Ding, Y.; Shentu, J.; Cui, W.; Chen, X.; Wei, X.; Xu, S. Taxifolin prevents β-amyloid-induced impairments of synaptic formation and deficits of memory via the inhibition of cytosolic phospholipase A 2/prostaglandin E 2 content. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Saito, S.; Tanaka, M.; Yamakage, H.; Kusakabe, T.; Shimatsu, A.; Ihara, M.; Satoh-Asahara, N. Pleiotropic neuroprotective effects of taxifolin in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 10031–10038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Park, H.J.; Shin, H.K.; Hong, K.W.; Kim, C.D. Concurrent treatment with taxifolin and cilostazol on the lowering of β-amyloid accumulation and neurotoxicity via the suppression of P-JAK2/P-STAT3/NF-κB/BACE1 signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taldaev, A.; Savina, A.D.; Olicheva, V.V.; Ivanov, S.V.; Terekhov, R.P.; Ilyasov, I.R.; Zhevlakova, A.K.; Selivanova, I.A. Protective Properties of Spheroidal Taxifolin Form in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.; Chohan, T.A.; Waheed, I.; Gilani, Z.; Akash, M.S.H. Taxifolin prevents postprandial hyperglycemia by regulating the activity of α-amylase: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico studies. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurumayum, S.; Bharadwaj, S.; Sheikh, Y.; Barge, S.R.; Saikia, K.; Swargiary, D.; Ahmed, S.A.; Thakur, D.; Borah, J.C. Taxifolin-3-O-glucoside from Osbeckia nepalensis Hook. mediates antihyperglycemic activity in CC1 hepatocytes and in diabetic Wistar rats via regulating AMPK/G6Pase/PEPCK signaling axis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 303, 115936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogoi, N.; Chowdhury, P.; Goswami, A.K.; Das, A.; Chetia, D.; Gogoi, B. Computational guided identification of a citrus flavonoid as potential inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 main protease. Mol. Divers. 2021, 25, 1745–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artem’Eva, O.; Pereselkova, D.; Fomichev, Y.P. Dihydroquercetin, the bioactive substance, to be used against pathogenic microorganisms as an alternative to antibiotics. Сельскохозяйственная Биология 2015, 50, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cushnie, T.T.; Lamb, A.J. Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 26, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhanataev, A.; Kulakova, A.; Nasonova, V.; Durnev, A. In vivo study of dihydroquercetin genotoxicity. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 145, 338–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, W.; Pattanayak, S.P.; Sinha, B.N. Evaluation of taxifolin and phloretin as antiangiogenic flavonoids: An in vivo, in vitro experimental analysis. Int. J. Pharm. Sci 2015, 7, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Li, N.; Zhang, M.; Lu, C.; Du, Z.; Zhu, W.; Wu, D. Taxifolin attenuates IMQ-induced murine psoriasis-like dermatitis by regulating T helper cell responses via Notch1 and JAK2/STAT3 signal pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 123, 109747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliciano, R.P.; Pritzel, S.; Heiss, C.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A. Flavonoid intake and cardiovascular disease risk. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 2, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xu, D.; Shan, T.; Zhang, F.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, D. Taxifolin protects against cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis during biomechanical stress of pressure overload. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 287, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernatova, I.; Liskova, S. Mechanisms modified by (−)-epicatechin and taxifolin relevant for the treatment of hypertension and viral infection: Knowledge from preclinical studies. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, K.; Uchida, Y.; Murakami, N.; Mizutani, K.; Masuda, H. Effect of astilbin in tea processed from leaves of engelhardtia chrysolepis., on the serum and liver lipid concentrations and on the erythrocyte and liver antioxidative enzyme activities of rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1996, 60, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itaya, S.; Igarashi, K. Effects of taxifolin on the serum cholesterol level in rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1992, 56, 1492–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyuk, V.A.; Kraemer, T.; Sies, H.; Schewe, T. Myeloperoxidase/nitrite-mediated lipid peroxidation of low-density lipoprotein as modulated by flavonoids. FEBS Lett. 2003, 537, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theriault, A.; Wang, Q.; Van Iderstine, S.C.; Chen, B.; Franke, A.A.; Adeli, K. Modulation of hepatic lipoprotein synthesis and secretion by taxifolin, a plant flavonoid1. J. Lipid Res. 2000, 41, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arutyunyan, T.V.; Korystova, A.F.; Kublik, L.N.; Levitman, M.K.; Shaposhnikova, V.V.; Korystov, Y.N. Effects of taxifolin on the activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme and reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in the aorta of aging rats and rats treated with the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor and dexamethasone. Age 2013, 35, 2089–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liskova, S.; Cacanyiova, S.; Cebova, M.; Berenyiova, A.; Kluknavsky, M.; Micurova, A.; Valachova, K.; Soltes, L.; Bernatova, I. Taxifolin reduces blood pressure via improvement of vascular function and mitigating the vascular inflammatory response in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukhovskaya, E.; Slashcheva, G.; Shaykhutdinova, E.; Ismailova, A.; Palikova, Y.A.; Palikov, V.; Rasskazova, E.; Semushina, S.; Perepechenova, N.; Sadovnikova, E. Taxifolin reduces blood pressure in elderly hypertensive male Wistar rats. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022, 174, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korystova, A.; Kublik, L.; Kim, Y.A.; Levitman, M.K.; Shaposhnikova, V.; Korystov, Y.N. Dihydroquercetin and fucoidin inhibit the increase of angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in the rat aorta after irradiation. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 165, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnikov, M.; Aliev, O.; Sidekhmenova, A.; Shamanaev, A.Y.; Anishchenko, A.; Nosarev, A.; Pushkina, E. Modes of hypotensive action of dihydroquercetin in arterial hypertension. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 162, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, E.-H.; Gong, D.-S.; Shiwakoti, S.; Adhikari, D.; Kim, H.J.; Oak, M.-H. Taxifolin as a major bioactive compound in the vasorelaxant effect of different pigmented rice bran extracts. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 799064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Bi, R.; Hao, J.; Wang, S.; Huo, Y.; Demoz, R.M.; Banda, R.; Tian, S.; Xin, C.; Fu, M. A study on the protective effects of taxifolin on human umbilical vein endothelial cells and THP-1 cells damaged by hexavalent chromium: A probable mechanism for preventing cardiovascular disease induced by heavy metals. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 3851–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Wang, J. Taxifolin protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and ferroptosis by adjusting microRNA-200a-mediated Nrf2 signaling pathway. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Wang, X.; Ye, Y.; Wang, T.; Su, Q.; Zhan, J.; Shen, J.; Zeng, M.; Zhao, M. Oxidative Stress Protection Mechanism of Taxifolin in H9C2 Cells. Chin. Gen. Pract. 2019, 22, 1794. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, G.; Cai, J.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, D.; Liu, Q.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, Z. Taxifolin alleviates apoptotic injury induced by DEHP exposure through cytochrome P450 homeostasis in chicken cardiomyocytes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 183, 109582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Shi, G.; Cai, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Z. Di-(2-ethyl hexyl) phthalate induces necroptosis in chicken cardiomyocytes by triggering calcium overload. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Shi, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q.; Gong, Y.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Z. Taxifolin ameliorates DEHP-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy via attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction and glycometabolism disorder in chicken. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coşgun, M.S.; Çoşkun, R.; Celik, A.I. The preventive effect of taxifolin on acrylamide-induced heart damage in rats. Rev. Nutr. 2022, 35, e210079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, E.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhu, X.; Hou, W. Inhibition of HMGB1 might enhance the protective effect of taxifolin in cardiomyocytes via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2021, 20, 316. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Chen, R.-c.; Yang, Z.-h.; Sun, G.-b.; Wang, M.; Ma, X.-j.; Yang, L.-j.; Sun, X.-b. Taxifolin prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy in vivo and in vitro by inhibition of oxidative stress and cell apoptosis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 63, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Jiang, H.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y. Cardioprotective effects of dihydroquercetin against ischemia reperfusion injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Ren, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, X.; Zhang, P.-C. Clinical development and informatics analysis of natural and semi-synthetic flavonoid drugs: A critical review. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 63, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustin, R.; Mayoux, E. Mammalian sugar transporters. In Glucose Homeostasis; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, E.M.; Ghezzi, C.; Loo, D.D. Novel and unexpected functions of SGLTs. Physiology 2017, 32, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajewska, A.; Wasiak, J.; Sapeda, N.; Młynarska, E.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. SGLT2 Inhibitors in Kidney Diseases—A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Xiao, Y.; Tai, S.; Yang, H.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, Z. Emerging roles of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors in diabetic cardiovascular diseases: Focusing on immunity, inflammation and metabolism. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 836849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moparthi, K.P.; Al Rushaidi, M.T.; Muddam, M.R.; Obajeun, O.A.; Abaza, A.; Jaramillo, A.P.; Idris, F.S.; Shaikh, H.A.; Vahora, I.; Nath, T.S. Efficacy and Safety of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors to Decrease the Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e44054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margonato, D.; Galati, G.; Mazzetti, S.; Cannistraci, R.; Perseghin, G.; Margonato, A.; Mortara, A. Renal protection: A leading mechanism for cardiovascular benefit in patients treated with SGLT2 inhibitors. Heart Fail. Rev. 2021, 26, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.M.; Battson, M.L.; Jarrell, D.K.; Hou, S.; Ecton, K.E.; Weir, T.L.; Gentile, C.L. SGLT2 inhibition via dapagliflozin improves generalized vascular dysfunction and alters the gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic mice. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, H.M.; Fukuda, D.; Yagi, S.; Soeki, T.; Shimabukuro, M.; Sata, M. Glycemic control with ipragliflozin, a novel selective SGLT2 inhibitor, ameliorated endothelial dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mouse. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2016, 3, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallow, K.M.; Helmlinger, G.; Greasley, P.J.; McMurray, J.J.; Boulton, D.W. Why do SGLT2 inhibitors reduce heart failure hospitalization? A differential volume regulation hypothesis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, F.; Scheen, A. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on systemic and tissue low-grade inflammation: The potential contribution to diabetes complications and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Metab. 2018, 44, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsu, Y.; Kokubo, H.; Bumdelger, B.; Yoshizumi, M.; Yamamotoya, T.; Matsunaga, Y.; Ueda, K.; Inoue, Y.; Inoue, M.-K.; Fujishiro, M. The SGLT2 inhibitor luseogliflozin rapidly normalizes aortic mRNA levels of inflammation-related but not lipid-metabolism-related genes and suppresses atherosclerosis in diabetic ApoE KO mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Flynn, E.R.; do Carmo, J.M.; Wang, Z.; da Silva, A.A.; Mouton, A.J.; Omoto, A.C.; Hall, M.E.; Hall, J.E. Direct cardiac actions of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition improve mitochondrial function and attenuate oxidative stress in pressure overload-induced heart failure. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 859253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahara, A.; Takasu, T.; Yokono, M.; Imamura, M.; Kurosaki, E. Characterization and comparison of SGLT2 inhibitors: Part 3. Effects on diabetic complications in type 2 diabetic mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 809, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallon, V.; Verma, S. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on kidney and cardiovascular function. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2021, 83, 503–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; De Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Law, G.; Desai, M.; Matthews, D.R. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Silverman, M.G.; Zelniker, T.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, F.; Cannon, C.P.; Cherney, D.Z.; Masiukiewicz, U.; Pratley, R.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; Frederich, R.; Charbonnel, B.; Mancuso, J.; Shih, W.J. Efficacy of ertugliflozin on heart failure–related events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: Results of the VERTIS CV Trial. Circulation 2020, 142, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabel, A.; Salama, S.A. Effect of taxifolin/dapagliflozin combination on colistin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pharmacological Activities | Taxifolin Dose | Molecular Targets/ Mechanisms | Study Type | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Vitro | In Vivo | ||||
| Antihyperlipidemic | 0.05% (w/w) | Liver total cholesterol ↓ Liver phospholipid ↓ TBARS ↓ | Wistar-strain rat | [54] | |
| 0.05% (w/w) 0.1% (w/w) | Total cholesterol ↓ HDL-cholesterol ↑ | Wistar-strain rat | [55] | ||
| 2 μM | NO2 radical scavenging MPO/Nitrite-induced LDL oxidation ↓ | Human LDL | [56] | ||
| 50, 100, 200 μM | HMG-CoA reductase ↓ apoB ↓ apoA-I ↑ | HepG2 cell | [57] | ||
| Antihypertension | 30, 100 μg/kg | ACE activity ↓ ROS/RNS ↓ 5-lipoxygenase ↓ NADPH oxidase ↓ | L-NAME and dexamethasone- treated Wistar rat | [58] | |
| 20 mg/kg | Blood pressure ↓ COX2 ↓ Total NOS activity ↑ IL-10 ↑ | SHR | [59] | ||
| 100 μg/kg | Systolic blood pressure ↓ | Aged Wistar rat | [60] | ||
| 100 μg/kg | ROS scavenging ACE activity ↓ | X-ray-irradiated Wistar rat | [61] | ||
| 20 mg/kg | Blood viscosity ↓ Vasodilation ↑ | SHR | [62] | ||
| 1–300 μM | eNOS ↑ PI3K/eNOS/cGMP pathway | Porcine coronary artery rings and endothelial cell | [63] | ||
| Cardiomyocyte protection | 30, 50 μM | Oxidative stress ↓ Cell apoptosis ↓ Cell adhesion ↓ | HUVECs THP-1 cell | [64] | |
| 10 μM 20 mg/kg | Ferroptosis ↓ Oxidative stress ↓ miR-200a expression ↑ Nrf2 ↑ | H9C2 cell | Dox-treated C57BL/6 mice | [65] | |
| 20, 50 mg/kg | Malondialdehyde ↓ Oxidative stress ↓ Nrf2, HO-1 ↑ | ISO-treated Swiss albino mice | [6] | ||
| 200 μM | iNOS, OPN ↓ HMGB1 ↑ | H9C2 cell | [66] | ||
| 0.5 μM | Cell apoptosis ↓ Oxidative stress ↓ Cytochrome P450 ↑ | Primary chicken cardiomyocytes | [67] | ||
| 0.5 μM | Ca2+ overload ↓ CaMKII-RIPK3 ↓ | Primary chicken cardiomyocytes | [68] | ||
| Cardioprotection | 0.5 μM | IL-6/JAK/STAT3 ↓ PPARs/PGC-1α ↑ | Primary chicken cardiomyocytes | [69] | |
| 50 mg/kg | Malondialdehyde ↓ Troponin I ↓ ROS scavenging Inhibition of NF-kB pathway | Acrylamide-treated Wistar rat | [70] | ||
| 100 μg/mL 200 mg/kg | HIF-1α ↓ eNOS, VEGF-α, TGF-β, FGF21 ↑ Activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR/STAT3 pathway | H9C2 cell | [71] | ||
| 5, 10, 25, 50 μM 0.2% (w/w) | Malondialdehyde ↓ MMP-9, TIMP1 ↓ Inhibition of MAPKs, TGF-β/Smad pathway | Neonatal rat cardiomyocytes | TAC model C57BL/6 mice | [52] | |
| 10, 20, 40 μg/mL 25, 50, 100 mg/kg | NADPH oxidase ↓ Angiotensin II ↓ p-JAK2, p-STAT3 ↑ | H9C2 cell | STZ-treated C57BL/6 mice | [72] | |
| I/R injury prevention | 2.5, 5, 10, 20, 40, 80 μM 5, 10, 20 μM | ER stress ↓ Cell apoptosis ↓ Nrf2, HO-1 ↑ Activation of PI3K/AKT pathway | H9C2 cell, Langendorff-perfused SD rat heart model | [73] | |
| 5, 15 mM | Bax, cytochrome C ↓ Malondialdehyde ↓ Bcl-2 ↑ SOD, GSH-PX ↑ | Langendorff-perfused SD rat heart model | [5] | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sim, H.-H.; Ko, J.-Y.; Gong, D.-S.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, J.J.; Lim, H.-K.; Kim, H.J.; Oak, M.-H. Exploring the Protective Effects of Taxifolin in Cardiovascular Health: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168051
Sim H-H, Ko J-Y, Gong D-S, Kim D-W, Kim JJ, Lim H-K, Kim HJ, Oak M-H. Exploring the Protective Effects of Taxifolin in Cardiovascular Health: A Comprehensive Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):8051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168051
Chicago/Turabian StyleSim, Hwan-Hee, Ju-Young Ko, Dal-Seong Gong, Dong-Wook Kim, Jung Jin Kim, Han-Kyu Lim, Hyun Jung Kim, and Min-Ho Oak. 2025. "Exploring the Protective Effects of Taxifolin in Cardiovascular Health: A Comprehensive Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 8051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168051
APA StyleSim, H.-H., Ko, J.-Y., Gong, D.-S., Kim, D.-W., Kim, J. J., Lim, H.-K., Kim, H. J., & Oak, M.-H. (2025). Exploring the Protective Effects of Taxifolin in Cardiovascular Health: A Comprehensive Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 8051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168051








