Co-Infection Dynamics of Helicobacter pylori and Helminths: A Double-Edged Sword
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Immunological Interactions in Co-Infection
2.1. Immune Response to H. pylori
2.2. Immune Response to Helminths
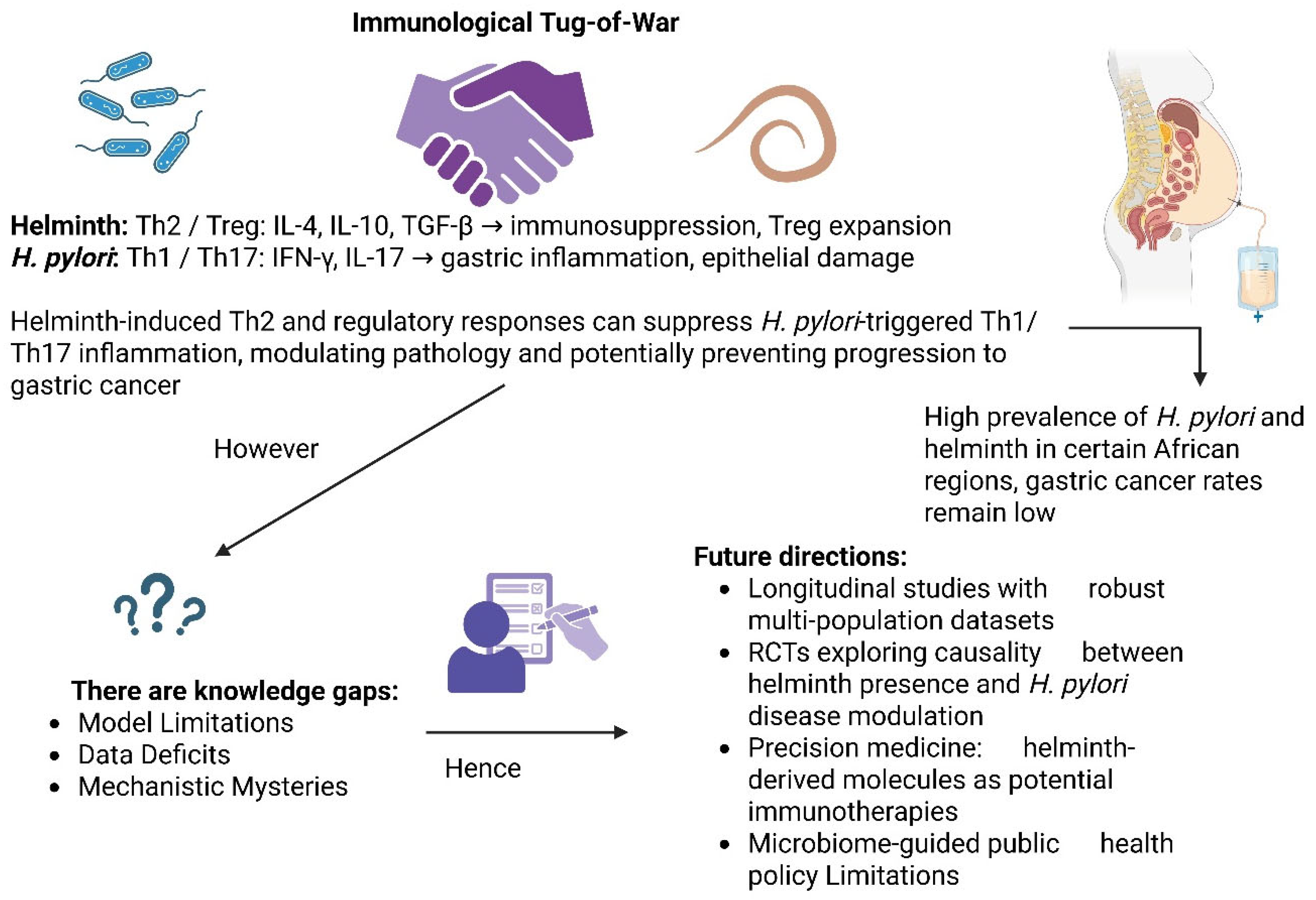
2.3. Modulatory Effects of Helminths on H. pylori
3. Epidemiology of H. pylori and Helminth Co-Infection
4. The Socioeconomic Factors That Influence the Geographic Distribution of These Co-Infections
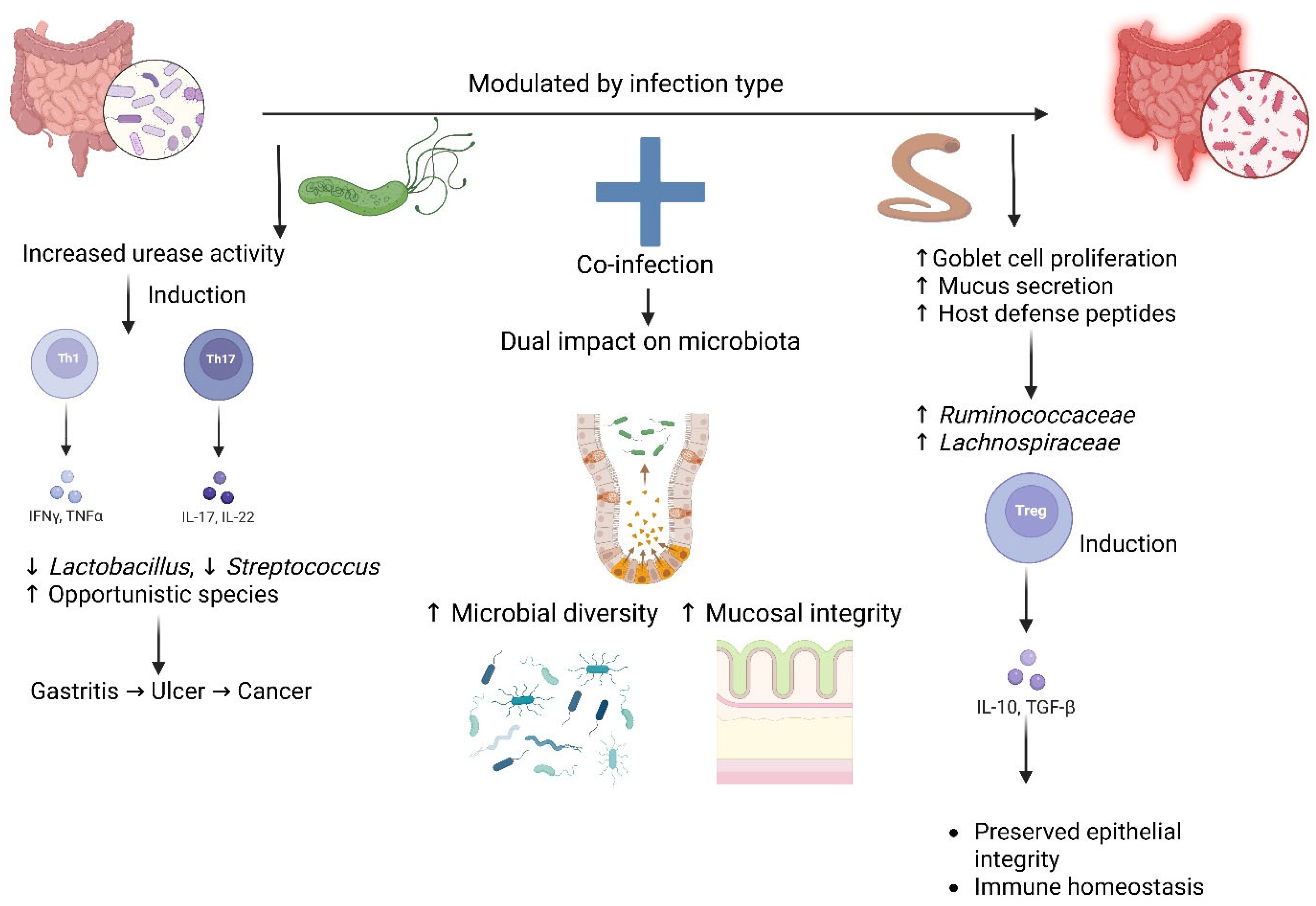
5. Microbiota Modulation During H. pylori and Helminth Co-Infection
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Öztekin, M.; Yılmaz, B.; Ağagündüz, D.; Capasso, R. Overview of Helicobacter pylori Infection: Clinical Features, Treatment, and Nutritional Aspects. Diseases 2021, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnichil, Z.; Nibret, E.; Hailegebriel, T.; Demelash, M.; Mekonnen, D. Prevalence and associated risk factors of Helicobacter pylori infection in East Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 55, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balen, J.; Raso, G.; Li, Y.-S.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Yuan, L.-P.; Williams, G.M.; Luo, X.-S.; Shi, M.-Z.; Yu, X.-L.; Utzinger, J.; et al. Risk factors for helminth infections in a rural and a peri-urban setting of the Dongting Lake area, People’s Republic of China. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 41, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andargie, Y.; Alelign, A.; Tekeste, Z. Prevalence and associated risk factors of soil-transmitted helminth infections among schoolchildren in Mekan Eyesus town, northwestern Ethiopia. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2024, 27, e00379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusters, J.G.; van Vliet, A.H.M.; Kuipers, E.J. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 449–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muttiah, B.; Wahid, W.; Sukri, A.; Hanafiah, A. Towards Effective Helicobacter pylori Eradication: Emerging Therapies in the Wake of Antibiotic Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; AlHussaini, K.I. Helicobacter pylori: A Contemporary Perspective on Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Treatment Strategies. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varyani, F.; Fleming, J.O.; Maizels, R.M. Helminths in the gastrointestinal tract as modulators of immunity and pathology. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G537–G549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, M.P.; Layland, L.E.; Hoerauf, A. Helminths and their implication in sepsis—A new branch of their immunomodulatory behaviour? Pathog. Dis. 2013, 69, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Lu, J. Helicobacter pylori Vaccine: Mechanism of Pathogenesis, Immune Evasion and Analysis of Vaccine Types. Vaccines 2025, 13, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Cao, Y.; Shi, H.N. Helminth infections and intestinal inflammation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 5125–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.P.J.; McManus, C.M.; Maizels, R.M. Regulatory T-cells in helminth infection: Induction, function and therapeutic potential. Immunology 2020, 160, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setshedi, M.; Watermeyer, G. The impact of Helicobacter pylori and intestinal helminth infections on gastric adenocarcinoma and inflammatory bowel disease in Sub-Saharan Africa. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1013779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewayani, A.; Fauzia, K.A.; Alfaray, R.I.; Waskito, L.A.; Doohan, D.; Rezkitha, Y.A.A.; Abdurachman, A.; Kobayashi, T.; I’tishom, R.; Yamaoka, Y.; et al. The Roles of IL-17, IL-21, and IL-23 in the Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastrointestinal Inflammation: A Review. Toxins 2021, 13, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhu, J.; Xu, H. Strategies of Helicobacter pylori in evading host innate and adaptive immunity: Insights and prospects for therapeutic targeting. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1342913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobiepanek, A.; Kuryk, Ł.; Garofalo, M.; Kumar, S.; Baran, J.; Musolf, P.; Siebenhaar, F.; Fluhr, J.W.; Kobiela, T.; Plasenzotti, R.; et al. The Multifaceted Roles of Mast Cells in Immune Homeostasis, Infections and Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Patel, G.K.; Ghoshal, U.C. Helicobacter pylori-Induced Inflammation: Possible Factors Modulating the Risk of Gastric Cancer. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, N.R.; Hartung, M.L.; Müller, A. Life in the human stomach: Persistence strategies of the bacterial pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Wang, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, H.; Cao, X.; Gu, Y. Mechanism and role of H. pylori CagA-induced NLRP3 inflammasome in gastric cancer immune cell infiltration. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 14335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijmons, D.; Guy, A.J.; Walduck, A.K.; Ramsland, P.A. Helicobacter pylori and the Role of Lipopolysaccharide Variation in Innate Immune Evasion. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 868225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheok, Y.Y.; Tan, G.M.Y.; Lee, C.Y.Q.; Abdullah, S.; Looi, C.Y.; Wong, W.F. Innate Immunity Crosstalk with Helicobacter pylori: Pattern Recognition Receptors and Cellular Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSorley, H.J.; Maizels, R.M. Helminth infections and host immune regulation. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 585–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inclan-Rico, J.M.; Siracusa, M.C. First Responders: Innate Immunity to Helminths. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogulur, I.; Mitamura, Y.; Yazici, D.; Pat, Y.; Ardicli, S.; Li, M.; D’Avino, P.; Beha, C.; Babayev, H.; Zhao, B.; et al. Type 2 immunity in allergic diseases. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2025, 22, 211–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, W.E.; Zhu, J. How are TH2-type immune responses initiated and amplified? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yin, W.; Westerberg, L.S.; Lee, P.; Gong, Q.; Chen, Y.; Dong, L.; Liu, C. Immune Dysregulation in IgG4-Related Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 738540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Appleton, J.A. Eosinophils in Helminth Infection: Defenders and Dupes. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzinelli-Guimaraes, P.H.; Nutman, T.B. Helminth parasites and immune regulation. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicchese, J.M.; Evans, S.; Hult, C.; Joslyn, L.R.; Wessler, T.; Millar, J.A.; Marino, S.; Cilfone, N.A.; Mattila, J.T.; Linderman, J.J.; et al. Dynamic balance of pro- and anti-inflammatory signals controls disease and limits pathology. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 285, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekki-Jóźwiak, J.; Bąska, P. The Roles of Various Immune Cell Populations in Immune Response against Helminths. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drurey, C.; Maizels, R.M. Helminth extracellular vesicles: Interactions with the host immune system. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 137, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-López, C.M.; Trelis, M.; Bernal, D.; Marcilla, A. Overview of the interaction of helminth extracellular vesicles with the host and their potential functions and biological applications. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 134, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, G.; Fumagalli, M.; Piazza, S.; Maranta, N.; Genova, F.; Sperandeo, P.; Sangiovanni, E.; Polissi, A.; Dell’agli, M.; De Fabiani, E. Investigating the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Early Response to Inflammation and Helicobacter pylori Infection in Human Gastric Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, J.G.; Beck, P.; Dangler, C.A.; Whary, M.T.; Wang, T.C.; Shi, H.N.; Nagler-Anderson, C. Concurrent enteric helminth infection modulates inflammation and gastric immune responses and reduces helicobacter-induced gastric atrophy. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larussa, T.; Leone, I.; Suraci, E.; Imeneo, M.; Luzza, F. Helicobacter pylori and T Helper Cells: Mechanisms of Immune Escape and Tolerance. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 981328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.E.; Sutherland, T.E. Host protective roles of type 2 immunity: Parasite killing and tissue repair, flip sides of the same coin. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whary, M.T.; Muthupalani, S.; Ge, Z.; Feng, Y.; Lofgren, J.; Shi, H.N.; Taylor, N.S.; Correa, P.; Versalovic, J.; Wang, T.C.; et al. Helminth co-infection in Helicobacter pylori infected INS-GAS mice attenuates gastric premalignant lesions of epithelial dysplasia and glandular atrophy and preserves colonization resistance of the stomach to lower bowel microbiota. Microbes Infect. 2014, 16, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Yamaoka, Y. Animal Models and Helicobacter pylori Infection. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cao, Z.; Liu, M.; Diamond, M.S.; Jin, X. The impact of helminth-induced immunity on infection with bacteria or viruses. Vet. Res. 2023, 54, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, U.C.; Chaturvedi, R.; Correa, P. The enigma of Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric cancer. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 29, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D. Solving the African enigma: Parasites may have their place. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmeier, H.; Krantz, I. The ‘African enigma’—Another explanation. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shan, C.; Zhu, Y.; Yao, X.; Lin, L.; Zhang, X.; Qian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Helminth-induced immune modulation in colorectal cancer: Exploring therapeutic applications. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1484686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallwood, T.B.; Giacomin, P.R.; Loukas, A.; Mulvenna, J.P.; Clark, R.J.; Miles, J.J. Helminth Immunomodulation in Autoimmune Disease. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Mejías-Luque, R.; Loffredo-Verde, E.; Toska, A.; Flossdorf, M.; Gerhard, M.; da Costa, C.P. Concomitant Infection of S. mansoni and H. pylori Promotes Promiscuity of Antigen-Experienced Cells and Primes the Liver for a Lower Fibrotic Response. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 231–244.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Blanchard, N.; LeibundGut-Landmann, S. Microbial (co)infections: Powerful immune influencers. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, M.; Sartelli, M.; McKimm, J.; Bin Abu Bakar, M. Health care-associated infections—An overview. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 2321–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Liu, H.; Ren, N.; Qadeer, A.; Tabios, I.K.B.; Fontanilla, I.K.C.; Leonardo, L.R.; Sripa, B.; Cheng, G. The Global Prevalence of and Factors Associated with Parasitic Coinfection in People Living with Viruses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pathogens 2025, 14, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayali, S.; Manfredi, M.; Gaiani, F.; Bianchi, L.; Bizzarri, B.; Leandro, G.; Di Mario, F.; Angelis, G.L.D. Helicobacter pylori, transmission routes and recurrence of infection: State of the art. Acta Biomed. 2018, 89, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangtakot, R.; Pinlaor, S.; Itthitaetrakool, U.; Chaidee, A.; Chomvarin, C.; Sangka, A.; Wilailuckana, C.; Pinlaor, P.; Blanke, S.R. Coinfection with Helicobacter pylori and Opisthorchis viverrini Enhances the Severity of Hepatobiliary Abnormalities in Hamsters. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00009-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navashenaq, J.G.; Shabgah, A.G.; Banach, M.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Penson, P.E.; Johnston, T.P.; Sahebkar, A. The interaction of Helicobacter pylori with cancer immunomodulatory stromal cells: New insight into gastric cancer pathogenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86 Pt 3, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ek, C.; Whary, M.T.; Ihrig, M.; Bravo, L.E.; Correa, P.; Fox, J.G. Serologic evidence that ascaris and toxoplasma infections impact inflammatory responses to Helicobacter pylori in Colombians. Helicobacter 2012, 17, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z.; El-Omar, E.; Lee, Y.Y. Dual infective burden of Helicobacter pylori and intestinal parasites: Good or bad news for the host? Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 39, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghipour, A.; Bahadory, S.; Badri, M.; Yadegar, A.; Mirsamadi, E.S.; Mirjalali, H.; Zali, M.R. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the co-infection of Helicobacter pylori with intestinal parasites: Public health issue or neglected correlation? Int. J. Environ. Heal. Res. 2020, 32, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wondmagegn, Y.M.; Girmay, G.; Amare, G.A.; Assefa, M.; Tamir, M.; Abriham, Z.Y.; Setegn, A. Prevalence of intestinal parasites and Helicobacter pylori co-infection in people with gastrointestinal symptoms in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aklilu, A.; Woldemariam, M.; Wanke, E.; Seid, M.; Manilal, A.; Khan, J.M.; Akbar, I. Intestinal parasitic co-infections associated with Helicobacter pylori among paediatric patients with gastrointestinal illness attending a general hospital in southern Ethiopia. BMC Pediatr. 2024, 24, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hameed, Y.F.A.; Boghdadi, A.M.; Ghobrial, C.M.; Hassan, M.A. Association of Helicobacter pylori and parasitic infections in childhood: Impact on clinical manifestations and implications. J. Parasit. Dis. 2021, 45, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aniekwe, O.; Jolaiya, T.; Ajayi, A.; Adeleye, I.; Gerhard, M.; Smith, S. Co-infection of Helicobacter pylori and intestinal parasites in children of selected low-income communities in Lagos State, Nigeria. Parasitol. Int. 2024, 101, 102896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshareef, S.A.; Hassan, A.A.; Abdelrahman, D.N.; AlEed, A.; Al-Nafeesah, A.; Adam, I. The prevalence and associated factors of Helicobacter pylori infection among asymptomatic adolescent schoolchildren in Sudan: A cross-sectional study. BMC Pediatr. 2023, 23, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whary, M.T.; Sundina, N.; Bravo, L.E.; Correa, P.; Quinones, F.; Caro, F.; Fox, J.G. Intestinal helminthiasis in Colombian children promotes a Th2 response to Helicobacter pylori: Possible implications for gastric carcinogenesis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2005, 14, 1464–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.; Perez, G.P.; Ximenez, C.; Muñoz, L.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Ramos, F.; Gomez, A.; Muñoz, O. The association of intestinal parasitosis and H. pylori infection in children and adults from a Mexican community with high prevalence of parasitosis. Helicobacter 2003, 8, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasri, P.; Saneian, H.; Famouri, F.; Khademian, M.; Salehi, F. Helicobacter pylori infection in pediatrics with gastrointestinal complaints. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2022, 14, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moreira, E.D., Jr.; Nassri, V.B.; Santos, R.S.; Matos, J.F.; de Carvalho, W.A.; Silvani, C.S.; Santana e Sant’ana, C. Association of Helicobacter pylori infection and giardiasis: Results from a study of surrogate markers for fecal exposure among children. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 2759–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin-Hameed, E.A.; Barajash, H.M. Helicobacter pylori and intestinal parasites co-infection: Estimation of risk factors among dyspeptic patients in Mukalla city, Hadhramout, Yemen. Hadhramout Univ. J. Nat. Appl. Sci. 2023, 20, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Boonyanugomol, W.; Chomvarin, C.; Sripa, B.; Bhudhisawasdi, V.; Khuntikeo, N.; Hahnvajanawong, C.; Chamsuwan, A. Helicobacter pylori in Thai patients with cholangiocarcinoma and its association with biliary inflammation and proliferation. HPB 2012, 14, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazuelo, M.B.; Epplein, M.; Correa, P. Gastric cancer: An infectious disease. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 24, 853–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justine, N.C.; Bhuko, J.; Rubagumya, S.L.; Basinda, N.S.; Ruganuza, D.M.; Zinga, M.M.; Briet, M.; Misko, V.R.; Legein, F.; Mohamed, H.; et al. and Risk Factors for Soil-transmitted Helminth Infections among School Children in Northwestern Tanzania. Pathogens 2024, 13, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, O.A.; Babalola, A.S.; Olapegba, T. Prevalence of soil-transmitted helminth infection among children under 2 years from urban and rural settings in Ogun state, Nigeria: Implication for control strategy. Egypt. Pediatr. Assoc. Gaz. 2022, 70, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumara, M. Helicobacter pylori in children: Think before you kill the bug! Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2023, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauziah, N.; Aviani, J.K.; Agrianfanny, Y.N.; Fatimah, S.N. Intestinal Parasitic Infection and Nutritional Status in Children under Five Years Old: A Systematic Review. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, N.; Dessie, G.; Rahman, M.M.; Khanam, R. Socioeconomic status and health behavior in children and adolescents: A systematic literature review. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1228632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, F.; la Paz, S.M.-D.; Leon, M.J.; Rivero-Pino, F. Effects of Malnutrition on the Immune System and Infection and the Role of Nutritional Strategies Regarding Improvements in Children’s Health Status: A Literature Review. Nutrients 2023, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirani, M.; Pakzad, R.; Haddadi, M.H.; Akrami, S.; Asadi, A.; Kazemian, H.; Moradi, M.; Kaviar, V.H.; Zomorodi, A.R.; Khoshnood, S.; et al. The global prevalence of gastric cancer in Helicobacter pylori-infected individuals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng’eTich, A.I.; Amoah, I.D.; Bux, F.; Kumari, S. Anthelmintic resistance in soil-transmitted helminths: One-Health considerations. Parasitol. Res. 2023, 123, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.T.; Issa, P.P.; Sinnathamby, E.S.; Granier, M.; Mayeux, H.; Eubanks, T.N.; Malone, K.; Ahmadzadeh, S.; Cornett, E.M.; Shekoohi, S.; et al. Helicobacter Pylori: A Review of Current Treatment Options in Clinical Practice. Life 2022, 12, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Hu, F.; Zhang, L.; Yang, G.; Ma, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, W.; Gao, W.; Dong, X. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection and identification of risk factors in rural and urban Beijing, China. Helicobacter 2009, 14, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshair, M.; Ugai, T.; Oze, I.; Kasugai, Y.; Koyanagi, Y.N.; Hara, K.; Ito, H.; Matsuo, K. Impact of socioeconomic status and sibling number on the prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection: A cross-sectional study in a Japanese population. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2022, 84, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldhuyzen van Zanten, S.J. Do socio-economic status, marital status and occupation influence the prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection? Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1995, 9 (Suppl. 2), 41–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spagnuolo, R.; Scarlata, G.G.M.; Paravati, M.R.; Abenavoli, L.; Luzza, F. Change in Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori Infection in the Treatment-Failure Era. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulled, N. Recommendations for empirical syndemics analyses: A stepwise methodological guide. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.W.; Durkin, M.J.; Olsen, M.A.; Keller, M.; Ma, Y.; O’nEil, C.A.; Butler, A.M. Rural-urban differences in antibiotic prescribing for uncomplicated urinary tract infection. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2021, 42, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shears, P. Poverty and infection in the developing world: Healthcare-related infections and infection control in the tropics. J. Hosp. Infect. 2007, 67, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, L.; DePriest, K.; Wilson, M.; Gross, D. Child Poverty, Toxic Stress, and Social Determinants of Health: Screening and Care Coordination. Online J. Issues Nurs. 2018, 23, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, B. Helicobacter pylori infection in developing countries: The burden for how long? Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaw, A.; Berhan, A.; Ayele, A.; Fentie, A.; Abebaw, A.; Malkamu, B.; Getie, B.; Erkihun, M.; Solomon, Y.; Eyayu, T.; et al. Prevalence of intestinal parasites and Helicobacter pylori coinfection, and contributing factors among patients with gastrointestinal manifestations at Addis Zemen primary hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. Gut Pathog. 2024, 16, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Placa, G.; Covino, M.; Candelli, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; Franceschi, F.; Merra, G. Relationship Between Human Microbiome and Helicobacter pylori. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgamato, C.; Rocco, A.; Compare, D.; Priadko, K.; Romano, M.; Nardone, G. Exploring the Link between Helicobacter pylori, Gastric Microbiota and Gastric Cancer. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheok, Y.Y.; Lee, C.Y.Q.; Cheong, H.C.; Vadivelu, J.; Looi, C.Y.; Abdullah, S.; Wong, W.F. An Overview of Helicobacter pylori Survival Tactics in the Hostile Human Stomach Environment. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikder, S.; Pierce, D.; Sarkar, E.R.; McHugh, C.; Quinlan, K.G.; Giacomin, P.; Loukas, A. Regulation of host metabolic health by parasitic helminths. Trends Parasitol. 2024, 40, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llinás-Caballero, K.; Caraballo, L. Helminths and Bacterial Microbiota: The Interactions of Two of Humans’ “Old Friends”. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Bonete, M.J.; Rajan, A.; Suriano, F.; Layunta, E. The Underrated Gut Microbiota Helminths, Bacteriophages, Fungi, and Archaea. Life 2023, 13, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lu, Y.; Xue, G.; Han, L.; Jia, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, P.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Y. Role of short-chain fatty acids in host physiology. Anim. Model. Exp. Med. 2024, 7, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, F.; Steinel, N.; Weber, J.; Ma, L.; Smith, C.; Correa, D.; Zhu, B.; Bolnick, D.; Wang, G. The gut microbiota response to helminth infection depends on host sex and genotype. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Pu, L.; Guo, A.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Du, X.; Guo, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. Helminth reshapes host gut microbiota and immunoregulation by deploying an antimicrobial program of innate immunity. Gut Microbes 2025, 17, 2496447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkaid, Y.; Hand, T.W. Role of the Microbiota in Immunity and Inflammation. Cell 2014, 157, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.O.; Yadegar, A.; Kargar, M.; Mirjalali, H.; Kafilzadeh, F. The impact of Helicobacter pylori infection on gut microbiota-endocrine system axis; modulation of metabolic hormone levels and energy homeostasis. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2020, 19, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; He, C.; Lu, N. Impacts of Helicobacter pylori infection and eradication on gastrointestinal microbiota: An up-to-date critical review and future perspectives. Chin. Med. J. 2024, 137, 2833–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbey, G.; Hanafiah, A.; Sproston, E. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastric Microbiota. Euroasian J. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 2020, 10, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zuo, T.; Frey, N.; Rangrez, A.Y. A systematic framework for understanding the microbiome in human health and disease: From basic principles to clinical translation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From Dietary Fiber to Host Physiology: Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Key Bacterial Metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Su, L.; Li, Y.; Long, S.R.; Chang, J.; Zhang, W.; Walker, W.A.; Xavier, R.J.; Cherayil, B.J.; Shi, H.N. Helminth-induced alterations of the gut microbiota exacerbate bacterial colitis. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 11, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosschot, T.P.; Reynolds, L.A. The impact of a helminth-modified microbiome on host immunity. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabavi-Rad, A.; Sadeghi, A.; Aghdaei, H.A.; Yadegar, A.; Smith, S.M.; Zali, M.R. The double-edged sword of probiotic supplementation on gut microbiota structure in Helicobacter pylori management. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2108655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogang, B.A.N.; Debrah, L.B.; Owusu, M.; Agyei, G.; Meyer, J.; Gmanyami, J.M.; Ritter, M.; Arndts, K.; Mensah, D.A.; Adjobimey, T.; et al. Helminth Coinfections Modulate Disease Dynamics and Vaccination Success in the Era of Emerging Infectious Diseases. Vaccines 2025, 13, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorani, M.; Tohumcu, E.; Del Vecchio, L.E.; Porcari, S.; Cammarota, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ianiro, G. The Influence of Helicobacter pylori on Human Gastric and Gut Microbiota. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-I.; Choi, J.-P.; Seo, J.; Kim, B.J.; Rho, M.; Han, J.K.; Kim, J.G. Helicobacter pylori-derived extracellular vesicles increased in the gastric juices of gastric adenocarcinoma patients and induced inflammation mainly via specific targeting of gastric epithelial cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeshi, K.; Ruscher, R.; Loukas, A.; Wangchuk, P. Immunomodulatory and biological properties of helminth-derived small molecules: Potential applications in diagnostics and therapeutics. Front. Parasitol. 2022, 1, 984152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruldas, K.; Dawson, K.; Saxena, M.; Titus, A.; Johnson, J.; Gwayi-Chore, M.-C.; Muliyil, J.; Kang, G.; Walson, J.L.; Khera, A.; et al. Evaluation of opportunities to implement community-wide mass drug administration for interrupting transmission of soil-transmitted helminths infections in India. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okesanya, O.J.; Eshun, G.; Ukoaka, B.M.; Manirambona, E.; Olabode, O.N.; Adesola, R.O.; Okon, I.I.; Jamil, S.; Singh, A.; Lucero-Prisno, D.E.; et al. and hygiene (WASH) practices in Africa: Exploring the effects on public health and sustainable development plans. Trop. Med. Health 2024, 52, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galactionova, K.; Sahu, M.; Gideon, S.P.; Kaliappan, S.P.; Morozoff, C.; Ajjampur, S.S.R.; Walson, J.; Means, A.R.; Tediosi, F. Costing interventions in the field: Preliminary cost estimates and lessons learned from an evaluation of community-wide mass drug administration for elimination of soil-transmitted helminths in the DeWorm3 trial. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e049734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Agnew, A.; Ye, X.-P.; Robinson, P.A.; Forman, D.; Crabtree, J.E. Helicobacter pylori and Schistosoma japonicum co-infection in a Chinese population: Helminth infection alters humoral responses to H. pylori and serum pepsinogen I/II ratio. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loke, P.; Lee, S.C.; Oyesola, O.O. Effects of helminths on the human immune response and the microbiome. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitman, J.D.; Sakanari, J.A.; Mitreva, M. Areas of Metabolomic Exploration for Helminth Infections. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Aspect | H. pylori Infection | Helminth Infection | Co-Infection Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immune Response Type | Th1 and Th17-dominant | Th2 and Regulatory (Treg) | Immune modulation: Th1 suppression, increased Treg/Th2 balance |
| Key Cytokines Involved | IL-2, IL-12, TNF-α, and IFN-γ (Th1); IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-21, and IL-22 (Th17) | IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-13, IL-10, and TGF-β | ↑ IL-4, IL-10, ↓ IFN-γ, ↓ IL-17A → anti-inflammatory environment |
| T Cell Polarization | Th1/Th17 skewing | Th2 skewing, Treg induction | Shift from Th1/Th17 to Th2/Treg profile |
| Innate Immune Cells Activated | Neutrophils, mast cells, and macrophages | Eosinophils, mast cells, basophils, and ILC2s | Balanced activation, reduced pro-inflammatory damage |
| Tissue Effect | Chronic gastritis, epithelial damage, gastric atrophy, and potential cancer | Tissue remodeling, parasite clearance, and mucosal repair | Reduced gastric inflammation, preserved mucosal integrity |
| Microbial Impact | Gastric dysbiosis, decreased α-diversity | ↑ SCFA-producing bacteria (Ruminococcaceae) | Improved microbial diversity, restoration of homeostasis |
| Immunoregulation | Limited via H. pylori immune evasion (Treg induction) | Strong: IL-10, TGF-β, and Treg proliferation | Enhanced Treg-mediated suppression of gastric pathology |
| Clinical Outcomes | Risk of gastric ulceration, metaplasia, and adenocarcinoma | Usually asymptomatic, chronic infection | Potential protection against H. pylori-associated disease progression |
| Experimental Evidence | Well-established in animal and human models | Strong in animal models, observed in endemic populations | Animal studies (INS-GAS mice); observational studies (Colombia, Venezuela) |
| Gaps in Knowledge | Need more research on chronic immune escape mechanisms | Limited clinical correlation with long-term outcomes | Scarcity of human trials; need for translational research in endemic populations |
| Country/Region | H. pylori Prevalence (%) | Helminth Prevalence (%) | Co-Infection Prevalence (%) | Parasite Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Egypt | ~69.4% | ~51.4% | 39.8% (95% CI: 27.8–51.9) | Mixed (helminths + protozoa) | High burden of both types |
| Ethiopia | — | — | 5.9% (95% CI: 4.1–7.6) | Mixed | One of the lowest rates |
| Uganda | — | — | 30.2% (children) | Mixed | Intermediate rates |
| Nigeria | 89.7% | — | ~7% | Mixed | High H. pylori but low co-infection |
| Sudan | — | — | 29.3% (pooled) | Mixed | Large variability |
| Colombia (Tumaco and Pasto) | ~93% | 25–54% | 21–45% (children) | Helminth-only | Mainly soil-transmitted helminths |
| Mexico | — | — | 50–70% (in H. pylori-infected children) | Mixed | Multiple intestinal parasites |
| Iran | — | — | 10–30% (in H. pylori-positive children) | Mixed | Protozoa + some helminths |
| Turkey | — | — | 15–45% (symptomatic children) | Protozoa-only | Primarily Giardia lamblia |
| Yemen | ~30% (dyspeptic patients) | — | — | Protozoa-only | Mainly Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia |
| Thailand | — | — | — | Helminth-only | Opisthorchis viverrini; cancer risk |
| Colombia (low gastric cancer areas) | — | — | — | Helminth-only | Higher Ascaris lumbricoides seropositivity |
| Global pooled | — | — | 31% (95% CI: 18.66–43.39) | Mixed | High heterogeneity |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muttiah, B.; Wahid, W.; Wahab, A.A.; Hanafiah, A. Co-Infection Dynamics of Helicobacter pylori and Helminths: A Double-Edged Sword. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8001. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168001
Muttiah B, Wahid W, Wahab AA, Hanafiah A. Co-Infection Dynamics of Helicobacter pylori and Helminths: A Double-Edged Sword. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):8001. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168001
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuttiah, Barathan, Wathiqah Wahid, Asrul Abdul Wahab, and Alfizah Hanafiah. 2025. "Co-Infection Dynamics of Helicobacter pylori and Helminths: A Double-Edged Sword" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 8001. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168001
APA StyleMuttiah, B., Wahid, W., Wahab, A. A., & Hanafiah, A. (2025). Co-Infection Dynamics of Helicobacter pylori and Helminths: A Double-Edged Sword. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 8001. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168001







