The Non-Traditional Cardiovascular Culprits in Chronic Kidney Disease: Mineral Imbalance and Uremic Toxin Accumulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mineral Metabolism
2.1. Dysregulation of Phosphate Homeostasis in CKD
2.2. Dysregulation of Calcium Homeostasis in CKD
2.3. Phosphate Imbalance on Vascular Calcification
2.4. Calcium Imbalance on Vascular Calcification
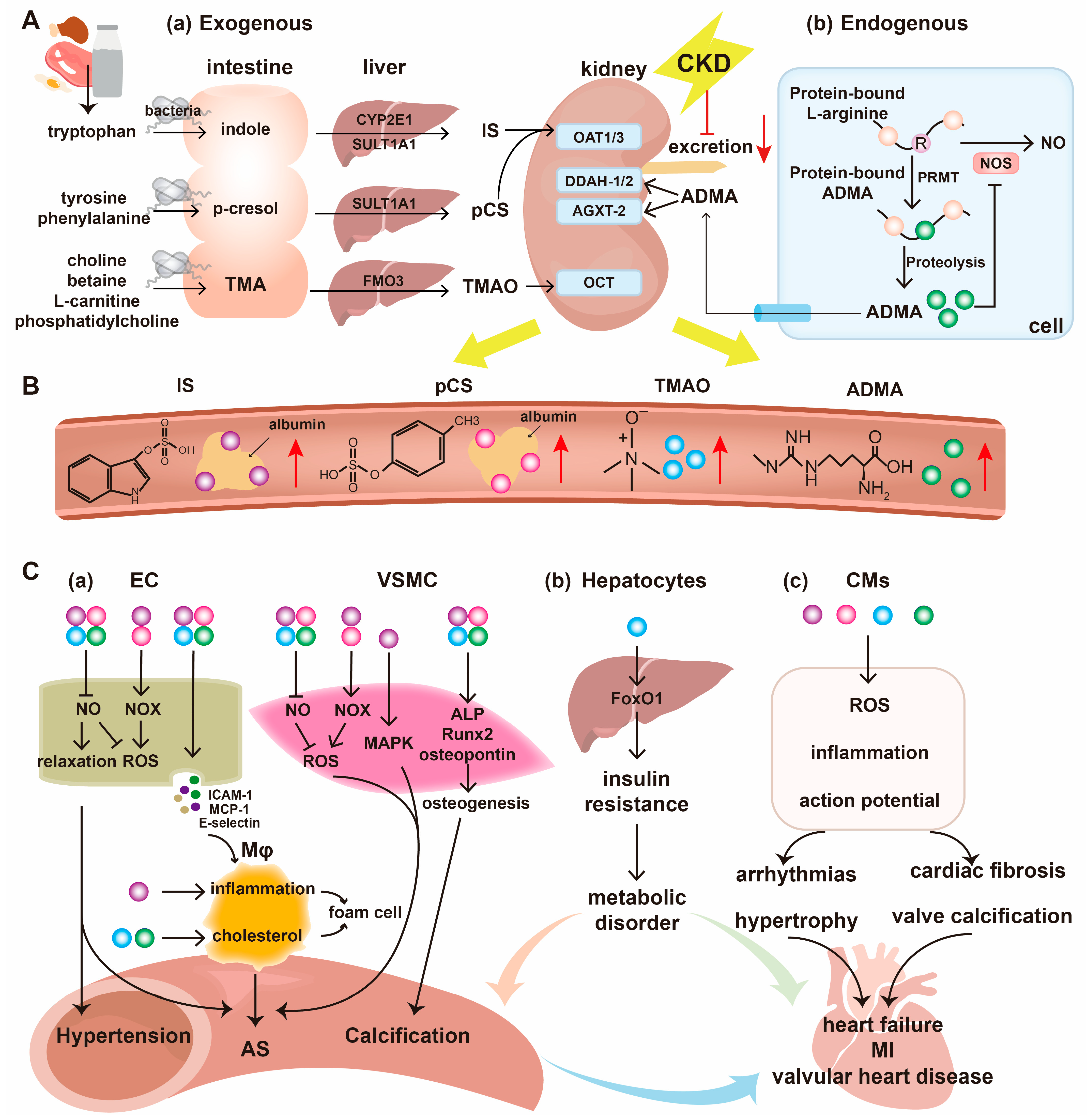
3. Uremic Toxins
3.1. Indoxyl Sulfate
3.1.1. Mechanisms for the Progression of CKD
3.1.2. Mechanisms for the Progression of CVD
3.2. P-Cresyl Sulfate
3.2.1. Mechanisms for the Progression of CKD
3.2.2. Mechanisms for the Progression of CVD
3.3. Trimethylamine N-Oxide
3.3.1. Mechanisms for the Progression of CKD
3.3.2. Mechanisms for the Progression of CVD
3.4. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine
3.4.1. Mechanisms for the Progression of CKD
3.4.2. Mechanisms for the Progression of CVD
4. Therapeutic Strategies for Specific Uremic Toxins
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Group KDIGOKCW. KDIGO 2024 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, S117–S314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, K.; Ballew, S.H.; Wang, A.Y.; Kalyesubula, R.; Schaeffner, E.; Agarwal, R. Epidemiology and risk of cardiovascular disease in populations with chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luyckx, V.A.; Tonelli, M.; Stanifer, J.W. The global burden of kidney disease and the sustainable development goals. Bull. World Health Organ. 2018, 96, 414–422C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M. Clinician’s guide to reducing inflammation to reduce atherothrombotic risk: JACC review topic of the week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 3320–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, N.; Katz, R.; Robinson-Cohen, C.; Odden, M.C.; Dalrymple, L.; Shlipak, M.G.; Sarnak, M.J.; Siscovick, D.S.; Zelnick, L.; Psaty, B.M.; et al. Absolute rates of heart failure, coronary heart disease, and stroke in chronic kidney disease: An analysis of 3 community-based cohort studies. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravid, J.D.; Kamel, M.H.; Chitalia, V.C. Uraemic solutes as therapeutic targets in CKD-associated cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.A. The basics of phosphate metabolism. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2024, 39, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, N.; Wagner, C.A. Mechanisms and regulation of intestinal phosphate absorption. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 8, 1065–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knöpfel, T.; Himmerkus, N.; Günzel, D.; Bleich, M.; Hernando, N.; Wagner, C.A. Paracellular transport of phosphate along the intestine. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 317, G233–G241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, M.; Gratton, E.; Forster, I.C.; Hernando, N.; Wagner, C.A.; Biber, J.; Sorribas, V.; Murer, H. Mechanisms of phosphate transport. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 482–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonston, D.; Grabner, A.; Wolf, M. FGF23 and klotho at the intersection of kidney and cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2024, 21, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, N.; Pastor-Arroyo, E.M.; Marks, J.; Schnitzbauer, U.; Knöpfel, T.; Bürki, M.; Bettoni, C.; Wagner, C.A. 1,25(OH)(2) vitamin D(3) stimulates active phosphate transport but not paracellular phosphate absorption in mouse intestine. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 1131–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa-Bellosta, R. Vascular calcification: Key roles of phosphate and pyrophosphate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, J.; Schinke, T. The role of the gastrointestinal tract in calcium homeostasis and bone remodeling. Osteoporos. Int. 2013, 24, 2737–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renkema, K.Y.; Alexander, R.T.; Bindels, R.J.; Hoenderop, J.G. Calcium and phosphate homeostasis: Concerted interplay of new regulators. Ann. Med. 2008, 40, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Hoefs, S.; van der Kemp, A.W.; Topala, C.N.; Bindels, R.J.; Hoenderop, J.G. The beta-glucuronidase klotho hydrolyzes and activates the TRPV5 channel. Science 2005, 310, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestenbaum, B.; Belozeroff, V. Mineral metabolism disturbances in patients with chronic kidney disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 37, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestenbaum, B.; Sampson, J.N.; Rudser, K.D.; Patterson, D.J.; Seliger, S.L.; Young, B.; Sherrard, D.J.; Andress, D.L. Serum phosphate levels and mortality risk among people with chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Obando, N.; Lahousse, L.; Brusselle, G.; Stricker, B.H.; Hofman, A.; Franco, O.H.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Zillikens, M.C. Serum phosphate levels are related to all-cause, cardiovascular and COPD mortality in men. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 33, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Park, K.S. Oxidative stress related to plasmalemmal and mitochondrial phosphate transporters in vascular calcification. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Quan, X.; Xu, S.; Das, R.; Cha, S.K.; Kong, I.D.; Shong, M.; Wollheim, C.B.; Park, K.S. Intracellular alkalinization by phosphate uptake via type III sodium-phosphate cotransporter participates in high-phosphate-induced mitochondrial oxidative stress and defective insulin secretion. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 3979–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.X.; Kircelli, F.; O’Neill, K.D.; Chen, X.; Moe, S.M. Verapamil inhibits calcification and matrix vesicle activity of bovine vascular smooth muscle cells. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Da Ly, D.; Xia, J.B.; Qi, X.F.; Lee, I.K.; Cha, S.K.; Park, K.S. Oxidative stress by Ca2+ overload is critical for phosphate-induced vascular calcification. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2020, 319, H1302–H1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, J.A.; Merkel, O.; Kohlwein, S.D.; Gebhardt, B.R.; Bohles, H.; Fotschl, U.; Koch, J.; Jaksch, M.; Lochmuller, H.; Horvath, R.; et al. Mitochondrial phosphate-carrier deficiency: A novel disorder of oxidative phosphorylation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 80, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhoj, E.J.; Li, M.; Ahrens-Nicklas, R.; Pyle, L.C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, V.W.; Clarke, C.; Wong, L.J.; Sondheimer, N.; Ficicioglu, C.; et al. Pathologic variants of the mitochondrial phosphate carrier SLC25A3: Two new patients and expansion of the cardiomyopathy/skeletal myopathy phenotype with and without lactic acidosis. JIMD Rep. 2015, 19, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Writzl, K.; Maver, A.; Kovacic, L.; Martinez-Valero, P.; Contreras, L.; Satrustegui, J.; Castori, M.; Faivre, L.; Lapunzina, P.; van Kuilenburg, A.B.P.; et al. De novo mutations in SLC25A24 cause a disorder characterized by early aging, bone dysplasia, characteristic face, and early demise. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 101, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Quan, X.; Hwang, K.H.; Xu, S.; Das, R.; Choi, S.K.; Wiederkehr, A.; Wollheim, C.B.; Cha, S.K.; Park, K.S. Mitochondrial oxidative stress mediates high-phosphate-induced secretory defects and apoptosis in insulin-secreting cells. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 308, E933–E941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozza, A.; Parisi, G.; De Leonardis, F.; Lasorsa, F.M.; Castegna, A.; Amorese, D.; Marmo, R.; Calcagnile, V.M.; Palmieri, L.; Ricquier, D.; et al. UCP2 transports C4 metabolites out of mitochondria, regulating glucose and glutamine oxidation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, X.; Das, R.; Xu, S.; Cline, G.W.; Wiederkehr, A.; Wollheim, C.B.; Park, K.S. Mitochondrial phosphate transport during nutrient stimulation of INS-1E insulinoma cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 381, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; French, S.; Evans, F.J.; Joubert, F.; Balaban, R.S. Metabolic network control of oxidative phosphorylation: Multiple roles of inorganic phosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 39155–39165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zheng, L.; Xu, H.; Tang, D.; Lin, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Wang, W.; Yuan, Q.; Tao, L.; et al. Oxidative stress contributes to vascular calcification in patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2020, 138, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Li, Z.; Chang, X.; Cong, G.; Hao, L. Quercetin attenuates vascular calcification by inhibiting oxidative stress and mitochondrial fission. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2017, 88, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Li, Y.; Dong, Q.; Fang, J.; Chen, A.; Lan, Z.; Ye, Y.; Yan, J.; Liang, Q. Wogonin inhibits oxidative stress and vascular calcification via modulation of heme oxygenase-1. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 958, 176070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Chen, A.; Liang, Q.; Dong, Q.; Fu, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Ye, Y.; Lan, Z.; et al. Up-regulation of heme oxygenase-1 by celastrol alleviates oxidative stress and vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 172, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, F.; Yang, X.; Chen, Y.; Duan, Y.; Yu, M.; Zhang, S.; Han, J. Procyanidin B2 reduces vascular calcification through inactivation of ERK1/2-RUNX2 pathway. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petsophonsakul, P.; Burgmaier, M.; Willems, B.; Heeneman, S.; Stadler, N.; Gremse, F.; Reith, S.; Burgmaier, K.; Kahles, F.; Marx, N.; et al. Nicotine promotes vascular calcification via intracellular Ca2+-mediated, Nox5-induced oxidative stress, and extracellular vesicle release in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 2196–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Smith, E.R.; Tiong, M.K.; Ruderman, I.; Toussaint, N.D. Interventions to attenuate vascular calcification progression in chronic kidney disease: A systematic review of clinical trials. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 1011–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.M.; Xu, M.J.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, G.; Guan, Y.; Kong, W.; Tang, C.; Wang, X. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species promote p65 nuclear translocation mediating high-phosphate-induced vascular calcification in vitro and in vivo. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, M.; Kinoshita, S.; Ozono, K.; Michigami, T. Inorganic phosphate activates the AKT/mTORC1 pathway and shortens the life span of an alpha-klotho-deficient model. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 2810–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi Nguyen, N.; Thi Nguyen, T.; Nguyen, H.T.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, M.J.; Qi, X.F.; Cha, S.K.; Lee, I.K.; Park, K.S. Inhibition of mitochondrial phosphate carrier prevents high phosphate-induced superoxide generation and vascular calcification. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes de Oca, A.; Madueño, J.A.; Martinez-Moreno, J.M.; Guerrero, F.; Muñoz-Castañeda, J.; Rodriguez-Ortiz, M.E.; Mendoza, F.J.; Almaden, Y.; Lopez, I.; Rodriguez, M.; et al. High-phosphate-induced calcification is related to SM22α promoter methylation in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2010, 25, 1996–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramann, R.; Couson, S.K.; Neuss, S.; Kunter, U.; Bovi, M.; Bornemann, J.; Knüchel, R.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Floege, J.; Schneider, R.K. Exposure to uremic serum induces a procalcific phenotype in human mesenchymal stem cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, e45–e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Abbadi, M.M.; Pai, A.S.; Leaf, E.M.; Yang, H.Y.; Bartley, B.A.; Quan, K.K.; Ingalls, C.M.; Liao, H.W.; Giachelli, C.M. Phosphate feeding induces arterial medial calcification in uremic mice: Role of serum phosphorus, fibroblast growth factor-23, and osteopontin. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Yamashita, M.; Horimai, C.; Hayashi, M. Smooth muscle-selective nuclear factor-κB inhibition reduces phosphate-induced arterial medial calcification in mice with chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e007248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Meng, L.; Ren, R.; Wang, X.; Sui, W.; Xue, F.; Xie, L.; Chen, A.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; et al. Paraspeckle protein NONO attenuates vascular calcification by inhibiting bone morphogenetic protein 2 transcription. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, Y.; Bing, C.; Akhtar, J.; Tingting, Z.; Kezhou, Y.; Rong, W. Lanthanum carbonate prevents accelerated medial calcification in uremic rats: Role of osteoclast-like activity. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, B.K.; Kozaki, K.; Iijima, K.; Eto, M.; Kojima, T.; Ota, H.; Senda, Y.; Maemura, K.; Nakano, T.; Akishita, M.; et al. Statins protect human aortic smooth muscle cells from inorganic phosphate-induced calcification by restoring Gas6-Axl survival pathway. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Z.W.; Fang, L.J.; Cheng, S.Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, N.F. Programmed cell death in atherosclerosis and vascular calcification. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.X.; O’Neill, K.D.; Chen, X.; Kiattisunthorn, K.; Gattone, V.H.; Moe, S.M. Activation of arterial matrix metalloproteinases leads to vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2011, 34, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radvar, E.; Mehta, K.; D’Ambrosio, A.; Mastroianni, G.; Al-Jawad, M.; Stevens, M.M.; Mata, A.; Elsharkawy, S. Investigating the role of elastin and extracellular matrix damage in cardiovascular calcification. J. Struct. Biol. 2025, 217, 108140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.; Sharpe, S.; Cerruti, M. Initiation of medial calcification: Revisiting calcium ion binding to elastin. J. Phys. Chem. B 2024, 128, 9631–9642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, A.W.; Yang, H.H.; Sigrist, M.K.; Brin, G.; Chum, E.; Gourlay, W.A.; Levin, A. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 exacerbate arterial stiffening and angiogenesis in diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 84, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Lin, T.; Jin, Y.; Berezowitz, A.G.; Wang, X.L.; Lu, J.; Cai, Y.; Guzman, R.J. Smooth muscle cell-specific matrix metalloproteinase 3 deletion reduces osteogenic transformation and medial artery calcification. Cardiovasc. Res. 2024, 120, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, P.; Wendling, A.A.; Cuevas, R.A.; Crane, A.; Chu, C.C.; Moorhead, W.J., 3rd; Wong, R.; Brown, M.; Tamakloe, J.; Suresh, S.; et al. Rapamycin reduces arterial mineral density and promotes beneficial vascular remodeling in a murine model of severe medial arterial calcification. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2025, 329, H191–H205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simionescu, A.; Philips, K.; Vyavahare, N. Elastin-derived peptides and TGF-beta1 induce osteogenic responses in smooth muscle cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 334, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shroff, R.C.; McNair, R.; Skepper, J.N.; Figg, N.; Schurgers, L.J.; Deanfield, J.; Rees, L.; Shanahan, C.M. Chronic mineral dysregulation promotes vascular smooth muscle cell adaptation and extracellular matrix calcification. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, K.; Uchida, N.; Nakanoh, H.; Fukushima, K.; Haraguchi, S.; Kitamura, S.; Wada, J. The gut-kidney axis in chronic kidney diseases. Diagnostics 2024, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, S.C.; Sirich, T.L. Indoxyl sulfate-review of toxicity and therapeutic strategies. Toxins 2016, 8, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banoglu, E.; Jha, G.G.; King, R.S. Hepatic microsomal metabolism of indole to indoxyl, a precursor of indoxyl sulfate. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2001, 26, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banoglu, E.; King, R.S. Sulfation of indoxyl by human and rat aryl (phenol) sulfotransferases to form indoxyl sulfate. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2002, 27, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronov, P.A.; Luo, F.J.; Plummer, N.S.; Quan, Z.; Holmes, S.; Hostetter, T.H.; Meyer, T.W. Colonic contribution to uremic solutes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1769–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, A.; Takeda, M.; Tojo, A.; Sekine, T.; Cha, S.H.; Khamdang, S.; Takayama, F.; Aoyama, I.; Nakamura, S.; Endou, H.; et al. Role of organic anion transporters in the tubular transport of indoxyl sulfate and the induction of its nephrotoxicity. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devine, E.; Krieter, D.H.; Rüth, M.; Jankovski, J.; Lemke, H.D. Binding affinity and capacity for the uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate. Toxins 2014, 6, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.L.; Liao, C.H.; Lu, K.C.; Ma, M.C. TRPV1 hyperfunction involved in uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate-mediated renal tubular damage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Yu, M.A.; Ryu, E.S.; Jang, Y.H.; Kang, D.H. Indoxyl sulfate-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and apoptosis of renal tubular cells as novel mechanisms of progression of renal disease. Lab. Investig. 2012, 92, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.C.; Sun, H.L.; Tsai, C.H.; Kuo, C.W.; Liu, K.L.; Lii, C.K.; Huang, C.S.; Li, C.C. 1,25(OH)(2) D(3) attenuates indoxyl sulfate-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal cell transition via inactivation of PI3K/Akt/β-catenin signaling in renal tubular epithelial cells. Nutrition 2020, 69, 110554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Y.; Chang, S.C.; Wu, M.S. Uremic toxins induce kidney fibrosis by activating intrarenal renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system associated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Y.; Lin, Y.T.; Huang, Y.T.; Cheng, H.C.; Chou, W.C.; Chang, Y.T.; Ling, T.C.; Hsieh, P.L.; Tsai, K.L. Klotho suppresses indoxyl sulfate-mediated apoptosis in human kidney proximal tubular (HK-2) cells through modulating the AKT/Nrf2 mechanism. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 24018–24029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Kitazato, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Tokumaru, K.; Shintani, Y.; Yoshitake, T.; Yasuno, K.; Maeda, H.; Tanaka, M.; Matsushita, K.; et al. Indoxyl sulfate contributes to selenium deficiency and renal ferroptosis by decreasing the expression of selenium transport protein SEPP1. Kidney360 2025. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemet, I.; Li, X.S.; Haghikia, A.; Li, L.; Wilcox, J.; Romano, K.A.; Buffa, J.A.; Witkowski, M.; Demuth, I.; König, M.; et al. Atlas of gut microbe-derived products from aromatic amino acids and risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3085–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.C.; Chang, J.C.; Lin, C.N.; Lee, C.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Chu, P.H.; Kou, G.; Lu, Y.A.; Yang, C.W.; Chen, Y.C. Serum indoxyl sulfate predicts adverse cardiovascular events in patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2019, 118, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taki, K.; Tsuruta, Y.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl sulfate and atherosclerotic risk factors in hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Nephrol. 2007, 27, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xiang, F.; Ji, J.; Ding, X.; Shen, B.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Xue, N.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, X.; et al. Indoxyl sulfate and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in early stages of chronic kidney disease. Ren. Fail. 2020, 42, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lano, G.; Burtey, S.; Sallée, M. Indoxyl sulfate, a uremic endotheliotoxin. Toxins 2020, 12, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, A.; Liu, F.; Srebrzynski, M.; Rother, S.; Adamowicz, K.; Wadowska, M.; Steiger, S.; Anders, H.J.; Schmaderer, C.; Koziel, J.; et al. Uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate promotes macrophage-associated low-grade inflammation and epithelial cell senescence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakamatsu, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Narita, I. Indoxyl sulfate-induced macrophage toxicity and therapeutic strategies in uremic atherosclerosis. Toxins 2024, 16, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Lai, Y.H.; Kuo, C.H.; Lin, Y.L.; Tsai, J.P.; Hsu, B.G. Association between serum indoxyl sulfate levels and endothelial function in non-dialysis chronic kidney disease. Toxins 2019, 11, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muteliefu, G.; Enomoto, A.; Jiang, P.; Takahashi, M.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl sulphate induces oxidative stress and the expression of osteoblast-specific proteins in vascular smooth muscle cells. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumur, Z.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl sulfate inhibits nitric oxide production and cell viability by inducing oxidative stress in vascular endothelial cells. Am. J. Nephrol. 2009, 29, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.; Wang, S.C.; Hsu, C.Y.; Miao, Y.; Martin, M.; Yin, Y.; Wu, C.C.; Wang, Y.T.; Wu, G.; Chien, S.; et al. MicroRNA-92a Mediates Endothelial Dysfunction in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 3251–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Osaka, M.; Higuchi, Y.; Nishijima, F.; Ishii, H.; Yoshida, M. Indoxyl sulfate induces leukocyte-endothelial interactions through up-regulation of E-selectin. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 38869–38875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumur, Z.; Shimizu, H.; Enomoto, A.; Miyazaki, H.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl sulfate upregulates expression of ICAM-1 and MCP-1 by oxidative stress-induced NF-kappaB activation. Am. J. Nephrol. 2010, 31, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Katsuki, S.; Chen, M.; Decano, J.L.; Halu, A.; Lee, L.H.; Pestana, D.V.S.; Kum, A.S.T.; Kuromoto, R.K.; Golden, W.S.; et al. Uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate promotes proinflammatory macrophage activation via the interplay of OATP2B1 and Dll4-Notch signaling. Circulation 2019, 139, 78–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Tsuruoka, S.; Ioka, T.; Ando, H.; Ito, C.; Akimoto, T.; Fujimura, A.; Asano, Y.; Kusano, E. Indoxyl sulfate stimulates proliferation of rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 1780–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto, F.C.; Barreto, D.V.; Liabeuf, S.; Meert, N.; Glorieux, G.; Temmar, M.; Choukroun, G.; Vanholder, R.; Massy, Z.A. Serum indoxyl sulfate is associated with vascular disease and mortality in chronic kidney disease patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adijiang, A.; Goto, S.; Uramoto, S.; Nishijima, F.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl sulphate promotes aortic calcification with expression of osteoblast-specific proteins in hypertensive rats. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 1892–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Jiang, H.; Gao, F.; Liang, S.; Wei, M.; Chen, L. Indoxyl sulfate-induced calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells via the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2019, 82, 2000–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, T.; Zhang, H.; Teng, J.; Ji, J.; Ding, X. Indoxyl sulfate enhance the hypermethylation of Klotho and promote the process of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muteliefu, G.; Shimizu, H.; Enomoto, A.; Nishijima, F.; Takahashi, M.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl sulfate promotes vascular smooth muscle cell senescence with upregulation of p53, p21, and prelamin A through oxidative stress. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2012, 303, C126–C134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opdebeeck, B.; Maudsley, S.; Azmi, A.; De Maré, A.; De Leger, W.; Meijers, B.; Verhulst, A.; Evenepoel, P.; D’Haese, P.C.; Neven, E. Indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate promote vascular calcification and associate with glucose intolerance. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.C.; Kuo, K.L.; Huang, H.L.; Lin, C.C.; Tsai, T.H.; Wang, C.H.; Chen, J.W.; Lin, S.J.; Huang, P.H.; Tarng, D.C. Indoxyl sulfate suppresses endothelial progenitor cell-mediated neovascularization. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arinze, N.V.; Yin, W.; Lotfollahzadeh, S.; Napoleon, M.A.; Richards, S.; Walker, J.A.; Belghasem, M.; Ravid, J.D.; Hassan Kamel, M.; Whelan, S.A.; et al. Tryptophan metabolites suppress the Wnt pathway and promote adverse limb events in chronic kidney disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e142260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekawanvijit, S.; Adrahtas, A.; Kelly, D.J.; Kompa, A.R.; Wang, B.H.; Krum, H. Does indoxyl sulfate, a uraemic toxin, have direct effects on cardiac fibroblasts and myocytes? Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.H.; Wang, C.P.; Chung, F.M.; Huang, L.L.; Yu, T.H.; Hung, W.C.; Lu, L.F.; Chen, P.Y.; Luo, C.H.; Lee, K.T.; et al. Uremic retention solute indoxyl sulfate level is associated with prolonged QTc interval in early CKD patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yisireyili, M.; Shimizu, H.; Saito, S.; Enomoto, A.; Nishijima, F.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl sulfate promotes cardiac fibrosis with enhanced oxidative stress in hypertensive rats. Life Sci. 2013, 92, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekawanvijit, S.; Kompa, A.R.; Manabe, M.; Wang, B.H.; Langham, R.G.; Nishijima, F.; Kelly, D.J.; Krum, H. Chronic kidney disease-induced cardiac fibrosis is ameliorated by reducing circulating levels of a non-dialysable uremic toxin, indoxyl sulfate. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnappa, S.; Tu, Y.K.; Yeh, Y.C.; Glorieux, G.; Vanholder, R.; Mooney, A. Association between protein-bound uremic toxins and asymptomatic cardiac dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease. Toxins 2018, 10, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.S.; Chen, J.; Zou, J.Z.; Zhong, Y.H.; Teng, J.; Ji, J.; Chen, Z.W.; Liu, Z.H.; Shen, B.; Nie, Y.X.; et al. Association of indoxyl sulfate with heart failure among patients on hemodialysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, B.; Yoshikawa, D.; Ishii, H.; Suzuki, S.; Inoue, Y.; Takeshita, K.; Tanaka, M.; Kumagai, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Okumura, S.; et al. Relation of plasma indoxyl sulfate levels and estimated glomerular filtration rate to left ventricular diastolic dysfunction. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 111, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryp, T.; Vanholder, R.; Vaneechoutte, M.; Glorieux, G. p-Cresyl Sulfate. Toxins 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Noguchi, T.; Kotani, S.; Nakajima, M.; Kadowaki, D.; Otagiri, M.; Maruyama, T. Organic anion transporters play an important role in the uptake of p-cresyl sulfate, a uremic toxin, in the kidney. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 2498–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.W.; Recht, N.S.; Hostetter, T.H.; Meyer, T.W. Removal of P-cresol sulfate by hemodialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 3430–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edamatsu, T.; Fujieda, A.; Itoh, Y. Phenyl sulfate, indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate decrease glutathione level to render cells vulnerable to oxidative stress in renal tubular cells. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Honda, D.; Tanaka, H.; Wu, Q.; Endo, M.; Noguchi, T.; Kadowaki, D.; Ishima, Y.; Kotani, S.; et al. p-Cresyl sulfate causes renal tubular cell damage by inducing oxidative stress by activation of NADPH oxidase. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruna, Y.; Kashihara, N.; Satoh, M.; Tomita, N.; Namikoshi, T.; Sasaki, T.; Fujimori, T.; Xie, P.; Kanwar, Y.S. Amelioration of progressive renal injury by genetic manipulation of Klotho gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2331–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Y.; Chang, S.C.; Wu, M.S. Suppression of Klotho expression by protein-bound uremic toxins is associated with increased DNA methyltransferase expression and DNA hypermethylation. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.W.; Jian, L.; Wu, S.C.; Chen, Y.L.; Pan, Y.R.; Chien, Y.C.; Wu, J.Y.; Yu, Y.L.; Yiang, G.T. Gamma-tocopherol vitamin E enhances the cytotoxicity of p-cresyl sulfate to renal tubular cells. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2025, 30, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, I.W.; Hsu, K.H.; Hsu, H.J.; Lee, C.C.; Sun, C.Y.; Tsai, C.J.; Wu, M.S. Serum free p-cresyl sulfate levels predict cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in elderly hemodialysis patients--a prospective cohort study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glorieux, G.; Vanholder, R.; Van Biesen, W.; Pletinck, A.; Schepers, E.; Neirynck, N.; Speeckaert, M.; De Bacquer, D.; Verbeke, F. Free p-cresyl sulfate shows the highest association with cardiovascular outcome in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.J.; Wu, V.; Wu, P.C.; Wu, C.J. Meta-analysis of the associations of p-cresyl sulfate (PCS) and indoxyl sulfate (IS) with cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in patients with chronic renal failure. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Enoki, Y.; Ishima, Y.; Kadowaki, D.; Kotani, S.; Nakajima, M.; Tanaka, M.; Matsushita, K.; Mori, Y.; et al. p-Cresyl sulfate, a uremic toxin, causes vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cell damages by inducing oxidative stress. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.P.; Lu, L.F.; Yu, T.H.; Hung, W.C.; Chiu, C.A.; Chung, F.M.; Yeh, L.R.; Chen, H.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Houng, J.Y. Serum levels of total p-cresylsulphate are associated with angiographic coronary atherosclerosis severity in stable angina patients with early stage of renal failure. Atherosclerosis 2010, 211, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepers, E.; Meert, N.; Glorieux, G.; Goeman, J.; Van der Eycken, J.; Vanholder, R. P-cresylsulphate, the main in vivo metabolite of p-cresol, activates leucocyte free radical production. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 22, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.J.; Ni, J.W.; Ding, F.H.; Fang, Y.H.; Wang, X.Q.; Wang, H.B.; Chen, X.N.; Chen, N.; Zhan, W.W.; Lu, L.; et al. p-Cresyl sulfate is associated with carotid arteriosclerosis in hemodialysis patients and promotes atherogenesis in apoE-/- mice. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijers, B.K.; Van Kerckhoven, S.; Verbeke, K.; Dehaen, W.; Vanrenterghem, Y.; Hoylaerts, M.F.; Evenepoel, P. The uremic retention solute p-cresyl sulfate and markers of endothelial damage. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 54, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourde-Chiche, N.; Dou, L.; Sabatier, F.; Calaf, R.; Cerini, C.; Robert, S.; Camoin-Jau, L.; Charpiot, P.; Argiles, A.; Dignat-George, F.; et al. Levels of circulating endothelial progenitor cells are related to uremic toxins and vascular injury in hemodialysis patients. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Su, X.; Ni, J.; Du, R.; Zhang, R.; Jin, W. p-Cresyl sulfate promotes the formation of atherosclerotic lesions and induces plaque instability by targeting vascular smooth muscle cells. Front. Med. 2016, 10, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liabeuf, S.; Barreto, D.V.; Barreto, F.C.; Meert, N.; Glorieux, G.; Schepers, E.; Temmar, M.; Choukroun, G.; Vanholder, R.; Massy, Z.A. Free p-cresylsulphate is a predictor of mortality in patients at different stages of chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.F.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Liou, J.C.; Liu, S.H.; Hung, C.F.; Lu, K.C.; Lin, C.C.; Wu, C.C.; Ka, S.M.; Wen, L.L.; et al. Scavenging intracellular ROS attenuates p-cresyl sulfate-triggered osteogenesis through MAPK signaling pathway and NF-κB activation in human arterial smooth muscle cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Ni, J.; Du, R.; Dai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Lu, L.; Zhang, R. p-Cresyl sulfate aggravates cardiac dysfunction associated with chronic kidney disease by enhancing apoptosis of cardiomyocytes. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e001852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, D.H.; Yeung, C.K.; Peter, R.M.; Ibarra, C.; Gasser, R.; Itagaki, K.; Philpot, R.M.; Rettie, A.E. Isoform specificity of trimethylamine N-oxygenation by human flavin-containing monooxygenase (FMO) and P450 enzymes: Selective catalysis by FMO3. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998, 56, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canyelles, M.; Borràs, C.; Rotllan, N.; Tondo, M.; Escolà-Gil, J.C.; Blanco-Vaca, F. Gut microbiota-derived TMAO: A causal factor promoting atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.H.; Wang, Z.; Kennedy, D.J.; Wu, Y.; Buffa, J.A.; Agatisa-Boyle, B.; Li, X.S.; Levison, B.S.; Hazen, S.L. Gut microbiota-dependent trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) pathway contributes to both development of renal insufficiency and mortality risk in chronic kidney disease. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Tang, W.H.W.; Li, X.S.; de Oliveira Otto, M.C.; Lee, Y.; Lemaitre, R.N.; Fretts, A.; Nemet, I.; Sotoodehnia, N.; Sitlani, C.M.; et al. The gut microbial metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide, incident CKD, and kidney function decline. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2024, 35, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapetanaki, S.; Kumawat, A.K.; Persson, K.; Demirel, I. The fibrotic effects of TMAO on human renal fibroblasts Is mediated by NLRP3, Caspase-1 and the PERK/Akt/mTOR pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefania, K.; Ashok, K.K.; Geena, P.V.; Katarina, P.; Isak, D. TMAO enhances TNF-alpha mediated fibrosis and release of inflammatory mediators from renal fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Yin, Z.; Liu, N.; Bian, X.; Yu, R.; Su, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y. Gut microbial metabolite TMAO contributes to renal dysfunction in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Q.; Zheng, B.; Liu, N.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Huang, X.; Zeng, X.; Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Ouyang, D. Trimethylamine N-Oxide exacerbates renal inflammation and fibrosis in rats with diabetic kidney disease. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 682482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yong, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, E. Suyin detoxification granule alleviates trimethylamine N-oxide-induced tubular ferroptosis and renal fibrosis to prevent chronic kidney disease progression. Phytomedicine 2024, 135, 156195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Buffa, J.A.; Roberts, A.B.; Sangwan, N.; Skye, S.M.; Li, L.; Ho, K.J.; Varga, J.; DiDonato, J.A.; Tang, W.H.W.; et al. Targeted inhibition of gut microbial trimethylamine N-oxide production reduces renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis and functional impairment in a murine model of chronic kidney disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 1239–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.; Jung, Y.; Hyeon, J.S.; Seo, A.; Jin, W.; Weon, B.; Shin, N.; et al. Antibiotic-induced intestinal microbiota depletion can attenuate the acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease transition via NADPH oxidase 2 and trimethylamine-N-oxide inhibition. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, 1239–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, T.; Powe, N.R.; Meyer, T.W.; Hwang, S.; Hai, X.; Melamed, M.L.; Banerjee, T.; Coresh, J.; Hostetter, T.H. Trimethylamine N-Oxide and cardiovascular events in hemodialysis patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, J.R.; House, J.A.; Ocque, A.J.; Zhang, S.; Johnson, C.; Kimber, C.; Schmidt, K.; Gupta, A.; Wetmore, J.B.; Nolin, T.D.; et al. Serum Trimethylamine-N-Oxide is elevated in CKD and correlates with coronary atherosclerosis burden. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.B.; Morse, B.L.; Djurdjev, O.; Tang, M.; Muirhead, N.; Barrett, B.; Holmes, D.T.; Madore, F.; Clase, C.M.; Rigatto, C.; et al. Advanced chronic kidney disease populations have elevated trimethylamine N-oxide levels associated with increased cardiovascular events. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 1144–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Gua, C.; Wu, B.; Chen, Y. Increased circulating trimethylamine N-oxide contributes to endothelial dysfunction in a rat model of chronic kidney disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 2071–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, A.; Abate, F.; Roggia, M.; Benedetti, G.; Caradonna, E.; Calderone, V.; Tenore, G.C.; Cosconati, S.; Novellino, E.; Stornaiuolo, M. Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) acts as inhibitor of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and hampers NO production and acetylcholine-mediated vasorelaxation in rat aortas. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, T.; Kojima, M.; Takayanagi, K.; Taguchi, K.; Kobayashi, T. Trimethylamine-N-oxide specifically impairs endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor-type relaxation in rat femoral artery. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Pan, B.; Chen, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, L.; Chen, B. Trimethylamine N-oxide in atherogenesis: Impairing endothelial self-repair capacity and enhancing monocyte adhesion. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37, BSR20160244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boini, K.M.; Hussain, T.; Li, P.L.; Koka, S. Trimethylamine-N-Oxide instigates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and endothelial dysfunction. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Klipfell, E.; Bennett, B.J.; Koeth, R.; Levison, B.S.; Dugar, B.; Feldstein, A.E.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Chung, Y.M.; et al. Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease. Nature 2011, 472, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Yang, C.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Hu, T.; Gu, Y.; Li, J. Trimethylamine N-oxide promotes atherosclerosis via CD36-dependent MAPK/JNK pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seldin, M.M.; Meng, Y.; Qi, H.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Z.; Hazen, S.L.; Lusis, A.J.; Shih, D.M. Trimethylamine N-Oxide promotes vascular inflammation through signaling of mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-κB. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Gregory, J.C.; Org, E.; Buffa, J.A.; Gupta, N.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Fu, X.; Wu, Y.; Mehrabian, M.; et al. Gut microbial metabolite TMAO enhances platelet hyperreactivity and thrombosis risk. Cell 2016, 165, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Yang, W.; Yang, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, A. Higher serum trimethylamine-N-oxide levels are associated with increased abdominal aortic calcification in hemodialysis patients. Ren. Fail. 2022, 44, 2019–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Liu, X.; Lu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Ou, C.; et al. Trimethylamine-N-Oxide promotes vascular calcification through activation of NLRP3 (nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich-containing family, pyrin domain-containing-3) Inflammasome and NF-κB (nuclear factor κB) signals. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Heaney, L.M.; Bhandari, S.S.; Jones, D.J.; Ng, L.L. Trimethylamine N-oxide and prognosis in acute heart failure. Heart 2016, 102, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.H.; Wang, Z.; Fan, Y.; Levison, B.; Hazen, J.E.; Donahue, L.M.; Wu, Y.; Hazen, S.L. Prognostic value of elevated levels of intestinal microbe-generated metabolite trimethylamine-N-oxide in patients with heart failure: Refining the gut hypothesis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 1908–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.H.W.; Lemaitre, R.N.; Jensen, P.N.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.S.; Nemet, I.; Lee, Y.; Lai, H.T.M.; de Oliveira Otto, M.C.; et al. Trimethylamine N-Oxide and related gut microbe-derived metabolites and incident heart failure development in community-based populations. Circ. Heart Fail. 2024, 17, e011569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organ, C.L.; Li, Z.; Sharp, T.E., 3rd; Polhemus, D.J.; Gupta, N.; Goodchild, T.T.; Tang, W.H.W.; Hazen, S.L.; Lefer, D.J. Nonlethal inhibition of gut microbial trimethylamine N-oxide production improves cardiac function and remodeling in a murine model of heart failure. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e016223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Peng, Y.; Yao, Y.; Xue, H.; Guo, Q.; Tian, D.; Xiao, L.; Teng, X.; et al. Trimethylamine N-oxide induces cardiac diastolic dysfunction by down-regulating Piezo1 in mice with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Life Sci. 2025, 369, 123554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.Y.; Aldujeli, A.; Haq, A.; Murphy, P.; Unikas, R.; Sharif, F.; Garg, S.; Brilakis, E.S.; Onuma, Y.; Serruys, P.W. Trimethylamine N-Oxide as a biomarker for left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and functional remodeling after STEMI. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Zhao, F.; Li, W.; Ouyang, Z.; Chen, L.; Tang, S.; et al. The gut microbiota metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide promotes cardiac hypertrophy by activating the autophagic degradation of SERCA2a. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yan, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q.; Deng, Y.; Ou, C.; Chen, M. Gut microbe-derived metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide induces cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis. Lab. Investig. 2019, 99, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Kong, B.; Shuai, W.; Fu, H.; Jiang, X.; Huang, H. 3,3-Dimethyl-1-butanol attenuates cardiac remodeling in pressure-overload-induced heart failure mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 78, 108341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savi, M.; Bocchi, L.; Bresciani, L.; Falco, A.; Quaini, F.; Mena, P.; Brighenti, F.; Crozier, A.; Stilli, D.; Del Rio, D. Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO)-induced impairment of cardiomyocyte function and the protective role of urolithin B-glucuronide. Molecules 2018, 23, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong-Nguyen, C.; Yilmaz, B.; Coles, B.; Sokol, H.; MacPherson, A.; Siepe, M.; Reineke, D.; Mosbahi, S.; Tomii, D.; Nakase, M.; et al. A scoping review evaluating the current state of gut microbiota and its metabolites in valvular heart disease physiopathology. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2025, 55, e14381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Lin, X.; Hu, D.; Li, J.; Xie, K.; Li, S.; Su, S.; Duan, X.; Zhong, G.; Lin, Y.; et al. Trimethylamine N-oxide aggravates human aortic valve interstitial cell inflammation by regulating the macrophages polarization through a N6-methyladenosine-mediated pathway. Atherosclerosis 2025, 402, 119109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Henderson, A.; Petriello, M.C.; Romano, K.A.; Gearing, M.; Miao, J.; Schell, M.; Sandoval-Espinola, W.J.; Tao, J.; Sha, B.; et al. Trimethylamine N-Oxide binds and activates PERK to promote metabolic dysfunction. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 1141–1151.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. Toxic dimethylarginines: Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) and symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA). Toxins 2017, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode-Böger, S.M.; Scalera, F.; Ignarro, L.J. The l-arginine paradox: Importance of the l-arginine/asymmetrical dimethylarginine ratio. Pharmacol Ther. 2007, 114, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiper, J.M.; Santa Maria, J.; Chubb, A.; MacAllister, R.J.; Charles, I.G.; Whitley, G.S.; Vallance, P. Identification of two human dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolases with distinct tissue distributions and homology with microbial arginine deiminases. Biochem. J. 1999, 343 Pt 1, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Kimoto, M.; Sasaoka, K. Dimethylarginine:pyruvate aminotransferase in rats. Purification, properties, and identity with alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase 2. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 20938–20945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva-Damaso, E.; Oliva-Damaso, N.; Rodriguez-Esparragon, F.; Payan, J.; Baamonde-Laborda, E.; Gonzalez-Cabrera, F.; Santana-Estupiñan, R.; Rodriguez-Perez, J.C. Asymmetric (ADMA) and symmetric (SDMA) dimethylarginines in chronic kidney disease: A clinical approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, A.Y.M.; Mantik, K.; Bahadory, F.; Stathakis, P.; Guiney, H.; Erlich, J.; Walker, R.; Poulton, R.; Horvath, A.R.; Endre, Z.H. Plasma arginine metabolites in health and chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 38, 2767–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedini, S.; Meinitzer, A.; Holme, I.; März, W.; Weihrauch, G.; Fellstrøm, B.; Jardine, A.; Holdaas, H. Asymmetrical dimethylarginine is associated with renal and cardiovascular outcomes and all-cause mortality in renal transplant recipients. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snauwaert, E.; Van Biesen, W.; Raes, A.; Holvoet, E.; Glorieux, G.; Van Hoeck, K.; Van Dyck, M.; Godefroid, N.; Vanholder, R.; Roels, S.; et al. Accumulation of uraemic toxins is reflected only partially by estimated GFR in paediatric patients with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, M.Y.; Douwes, R.M.; van Londen, M.; Minovic, I.; Frenay, A.R.; de Borst, M.H.; van den Berg, E.; Heiner-Fokkema, M.R.; Kayacelebi, A.A.; Bollenbach, A.; et al. Effect of renal function on homeostasis of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA): Studies in donors and recipients of renal transplants. Amino Acids 2019, 51, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannemann, J.; Zummack, J.; Hillig, J.; Rendant-Gantzberg, L.; Boger, R. Association of variability in the DDAH1, DDAH2, AGXT2 and PRMT1 genes with circulating ADMA concentration in human whole blood. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayoub, H.; Achan, V.; Adimoolam, S.; Jacobi, J.; Stuehlinger, M.C.; Wang, B.Y.; Tsao, P.S.; Kimoto, M.; Vallance, P.; Patterson, A.J.; et al. Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase regulates nitric oxide synthesis: Genetic and physiological evidence. Circulation 2003, 108, 3042–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiper, J.; Nandi, M.; Torondel, B.; Murray-Rust, J.; Malaki, M.; O’Hara, B.; Rossiter, S.; Anthony, S.; Madhani, M.; Selwood, D.; et al. Disruption of methylarginine metabolism impairs vascular homeostasis. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D. Urinary dimethylamine (DMA) and its precursor asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) in clinical medicine, in the context of nitric oxide (NO) and beyond. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Zhou, Z.; Miura, H.; Papapetropoulos, A.; McCarthy, E.T.; Sharma, R.; Savin, V.J.; Lianos, E.A. ADMA injures the glomerular filtration barrier: Role of nitric oxide and superoxide. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2009, 296, F1386–F1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W. Actin cytoskeleton-dependent pathways for ADMA-induced NF-kappaB activation and TGF-beta high expression in human renal glomerular endothelial cells. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2012, 44, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.J.; Oh, K.S.; Nho, J.H.; Kim, G.Y.; Kim, D.I. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) treatment induces apoptosis in cultured rat mesangial cells via endoplasmic reticulum stress activation. Cell Biol. Int. 2016, 40, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayachandran, I.; Sundararajan, S.; Venkatesan, S.; Paadukaana, S.; Balasubramanyam, M.; Mohan, V.; Manickam, N. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) accelerates renal cell fibrosis under high glucose condition through NOX4/ROS/ERK signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihout, F.; Shweke, N.; Bige, N.; Jouanneau, C.; Dussaule, J.C.; Ronco, P.; Chatziantoniou, C.; Boffa, J.J. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) induces chronic kidney disease through a mechanism involving collagen and TGF-beta1 synthesis. J. Pathol. 2011, 223, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Han, X.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, C.; Fang, X.; Li, Q.; Liu, F.; Xia, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Bupropion decreases plasma levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine and ameliorates renal injury by modulation of Ddah1, Oatp4c1, Oct2, and Mate1 in rats with adenine-induced chronic renal injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1565713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Ueda, S.; Yamagishi, S.; Matsuguma, K.; Shibata, R.; Fukami, K.; Matsuoka, H.; Imaizumi, T.; Okuda, S. Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase prevents progression of renal dysfunction by inhibiting loss of peritubular capillaries and tubulointerstitial fibrosis in a rat model of chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhao, C.; Wang, H.; Lei, T.; Liu, S.; Cao, J.; Lu, Z. Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1 deficiency induces the epithelial to mesenchymal transition in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells and exacerbates kidney damage in aged and diabetic mice. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 27, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, J.A.; Caplin, B.; Boruc, O.; Bruce-Cobbold, C.; Cutillas, P.; Dormann, D.; Faull, P.; Grossman, R.C.; Khadayate, S.; Mas, V.R.; et al. Reduced renal methylarginine metabolism protects against progressive kidney damage. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 3045–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaida, Y.; Ueda, S.; Yamagishi, S.; Nakayama, Y.; Ando, R.; Iwatani, R.; Fukami, K.; Okuda, S. Proteinuria elevates asymmetric dimethylarginine levels via protein arginine methyltransferase-1 overexpression in a rat model of nephrotic syndrome. Life Sci. 2012, 91, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Lin, P.; Li, L.; Chen, D.; Yang, X.; Xu, L.; Zhou, B.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, C.; et al. Reduced asymmetric dimethylarginine accumulation through inhibition of the type I protein arginine methyltransferases promotes renal fibrosis in obstructed kidneys. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 6948–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, M.; Yang, F.; Lin, J.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, M.; Chen, D.; Tan, B.; Huang, D.; Ye, C. Protein arginine methyltransferase 3 inhibits renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis through asymmetric dimethylarginine. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 995917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willeit, P.; Freitag, D.F.; Laukkanen, J.A.; Chowdhury, S.; Gobin, R.; Mayr, M.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Chowdhury, R. Asymmetric dimethylarginine and cardiovascular risk: Systematic review and meta-analysis of 22 prospective studies. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e001833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrauben, S.J.; Sapa, H.; Xie, D.; Zhang, X.; Anderson, A.H.; Shlipak, M.G.; Hsu, C.Y.; Shafi, T.; Mehta, R.; Bhat, Z.; et al. Association of urine and plasma ADMA with atherosclerotic risk in DKD cardiovascular disease risk in diabetic kidney disease: Findings from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 38, 2809–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, N.; Theofilis, P.; Oikonomou, E.; Lazaros, G.; Sagris, M.; Tousoulis, D. Asymmetric dimethylarginine as a biomarker in coronary artery disease. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2023, 23, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.J.; Tommasi, S.; Faull, R.; Gleadle, J.M.; Mangoni, A.A.; Selvanayagam, J.B. Arginine metabolites as biomarkers of myocardial ischaemia, assessed with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in chronic kidney disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ilyas, I.; Little, P.J.; Li, H.; Kamato, D.; Zheng, X.; Luo, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Han, J.; et al. Endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases and beyond: From mechanism to pharmacotherapies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 924–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowsett, L.; Higgins, E.; Alanazi, S.; Alshuwayer, N.A.; Leiper, F.C.; Leiper, J. ADMA: A key player in the relationship between vascular dysfunction and inflammation in atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallance, P.; Leone, A.; Calver, A.; Collier, J.; Moncada, S. Accumulation of an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis in chronic renal failure. Lancet 1992, 339, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinli, H.; Xin, X.; Guangshuo, Z.; Atzler, D.; Kimoto, M.; Chen, J.; Schwedhelm, E.; Lüneburg, N.; Böger, R.H.; Zhang, P.; et al. Vascular endothelial-specific dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase-1-deficient mice reveal that vascular endothelium plays an important role in removing asymmetric dimethylarginine. Circulation 2009, 120, 2222–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. Targeting on asymmetric dimethylarginine-related nitric oxide-reactive oxygen species imbalance to reprogram the development of hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Ohtake, T.; Mochida, Y.; Ishioka, K.; Oka, M.; Maesato, K.; Moriya, H.; Hidaka, S. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) as a novel risk factor for progression of coronary artery calcification in patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.S.; Lu, T.M.; Chen, C.H.; Guo, B.C.; Hsu, C.P. Hyperuricemia induces endothelial dysfunction and accelerates atherosclerosis by disturbing the asymmetric dimethylarginine/dimethylarginine dimethylaminotransferase 2 pathway. Redox Biol. 2021, 46, 102108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, O.; Tsutsui, M.; Morishita, T.; Tasaki, H.; Ueno, S.; Nakata, S.; Tsujimoto, T.; Toyohira, Y.; Hayashida, Y.; Sasaguri, Y.; et al. Asymmetric dimethylarginine produces vascular lesions in endothelial nitric oxide synthase-deficient mice: Involvement of renin-angiotensin system and oxidative stress. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 1682–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veresh, Z.; Racz, A.; Lotz, G.; Koller, A. ADMA impairs nitric oxide-mediated arteriolar function due to increased superoxide production by angiotensin II-NAD(P)H oxidase pathway. Hypertension 2008, 52, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, I.V.; Kajstura, M.; Sawamura, T.; Goligorsky, M.S. Asymmetric dimethylarginine upregulates LOX-1 in activated macrophages: Role in foam cell formation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2004, 287, H782–H790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Zhao, J.F.; Hsu, C.P.; Kou, Y.R.; Lu, T.M.; Lee, T.S. The detrimental effect of asymmetric dimethylarginine on cholesterol efflux of macrophage foam cells: Role of the NOX/ROS signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 143, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, M.H.; Reis, T.; Husain-Syed, F.; Vanholder, R.; Hutchison, C.; Stenvinkel, P.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Cozzolino, M.; Juillard, L.; Kashani, K.; et al. Classification of uremic toxins and their role in kidney failure. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1918–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C.; Tian, Y.C.; Lu, C.L.; Wu, M.J.; Lim, P.S.; Chiu, Y.W.; Kuo, K.L.; Liu, S.H.; Chou, Y.C.; Sun, C.A.; et al. AST-120 improved uremic pruritus by lowering indoxyl sulfate and inflammatory cytokines in hemodialysis patients. Aging 2024, 16, 4236–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.H.; Im, H.; Park, S.; Song, B.; Park, D.K.; Kim, D.S.; Gil, H.W. AST-120 protects cognitive and emotional impairment in chronic kidney disease induced by 5/6 nephrectomy. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Lockwood, M.B.; Rhee, C.M.; Tantisattamo, E.; Andreoli, S.; Balducci, A.; Laffin, P.; Harris, T.; Knight, R.; Kumaraswami, L.; et al. Patient-centred approaches for the management of unpleasant symptoms in kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billing, A.M.; Kim, Y.C.; Gullaksen, S.; Schrage, B.; Raabe, J.; Hutzfeldt, A.; Demir, F.; Kovalenko, E.; Lasse, M.; Dugourd, A.; et al. Metabolic communication by SGLT2 inhibition. Circulation 2024, 149, 860–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marengo, M.; Migliori, M.; Merlotti, G.; Naso, E.; Dellepiane, S.; Medica, D.; Cappellano, G.; Cortazzi, S.; Colombatto, A.; Quercia, A.D.; et al. High-flux hemodialysis with polymethylmethacrylate membranes reduces soluble CD40L, a mediator of cardiovascular disease in uremia. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2025, gfaf101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velenosi, T.J.; Hennop, A.; Feere, D.A.; Tieu, A.; Kucey, A.S.; Kyriacou, P.; McCuaig, L.E.; Nevison, S.E.; Kerr, M.A.; Urquhart, B.L. Untargeted plasma and tissue metabolomics in rats with chronic kidney disease given AST-120. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, N.; Hasebe, N.; Sumitomo, K.; Fujino, T.; Fukuzawa, J.; Hirayama, T.; Kikuchi, K. An oral adsorbent, AST-120, suppresses oxidative stress in uremic rats. Am. J. Nephrol. 2006, 26, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Zuo, Y.; Ma, J.; Yancey, P.G.; Hunley, T.E.; Motojima, M.; Fogo, A.B.; Linton, M.F.; Fazio, S.; Ichikawa, I.; et al. Oral activated charcoal adsorbent (AST-120) ameliorates extent and instability of atherosclerosis accelerated by kidney disease in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 2491–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takkavatakarn, K.; Wuttiputinun, T.; Phannajit, J.; Praditpornsilpa, K.; Eiam-Ong, S.; Susantitaphong, P. Protein-bound uremic toxin lowering strategies in chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Nephrol. 2021, 34, 1805–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Hsu, C.Y.; Tain, Y.L.; Ng, H.Y.; Cheng, B.C.; Yang, C.C.; Wu, C.H.; Chiou, T.T.; Lee, Y.T.; Liao, S.C. Effects of AST-120 on blood concentrations of protein-bound uremic toxins and biomarkers of cardiovascular risk in chronic dialysis patients. Blood Purif. 2014, 37, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedillo-Flores, R.; Cuevas-Budhart, M.A.; Cavero-Redondo, I.; Kappes, M.; Ávila-Díaz, M.; Paniagua, R. Impact of gut microbiome modulation on uremic toxin reduction in chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongprayoon, C.; Kaewput, W.; Hatch, S.T.; Bathini, T.; Sharma, K.; Wijarnpreecha, K.; Ungprasert, P.; D’Costa, M.; Mao, M.A.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Effects of probiotics on inflammation and uremic toxins among patients on dialysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Klein, K.; Johnson, D.W.; Campbell, K.L. Pre-, pro-, and synbiotics: Do they have a role in reducing uremic toxins? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Nephrol. 2012, 2012, 673631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Johnson, D.W.; Morrison, M.; Pascoe, E.M.; Coombes, J.S.; Forbes, J.M.; Szeto, C.C.; McWhinney, B.C.; Ungerer, J.P.; Campbell, K.L. Synbiotics wasing renal failure by improving gut microbiology (SYNERGY): A randomized trial. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 11, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poesen, R.; Mutsaers, H.A.; Windey, K.; van den Broek, P.H.; Verweij, V.; Augustijns, P.; Kuypers, D.; Jansen, J.; Evenepoel, P.; Verbeke, K.; et al. The influence of dietary protein intake on mammalian tryptophan and phenolic metabolites. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Iorio, B.R.; Rocchetti, M.T.; De Angelis, M.; Cosola, C.; Marzocco, S.; Di Micco, L.; di Bari, I.; Accetturo, M.; Vacca, M.; Gobbetti, M.; et al. Nutritional therapy modulates intestinal microbiota and reduces serum levels of total and free indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate in chronic kidney disease (medika study). J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agus, A.; Planchais, J.; Sokol, H. Gut microbiota regulation of tryptophan metabolism in health and disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, B.; Buzkova, P.; Robbins, J.A.; Fink, H.A.; Raiford, M.; Isales, C.M.; Shikany, J.M.; Coughlin, S.S.; Carbone, L.D. The association of aromatic amino acids with incident hip fracture, aBMD, and body composition from the Cardiovascular Health Study. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2019, 105, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, L.; Buzkova, P.; Robbins, J.A.; Fink, H.A.; Barzilay, J.I.; Elam, R.E.; Isales, C. Association of serum levels of phenylalanine and tyrosine with hip fractures and frailty in older adults: The cardiovascular health study. Arch. Osteoporos. 2024, 19, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yoshihara, K.; Miyata, N.; Hata, T.; Altaisaikhan, A.; Takakura, S.; Asano, Y.; Izuno, S.; Sudo, N. Dietary tryptophan, tyrosine, and phenylalanine depletion induce reduced food intake and behavioral alterations in mice. Physiol. Behav. 2022, 244, 113653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.; Abrams, J.; Nutt, D. Tryptophan depletion and its implications for psychiatry. Br. J. Psychiatry 2001, 178, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, G.; Goodwin, G.M.; Cowen, P.J.; Harmer, C.J. Low-dose tryptophan depletion in recovered depressed patients induces changes in cognitive processing without depressive symptoms. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 57, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, C.; Benoit, B.; Bres, E.; Chanon, S.; Vieille-Marchiset, A.; Pinteur, C.; Pesenti, S.; Glorieux, G.; Picard, C.; Fouque, D.; et al. A low aromatic amino-acid diet improves renal function and prevent kidney fibrosis in mice with chronic kidney disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, Z.S.; Uysal, S.; Guner, G.; Yilmaz, O.; Posaci, C. Effects of oral L-arginine supplementation on blood pressure and asymmetric dimethylarginine in stress-induced preeclamptic rats. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2008, 26, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Sheen, J.M.; Chen, C.C.; Yu, H.R.; Tiao, M.M.; Kuo, H.C.; Huang, L.T. Maternal citrulline supplementation prevents prenatal dexamethasone-induced programmed hypertension. Free Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.J.; Lin, K.M.; Kuo, H.C.; Huang, C.F.; Lin, Y.J.; Huang, L.T.; Tain, Y.L. Two different approaches to restore renal nitric oxide and prevent hypertension in young spontaneously hypertensive rats: L-citrulline and nitrate. Transl. Res. 2014, 163, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Chu, Y.H.; Wang, C.C.; Wang, C.H.; Tain, Y.L.; Yang, H.W. Rapid detection of gut microbial metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide for chronic kidney disease prevention. Biosensors 2021, 11, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, C.; Bennis, Y.; Titeca-Beauport, D.; Caillard, P.; Cluet, Y.; Kamel, S.; Choukroun, G.; Maizel, J.; Liabeuf, S.; Bodeau, S. Two rapid, accurate liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry methods for the quantification of seven uremic toxins: An application for describing their accumulation kinetic profile in a context of acute kidney injury. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2020, 1152, 122234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Uremic Toxin | Structure | Size (MW) | Protein Binding | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indoxyl sulfate | C8H7NO4S | 213.2 | 86–98% bound to albumin | Dietary tryptophan |
| p-Cresyl sulfate | C7H8O4S | 188.2 | 91–95% bound to albumin | Dietary tyrosine and phenylalanine |
| Trimethylamine N-oxide | C3H9NO | 75.1 | Free water-soluble | Dietary phosphatidylcholine, choline, betaine, and L-carnitine |
| Asymmetric dimethylarginine | C8H18N4O2 | 202.3 | 30% bound to albumin | Non-proteinogenic amino acid synthesized through post-translational methylation of arginine |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Meng, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, M. The Non-Traditional Cardiovascular Culprits in Chronic Kidney Disease: Mineral Imbalance and Uremic Toxin Accumulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7938. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167938
Lu Y, Meng L, Wang X, Zhang Y, Zhang C, Zhang M. The Non-Traditional Cardiovascular Culprits in Chronic Kidney Disease: Mineral Imbalance and Uremic Toxin Accumulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7938. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167938
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yue, Linlin Meng, Xinlu Wang, Yun Zhang, Cheng Zhang, and Meng Zhang. 2025. "The Non-Traditional Cardiovascular Culprits in Chronic Kidney Disease: Mineral Imbalance and Uremic Toxin Accumulation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7938. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167938
APA StyleLu, Y., Meng, L., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Zhang, C., & Zhang, M. (2025). The Non-Traditional Cardiovascular Culprits in Chronic Kidney Disease: Mineral Imbalance and Uremic Toxin Accumulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7938. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167938







