Monoterpene Indole Alkaloids with Antimicrobial Activity Against Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antibacterial Activity
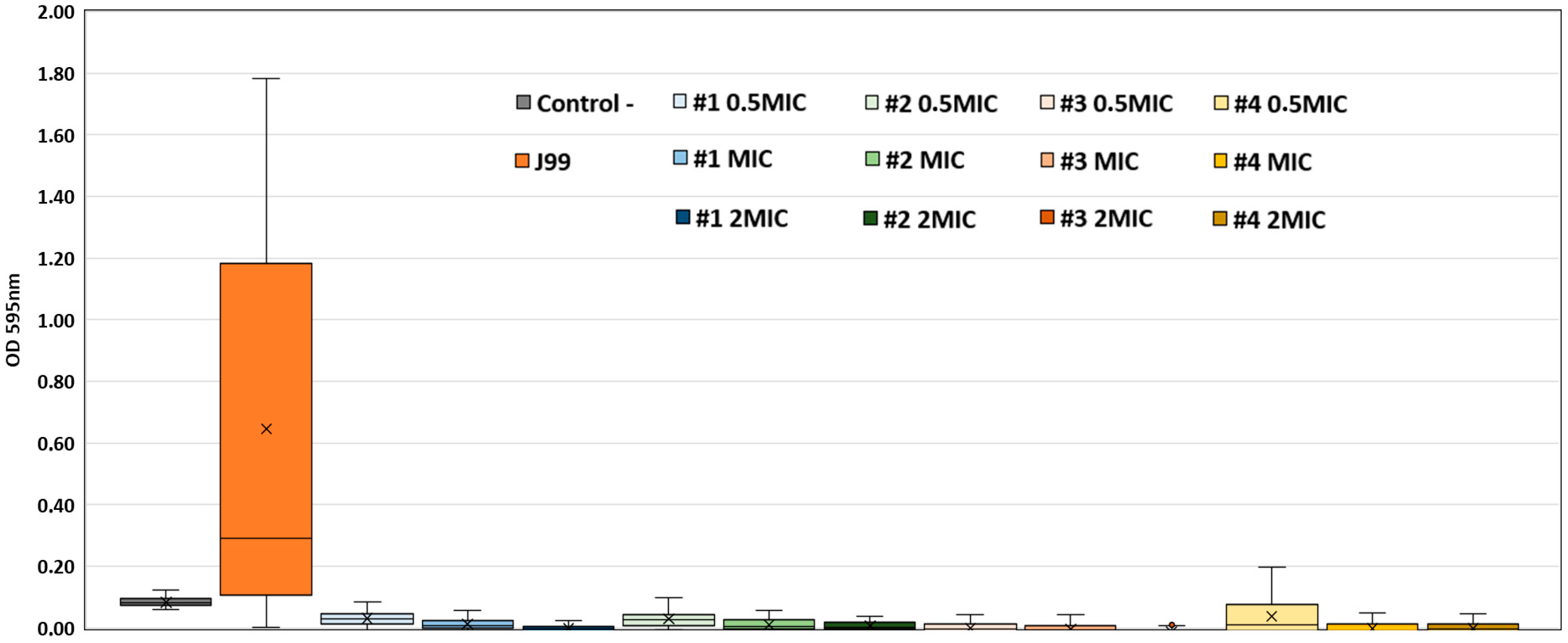
2.2. Anti-Biofilm Activity
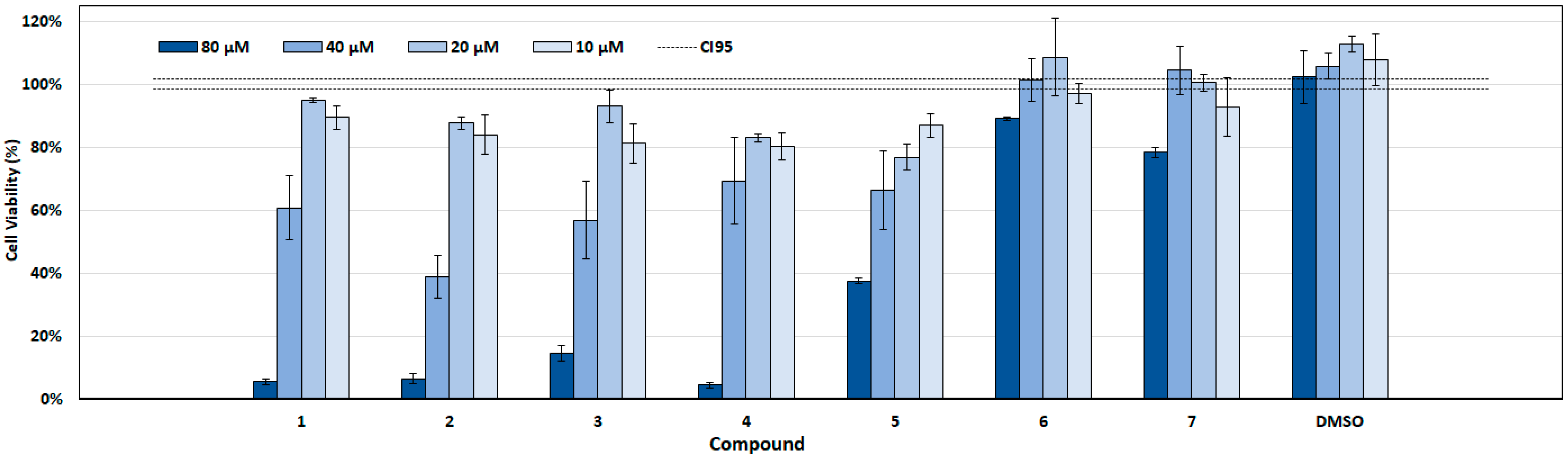
2.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
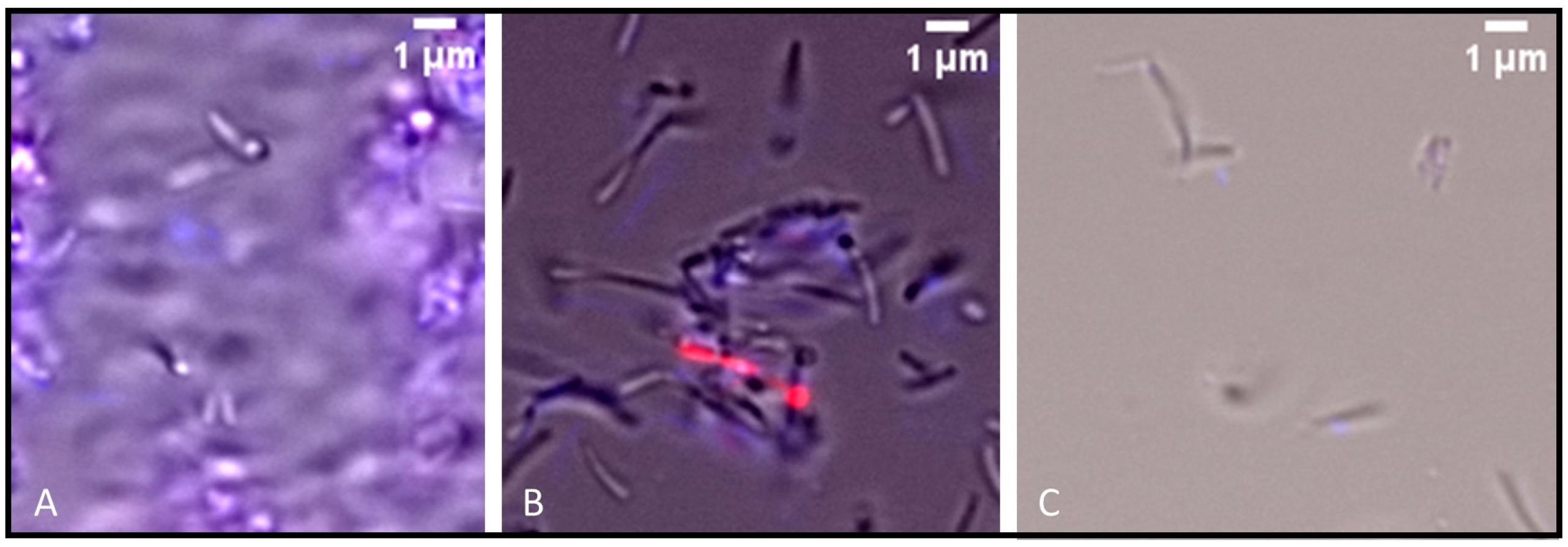
2.4. Preliminary Assessment of Antibacterial Mechanism of Action
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Natural Compounds Library
5.2. In Vitro Valuation of Anti-H. pylori Activity
5.3. Biofilm Formation Assay
5.4. Cytotoxicity Assessment of Compounds
5.5. Membrane Integrity Assay in H. pylori
5.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gisbert, J.P. Helicobacter pylori y enfermedad gástrica. Med. Clin. 2025, 165, 106974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, C.; Liou, J.-M.; Alboraie, M.; Bornschein, J.; Campos Nunez, C.; Coelho, L.G.; Quach, D.T.; Fallone, C.A.; Chen, Y.-C.; Gerhard, M.; et al. Helicobacter pylori antibiotic resistance: A global challenge in search of solutions. Gut 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyssen, O.P.; Martínez, B.; Mégraud, F.; Savarino, V.; Fallone, C.A.; Bazzoli, F.; Gisbert, J.P. Sequential versus standard triple therapy for first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication: An update. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Yang, H. In vitro effects of Lactobacillus plantarum LN66 and antibiotics used alone or in combination on Helicobacter pylori mature biofilm. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaf, N.; Amhis, W.; Saoula, H.; Abid, A.; Nakmouche, M.; Balamane, A.; Ali Arous, N.; Ouar-Korichi, M.; Vale, F.F.; Bénéjat, L.; et al. Prevalence, antibiotic resistance, and MLST typing of Helicobacter pylori in Algiers, Algeria. Helicobacter 2017, 22, e12446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mégraud, F. Antibiotic resistance is the key element in treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1300–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Camargo, M.C.; El-Omar, E.; Liou, J.-M.; Peek, R.; Schulz, C.; Smith, S.I.; Suerbaum, S. Helicobacter pylori infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshenawi, Y.; Hu, S.; Hathroubi, S. Biofilm of Helicobacter pylori: Life cycle, features, and treatment options. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parreira, P.; Fátima Duarte, M.; Reis, C.A.; Martins, M.C.L. Helicobacter pylori infection: A brief overview on alternative natural treatments to conventional therapy. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manach, C.; Scalbert, A.; Morand, C.; Rémésy, C.; Jiménez, L. Polyphenols: Food sources and bioavailability. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 727–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jubair, N.; Rajagopal, M.; Chinnappan, S.; Abdullah, N.B.; Fatima, A. Review on the antibacterial mechanism of plant-derived compounds against multidrug-resistant bacteria (MDR). Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 3663315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Fakhrany, O.M.; Elekhnawy, E. Helicobacter pylori in the post-antibiotics era: From virulence factors to new drug targets and therapeutic agents. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemian, A.; Fattahi, A.; Shokouhi Mostafavi, S.K.; Almarzoqi, A.H.; Memariani, M.; Ben Braiek, O.; Yassine, H.M.; Mostafavi, N.S.S.; Ahmed, M.M.; Mirforughi, S.A. Herbal medicine as an auspicious therapeutic approach for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection: A concise review. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 16847–16860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Cai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Gao, S.; Geng, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Jia, J.; Sun, Y. Bifunctional enzyme SpoT is involved in biofilm formation of Helicobacter pylori with multidrug resistance by upregulating efflux pump Hp1174 (GluP). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00957-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, C.M.; Naidoo, Y.; Dewir, Y.H.; Murthy, H.N.; El-Hendawy, S.; Al-Suhaibani, N. Major bioactive alkaloids and biological activities of Tabernaemontana species (Apocynaceae). Plants 2021, 10, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcellano, R.C.; Cort, J.R.; Moinuddin, S.G.A.; Franzblau, S.G.; Ma, R.; Aguinaldo, A.M. An iboga alkaloid chemotaxonomic marker from endemic Tabernaemontana ternifolia with antitubercular activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor Azman, N.S.; Hossan, M.S.; Nissapatorn, V.; Uthaipibull, C.; Prommana, P.; Jin, K.T.; Rahmatullah, M.; Mahboob, T.; Raju, C.S.; Jindal, H.M.; et al. Anti-infective activities of 11 plants species used in traditional medicine in Malaysia. Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 194, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-Q.; Jia, J.; Hu, J.-Y.; Wu, J.; Sun, W.-T.; Zheng, M.; Wang, X.; Zhu, K.-K.; Jiang, C.-S.; Yang, S.-P.; et al. Iboga-type alkaloids with indolizidino[8,7-b]indole scaffold and bisindole alkaloids from Tabernaemontana bufalina Lour. Phytochemistry 2022, 196, 113089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, A.M.; Reis, M.; Duarte, N.; Spengler, G.; Molnár, J.; Ferreira, M.-J.U. Epoxylathyrol Derivatives: Modulation of ABCB1-mediated multidrug resistance in human colon adenocarcinoma and mouse T-lymphoma cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2215–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, M.; Paterna, A.; Mónico, A.; Molnar, J.; Lage, H.; Ferreira, M.-J. Diterpenes from Euphorbia piscatoria: Synergistic interaction of lathyranes with doxorubicin on resistant cancer cells. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, F.; Madureira, A.M.; Sancha, S.; Mulhovo, S.; Luo, X.; Duarte, A.; Ferreira, M.-J.U. Cleistochlamys kirkii chemical constituents: Antibacterial activity and synergistic effects against resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 178, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.J.; Gajdács, M.; Kincses, A.; Spengler, G.; dos Santos, D.J.V.A.; Ferreira, M.-J.U. Nitrogen-containing naringenin derivatives for reversing multidrug resistance in cancer. Bioorg Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterna, A.; Khonkarn, R.; Mulhovo, S.; Moreno, A.; Madeira Girio, P.; Baubichon-Cortay, H.; Falson, P.; Ferreira, M.-J.U. Monoterpene indole alkaloid azine derivatives as MDR reversal agents. Bioorg Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancha, S.A.R.; Dobiasová, S.; Nejedlý, T.; Strnad, O.; Viktorová, J.; Ferreira, M.-J.U. Lycorine and homolycorine derivatives for chemo-sensitizing resistant human ovarian adenocarcinoma cells. Phytomedicine 2024, 126, 155460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzia, K.A.; Miftahussurur, M.; Syam, A.F.; Waskito, L.A.; Doohan, D.; Rezkitha, Y.A.A.; Matsumoto, T.; Tuan, V.P.; Akada, J.; Yonezawa, H.; et al. Biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance phenotype of Helicobacter pylori clinical isolates. Toxins 2020, 12, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelstein, A.D.; Tsuchida, M.A.; Amodaj, N.; Pinkard, H.; Vale, R.D.; Stuurman, N. Advanced methods of microscope control using µManager software. J. Biol. Methods 2014, 1, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cos, P.; Vlietinck, A.J.; Berghe, D.V.; Maes, L. Anti-infective potential of natural products: How to develop a stronger in vitro ‘proof-of-concept’. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 106, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brackman, G.; Cos, P.; Maes, L.; Nelis, H.J.; Coenye, T. Quorum sensing inhibitors increase the susceptibility of bacterial biofilms to antibiotics in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 2655–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J. Indole as an intercellular signal in microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 426–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Luxami, V.; Paul, K. Investigating the antibacterial efficiency and mechanism of indole- and naphthalimide-mediated benzimidazoles: Membrane damage, metabolic inactivation, and oxidative stress against Bacillus subtilis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 24830–24850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, L.; Lin, F.; Ling, B. Indole derivatives display antimicrobial and antibiofilm effects against extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e0338824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzoyem, J.P.; Aro, A.O.; McGaw, L.J.; Eloff, J.N. Antimycobacterial activity against different pathogens and selectivity index of fourteen medicinal plants used in southern Africa to treat tuberculosis and respiratory ailments. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2016, 102, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallant, C.A.; Cromarty, A.D.; Steenkamp, V. Effect of an alkaloidal fraction of Tabernaemontana elegans (Stapf.) on selected microorganisms. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 140, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Pires, D.; Aínsa, J.A.; Gracia, B.; Mulhovo, S.; Duarte, A.; Anes, E.; Ferreira, M.-J.U. Antimycobacterial evaluation and preliminary phytochemical investigation of selected medicinal plants traditionally used in Mozambique. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, M.-J.U.; Paterna, A. Monoterpene indole alkaloids as leads for targeting multidrug resistant cancer cells from the African medicinal plant Tabernaemontana elegans. Phytochem. Rev. 2019, 18, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Präbst, K.; Engelhardt, H.; Ringgeler, S.; Hübner, H. Basic colorimetric proliferation assays: MTT, WST, and resazurin. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1601, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grela, E.; Kozłowska, J.; Grabowiecka, A. Current methodology of MTT assay in bacteria—A review. Acta Histochem. 2018, 120, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Chemical Scaffold | Plant Species (Family) | Chemical Scaffold | Plant Species (Family) |
|---|---|---|---|
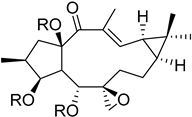 Macrocyclic lathyrane diterpenes and acylated derivatives | Euphorbia boetica Boiss. (Euphorbiaceae) [19] | 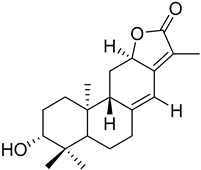 ent-abietane diterpenes | Euphorbia piscatoria Ait. (Euphorbiacae) [20] |
 Tetracyclic triterpenes | Cleistochlamys kirkii (Benth) Oliv. (Annonaceae) [21] | 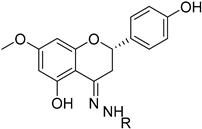 Flavonoid derivatives | Euphorbia pedroi (Euphorbiacae) [22] |
 Monoterpene indole alkaloid azine derivatives | Tabernaemontana elegans (Apocynaceae) [23] | 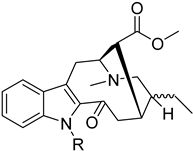 Monoterpene indole alkaloid alkylated derivatives | Tabernaemontana elegans (Apocynaceae) [23] |
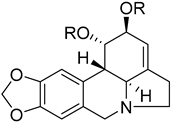 Amaryllidaceae-type alkaloids and derivatives | Pancratium maritimum L. (Amaryllidaceae) [24] | 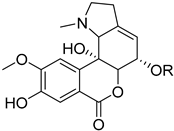 Amaryllidaceae-type alkaloids and derivatives | Pancratium maritimum L. (Amaryllidaceae) [24] |
| Compound | Name | MIC (MBC) (µM) | MIC (µg/mL) * | Anti-Biofilm Activity | CC50 (µM) | “SI” (CC50/MIC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dregamine(4′-chlorobenzylidene)hydrazone | 20 (-) | 9.82 | + | 44.1 ± 1.7 | >2.2 |
| 2 | Dregamine(4′-bromobenzylidene)hydrazone | 20 (20) | 10.71 | + | 34.8 ± 1.7 | >1.7 |
| 3 | Dregamine(phenylallylidene)hydrazone | 20 (20) | 9.65 | + | 44.1 ± 2.4 | >2.2 |
| 4 | Dregamine(indolylmethylene)hydrazone | 10 (-) | 4.96 | + | 47.0 ± 2.2 | >4.7 |
| 5 | Dregamine(2′-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazone | 20 (-) | 9.45 | - | 55.8 ± 4.5 | >2.8 |
| 6 | Dregamine(6′bromo-3′indolylmethylene)hydrazone | 10 (20) | 5.75 | - | >80 µM ** | >8.0 |
| 7 | Tabernaelegantinine A | 20 (-) | 15.25 | - | >80 µM ** | >4.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marques, A.T.; Tanoeiro, L.; Paterna, A.; Caeiro, M.F.; Cardoso, D.; Mulhovo, S.; Vital, J.S.; Pimentel, A.C.; Ferreira, M.-J.U.; Vale, F.F. Monoterpene Indole Alkaloids with Antimicrobial Activity Against Helicobacter pylori. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167904
Marques AT, Tanoeiro L, Paterna A, Caeiro MF, Cardoso D, Mulhovo S, Vital JS, Pimentel AC, Ferreira M-JU, Vale FF. Monoterpene Indole Alkaloids with Antimicrobial Activity Against Helicobacter pylori. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167904
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarques, Andreia T., Luís Tanoeiro, Angela Paterna, Maria Filomena Caeiro, David Cardoso, Silva Mulhovo, Joana S. Vital, Ana Carolina Pimentel, Maria-José U. Ferreira, and Filipa F. Vale. 2025. "Monoterpene Indole Alkaloids with Antimicrobial Activity Against Helicobacter pylori" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167904
APA StyleMarques, A. T., Tanoeiro, L., Paterna, A., Caeiro, M. F., Cardoso, D., Mulhovo, S., Vital, J. S., Pimentel, A. C., Ferreira, M.-J. U., & Vale, F. F. (2025). Monoterpene Indole Alkaloids with Antimicrobial Activity Against Helicobacter pylori. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167904







