CD20-Negative Large B-Cell Lymphomas: The Diagnostic Challenge of Tumors with Downregulation of Mature B-Cell Marker Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Plasmablastic Lymphoma (PBL)
2.1. Clinical Presentation, Epidemiology and Etiology
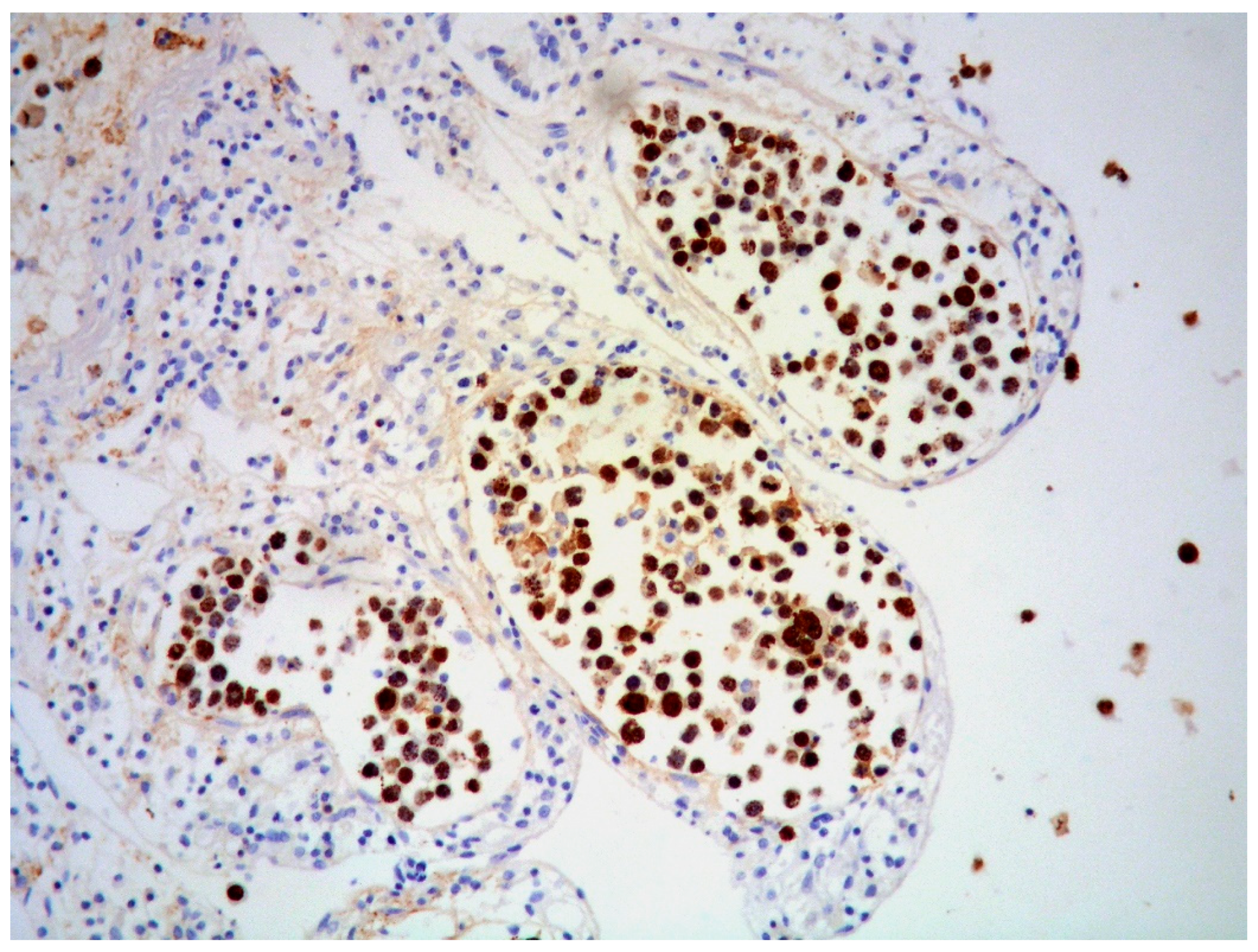
2.2. Morphology and Immunophenotype
2.3. MYC Aberrations in PBL
2.4. Other Molecular Aberrations
2.5. Treatment
3. Primary Effusion Lymphoma (PEL)
3.1. Clinical Presentation, Epidemiology and Etiology
3.2. KSHV/HHV8
3.3. Morphology, Immunophenotype and Molecular Features
3.4. Outcome and Treatment
4. ALK-Positive Large B-Cell Lymphoma (ALK-Positive LBCL)
4.1. Clinical Presentation, Epidemiology and Etiology
4.2. Morphology, Immunophenotype and Molecular Features
4.3. Outcome and Treatment
5. HHV8-Positive Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (HHV8-Positive DLBCL)
5.1. Clinical Presentation, Epidemiology and Etiology
5.2. Morphology, Immunophenotype and Molecular Features
5.3. Outcome and Treatment
5.4. Summary of the Main Differential Diagnoses in Cases of Lymphomas with Plasma Cell Differentiation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. WHO Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumors, 5th ed.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Campo, E.; Jaffe, E.S.; Cook, J.R.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Anderson, K.C.; Brousset, P.; Cerroni, L.; de Leval, L.; Dirnhofer, S.; et al. The International Consensus Classification of mature lymphoid neoplasms: A report from the Clinical Advisory Committee. Blood 2022, 140, 1229–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, A.A.; Sugden, B. EBV is necessary for proliferation of dually infected primary effusion lymphoma cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6963–6968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezk, S.A.; Weiss, L.M. EBV-associated lymphoproliferative disorders: Update in classification. Surg. Pathol. 2019, 12, 745–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues; Swerdlow, S.H., Campo, E., Harris, N.L., Jaffe, E.S., Pileri, S.A., Stein, H., Thiele, J., Eds.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Delecluse, H.J.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Dallenbach, F.; Hummel, M.; Marafioti, T.; Schneider, U.; Huhn, D.; Schmidt-Westhausen, A.; Reichart, P.A.; Gross, U.; et al. Plasmablastic lymphomas of the oral cavity: A new entity associated with the human immunodeficiency virus infection. Blood 1997, 89, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanelli, M.; Sanguedolce, F.; Palicelli, A.; Zizzo, M.; Martino, G.; Caprera, C.; Fragliasso, V.; Soriano, A.; Valle, L.; Ricci, S.; et al. EBV-driven lymphoproliferative disorders and lymphomas of the gastrointestinal tract: A spectrum of entities with a common denominator (Part 2). Cancers 2021, 13, 4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morscio, J.; Dierickx, D.; Nijs, J.; Verhoef, G.; Bittoun, E.; Vanoeteren, X.; Wlodarska, I.; Sagaert, X.; Tousseyn, T. Clinicopathologic comparison of plasmablastic lymphoma in HIV-positive, immunocompetent and posttransplant patients single-center series of 25 cases and meta-analysis of 277 reported cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 38, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.J.; Bibas, M.; Miranda, R.N. The biology and treatment of plasmablastic lymphoma. Blood 2015, 125, 2323–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, C.M.; Smith, L.B. Plasmablastic lymphoma: A review of clinicopathologic features and differential diagnosis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2016, 140, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguedolce, F.; Zanelli, M.; Zizzo, M.; Martino, G.; Rossi, C.; Parente, P.; Ascani, S. Clinical, pathological and molecular features of plasmablastic lymphoma arising in the gastrointestinal tract: A review and reappraisal. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, K.D.; Sabunciyan, S.; Langmead, B.; Nagy, N.; Curley, R.; Klein, G.; Klein, E.; Salamon, D.; Feinberg, A.P. Large-scale hypomethylated blocks associated with Epstein-Barr virus-induced B-cell immortalization. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.; Abrisqueta, P. Plasmablastic lymphoma: Current perspectives. Blood Lymphat. Cancer Targets Ther. 2018, 8, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.J.; Chuang, S.S. Lymphoid neoplasms with plasmablastic differentiation: A comprehensive review and diagnostic approaches. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2020, 27, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, F.; Chang, C.C.; Medeiros, L.J.; Udden, M.M.; Cho-Vega, J.H.; Lau, C.C.; Finch, C.J.; Vilchez, R.A.; McGregor, D.; Jorgensen, J.L. Plasmablastic lymphomas and plasmablastic plasma cell myelomas have nearly identical immunophenotypic profiles. Mod. Pathol. 2005, 18, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, C.; Fabiani, B.; Do, C.; Tchernonog, E.; Cartron, G.; Gravelle, P.; Amara, N.; Malot, S.; Palisoc, M.M.; Copie-Bergman, C.; et al. Immune-checkpoint expression in Epstein-Barr virus positive and negative plasmablastic lymphoma: A clinical and pathological study in 82 patients. Haematologica 2016, 101, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loghavi, S.; Alayed, K.; Aladily, T.N.; Zuo, Z.; Ng, S.B.; Tang, G.; Hu, S.; Yin, C.C.; Miranda, R.N.; Medeiros, L.J.; et al. Stage, age, and EBV status impact outcomes of plasmablastic lymphoma patients: A clinicopathologic analysis of 61 patients. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanelli, M.; Ragazzi, M.; Valli, R.; De Marco, L.; Cecinato, P.; Azzolini, F.; Ferrari, A.; Bacci, F.; Ascani, S. Unique presentation of a plasmablastic lymphoma superficially involving the entire large bowel. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2015, 211, 1030–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.; Papenhausen, P.; Shao, H. The role of c-MYC in B-cell lymphomas: Diagnostic and molecular aspects. Genes 2017, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valera, A.; Balague, O.; Colomo, L.; Martinez, A.; Delabie, J.; Taddesse-Heath, L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Campo, E. IG/MYC rearrangements are the main cytogenetic alteration in plasmablastic lymphomas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 1686–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pather, S.; Mashele, T.; Willem, P.; Patel, M.; Perner, Y.; Motaung, M.; Nagiah, N.; Waja, F.; Philip, V.; Lakha, A.; et al. MYC status in HIV-associated plasmablastic lymphoma: Dual colour CISH, FISH and immunohistochemistry. Histopathology 2021, 79, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Moreno, S.; Martinez-Magunacelaya, N.; Zecchini-Barrese, T.; de Villambrosia, S.G.; Linares, E.; Ranchal, T.; Rodriguez-Pinilla, M.; Batlle, A.; Cereceda-Company, L.; Revert-Arce, J.B.; et al. Plasmablastic lymphoma phenotype is determined by genetic alterations in MYC and PRDM1. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramis-Zaldivar, J.E.; Gonzalez-Farre, B.; Nicolae, A.; Pack, S.; Clot, G.; Nadeu, F.; Mottok, A.; Horn, H.; Song, J.Y.; Fu, K.; et al. MAPK and JAK-STAT pathways dysregulation in plasmablastic lymphoma. Haematologica 2021, 106, 2682–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontzek, F.; Staiger, A.M.; Zapukhlyak, M.; Xu, W.; Bonzheim, I.; Borgmann, V.; Sander, P.; Baptista, M.J.; Heming, J.-N.; Berning, P.; et al. Molecular and functional profiling identifies therapeutically targetable vulnerabilities in plasmablastic lymphoma. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.J.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Redd, R.A.; Lawrence, M.S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Li, A.J.; Ziepert, M.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 670–690. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Filip, I.; Gomez, K.; Engelbrecht, D.; Meer, S.; Lalloo, P.N.; Patel, P.; Perner, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Genomic characterization of HIV-associated plasmablastic lymphoma identifies pervasive mutations in the JAK-STAT pathway. Blood Cancer Discov. 2020, 1, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Reyero, J.; Magunacelaya, N.M.; de Villambrosia, S.G.; Loghavi, S.; Mediavilla, A.G.; Tonda, R.; Beltran, S.; Gut, M.; Gonzalez, A.P.; d’Ámore, E.; et al. Genetic lesions in MYC and STAT3 drive oncogenic transcription factor overexpression in plasmablastic lymphoma. Haematologica 2021, 106, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindiapina, P.; Ahmed, E.H.; Mozhenkova, A.; Abebe, T.; Baiocchi, R.A. Immunology of EBV-related lymphoproliferative disease in HIV-positive individuals. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, M.; Wei, H.; Chen, Y. Targeting MCL-1 in cancer: Current status and perspectives. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelenetz, A.D.; Gordon, L.I.; Abramson, J.S.; Advani, R.H.; Andreadis, B.; Bartlett, N.L.; Budde, L.E.; Caimi, P.; Chang, J.E.; Christian, B.; et al. National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). Guidelines Insights: B-cell lymphomas. J. Natl. Compr. Canc Netw. 2023, 21, 1118–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makady, N.F.; Ramzy, D.; Ghaly, R.; Abdel-Malek, R.R.; Shohdy, K.S. The emerging treatment options of plasmablastic lymphoma: Analysis of 173 individual patient outcomes. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021, 21, e255–e263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-J.; Li, J.-W.; Chen, K.-L.; Li, J.; Zhong, M.-Z.; Liu, X.-L.; Yi, P.-Y.; Zhou, H. HIV-negative plasmablastic lymphoma: Report of 8 cases and a comprehensive review of 394 published cases. Blood Res. 2020, 55, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, J.J.; Guerrero-Garcia, T.; Baldini, F.; Tchernonog, E.; Cartron, G.; Ninkovic, S.; Cwynarski, K.; Dierickx, D.; Tousseyn, T.; Lansigan, F.; et al. Bortezomib plus EPOCH is effective as frontline treatment in patients with plasmablastic lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 184, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Garcia, T.A.; Mogollon, R.J.; Castillo, J.J. Bortezomib in plasmablastic lymphoma: A glimpse of hope for a hard-to-treat disease. Leuk. Res. 2017, 62, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.; Imaizumi, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Niino, D.; Hourai, M.; Sato, S.; Sawayama, Y.; Hata, T.; Ohshima, K.; Miyazaki, Y. Bortezomib- and lenalidomide-based treatment of refractory plasmablastic lymphoma. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2020, 43, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.J.; Chapuy, B.; Ouyang, J.; Sun, H.H.; Roemer, M.G.; Xu, M.L.; Yu, H.; Fletcher, C.D.M.; Freeman, G.J.; Shipp, M.A.; et al. PD-L1 expression is characteristic of a subset of aggressive B-cell lymphomas and virus-associated malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3462–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Crabill, G.A.; Pritchard, T.S.; McMiller, T.L.; Wei, P.; Pardoll, D.M.; Pan, F.; Topalian, S.L. Mechanisms regulating PD-L1 expression on tumor and immune cells. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topalian, S.L.; Drake, C.G.; Pardoll, D.M. Immune checkpoint blockade: A common denominator approach to cancer therapy. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, C.; Gajewski, T.F.; Mackensen, A. Interaction of PD-L1 on tumor cells with PD-1 on tumor-specific T cells as a mechanism of immune evasion: Implications for tumor immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2005, 54, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broggi, G.; Angelico, G.; Farina, J.; Tinnirello, G.; Barresi, V.; Zanelli, M.; Palicelli, A.; Certo, F.; Barbagallo, G.; Magro, G.; et al. Tumor-associated microenvironment, PD-L1 expression and their relationship with immunotherapy in glioblastoma, IDH-wild type: A comprehensive review with emphasis on the implications for neuropathologists. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2024, 254, 155144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damlaj, M.; Alzayed, M.; Alahmari, B.; Alhejazi, A.; Alaskar, A.; Alzahrani, M. Therapeutic potential of checkpoint inhibitors in refractory plasmablastic lymphoma. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019, 19, e559–e563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijenthira, A.; Kuruvilla, J.; Crump, M.; Jain, M.; Prica, A. Cost-effectiveness analysis of frontline polatuzumab-rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone and/or second-line chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy versus standard of care for treatment of patients with intermediate-to high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri, R.; Qualtieri, J.; Garfall, A.L. Axicabtagene ciloleucel for CD19+ plasmablastic lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, E28–E30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, C.; Finel, H.; McQuaker, G.; Vandenberghe, E.; Rossi, G.; Dreger, P. Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for plasmablastic lymphoma: The European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation experience. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015, 21, 1146–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.T.; Giri, A.; Park, Y.; Patel, K.K.; Link, B.K.; Nowakowski, G.S.; Maliske, S.M.; Fortin, S.; Chavez, J.C.; Saeed, H.; et al. Outcomes of patients with limited-stage plasmablastic lymphoma: A multi-institutional retrospective study. Am. J. Hematol. 2023, 98, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.J.; Furman, M.; Beltran, B.E.; Bibas, M.; Bower, M.; Chen, W.; Diez-Martin, J.L.; Liu, J.J.; Miranda, R.N.; Montoto, S.; et al. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated plasmablastic lymphoma: Poor prognosis in the era of highly active-antiretroviral therapy. Cancer 2012, 118, 5270–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesarman, E.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.S.; Said, J.W.; Knowles, D.M. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body cavity-based lymphomas. NEJM 1995, 332, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidano, G.; Carbone, A. Primary effusion lymphoma: A liquid phase lymphoma of fluid-filled body cavities. Adv. Cancer Res. 2001, 80, 115–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simonelli, C.; Spina, M.; Cinelli, R.; Talamini, R.; Tedeschi, R.; Gloghini, A.; Vaccher, E.; Carbone, A.; Tirelli, U. Clinical features and outcome of primary effusion lymphoma in HIV-infected patients: A single-institution study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 3948–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanelli, M.; Sanguedolce, F.; Zizzo, M.; Palicelli, A.; Bassi, M.C.; Santandrea, G.; Martino, G.; Soriano, A.; Caprera, C.; Corsi, M.; et al. Primary effusion lymphoma occurring in the setting of transplanted patients: A systematic review of a rare, life-threatening post-transplantation occurrence. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadburn, A.; Hyjek, E.; Mathew, S.; Cesarman, E.; Said, J.; Knowles, D.M. KSHV-positive solid lymphomas represent an extra-cavitary variant of primary effusion lymphoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2004, 28, 1401–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Leventaki, V.; Bhaijee, F.; Jackson, C.C.; Medeiros, L.J.; Vega, F. Extracavitary/solid variant of primary effusion lymphoma. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2012, 16, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.G.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Lu, Z.B.L.; Quinto, T.; Rozenvald, I.B.; Liu, L.T.; Wilson, D.; Reddy, V.; Huang, Q.; Wang, H.Y.; et al. Extracavitary KSHV-associated large B-cell lymphoma: A distinct entity or a subtype of primary effusion lymphoma? Study of 9 cases and review of an additional 43 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costes, V.; Faumont, N.; Cesarman, E.; Rousset, T.; Meggetto, F.; Delsol, G.; Brousset, P. Human herpesvirus-8-associated lymphoma of the bowel in human immunodeficiency virus-positive patients without history of primary effusion lymphoma. Hum. Pathol. 2002, 33, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, J.T.; Ribera, J.M.; Juncà, J.; Millá, F. Anorectal lymphoma without effusion associated with human herpesvirus-8 and type 1 Epstein-Barr virus in an HIV-infected patient. Hum. Pathol. 2003, 34, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, G.; Cai, J.; Yue, C.; Qing, X. Extracavitary/solid variant of primary effusion lymphoma presenting as a gastric mass. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2015, 99, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantanowitz, L.; Wu, Z.; Dezube, B.J.; Pihan, G. Extracavitary primary effusion lymphoma of the anorectum. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma 2005, 6, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanelli, M.; Bertuzzi, C.; Zizzo, M.; Martino, G.; Sabattini, E.; Ascani, S. Extracavitary primary effusion lymphoma in a post-transplantation patient. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 187, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePond, W.; Said, J.W.; Tasaka, T.; de Vos, S.; Kahn, D.; Cesarman, E.; Knowles, D.M.; Koeffler, H.P. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus and human herpesvirus 8 (KSHV/HHV8)-associated lymphoma of the bowel. Report of two cases in HIV-positive men with secondary effusion lymphomas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1997, 21, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oster, C.; Stein, T.; Kitahara, S.; Alkan, S.; Huang, Q. Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus 8-associated extracavitary primary effusion lymphoma presenting as multiple lymphomatous polyposis. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 79, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Cesarman, E.; Pessin, M.; Lee, F.; Culpepper, J.; Knowels, D.M.; Moore, P.S. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma. Science 1994, 266, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepfish, A.; Sarid, R.; Shtalrid, M.; Shvidel, L.; Berrebi, A.; Schattner, A. Primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) in HIV-negative patients-a distinct clinical entity. Leuk. Lymphoma 2001, 41, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellet Madan, R.; Hand, J.; AST Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Human herpesvirus 6, 7, and 8 in solid organ transplantation: Guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riva, G.; Luppi, M.; Barozzi, P.; Forghieri, F.; Potenza, L. How I treat HHV8/KSHV-related diseases in post-transplant patients. Blood 2012, 120, 4150–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppi, M.; Barozzi, P.; Rasini, V.; Torelli, G. HHV-8 infection in the transplantation setting: A concern only for solid organ transplant patients? Leuk. Lymphoma 2002, 43, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulier, J.; Grollet, L.; Oksenhendler, E.; Cacoub, P.; Cazals-Hatem, D.; Babinet, P.; d’Agay, M.F.; Clauvel, J.P.; Raphael, M.; Degos, L. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman’s disease. Blood 1995, 86, 1276–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, M.Q.; Diss, T.C.; Liu, H.; Ye, H.; Hamoudi, R.A.; Cabecadas, J.; Dong, H.Y.; Lee Harris, N.; Chan, J.K.C.; Rees, J.W.; et al. KSHV- and EBV-associated germinotropic lymphoproliferative disorder. Blood 2002, 100, 3415–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanelli, M.; Zizzo, M.; Bisagni, A.; Froio, E.; De Marco, L.; Valli, R.; Filosa, A.; Luminari, S.; Martino, G.; Massaro, F.; et al. Germinotropic lymphoproliferative disorder: A systematic review. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 2243–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanelli, M.; Fraternali Orcioni, G.; Zizzo, M.; De Marco, L.; Martino, G.; Cerrone, G.; Cabras, A.D.; Ascani, S. HHV-8- and EBV-positive germinotropic lymphoproliferative disorder. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 2439–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, I.; Rossi, G.; Rullo, E.; Ascoli, V. Classic KSHV/HHV-8-positive Primary Effusion Lymphoma (PEL): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case Reports. Mediterranean H Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 14, e2022020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Coleman, T.; Zhang, J.; Fagot, A.; Kotalik, C.; Zhao, L.; Trivedi, P.; Jones, C.; Zhang, L. Epstein-Barr virus inhibits Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus lytic replication in primary effusion lymphomas. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 6068–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, S.; Goto, H.; Yotsumoto, M. Current status of treatment for primary effusion lymphoma. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2014, 3, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delsol, G.; Lamant, L.; Mariame, B.; Pulford, K.; Dastugue, N.; Brousset, P.; Rigal-Huguet, F.; al Saati, T.; Cerretti, D.P.; Morris, S.W.; et al. A new subtype of large B-cell lymphoma expressing the ALK kinase and lacking the 2;5 translocation. Blood 1997, 89, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.; Hu, S.; Li, M.; Zhou, Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Reddy, V.; Sanmann, J.N.; Smith, L.M.; Chen, M.; Gao, Z.; et al. ALK-positive large B-cell lymphoma. A clinicopathologic study of 26 cases with review of additional 108 cases in the literature. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanelli, M.; Valli, R.; Capodanno, I.; Ragazzi, M.; Ascani, S. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive large B-cell lymphoma: Description of a case with an unexpected clinical outcome. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2015, 23, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.J.; Beltran, B.E.; Malpica, L.; Marques-Piubelli, M.L.; Miranda, R.N. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive large B-cell lymphoma (ALK + LBCL): A systematic review of clinicopathological features and management. Leuk. Lymphoma 2021, 62, 2845–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascoyne, R.D.; Lamant, L.; Martin-Subero, J.I.; Lestou, V.S.; Lee Harris, N.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K.; Seymour, J.F.; Campbell, L.J.; Horsman, D.E.; Auvigne, I.; et al. ALK-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is associated with Clathrin-ALK rearrangements: Report of 6 cases. Blood 2003, 102, 2568–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onciu, M.; Behm, F.G.; Downing, J.R.; Shurtleff, S.A.; Raimondi, S.C.; Ma, Z.; Morris, S.W.; Kennedy, W.; Jones, S.C.; Sandlund, J.T. ALK-positive plasmablastic B-cell lymphoma with expression of the NPM-ALK fusion transcript: Report of 2 cases. Blood 2003, 102, 2642–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Roosbroeck, K.; Cools, J.; Dierickx, D.; Thomas, J.; Vandenberghe, P.; Stul, M.; Delabie, J.; De Wolf-Peeters, C.; Marynen, P.; Wlodarska, I. ALK-positive large B-cell lymphomas with cryptic SEC31A-ALK and NPM1-ALK fusions. Haematologica 2010, 95, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Soda, M.; Togashi, Y.; Ota, Y.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Hatano, S.; Asaka, R.; Noguchi, M.; Mano, H. Identification of a novel fusion, SQSTM1-ALK in ALK-positive large B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2011, 96, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.E.; Kang, S.Y.; Takeuchi, K.; Ko, Y.H. Identification of RANBP2-ALK fusion in ALK-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 32, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Miron, P.M.; Hutchinson, L.; Woda, B.A.; Nath, R.; Cerny, J.; Yu, H. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive large B-cell lymphoma with complex karyotype and novel ALK gene rearrangements. Hum. Pathol. 2011, 42, 1562–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, K.; Nakasone, H.; Togashi, Y.; Sakata, S.; Tsuyama, N.; Baba, S.; Dobashi, A.; Asaka, R.; Tsai, C.-C.; Chuang, S.-S.; et al. ALK-positive large B-cell lymphoma: Identification of EML4-ALK and a review of the literature focusing on the ALK immunohistochemical staining pattern. Int. J. Hematol. 2016, 103, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ise, M.; Kageyama, H.; Araki, A.; Itami, M. Identification of a novel GORASP2-ALK fusion in an ALK-positive large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, A.; Shahmarvand, N.; Nagy, A.; Kumar, J.; Van Ziffle, J.; Devine, P.; Huang, F.; Lezama, L.; Li, P.; Ohgami, R.S. TFG::ALK fusion in ALK positive large B-cell lymphoma: A case report and review of literature. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1174606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.J.; Seth, A.; Ali, N.; Chandar, A.; Bains, A. ALK-positive large B-cell lymphoma with multiple epithelial antigen expression and PABPC1::ALK fusion: A novel molecular alteration. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2023, 47, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yi, H.; Liu, Q.; Guo, T.; Li, A.; Ouyang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Dong, L.; et al. ALK-positive large B-cell lymphoma: A clinicopathological and molecular characteristics analysis of seven cases. Pathology 2024, 56, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.-N.; Yu, B.-H.; Wang, W.-G.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Li, X.Q. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive large B-cell lymphoma: Clinico-pathological study of 17 cases with review of literature. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butrynski, J.E.; D’Adamo, D.R.; Hornick, J.L.; Cin, P.D.; Antonescu, C.R.; Jhanwar, S.C.; Ladanyi, M.; Capelletti, M.; Rodig, S.J.; Ramaiya, N.; et al. Crizotinib in ALK-rearranged inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, E.L.; Bang, Y.J.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Solomon, B.; Maki, R.G.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Dezube, B.J.; Jänne, P.A.; Costa, D.B.; et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerchietti, L.; Damm-Welk, C.; Vater, I.; Klapper, W.; Harder, L.; Pott, C.; Yang, S.N.; Reiter, A.; Siebert, R.; Melnick, A.; et al. Inhibition of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) activity provides a therapeutic approach for CLTC-ALK-positive human diffuse large B cell lymphomas. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ouyang, J.; Zhou, R.; Chen, B.; Xu, Y. Promising response of anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive large B-cell lymphoma to crizotinib salvage treatment: Case report and review of literature. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 6977–6985. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wass, M.; Behlendorf, T.; Schadlich, B.; Mottok, A.; Rosenwald, A.; Schmoll, H.J.; Jordan, K. Crizotinib in refractory alk-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A case report with a short-term response. Eur. J. Hematol. 2014, 92, 268–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takiar, R.; Phillips, T.J. Durable responses with ALK inhibitors for primary refractory anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 2912–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirk, B.; Malysz, J.; Choi, E.; Songdej, N. Lorlatinib induces rapid and durable response in refractory anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive large B-cell lymphoma. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2023, 7, e2200536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera, A.; Colomo, L.; Martinez, A.; de Jong, D.; Balaguè, O.; Matheu, G.; Martinez, M.; Taddesse-Heath, L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Bacchi, C.E.; et al. ALK-positive large B-cell lymphomas express a terminal B-cell differentiation program and activated STAT3 but lack MYC rearrangements. Mod. Pathol. 2013, 26, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amore, E.S.; Visco, C.; Menin, A.; Famengo, B.; Bonvini, P.; Lazzari, E. STAT3 pathway is activated in ALK-positive large B-cell lymphoma carrying SQSTM1-ALK rearrangement and provides a possible therapeutic target. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; Swerdlow, S.H., Campo, E., Harris, N.L., Jaffe, E.S., Pileri, S.A., Stein, H., Thiele, J., Eds.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Du, M.-Q.; Liu, H.; Diss, T.C.; Ye, H.; Hamoudi, R.A.; Dupin, N.; Meignin, V.; Oksenhendler, E.; Boshoff, C.; Isaacson, P.G. Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infects monotypic (IgM lambda) but polyclonal naïve B-cells in Castleman disease and associated lymphoproliferative disorders. Blood 2001, 97, 2130–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Farre, B.; Martinez, D.; Lopez-Guerra, M.; Xipell, M.; Monclus, E.; Rovira, J.; Garcia, F.; Lopez-Guillermo, A.; Colomo, L.; Campo, E.; et al. HHV8-related lymphoid proliferations: A broad spectrum of lesions from reactive lymphoid hyperplasia to overt lymphoma. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupin, N.; Diss, T.L.; Kellam, P.; Tulliez, M.; Du, M.Q.; Sicard, D.; Weiss, R.A.; Isaacson, P.G.; Boshoff, C. HHV-8 is associated with a plasmablastic variant of Castleman disease that is linked to HHV-8-positive plasmablastic lymphoma. Blood 2000, 95, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadburn, A.; Said, J.; Gratzinger, D.; Chan, J.K.C.; de Jong, D.; Jaffe, E.S.; Natkunam, Y.; Goodland, J.R. HHV8/KSHV-positive lymphoproliferative disorders and the spectrum of plasmablastic and plasma cell neoplasms: 2015 SH/EAHP Worshop Report part 3. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 147, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksenhendler, E.; Boulanger, E.; Galicier, L.; Du, M.Q.; Dupin, N.; Diss, T.C.; Hamoudi, R.; Daniel, M.T.; Agbalika, F.; Boshoff, C.; et al. High incidence of Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma in patients with HIV infection and multicentric Castleman disease. Blood 2002, 99, 2331–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukswai, N.; Lyapichev, K.; Khoury, J.D.; Medeiros, L.J. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma variants: An update. Pathology 2020, 52, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, F.; Miranda, R.N.; Medeiros, L.J. KSHV/HHV8-positive large B-cell lymphomas and associated diseases: A heterogeneous group of lymphoproliferative processes with significant clinicopathological overlap. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.C.; Sparano, J.A.; Chadburn, A.; Reid, E.G.; Ambinder, R.F.; Siegel, E.R.; Moore, P.C.; Rubinstein, P.G.; Durand, C.M.; Cesarman, E.; et al. Impact of Myc in HIV-associated non-Hodgkin lymphomas treated with EPOCH and outcomes with vorinostat (AMC-075 trial). Blood 2020, 136, 1284–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qunaj, L.; Castillo, J.J.; Olszewski, A.J. Survival of patients with CD20-negative variants of large B-cell lymphoma: An analysis of the National Cancer Data Base. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018, 59, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bower, M.; Carbone, A. KSHV/HHV8-associated lymphoproliferative disorders: Lessons learnt from people living with HIV. Hemato 2021, 2, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noy, A. Optimizing treatment of HIV-associated lymphoma. Blood 2019, 134, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casper, C. New approaches to the treatment of human herpesvirus 8-associated disease. Rev. Med. Virol. 2008, 18, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhen, D. Demographic characteristics and prognosis of HHV8-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified. Medicine 2023, 102, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
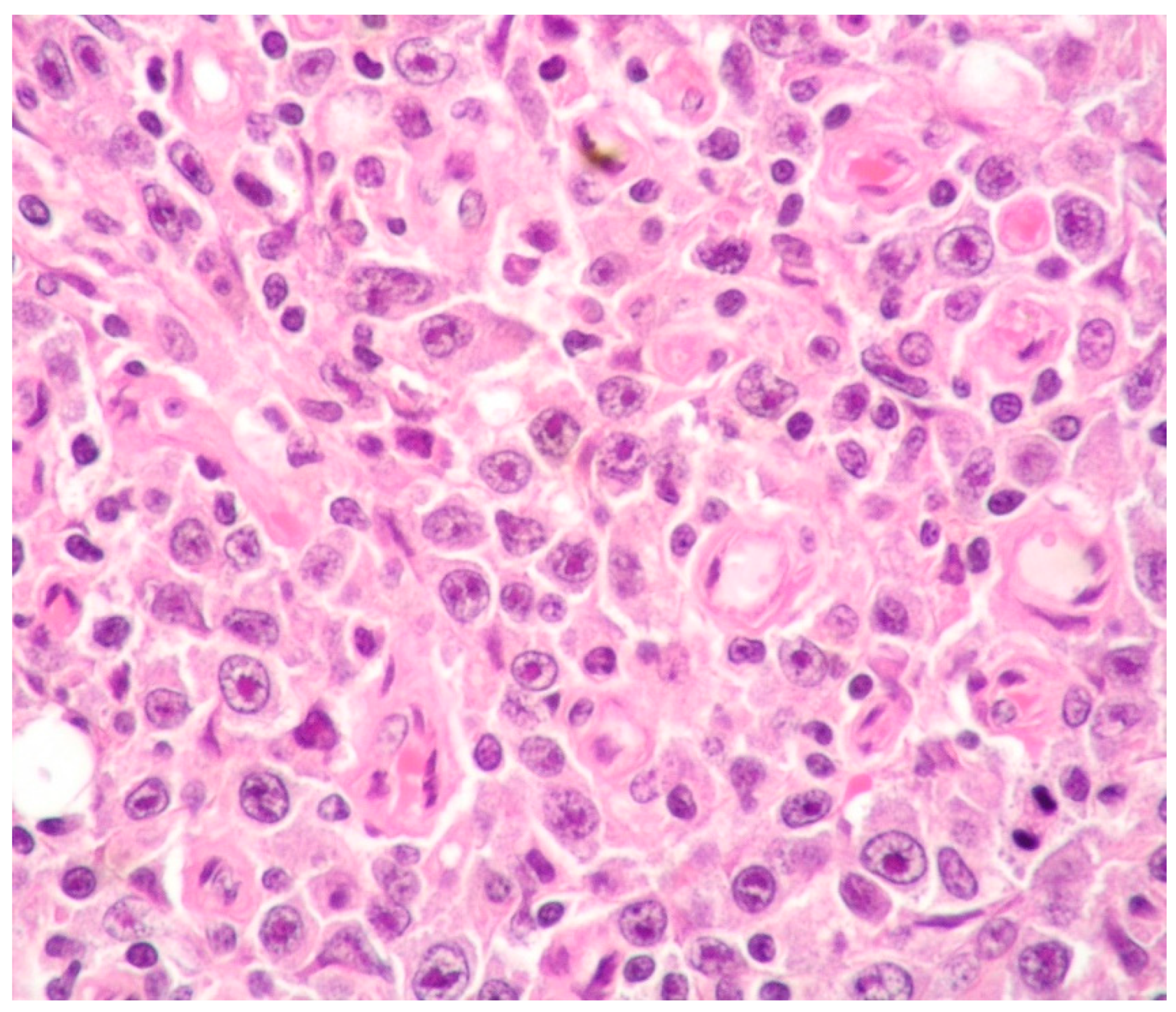
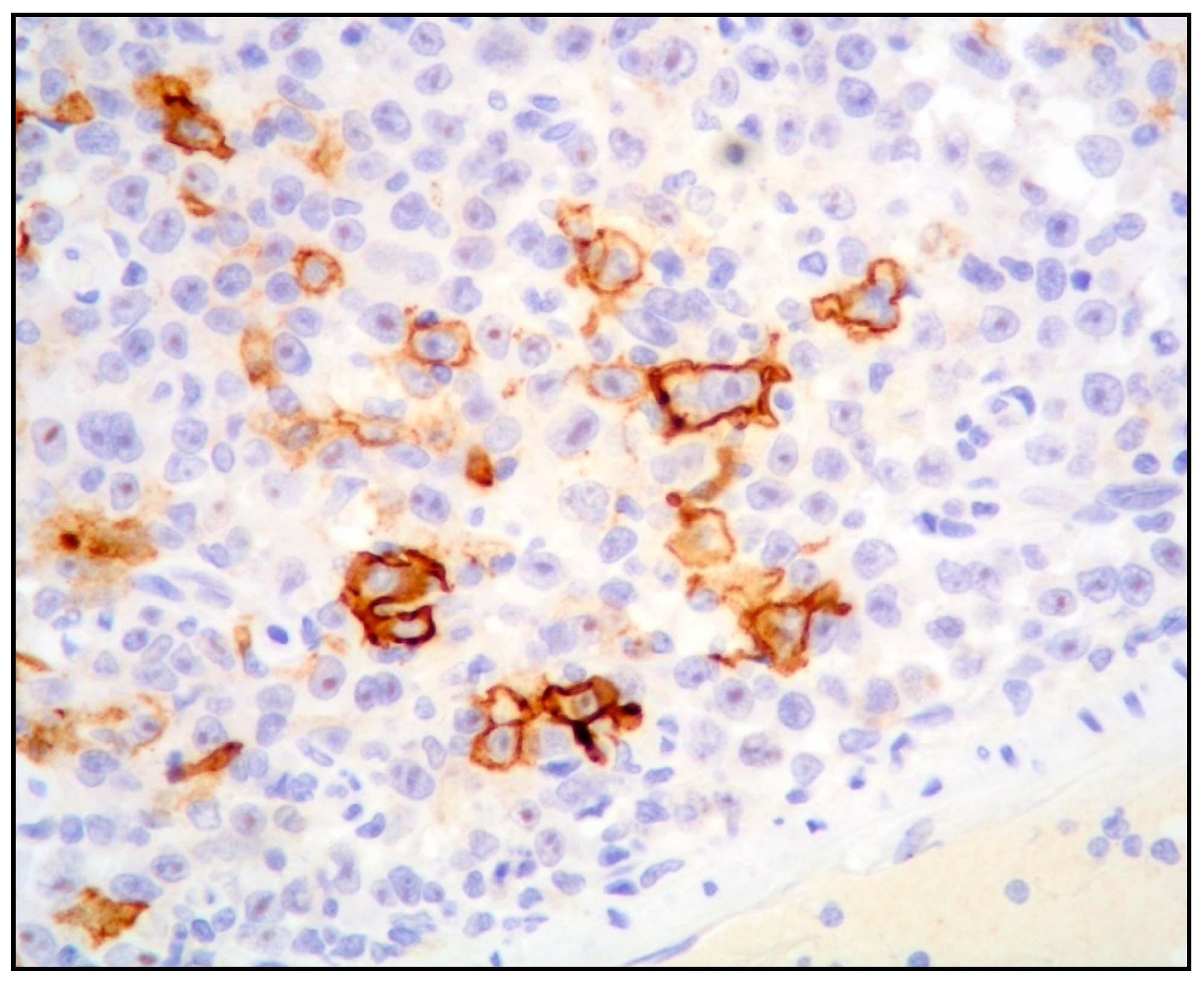
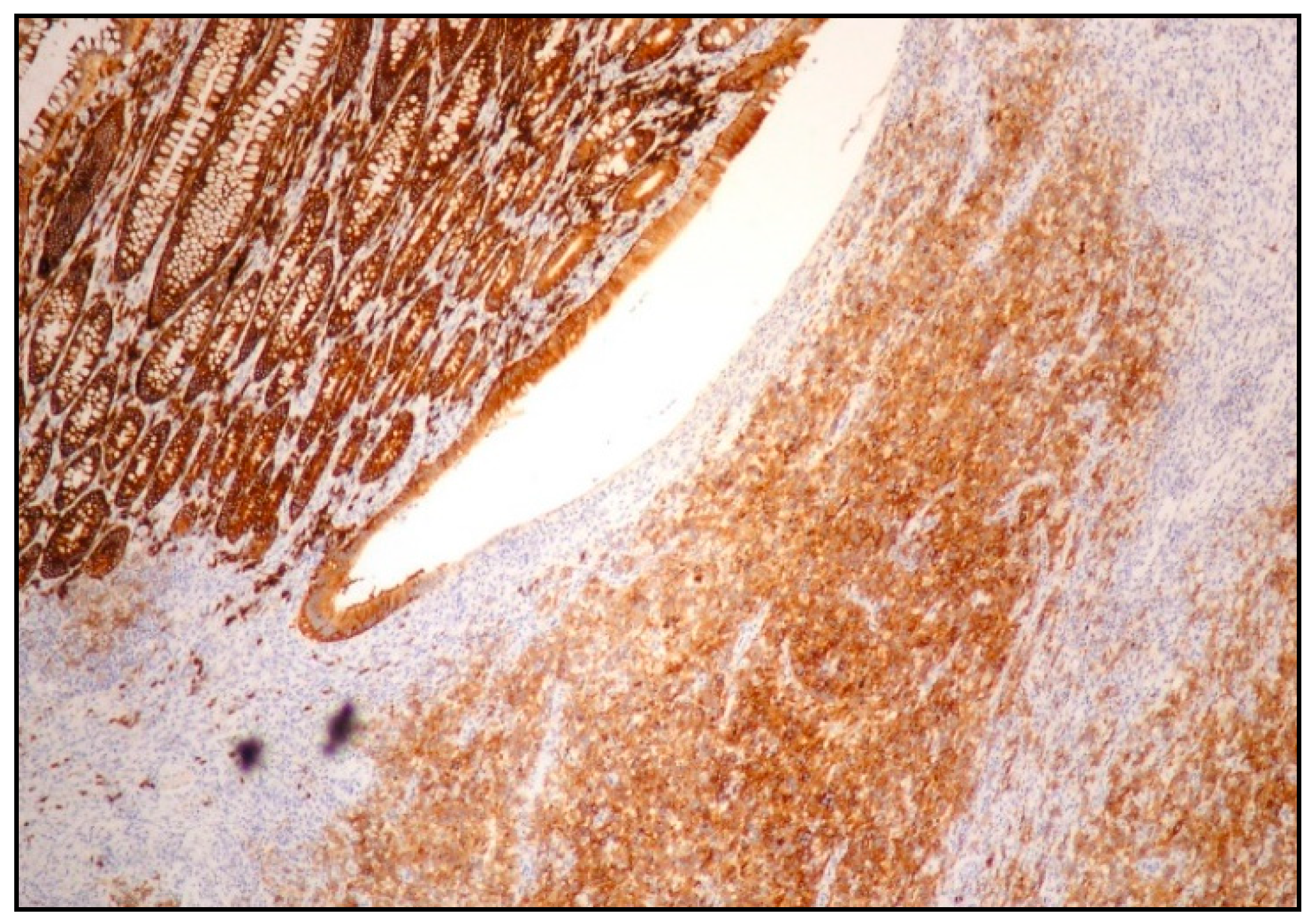
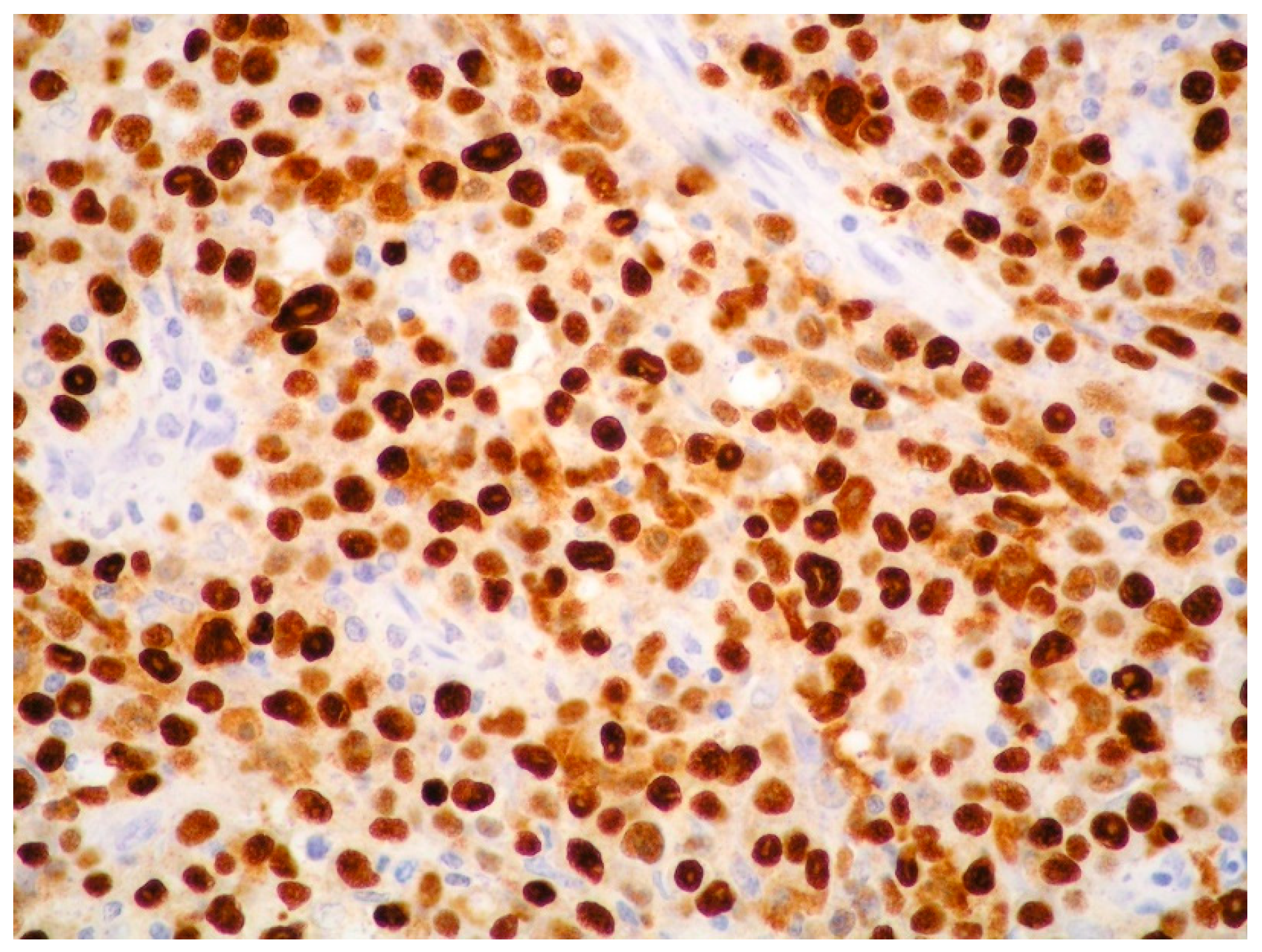

| PEL | PBL | ALK+ LBCL | HHV8+ DLBCL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV | + (− in elderly) | + (often) | - | Generally + |
| Immunodeficiency | Usually present (HIV-associated, post-transplant, immunosenescence) | Usually present (HIV-related, post- transplant or iatrogenic) | - | Usually present |
| Age/Sex/ Outcome | Adults, often males (HIV+ patients are younger) poor | Often adults, frequently males (HIV+ patients are younger) poor | Adults, often males poor | Adults poor |
| Clinical manifestations | Classic PEL: body cavities effusion EC-PEL: lymph nodes and extranodal sites | More often extranodal disease; rarely lymph nodes | More often nodal disease (in 1/3 of cases, nodal and extranodal disease) | Multiple lymph nodes, extranodal sites, spleen, BM |
| Association with HHV8+ MCD | rare | - | - | frequent |
| Histology | Large cells with IB and PB features | Diffuse proliferation of PBs/IBs | Sinusoidal and/or diffuse growth pattern of IBs and PBs | Sheets of PBs/IBs effacing organ architecture |
| CD20 | - (may be + in EC-PEL) | - or weakly + in a small number of cells | - (or weakly +) | +/− |
| PAX5 | - (may be + in EC-PEL) | - or weakly + in a small number of cells | - (or weakly +) | - |
| CD79alpha | - (may be + in EC-PEL) | + in 40% of cases | - (or weakly +) | - |
| MUM1/IRF4 | + | + | + | + |
| CD38 | + | + | + | −/+ |
| CD138 | + | + | + | - |
| CD30 | + | + | - | - (rarely +) |
| EMA | Often + | + | + | - |
| ALK | - | - | + | - |
| T-cell markers | Occasionally + (mainly in EC-PEL) | Occasionally + | + in half of cases (CD4) | - |
| Light chain restriction | Usually absent | + (often IgG kappa or lambda) | + (in 85% of cases) | + cIgM lambda |
| HHV8 | + | - | - | + |
| EBV (by EBER) | + (EBER− in HIV-negative elderly individuals and in post transplantation cases) | + in 60–75% of cases (more often in HIV+ and post-transplant cases) | - | - |
| Clonality | Monoclonal (IG genes hypermutated). | Monoclonal | Monoclonal | Monoclonal (IgG genes unmutated) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zanelli, M.; Zizzo, M.; Sanguedolce, F.; Ricci, S.; Palicelli, A.; Bisagni, A.; Fragliasso, V.; Broggi, G.; Salzano, S.; Boutas, I.; et al. CD20-Negative Large B-Cell Lymphomas: The Diagnostic Challenge of Tumors with Downregulation of Mature B-Cell Marker Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167843
Zanelli M, Zizzo M, Sanguedolce F, Ricci S, Palicelli A, Bisagni A, Fragliasso V, Broggi G, Salzano S, Boutas I, et al. CD20-Negative Large B-Cell Lymphomas: The Diagnostic Challenge of Tumors with Downregulation of Mature B-Cell Marker Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167843
Chicago/Turabian StyleZanelli, Magda, Maurizio Zizzo, Francesca Sanguedolce, Stefano Ricci, Andrea Palicelli, Alessandra Bisagni, Valentina Fragliasso, Giuseppe Broggi, Serena Salzano, Ioannis Boutas, and et al. 2025. "CD20-Negative Large B-Cell Lymphomas: The Diagnostic Challenge of Tumors with Downregulation of Mature B-Cell Marker Expression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167843
APA StyleZanelli, M., Zizzo, M., Sanguedolce, F., Ricci, S., Palicelli, A., Bisagni, A., Fragliasso, V., Broggi, G., Salzano, S., Boutas, I., Koufopoulos, N., Tamagnini, I., Camposeo, C., Morini, A., Caltabiano, R., Cimino, L., Fabozzi, M., Parente, P., Mangone, L., ... Ascani, S. (2025). CD20-Negative Large B-Cell Lymphomas: The Diagnostic Challenge of Tumors with Downregulation of Mature B-Cell Marker Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167843













