Bi-Allelic Loss-of-Function Variant in MAN1B1 Cause Rafiq Syndrome and Developmental Delay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Evaluation of Affected Individuals
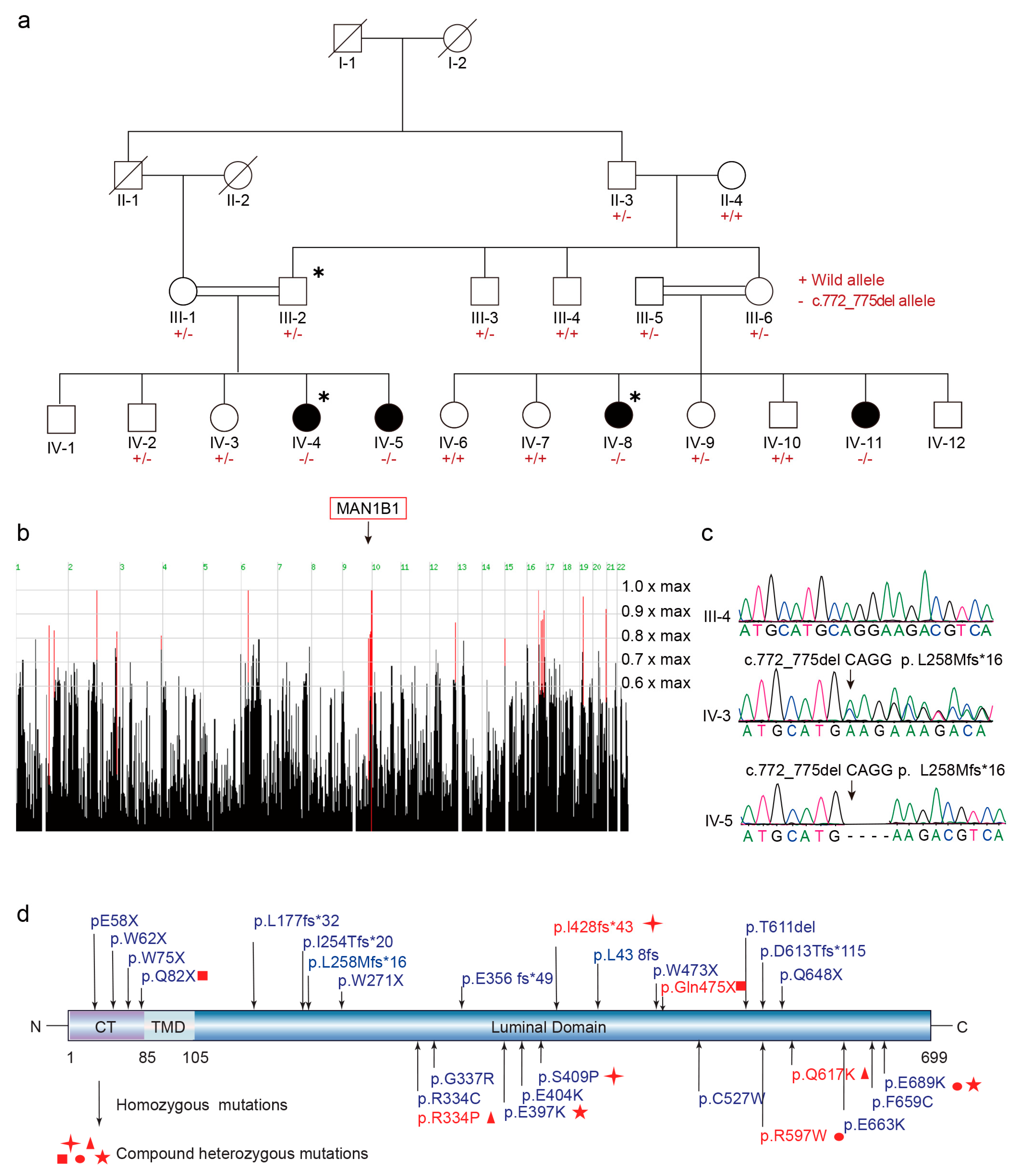
2.2. MAN1B1 Is the Candidate Causal Gene in the Family
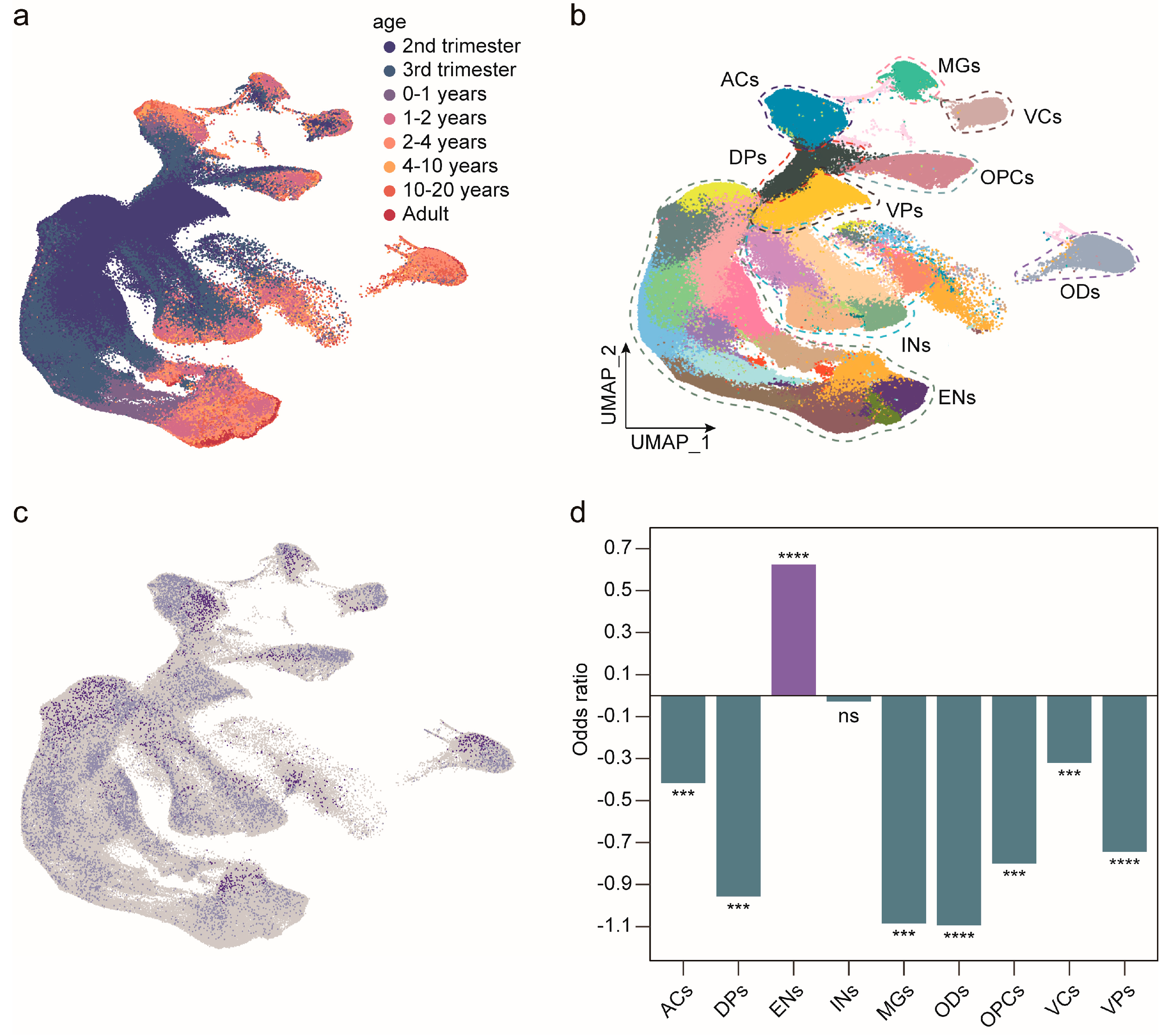
2.3. Expression of MAN1B1 Is Positively Correlated with the Development of Excitatory Neurons in the Human Brain
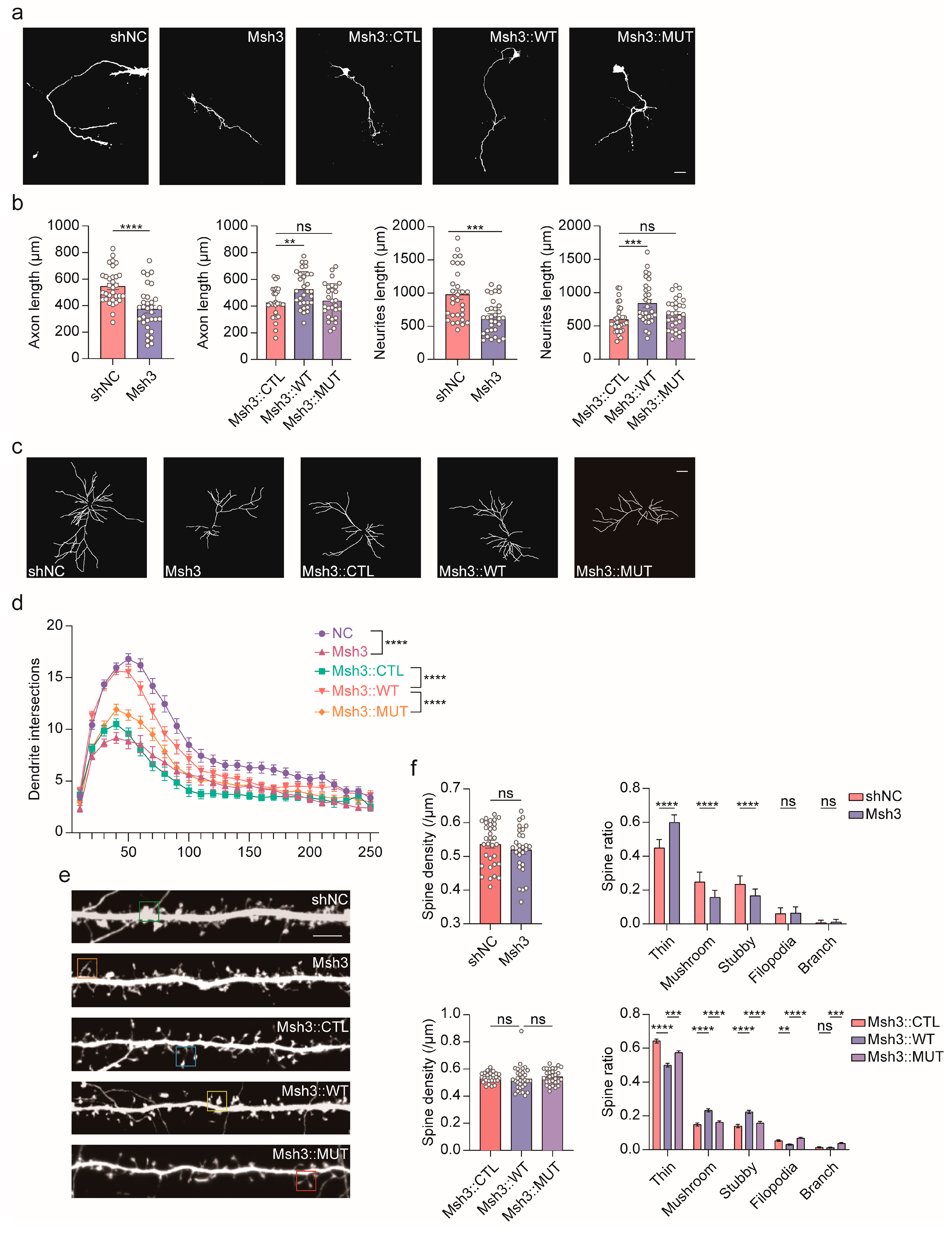
2.4. Man1b1 Deficiency Impairs Axonal Outgrowth and Synapse Development in the Mouse Brain
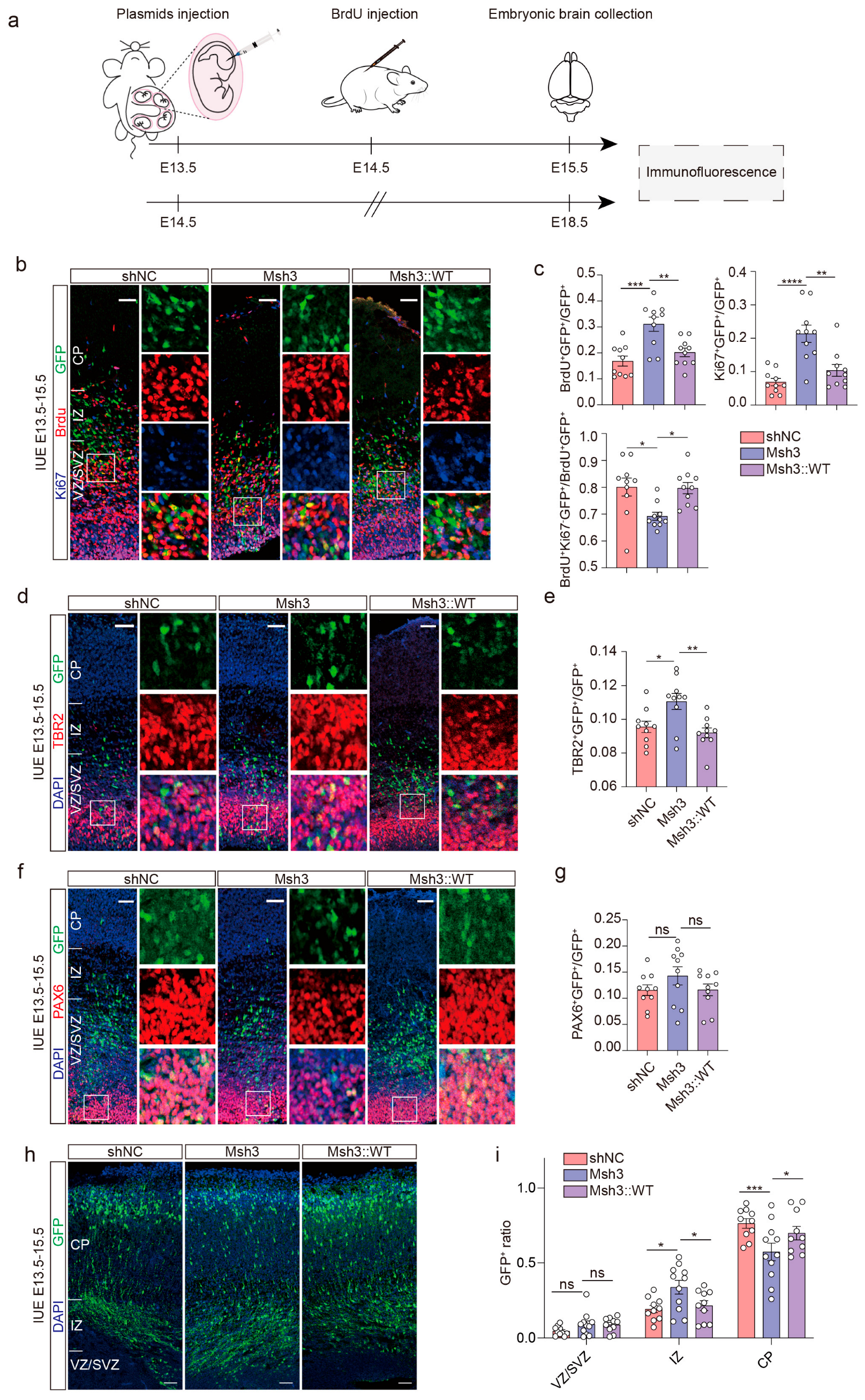
2.5. Man1b1 Deficiency Promotes Mouse Neural Stem Cells’ Proliferation and Inhibits Migration
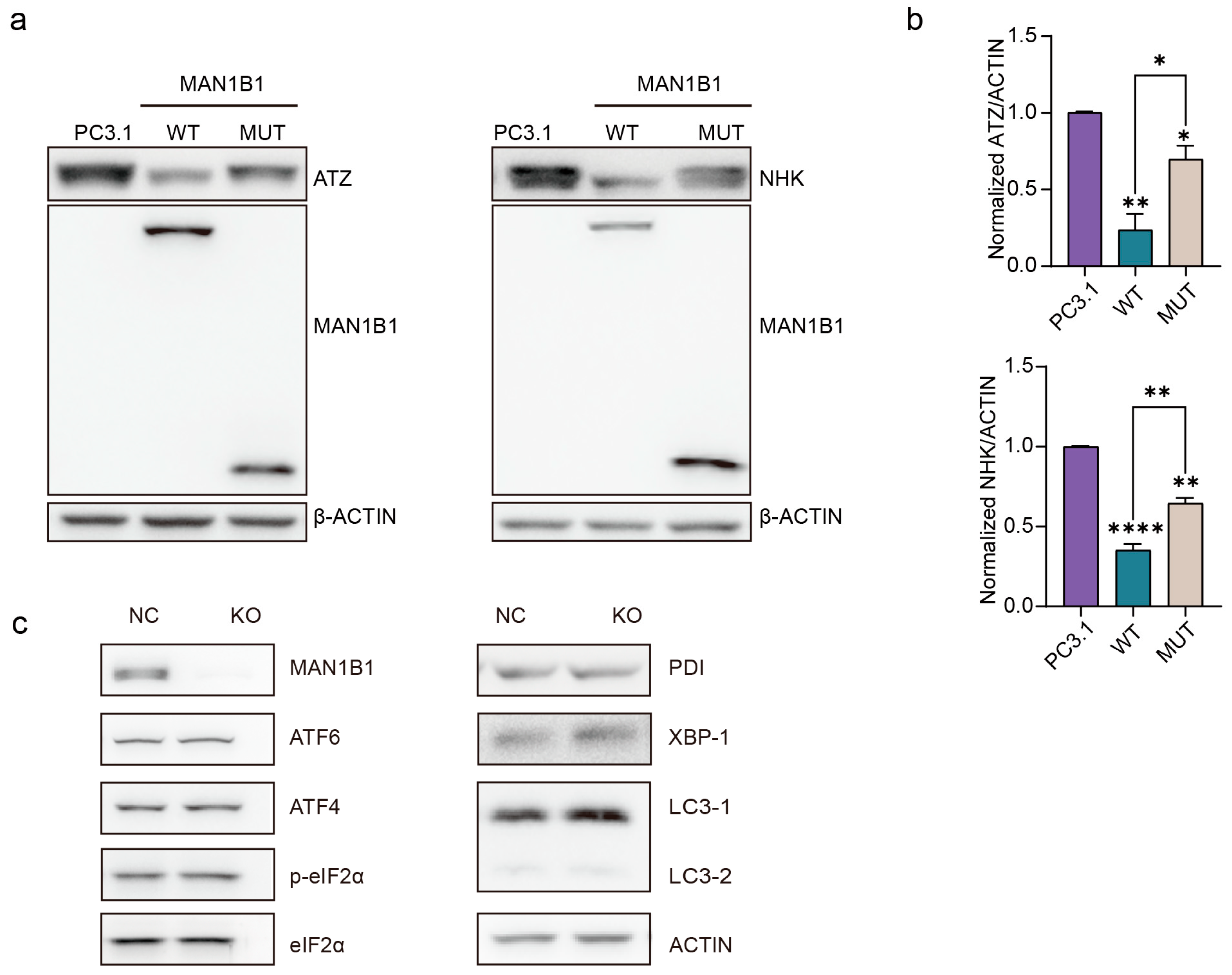
2.6. The MAN1B1 Mutation Causes Slower Degradation of Misfolded Proteins and Does Not Impact Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stress
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Exome Sequencing, Bioinformatics Analysis, and Co-Segregation Validation
4.2. Expression Pattern of MAN1B1 in the Developing Human Brain
4.3. Plasmid Construction
4.4. Reverse Transcription and Real-Time PCR
4.5. Mouse Primary Neuron Culture and Transfection
4.6. Immunofluorescence
4.7. In Utero Electroporation
4.8. Transient Transfection and Western Blotting
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDG-II | II congenital disorder of glycosylation |
| RAFQS | Rafiq syndrome |
| CDG | Congenital disorders of glycosylation |
| ERManI | endoplasmic reticulum mannosyl-oligosaccharide 1,2-α-mannosidase |
| ERAD | endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation |
| E14.5 | The embryonic 14.5 |
| ID | intellectual disability |
| WES | whole-exome sequencing |
| gnomAD | Genome Aggregation Database |
| ExAC | Exome Aggregation Consortium |
| ACMG | American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics |
| DIV2 | day 2 |
| AAT | alpha1antitrypsin |
| NHK | Null Hong Kong |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
References
- Ondruskova, N.; Cechova, A.; Hansikova, H.; Honzik, T.; Jaeken, J. Congenital disorders of glycosylation: Still “hot” in 2020. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2021, 1865, 129751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, R.; Brasil, S.; Poejo, J.; Jaeken, J.; Pascoal, C.; Videira, P.A.; Dos Reis Ferreira, V. Congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG): State of the art in 2022. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2023, 18, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoal, C.; Francisco, R.; Mexia, P.; Pereira, B.L.; Granjo, P.; Coelho, H.; Barbosa, M.; Dos Reis Ferreira, V.; Videira, P.A. Revisiting the immunopathology of congenital disorders of glycosylation: An updated review. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1350101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, A.G.; Woods, C.W.; Snow, T.M. Congenital disorders of glycosylation. Adv. Neonatal Care 2012, 12, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakson, R.; Beedgen, L.; Bernhard, P.; Alp, K.M.; Lübbehusen, N.; Röth, R.; Niesler, B.; Luzarowski, M.; Shevchuk, O.; Mayer, M.P.; et al. Targeted Proteomics Reveals Quantitative Differences in Low-Abundance Glycosyltransferases of Patients with Congenital Disorders of Glycosylation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özgün, N.; Saka Güvenç, M. Rafiq Syndrome: Old Variant in MAN1B1 Gene and Some New Phenotypic Features. Iran. J. Child Neurol. 2025, 19, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskafi, R.; AbuRahmeh, B.; Aljuneidi, R.; AlShweiki, H.; Abdelnabi, S.; Abukhalaf, A.; Maraqa, B. A Case of Rafiq Syndrome (MAN1B1-CDG) in a Palestinian Child, With Brief Literature Review of 44 Cases. J. Investig. Med. High Impact Case Rep. 2025, 13, 23247096251313731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, N.; Ohto, T.; Enokizono, T.; Wada, Y.; Kohmoto, T.; Imoto, I.; Haga, Y.; Seino, J.; Suzuki, T. Siblings with MAN1B1-CDG Showing Novel Biochemical Profiles. Cells 2021, 10, 3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhalsanova, I.Z.; Ravzhaeva, E.G.; Postrigan, A.E.; Seitova, G.N.; Zhigalina, D.I.; Udalova, V.Y.; Danina, M.M.; Kanivets, I.V.; Skryabin, N.A. Case Report: Compound Heterozygous Variants of the MAN1B1 Gene in a Russian Patient with Rafiq Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligezka, A.N.; Mohamed, A.; Pascoal, C.; Ferreira, V.D.R.; Boyer, S.; Lam, C.; Edmondson, A.; Krzysciak, W.; Golebiowski, R.; Perez-Ortiz, J.; et al. Patient-reported outcomes and quality of life in PMM2-CDG. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2022, 136, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Okamoto, N. Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry of Transferrin: Use of Quadrupole Mass Analyzers for Congenital Disorders of Glycosylation. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 11, A0103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannotti, M.J.; Figard, L.; Sokac, A.M.; Sifers, R.N. A Golgi-localized Mannosidase (MAN1B1) Plays a Non-enzymatic Gatekeeper Role in Protein Biosynthetic Quality Control. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 11844–11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Wang, S.; Utama, B.; Huang, L.; Blok, N.; Estes, M.K.; Moremen, K.W.; Sifers, R.N. Golgi localization of ERManI defines spatial separation of the mammalian glycoprotein quality control system. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 2810–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Makashova, O.; Chevillard, P.M.; Josey, V.; Li, B.; Prager-Khoutorsky, M. Constitutive cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the organum vasculosum lamina terminalis and subfornical organ of adult rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2024, 36, e13377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, L.; Yuan, F.; Fan, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Feng, W.; Zhang, H.G.; Chen, S.Y. Ethanol exposure disrupted the formation of radial glial processes and impaired the generation and migration of outer radial glial cells in forebrain organoids derived from human embryonic stem cells. Exp. Neurol. 2023, 362, 114325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hevner, R.F. Intermediate progenitors and Tbr2 in cortical development. J. Anat. 2019, 235, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Cheng, X.; Sifers, R.N. Golgi-situated endoplasmic reticulum α-1, 2-mannosidase contributes to the retrieval of ERAD substrates through a direct interaction with γ-COP. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Swulius, M.T.; Moremen, K.W.; Sifers, R.N. Elucidation of the molecular logic by which misfolded alpha 1-antitrypsin is preferentially selected for degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8229–8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, M.A.; Kuss, A.W.; Puettmann, L.; Noor, A.; Ramiah, A.; Ali, G.; Hu, H.; Kerio, N.A.; Xiang, Y.; Garshasbi, M.; et al. Mutations in the alpha 1,2-mannosidase gene, MAN1B1, cause autosomal-recessive intellectual disability. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 89, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rymen, D.; Peanne, R.; Millon, M.B.; Race, V.; Sturiale, L.; Garozzo, D.; Mills, P.; Clayton, P.; Asteggiano, C.G.; Quelhas, D.; et al. MAN1B1 deficiency: An unexpected CDG-II. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.H.; Collette, J.R.; Sifers, R.N. The cytoplasmic tail of human mannosidase Man1b1 contributes to catalysis-independent quality control of misfolded alpha1-antitrypsin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 24825–24836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelow, D.; Schuelke, M.; Hildebrandt, F.; Nurnberg, P. HomozygosityMapper--an interactive approach to homozygosity mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W593–W599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speir, M.L.; Bhaduri, A.; Markov, N.S.; Moreno, P.; Nowakowski, T.J.; Papatheodorou, I.; Pollen, A.A.; Raney, B.J.; Seninge, L.; Kent, W.J.; et al. UCSC Cell Browser: Visualize your single-cell data. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 4578–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becht, E.; McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Dutertre, C.A.; Kwok, I.W.H.; Ng, L.G.; Ginhoux, F.; Newell, E.W. Dimensionality reduction for visualizing single-cell data using UMAP. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 37, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapnell, C.; Cacchiarelli, D.; Grimsby, J.; Pokharel, P.; Li, S.; Morse, M.; Lennon, N.J.; Livak, K.J.; Mikkelsen, T.S.; Rinn, J.L. The dynamics and regulators of cell fate decisions are revealed by pseudotemporal ordering of single cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Mao, Q.; Tang, Y.; Wang, L.; Chawla, R.; Pliner, H.A.; Trapnell, C. Reversed graph embedding resolves complex single-cell trajectories. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 979–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin, G.M.; Lee, S.H.; Singh, D.; Yuan, Y.; Ng, Y.G.; Reichardt, L.F.; Arikkath, J. Culturing pyramidal neurons from the early postnatal mouse hippocampus and cortex. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1741–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient ID | IV-4 | IV-5 | IV-8 | IV-11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | female | female | female | female |
| Age at last evaluation | 16 years | 6 years | 10 years | 4 years |
| Head circumference (cm) | 53.34 | 50.8 | 53.34 | 48.26 |
| Height (cm) | 152.4 | 96 | 121.92 | 80 |
| Weight (kg) | 35 | 24 | 25 | 15 |
| BMI | 15.1 | 26 | 16.8 | 23.4 |
| Delayed walking (age) | +(2 years) | +(2 years) | +(2 years) | +(2 years) |
| Delayed speech (age) | +(3 years) | +(3 years) | +(3 years) | +(3 years) |
| Intellectual disability | Mild | Mild | Moderate | Moderate |
| Eye symptom | Strabismus | − | Strabismus | Strabismus |
| Dysarthria | + | + | + | + |
| Scoliosis | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Lower limb weakness, feet equinovarus, or hammertoes | − | N/A | − | − |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zang, L.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, S.; Hu, Z.; Xia, K.; Ahmed, A.; Tian, Q. Bi-Allelic Loss-of-Function Variant in MAN1B1 Cause Rafiq Syndrome and Developmental Delay. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167820
Zang L, Han Y, Zhang Q, Luo S, Hu Z, Xia K, Ahmed A, Tian Q. Bi-Allelic Loss-of-Function Variant in MAN1B1 Cause Rafiq Syndrome and Developmental Delay. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167820
Chicago/Turabian StyleZang, Liyu, Yaoling Han, Qiumeng Zhang, Si Luo, Zhengmao Hu, Kun Xia, Ashfaque Ahmed, and Qi Tian. 2025. "Bi-Allelic Loss-of-Function Variant in MAN1B1 Cause Rafiq Syndrome and Developmental Delay" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167820
APA StyleZang, L., Han, Y., Zhang, Q., Luo, S., Hu, Z., Xia, K., Ahmed, A., & Tian, Q. (2025). Bi-Allelic Loss-of-Function Variant in MAN1B1 Cause Rafiq Syndrome and Developmental Delay. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167820





