Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Compounds Isolated from Digitalis purpurea L. in TNF-α/IFN-γ-Induced HaCaT Keratinocytes and a Three-Dimensionally Reconstructed Human Skin Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
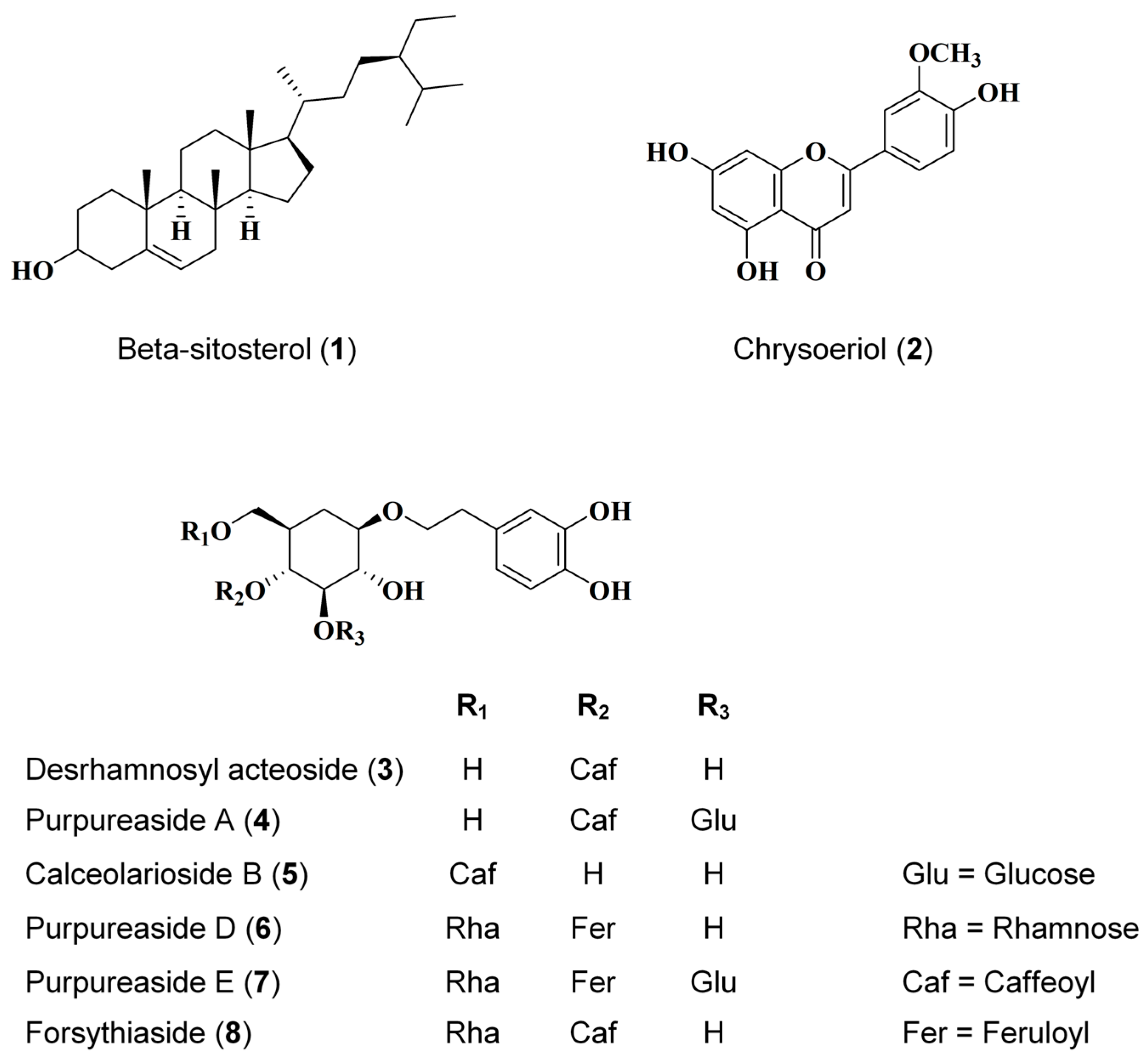
2.1. Identification of Eight Compounds Isolated from D. purpurea L.
2.2. Cytotoxicity of Eight Compounds Isolated from D. purpurea L. in HaCaTs
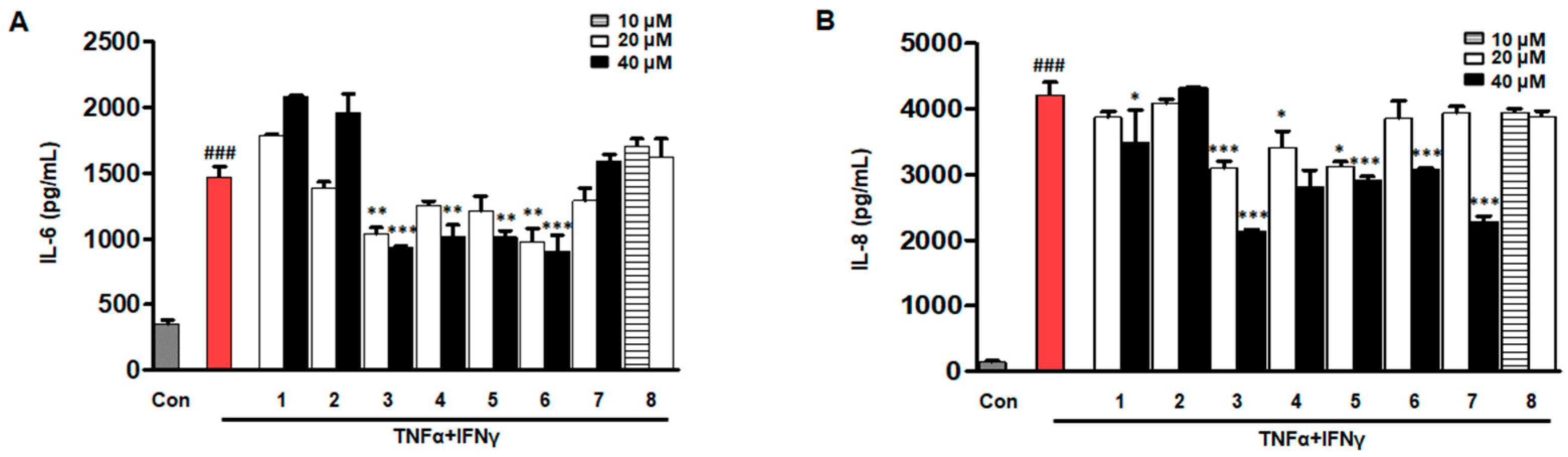
2.3. Effects of Eight Compounds Isolated from D. purpurea L. on IL-6/IL-8 in TNF-α/IFN-γ HaCaTs
2.4. Effects of Compounds 3–6 on RANTES and MDC in TNF-α/IFN-γ-Induced HaCaTs
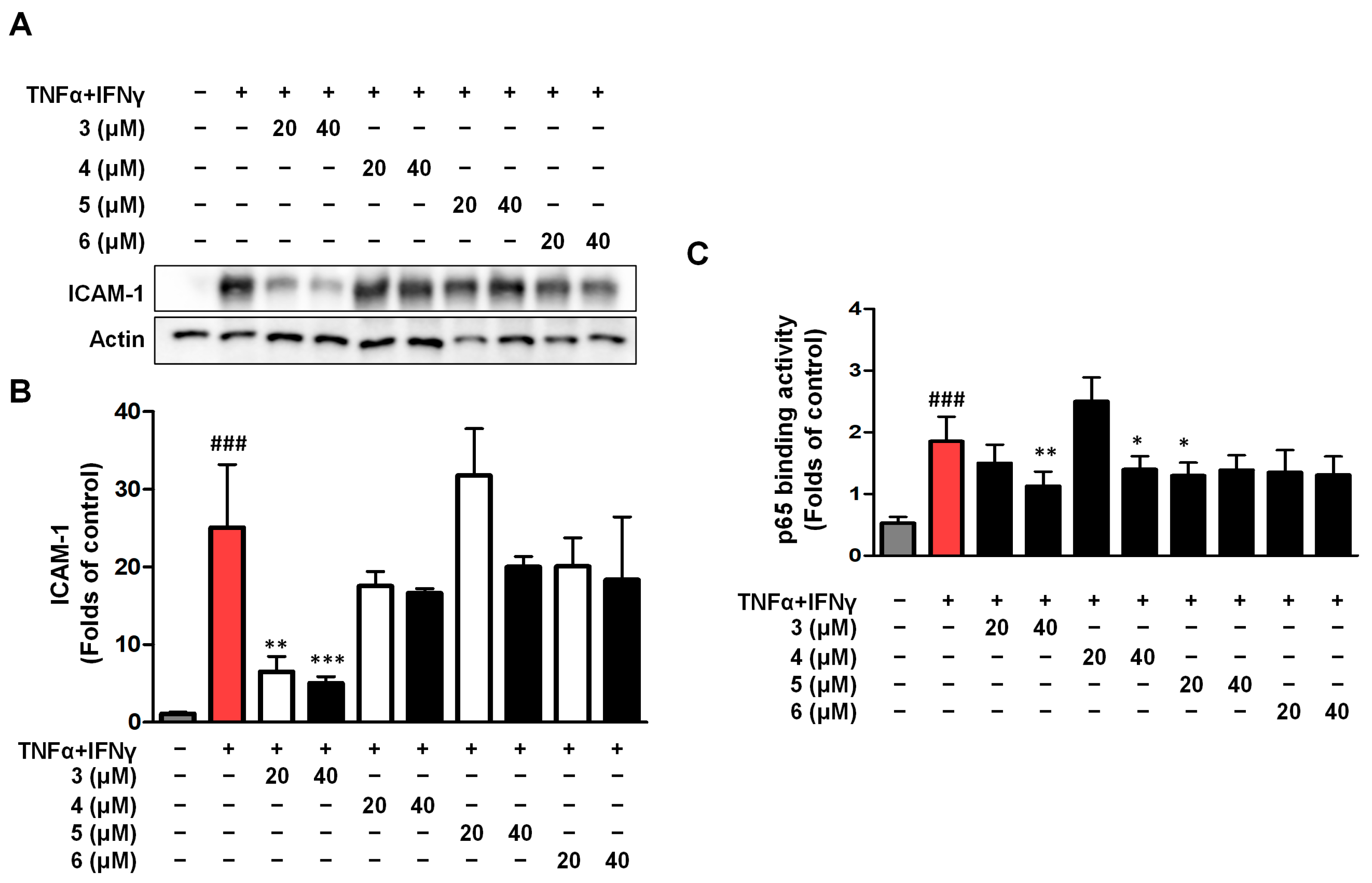
2.5. Effects of Compounds 3–6 on ICAM-1 Expression and NF-κB (p65) Binding Activity in TNF-α/IFN-γ HaCaTs
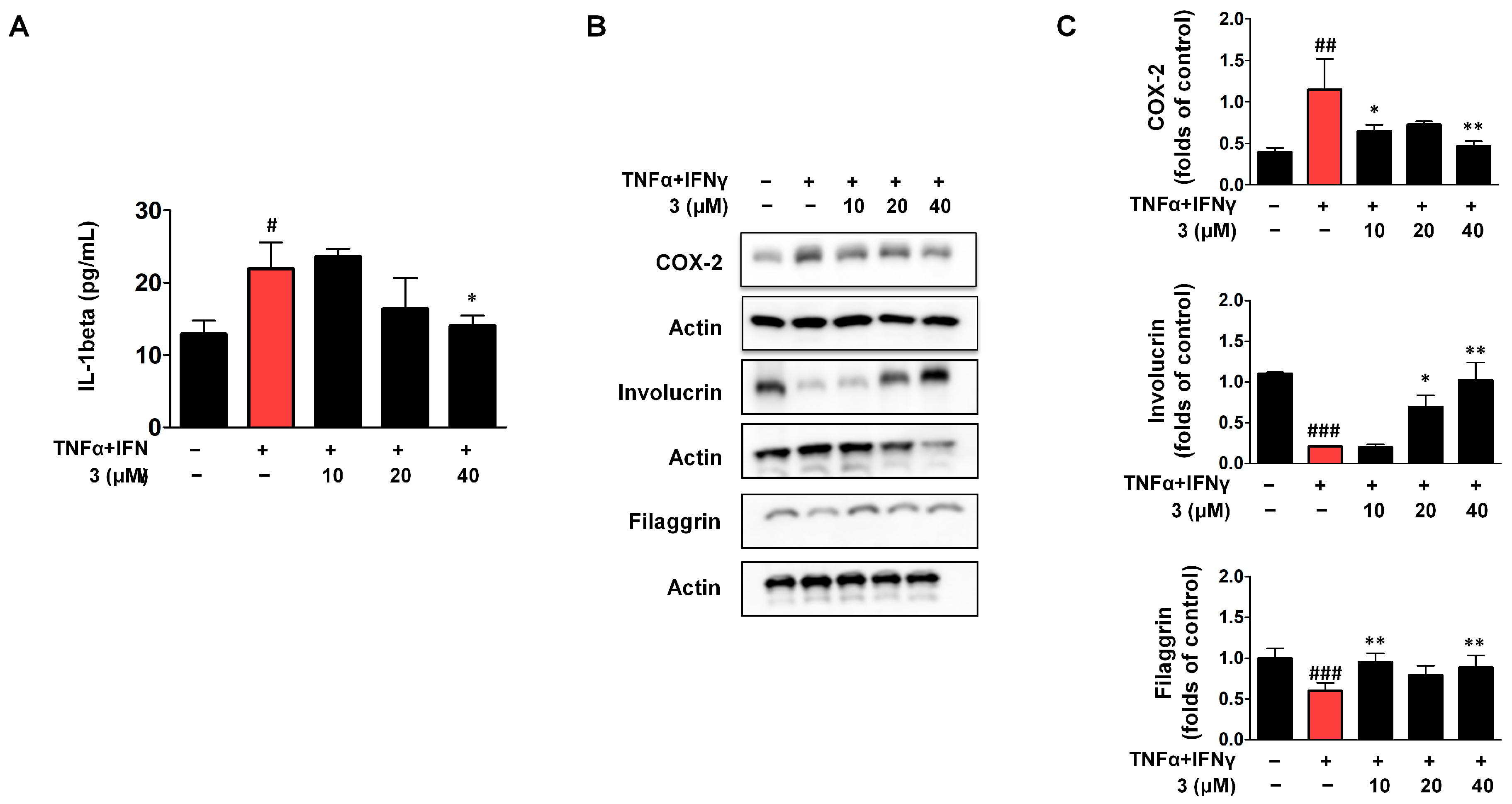
2.6. Effects of Compounds 3 on IL-1β Secretion and the Expression of COX-2/Involucrin/Filaggrin in TNF-α/IFN-γ HaCaTs
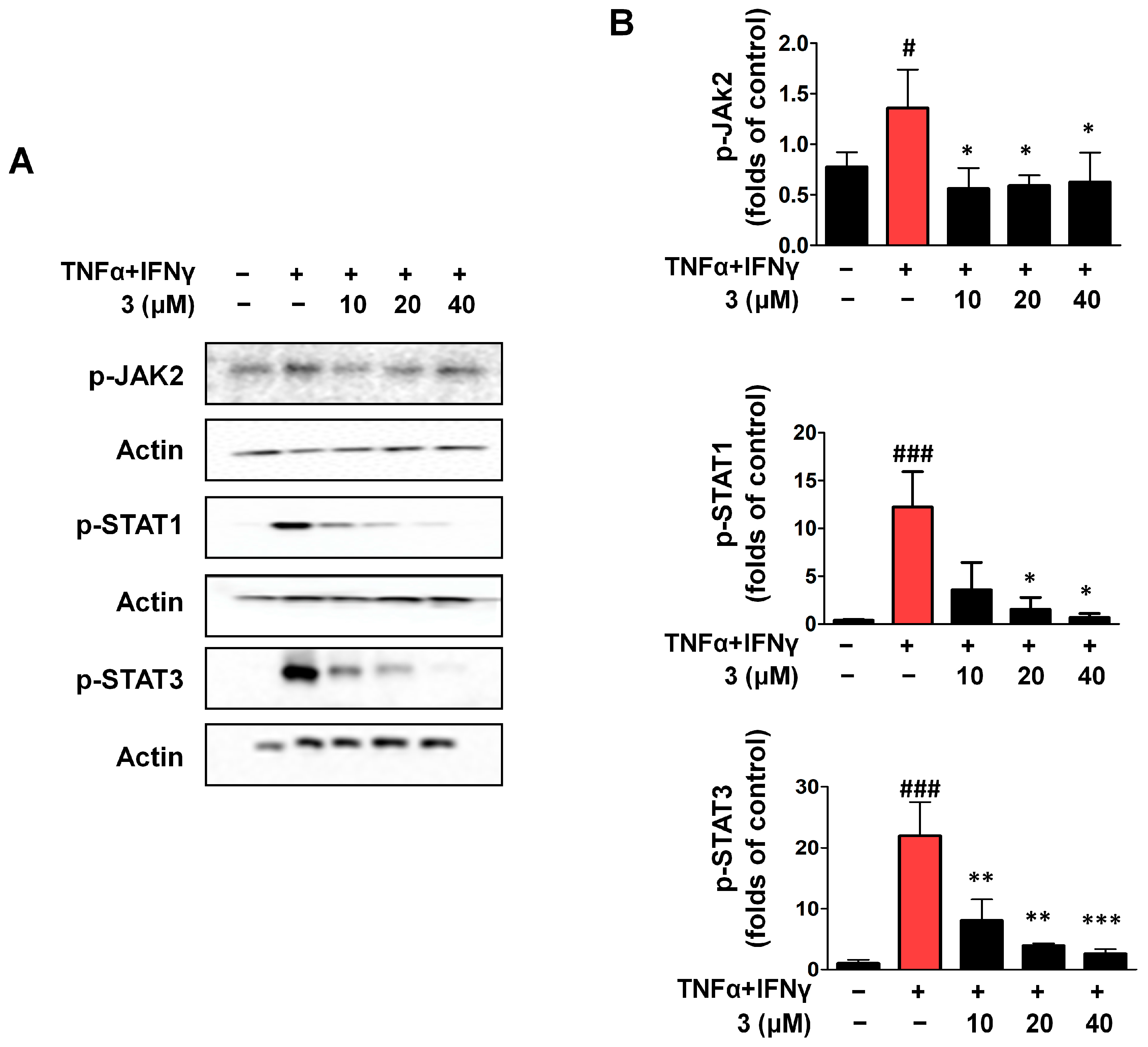
2.7. Compound 3 Inhibited Activation of the JAK2/STAT (1/3) Signaling Pathway in TNF-α/IFN-γ HaCaTs
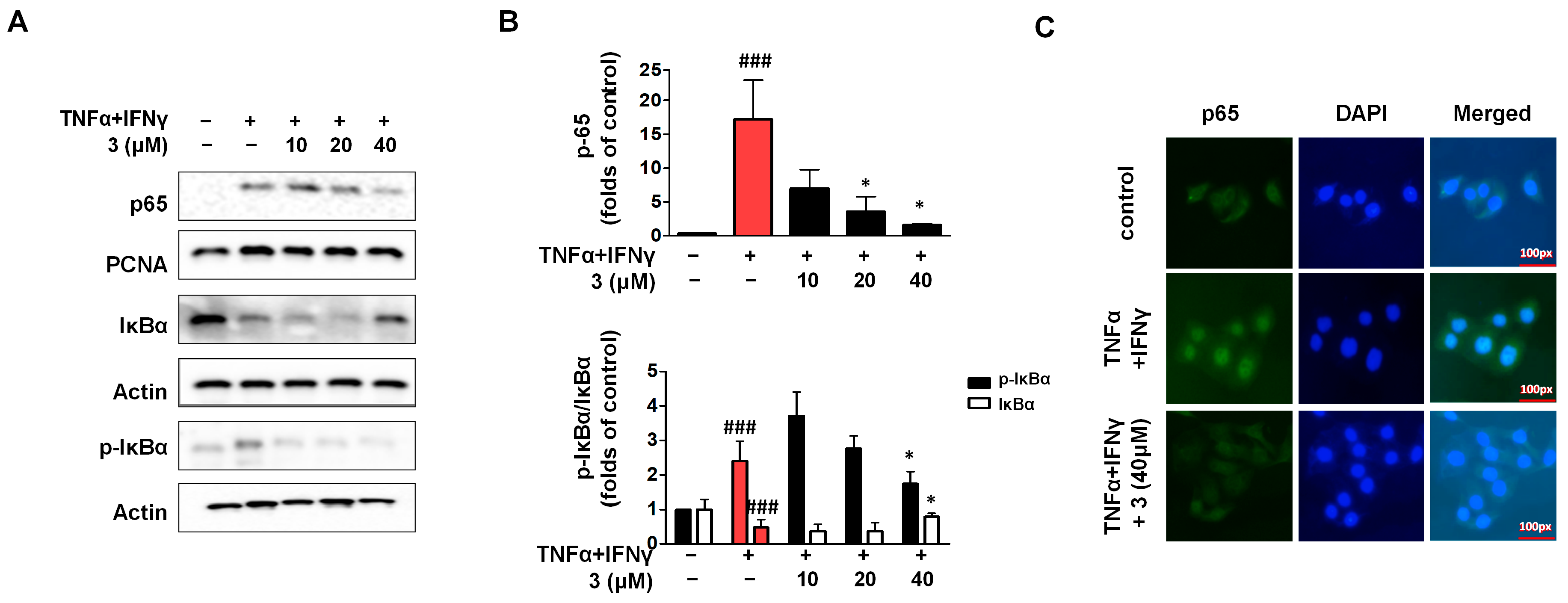
2.8. Compound 3 Inhibited Activation of the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in TNF-α/IFN-γ HaCaTs
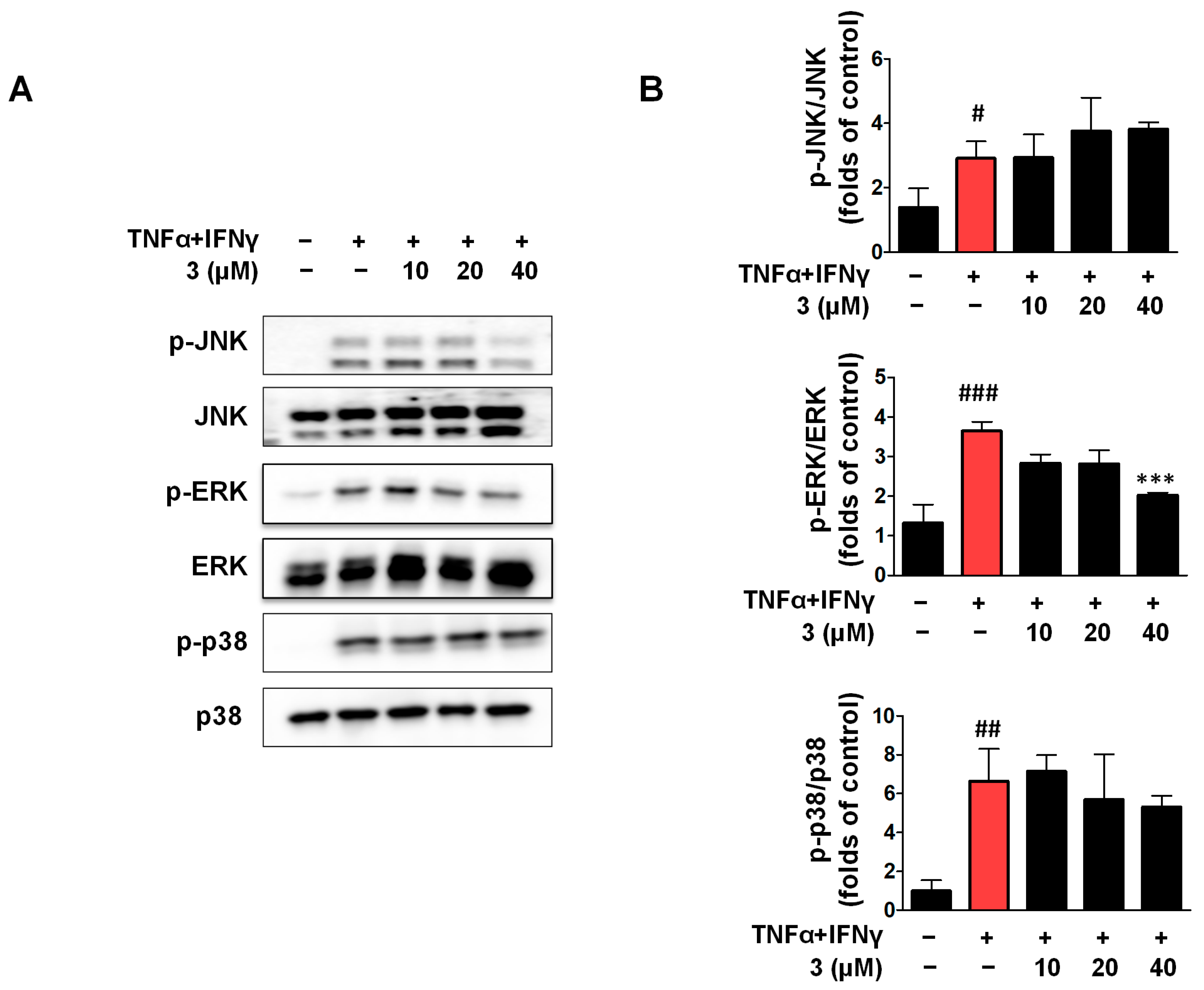
2.9. Compound 3 Inhibited the Activation of JNK and ERK in the MAPK Signaling Pathway
2.10. IL-8 and TARC Secretion Was Inhibited by Compound 3 in the 3D-Reconstructed Human Skin Model
2.11. Effects of Compound 3 on H&E Staining and Involucrin and Loricrin IHC Analysis in the 3D-Reconstructed Human Skin Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Preparation
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. 2,5-Iphenyl-2H-Tetrazolium Bromide (MTT) Assay
4.4. IL-6, IL-8, MDC, and RANTES Detection in Cell Culture Supernatants
4.5. Protein Extracts
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Immunofluorescence (IF)
4.8. Three-Dimensional (3D)-Reconstructed Human Skin Model
4.9. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining and Immunohistochemical (IHC) Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Atopic dermatitis |
| Digitalis purpurea L. | D. Purpurea L. |
| 3D | Three-dimensionally |
| 2D | Two-dimensionally |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor |
| IFN-γ | interferon-γ |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-B |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| IκBα | I kappa B-alpha |
| STAT | Signal Transduction and Transcription Activating Factor |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| TJ | Tight junctions |
| AMPs | Antimicrobial peptides |
| RANTES | Regulated upon Activation Normal T-cell Expressed and Secreted |
| TARC | Thymus to release activated regulatory chemokine |
| MDC | Macrophage-derived chemokine |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-8 | Interleukin-8 |
| IL-4 | Interleukin-4 |
| IL-13 | Interleukin-13 |
| TEWL | Trans-epidermal water loss |
| ICAM-1 | Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 |
References
- Ma, H.L.; Williams, C.M.; Collins, M.; Rahman, S. The Pathology and Immunology of Atopic Dermatitis. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2011, 10, 486–496. [Google Scholar]
- Boguniewicz, M.; Leung, D.Y.M. Atopic dermatitis: A disease of altered skin barrier and immune dysregulation. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 242, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, Y.E.; Renert, Y.; Brunner, P.M. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 2025, 405, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, K.; Patel, N.; Rao, S.; Strowd, L.C. The Future of Atopic Dermatitis Treatment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2024, 1447, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miot, H.A.; Criado, P.R.; Castro, C.C.S.; Ianhez, M.; Talhari, C.; Ramos, P.M. JAK-STAT pathway inhibitors in dermatology. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2023, 98, 656–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, L.; D’Onghia, M.; Lazzeri, L.; Rubegni, G.; Cinotti, E. Blocking the IL-4/IL-13 Axis versus the JAK/STAT Pathway in Atopic Dermatitis: How Can We Choose? J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabhadkar, M.; Kulkarni, M. Novel drug delivery systems in topical treatment of atopic dermatitis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 13. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.K.; Hsiao, C.Y.; Alshetaili, A.; Aljuffali, I.A.; Chen, E.L.; Fang, J.Y. Lipid-based nanoformulation optimization for achieving cutaneous targeting: Niosomes as the potential candidates to fulfill this aim. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 186, 106458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanesi, C. Keratinocytes in allergic skin diseases. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 10, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänel, K.; Cornelissen, C.; Lüscher, B.; Baron, J.M. Cytokines and the Skin Barrier. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 6720–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, L.A.; Cork, M.J.; Amagai, M.; De Benedetto, A.; Kabashima, K.; Hamilton, J.D.; Rossi, A.B. Type 2 inflammation contributes to skin barrier dysfunction in atopic dermatitis. JID Innov. 2022, 2, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berke, R.; Singh, A.; Guralnick, M. Atopic dermatitis: An overview. Am. Fam. Physician. 2012, 86, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, T.; Hanzawa, N.; Sugiyama, M. Effect of Lactobacillus strains on thymus and chemokine expression in keratinocytes and development of atopic dermatitis-like symptoms. Benef. Microbes. 2018, 15, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tüzün, Y.; Antonov, M.; Dolar, N.; Wolf, R. Keratinocyte cytokine and chemokine receptors. Dermatol. Clin. 2007, 25, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickoloff, B.J.; Xin, H.; Nestle, F.O.; Qin, J.Z. The cytokine and chemokine network in psoriasis. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 25, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogulur, I.; Pat, Y.; Ardicli, O.; Barletta, E.; Cevhertas, L.; Fernandez-Santamaria, R.; Huang, M.; Imam, M.B.; Koch, J.; Ma, S.; et al. Advances and highlights in biomarkers of allergic diseases. Allergy 2021, 76, 3659–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Hsiao, C.Y.; Hsu, Y.J.; Ko, H.H.; Chang, D.C.; Hung, C.F. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Cycloheterophyllin on Dinitrochlorobenzene-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in HaCaT Cells and BALB/c Mice. Molecules 2022, 27, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meesters, L.D.; Niehues, H.; Johnston, L.; Smits, J.P.H.; Zeeuwen, P.L.J.M.; Brown, S.J.; van den Bogaard, E.H. Keratinocyte signaling in atopic dermatitis: Investigations in organotypic skin models toward clinical application. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 1231–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fender, J.; Klöcker, J.; Boivin-Jahns, V.; Ravens, U.; Jahns, R.; Lorenz, K. “Cardiac glycosides”—quo vaditis?—past, present, and future? Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 9521–9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.W. Digitalis: Mechanisms of action and clinical use. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 318, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Han, S.H. Effects of phenylethanoid glycosides from Digitalis purpurea L. on the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2005, 57, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebenciucova, E.; VanHaerents, S. Interleukin-6: At the Interface of Human Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1255533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztürk, P.; Aral, M.; Kurutaș, E.B.; Kİreççİ, E.; Çelİk, M. Serum Levels of IL-8, Tnf-α and IL-6 in Children with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Curr. Pediatr. 2012, 10, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Clausen, M.L.; Kezic, S.; Olesen, C.M.; Agner, T. Cytokine concentration across the stratum corneum in atopic dermatitis and healthy controls. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Youn, G.S.; An, S.Y.; Kwon, H.Y.; Choi, S.Y.; Park, J. 2,3-Dimethoxy-2′-hydroxychalcone ameliorates TNF-α-induced ICAM-1 expression and subsequent monocyte adhesiveness via NF-kappaB inhibition and HO-1 induction in HaCaTs. BMB Rep. 2016, 49, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanesi, C.; Cavani, A.; Girolomoni, G. IL-17 is produced by nickel-specific T lymphocytes and regulates ICAM-1 expression and chemokine production in human keratinocytes: Synergistic or antagonist effects with IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, X.; Escames, G.; Lei, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Jing, T.; Yao, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, Z.; et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Contributions to inflammation-related diseases. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2023, 28, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.M.; Wiesolek, H.L.; Sumagin, R. ICAM-1: A master regulator of cellular responses in inflammation, injury resolution, and tumorigenesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Jia, J. Natural cox-2 inhibitors as promising anti-inflammatory agents: An update. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 3622–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, I. Distinct functions of COX-1 and COX-2. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2002, 68, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.E.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Boguniewicz, M. Loricrin and involucrin expression is down-regulated by Th2 cytokines through STAT-6. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 126, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mei, Y.; Long, X.; Tan, R.; Liang, W.; Sun, L. Acitretin modulates HaCaTs proliferation through STAT1- and STAT3-dependent signaling. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Jiang, X.; Wang, G.; Xu, Y.; Pan, R.; Yu, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Yu-Ping-Feng-San alleviates inflammation in atopic dermatitis mice by TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 329, 118092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Lai, Z. Glabridin attenuates atopic dermatitis progression through downregulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Genes Genom. 2021, 43, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, P.P.; Blenis, J. ERK and p38 MAPK-activated protein kinases: A family of protein kinases with diverse biological functions. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 320–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Lee, S.; Wang, H.; Lee, G.; Kim, S.; Ryu, Y.-H.; Chang, N.H.; Kang, Y.-W. Analysis of Skin Regeneration and Barrier-Improvement Efficacy of Polydeoxyribonucleotide Isolated from Panax Ginseng (C.A. Mey.) Adventitious Root. Molecules. 2023, 28, 7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.G.; Choi, D.; Lim, K.M. Evaluation of Skin Irritation of Acids Commonly Used in Cleaners in 3D-Reconstructed Human Epidermis Model, KeraSkinTM. Toxics 2022, 10, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.-S.; Chang, Y.J.; Jeong, T.-C.; Kang, M.-J.; Kim, T.-S.; Yoon, H.S.; Lee, G.Y.; et al. Me-too validation study for in vitro skin irritation test with a reconstructed human epidermis model, KeraSkin™ for OECD test guideline 439. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 117, 104725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kang, N.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, I.S.; Kim, Y. Round Robin Study for Evaluation an in vitro skin irritation test for medical device extracts using KeraSkinTM in Korea. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 192, 114942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshari, M.; Kolackova, M.; Rosecka, M.; Čelakovská, J.; Krejsek, J. Unraveling the skin; a comprehensive review of atopic dermatitis, current understanding, and approaches. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1361005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, F.; Moghadam, A.; Tahmasebi, A.; Niazi, A. Identification of key genes involved in secondary metabolite biosynthesis in Digitalis purpurea. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0277293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhai, H.; Rathee, S.; Jain, S.K.; Patil, U.K. The Potential of Natural Products in the Management of Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2024, 30, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iraci, F.; Herdeg, C.; Holzwarth, M.; Storz, M.A. Of mixed vegetables and cardiac arrhythmias—Digitalis purpurea confused with Borago officinalis: A case series of accidental digitoxin intoxications. J. Cardiol. Cases 2023, 28, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.S.; Fuhro, V.M.; de Souza Nogueira, J.; Romana-Souza, B. Polyphenol hydroxytyrosol present olive oil improves skin wound healing of diabetic mice. Wound Repair Regen. 2024, 32, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, H.; Liu, C.; Akanji, T.; Gutkowski, J.; Li, R.; Ma, H.; Wan, Y.; Wu, P.; Li, D.; et al. Dietary polyphenol oleuropein and its metabolite hydroxytyrosol are moderate skin permeable elastase and collagenase inhibitors with synergistic cellular antioxidant effects in human skin fibroblasts. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 73, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, H.; Shao, S.; Shen, Y.; Xiao, F.; Sun, J.; Piao, S.; Zhao, D.; Li, G.; Yan, M. Compound traditional Chinese medicine dermatitis ointment ameliorates inflammatory responses and dysregulation of itch-related molecules in atopic dermatitis. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bogaard, E.H.; Elias, P.M.; Goleva, E.; Berdyshev, E.; Smits, J.P.H.; Danby, S.G.; Cork, M.J.; Leung, D.Y.M. Targeting Skin Barrier Function in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2023, 111, 335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmuth, M.; Eckmann, S.; Moosbrugger-Martinz, V.; Ortner-Tobider, D.; Blunder, S.; Trafoier, T.; Gruber, R.; Elias, P.M. Skin Barrier in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 144, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.D.; Gu, Y.J.; Wang, D.C.; Niu, Y.; Xu, Z.-R.; Jin, Z.-Q.; Wang, X.-X.; Li, S.-J. Therapeutic effects of myricetin on atopic dermatitis in vivo and in vitro. Phytomedicine 2022, 102, 154200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Liu, R.; Hu, X.; Liang, T.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Z. MAPK signaling pathway-targeted marine compounds in cancer therapy. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.S.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, H.J. A human 3D skin model based on KeraSkin™ for screening skin irritation of chemicals. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2020, 43, 999–1010. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Test No. 439: In Vitro Skin Irritation: Reconstructed Human Epidermis Test Method. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals; Section 4; OECD: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Jin, H.G.; Shin, J.E.; Hong, J.; Woo, E.R. Phenylethanoid Glycosides from Digitalis purpurea L. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, 32, 1721–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, M.R.; Woo, E.R.; Kim, Y.G.; Kang, K.W. Chrysoeriol potently inhibits the induction of nitric oxide synthase by blocking AP-1 activation. J. Biomed. Sci. 2005, 12, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, L.; Lee, H.; Liu, Z.; Woo, E.-R.; Lee, D.-S. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Compounds Isolated from Digitalis purpurea L. in TNF-α/IFN-γ-Induced HaCaT Keratinocytes and a Three-Dimensionally Reconstructed Human Skin Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167747
Dong L, Lee H, Liu Z, Woo E-R, Lee D-S. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Compounds Isolated from Digitalis purpurea L. in TNF-α/IFN-γ-Induced HaCaT Keratinocytes and a Three-Dimensionally Reconstructed Human Skin Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167747
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Linsha, Hwan Lee, Zhiming Liu, Eun-Rhan Woo, and Dong-Sung Lee. 2025. "Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Compounds Isolated from Digitalis purpurea L. in TNF-α/IFN-γ-Induced HaCaT Keratinocytes and a Three-Dimensionally Reconstructed Human Skin Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167747
APA StyleDong, L., Lee, H., Liu, Z., Woo, E.-R., & Lee, D.-S. (2025). Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Compounds Isolated from Digitalis purpurea L. in TNF-α/IFN-γ-Induced HaCaT Keratinocytes and a Three-Dimensionally Reconstructed Human Skin Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167747





