Mitigating Effect of Ginger Extract on Survival Rate and Muscle Quality of Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus) Under Transportation Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
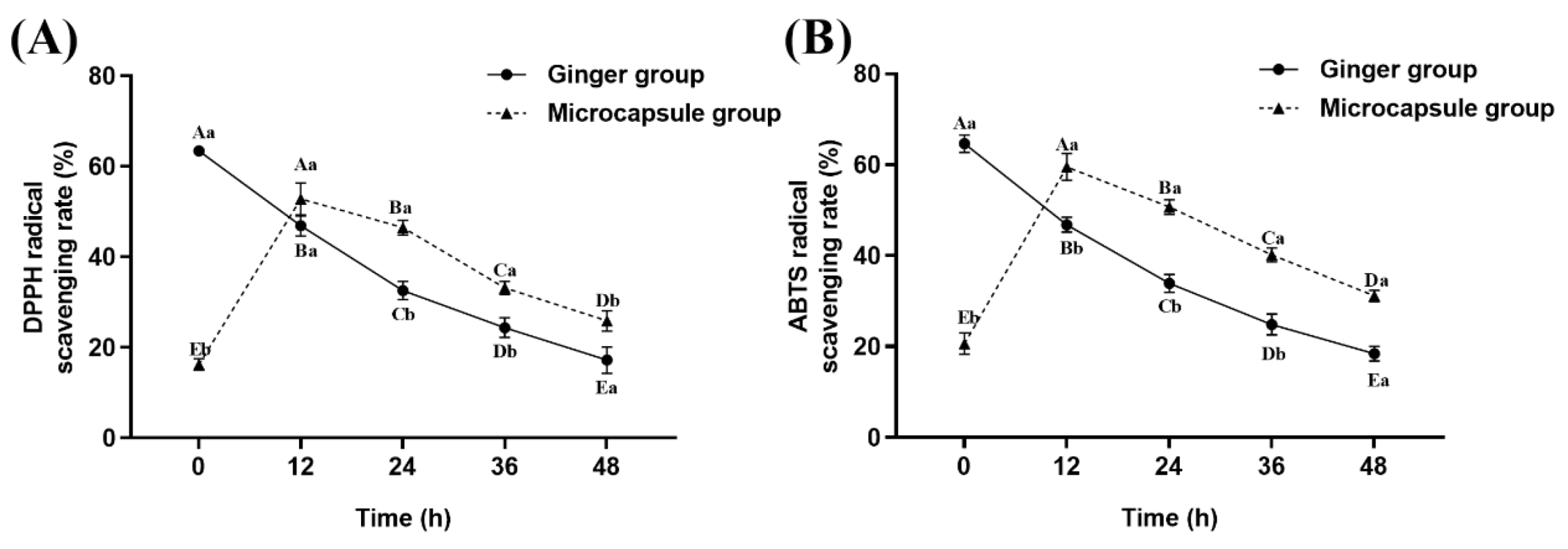
2.1. Free Radical Scavenging Ability of Ginger Treated with Microcapsules
2.2. Changes in Survival Rate of Fish During Transportation
2.3. Changes in Water Parameters During Transportation
2.3.1. Dissolved Oxygen
2.3.2. pH
2.3.3. Ammonia Nitrogen
2.3.4. Nitrite
2.3.5. TDS
2.4. Changes in Blood Stress Indicators of Fish During Transportation
2.4.1. Biochemical Indicators
- (1)
- Energy metabolism parameters
- (2)
- Hormone parameter
- (3)
- Renal metabolism parameters
- (4)
- Liver metabolism parameters
2.4.2. Redox Parameters
2.4.3. Gene Expression
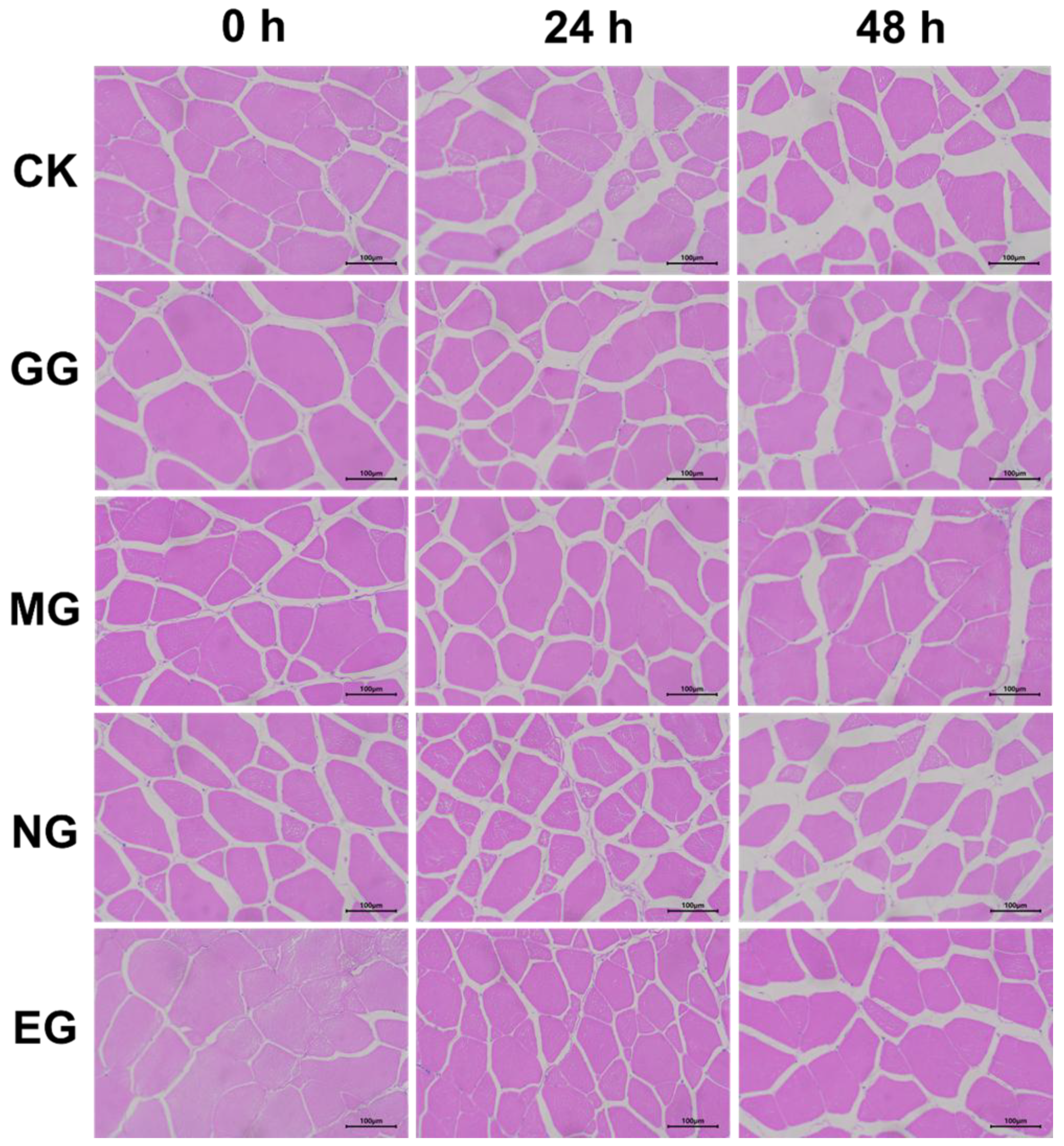
2.5. Histological Changes in Gill and Liver of Fish After 48 h of Transportation
2.6. Changes in Muscle Quality of Fish During Transportation
2.6.1. Cellular Structure
2.6.2. Physical Properties
- (1)
- Shear force and drip loss
- (2)
- Color
2.6.3. Muscle Glycogen, pH, and Lactate
2.6.4. ATP and Its Metabolites
2.7. Changes in Apoptosis of Fish During Transportation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Ethic Statement
3.3. Preparation of Microcapsules
3.4. Determination of Free Radical Scavenging Ability
3.5. Sample Preparation
- (1)
- Simulated Transportation Program
- (2)
- The Effects of Different Addition Methods of Ginger Extract on Survival Rate
- (3)
- The Effects of Different Addition Methods of Ginger Extract on Stress Response and Muscle Quality of Fish
3.6. Survival Rate
- wt: Survival rate of each group at different times;
- nt: Survival quantity of each group at different times;
- n: The initial quantity for each group is 10 in this experiment.
3.7. Determination of Water Indicators
3.8. Determination of Biochemical Parameter
3.9. Determination of Redox System Indicators
3.10. Observation of Tissue Structure
3.11. Determination of mRNA Relative Expression of hsp70, hsp90, caspase3, and il-6 in Blood
3.11.1. Total RNA Extraction
3.11.2. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative PCR
3.12. Determination Muscle Quality of Fish
- (1)
- Shear Force
- (2)
- Drip Loss
- (3)
- Color
- (4)
- Lactic Acid, Muscle Glycogen and pH
- (5)
- ATP and Its Metabolites
3.13. Determination of caspase 3, caspase 8, caspase 9, bcl-2, bax in Fish Muscle
3.14. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, H.; Zhang, T.; Yongsawadigul, J.; Yin, T.; You, J.; Ru, L. Changes in survival rate and muscle quality of Megalobrama amblycephala infish bags during the process of keeping-alive. J. Fish. China 2024, 48, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; You, X.; Sun, W.; Xiong, G.; Shi, L.; Qiao, Y.; Wu, W.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Ding, A.; et al. Insight into acute heat stress on meat qualities of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during short-time transportation. Aquaculture 2021, 543, 737013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Xiong, G.; Sun, W.; Wu, W.; Ding, A.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Shi, L. Effects of hypoxia on meat qualities and muscle metabolism in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during short-time transportation and its relief by reoxygenation. Aquaculture 2023, 570, 739404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Rahman, Z.; Tian, Y.; Yin, T.; Xiong, S.; You, J.; Liu, R.; Wang, L.; Huang, Q.; Ma, H. Comprehensive molecular biology and metabolomics analysis reveal the changes on muscle quality of Megalobrama amblycephala exposure to ammonia nitrogen during transportation. Food Res. Int. 2025, 212, 116372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, S.; You, J.; Liu, R.; Xu, D.; Huang, Q.; Ma, H.; Yin, T. A comprehensive review of the mechanisms on fish stress affecting muscle qualities: Nutrition, physical properties, and flavor. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, L.; Yin, T.; You, J.; Liu, R.; Huang, Q.; Shi, L.; Wang, L.; Liao, T.; Wang, W.; et al. Recent understanding of stress response on muscle quality of fish: From the perspective of industrial chain. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 140, 104145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Yin, T.; Song, Z.; Xiong, S.; Liu, R.; You, J.; Huang, Q. Superior ammonia nitrogen adsorption capacity and reusability biochar microsphere applied in live fish transportation. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 514, 163261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; You, J.; Liu, R.; Long, Y.; Song, G.; Benjakul, S.; Xiong, S.; Rahman, Z.; Huang, Q.; Chen, S.; et al. Fasting influences the muscle quality of fish during transportation by regulating the balance between energy metabolism and ammonia nitrogen stress. J. Adv. Res. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Khoder, R.M.; Mei, J.; Yang, H.; Huang, Q.; You, J.; Yin, T.; Liu, R. The impact of the addition of vitamin C, NaCl, clove oil on the muscle of live blunt-snout bream during transportation. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Bian, M.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J. Salinity mediates the damage caused by acute and chronic ammonia stress in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacchi, L.; Lowrey, L.; Musharrafieh, R.; Crossey, K.; Larragoite, E.T.; Salinas, I. Effects of transportation stress and addition of salt to transport water on the skin mucosal homeostasis of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2015, 435, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Hoseini, S.M.; Weber, R.A.; da Silva, E.; Rajabiesterabadi, H.; Arghideh, M.; Delavar, F.H. Alleviation of transportation-induced stress in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, using brackish water. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 27, 101378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, E.; Wang, J.; Qin, W.; Dong, X.; Shao, Z. Research progress on effects of salinity on growth performance, muscle quality and tissue structure of fish. Open J. Fish. Res. 2020, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ding, H.; Dong, X.; Qu, L.; Xia, T.; Chen, X.; Cheng, H.; Ding, Z. Anaesthetic effects of eugenol on preservation and transportation of yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 3796–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, N.; Le, Q.; Hu, J.; Yang, Y.; Kuang, S.; Zhang, M.; Sun, Y.; Gu, W.; et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals the influence of anaesthetic stress on the immune system of crucian carp (Carassius auratus) under the process of treatment and low concentration transport by MS-222 and Eugenol. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 3138–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, F.; Vaezi, G.; Sharafi, S.; Rahbarian, R. 6-gingerol effect on rat liver following exposure to gold nanoparticles: From histopathologic findings to inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2024, 38, e23793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Huang, G.; Lu, Y.; Chang, L. Anti-inflammatory effects of an aqueous extract of Welsh onion green leaves in mice. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, G.; Rashidian, G.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Naserabad, S.S.; Doan, H.V. Ginger (Zingiber officinale) extract affects growth performance, body composition, haematology, serum and mucosal immune parameters in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 99, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Chen, Y.P.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Chung, H.Y. Antioxidant activities of ginger extract and its constituents toward lipids. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beristain-Bauza, S.D.C.; Paola, H.-C.; Soledad, C.-P.T.; Raúl, Á.-S.; Israel, R.-L.I.; Ochoa-Velasco, C.E. Antimicrobial activity of ginger (zingiber officinale) and its application in food products. Food Rev. Int. 2019, 35, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, D.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y. 1,8-cineole and ginger extract (Zingiber officinale Rosc) as stress mitigator for transportation of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides L.). Aquaculture 2022, 561, 738622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Xuan, S.; Wu, W.; Qu, L. Encapsulation efficiency and controlled release of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide microcapsules by spray drying using different combinations of wall materials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, I.; Chin, N.L. Antioxidant properties of dried ginger (zingiber officinale roscoe) var. Bentong. Foods 2023, 12, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Effects of Two-Phase Metabolic Modification on Curcumin and 6-Gingerol in Protecting Pc12 Cells from Oxidative Damage. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Agricultural University, Taian, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, H.S.; Song, J.A.; Park, H.-S.; Choi, Y.J.; Choi, C.Y. Physiological and oxidative stress response of goldfish Carassius auratus induced by a light dimming system. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 46, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kültz, D. Physiological mechanisms used by fish to cope with salinity stress. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motamedi-Tehrani, J.; Peyghan, R.; Shahriari, A.; Razijalali, M.; Ebrahimi, E. Combined effects of ammonia-N exposure and salinity changes on hematological and serum biochemical factors and thyroid hormones in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Heliyon 2024, 10, e29103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, E.; Motamedi-Tehrani, J.; Peyghan, R. Effect of short-term stress and interaction of salinity and ammonia-n levels, associated with food deprivation on fatty acid profile and body composition in nile tilapia (oreochromis niloticus). Aquac. Nutr. 2025, 2025, 8840365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liew, H.; Sun, B.; Wang, S.; Luo, L.; Zhang, L.; Liang, L. Effects of bicarbonate stress on serum ions and gill transporters in alkali and freshwater forms of amur ide (leuciscus waleckii). Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 676096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Cao, J.; Qin, X.; Qiu, W.; Mei, J.; Xie, J. Toxic Effects on Bioaccumulation, Hematological Parameters, Oxidative Stress, Immune Responses and Tissue Structure in Fish Exposed to Ammonia Nitrogen: A Review. Animals 2021, 11, 3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, F.; Saoca, C.; Sanfilippo, M.; Capillo, G.; Spanò, N.; Piccione, G. Response of vanadium bioaccumulation in tissues of Mugil cephalus (Linnaeus 1758). Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 689, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, F.; Saoca, C.; Ferrantelli, V.; Cammilleri, G.; Capillo, G.; Piccione, G. Relationship between arsenic accumulation in tissues and hematological parameters in mullet caught in Faro Lake: A preliminary study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 8821–8827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kang, Y.J.; Kim, K.I.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, J. Toxic effects of nitrogenous compounds (ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate) on acute toxicity and antioxidant responses of juvenile olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 67, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.H.; Chen, S.Q.; Ouyang, K.; Kuang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Tang, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.P.; Li, L. Evaluation of Ammonia Nitrogen Exposure in Immune Defenses Present on Spleen and Head-Kidney of Wuchang Bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, R.; Liu, B.; Han, C.; Huang, B.; Lei, J.L. Effects of ammonia exposure on stress and immune response in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 3149–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.A.; Elphick, J.R.; McPherson, C.A.; Chapman, P.M. Effect of total dissolved solids on fertilization and development of two salmonid species. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 95, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.V.; Kumar, A.; Middha, S.K.; Paital, B.; Mathur, S.; Johnson, R.; Kademan, A.; Usha, T.; Hemavathi, K.N.; Dayal, S.; et al. Water physicochemical factors and oxidative stress physiology in fish, a review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1240813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber-Scannell, P.; Duffy, L. Effects of Total Dissolved Solids on Aquatic Organisms: A Review of Literature and Recommendation for Salmonid Species. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, M.F.; Khadim, M.; Rafiq, M.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Wan, C.C. Pharmacological properties and health benefits of eugenol: A comprehensive review. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 2497354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, K.; Anand, B.G.; Shekhawat, D.S.; Kar, K. Eugenol prevents amyloid formation of proteins and inhibits amyloid-induced hemolysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Ou, Y.; Lan, J.; Wen, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, H. The survival and structural changes in gill of juvenile eleutheronema tetradactylum under different salinities. J. South. Agric. 2021, 52, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H. Physiological Response Mechanism of Gill Tissue of Hybrid Sturgeon (Huso Dauricus♀×Acipenser Schrenckii♂) Under Carbonate Alkali Stress. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Yang, Y. Advance in pharmacological research of eugenol. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2013, 52, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Zhang, C.; Mai, K. A review on function and regulatory mechanism of Na+ and Cl− transporters in fish. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 28, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usta, J.; Kreydiyyeh, S.; Bajakian, K.; Nakkash-Chmaisse, H. In vitro effect of eugenol and cinnamaldehyde on membrane potential and respiratory chain complexes in isolated rat liver mitochondria. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Liang, X.; Chen, W.; Huang, Y.; Fan, X.; Qin, X. Stress-relieving effect of basil essential oil on temporarily cultured pearl gentian grouper (epinephelus fuscoguttatusi♀×epinephelus lanceolatus♂) before transportation. J. Guangdong Ocean Univ. 2023, 43, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Miao, Z.; Feng, S.; Xu, S. Chlorpyrifos-mediated mitochondrial calcium overload induces EPC cell apoptosis via ROS/AMPK/ULK1. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 141, 109053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, J. Cytometabonomic study of anti-inflammatory activity of dehydrodiisoeugenol. Res. Pract. Chin. Med. 2024, 38, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, L.; Luo, W. 6-shogaol protects against isoproterenol-induced cardiac injury in rats through attenuating oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and activating nuclear respiratory factor-2/heme oxygenase-1 signaling pathway. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2022, 19, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Bal, C.; Xlong, G.; Wang, J.; Ll, N.; Zu, X.; Ll, H.; Llao, T. Effect of eugenol anesthesia on waterless live transportation of micropterus salmoides. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Lv, W. Effects of transportation density and salinity on cortisol, glycogen and lactate of large yellow croaker(Larimichthys crocea) juveniles. J. Fish. China 2014, 38, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Dong, H.; Zhao, W.; Chen, F.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Gong, B.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, J. Anesthetic effect and tissue oxidative injury for Litopenaeus vannamei by two anesthetics. South China Fish. Sci. 2023, 19, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Fu, L.; Zhou, W.; Liu, D.; Zhao, H. A review on the pharmacological effects of eugenol. Clin. J. Chin. Med. 2024, 16, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, H.; Sun, R.; Yu, D.; Yang, F.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xia, W. The apoptosis of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) muscle during postmortem condition regulated by the cytokines via TOR and NF-κB signaling pathways. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, R.J.; Nogusa, S.; Chen, P.; Maki, J.L.; Lerro, A.; Andrake, M.; Rall, G.F.; Degterev, A.; Balachandran, S. Interferon-induced RIP1/RIP3-mediated necrosis requires PKR and is licensed by FADD and caspases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E3109–E3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganjikunta, V.S.; Maddula, R.R.; Bhasha, S.; Sahukari, R.; Kondeti Ramudu, S.; Chenji, V.; Kesireddy, S.R.; Zheng, Z.; Korivi, M. Cardioprotective Effects of 6-Gingerol against Alcohol-Induced ROS-Mediated Tissue Injury and Apoptosis in Rats. Molecules 2022, 27, 8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H. Preparation of Proanthocyanidin Microcapsules and Its Performance Study. Master’s Thesis, Henan University of Technology, Zhengzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G. Study on enzymatic extraction of resveratrol from strawberry and its antioxidant activity. Henan Chem. Ind. 2024, 41, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Zeng, Q.-H.; Zhao, N.-N.; Cheng, S.; Ll, Y.; Llu, G.-G. Detection of ginger anti-radical ability. Food Res. Dev. 2014, 35, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Nong, W.; Wei, X.; Zhu, M.; Mao, L. Impacts of a novel live shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) water-free transportation strategy on flesh quality: Insights through stress response and oxidation in lipids and proteins. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; You, J.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Liao, T.; Huang, Q.; Xiong, S.; Yin, T. Insight into the mechanism on texture change of Wuchang bream muscle during live transportation using a UPLC-QTOF-MS based metabolomics method. Food Chem. 2023, 398, 133796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Liu, S.; Zuo, F.; Geng, Y.; Ouyang, P.; Chen, D.; Yang, S.; Zheng, W.; Xiong, Y.; Cai, W.; et al. The IL17 signaling pathway: A potential signaling pathway mediating gill hyperplasia and inflammation under ammonia nitrogen stress was identified by multi-omics analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 867, 161581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D. The Exploration of Sinonovacula Constricta and Meretrix Meretrix in ATP Degradation Pathways and Its Quality Changes During Chilled Storage. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
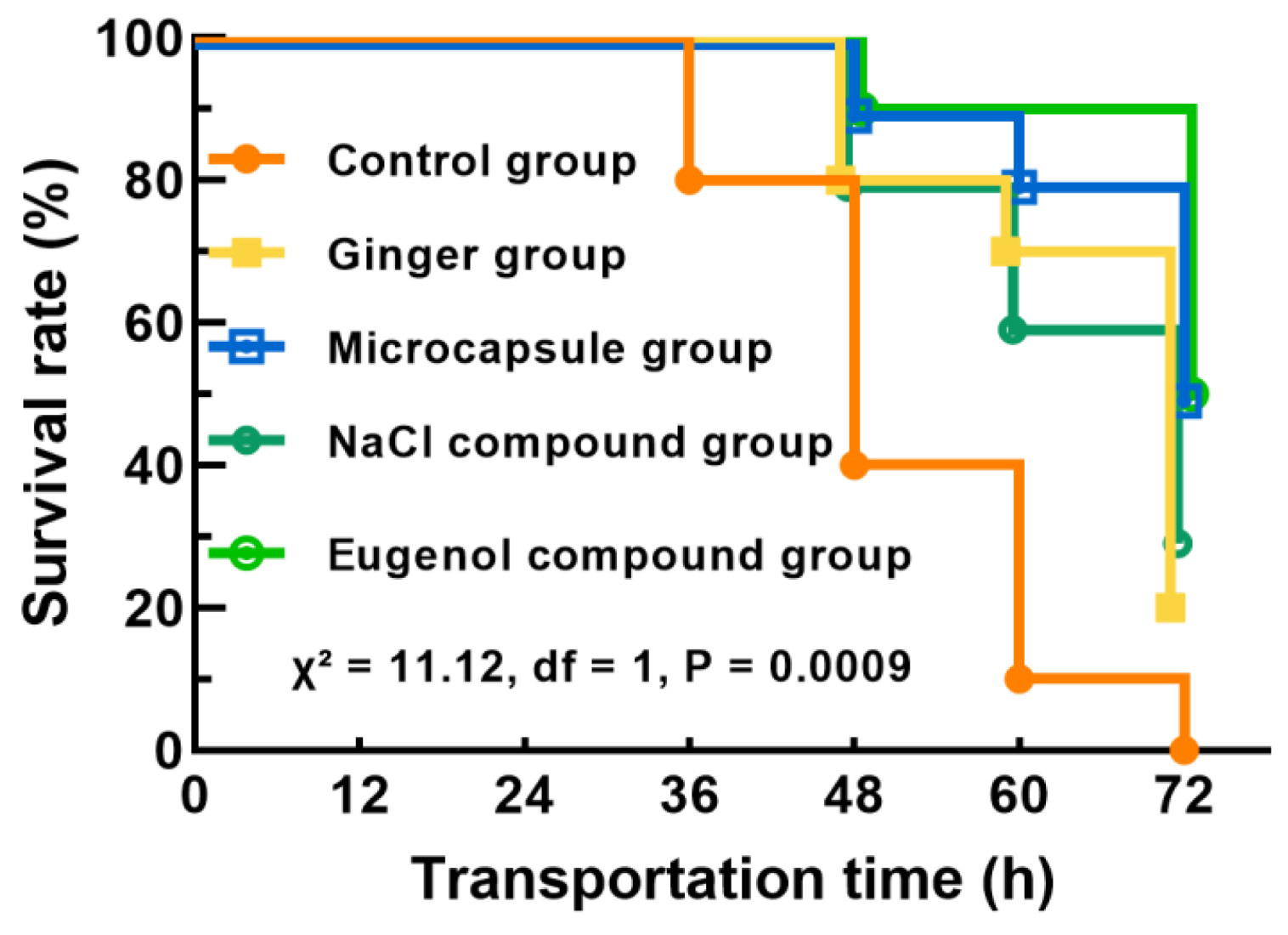
 : Control group;
: Control group;  : Ginger group;
: Ginger group;  : Microcapsule group;
: Microcapsule group;  : NaCl compound group;
: NaCl compound group;  : Eugenol compound group.
: Eugenol compound group.
 : Control group;
: Control group;  : Ginger group;
: Ginger group;  : Microcapsule group;
: Microcapsule group;  : NaCl compound group;
: NaCl compound group;  : Eugenol compound group.
: Eugenol compound group.
 : Control group;
: Control group;  : Ginger group;
: Ginger group;  : Microcapsule group;
: Microcapsule group;  : NaCl compound group;
: NaCl compound group;  : Eugenol compound group.
: Eugenol compound group.
 : Control group;
: Control group;  : Ginger group;
: Ginger group;  : Microcapsule group;
: Microcapsule group;  : NaCl compound group;
: NaCl compound group;  : Eugenol compound group.
: Eugenol compound group.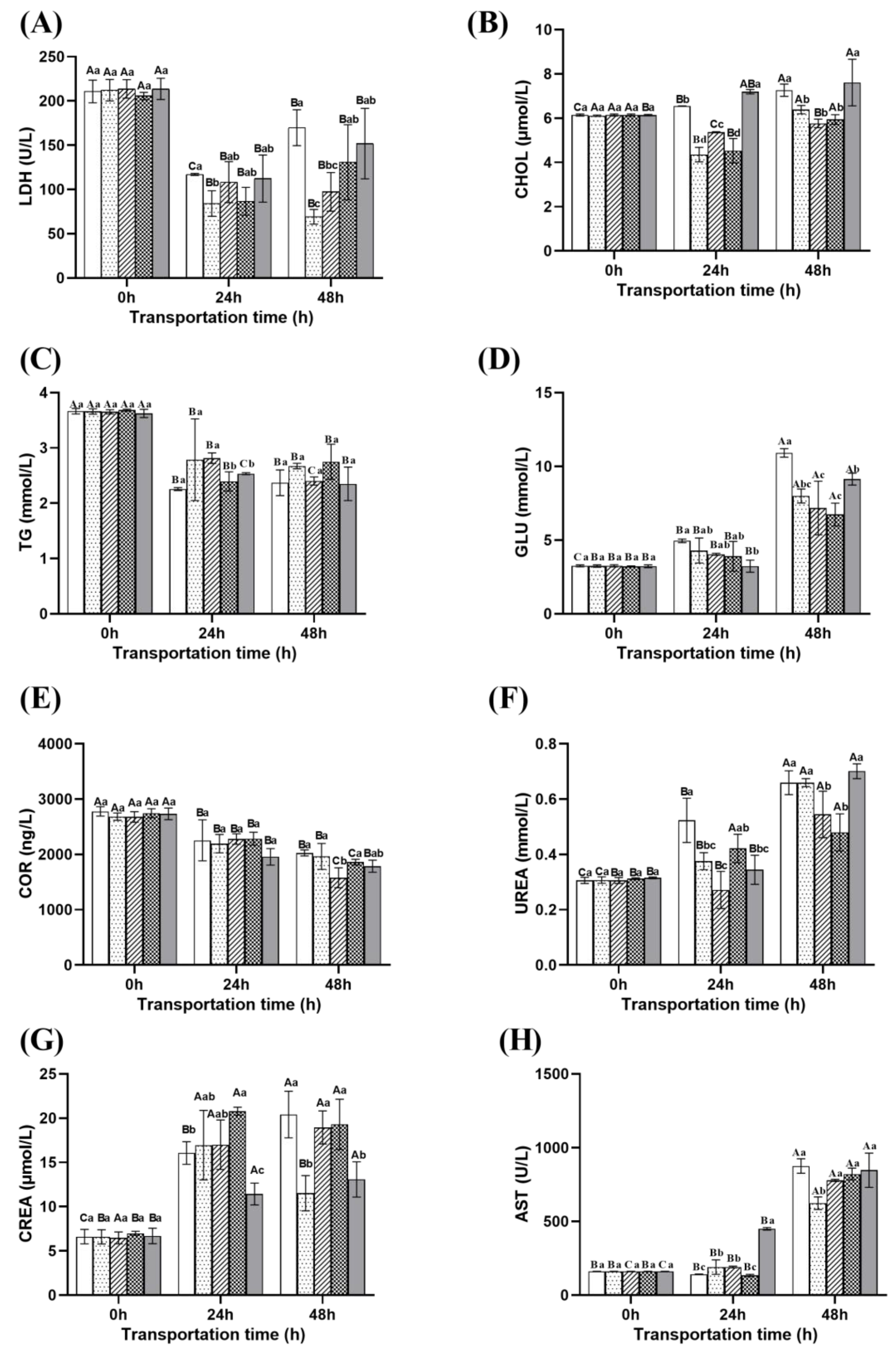
 : Control group;
: Control group;  : Ginger group;
: Ginger group;  : Microcapsule group;
: Microcapsule group;  : NaCl com pound group;
: NaCl com pound group;  : Eugenol compound group.
: Eugenol compound group.
 : Control group;
: Control group;  : Ginger group;
: Ginger group;  : Microcapsule group;
: Microcapsule group;  : NaCl com pound group;
: NaCl com pound group;  : Eugenol compound group.
: Eugenol compound group.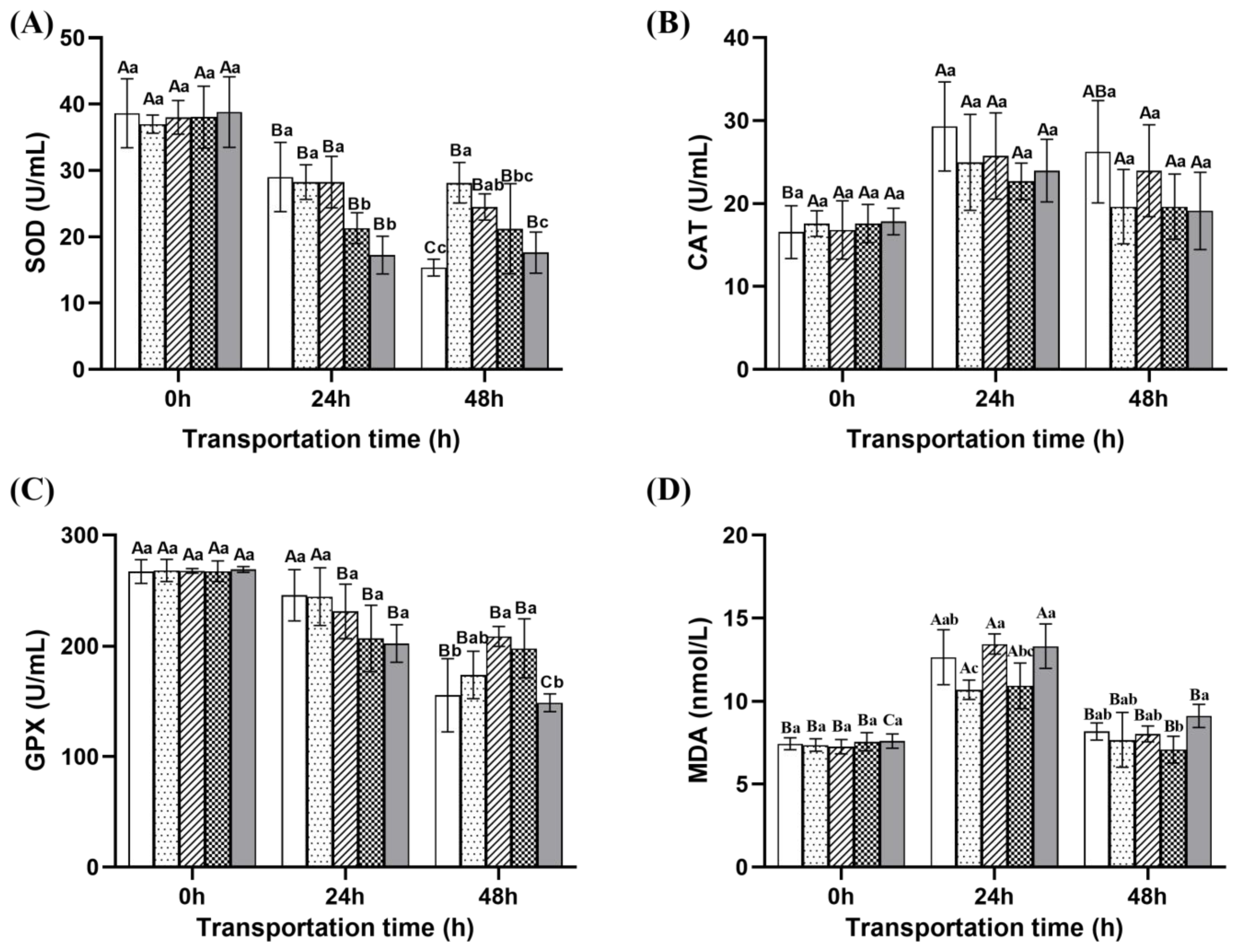
 : Control group;
: Control group;  : Ginger group;
: Ginger group;  : Microcapsule group;
: Microcapsule group;  : NaCl compound group;
: NaCl compound group;  : Eugenol compound group.
: Eugenol compound group.
 : Control group;
: Control group;  : Ginger group;
: Ginger group;  : Microcapsule group;
: Microcapsule group;  : NaCl compound group;
: NaCl compound group;  : Eugenol compound group.
: Eugenol compound group.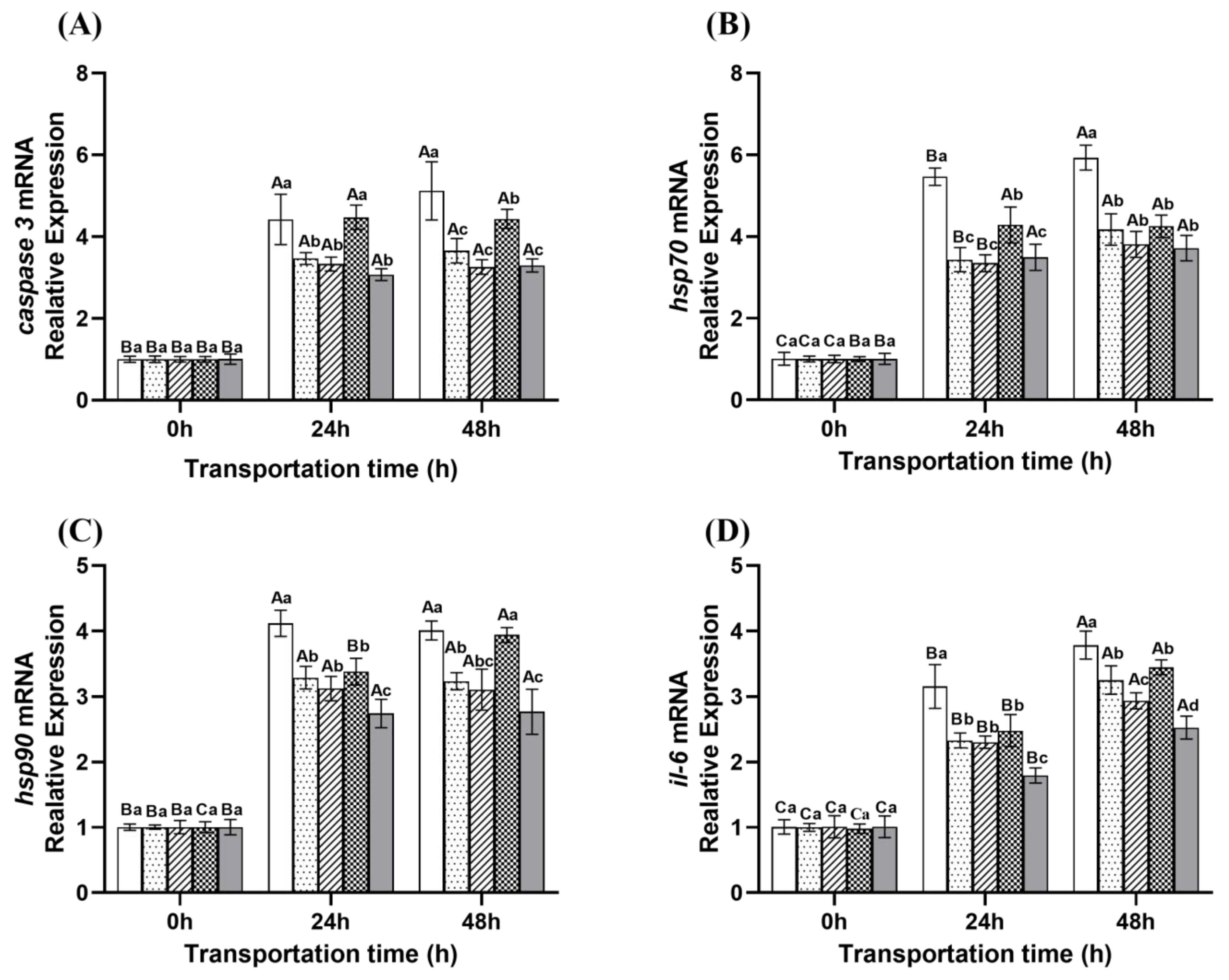

 : Control group;
: Control group;  : Ginger group;
: Ginger group;  : Microcapsule group;
: Microcapsule group;  : NaCl compound group;
: NaCl compound group;  : Eugenol compound group.
: Eugenol compound group.
 : Control group;
: Control group;  : Ginger group;
: Ginger group;  : Microcapsule group;
: Microcapsule group;  : NaCl compound group;
: NaCl compound group;  : Eugenol compound group.
: Eugenol compound group.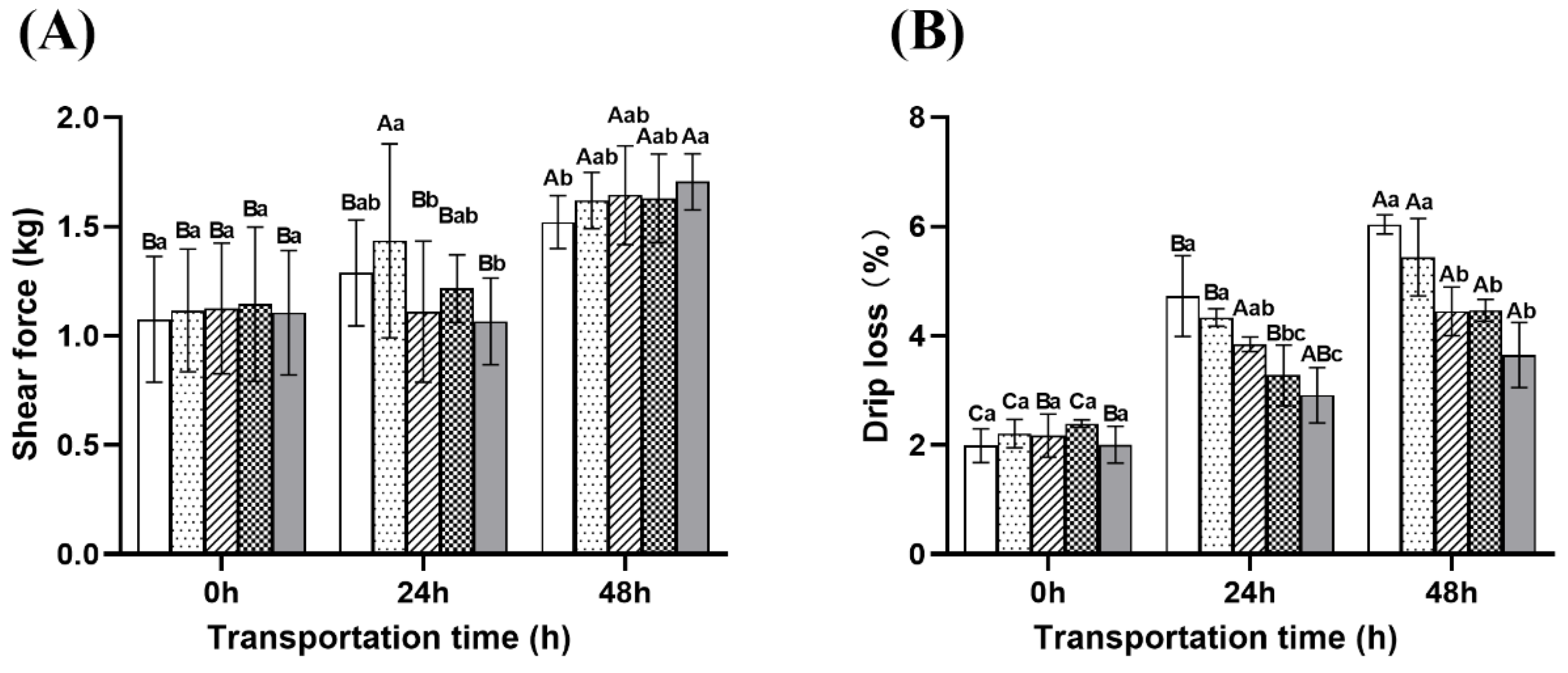
 : Control group;
: Control group;  : Ginger group;
: Ginger group;  : Microcapsule group;
: Microcapsule group;  : NaCl compound group;
: NaCl compound group;  : Eugenol compound group.
: Eugenol compound group.
 : Control group;
: Control group;  : Ginger group;
: Ginger group;  : Microcapsule group;
: Microcapsule group;  : NaCl compound group;
: NaCl compound group;  : Eugenol compound group.
: Eugenol compound group.
 : Control group;
: Control group;  : Ginger group;
: Ginger group;  : Microcapsule group;
: Microcapsule group;  : NaCl compound group;
: NaCl compound group;  : Eugenol compound group.
: Eugenol compound group.
 : Control group;
: Control group;  : Ginger group;
: Ginger group;  : Microcapsule group;
: Microcapsule group;  : NaCl compound group;
: NaCl compound group;  : Eugenol compound group.
: Eugenol compound group.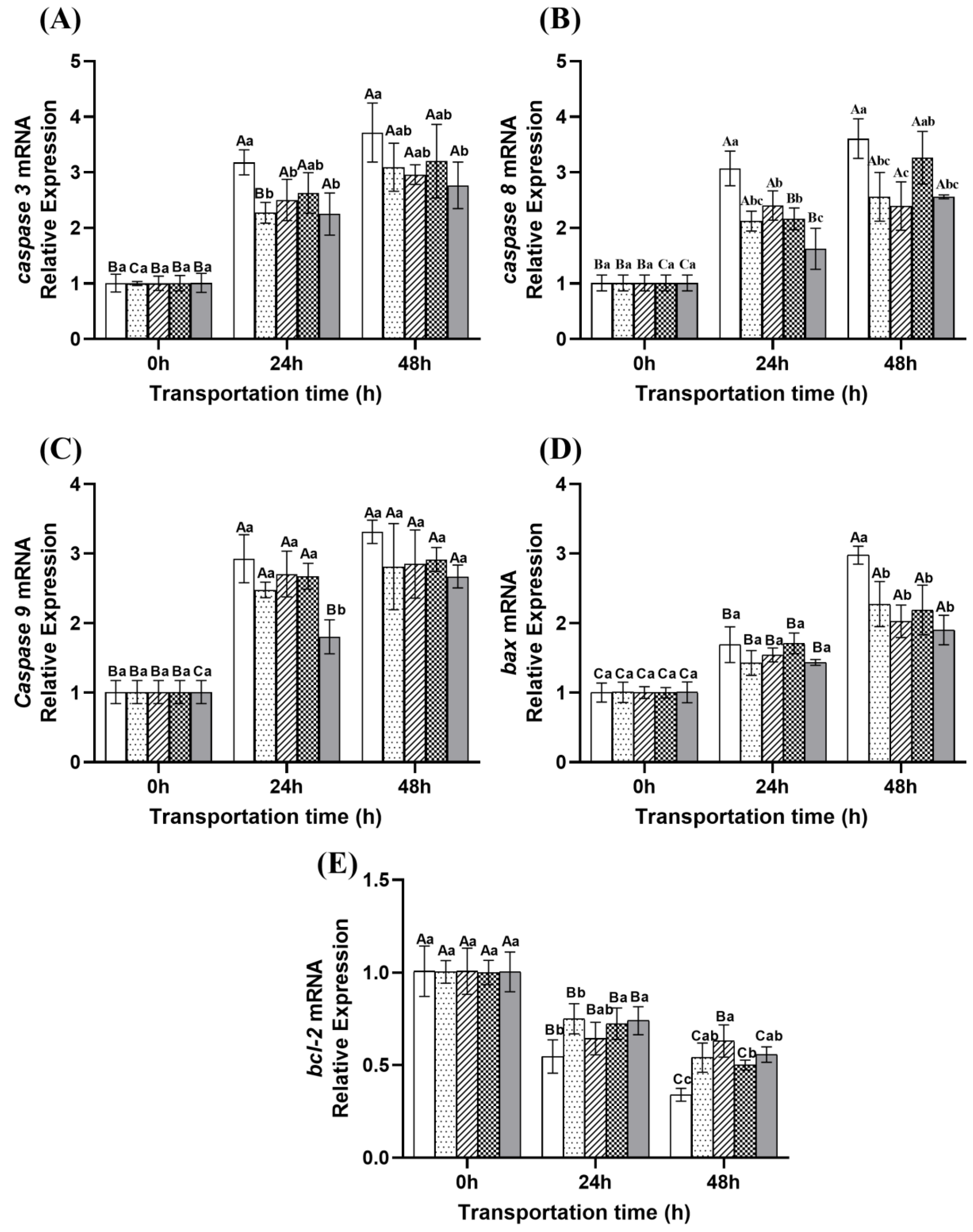
| Transportation Time/h | Group | L* | a* | b* | W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | CK | 48.48 ± 1.37 Ba | 3.33 ± 0.88 Aa | 1.26 ± 0.61 Aa | 48.35 ± 1.44 Ba |
| GG | 48.57 ± 1.23 Ba | 2.95 ± 0.26 Aa | 1.13 ± 0.34 Ba | 48.47 ± 1.24 Ba | |
| MG | 48.08 ± 1.27 Ba | 3.01 ± 1.36 Aa | 1.6 ± 0.48 Aa | 47.95 ± 1.34 Ba | |
| NG | 49.45 ± 1.15 Ba | 2.59 ± 0.66 Aa | 1.25 ± 0.58 Aa | 49.36 ± 1.16 Ba | |
| EG | 48.1 ± 0.78 Ba | 2.69 ± 0.77 Aa | 1.23 ± 0.39 Ba | 48.01 ± 0.79 Ba | |
| 24 | CK | 46.93 ± 0.66 Bc | 1.96 ± 0.46 Bb | 1.68 ± 0.27 Aa | 46.86 ± 0.66 Bc |
| GG | 47.64 ± 0.78 Bc | 2.79 ± 0.53 Aa | 2.25 ± 0.63 Aa | 47.51 ± 0.79 Bc | |
| MG | 50.52 ± 0.67 Aa | 2.27 ± 0.32 Aab | 1.89 ± 0.41 Aa | 50.43 ± 0.66 Aa | |
| NG | 51.31 ± 0.49 Aa | 2.21 ± 0.69 Aab | 2.03 ± 0.54 Aa | 51.21 ± 0.47 Aa | |
| EG | 49.34 ± 0.78 Bb | 2.86 ± 0.48 Aa | 2.03 ± 0.18 Aa | 49.22 ± 0.8 Bb | |
| 48 | CK | 50.94 ± 0.75 Abc | 2.92 ± 0.48 ABa | 1.58 ± 0.47 Aa | 50.82 ± 0.73 Ab |
| GG | 51.4 ± 0.51 Aabc | 1.94 ± 0.53 Bb | 1.68 ± 0.44 ABa | 51.32 ± 0.51 Aab | |
| MG | 50.71 ± 0.67 Ac | 1.92 ± 0.45 Ab | 1.52 ± 0.33 Aa | 50.65 ± 0.68 Ab | |
| NG | 51.97 ± 0.5 Aab | 1.67 ± 0.38 Ab | 1.33 ± 0.44 Aa | 51.92 ± 0.49 Aa | |
| EG | 52.37 ± 0.88 Aa | 1.59 ± 0.13 Bb | 1.38 ± 0.36 Ba | 52.32 ± 0.89 Aa |
| Transportation Time/h | Group | ATP (mg/100 g) | ADP (mg/100 g) | IMP (mg/100 g) | Hx (mg/100 g) | AMP (mg/100 g) | HxR (mg/100 g) | K (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | CK | 3.51 ± 0.19 Ba | 1.09 ± 0.05 Aa | 183.37 ± 2.18 Ca | 2.9 ± 0.17 Ba | 5.52 ± 0.08 Ba | 3.97 ± 0.19 Ca | 3.43 ± 0.02 Ba |
| GG | 3.57 ± 0.16 Ba | 1.03 ± 0.07 Aa | 183.99 ± 1.59 Ba | 2.88 ± 0.15 Ba | 5.55 ± 0.07 Aa | 3.94 ± 0.24 Aa | 3.4 ± 0.04 Aa | |
| MG | 3.45 ± 0.1 Ba | 1.06 ± 0.09 Aa | 183.57 ± 2.13 Aa | 2.99 ± 0.16 Aa | 5.5 ± 0.05 Aa | 3.84 ± 0.24 Ba | 3.41 ± 0.05 Aa | |
| NG | 3.56 ± 0.17 Ba | 1.04 ± 0.09 Aa | 182.57 ± 0.94 Ca | 2.98 ± 0.17 Ca | 5.55 ± 0.07 Aa | 3.82 ± 0.21 Ba | 3.41 ± 0.05 Ba | |
| EG | 3.52 ± 0.16 Ca | 1.05 ± 0.08 Aa | 183.38 ± 1.78 Ba | 2.94 ± 0.16 Ba | 5.53 ± 0.07 Aa | 3.89 ± 0.22 Ba | 3.41 ± 0.04 Aa | |
| 24 | CK | 5.57 ± 1.01 Aab | 0.64 ± 0.1 Ba | 202.9 ± 11.32 Ba | 3.52 ± 0.11 Aa | 6.5 ± 0.3 Aa | 4.66 ± 0.13 Ba | 3.66 ± 0.17 ABa |
| GG | 4.63 ± 0.46 Ab | 0.62 ± 0.18 Ba | 200.66 ± 3.34 Aa | 3.46 ± 0.18 ABa | 4.46 ± 1.23 ABb | 4.18 ± 0.14 Aa | 3.51 ± 0.04 Aa | |
| MG | 5.25 ± 0.94 Ab | 0.31 ± 0.03 Bb | 219.03 ± 38.61 Aa | 3.53 ± 0.25 Aa | 3.37 ± 0.99 Bb | 4.11 ± 0.77 ABa | 3.31 ± 0.58 Aa | |
| NG | 6.55 ± 0.12 Aa | 0.34 ± 0.02 Bb | 206.19 ± 3.21 Ba | 3.88 ± 0.17 Ba | 3.82 ± 0.09 Bb | 3.44 ± 0.06 Bb | 3.27 ± 0.1 Ba | |
| EG | 6.56 ± 0.26 Aa | 0.29 ± 0.07 Bb | 198.33 ± 3.74 Ba | 2.21 ± 0.5 Bb | 3.66 ± 0.18 Bb | 3.43 ± 0.07 Cb | 2.63 ± 0.24 Bb | |
| 48 | CK | 3.27 ± 0.41 Bb | 0.55 ± 0.07 Ba | 233.29 ± 14.72 Aa | 4.57 ± 0.68 Aa | 2.82 ± 0.18 Cb | 5.1 ± 0.23 Aa | 3.87 ± 0.23 Aa |
| GG | 4.14 ± 0.86 ABb | 0.28 ± 0.04 Cb | 207.44 ± 8.26 Ab | 4.06 ± 0.76 Aa | 3.42 ± 0.89 Bb | 4.19 ± 0.11 Ac | 3.7 ± 0.46 Aa | |
| MG | 4.02 ± 0.91 Bb | 0.35 ± 0.07 Bb | 208.79 ± 6.14 Ab | 4.29 ± 1.51 Aa | 2.93 ± 0.83 Bb | 4.77 ± 0.36 Aab | 4.03 ± 0.7 Aa | |
| NG | 3.41 ± 0.36 Bb | 0.34 ± 0.07 Bb | 222.03 ± 11.6 Aab | 4.39 ± 0.36 Aa | 2.42 ± 0.16 Cb | 4.32 ± 0.48 Abc | 3.67 ± 0.17 Aa | |
| EG | 5.58 ± 0.29 Ba | 0.36 ± 0.05 Bb | 217.3 ± 18.3 Aab | 4.33 ± 0.67 Aa | 6.13 ± 1.71 Aa | 4.75 ± 0.3 Aab | 3.83 ± 0.44 Aa |
| Target Gene | Primer Sequence (5′→3′) | GenBank Accession Numbers | PCR Product Lengths |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heat shock protein 70 (hsp70) | S: ACACGACTGGTCCATTTCTGC | XM_026208615.1 | 71 |
| A: ACTTCGTTGTCTCTCCGGTC | |||
| Heat shock protein 90 (hsp90) | S: ATGAGGACAAGGACAAACCGAA | KT985291.1 | 138 |
| A: GTCTTGTAGAAGGCTTTGTATCGTC | |||
| Cysteine-aspartic acid protease 3 (caspase 3) | S: ACAGGCATGAACCAACGGAA | XM_026203855.1 | 174 |
| A: ACACACTAACGAAGCACAACG | |||
| Interleukin 6 (il-6) | S: GACGGCTGTCTGTCCAGAAACT | XM_051873835.1 | 132 |
| A: GATGTCGTTGACCAGGGTTGAG | |||
| Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gapdh) | S: AGGCATTCTGGGATACACGGAG | XM_026284269.1 | 242 |
| A: GATGGGAGAACGGTGGGTCA |
| Target Gene | Primer Sequence (5′→3′) | GenBank Accession Numbers | PCR Product Lengths |
| Cysteine-aspartic acid protease 3 (caspase 3) | S: ACAGGCATGAACCAACGGAA | XM_026203855.1 | 174 |
| A: ACACACTAACGAAGCACAACG | |||
| Cysteine-aspartic acid protease 8 (caspase 8) | S: TACGACTGAACGAGCAAGCA | XM_026259219.1 | 141 |
| A: ATGCGTCACGTTGTAGCAGA | |||
| Cysteine-aspartic acid protease 9 (caspase 9) | S: AACAAGACGTGACCAAGCCAG | XM_026241892.1 | 173 |
| A: GCGAAGGCTGTATGGGGACA | |||
| B-cell lymphoma 2 (bcl-2) | S: CTGATGCCTTTTTGGCCGTTG | BAG06937.2 | 182 |
| A: CGACACTAGGCTCTTGCGA | |||
| Bcl-2-associated X protein (bax) | S: CTTTGCGTGTCGGCTTGTC | XM_026262398.1 | 133 |
| A: CTCCCATCCACCCTGTTCC | |||
| Glyceralde-hyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gapdh) | S: AGGCATTCTGGGATACACGGAG | XM_026284269.1 | 242 |
| A: GATGGGAGAACGGTGGGTCA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, L.; Liu, C.; Yin, T.; Xiong, S.; You, J.; Liu, R.; Huang, Q. Mitigating Effect of Ginger Extract on Survival Rate and Muscle Quality of Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus) Under Transportation Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167689
Peng L, Liu C, Yin T, Xiong S, You J, Liu R, Huang Q. Mitigating Effect of Ginger Extract on Survival Rate and Muscle Quality of Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus) Under Transportation Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167689
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Ling, Chaoping Liu, Tao Yin, Shanbai Xiong, Juan You, Ru Liu, and Qilin Huang. 2025. "Mitigating Effect of Ginger Extract on Survival Rate and Muscle Quality of Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus) Under Transportation Stress" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167689
APA StylePeng, L., Liu, C., Yin, T., Xiong, S., You, J., Liu, R., & Huang, Q. (2025). Mitigating Effect of Ginger Extract on Survival Rate and Muscle Quality of Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus) Under Transportation Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167689







