The Relationship Between Microbiota, Nutrition, and Gastrointestinal Tract Symptoms in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Selection Process
2.4. Data Extraction, Date Items, and Result Synthesis
2.5. Quality Assessment
3. Results
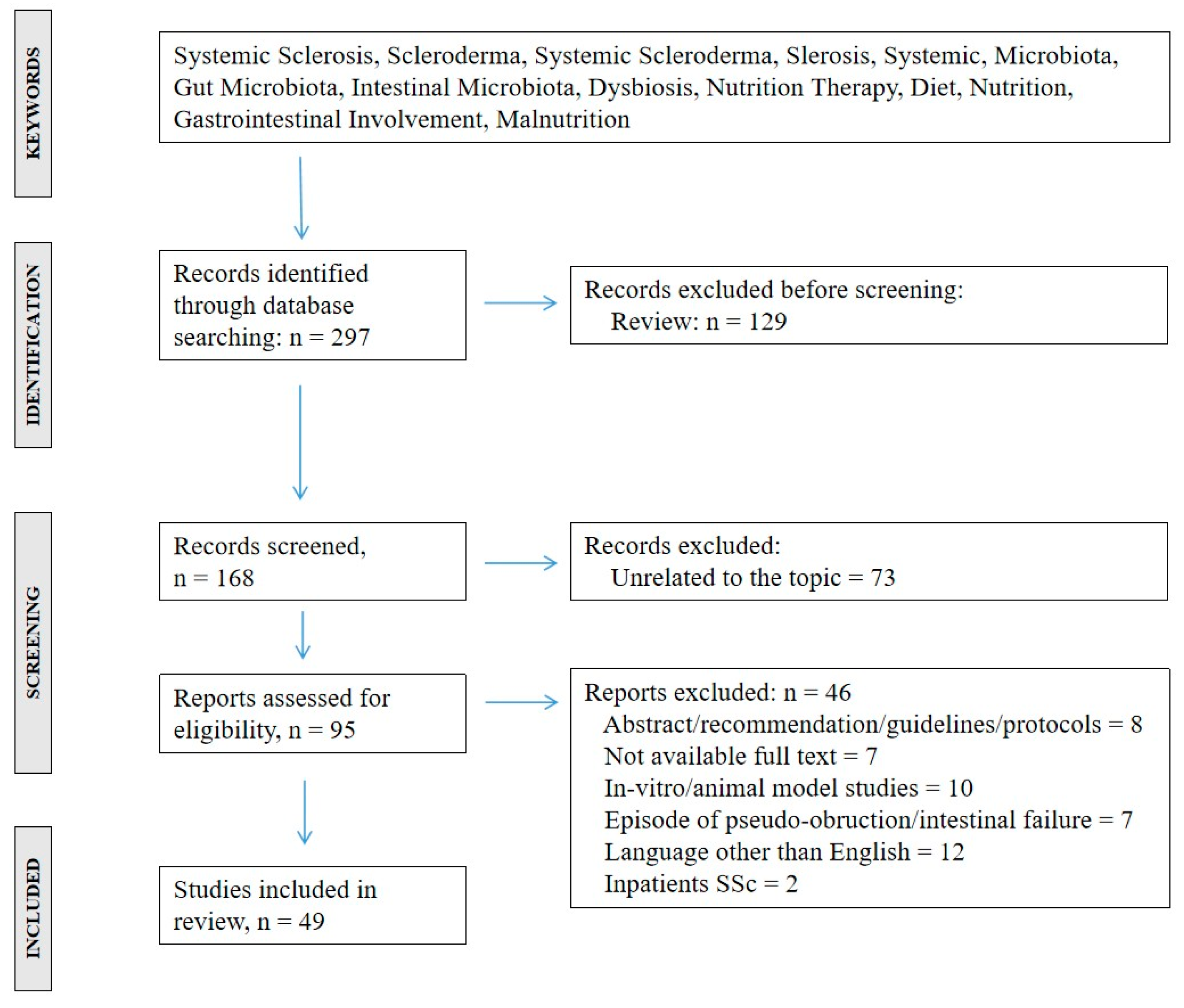
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Relationship Between Gut Microbiota and Gastrointestinal Involvement
| Ref | Sample Size | Age (yrs) | Comparison Group | GM Composition | GM and GI Symptoms’ Relation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [11] | 17 SSc | 52.1 [46.6–63.0] | SSc vs. HCs | ↑ Fusobacterium, γ-Proteobacteria (potential pathobiont) ↑ Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus ↓ Faecalibacterium, Clostridium (commensal bacteria) | N/A |
| 17 HCs | 55.0 [51.0–62.0] | SSc/GI+ vs. SSc/GI− | N/A | ↑Fusobacterium ↓Bacteroides fragilis | |
| [12] | 9 SSc/GI+ | 55.3 [36–79] | SSc/GI− vs. HCs | ↑ Streptococcus salivarius | N/A |
| 9 SSc/GI− | 57.4 [34–78] | SSc/GI+ vs. HCs | N/A | ↑ Lactobacillus, Eubacterium, Acinetobacter ↓ Roseburia, Clostridium, Ruminococcus | |
| 9 HCs | 54.8 [26–78] | SSc/GI− vs. SSc/GI+ | N/A | ↑ Streptococcus salivarius | |
| [13] | 59 SSc | 56.5 ± 12.7 | SSc vs. HCs | ↓ protective butyrate-production bacteria ↑ proinflammatory noxius genera (Desulfovibrio) | N/A |
| 29 HCs | 49.3 ± 12.9 | SSc/GI+ vs. HCs | N7A | 10 different genera between HCs, SSc/GI+, and SSc/GI | |
| [14] | 63 SSc | 52.5 ± 14.2 | SSc vs. HCs | ↑Firmicutes philum, Streptococcus, Lactobacillus, Blautia, Ruminococcus, Phascolarctobacterium genera ↓Sutterella, Bacteroides, Odoribacter, Roseburia genera | N/A |
| 17 HCs | 50.8 ± 14.3 | ||||
| [15] | 19 SSc | 51.3 [48.7–59.4] | ↑ Bacteroides, Prevotella, genera from the Clostridiales order | Bacteroides → Total GI symptoms Prevotella → Diarrhea Genera from Clostridiales order →Distension/ bloating | |
| [16] | 106 SSc 85 HCs | 55.3 ± 15.9 | SSc vs. HCs | ↓ Commensal genera (e.g., Faecalibacterium) ↑ Pathobiont genera (e.g., Desulfovibrio) | SIBO as indicator of dysbiosis in several sites of GI tract |
| [17] | 66 SSc | 55.4 ± 11.8 | SSc/GI+ vs. SSc/GI− | N/A | ↑ Klebsiella, Enterococcus |
| Non-low FODMAP vs. low FODMAP | ↑ Enterococcus | Similar microbial composition and GI symptoms | |||
| [18] | 26 SSc | 64.8 ± 11.9 | SSc vs. HCs | ↑ Acidaminococcaceae and Sutterellaceae families ↓Peptostreptococcaceae family, Anaerostipes, Blautia, Romboutsia, and Turicibacter genera | N/A |
| 18 VEDOSS | 51.7 ± 16.1 | VEDOSS vs. HCs | ↓ Bacilli class, Blautia, Romboutsia, Streptococcus, Turicibacter | N/A | |
| 20 HCs | 50.8 ± 14.3 | VEDOSS vs. SSc | N/A | N/A |
| Ref | Study Design | Sample Size | Age (yrs) | SSc Severity | Intervention Group n (Females) | Comparison Group n (Females) | Treatment Duration | Effects on GI Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [19] | Perspective study. Participants were supplemented with either Align (Bifidobacterium infantis; 10^9 CFU per capsule) or Culturelle (Lactobacillus GG; 10^9 CFU per capsule) once a day | 10 SSc | 51.7 | UCLA STCT GIT 2.0 total score 1.25–3.00 | 10 (9) | - | 2 months supplementation | Improvement in total GIT 2.0 score, reflux, bloating/distention, and emotional scales |
| [20] | RCT placebo controlled. Participants were randomized (1:1) to receive 60 days of high dose multi-strain probiotics (Vivomixx 1800 billion units/day) or identical placebo, followed by an additional 60 days of probiotics in both groups | 40 SSc | UCLA STCT GIT 2.0 total score > 0.10 | 19 (19) | 21 (16) | 60 + 60 days | No change in UCLA STCT GIT 2.0 after 60 or 120 days of treatment Significant improvement in GI-reflux after 120 days | |
| 21 Placebo-Probiotics | 50.7 ± 8.0 | |||||||
| 19 Probiotics-Probiotics | 51.4 ± 13.7 | |||||||
| [21] | RCT placebo controlled. Participants were randomly assigned to receive a daily dose of probiotics (Lactobacillus paracasei, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus acidophillus, and Bifidobacterium lactis, 10^9 CFU per capsule) or placebo for 8 weeks | 73 SSc | UCLA STCT GIT 2.0 total score > 0.50 | 37 (34) | 36 (34) | 8 weeks | No difference in the UCLA STCT GIT 2.0 score after 8 weeks Probiotic group: ↓ Th17 No difference in the Th1, Th2 and regulatory T cells No difference in HAQ-DI score | |
| 37 Probiotic group | 46.7 ± 13.1 | |||||||
| 36 Placebo | 47.1 ± 11.9 | |||||||
| [22] | A double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study | 9 SSc | 62.0 ± 5.7 | UCLA STCT GIT 2.0 total score 0.72 ± 0.5 | 5 FMT | 4 Placebo | 16 week after FMT | FMT with ACHIM reduces lower GI symptoms, altering the GM |
| [23] | A phase 2 randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study | 67 SSc | 58.9 ± 11.5 | UCLA STCT GIT 2.0 total score 0.9 ± 0.5 | 33 (33) ACHIM | 34 (29) Placebo | 12 week after FMT | No change in lower GI symptoms after FMT |
3.4. Relationship Between Malnutrition and Gastrointestinal Involvement
| Ref | Total Sample and Subgroups | Age (yrs) | Criteria, and Total Score of GI Involvement | n (%) of GI Involvement | Malnutrition Criteria | Malnutrition Associations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [8] | 24 SSc | 54 ± 13 | UCLA SCTC GIT 2.0 | 17 (71) | MUST SGA | Malnutrition risk prevalence: 37.5% (MUST) Malnutrition prevalence: 50% (SGA) Malnutrition status was associated with total UCLA SCTC GIT 2.0 score, reflux, distention/bloating, soilage, diarrhea, social function, and emotional well-being |
| [24] | 160 SSc | 61.7 [53.9–68.0] | Medsger's severity scale | 82 (51.2) | BMI | Malnutrition prevalence: 15% Malnutrition was associated with disease activity, low serum prealbumin, but not with GI involvement |
| 24 Malnourished patients | 61.7 [54.0–67.9] | 16 (66.7) | ||||
| 136 No- malnourished patients | 61.1 [47.2–68.5] | 66 (48.5) | ||||
| [25] | 52 SSc 51 HCs | N/A | N/A | N/A | BMI | SSc patients have a lower BMI BMI was associated to quality of life, but not to GI symptoms. GI symptoms was associated with life quality No associations between low BMI and upper GI symptoms (heartburn, nausea, vomiting, dysphagia, and epigastric pain) |
| [26] | 129 SSc | 59.1 ± 13.8 | N/A | N/A | MUST | Malnutrition risk prevalence: 10.9%. Malnutrition was associated with the quality of life |
| [27] | 141 SSc | 63 ± 13 | UCLA SCTC GIT 2.0 | 16 (11.3) | ESPEN | Malnutrition prevalence: 9.2% Sarcopenia prevalence: 20.7% Malnutrition is associated with GI symptoms, low muscularity, reduced FVC, and DLCO Malnutrition and sarcopenia affect disease severity, especially for the lung |
| [28] | 120 SSc | 64 ± 15 | N/A | 111 (93) | MUST PNDS | Malnutrition prevalence: 59.2% Malnutrition risk: 58% Malnutrition was associated with cardiac involvement, number of GI organs involved, gastroesophageal reflux disease, chronic intestinal pseudo obstruction |
| [29] | 62 SSc | 62 [32–78] | N/A | 26 (42) esophageal involvement | ESPEN | Malnutrition prevalence: 19% Sarcopenia prevalence: 42% (RSMI) and 55% (HGS) Sarcopenia was associated with esophageal involvement |
| [30] | 176 Established SSc | 58 [49–67] | UCLA SCTC GIT 2.0 | 231 (92.4) | EUSTAR | Malnutrition prevalence: 48.3% Micronutrients deficiences were very common, especially in folic acid, selenium, prealbumin, and zinc Micronutrient deficiencies was associated with low BMI, but not with GI involvement, except for prealbumin |
| 74 early SSc | 52 [38–61] | |||||
| [31] | 36 postmenopausal female patients with SSc | N/A | N/A | 12 (33) | ESPEN | Malnutrition prevalence: 36.1% ↓weight, BMI, hemoglobin, albumin, parathyroid hormone, 25-hydroxyvitamin D, lumbar spine T-score, bone mineral density values, and trabecular bone score values Bone status correlated with serum biomarkers of malnutrition, and GI symptoms |
| 13 Malnourished patients | 54 [43–75] | |||||
| 23 Non-malnourished patients | 66 [43–85] | |||||
| [32] | 134 SSc | 50.2 ± 12.3 | UCLA SCTC GIT 2.0 (0.24 ± 0.27) | 20 (15) | MUST | Malnutrition risk prevalence: 15% Malnutrition was associated with limited pulmonary function, lung involvement, pulmonary hypertension, capillary rarefaction Capillary rarefaction was independently associated with medium to high malnutrition risk Capillary rarefaction and severe skin involvement were determining factors for malnutrition and GI symptoms |
| [33] | 56 SSc | 54.1 ± 11.9 | N/A | 43 (76.8) | ESPEN 7-SGA SNAQ GLIM | Malnutrition prevalence: 17.9% (ESPEN 2015), 23.2% (7-SGA), 16.1% (SNAQ), and 62.5% (GLIM) Malnutrition was associated with GI symptoms |
| [34] | 98 SSc | 52.7 ± 11.3 | N/A | 14 (14.6) | MUST | Malnutrition prevalence: 100% (including both in- and outpatients) Malnourished patients had high mRSS Malnutrition risk was associated with interstitial lung disease and bowel involvement, and depressive symptoms, but not with GI symptoms |
| [35] | 168 SSc | 61 [25–81] | UCLA SCTC GIT 2.0 (0.9 ± 0.9) | N/A | MUST | Malnutrition prevalence: 16% BMI was associated with small intestinal involvement and disease severity |
| [36] | 102 SSc | 55 ± 14 | N/A | N/A | GLIM ESPEN | Malnutrition prevalence: 8.8% (ESPEN), 16.6% (GLIM) According to GLIM, disease activity index and disease severity scale were associated with malnutrition, but not for ESPEN Malnutrition was not associated with GI symptoms |
| [37] | 60 SSc | 53 [43–63] | UCLA SCTC GIT 2.0 (0.53 [0.19–0.89]) | 9 (13) | ESPEN GLIM | Malnutrition prevalence: 11.6% (ESPEN), 23.2% (GLIM) FFMI, but not malnutrition, was associated with GI symptoms (distension/bloating) |
| [38] | 101 SSc | 55 [47–66] | N/A | 10 (9.9) | GLIM | Malnutrition prevalence: 21.8% Malnutrition according GLIM criteria was associated with GI symptoms, hospitalization, and survival |
| [39] | 100 SSc | 62 [53–70] | UCLA SCTC GIT 2.0 (0.18 [0.04–0.41]) | 20 (20) | GLIM | Malnutrition prevalence: 29% Malnourished patients had increased GI symptoms. GI symptoms was associated with depression score (cognitive impairment prevalence: 50% according Montreal Cognitive Assessment). Malnutrition was associated with age, dysphagia, and mRSS |
| [40] | 75 SSc | 59.6 ± 10.6 | UCLA SCTC GIT 2.0 (0.5 [0.2–1.1]) | 44 (58) | MNA- SF | Malnutrition prevalence: 30.7% Malnutrition was associated with severe GI symptoms, poor quality of life, and skin involvement |
| [41] | 1903 SSc | 47.3 [36.4–57.0] | UCLA SCTC GIT 2.0 (0.5 [0.2–1.0]) | 1389 (73) | GLIM | Malnutrition prevalence: 34% Malnutrition was associated with GI involvement, multimorbidity, cardiopulmonary disease, inflammation, hypoalbuminaemia, and anaemia |
| [42] | 82 SSc | 49.4 ± 13.0 | UCLA SCTC GIT 2.0 (0.50 [0.04–1.49]) | 51 (62.2) | CONUT PNI | CONUT score: 1.45 ± 1.35 PNI: 43.59 ± 5.01 Malnutrition, as measured by CONUT and PNI, was associated with GI involvement |
3.5. Effects of the Nutritional Intervention on Gastrointestinal Involvement
| Ref | Study Sample | Age (yrs) | Study Type (Years) | Nutritional Intervention Type | Nutritional Intervention Duration | Main Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [17] | 66 SSc | 55.4 ± 11.8 | Prospective study (N/A) | Low-FODMAP | 10 days | Similar microbial composition and GI symptoms |
| [43] | 80 SSc | Prospective observational study (2011–2014) | Low fructose diet | 1 month | Fructose malabsorption: 40% Correlation between fructose malabsorption and GSS score and absence of delayed gastric emptying Low-FODMAP: ↓ nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, abdominal tenderness, and GSS score | |
| 32 Fructose malabsorption | 54 [27–79] | |||||
| 48 no-Fructose malaborption | 53 [22–79] | |||||
| [44] | 42 SSc | 52 ± 12 | Prospective observational study (N/A) | Nutritional counseling | N/A | ↑> sodium intake Close association between dietary factors and body composition and GI symptoms. Malnutrition and weight loss were associated with pulmonary hypertension, heart failure, serum albumin, and skin fibrosis, but not advanced age |
| [45] | 18 SSc | 51 ± 11 | Prospective study (N/A) | ON support | 6 week + usual medical therapy | ↓Nutrition symptom scores (12.8 vs. 7.6), and sarcopenia (54% vs. 39%) ↑ Appendicular lean height (5.6 ± 0.8 vs. 5.8 ± 0.8 kg/m2) No changes in caloric intake (1400 vs. 1577 kcal/d) and macronutrient distribution (% fat, protein, carbohydrate) |
| [46] | 10+ SSc | 63 ± 12 | Prospective study (N/A) | Counselling + ON support | 12 months | Dietary intervention maintained body weight and food intake No change in nutritional biochemical parameters, psychopathology and quality of life |
| [47] | 15 SSc | N/A | Retrospective study (1979–1987) | PN support | 2–90 months | ↑ Quality of life Complications: catheter-related septicaemia (13%), superior vena cava obstruction (13%). 46% dead, none directly from GI disease or from the PN |
| [48] | 5 SSc | - | Cases Reports | PN (4 cases) and EN (1 case) support | PN: 12–86 months EN: 16 months | ↑ nutritional status, BMI, quality of life 60% dead from their disease |
| [49] | 8 SSc | 51 [42–56] | Retrospective comparative study (1993–2006) | PN support | 40 [0.8–192] months | Complication: catheter-related infection (25%), line infection (25%), loss of autonomy (75%) |
| [50] | 12 SSc | 49 ± 4 | Retrospective study (1998–2010) | HTPN support | 5–270 months | ↑ BMI: from 16.8 [12.3–21.3] kg/m2 to 18.3 [17.0–21.7] kg/m2 at 6 months and 19.7 [17.0-24.6] kg/m2 at 12 months No change in Karnofsky score (from 58.00 ± 3.27 to 39.00 ± 13.29 at 12 months) |
| [51] | 25 SSc | 55 [24–79] | Retrospective study (1990–1992) | PN support | 3 months | Nutritional intervention duration: Mortality: 25% at 2-, 63% at 5-, and 77% at 10- years, but none directly from the PN Complication: catheter-related occlusion, sepsis, and thrombosis |
| [52] | 5 SSc | 62.2 | Retrospective study (2008–2013) | PN support | 12 months | ↓Nutritional risk screening score (from 4.4 [4,5] to 1.4 [1,2] ↑BMI (from 19.1 [17.4–20.3] kg/m2 to 21.0 [18.3–23.4] kg/m2 ↑ Quality of life Complication: catheter-related infection (40%) |
3.6. Systemic Sclerosis and Predictors of Mortality
| Ref | Sample Size | Age (yrs) | Follow up | Predictor factors of Mortality | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [36] | 101 SSc | 55 [47–66] | 48 months | Malnutrition according GLIM criteria | 4.38 (1.70–11.24) | 0.002 |
| [53] | 124 SSc | 54.0 ± 13.0 | 14.9 ± 6.7 months | Malnutrition | N/A | - |
| 295 HCs | 48.2 ± 11.8 | |||||
| [54] | 160 SSc | 62 [54–68] | 46 months | Disease activity | 6.3 (1.8–21.7) | 0.004 |
| MUST | 8.3 (2.1–32.1) | 0.002 | ||||
| [55] | 299 SSc | 61 ± 11.8 | 48 [25–58] months | Low prealbumin | 3.00 (1.52–5.97) | 0.002 |
| Lung involvement | 5.00 (2.45–10.34) | <0.001 | ||||
| Multiple visceral organ involvement | 3.94 (2.01–7.74) | <0.001 | ||||
| [56] | 349 SSc | 46.2 ± 4.1 | 2.1 years | Smoking | 4.0 (1.5–10.6) | ≤0.05 |
| SSc-overlap | 6.0 (1.8–19.1) | ≤0.05 | ||||
| Baseline renal involvement | 2.5 (2.2–11.7) | ≤0.05 | ||||
| PAP ≥ 40 mmHg | 2.6 (1.1–6.5) | ≤0.05 | ||||
| Peripheral vasculopathy therapy | 2.6 (1.1–6.5) | ≤0.05 | ||||
| Parenteral nutrition | 8.8 (2.2–34.3) | ≤0.05 | ||||
| [57] | 220 SSc | 51.16 ± 14.52 | 5.85 ± 4.10 years | Gener, male | 5.84 (1.31–26.00) | 0.020 |
| Severe malnutrition | 3.77 (1.23–11.06) | 0.021 | ||||
| Severe general symptoms | 5.12 (1.74–14-97) | 0.003 | ||||
| [58] | 104 SSc | 55 [45–66] | 48 months | Bioelectrical impedence analysis-derived phase angle | 0.283 (0.083–0.965) | 0.044 |
4. Discussion
5. Future Perspectives and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SSc | Systemic Sclerosis |
| HCs | Healthy Controls |
| GM | Gut Microbiota |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| SIBO | Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth |
| VEDOSS | Very Early Diagnosis of Systemic Sclerosis |
| ILD | Interstitial Lung Disease |
| FMT | Fecal Microbiota Transplantation |
| UCLA GIT 2.0 | University of California Los Angeles Scleroderma Clinical Trials Consortium Gastrointestinal Tract 2.0 |
| ONS | Oral Nutrition Support |
| EN | Enteral Nutrition |
| PN | Parenteral Nutrition |
| MUST | Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool |
| ESPEN | European Society of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism |
| GLIM | Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition |
| SNAQ | Short Nutritional Assessment Questionnaire |
| 7-SGA | Subjective Global Assessment, 1–7 points |
| RCTs | Randomized Controlled Trials |
| SCFA | Short-Chain Fatty Acid |
References
- Benfaremo, D.; Svegliati, S.; Paolini, C.; Agarbati, S.; Moroncini, G. Systemic Sclerosis: From Pathophysiology to Novel Therapeutic Approaches. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahan, Z.H. Gastrointestinal involvement in systemic sclerosis: An update. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2019, 31, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahan, Z.H.; Hummers, L.K. Gastrointestinal involvement in systemic sclerosis: Diagnosis and management. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2018, 30, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann-Vold, A.M.; Volkmann, E.R. Gastrointestinal involvement in systemic sclerosis: Effects on morbidity and mortality and new therapeutic approaches. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2021, 6, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakkas, L.I.; Simopoulou, T.; Daoussis, D.; Liossis, S.N.; Potamianos, S. Intestinal Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis: A Clinical Review. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmann, E.R. Intestinal microbiome in scleroderma: Recent progress. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2017, 29, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrisroe, K.; Baron, M.; Frech, T.; Nikpour, M. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in systemic sclerosis. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2020, 5, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaugh, M.A.; Frech, T.M. Nutritional status and gastrointestinal symptoms in systemic sclerosis patients. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Pakeerathan, V.; Jones, M.P.; Kashyap, P.C.; Virgo, K.; Fairlie, T.; Morrison, M.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Holtmann, G.J. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Complicating Gastrointestinal Manifestations of Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2023, 29, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkmann, E.R.; Chang, Y.; Barroso, N.; Furst, D.E.; Clements, P.J.; Gorn, A.H.; Roth, B.E.; Conklin, J.L.; Getzug, T.; Borneman, J.; et al. Association of Systemic Sclerosis with a Unique Colonic Microbial Consortium. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrone, V.; Puglisi, E.; Cardinali, M.; Schnitzler, T.S.; Svegliati, S.; Festa, A.; Gabrielli, A.; Morelli, L. Gut microbiota profile in systemic sclerosis patients with and without clinical evidence of gastrointestinal involvement. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellocchi, C.; Fernández-Ochoa, Á.; Montanelli, G.; Vigone, B.; Santaniello, A.; Milani, C.; Quirantes-Piné, R.; Borrás-Linares, I.; Ventura, M.; Segura-Carrettero, A.; et al. Microbial and metabolic multi-omic correlations in systemic sclerosis patients. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1421, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalello, G.; Bosello, S.L.; Sterbini, F.P.; Posteraro, B.; De Lorenzis, E.; Canestrari, G.B.; Gigante, L.; Verardi, L.; Ferraccioli, G.; Sanguinetti, M.; et al. Gut microbiota analysis in systemic sclerosis according to disease characteristics and nutritional status. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Volkmann, E.R.; Hoffmann-Vold, A.M.; Chang, Y.L.; Lagishetty, V.; Clements, P.J.; Midtvedt, Ø.; Molberg, Ø.; Braun, J.; Jacobs, J.P. Longitudinal Characterisation of the Gastrointestinal Tract Microbiome in Systemic Sclerosis. Eur. Med. J. 2020, 7, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andréasson, K.; Lee, S.M.; Lagishetty, V.; Wu, M.; Howlett, N.; English, J.; Hesselstrand, R.; Clements, P.J.; Jacobs, J.P.; Volkmann, E.R. Disease Features and Gastrointestinal Microbial Composition in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis from Two Independent Cohorts. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2022, 4, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.D.; Andréasson, K.; McMahan, Z.H.; Bukiri, H.; Howlett, N.; Lagishetty, V.; Lee, S.M.; Jacobs, J.P.; Volkmann, E.R. Gastrointestinal tract involvement in systemic sclerosis: The roles of diet and the microbiome. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2023, 60, 152185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellando-Randone, S.; Russo, E.; Di Gloria, L.; Lepri, G.; Baldi, S.; Fioretto, B.S.; Romano, E.; Ghezzi, G.; Bertorello, S.; El Aoufy, K.; et al. Gut microbiota in very early systemic sclerosis: The first case-control taxonomic and functional characterisation highlighting an altered butyric acid profile. RMD Open 2024, 10, e004647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frech, T.M.; Khanna, D.; Maranian, P.; Frech, E.J.; Sawitzke, A.D.; Murtaugh, M.A. Probiotics for the treatment of systemic sclerosis-associated gastrointestinal bloating/ distention. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2011, 29, S22–S25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Low, A.H.L.; Teng, G.G.; Pettersson, S.; de Sessions, P.F.; Ho, E.X.P.; Fan, Q.; Chu, C.W.; Law, A.H.N.; Santosa, A.; Lim, A.Y.N.; et al. A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial of probiotics in systemic sclerosis associated gastrointestinal disease. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 49, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marighela, T.F.; Arismendi, M.I.; Marvulle, V.; Brunialti, M.K.C.; Salomão, R.; Kayser, C. Concise report Effect of probiotics on gastrointestinal symptoms and immune parameters in systemic sclerosis: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 1985–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fretheim, H.; Chung, B.K.; Didriksen, H.; Bækkevold, E.S.; Midtvedt, Ø.; Brunborg, C.; Holm, K.; Valeur, J.; Tennøe, A.H.; Garen, T.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation in systemic sclerosis: A double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized pilot trial. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fretheim, H.; Barua, I.; Bakland, G.; Dhainaut, A.; Halse, A.-K.; Carstens, M.N.; Didriksen, H.; Midtvedt, Ø.; E A Lundin, K.; Aabakken, L.; et al. Faecal microbiota transplantation in patients with systemic sclerosis and lower gastrointestinal tract symptoms in Norway (ReSScue): A phase 2, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Rheumatol. 2025, 7, e323–e332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporali, R.; Caccialanza, R.; Bonino, C.; Klersy, C.; Cereda, E.; Xoxi, B.; Crippa, A.; Rava, M.L.; Orlandi, M.; Bonardi, C.; et al. Disease-related malnutrition in outpatients with systemic sclerosis. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skare, T.; Culpi, M.; Yokoo, P.; Dias, M. Gastrointestinal symptoms in scleroderma patients and its influence in body mass index and quality of life. Acta Reum. Port. 2014, 39, 242–247. [Google Scholar]
- Preis, E.; Franz, K.; Siegert, E.; Makowka, A.; March, C.; Riemekasten, G.; Cereda, E.; Norman, K. The impact of malnutrition on quality of life in patients with systemic sclerosis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caimmi, C.; Caramaschi, P.; Venturini, A.; Bertoldo, E.; Vantaggiato, E.; Viapiana, O.; Ferrari, M.; Lippi, G.; Frulloni, L.; Rossini, M. Malnutrition and sarcopenia in a large cohort of patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilic, D.T.; Akdogan, A.; Kilic, L.; Sari, A.; Erden, A.; Armagan, B.; Kilickaya, M.; Kalyoncu, U.; Turhan, T.; Kiraz, S.; et al. Evaluation of Vitamin B12 Deficiency and Associated Factors in Patients With Systemic Sclerosis. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 24, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corallo, C.; Fioravanti, A.; Tenti, S.; Pecetti, G.; Nuti, R.; Giordano, N. Sarcopenia in systemic sclerosis: The impact of nutritional, clinical, and laboratory features. Rheumatol. Int. 2019, 39, 1767–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Läubli, J.; Dobrota, R.; Maurer, B.; Jordan, S.; Misselwitz, B.; Fox, M.; Distler, O. Impaired micronutrients and prealbumin in patients with established and very early systemic sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Paolino, S.; Pacini, G.; Schenone, C.; Patanè, M.; Sulli, A.; Sukkar, S.G.; Lercara, A.; Pizzorni, C.; Gotelli, E.; Cattelan, F.; et al. Nutritional Status and Bone Microarchitecture in a Cohort of Systemic Sclerosis Patients. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcinkaya, Y.; Erturk, Z.; Unal, A.U.; Kaymaz Tahra, S.; Pehlivan, O.; Atagunduz, P.; Direskeneli, H.; Inanç, N. The assessment of malnutrition and severity of gastrointestinal disease by using symptom-based questionnaires in systemic sclerosis: Is it related to severe organ involvement or capillary rarefaction at microcirculation? Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Wojteczek, A.; Dardzińska, J.A.; Małgorzewicz, S.; Gruszecka, A.; Zdrojewski, Z. Prevalence of malnutrition in systemic sclerosis patients assessed by different diagnostic tools. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türk, İ.; Cüzdan, N.; Çiftçi, V.; Arslan, D.; Doğan, M.C.; Unal, İ. Malnutrition, associated clinical factors, and depression in systemic sclerosis: A cross-sectional study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hvas, C.L.; Harrison, E.; Eriksen, M.K.; Herrick, A.L.; McLaughlin, J.T.; Lal, S. Nutritional status and predictors of weight loss in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 40, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosato, E.; Gigante, A.; Gasperini, M.L.; Proietti, L.; Muscaritoli, M. Assessing Malnutrition in Systemic Sclerosis With Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition and European Society of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism Criteria. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2021, 45, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosato, E.; Gigante, A.; Pellicano, C.; Villa, A.; Iannazzo, F.; Alunni Fegatelli, D.; Muscaritoli, M. Symptoms related to gastrointestinal tract involvement and low muscularity in systemic sclerosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 41, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosato, E.; Gigante, A.; Colalillo, A.; Pellicano, C.; Alunni Fegatelli, D.; Muscaritoli, M. GLIM-diagnosed malnutrition predicts mortality and risk of hospitalization in systemic sclerosis: A retrospective study. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 117, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfaremo, D.; Pacenti, N.; Paterno, I.; Dichiara, C.; Galli, F.L.; Moroncini, G. Role of cognitive impairment and malnutrition as determinants of quality of life in patients with systemic sclerosis. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2024, 9, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano-García, L.; Redondo-Rodríguez, R.; Mena-Vázquez, N.; Manrique-Arija, S.; García-Studer, A.; Ortiz-Marquez, F.; Borregón-Garrido, P.; Fernández-Nebro, A. Severity and impact of digestive impairment perceived by patients with systemic sclerosis: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e083419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairley, J.L.; Hansen, D.; Quinlivan, A.; Proudman, S.; Sahhar, J.; Ngian, G.-S.; Walker, J.; Host, L.V.; Morrisroe, K.; Stevens, W.; et al. Frequency and implications of malnutrition in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2025, 64, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öz, N.; Gezer, H.H.; Karabulut, Y.; Duruöz, M.T. Association of nutritional status indices with gastrointestinal symptoms in systemic sclerosis: A cross-sectional study. Rheumatol. Int. 2025, 45, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marie, I.; Leroi, A.M.; Gourcerol, G.; Levesque, H.; Ménard, J.F.; Ducrotte, P. Fructose Malabsorption in Systemic Sclerosis. Medicine 2015, 94, e1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlui, A.M.; Cardoneanu, A.; Macovei, L.A.; Rezus, C.; Boiculese, L.V.; Graur, M.; Rezus, E. Diet Scleroderma: Is There A Need Interv? Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerfler, B.; Allen, T.S.; Southwood, C.; Brenner, D.; Hirano, I.; Sheean, P. Medical Nutrition Therapy for Patients With Advanced Systemic Sclerosis (MNT PASS): A Pilot Intervention Study. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2017, 41, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Santamaria, V.; Puig, C.; Soldevillla, C.; Barata, A.; Cuquet, J.; Recasens, A. Nutritional support in patients with systemic sclerosis. Reum. Clin. 2014, 10, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.C.; Clements, P.J.; Berquist, W.E.; Furst, D.E.; Paulus, H.E. Home central venous hyperalimentation in fifteen patients with severe scleroderma bowel disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1989, 32, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, G.; Grant, J.P. Nutritional support in patients with systemic scleroderma. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1989, 13, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.; Teubner, A.; Shaffer, J.; Herrick, A.L. Home parenteral nutrition–an effective and safe long-term therapy for systemic sclerosis-related intestinal failure. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jawa, H.; Fernandes, G.; Saqui, O.; Allard, J.P. Home parenteral nutrition in patients with systemic sclerosis: A retrospective review of 12 cases. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 1004–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E.; Herrick, A.L.; Dibb, M.; McLaughlin, J.T.; Lal, S. Long-term outcome of patients with systemic sclerosis requiring home parenteral nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanga, Z.; Aeberhard, C.; Scharer, P.; Kocher, A.; Adler, S.; Villiger, P.M. Home parenteral nutrition is beneficial in systemic sclerosis patients with gastrointestinal dysfunction. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 45, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, L.; O Becker, M.; Brueckner, C.S.; Bellinghausen, C.-J.; Becker, C.; Schneider, U.; Haeupl, T.; Hanke, K.; Hensel-Wiegel, K.; Ebert, H.; et al. Nutritional status as marker for disease activity and severity predicting mortality in patients with systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1951–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cereda, E.; Codullo, V.; Klersy, C.; Breda, S.; Crippa, A.; Rava, M.L.; Orlandi, M.; Bonardi, C.; Fiorentini, M.L.; Caporali, R.; et al. Disease-related nutritional risk and mortality in systemic sclerosis. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codullo, V.; Cereda, E.; Klersy, C.; Cavazzana, I.; Alpini, C.; Bonardi, C.; Turri, A.; Franceschini, F.; Caccialanza, R.; Montecucco, C.; et al. Serum prealbumin is an independent predictor of mortality in systemic sclerosis outpatients. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosa, A.; Tan, C.S.; Teng, G.G.; Fong, W.; Lim, A.; Law, W.G.; Chan, G.; Ng, S.C.; Low, A. Lung and gastrointestinal complications are leading causes of death in SCORE, a multi-ethnic Singapore systemic sclerosis cohort. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 45, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Domínguez, M.P.; García-Collinot, G.; Saavedra, M.A.; Montes-Cortes, D.H.; Morales-Aguilar, R.; Carranza-Muleiro, R.A.; Vera-Lastra, O.L.; Jara, L.J. Malnutrition is an independent risk factor for mortality in Mexican patients with systemic sclerosis: A cohort study. Rheumatol. Int. 2017, 37, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosato, E.; Gigante, A.; Pellicano, C.; Colalillo, A.; Alunni-Fegatelli, D.; Muscaritoli, M. Phase angle, nutritional status, and mortality in systemic sclerosis: An exploratory pilot study. Nutrition 2023, 107, 111946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codullo, V.; Cereda, E.; Crepaldi, G.; Cappello, S.; Montecucco, C.; Caccialanza, R.; Caporali, R. Disease-related malnutrition in systemic sclerosis: Evidences and implications. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, S190–S194. [Google Scholar]
- Savarino, E.; Furnari, M.; de Bortoli, N.; Martinucci, I.; Bodini, G.; Ghio, M.; Savarino, V. Gastrointestinal involvement in systemic sclerosis. Presse Med. 2014, 43, e279–e291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, M.; Heal, C.; Siegert, E.; Hachulla, E.; Airó, P.; Riccardi, A.; Distler, O.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; EUSTAR Collaborators. Significant weight loss in systemic sclerosis: A study from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1123–1125, Erratum in Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, e34. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217035corr1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratton, R.J.; Hackston, A.; Longmore, D.; Dixon, R.; Price, S.; Stroud, M.; King, C.; Elia, M. Malnutrition in hospital outpatients and inpatients: Prevalence, concurrent validity and ease of use of the ‘malnutrition universal screening tool’ (‘MUST’) for adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, T.; Bosaeus, I.; Barazzoni, R.; Bauer, J.; Van Gossum, A.; Klek, S.; Muscaritoli, M.; Nyulasi, I.; Ockenga, J.; Schneider, S.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for malnutrition—An ESPEN Consensus Statement. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.I.T.D.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.J.; et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition—A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruizenga, H.M.; Seidell, J.C.; de Vet, H.C.; Wierdsma, N.J.; van Bokhorst-de van der Schueren, M.A. Development and validation of a hospital screening tool for malnutrition: The short nutritional assessment questionnaire (SNAQ). Clin. Nutr. 2005, 24, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, F.J.; Daniel de Mello, P.; Daniel de Mello, E. Subjective global assessment of nutritional status—A systematic review of the literature. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmann, E.R.; Hoffmann-Vold, A.-M.; Chang, Y.-L.; Jacobs, J.P.; Tillisch, K.; A Mayer, E.; Clements, P.J.; Hov, J.R.; Kummen, M.; Midtvedt, Ø.; et al. Systemic sclerosis is associated with specific alterations in gastrointestinal microbiota in two independent cohorts. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2017, 4, e000134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellocchi, C.; Volkmann, E.R. Update on the Gastrointestinal Microbiome in Systemic Sclerosis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2018, 20, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panopoulos, S.; Bournia, V.K.; Konstantonis, G.; Fragiadaki, K.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Tektonidou, M.G. Predictors of morbidity and mortality in early systemic sclerosis: Long-term follow-up data from a single-centre inception cohort. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavesio, Y.M.; Pasta, A.; Calabrese, F.; Alessandri, E.; Cutolo, M.; Paolino, S.; Pizzorni, C.; Sulli, A.; Savarino, V.; Giannini, E.G.; et al. Association between esophageal motor disorders and pulmonary involvement in patients affected by systemic sclerosis: A retrospective study. Rheumatol. Int. 2024, 44, 2905–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaffi, F.; Di Carlo, M.; Carotti, M.; Fraticelli, P.; Gabrielli, A.; Giovagnoni, A. Relationship between interstitial lung disease and oesophageal dilatation on chest high-resolution computed tomography in patients with systemic sclerosis: A cross-sectional study. Radiol. Med. 2018, 123, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, R.; Yamamichi, N.; Shimamoto, T.; Sumida, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Minatsuki, C.; Kodashima, S.; Ono, S.; Niimi, K.; Tsuji, Y.; et al. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease-Related Disorders of Systemic Sclerosis Based on the Analysis of 66 Patients. Digestion 2018, 98, 01–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teaw, S.; Hinchcliff, M.; Cheng, M. A review and roadmap of the skin, lung and gut microbiota in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 5498–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccia, C.; Bonomi, F.; Cricchio, A.L.; Russo, E.; Peretti, S.; Bandini, G.; Lepri, G.; Bartoli, F.; Moggi-Pignone, A.; Guiducci, S.; et al. The Potential Role of Butyrate in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pessemier, B.; Grine, L.; Debaere, M.; Maes, A.; Paetzold, B.; Callewaert, C. Gut-Skin Axis: Current Knowledge of the Interrelationship between Microbial Dysbiosis and Skin Conditions. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, D.; Li, S.; Wang, N.; Tan, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Y. The Cross-Talk Between Gut Microbiota and Lungs in Common Lung Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yao, Q.; Tan, W.; Bai, F. Gut microbiome and metabolomics in systemic sclerosis: Feature, link and mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1475528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.L.; Garcia-Reyero, N.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Tubbs, C.W.; Bisesi, J.H., Jr. Regulation of endocrine systems by the microbiome: Perspectives from comparative animal models. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 292, 113437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagliaro, G.; Battino, M. The use of probiotics in gastrointestinal diseases. Mediterr. J. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 3, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Sharma, P.K.; Malviya, R. Prebiotics: Future Trends Health care. Mediterr. J. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 5, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, S.W.; Low, A.H.L. Is faecal microbiota transplantation ready for prime time in systemic sclerosis? Lancet Rheumatol. 2025, 7, e305–e307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.C.; Noviani, M.; Leung, Y.Y.; Low, A.H.L. The microbiome and systemic sclerosis: A review of current evidence. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 35, 101687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, E.; Herrick, A.L.; McLaughlin, J.T.; Lal, S. Malnutrition in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radić, M.; Kolak, E.; Đogaš, H.; Gelemanović, A.; Bučan Nenadić, D.; Vučković, M.; Radić, J. Body composition parameters in systemic sclerosis-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2024, 63, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grygiel-Górniak, B.; Puszczewicz, M. Oxidative damage and antioxidative therapy in systemic sclerosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 389582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönenberger, K.A.; Schüpfer, A.C.; Gloy, V.L.; Hasler, P.; Stanga, Z.; Kaegi-Braun, N.; Reber, E. Effect of Anti-Inflammatory Diets on Pain in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanesco, S.; Hall, W.; Gibson, R.; Griffiths, C.; Maruthappu, T. Approaches to nutrition intervention in plaque psoriasis, a multi-system inflammatory disease-The Diet and Psoriasis Project (DIEPP). Nutr Bull. 2022, 47, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jarr, K.; Layton, C.; Gardner, C.D.; Ashouri, J.F.; Abreu, M.T.; Sinha, S.R. Therapeutic Implications of Diet in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Related Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Nutrients 2021, 13, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidurrizaga-De Amezaga, C.A.; Zulet, M.A.; Marti, A.; Martinez-Gonzalez MAMartinez, J.A. The Mediterranean food pattern: A good recipe for patients with the metabolic syndrome. Mediterr. J. Nutr. Metab. 2008, 1, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Covas, M.-I.; Corella, D.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Ruiz-Gutiérrez, V.; Fiol, M.; Lapetra, J.; et al. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease with a Mediterranean diet. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargin, D.; Tomaino, L.; Serra-Majem, L. Experimental Outcomes of the Mediterranean Diet: Lessons Learned from the Predimed Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, M.K.; Sebastian, R.S.; Goldman, J.D.; Wilkinson Enns, C.; Moshfegh, A.J. Consuming Vegetable-Based Salad Is Associated with Higher Nutrient Intakes and Diet Quality among US Adults, What We Eat in America, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2014. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2019, 119, 2085–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippis, F.; Pellegrini, N.; Vannini, L.; Jeffery, I.B.; La Storia, A.; Laghi, L.; Serrazanetti, D.I.; Di Cagno, R.; Ferrocino, I.; Lazzi, C.; et al. High-level adherence to a Mediterranean diet beneficially impacts the gut microbiota and associated metabolome. Gut 2016, 65, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gori, F.; Tomaino, L.; La Vecchia, C.; Servida, S.; Vigna, L. The Relationship Between Microbiota, Nutrition, and Gastrointestinal Tract Symptoms in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167685
Gori F, Tomaino L, La Vecchia C, Servida S, Vigna L. The Relationship Between Microbiota, Nutrition, and Gastrointestinal Tract Symptoms in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Review of the Literature. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167685
Chicago/Turabian StyleGori, Francesca, Laura Tomaino, Carlo La Vecchia, Simona Servida, and Luisella Vigna. 2025. "The Relationship Between Microbiota, Nutrition, and Gastrointestinal Tract Symptoms in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Review of the Literature" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167685
APA StyleGori, F., Tomaino, L., La Vecchia, C., Servida, S., & Vigna, L. (2025). The Relationship Between Microbiota, Nutrition, and Gastrointestinal Tract Symptoms in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Review of the Literature. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167685







