Dietary Supplementation with Probiotics Alleviates Intestinal Injury in LPS-Challenged Piglets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Growth Performance and Diarrhea Incidence
2.2. Prostaglandin (PG) and Cortisol (COR) in Serum
2.3. D-Xylose Concentration and Diamine Oxidase (DAO) Activity in Plasma
2.4. Morphological Characterization of the Small Intestine
2.5. Disaccharidase and Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) Activity in the Small Intestine
2.6. mRNA Levels for Genes in the Small Intestine
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals and Design
4.2. Prostaglandin (PG) and Cortisol (COR) in Serum
4.3. D-Xylose Concentration and Diamine Oxidase (DAO) Activity in Plasma
4.4. Intestinal Morphology Analysis
4.5. Disaccharidase Activity in the Small Intestine
4.6. Activity of Intestinal Mucosa Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis of mRNA
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abraham, B.P.; Quigley, E.M.M. Probiotics in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 2017, 46, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Goldenberg, J.Z.; Humphrey, C.; El Dib, R.; Johnston, B.C. Probiotics for the prevention of pediatric antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 4, CD004827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, R.; Mainardi, E. Prebiotics and Probiotics Supplementation in Pigs as a Model for Human Gut Health and Disease. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shamshirgaran, M.A.; Golchin, M.; Mohammadi, E. Lactobacillus casei displaying Clostridium perfringens NetB antigen protects chickens against necrotic enteritis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 6441–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Z. Dietary Additive Probiotics modulation of the intestinal microbiota. Protein Pept. Lett. 2017, 24, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazziotta, C.; Tognon, M.; Martini, F.; Torreggiani, E.; Rotondo, J.C. Probiotics Mechanism of Action on Immune Cells and Beneficial Effects on Human Health. Cells 2023, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pereira, W.A.; Franco, S.M.; Reis, I.L.; Mendonça, C.M.N.; Piazentin, A.C.M.; Azevedo, P.O.S.; Tse, M.L.P.; De Martinis, E.C.P.; Gierus, M.; Oliveira, R.P.S. Beneficial effects of probiotics on the pig production cycle: An overview of clinical impacts and performance. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 269, 109431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokryazdan, P.; Faseleh Jahromi, M.; Liang, J.B.; Ho, Y.W. Probiotics: From isolation to application. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2017, 36, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, S.K.; El-Bedewy, M.M. Effect of probiotics on pro-inflammatory cytokines and NF-kappaB activation in ulcerative colitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 4145–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, R.X.; Lee, S.I.; Kim, I.H. Effects of multistrain probiotics on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, blood profiles, faecal microbial shedding, faecal score and noxious gas emission in weaning pigs. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 100, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Ding, Z.; Shi, H.; Qian, W.; Hou, X.; Lin, R. The Role of probiotics in lipopolysaccharide-induced autophagy in intestinal epithelial cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 2464–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liao, L.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, P.; Chen, X.; Liu, F. Lactobacillus casei LC01 Regulates Intestinal Epithelial Permeability through miR-144 Targeting of OCLN and ZO1. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Eun, C.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Han, D.S.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, A.R.; Park, Y.K. Lactobacillus casei prevents impaired barrier function in intestinal epithelial cells. Apmis 2011, 119, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, R.; Kim, I.H. Effects of Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis complex on growth performance and faecal noxious gas emissions in growing-finishing pigs. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 1554–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Wang, X.; Duan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Azad, M.A.K.; Wang, Z.; Blachier, F.; Kong, X. Dietary Supplementation With Bacillus subtilis Promotes Growth and Gut Health of Weaned Piglets. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 600772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yeung, C.Y.; Chiang Chiau, J.S.; Chan, W.T.; Jiang, C.B.; Cheng, M.L.; Liu, H.L.; Lee, H.C. In vitro prevention of salmonella lipopolysaccharide-induced damages in epithelial barrier function by various lactobacillus strains. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2013, 2013, 973209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Hou, M.; Gao, T.; Sun, J.; Luo, H.; Wang, F.; Zhong, F.; Ma, A.; Cai, J. Lactobacillus casei Improve Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs-Induced Intestinal Adverse Reactions in Rat by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhao, D.; Wu, T.; Yi, D.; Wang, L.; Li, P.; Zhang, J.; Wu, G. Dietary Supplementation with Lactobacillus casei alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury in a porcine model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, D.; Hou, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, D.; Ding, B.; Wu, T.; Wu, G. Gene expression profiles in the intestine of lipopolysaccharide-challenged piglets. Front. Biosci. 2016, 21, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, Q.; Chang, J.; Yin, Q.; Song, A.; Li, Z.; Lu, F. Effects of lactobacillus casei and enterococcus faecalis on growth performance, immune function and gut microbiota of suckling piglets. Archiv. Fã¼r Tierernaehrung. 2017, 71, 120–133. [Google Scholar]
- Zong, X.; Wang, T.H.; Lu, Z.Q.; Song, D.G.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.Z. Effects of clostridium butyricum or in combination with bacillus licheniformis on the growth performance, blood indexes, and intestinal barrier function of weanling piglets. Livest. Sci. 2019, 220, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Z.; Ding, B.; Zhu, H.; Wu, G. Protective effects of N-acetylcysteine on intestinal functions of piglets challenged with lipopolysaccharide. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholzen, T.; Gerdes, J. The Ki-67 protein: From the known and the unknown. J. Cell. Physiol. 2000, 182, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Men, X.; Xu, Z. Probiotics and probiotic metabolic product improved intestinal function and ameliorated LPS-induced injury in rats. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Li, X.; Rezaei, R.; Meininger, C.J.; McNeal, C.J.; Wu, G. Safety of long-term dietary supplementation with L-arginine in pigs. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.M.; Lee, E.K.; Gong, S.Y.; Sohng, J.K.; Kang, Y.J.; Jung, H.J. Sparassis crispa exerts anti-inflammatory activity via suppression of TLR-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophage cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 231, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, L.; Yi, D.; Ding, B.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, G. N-acetylcysteine reduces inflammation in the small intestine by regulating redox, EGF and TLR4 signaling. Amino Acids 2013, 45, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozovic, D.; Racic, M.; Ivkovic, N. Salivary cortisol levels as a biological marker of stress reaction. Med. Arch. 2013, 67, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funk, C.D. Prostaglandins and leukotrienes: Advances in eicosanoid biology. Science 2001, 294, 1871–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeager, M.P.; Pioli, P.A.; Guyre, P.M. Cortisol exerts bi-phasic regulation of inflammation in humans. Dose Response 2011, 9, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehkamp, J.; Fellermann, K.; Herrlinger, K.R.; Bevins, C.L.; Stange, E.F. Mechanisms of disease: Defensins in gastrointestinal diseases. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 2, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.; Dou, X.; Liu, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H. Immunomodulation and signaling mechanism of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and its components on porcine intestinal epithelial cells stimulated by lipopolysaccharide. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2017, 50, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.; Qi, S.; Cui, Y.; Dou, X.; Luo, X.M.; Liu, J.; Wang, H. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation and Barrier Dysfunction by Regulating MAPK/NF-κB Signaling and Modulating Metabolome in the Piglet Intestine. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Q. Co-administration of Bacillus subtilis RJGP16 and Lactobacillus salivarius B1 strongly enhances the intestinal mucosal immunity of piglets. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 94, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldhuizen, E.J.; van Dijk, A.; Tersteeg, M.H.; Kalkhove, S.I.; van der Meulen, J.; Niewold, T.A.; Haagsman, H.P. Expression of beta-defensins pBD-1 and pBD-2 along the small intestinal tract of the pig: Lack of up-regulation in vivo upon Salmonella typhimurium infection. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Research Council, Nutrient Requirements of Swine, 11th rev. ed; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Wang, L.; Hou, Y.; Yi, D.; Li, Y.; Ding, B.; Zhu, H.; Wu, G. Dietary supplementation with glutamate precursor α-ketoglutarate attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury in young pigs. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, D.; Hou, Y.; Wang, L.; Long, M.; Hu, S.; Mei, H.; Yan, L.; Hu, C.A.; Wu, G. N-acetylcysteine stimulates protein synthesis in enterocytes independently of glutathione synthesis. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Han, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, J. Dietary l-arginine supplementation improves intestinal function in weaned pigs after an Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide challenge. Asian Aust. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 22, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, D.; Hou, Y.; Xiao, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, G. N-Acetylcysteine improves intestinal function in lipopolysaccharides-challenged piglets through multiple signaling pathways. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 1915–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2∆∆Ct method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


 Control group = piglets fed the basal diet and that received oral administration of saline;
Control group = piglets fed the basal diet and that received oral administration of saline;  LPS group = piglets fed the basal diet and challenged with LPS;
LPS group = piglets fed the basal diet and challenged with LPS;  LPS + Lactobacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 6 × 106 cfu/g L. casei and challenged with LPS;
LPS + Lactobacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 6 × 106 cfu/g L. casei and challenged with LPS;  LPS + Bacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 3 × 106 cfu/g B. subtilis and 3 × 106 cfu/g B. licheniformis and challenged with LPS. Bars not sharing a common lowercase letter differ significantly (p < 0.05).
LPS + Bacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 3 × 106 cfu/g B. subtilis and 3 × 106 cfu/g B. licheniformis and challenged with LPS. Bars not sharing a common lowercase letter differ significantly (p < 0.05).
 Control group = piglets fed the basal diet and that received oral administration of saline;
Control group = piglets fed the basal diet and that received oral administration of saline;  LPS group = piglets fed the basal diet and challenged with LPS;
LPS group = piglets fed the basal diet and challenged with LPS;  LPS + Lactobacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 6 × 106 cfu/g L. casei and challenged with LPS;
LPS + Lactobacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 6 × 106 cfu/g L. casei and challenged with LPS;  LPS + Bacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 3 × 106 cfu/g B. subtilis and 3 × 106 cfu/g B. licheniformis and challenged with LPS. Bars not sharing a common lowercase letter differ significantly (p < 0.05).
LPS + Bacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 3 × 106 cfu/g B. subtilis and 3 × 106 cfu/g B. licheniformis and challenged with LPS. Bars not sharing a common lowercase letter differ significantly (p < 0.05).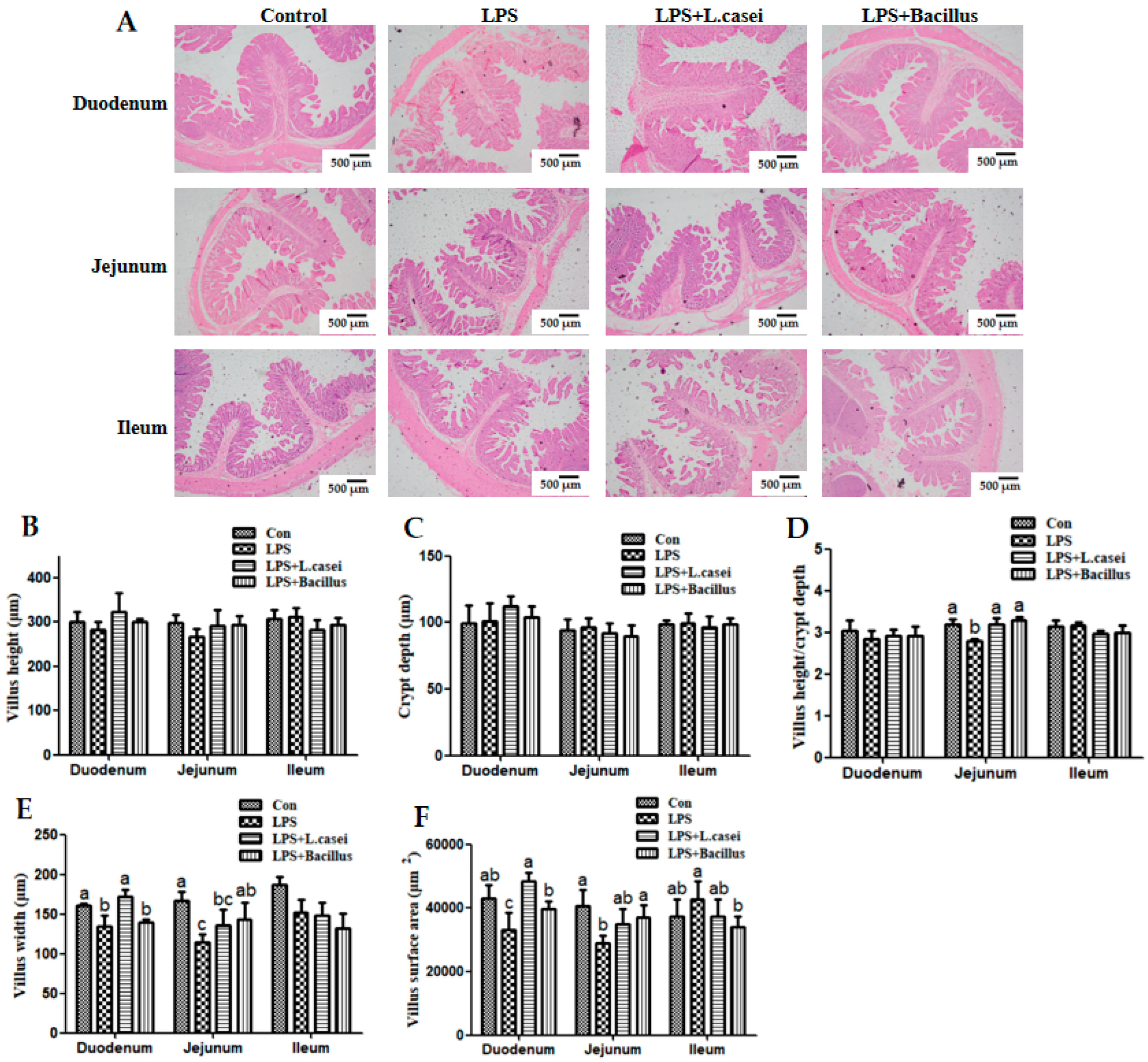
 Control group = piglets fed the basal diet and that received oral administration of saline;
Control group = piglets fed the basal diet and that received oral administration of saline;  LPS group = piglets fed the basal diet and challenged with LPS;
LPS group = piglets fed the basal diet and challenged with LPS;  LPS + Lactobacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 6 × 106 cfu/g L. casei and challenged with LPS;
LPS + Lactobacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 6 × 106 cfu/g L. casei and challenged with LPS;  LPS + Bacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 3 × 106 cfu/g B. subtilis and 3 × 106 cfu/g B. licheniformis and challenged with LPS. Bars not sharing a common lowercase letter differ significantly (p < 0.05).
LPS + Bacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 3 × 106 cfu/g B. subtilis and 3 × 106 cfu/g B. licheniformis and challenged with LPS. Bars not sharing a common lowercase letter differ significantly (p < 0.05).
 Control group = piglets fed the basal diet and that received oral administration of saline;
Control group = piglets fed the basal diet and that received oral administration of saline;  LPS group = piglets fed the basal diet and challenged with LPS;
LPS group = piglets fed the basal diet and challenged with LPS;  LPS + Lactobacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 6 × 106 cfu/g L. casei and challenged with LPS;
LPS + Lactobacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 6 × 106 cfu/g L. casei and challenged with LPS;  LPS + Bacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 3 × 106 cfu/g B. subtilis and 3 × 106 cfu/g B. licheniformis and challenged with LPS. Bars not sharing a common lowercase letter differ significantly (p < 0.05).
LPS + Bacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 3 × 106 cfu/g B. subtilis and 3 × 106 cfu/g B. licheniformis and challenged with LPS. Bars not sharing a common lowercase letter differ significantly (p < 0.05).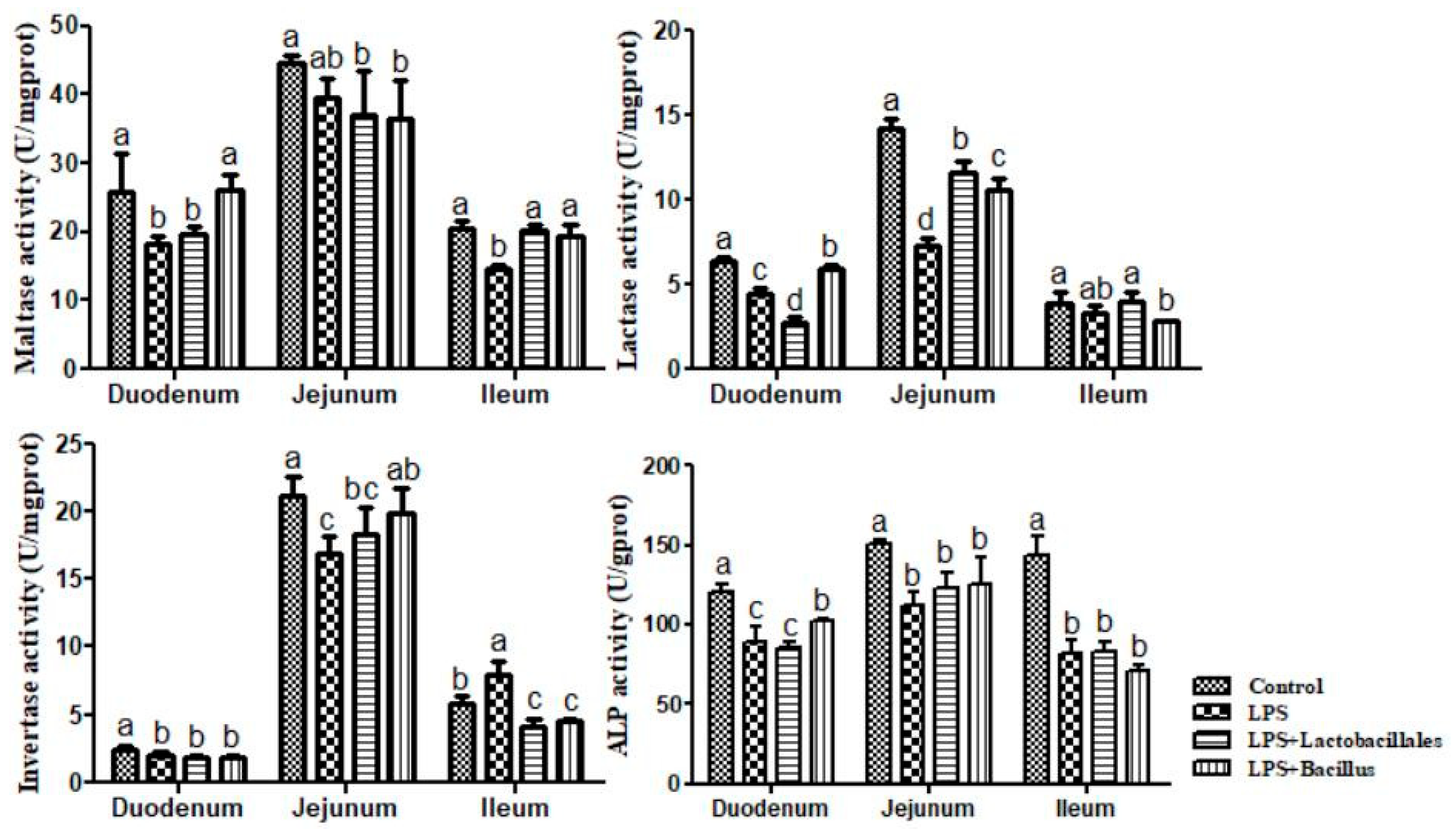
 Control group = piglets fed the basal diet and that received oral administration of saline;
Control group = piglets fed the basal diet and that received oral administration of saline;  LPS group = piglets fed the basal diet and challenged with LPS;
LPS group = piglets fed the basal diet and challenged with LPS;  LPS + Lactobacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 6 × 106 cfu/g L. casei and challenged with LPS;
LPS + Lactobacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 6 × 106 cfu/g L. casei and challenged with LPS;  LPS + Bacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 3 × 106 cfu/g B. subtilis and 3 × 106 cfu/g B. licheniformis and challenged with LPS. Bars not sharing a common lowercase letter differ significantly (p < 0.05).
LPS + Bacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 3 × 106 cfu/g B. subtilis and 3 × 106 cfu/g B. licheniformis and challenged with LPS. Bars not sharing a common lowercase letter differ significantly (p < 0.05).
 Control group = piglets fed the basal diet and that received oral administration of saline;
Control group = piglets fed the basal diet and that received oral administration of saline;  LPS group = piglets fed the basal diet and challenged with LPS;
LPS group = piglets fed the basal diet and challenged with LPS;  LPS + Lactobacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 6 × 106 cfu/g L. casei and challenged with LPS;
LPS + Lactobacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 6 × 106 cfu/g L. casei and challenged with LPS;  LPS + Bacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 3 × 106 cfu/g B. subtilis and 3 × 106 cfu/g B. licheniformis and challenged with LPS. Bars not sharing a common lowercase letter differ significantly (p < 0.05).
LPS + Bacillus group = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with 3 × 106 cfu/g B. subtilis and 3 × 106 cfu/g B. licheniformis and challenged with LPS. Bars not sharing a common lowercase letter differ significantly (p < 0.05).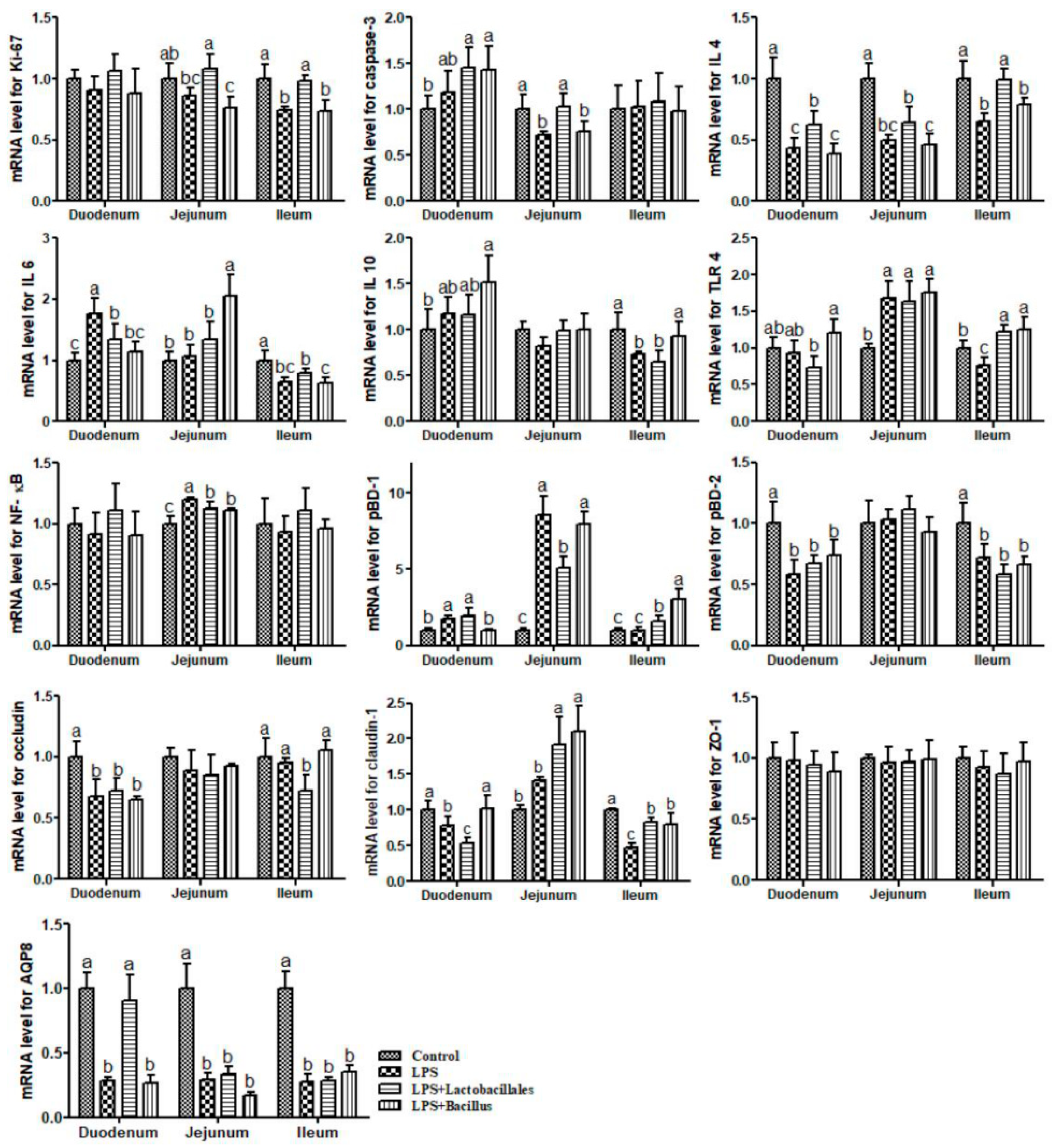
| Items | Content | Items | Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ingredient (%) | Nutrient composition | ||
| Corn | 61.88 | Digestion energy † (MJ/kg) | 14.22 |
| Soybean meal | 21.98 | Crude protein § (%) | 20.9 |
| Wheat middlings | 4.00 | Total threonine † (%) | 0.74 |
| Whey powder | 3.00 | Total methionine † (%) | 0.30 |
| Fish meal | 3.00 | Total methionine + cystine † (%) | 0.65 |
| Soya protein concentrate | 1.50 | Total lysine † (%) | 1.15 |
| CaHPO4 | 1.25 | Total tryptophan † (%) | 0.21 |
| Premix * | 1.00 | Ca § (%) | 0.70 |
| Limestone | 0.69 | Total P § (%) | 0.60 |
| Acidifier | 0.30 | Available P † (%) | 0.32 |
| NaCl | 0.30 | ||
| Mold inhibitor | 0.10 | ||
| Soybean oil | 0.50 | ||
| Choline chloride | 0.20 | ||
| L-Lysine·HCl (78.8% lysine) | 0.25 | ||
| DL-Methionine (99% methionine) | 0.05 | ||
| Total | 100.00 |
| Genes | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) | Annealing Temperatures (°C) | Accession Numbers | Primer’s Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ki-67 | CGCAACCAAGCAAC | ACAGTGCCAAACTGGGAGAAA | 60 | NM_001101827 | 106 |
| Caspase-3 | GAACTCTAACTGGCAAACCCAAA | GTCCCACTGTCCGTCTCAATC | 60 | NM_214131.1 | 92 |
| IL-4 | TACCAGCAACTTCGTCCAC | ATCGTCTTTAGCCTTTCCAA | 60 | NM_214123.1 | 89 |
| IL 6 | TACTGGCAGAAAACAACCTG | GTACTAATCTGCACAGCCTC | 60 | NM_214399.1 | 93 |
| IL 10 | CGGCGCTGTCATCAATTTCTG | CCCCTCTCTTGGAGCTTGCTA | 60 | NM_214041.1 | 103 |
| TLR 4 | GCCTTTCTCTCCTGCCTGAG | AGCTCCATGCATTGGTAACTAATG | 60 | NM_001113039.2 | 94 |
| NF-κB | CTCGCACAAGGAGACATGAA | ACTCAGCCGGAAGGCATTAT | 60 | NM_001048232.1 | 107 |
| pBD-1 | ACCGCCTCCTCCTTGTATTC | CACAGGTGCCGATCTGTTTC | 60 | NM_213838 | 94 |
| pBD-2 | TTGCTGCTGCTGACTGTCTG | CTTGGCCTTGCCACTGTAAC | 60 | NM_214442 | 91 |
| Occludin | TATGAGACAGACTACACAACTGGCGGCGAGTCC | ATCATAGTCTCCAACCATCTTCTTGATGTG | 60 | XM_005672522.3 | 93 |
| Claudin-1 | GGTGCCCTACTTTGCTGCTC | CCCACACGGTTTTGTCCTTT | 60 | NM_001244539.1 | 108 |
| ZO-1 | AGGCGATGTTGTATTGAAGATAAATG | TTTTTGCATCCGTCAATGACA | 60 | CK453343 | 92 |
| AQP8 | TGTGTCTGGAGCCTGCATGAAT | AGCAGGAATCCCACCATCTCA | 60 | NM_001112683.1 | 108 |
| RPL4 | GAGAAACCGTCGCCGAAT | GCCCACCAGGAGCAAGTT | 60 | XM_005659862.3 | 102 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, D.; Zhang, J.; Yi, D.; Wu, T.; Dou, M.; Wang, L.; Hou, Y. Dietary Supplementation with Probiotics Alleviates Intestinal Injury in LPS-Challenged Piglets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157646
Zhao D, Zhang J, Yi D, Wu T, Dou M, Wang L, Hou Y. Dietary Supplementation with Probiotics Alleviates Intestinal Injury in LPS-Challenged Piglets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157646
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Di, Junmei Zhang, Dan Yi, Tao Wu, Maoxin Dou, Lei Wang, and Yongqing Hou. 2025. "Dietary Supplementation with Probiotics Alleviates Intestinal Injury in LPS-Challenged Piglets" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157646
APA StyleZhao, D., Zhang, J., Yi, D., Wu, T., Dou, M., Wang, L., & Hou, Y. (2025). Dietary Supplementation with Probiotics Alleviates Intestinal Injury in LPS-Challenged Piglets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157646






