Dual Effect of 4-Methylumbelliferone on INS1E Cells: Enhancing Migration and Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
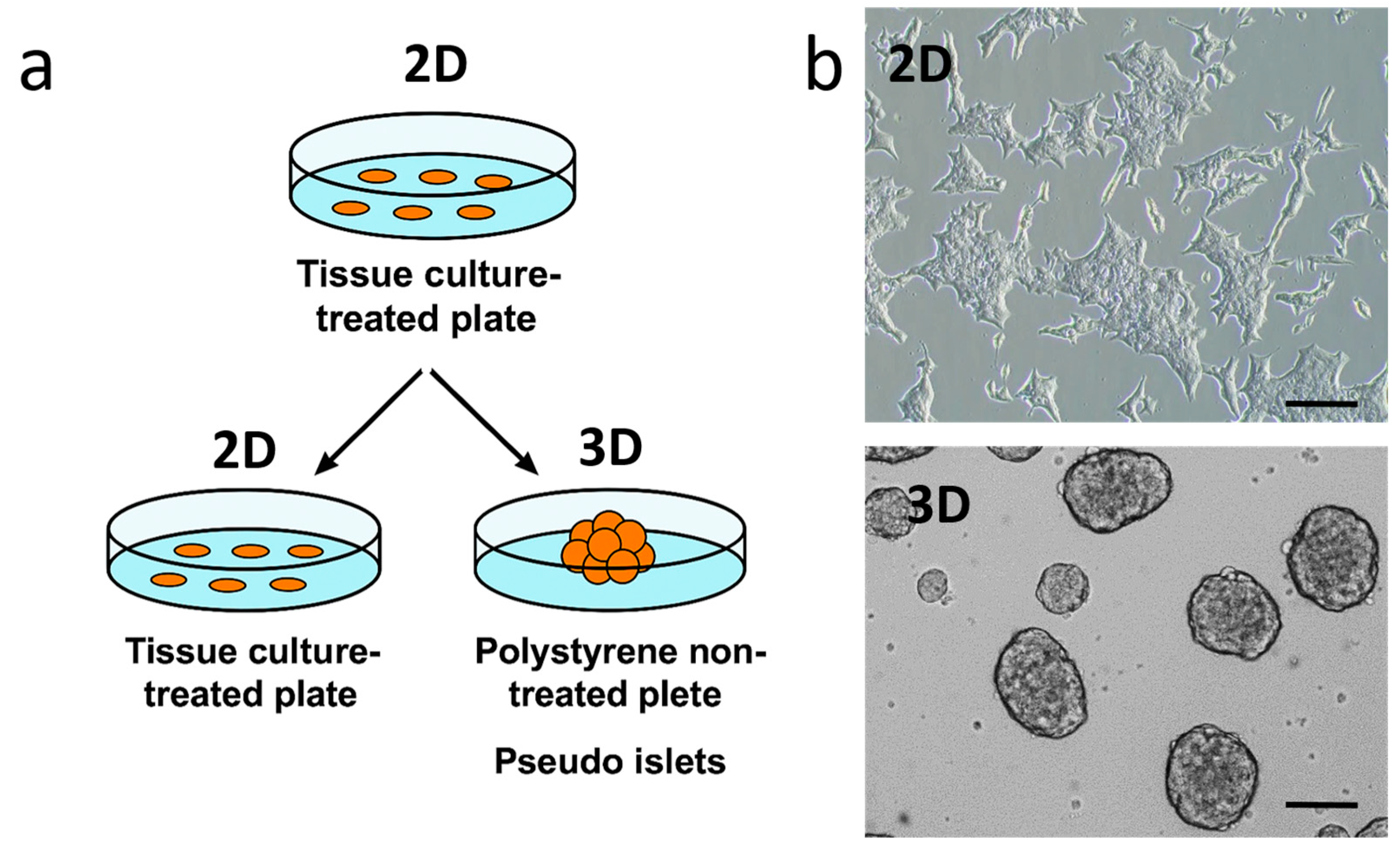
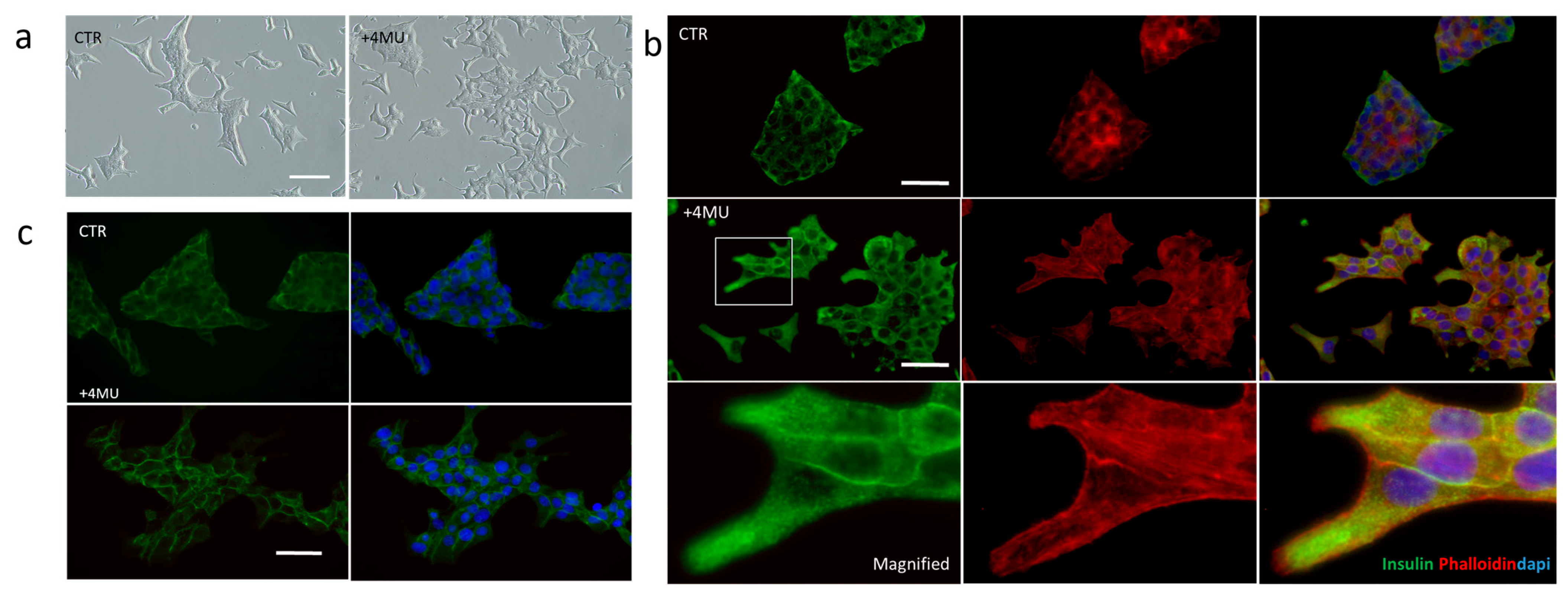
2.1. 4MU Treatment Influences Morphology and Adhesiveness in INS1E Cells Cultivated in 2D and 3D Conditions
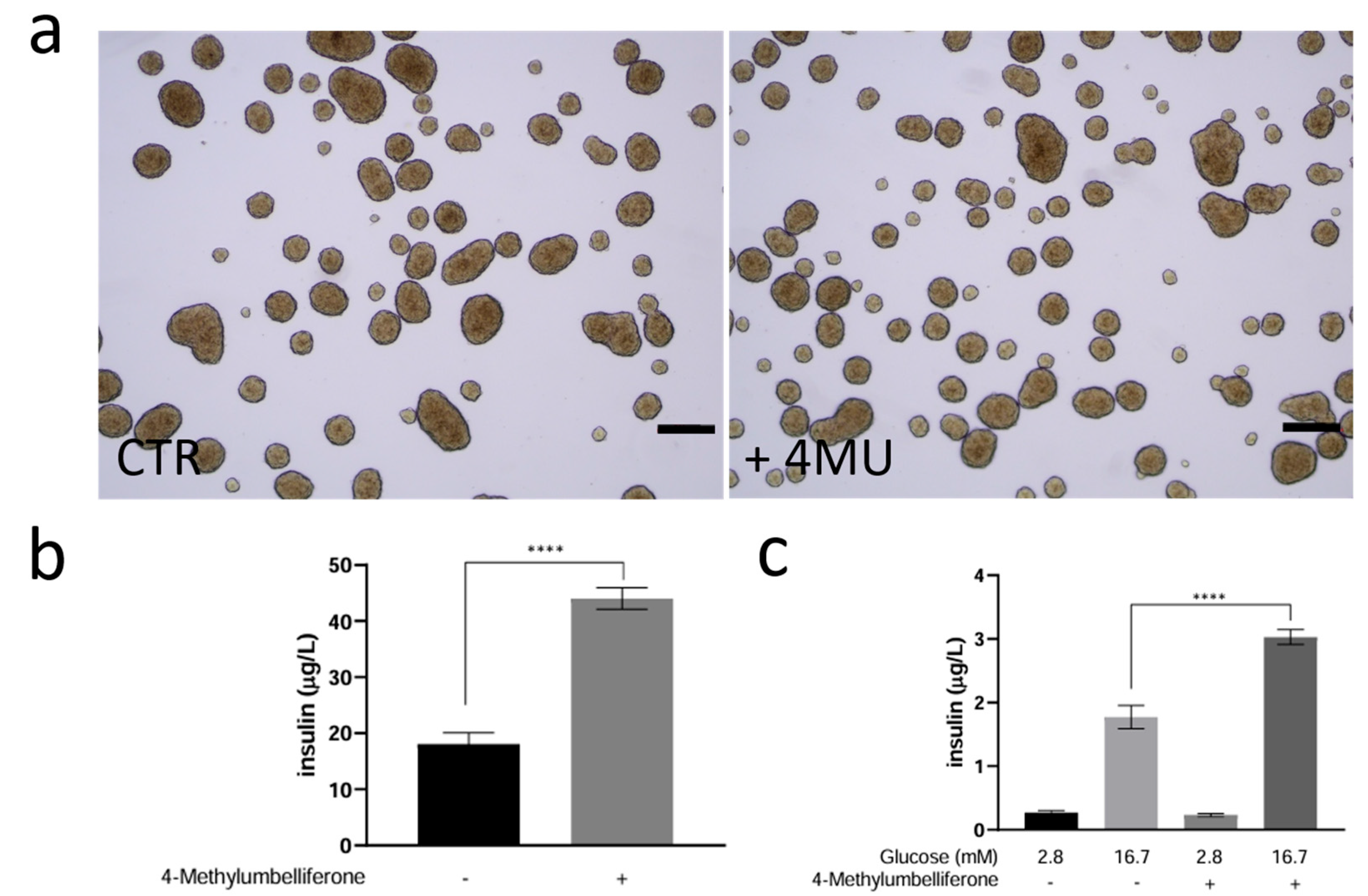
2.2. Study of 4MU Effects on Basal and Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion (GSIS) Through Modulation of Granule Trafficking in INS1E Cells Cultured in 3D
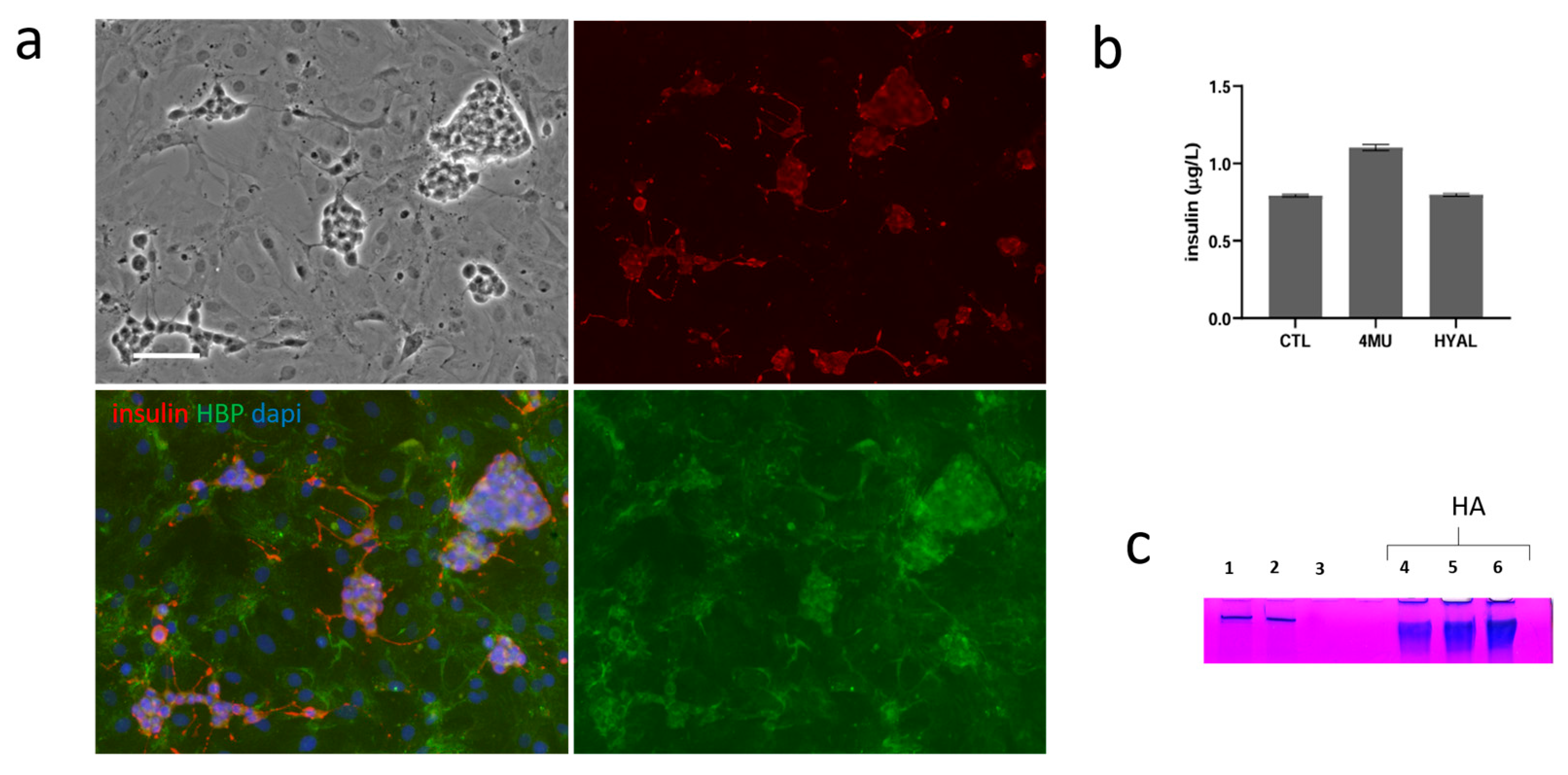
2.3. Co-Culture of INS1E with Stromal Vascular Fraction and the Role of HA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Isolation of Stromal Vascular Fraction from Rat Adipose Tissue
4.3. Quantification of Basal Insulin
4.4. Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion (GSIS) Assay
4.5. Cell Viability
4.6. Immunofluorescence Analyses
4.7. Quantification of HA
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cnop, M.; Welsh, N.; Jonas, J.C.; Jörns, A.; Lenzen, S.; Eizirik, D.L. Mechanisms of pancreatic β-cell death in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: Many differences, few similarities. Diabetes 2005, 54 (Suppl. 2), S97–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essaouiba, A.; Jellali, R.; Shinohara, M.; Scheidecker, B.; Legallais, C.; Sakai, Y.; Leclerc, E. Analysis of the behavior of 2D monolayers and 3D spheroid human pancreatic beta cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells in a microfluidic environment. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 330, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohandas, S.; Gayatri, V.; Kumaran, K.; Gopinath, V.; Paulmurugan, R.; Ramkumar, K.M. New Frontiers in Three-Dimensional Culture Platforms to Improve Diabetes Research. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbach, L.; Roma, L.P.; Schmitt, B.M.; Becker, V.; Körbel, C.; Wrublewsky, S.; Pack, M.; Später, T.; Metzger, W.; Menger, M.M.; et al. Improvement of islet transplantation by the fusion of islet cells with functional blood vessels. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e12616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamone, M.; Rigogliuso, S.; Nicosia, A.; Campora, S.; Bruno, C.M.; Ghersi, G. 3D Collagen Hydrogel Promotes In vitro Langerhans Islets Vascularization through ad-MVFs Angiogenic Activity. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanczyk, M.; Layland, S.L.; Schenke-Layland, K. The role of extracellular matrix in biomechanics and its impact on bioengineering of cells and 3D tissues. Matrix Biol. 2020, 85–86, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, B.M.; Bouças, A.P.; Oliveira, F.D.; Reis, K.P.; Ziegelmann, P.; Bauer, A.C.; Crispim, D. Effect of co-culture of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells with pancreatic islets on viability and function outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Islets 2017, 9, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogal, J.; Zbinden, A.; Schenke-Layland, K.; Loskill, P. Stem-cell based organ-on-a-chip models for diabetes research. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 140, 101–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.J.; Zavortink, M.; Ludick, C.; Templin, R.; Webb, R.; Webb, R.; Ma, W.; Poronnik, P.; Parton, R.G.; Gaisano, H.Y.; et al. Cell polarity defines three distinct domains in pancreatic β-cells. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.J.; Do, O.H.; Cottle, L.; Ma, W.; Kosobrodova, E.; Cooper-White, J.; Bilek, M.; Thorn, P. Local Integrin Activation in Pancreatic β Cells Targets Insulin Secretion to the Vasculature. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 2819–2826.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, S.E.; Gannon, M. Extracellular Matrix-Associated Factors Play Critical Roles in Regulating Pancreatic β-Cell Proliferation and Survival. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, N.; Sunkari, V.G.; Kaber, G.; Hasbun, S.; Lam, D.N.; Speake, C.; Sanda, S.; McLaughlin, T.L.; Wight, T.N.; Long, S.R.; et al. Hyaluronan levels are increased systemically in human type 2 but not type 1 diabetes independently of glycemic control. Matrix Biol. 2019, 80, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, N.; de la Zerda, A.; Kaber, G.; Johnson, P.Y.; Hu, K.H.; Kratochvil, M.J.; Yadava, K.; Zhao, W.; Cui, Y.; Navarro, G.; et al. Hyaluronan content governs tissue stiffness in pancreatic islet inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, P.L.; Nagy, N.; Kaber, G.; Barlow, G.L.; Ramesh, A.; Xie, B.J.; Linde, M.H.; Haddock, N.L.; Lester, C.A.; Tran, Q.L.; et al. Hyaluronan synthesis inhibition impairs antigen presentation and delays transplantation rejection. Matrix Biol. 2021, 96, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itano, N. Simple primary structure, complex turnover regulation and multiple roles of hyaluronan. J. Biochem. 2008, 144, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikari, S.; Kettunen, T.; Tiainen, S.; Häyrinen, J.; Masarwah, A.; Sudah, M.; Sutela, A.; Vanninen, R.; Tammi, M.; Auvinen, P. UDP-sugar accumulation drives hyaluronan synthesis in breast cancer. Matrix Biol. 2018, 67, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, N.J.; Weber, C.; Price, N.; Banuelos, A.; Schultz, M.; Huey, B.; Harnois, E.; Gibson, C.; Steyn, L.V.; Papas, K.K.; et al. Insulinoma-derived pseudo-islets for diabetes research. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 321, C247–C256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, G.C.; Li, C.M.; Pasolini, I.; Pete, S.I.; Verheyen, C.; Vignolo, S.M.; De Toni, T.; Stock, A.A.; Tomei, A.A. High-Yield Generation of Glucose-Responsive Pseudoislets From Murine Insulinoma Cells for In vitro Studies and Longitudinal Monitoring of Graft Survival In vivo. Cell Transplant. 2025, 34, 09636897251315123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arous, C.; Halban, P.A. The skeleton in the closet: Actin cytoskeletal remodeling in β-cell function. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 309, E611–E620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peercy, B.E.; Hodson, D.J. Synchronizing beta cells in the pancreas. elife 2024, 13, e95103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, W.C.; Shepherd, P.R. β-Cells retain a pool of insulin-containing secretory vesicles regulated by adherens junctions and the cadherin-binding protein p120 catenin. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cognard, E.; Dargaville, C.G.; Hay, D.L.; Shepherd, P.R. Identification of a pathway by which glucose regulates β-catenin signalling via the cAMP/protein kinase A pathway in β-cell models. Biochem. J. 2013, 449, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntamo, Y.; Samodien, E.; Burger, J.; Muller, N.; Muller, C.J.F.; Chellan, N. In vitro Characterization of Insulin–Producing β-Cell Spheroids. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 623889, Erratum in Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 662574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Chanmee, T.; Itano, N. Hyaluronan: Metabolism and Function. Biomocules 2020, 10, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakizaki, I.; Kojima, K.; Takagaki, K.; Endo, M.; Kannagi, R.; Ito, M.; Maruo, Y.; Sato, H.; Yasuda, T.; Mita, S.; et al. A novel mechanism for the inhibition of hyaluronan biosynthesis by 4-methylumbelliferone. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 33281–33289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasapera, A.M.; Schneider, I.C.; Rericha, E.; Schlaepfer, D.D.; Waterman, C.M. Myosin II activity regulates vinculin recruitment to focal adhesions through FAK-mediated paxillin phosphorylation. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 188, 877–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merglen, A.; Theander, S.; Rubi, B.; Chaffard, G.; Wollheim, C.B.; Maechler, P. Glucose Sensitivity and Metabolism-Secretion Coupling Studied during Two-Year Continuous Culture in INS-1E Insulinoma Cells. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adamo, G.; Romancino, D.; Gargano, P.; Sarullo, M.; Nicosia, A.; Picciotto, S.; Smeraldi, G.; Bongiovanni, A.; Salamone, M. Dual Effect of 4-Methylumbelliferone on INS1E Cells: Enhancing Migration and Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157637
Adamo G, Romancino D, Gargano P, Sarullo M, Nicosia A, Picciotto S, Smeraldi G, Bongiovanni A, Salamone M. Dual Effect of 4-Methylumbelliferone on INS1E Cells: Enhancing Migration and Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157637
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdamo, Giorgia, Daniele Romancino, Paola Gargano, Marta Sarullo, Aldo Nicosia, Sabrina Picciotto, Giulia Smeraldi, Antonella Bongiovanni, and Monica Salamone. 2025. "Dual Effect of 4-Methylumbelliferone on INS1E Cells: Enhancing Migration and Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157637
APA StyleAdamo, G., Romancino, D., Gargano, P., Sarullo, M., Nicosia, A., Picciotto, S., Smeraldi, G., Bongiovanni, A., & Salamone, M. (2025). Dual Effect of 4-Methylumbelliferone on INS1E Cells: Enhancing Migration and Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157637







