Assessment of Hydrogels for Intra-Articulate Application, Based on Sodium Hyaluronate Doped with Synthetic Polymers and Incorporated with Diclofenac Sodium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
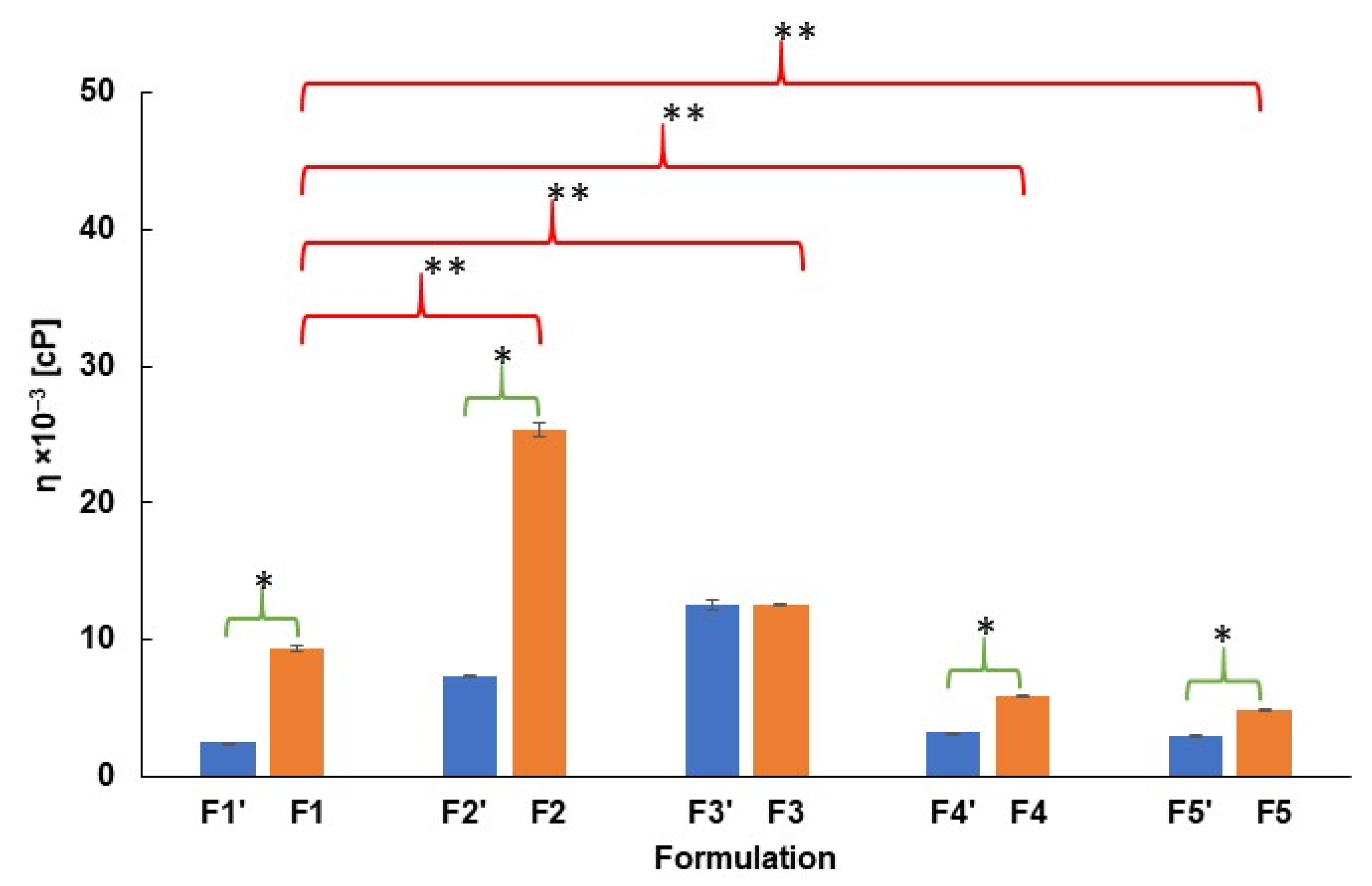
2.1. pH and Viscosity Investigation
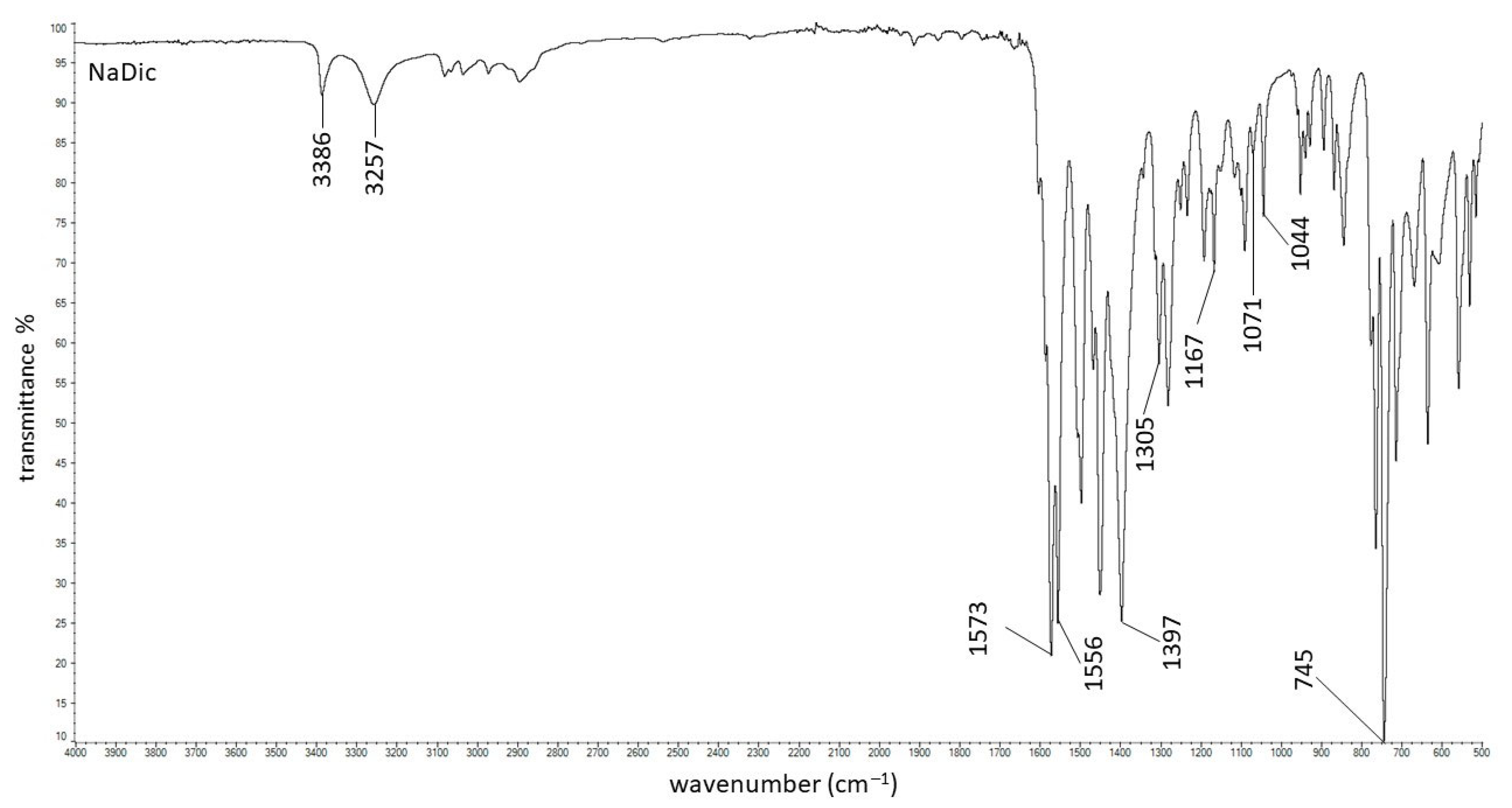
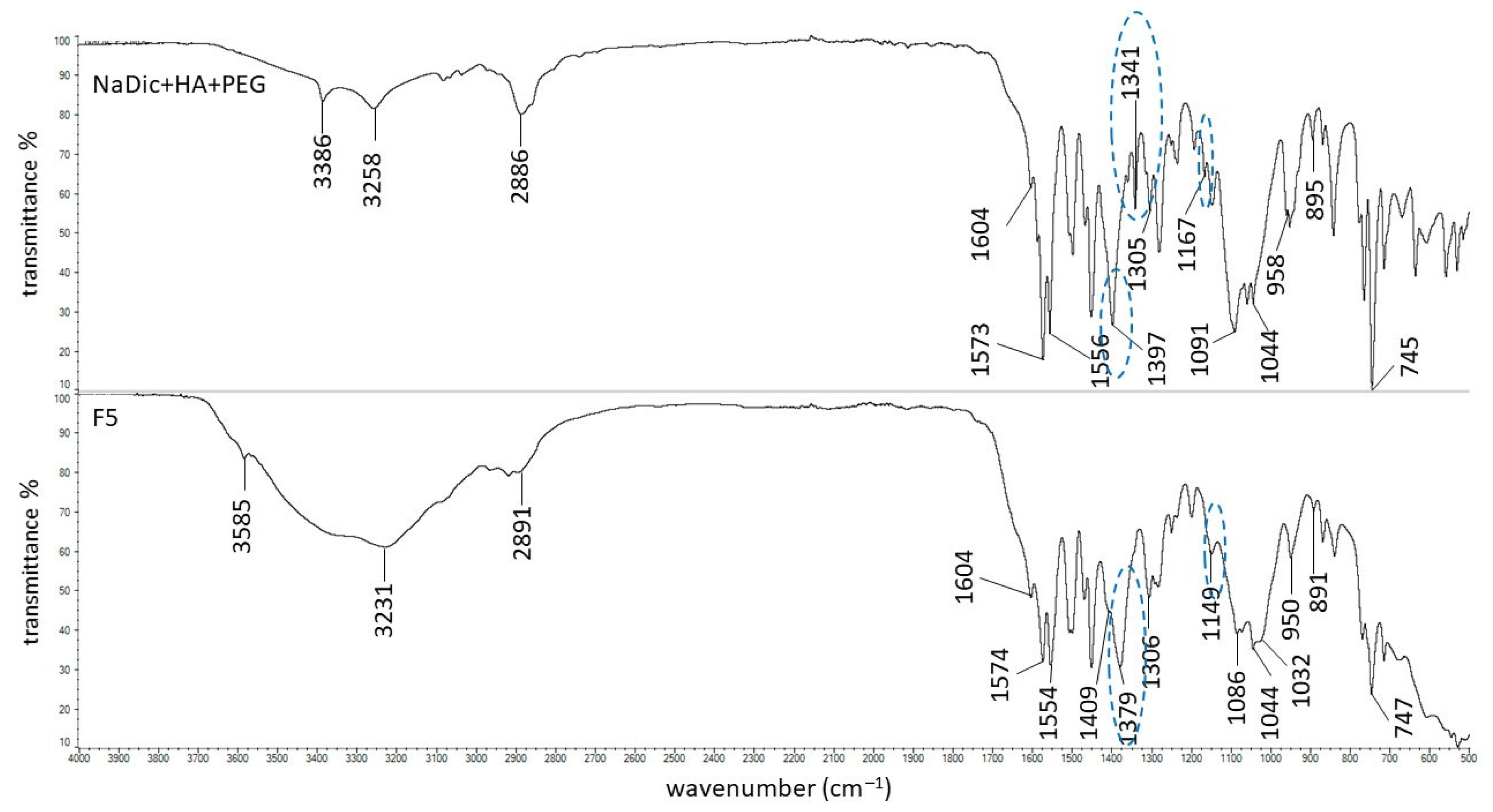
2.2. FTIR-ATR Study
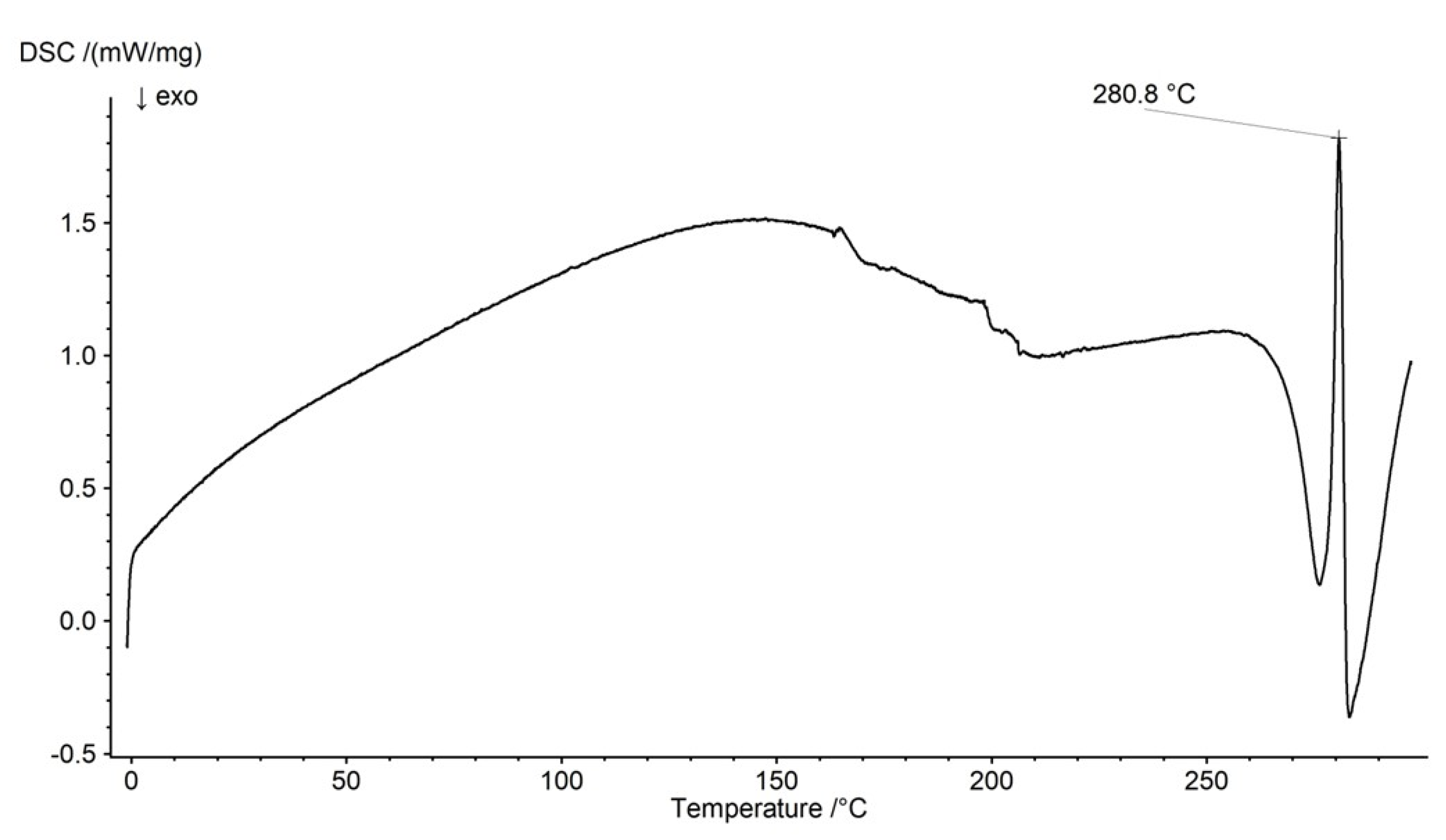
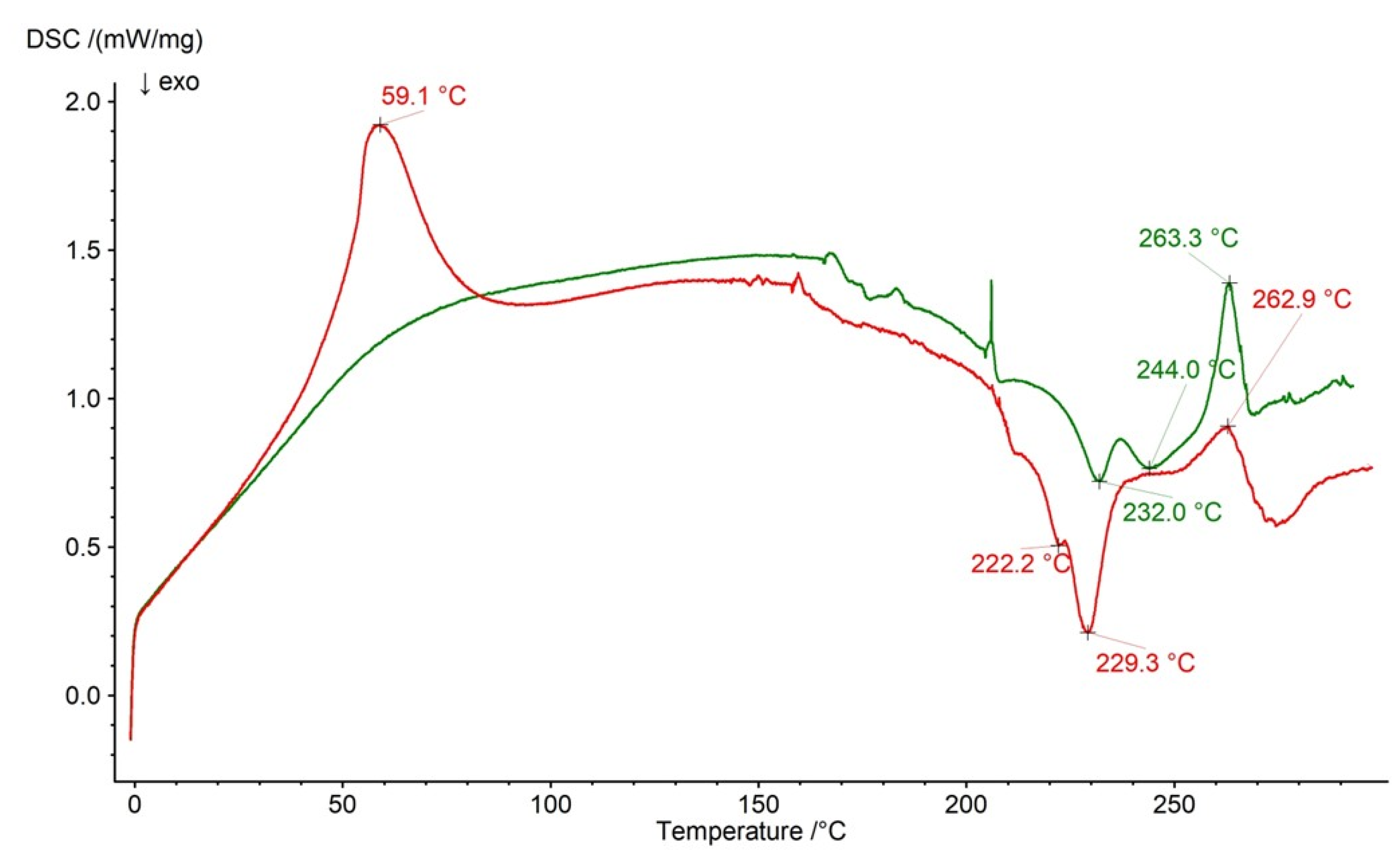
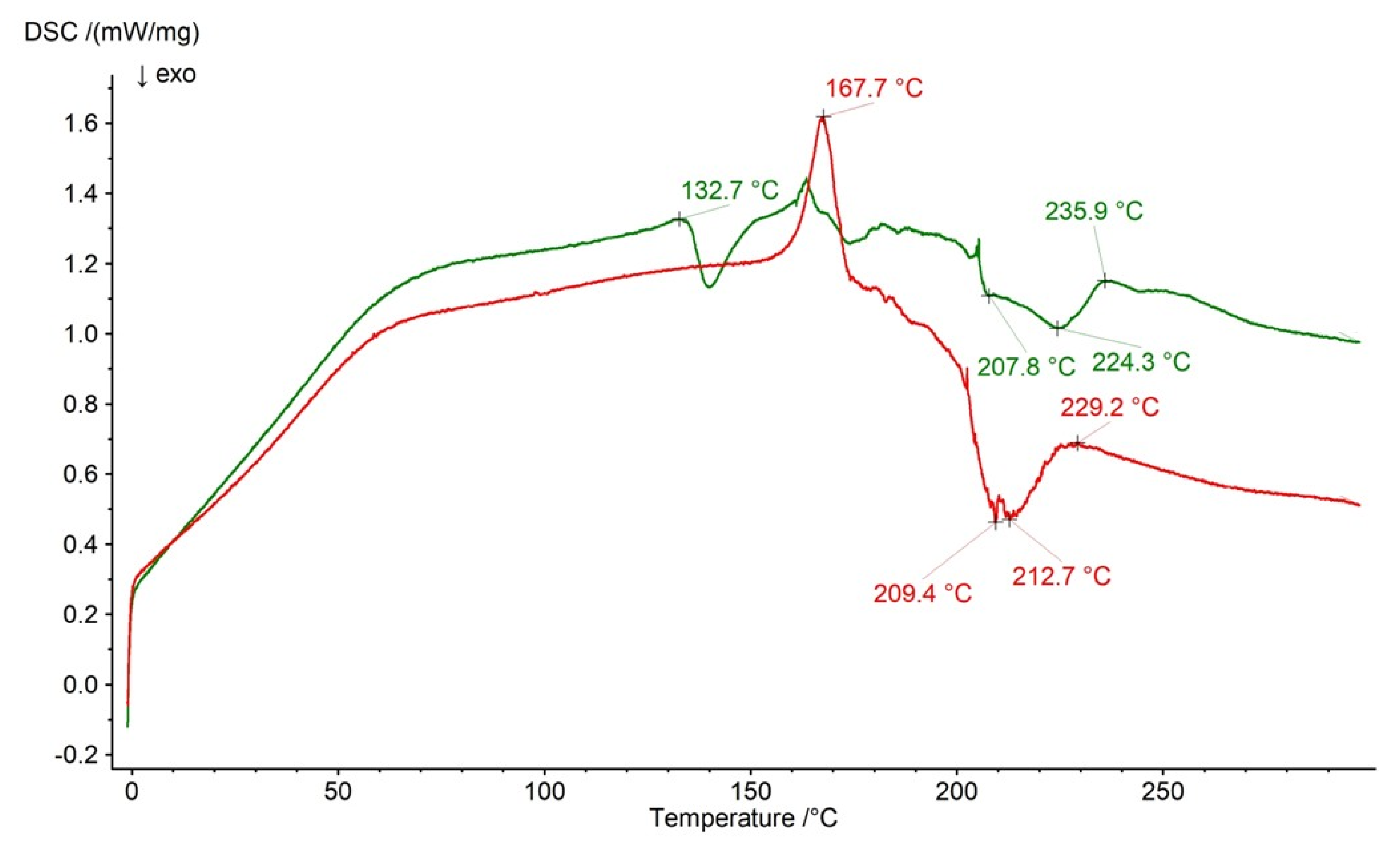
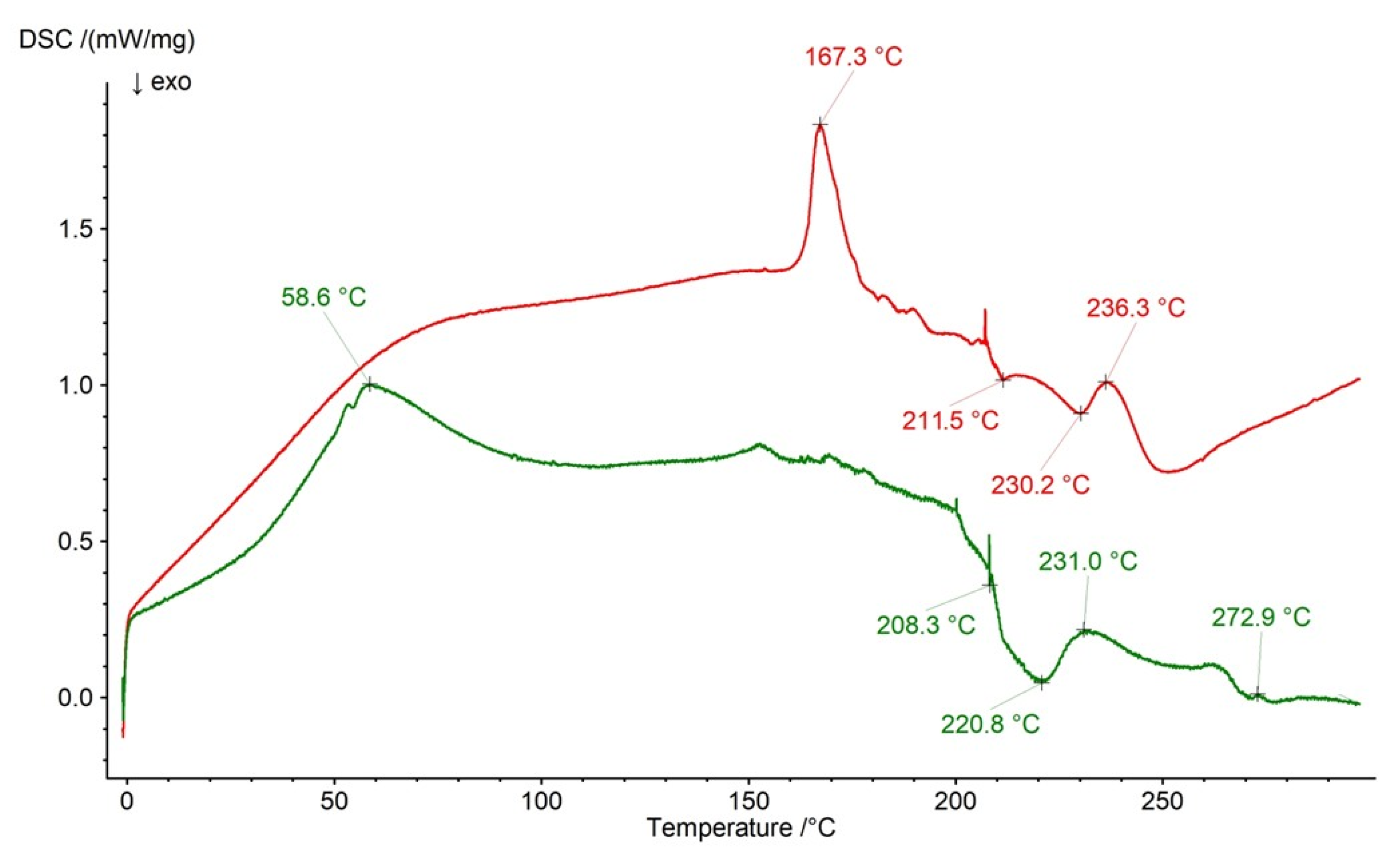
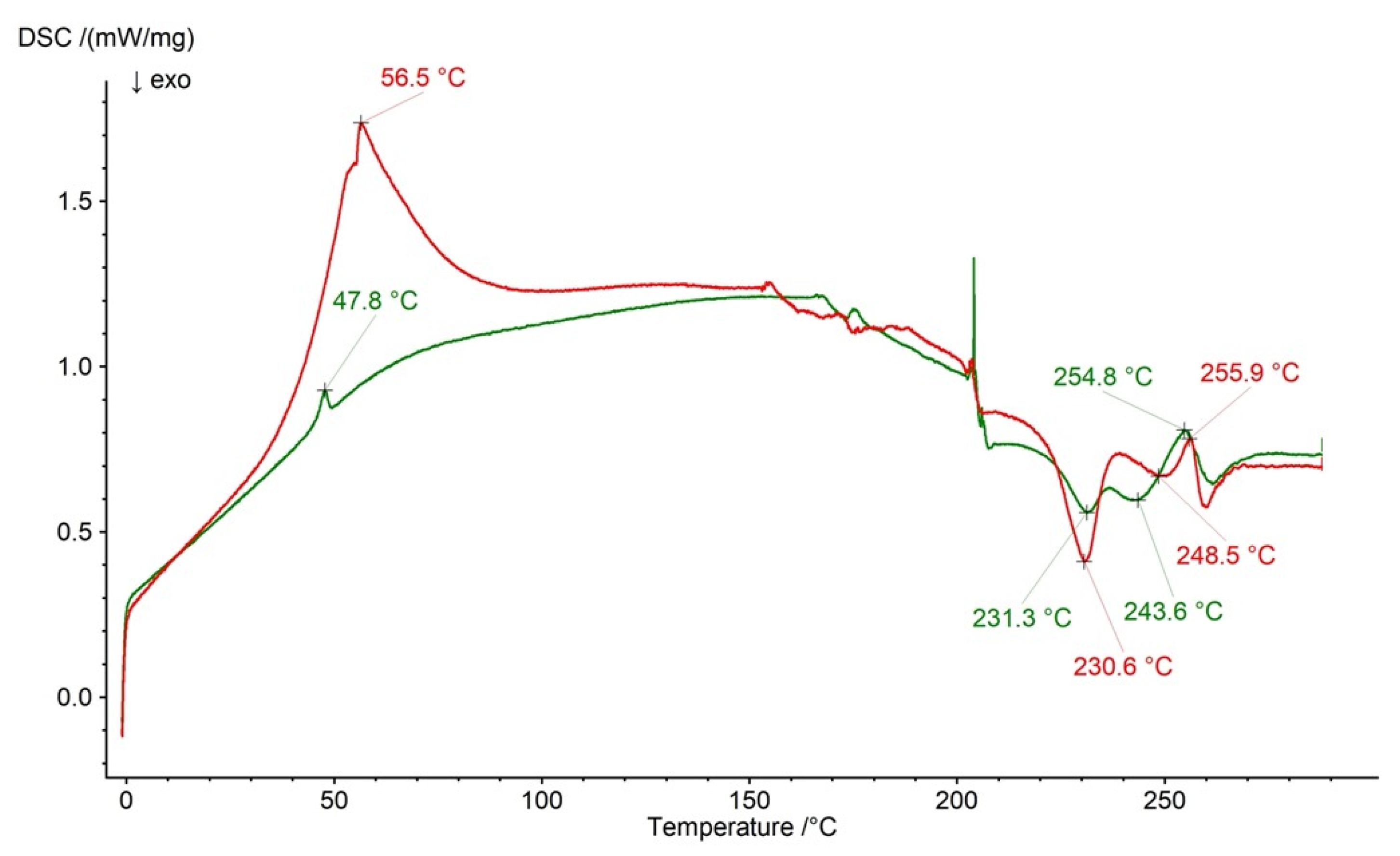
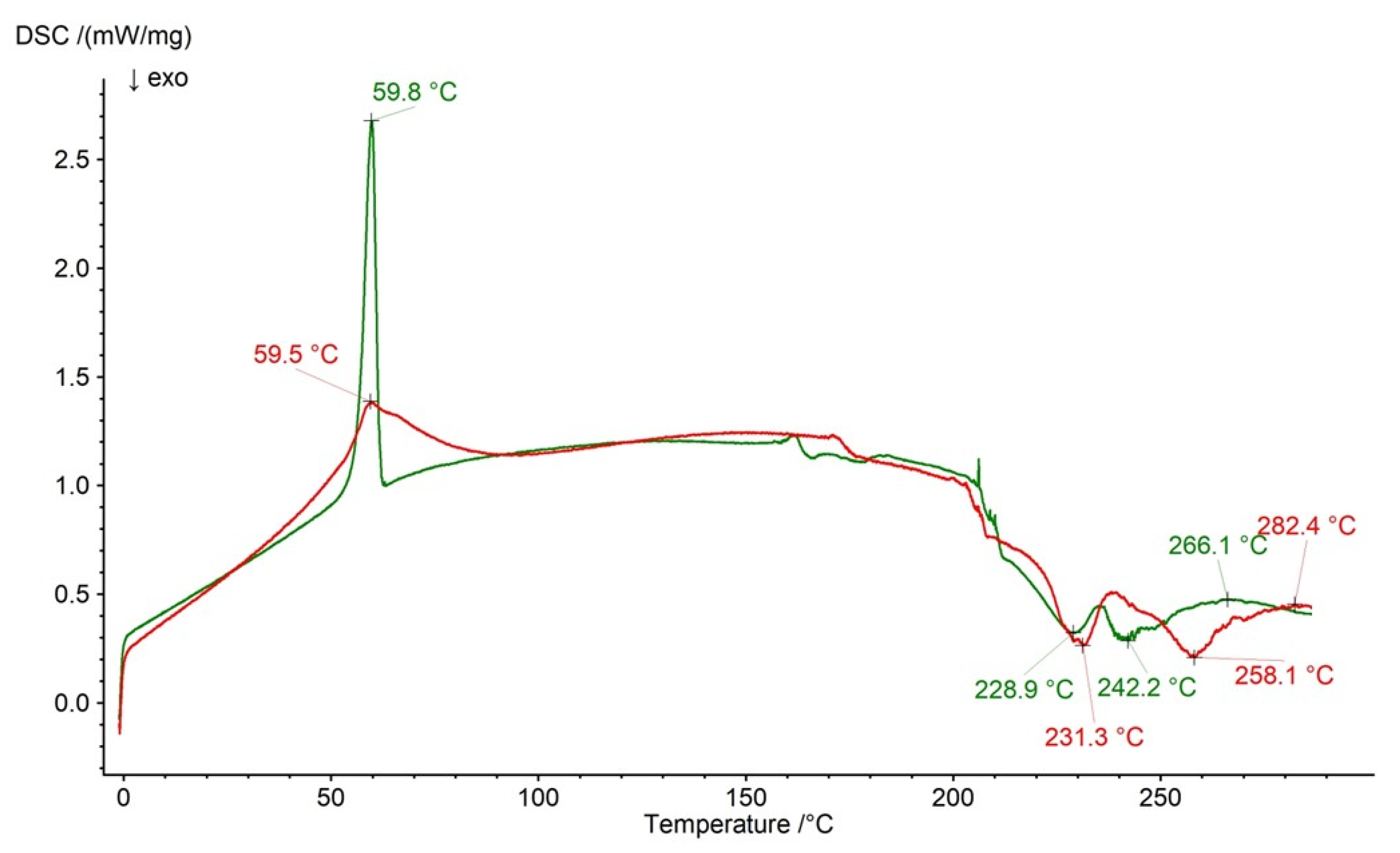
2.3. DSC Analysis
2.4. Release Study
2.5. Kinetic Analysis
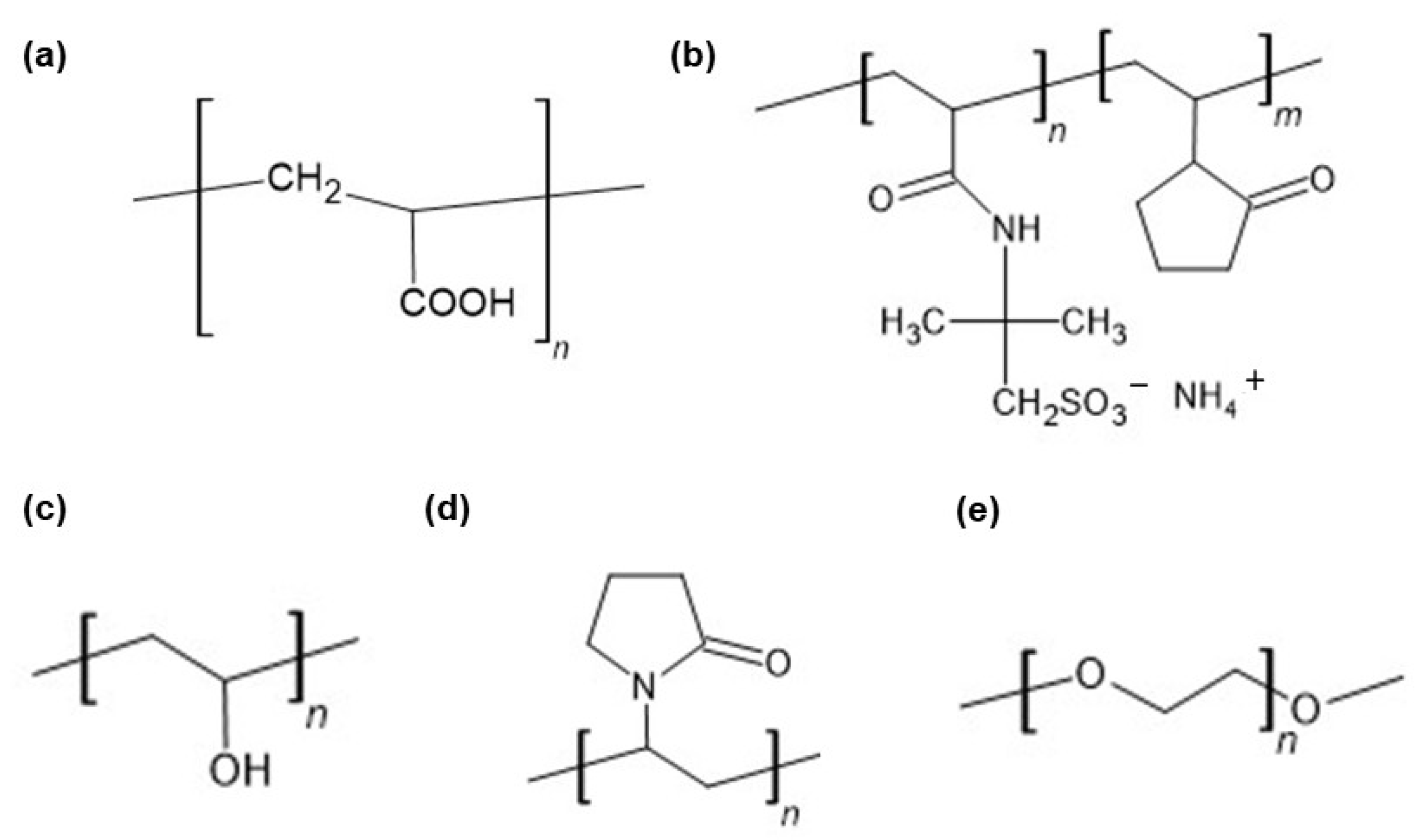
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Hydrogels Preparation
3.2. pH and Viscosity Measurements
3.3. ATR−FTIR Measurements
3.4. DSC Study
3.5. Release Tests
3.6. Difference Factor f1 and Similarity Factor f2
3.7. Kinetic Calculations
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gul, R.; Nazir, I.; Amirzada, M.I.; Jahan, F.; Naseer, F.; Baig, T.A. Aging and Synovial Joint Function: Changes in Structure and Implications for Mobility. In Advancements in Synovial Joint Science—Structure, Function, and Beyond; Zorzi, A.R., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, D.J.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet 2019, 393, 1745–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kołodziejska, J.; Kołodziejczyk, M. Diclofenac in the treatment of pain in patients with rheumatic diseases. Reumatologia 2018, 56, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revel, F.B.; Fayet, M.; Hagen, M. Topical Diclofenac, an Efficacious Treatment for Osteoarthritis: A Narrative Review. Reumatol. Ther. 2020, 7, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, Y.; Mizuno, M.; Ozeki, N.; Katano, H.; Komori, K.; Fujii, S.; Otabe, K.; Horie, M.; Koga, H.; Tsuji, K.; et al. Yields and chondrogenic potential of primary synovial mesenchymal stem cells are comparable between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boff, D.; Crijns, H.; Teixeira, M.M.; Amaral, F.A.; Proost, P. Neutrophils: Beneficial and Harmful Cells in Septic Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. 2018, 19, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemann, A.; Ihling, A.; Thomas, J.; Schneider, B.; Thews, O.; Gekle, M. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta Acidic environment activates in fl ammatory programs in fi broblasts via a cAMP—MAPK pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomšík, E.; Gunár, K.; Krunclová, T.; Ivanko, I.; Trousil, J.; Fojt, J.; Hybášek, V.; Daniel, M.; Sepitka, J.; Judl, T.; et al. Development of Smart Sensing Film with Nonbiofouling Properties for Potentiometric Detection of Local pH Changes Caused by Bacterial and Yeast Infections Around Orthopedic Implants. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 10, 2201878–2201888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, M.; Fleaca, R.S.; Boicean, A.; Bratu, D.; Birlutiu, V.; Rus, L.L.; Tantar, C.; Mitariu, S.I.C. Assesment of Synovial Fluid pH in Osteoarthritis of the HIP and Knee. Rev. Chim. 2017, 68, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driban, J.B.; Balasubramanian, E.; Amin, M.; Sitler, M.R.; Ziskin, M.C.; Barbe, M.F. The Potential of Multiple Synovial-Fluid Protein-Concentration Analyses in the Assessment of Knee Osteoarthritis. J. Sport Rehabil. 2010, 19, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Faryna, A.; Goldenberg, K.I.M. Joint Fluid. In Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations, 3rd ed.; Walker, H., Hall, W., Hurst, J., Eds.; Butterworths: Boston, MA, USA, 1990. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21250045/ (accessed on 23 June 2025).
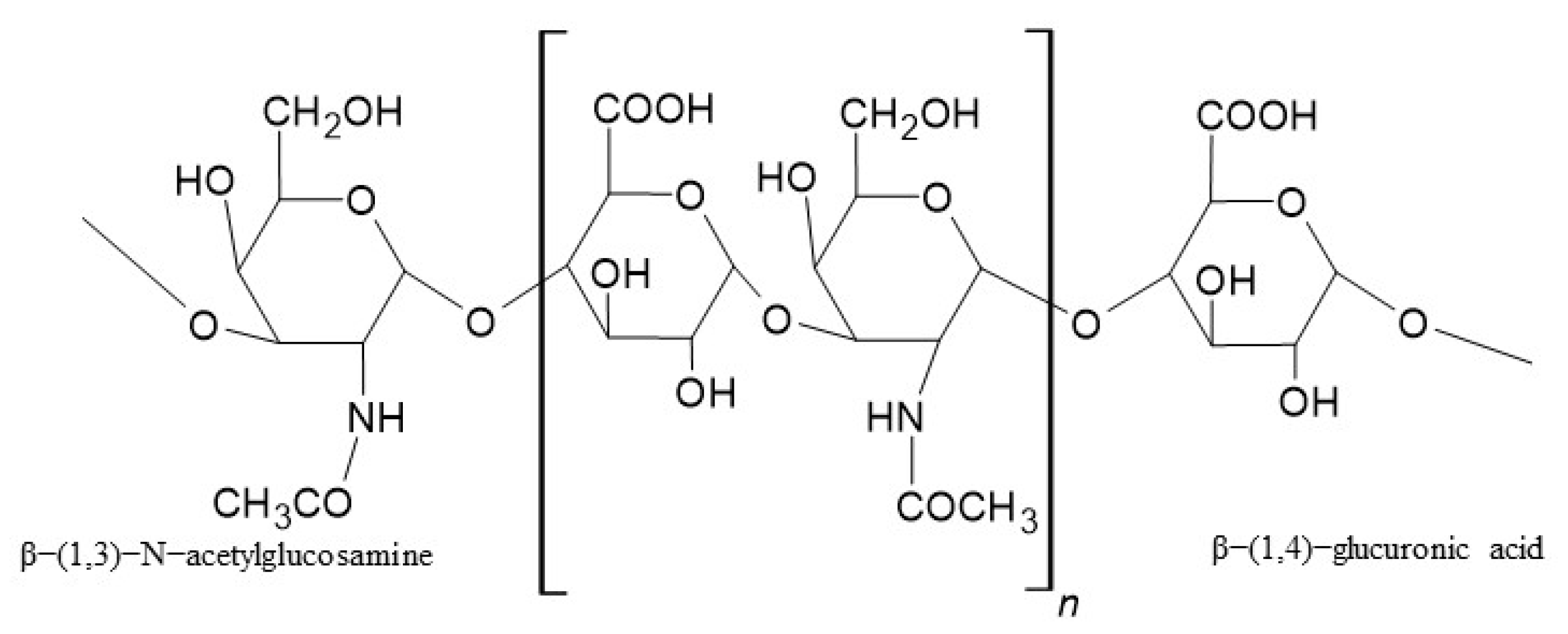
- Valachová, K.; Hassan, M.E.; Šoltés, L. Hyaluronan: Sources, Structure, Features and Applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 739–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snetkov, P.; Zakharova, K.; Morozkina, S.; Olekhnovich, R. Hyaluronic Acid: The Influence of Molecular Weight and Degradable Properties of Biopolymer. Polymers 2020, 12, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaconisi, G.N.; Lunetti, P.; Gallo, N.; Cappello, A.R.; Fiermonte, G.; Dolce, V.; Capobianco, L. Hyaluronic Acid: A Powerful Biomolecule with Wide-Ranging Applications—A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10296–10318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprott, H.; Fleck, C. Hyaluronic Acid in Rheumatology. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2247–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.-H.; Lu, P.W.-A.; Lin, C.-W.; Lu, E.W.-H.; Yang, S.-F. Different molecular weights of hyaluronan research in knee osteoarthritis: A state-of-the-art review. Matrix Biol. 2023, 117, 46–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdiaki, A.; Neagu, M.; Spyridaki, I.; Kuskov, A.; Perez, S.; Nikitovic, D. Hyaluronan and Reactive Oxygen Species Signaling —Novel Cues from the Matrix? Antioxidants 2023, 12, 824–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavda, S.; Rabbani, S.A.; Wadhwa, T. Role and Effectiveness of Intra-articular Injection of Hyaluronic Acid in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e24503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferkel, E.; Manjoo, A.; Martins, D.; Bhandari, M.; Sethi, P.; Nicholls, M. Intra-articular Hyaluronic Acid Treatments for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review of Product Properties. Cartilage 2023, 14, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Guilak, F. Engineering Hyaluronic Acid for the Development of New Treatment Strategies for Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8662–8677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkaban, H.; Barani, M.; Akbarizadeh, M.R.; Chauhan, N.P.S.; Jadoun, S.; Soltani, M.D.; Zarrintaj, P. Polyacrylic Acid Nanoplatforms: Antimicrobial, Tissue Engineering, and Cancer Theranostic Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratiwi, P.D.; Rizki, N.P.; Sciences, H. Optimization of carbopol 940 and glycerol concentration in antioxidant gel of alstonia scholaris l. Leaf extract with simplex lattice design method. Indones. J. Cosmet. 2023, 1, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, T.H.N.; de Souza, D.F.S.; Aguiar, F.H.B.; Ambrosano, G.M.B.; Lima, D.A.N.L. Effect of ammonium acryloyldimethyltaurate copolymer on the physical and chemical properties of bleached dental enamel. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 2701–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarnykh, T.G.; Ivaniuk, O.I.; Kovalevska, I.V.; Kukhtenko, H.P.; Kutsenko, S. Rheology-based substantiation of a gel-former choice for vaginal gel. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2018, 10, 2825–2828. [Google Scholar]
- Clariant, Technical Tip, Aristoflex AVC. Available online: https://soap-formula.ru/assets/sertifikati_new/emulgatiri_zagustiteli/ARISTOFLEX_AVC_TIPS.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Baranova, I.I.; Kovalenko, M.; Khokhlenkova, N.V.; Martyniuk, T.V.; Kutsenko, S.A. Prospects of Using Synthetic and Semi-Synthetic Gelling Substances in Development of Medicinal and Cosmetic Gels. Asian J. Pharm. 2017, 11, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodorescu, M.; Bercea, M.; Morariu, S. Biomaterials of PVA and PVP in medical and pharmaceutical applications: Perspectives and challenges. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, P.; De Marco, I. The use of poly(N-vinyl pyrrolidone) in the delivery of drugs: A review. Polymers 2020, 12, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, M.; Xu, C.; Shao, C.; Jia, L.; Huang, Z.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; et al. Polyethylene glycol 4000 treatment for children with constipation: A randomized comparative multicenter study. Exp. Ther. Med. 2012, 3, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turecek, P.L.; Siekmann, J. PEG-protein conjugates: Nonclinical and clinical toxicity considerations. In Polymer-Protein Conjugates from PEGylated and Beyond; Pasut, G., Zalipsky, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2019; pp. 61–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katturajan, R.; Sabina, E.P. Joint Inflammation: Insights of Osteoarthritis, Gouty and Rheumatoid Arthritis and its Prevalence, Mechanism, Medications and Remedies. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 83, 886–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, C.; Essex, M.N.; Li, C.; Park, P.W. Celecoxib versus diclofenac for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: 12-week randomized study in Norwegian patients. J. Int. Med. Res. 2016, 44, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazali, W.S.; Zainudin, W.M.K.B.W.; Yahya, N.K.; Ismail, A.M.; Wong, K.K. Older age and diclofenac are associated with increased risk of upper gastrointestinal bleeding in gout patients. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadsworth, L.T.; Kent, J.D.; Holt, R.J.; Wadsworth, L.T.; Kent, J.D.; Efficacy, R.J.H. Topical solution for osteoarthritis of the knee: A Original article Efficacy and safety of diclofenac sodium 2% topical solution for osteoarthritis of the knee. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2016, 32, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, R.A.; Davis, D.D. Diclofenac. In StatPearls; [Updated 22 May 2023]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557879/ (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Francio, V.T.; Davani, S.; Towery, C.; Brown, T.L. Oral Versus Topical Diclofenac Sodium in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis Oral Versus Topical Diclofenac Sodium in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. J. Pain Palliat. Care Pharmacother. 2017, 31, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
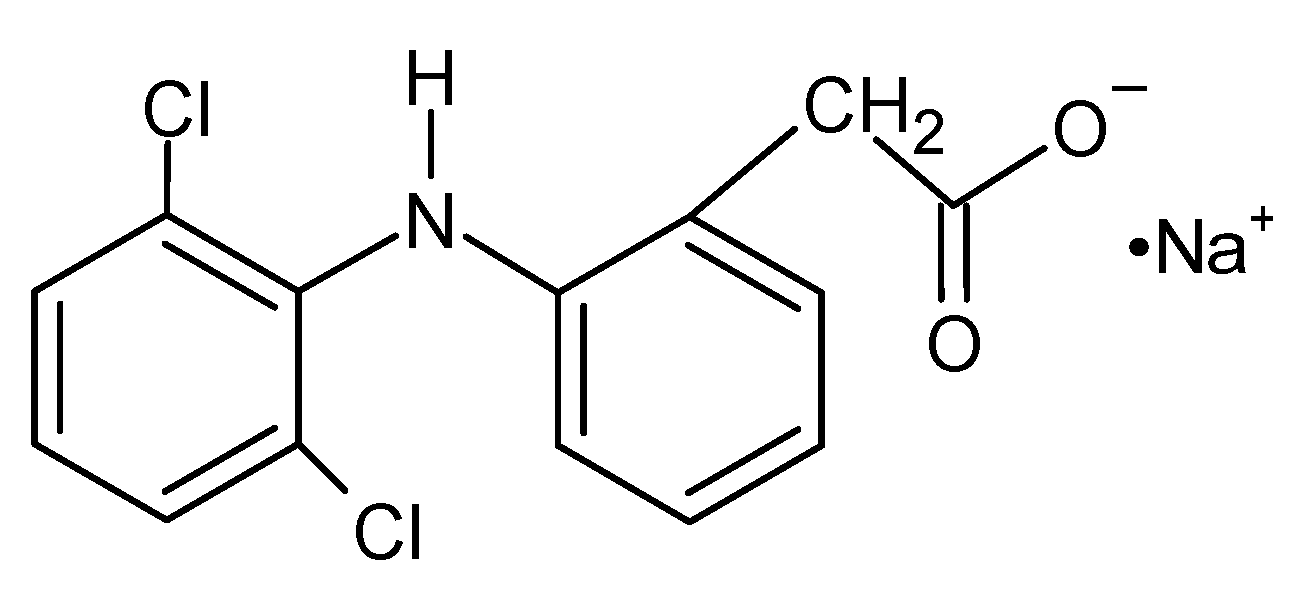
- Panchal, N.; Kaur, M.; Tharmatt, A.; Thakur, S.; Jain, S.K. Development, Characterization and Evaluation of Parenteral Formulation of Diclofenac Sodium. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, R.; Bosch, B.; Brune, K.; Patrignani, P.; Young, C. Advances in NSAID Development: Evolution of Diclofenac Products Using Pharmaceutical Technology. Drugs 2015, 75, 859–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, T.J. Diclofenac: An update on its mechanism of action and safety profile. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2010, 26, 1715–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gull, N.; Khan, S.M.; Butt, O.M.; Islam, A.; Shah, A.; Jabeen, S.; Khan, S.U.; Khan, A.; Khan, R.U.; Butt, M.T.Z. Inflammation targeted chitosan-based hydrogel for controlled release of diclofenac sodium. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, M.; Wu, P.-C.; Minhas, M.U. Using Carbomer-Based Hydrogels for Control the Release Rate of Diclofenac Sodium: Preparation and In Vitro Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, H.; Rong, J.; Tu, M.; Zeng, R.; Zhao, J. β-cyclodextrin-conjugated hyaluronan hydrogel as a potential drug sustained delivery carrier for wound healing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 43072, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçüktürkmen, B.; Öz, U.C.; Bozkir, A. In Situ Hydrogel Formulation for Intra-Articular Application of Diclofenac Sodium-Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 14, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik-Pastuszka, D.; Iwaszkiewicz, R.; Musiał, W. The Effects of Synthetic Polymers on the Release Patterns of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride from Sodium Hyaluronate Hydrogels. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 39–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaka, A.; Ibrahim, T.H.; Khamis, M. Removal of selected non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from wastewater using reduced graphene oxide magnetite. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 212, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.drugfuture.com/pharmacopoeia/usp32/pub/data/v32270/usp32nf27s0_m24962.html (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Giubertoni, G.; Koenderink, G.H.; Bakker, H.J. Direct Observation of Intrachain Hydrogen Bonds in Aqueous Hyaluronan. J. Phys. Chem. A 2019, 123, 8220–8225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.C.C.; Sallum, L.O.; Aguiar, A.S.N.; Camargo, A.J.; Oliveira, H.C.B.; Napolitano, H.B. Exploring the aqueous solubility and intermolecular interactions of diclofenac Diethylammonium: A molecular modeling study in solid state and solvation processes. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 401, 124613–124632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, A.N.M.; Azmi, N.A.; Sabari, N.H.M.; Harun, A.F.; Haris, M.S. An insight into the use and advantages of Carbopol in topical mucoadhesive drug delivery system: A systematic review. J. Pharm. 2023, 3, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoerunnisa, F.; Yolanda, Y.D.; Nurhayati, M.; Hendrawan, H.; Sanjaya, E.H.; Triwardono, J.; Astuti, W.D.; Handayani, M.; Oh, W.D.; Ooi, B.S. pH-responsive chitosan/poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) based hydrogel composites: Antibacterial properties and release kinetics of diclofenac sodium. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 92, 105308–105319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowska, K.; Szulc, M. Characterisation of hyaluronic acid blends modified by poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone). Molecules 2021, 26, 5233–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, A.; Saha, P.; Jha, K.K.; Sukumar, N.; Sarma, B.K. Reciprocal carbonyl-carbonyl interactions in small molecules and proteins. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, D.B.; Shkel, I.A.; Phan, N.M.; Sternke, M.; Lingeman, E.; Cheng, X.; Cheng, L.; O’Connor, K.; Record, M.T. Chemical Interactions of Polyethylene Glycols (PEGs) and Glycerol with Protein Functional Groups: Applications to Effects of PEG and Glycerol on Protein Processes. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 3528–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Deygen, I.M.; Musatova, O.E.; Orlov, V.N.; Melik-Nubarov, N.S.; Grozdova, I.D. Poly (Ethylene Glycol) Interacts with Hyaluronan in Aqueous Media. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, M.M.; Fresno, M.J.; Ramírez, A. Rheological study of binary gels with Carbopol® UltrezTM 10 and hyaluronic acid. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Bures, P.; Leobandung, W.; Ichikawa, H. Hydrogels in pharmaceutical formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xu, T.; Chen, W.; Wang, R.; Xu, Z.; Ye, Z.; Chi, B. Improvement of toughness for the hyaluronic acid and adipic acid dihydrazide hydrogel by PEG. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, L.R.; Emmett, M.; Santa Ana, C.A.; Fordtran, J.S. Osmotic effects of polyethylene glycol. Gastroenterology 1988, 94, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, A.M.; Jiang, H.; Shui, Z.; Cao, X.; Huang, X.; Imran, S.; Ahmad, B.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Shang, Y.; et al. Interactive effect of shade and PEG-induced osmotic stress on physiological responses of soybean seedlings. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 2382–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eraga, S.; Olayemi, O.; Obidiro, O.; Iwuagwu, M. Effects of starch pre-gelatinization on the physicochemical and tableting properties of a co-processed excipient for direct compression. West Afr. J. Pharm. 2024, 35, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fini, A.; Cavallari, C.; Ospitali, F. Diclofenac salts. V. examples of polymorphism among diclofenac Salts with Alkyl-hydroxy Amines Studied by DSC and HSM. Pharmaceutics 2010, 2, 136–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Bala, V.C.; Singh, H.; Jayant, R. Formulation and Evaluation of Diclofenac Sodium Microemulsion Subcutaneous Drug Delivery System. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2021, 12, 4418–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik-Pastuszka, D.; Skrzypczyk, A.; Musiał, W. The interactions and release kinetics of sodium hyaluronate implemented in nonionic and anionic polymeric hydrogels, studied by immunoenzymatic ELISA test. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tama, D.; Mahuli, M.; Anandamoy, R. Formulation and characterization of papaya leaf gel. GSC Biol. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 10, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, L.; Galleguillos, R. Rheology Modifiers and Consumer Perception. In Harry’s Cosmeticology, 9th ed.; Rosen, M.R., Ed.; Chemical Publishing Company: Palm Springs, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 766–807. [Google Scholar]
- Helberg, R.M.L.; Dai, Z.; Ansaloni, L.; Deng, L. PVA/PVP blend polymer matrix for hosting carriers in facilitated transport membranes: Synergistic enhancement of CO2 separation performance. Green Energy Environ. 2020, 5, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamimi, M.A.; Elzayat, E.M.; Qamar, W.; Alshehri, S.M.; Sherif, A.Y.; Haq, N.; Shakeel, F. Evaluation of the bioavailability of hydrocortisone when prepared as solid dispersion. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, R.R.; Ayalasomayajula, L.U.; Raju, A.N.; Kumari, K.T.; Kumar, P.R. Formulation and evaluation of diclofenac sodium oro dispersible tablets using different superdisintegrants by direct compression technique. Der Pharm. Lett. 2016, 8, 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Tudja, P.; Khan, M.Z.I.; Meštrović, E.; Horvat, M.; Golja, P. Thermal behaviour of diclofenac sodium: Decomposition and melting characteristics. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 49, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropes, M.W.; Bauer, W. Synovial Fluid Changes in Joint Disease; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Goldie, I.; Nachemson, A. Synovial pH in rheumatoid knee-joints. Acta Orthop. Scandfnav. 1969, 40, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamäki, K.; Nordström, T.; Nurmi, K.; Åkerman, K.E.; Kovanen, P.T.; Öörni, K.; Eklund, K.K. Extracellular Acidosis Is a Novel Danger Signal Alerting. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 13410–13419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Ryu, H.J.; Baek, H.-M.; Shin, D.M.; Hong, J.H. Dynamic synovial fi broblasts are modulated by NBCn1 as a potential target in rheumatoid arthritis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 54, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigata, M.; Meinert, C.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Bock, N. Hydrogels as drug delivery systems: A review of current characterization and evaluation techniques. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikušová, V.; Ferková, J.; Žigrayová, D.; Krchňák, D.; Mikuš, P. Comparative Study of Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels: Rheological and Texture Properties and Ibuprofen Release. Gels 2022, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erikci, S.; van den Bergh, N.; Boehm, H. Kinetic and Mechanistic Release Studies on Hyaluronan Hydrogels for Their Potential Use as a pH-Responsive Drug Delivery Device. Gels 2024, 10, 731–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djekic, L.; Martinović, M.; Dobričić, V.; Čalija, B.; Medarević, Đ.; Primorac, M. Comparison of the Effect of Bioadhesive Polymers on Stability and Drug Release Kinetics of Biocompatible Hydrogels for Topical Application of Ibuprofen. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musel, J.; Komersov, A.; Matzick, K.; Skalick, B. A Critical Overview of FDA and EMA Statistical Methods to Compare In Vitro Drug Dissolution Profiles of Pharmaceutical Products. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1703–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.P.; Lesko, L.J.; Fan, J.; Fleischer, N.; Handerson, J.; Malinowski, H.; Makary, M.; Ouderkirk, L.; Roy, S.; Sathe, P.; et al. FDA guidance for industry 1 dissolution testing of immediate release solid oral dosage forms. Dissolut. Technol. 1997, 4, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrucci, R.H.; Harwood, W.S.; Herring, G.F.; Madura, J.D. General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Atkins, P.; de Paula, J. Physical Chemistry for the Life Sciences; W.H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, P.; Lobo, J.M.S. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggi, R.B.; Kilaru, N.B. Calculation of predominant drug release mechanism using Peppas-Sahlin model (substitution method): A linear regression approach. Asian J. Pharm. Technol. 2016, 6, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbuchulem, K.I. How Confident Is the Confidence Interval. Ann. Ib. Postgrad. Med. 2022, 20, 101–202. [Google Scholar]
- Greenland, S.; Senn, S.J.; Rothman, K.J.; Carlin, J.B.; Poole, C.; Goodman, S.N.; Altman, D.G. Statistical tests, p values, confidence intervals, and power: A guide to misinterpretations. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 31, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urząd Rejestracji Produktów Leczniczych Wyrobów Medycznych i Produktów Biobójczych. Charakterystyka produktu leczniczego. 2004. Available online: https://leksykon.com.pl/baza-chpl/d/diclogel-zel-10-mg-g-chpl.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Urząd Rejestracji Produktów Leczniczych Wyrobów Medycznych i Produktów Biobójczych. Charakterystyka produktu leczniczego. 2023. Available online: https://leksykon.com.pl/baza-chpl/m/mel-max-actigel-zel-20-mg-g-chpl.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Urząd Rejestracji Produktów Leczniczych Wyrobów Medycznych i Produktów Biobójczych. Charakterystyka produktu leczniczego. 2016. Available online: https://leksykon.com.pl/baza-chpl/s/solacutan-zel-30-mg-g-chpl.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Available online: https://www.gdziepolek.pl/produkty/107636/biolevox-ha-tendon-iniekcja/ulotka/260160?ns=true (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Available online: https://gdziepolek.blob.core.windows.net/product-documents/doc202785/biolevox-ha-ulotka.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Available online: https://gdziepolek.blob.core.windows.net/product-documents/doc202774/biolevox-ha-one-ulotka.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Council of Europe. European Pharmacopeia 11.0. In Dissolution Test for Solid Dosage Forms; European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & Health Care (EDQM): Strasbourg, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Polska Farmakopea XII; Urząd Rejestracji Produktów Leczniczych, Wyrobów Medycznych i Produktów Biobójczych: Warszawa, Poland, 2020.
- Shrestha, M.; Bhagan, S.; Walters, M.J. Memorandum: Recommended Approaches for Reviewing Nicotine Dissolution Profile Differences for Smokeless Tobacco Products and Other Orally Placed Tobacco Products in Pre-Market Tobacco Applications; US Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research: Rockville, MD, USA, 2021; pp. 1–5. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/177444/download (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Amini, E.; Kurumaddali, A.; Bhagwat, S.; Berger, S.M.; Hochhaus, G. Optimization of the Transwell® System for Assessing the Dissolution Behavior of Orally Inhaled Drug Products through In Vitro and In Silico Approaches. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1109–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei, F.; Lahiji, M.G.; Sadat, T.; Kashi, J.; Najafi, F. Drug release kinetics and biological properties of a novel local drug carrier system. Dent. Res. J. 2021, 18, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarizadeh, M.; Esfandiari, N.; Honarvar, B.; Sajadian, S.A.; Azdarpour, A. Kinetic Modeling to Explain the Release of Medicine from Drug Delivery Systems. Chem. Bio Eng. 2023, 10, 1006–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarachi, C.S.; Onunkwo, G.; Onyishi, I. Kinetics and mechanisms of drug release from swellable and non swellable matrices: A review. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. 2013, 4, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
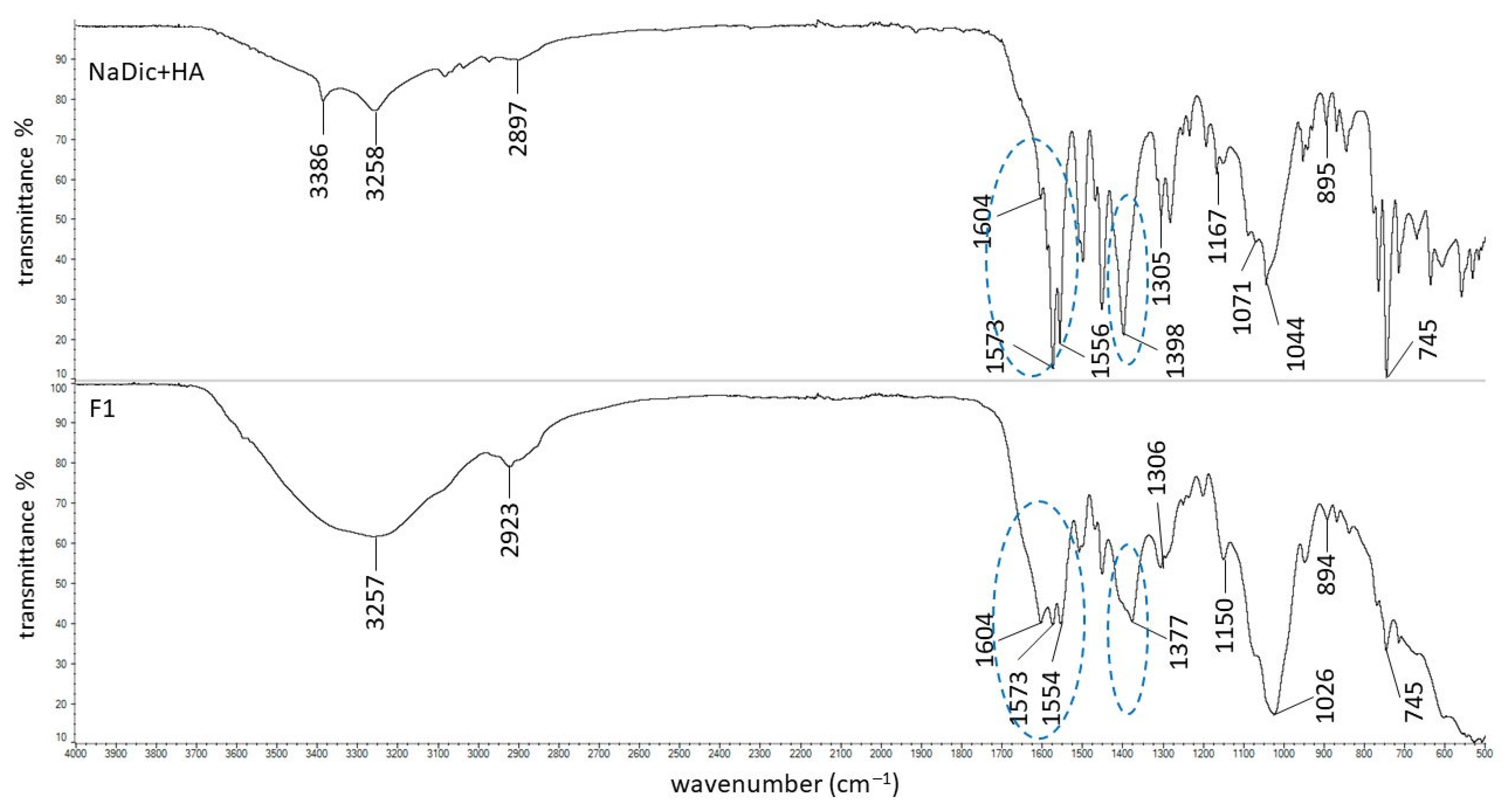
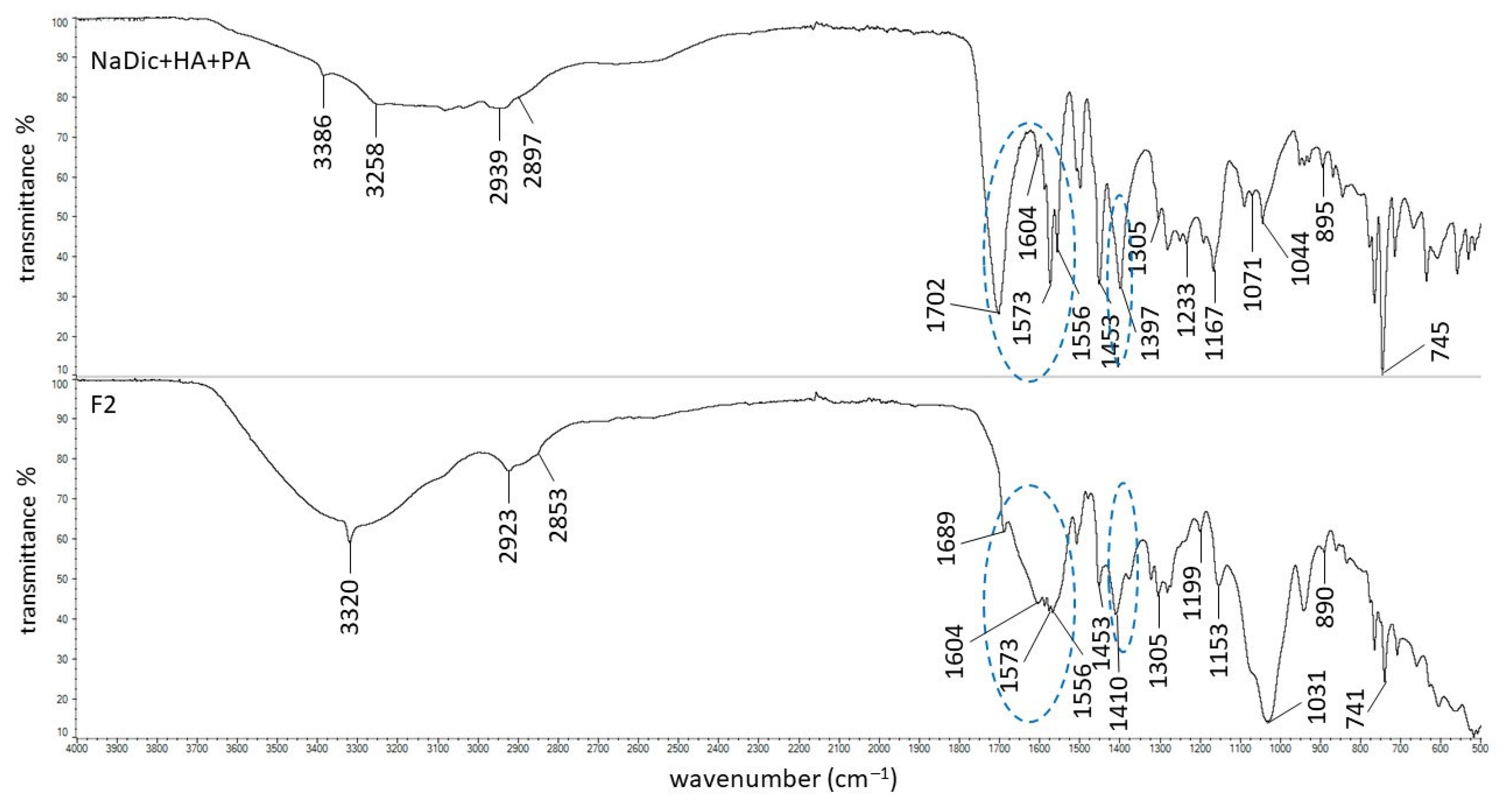
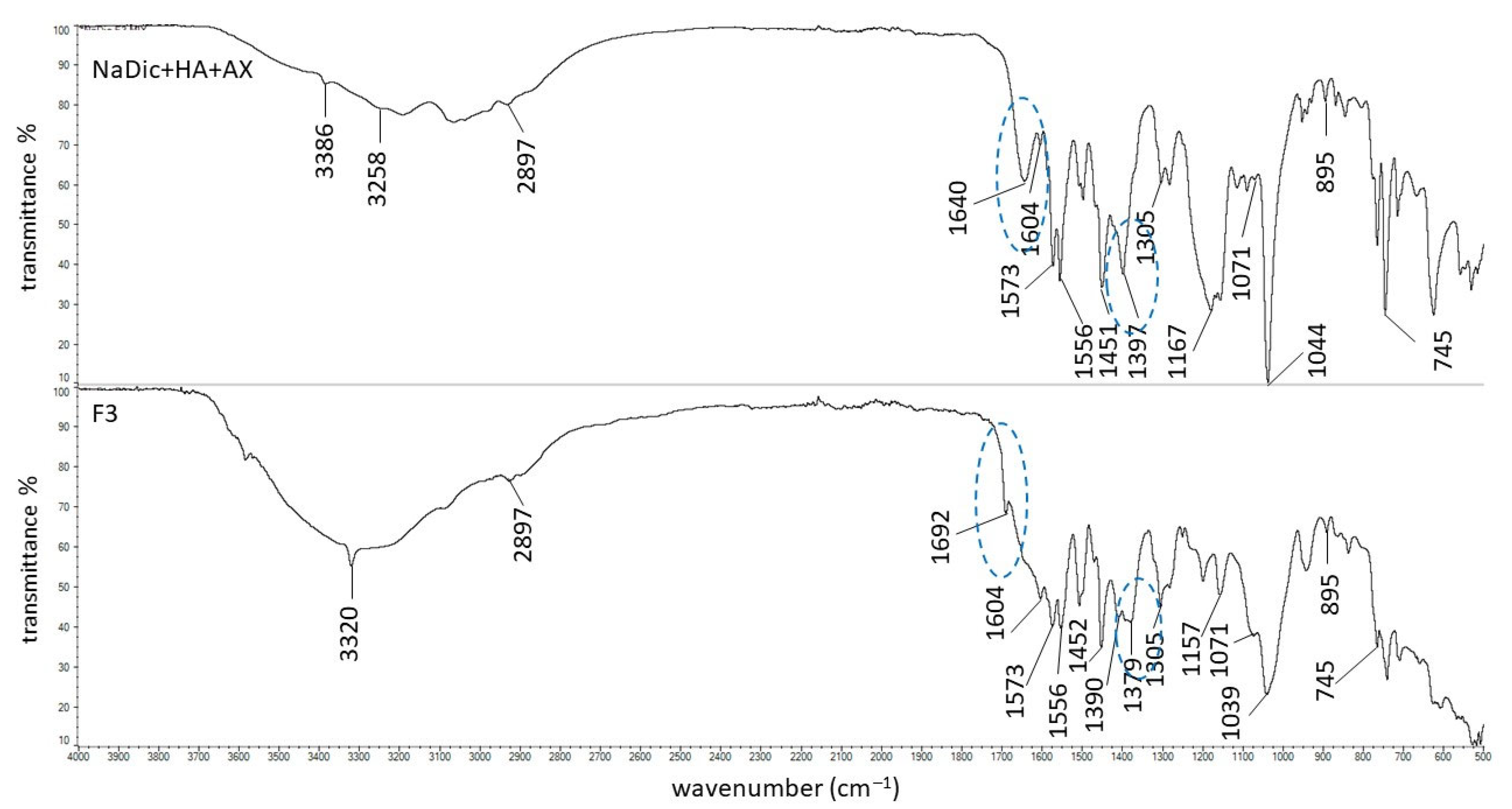
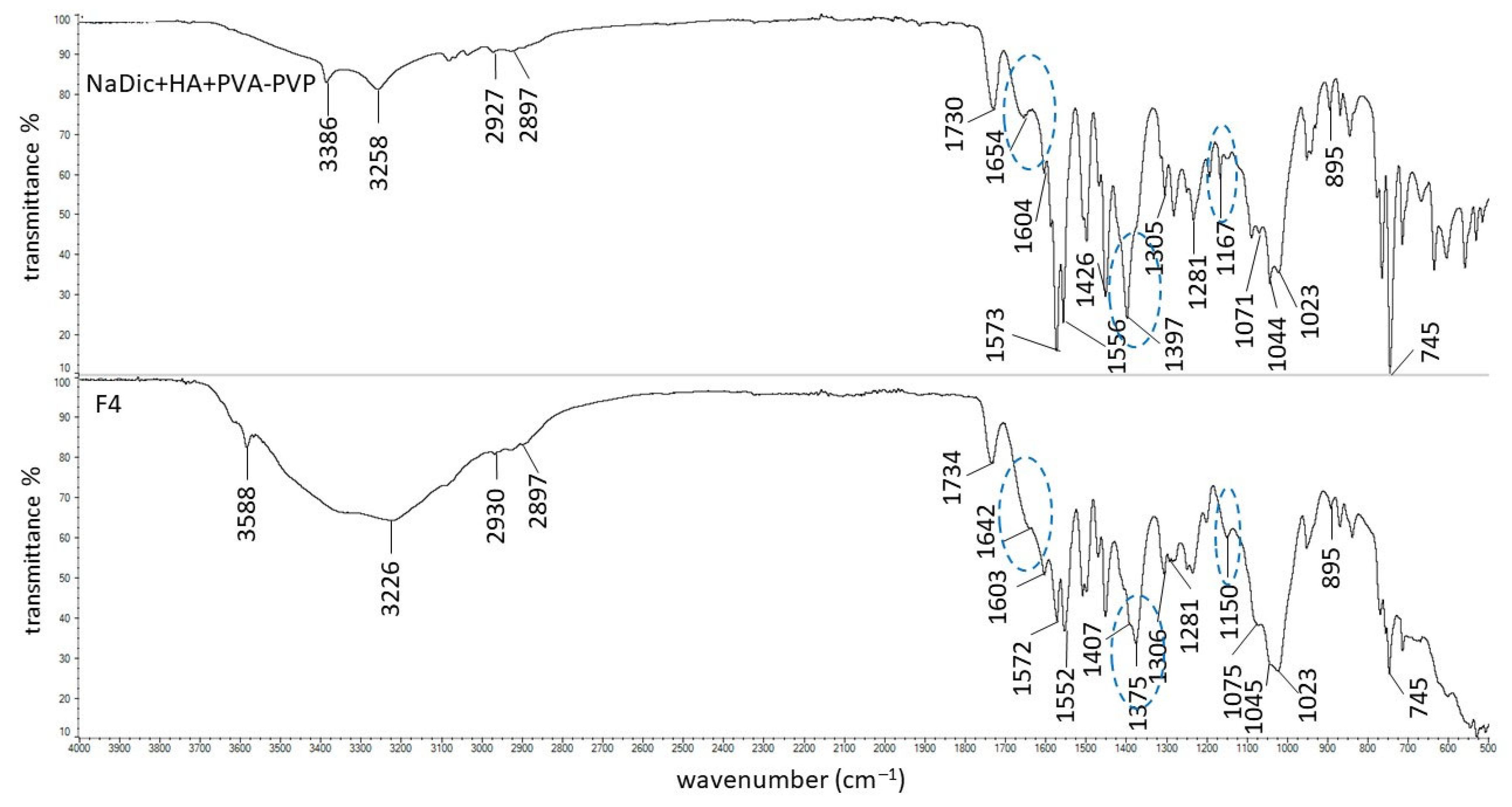
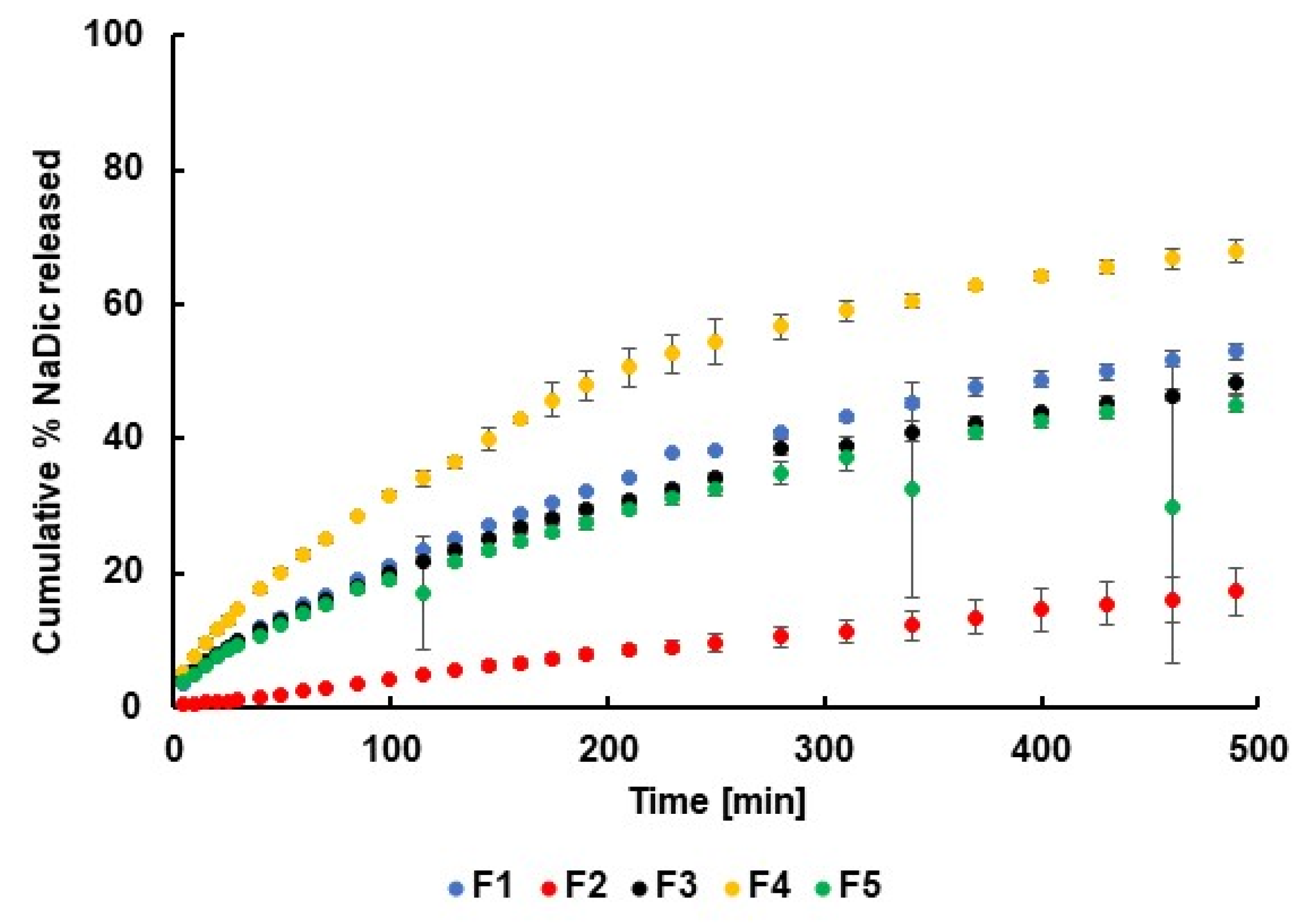
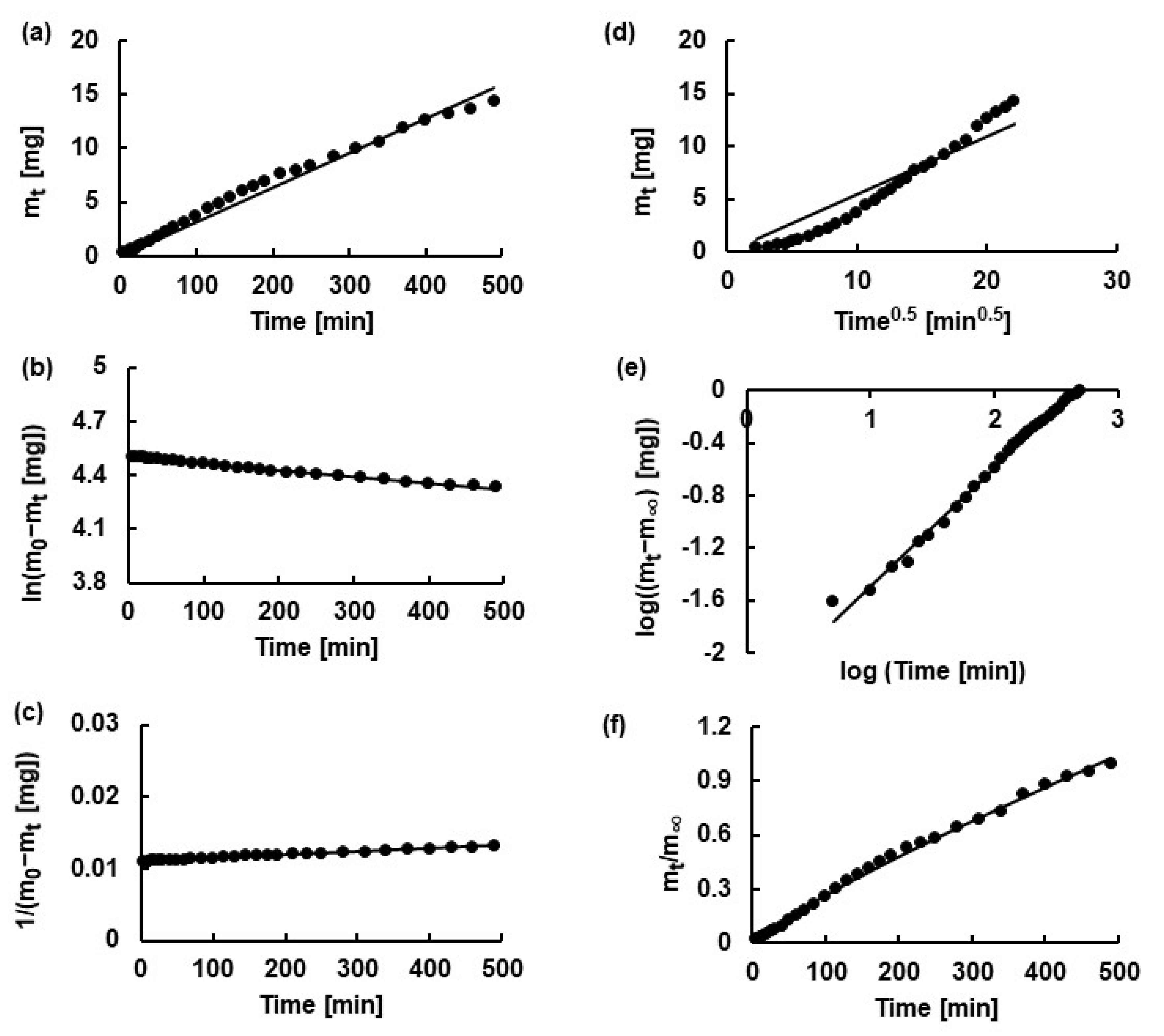
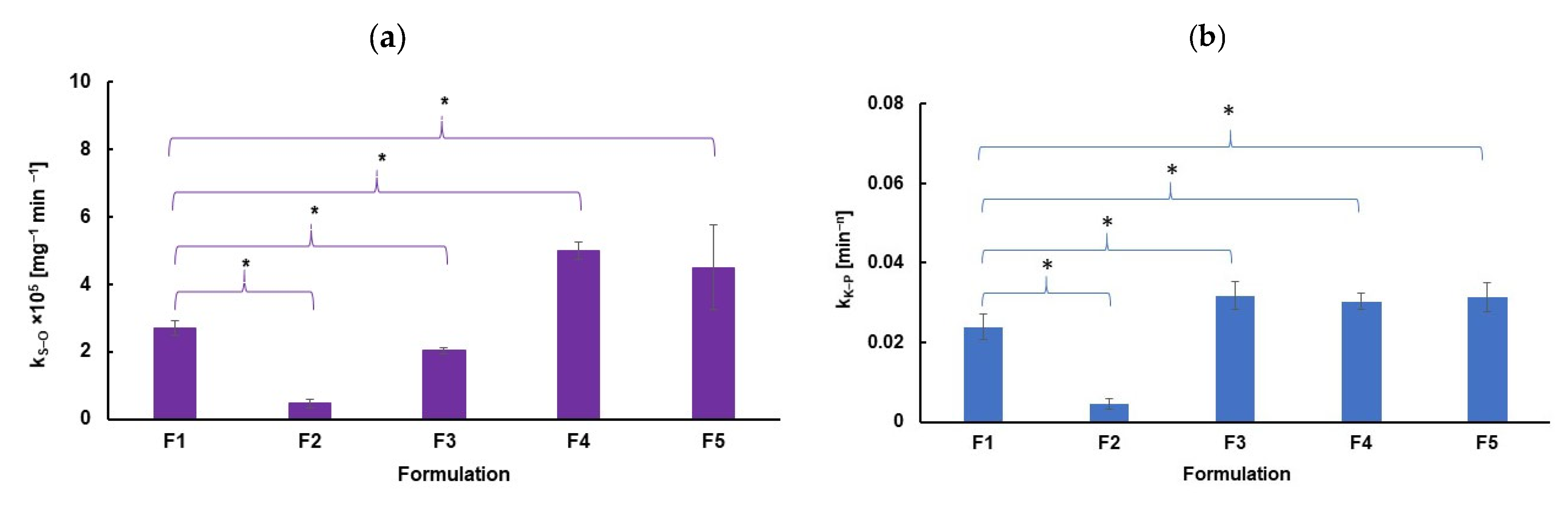
| Formulation | NaDic [g] | HA [g] | PA [g] | AX [g] | PVA− PVP [g] | PEG [g] | Water [g] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 2 | 4 | — | — | — | — | 194 |
| F2 | 2 | 4 | 1 | — | — | — | 193 |
| F3 | 2 | 4 | — | 1 | — | — | 193 |
| F4 | 2 | 4 | — | — | 1 | — | 193 |
| F5 | 2 | 4 | — | — | — | 1 | 193 |
| Formulation | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.20 ± 0.11 | 5.71 ± 0.05 | 7.87 ± 0.03 | 7.71 ± 0.01 | 7.69 ± 0.05 |
| f1 | f2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formulation | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 |
| F1 | 75.06 | 8.33 | 39.97 | 15.96 | 31.74 | 75.20 | 45.88 | 59.91 |
| Kinetic Model | Kinetic Parameters | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z−O | k0 × 10 [mg × min−1] | 1.24 ± 0.10 | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 1.08 ± 0.09 | 1.57 ± 0.16 | 0.89 ± 0.10 |
| t0.5 [min] | 363 ± 29 | 1371 ± 43 | 413 ± 36 | 277 ± 28 | 2460 ± 58 | |
| R2 | 0.9571 ± 0.0049 | 0.9932 ± 0.0032 | 0.9498 ± 0.0044 | 0.9327 ± 0.0033 | 0.8962 ± 0.0667 | |
| F−O | k1 × 103 [min−1] | 1.59 ± 0.07 | 0.386 ± 0.013 | 1.27 ± 0.07 | 2.31 ± 0.16 | 1.09 ± 0.17 |
| t0.5 [min] | 435 ± 20 | 1862 ± 65 | 545 ± 29 | 301 ± 21 | 641 ± 115 | |
| R2 | 0.9855 ± 0.0043 | 0.9922 ± 0.0022 | 0.9806 ± 0.0056 | 0.9667 ± 0.0114 | 0.8176 ± 0.1898 | |
| S−O | k2 × 105 [mg−1 × min−1] | 2.72 ± 5.12 | 0.472 ± 0.015 | 2.03 ± 0.06 | 5.01 ± 0.16 | 4.50 ± 0.15 |
| t0.5 [min] | 409 ± 8 | 2461 ± 74 | 550 ± 16 | 230 ± 7 | 306 ± 10 | |
| R2 | 0.9971 ± 0.0032 | 0.9935 ± 0.0029 | 0.9939 ± 0.0045 | 0.9918 ± 0.0091 | 0.9908 ± 0.0088 | |
| H | kH [mg × min−1/2] | 2.20 ± 0.06 | 0.568 ± 0.047 | 1.93 ± 0.04 | 2.81 ± 0.06 | 1.59 ± 0.12 |
| t0.5 [min] | 421 ± 22 | 6604 ± 1027 | 543 ± 20 | 239 ± 11 | 663 ± 98 | |
| R2 | 0.9954 ± 0.0015 | 0.9567 ± 0.016 | 0.9976 ± 0.0009 | 0.9963 ± 0.0016 | 0.9529 ± 0.0502 | |
| K−P | kK-P × 102 [min−n] | 2.39 ± 0.11 | 0.460 ± 0.001 | 3.17 ± 0.01 | 3.38 ± 0.28 | 3.15 ± 0.20 |
| t0.5 [min] | 144 ± 11 | 224 ± 58 | 137 ± 13 | 121 ± 19 | 131 ± 30 | |
| R2 | 0.9983 ± 0.0005 | 0.9858 ± 0.0056 | 0.9971 ± 0.0010 | 0.9933 ± 0.0023 | 0.9954 ± 0.0057 | |
| n | 0.61 ± 0.01 | 0.88 ± 0.04 | 0.56 ± 0.01 | 0.59 ± 0.02 | 0.56 ± 0.01 | |
| P−S | k1 P-S × 106 [min−n’] | 1.67 ± 4.11 | 0.62 ± 1.50 | 0.01 ± 0.001 | 0.01 ± 0.001 | 0.01 ± 0.001 |
| k2P-S × 102 [min−n’] | 2.68 ± 0.31 | 0.529 ± 0.19 | 2.77 ± 1.09 | 4.25 ± 0.12 | 3.07 ± 0.27 | |
| 0.30 ± 0.01 | 0.43 ± 0.05 | 0.30 ± 0.05 | 0.26 ± 0.26 | 0.29 ± 0.51 | ||
| best fit * | S-O, H, K-P | Z-O, F-O, S-O | S-O, H, K-P | S-O, H, K-P | S-O, K-P | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wójcik-Pastuszka, D.; Grabara, M.; Musiał, W. Assessment of Hydrogels for Intra-Articulate Application, Based on Sodium Hyaluronate Doped with Synthetic Polymers and Incorporated with Diclofenac Sodium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157631
Wójcik-Pastuszka D, Grabara M, Musiał W. Assessment of Hydrogels for Intra-Articulate Application, Based on Sodium Hyaluronate Doped with Synthetic Polymers and Incorporated with Diclofenac Sodium. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157631
Chicago/Turabian StyleWójcik-Pastuszka, Dorota, Maja Grabara, and Witold Musiał. 2025. "Assessment of Hydrogels for Intra-Articulate Application, Based on Sodium Hyaluronate Doped with Synthetic Polymers and Incorporated with Diclofenac Sodium" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157631
APA StyleWójcik-Pastuszka, D., Grabara, M., & Musiał, W. (2025). Assessment of Hydrogels for Intra-Articulate Application, Based on Sodium Hyaluronate Doped with Synthetic Polymers and Incorporated with Diclofenac Sodium. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157631





