Suppression of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 in the Ventromedial Hypothalamus Induces Hyperphagia and Obesity in Male Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
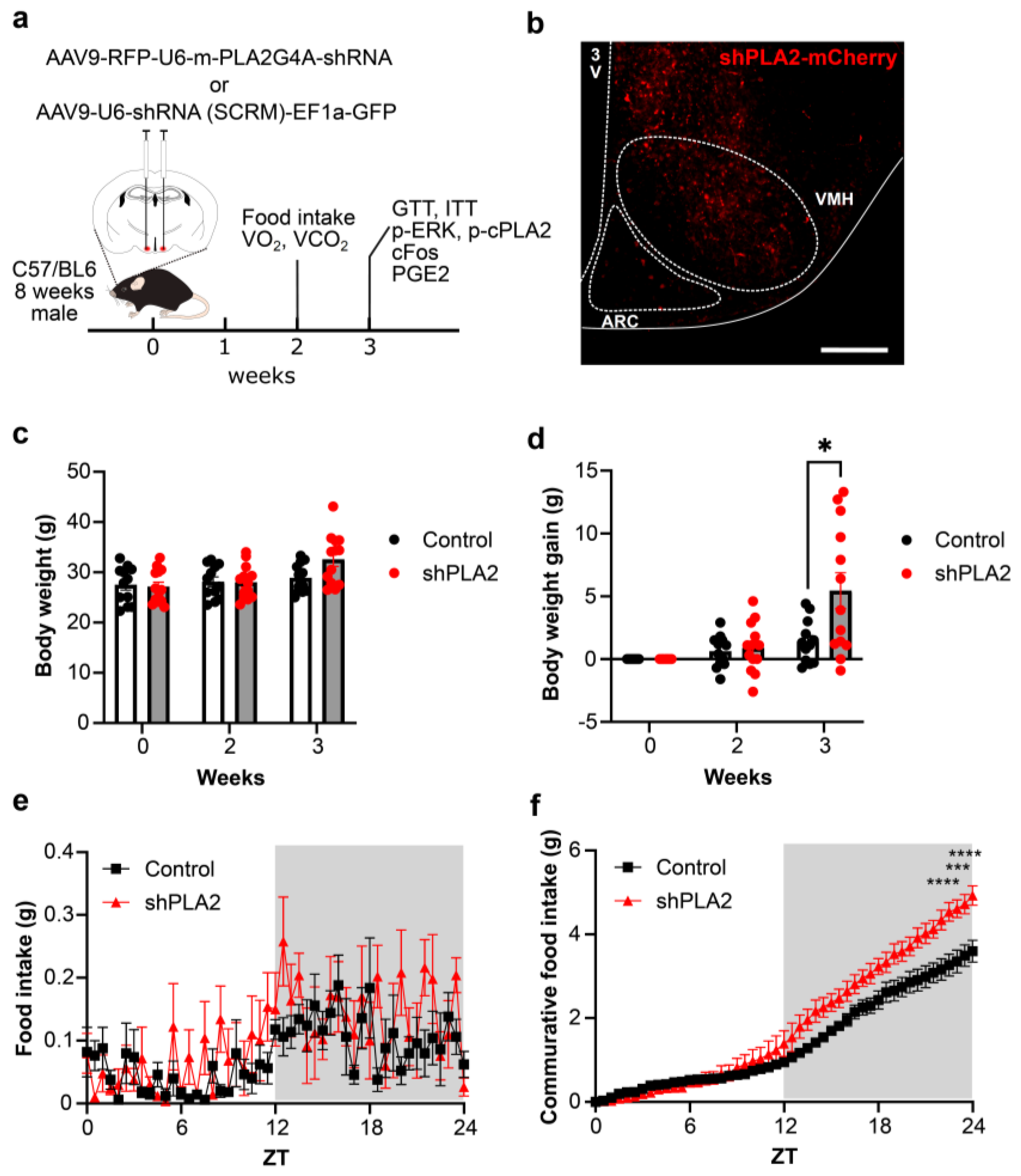
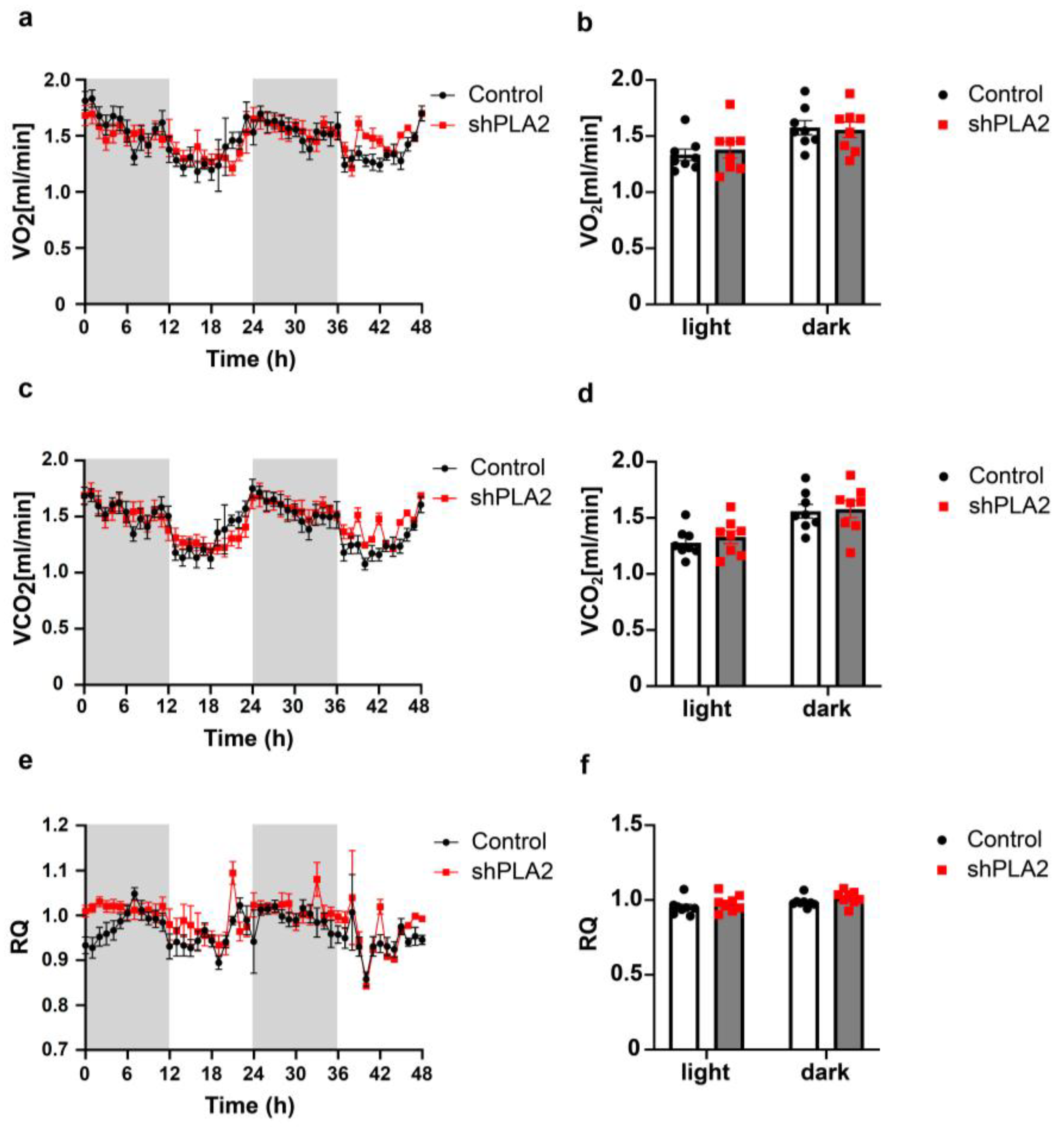
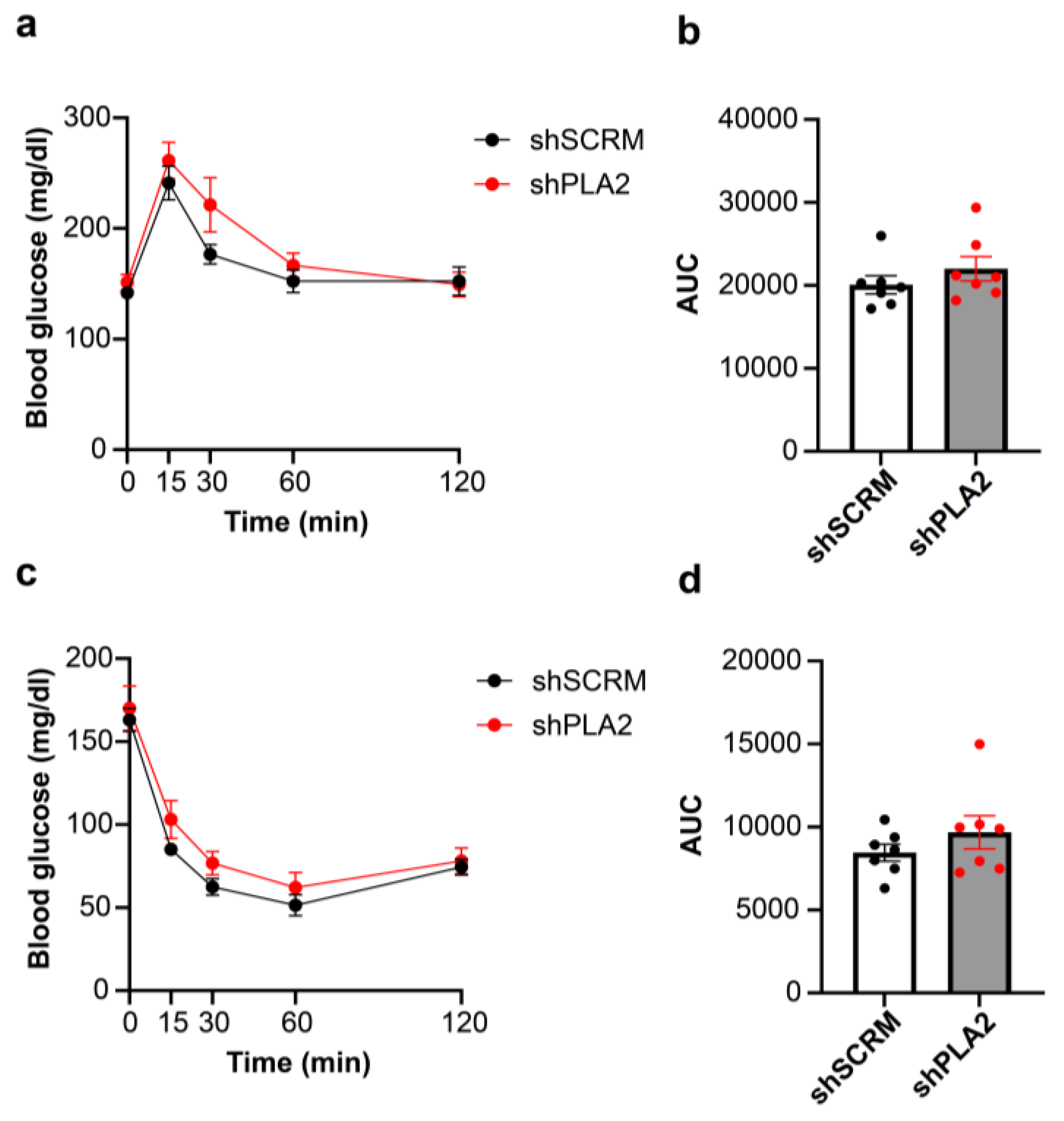
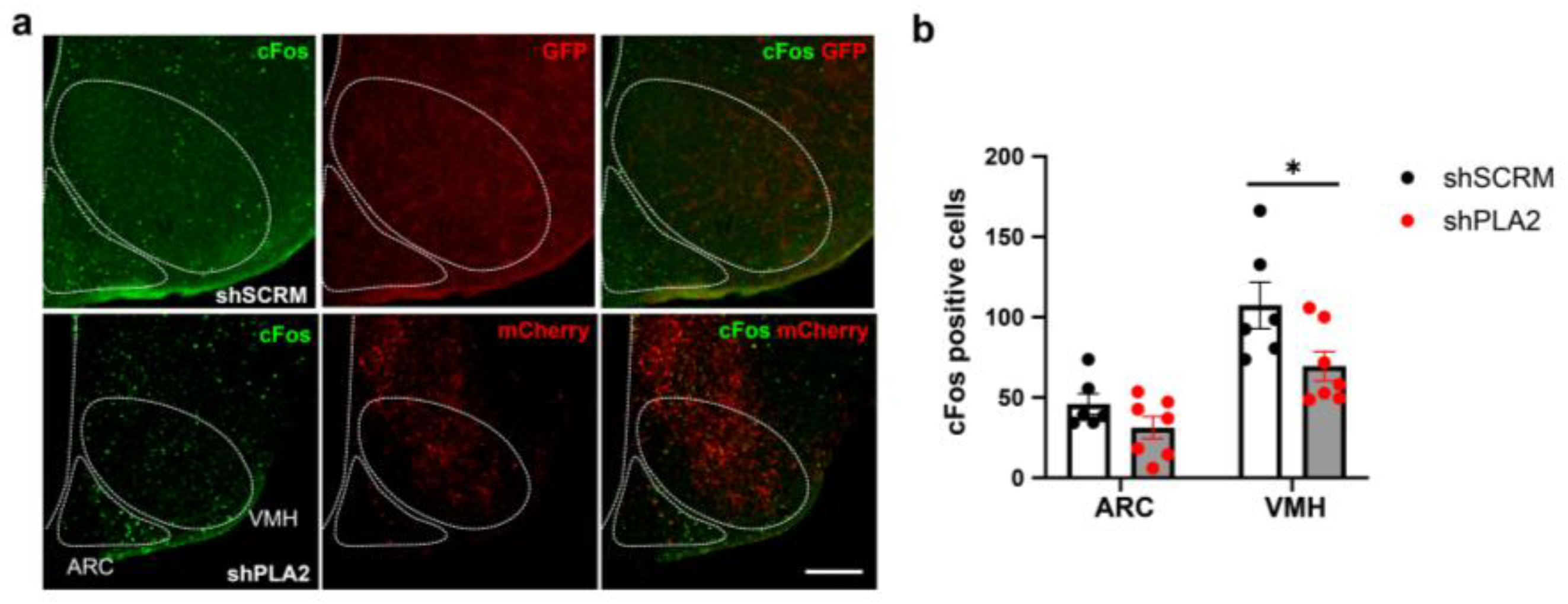
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Cannula Implantation and Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Injection
4.3. Body Weight Gain, Food Intake, and Oxygen Consumption
4.4. Prostaglandin E2 ELISA
4.5. p-ERK and p-cPLA2 Immunohistochemistry
4.6. cFos Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| cPLA2 | cytosolic phospholipase A2 |
| SCRM | scrumble |
| VMH | ventromedial hypothalamus |
| PGs | Prostaglandins |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| KD | knockdown |
| COX | cyclooxygenase |
| dm | dorsomedial |
| ARC | arcuate nucleus |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| NTS | nucleus tractus solitarius |
| CCK | cholecystokinin |
References
- Narumiya, S.; Furuyashiki, T. Fever, inflammation, pain and beyond: Prostanoid receptor research during these 25 years. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecchi, E.; Dallaporta, M.; Thirion, S.; Salvat, C.; Berenbaum, F.; Jean, A.; Troadec, J.D. Involvement of central microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 in IL-1-induced anorexia. Physiol Genom. 2006, 25, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayaishi, O. Molecular mechanisms of sleep-wake regulation: A role of prostaglandin D2. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2000, 355, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, Y.; Furuyashiki, T.; Yamada, K.; Nagai, T.; Bito, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Kitaoka, S.; Ushikubi, F.; Nabeshima, T.; Narumiya, S. Prostaglandin E receptor EP1 controls impulsive behavior under stress. In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Washington, DC, USA, 24 November 2005; Volume 102, pp. 16066–16071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Furuyashiki, T.; Kitaoka, S.; Senzai, Y.; Imoto, Y.; Segi-Nishida, E.; Deguchi, Y.; Breyer, R.M.; Breyer, M.D.; Narumiya, S. Prostaglandin E 2-mediated attenuation of mesocortical dopaminergic pathway is critical for susceptibility to repeated social defeat stress in mice. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 4319–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohinata, K.; Yoshikawa, M. Central prostaglandins in food intake regulation. Nutrition 2008, 24, 798–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapirstein, A.; Bonventre, J.V. Specific physiological roles of cytosolic phospholipase A2 as defined by gene knockouts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2000, 1488, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.I.; Romanovsky, A.A. Prostaglandin E2 as a mediator of fever: Synthesis and catabolism. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 1977–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.L.; Matsunaga, H.; Sugiura, Y.; Hayasaka, T.; Yamamoto, I.; Ishimoto, T.; Imoto, D.; Suematsu, M.; Iijima, N.; Kimura, K.; et al. Prostaglandin in the ventromedial hypothalamus regulates peripheral glucose metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Xu, S.; Sugiura, Y.; Arima, Y.; Hayasaka, T.; Lee, M.L.; Ishimoto, T.; Araki, Y.; Ngurari, S.; Niu, Z.; et al. Hypothalamic prostaglandins facilitate recovery from hypoglycemia but exacerbate recurrent hypoglycemia in mice. Biorxiv 2024. submitted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmouni, K.; Sigmund, C.D.; Haynes, W.G.; Mark, A.L. Hypothalamic ERK Mediates the Anorectic and Thermogenic Sympathetic Effects of Leptin. Diabetes 2009, 58, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, G.M.; Patterson, L.M.; Berthoud, H.R. Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1/2 Signaling Pathway in Solitary Nucleus Mediates Cholecystokinin-Induced Suppression of Food Intake in Rats. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 10240–10247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, G.M.; Duos, B.; Patterson, L.M.; Berthoud, H.R. Melanocortinergic Modulation of Cholecystokinin-Induced Suppression of Feeding through Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Signaling in Rat Solitary Nucleus. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 3739–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthoud, H.R.; Sutton, G.M.; Townsend, R.L.; Patterson, L.M.; Zheng, H. Brainstem mechanisms integrating gut-derived satiety signals and descending forebrain information in the control of meal size. Physiol. Behav. 2006, 89, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Xu, B.; Inoue, H.; Chen, Q.M. p38 MAPK mediates COX-2 gene expression by corticosterone in cardiomyocytes. Cell Signal. 2008, 20, 1952–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, H.; Zigman, J.M.; Ye, C.; Lee, C.E.; McGovern, R.A.; Tang, V.; Kenny, C.D.; Christiansen, L.M.; White, R.D.; Edelstein, E.A.; et al. Leptin Directly Activates SF1 Neurons in the VMH, and This Action by Leptin Is Required for Normal Body-Weight Homeostasis. Neuron 2006, 49, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöckener, T.; Hess, S.; Belgardt, B.F.; Paeger, L.; Verhagen, L.A.W.; Husch, A.; Sohn, J.-W.; Hampel, B.; Dhillon, H.; Zigman, J.M.; et al. High-fat feeding promotes obesity via insulin receptor/PI3K-dependent inhibition of SF-1 VMH neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viskaitis, P.; Irvine, E.E.; Smith, M.A.; Choudhury, A.I.; Alvarez-Curto, E.; Glegola, J.A.; Hardy, D.G.; Pedroni, S.M.A.; Pessoa, M.R.P.; Fernando, A.B.P.; et al. Modulation of SF1 Neuron Activity Coordinately Regulates Both Feeding Behavior and Associated Emotional States. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 3559–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, K.; Yano, M.; Miyake, H.; Kimura, H. Termination mechanism of CREB-dependent activation of COX-2 expression in early phase of adipogenesis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 384, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, S.; Ishikawa, F.; Sasaki, T.; Terkelsen, M.K.; Ravnskjaer, K.; Jinno, T.; Tanaka, J.; Goto, T.; Inoue, K. Loss of CREB Coactivator CRTC1 in SF1 Cells Leads to Hyperphagia and Obesity by High-fat Diet But Not Normal Chow Diet. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddinger, S.B.; Kahn, C.R. FROM MICE TO MEN: Insights into the Insulin Resistance Syndromes. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2006, 68, 123–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, L.J.; Cai, F.; Belsham, D.D. Hypothalamic Preproghrelin Gene Expression Is Repressed by Insulin via Both PI3-K/Akt and ERK1/2 MAPK Pathways in Immortalized, Hypothalamic Neurons. Neuroendocrinology 2009, 89, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternson, S.M.; Shepherd, G.M.G.; Friedman, J.M. Topographic mapping of VMH→ arcuate nucleus microcircuits and their reorganization by fasting. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1356–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffens, A.B.; Scheurink, A.J.; Porte, D.; Woods, S.C. Penetration of peripheral glucose and insulin into cerebrospinal fluid in rats. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1988, 255, R200–R204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakic, T.; Jevdjovic, T.; Djordjevic, J.; Vujovic, P. Short-term fasting differentially regulates PI3K/AkT/mTOR and ERK signalling in the rat hypothalamus. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2020, 192, 111358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Peters, M.; Urban, N.; Knowlton, J.; Napierala, T.; Gabrysiak, J. Mice lacking DUSP6/8 have enhanced ERK1/2 activity and resistance to diet-induced obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 533, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, C.; Yu, F.; Wang, Y.; Gu, J.; Ma, L.; Ho, G. ERK1/2 mediates glucose-regulated POMC gene expression in hypothalamic neurons. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 54, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorato, R.; Menezes, A.M.; Giusti-Paiva, A.; De Castro, M.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; Elias, L.L.K. Prostaglandin mediates endotoxaemia-induced hypophagia by activation of pro-opiomelanocortin and corticotrophin-releasing factor neurons in rats. Exp. Physiol. 2009, 94, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skibicka, K.P.; Alhadeff, A.L.; Leichner, T.M.; Grill, H.J. Neural controls of prostaglandin 2 pyrogenic, tachycardic, and anorexic actions are anatomically distributed. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 2400–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellerstein, M.K.; Meydani, S.N.; Meydani, M.; Wu, K.; Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-1-induced anorexia in the rat. Influence of prostaglandins. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 84, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elander, L.; Engström, L.; Hallbeck, M.; Blomqvist, A. IL-1 and LPS induce anorexia by distinct mechanisms differentially dependent on microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.M.; Vogt, S.K.; Burney, M.W.; Muglia, L.J.; Bur-Ney, M.W. COX-2 inhibition attenuates anorexia during systemic inflammation without impairing cytokine production. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 282, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, C.C. Properties and Regulation of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 16709–16712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaser, A.B.; Kuiri, J.; Natunen, T.; Hruška, P.; Potěšil, D.; Auriola, S.; Hiltunen, M.; Terasaki, T.; Lehtonen, M.; Jalkanen, A.; et al. Enhanced drug delivery by a prodrug approach effectively relieves neuroinflammation in mice. Life Sci. 2022, 310, 121088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsberth, C.; Elander, L.; Hamzic, N.; Norell, M.; Lönn, J.; Engström, L.; Blomqvist, A. The role of interleukin-6 in lipopolysaccharide-induced fever by mechanisms independent of prostaglandin e2. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 1850–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engström, L.; Ruud, J.; Eskilsson, A.; Larsson, A.; Mackerlova, L.; Kugelberg, U.; Qian, H.; Vasilache, A.M.; Larsson, P.; Engblom, D.; et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced fever depends on prostaglandin E2 production specifically in brain endothelial cells. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 4849–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abe, T.; Ishimoto, T.; Araki, Y.; Niu, Z.; Li, C.; He, J.; Ngurari, S.; Toda, C. Suppression of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 in the Ventromedial Hypothalamus Induces Hyperphagia and Obesity in Male Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157532
Abe T, Ishimoto T, Araki Y, Niu Z, Li C, He J, Ngurari S, Toda C. Suppression of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 in the Ventromedial Hypothalamus Induces Hyperphagia and Obesity in Male Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157532
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbe, Takashi, Taiga Ishimoto, Yudai Araki, Ziwei Niu, Changwen Li, Jinxiao He, Samson Ngurari, and Chitoku Toda. 2025. "Suppression of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 in the Ventromedial Hypothalamus Induces Hyperphagia and Obesity in Male Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157532
APA StyleAbe, T., Ishimoto, T., Araki, Y., Niu, Z., Li, C., He, J., Ngurari, S., & Toda, C. (2025). Suppression of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 in the Ventromedial Hypothalamus Induces Hyperphagia and Obesity in Male Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157532





