Tailored Levofloxacin Incorporated Extracellular Matrix Nanoparticles for Pulmonary Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Nanoparticle Characterization
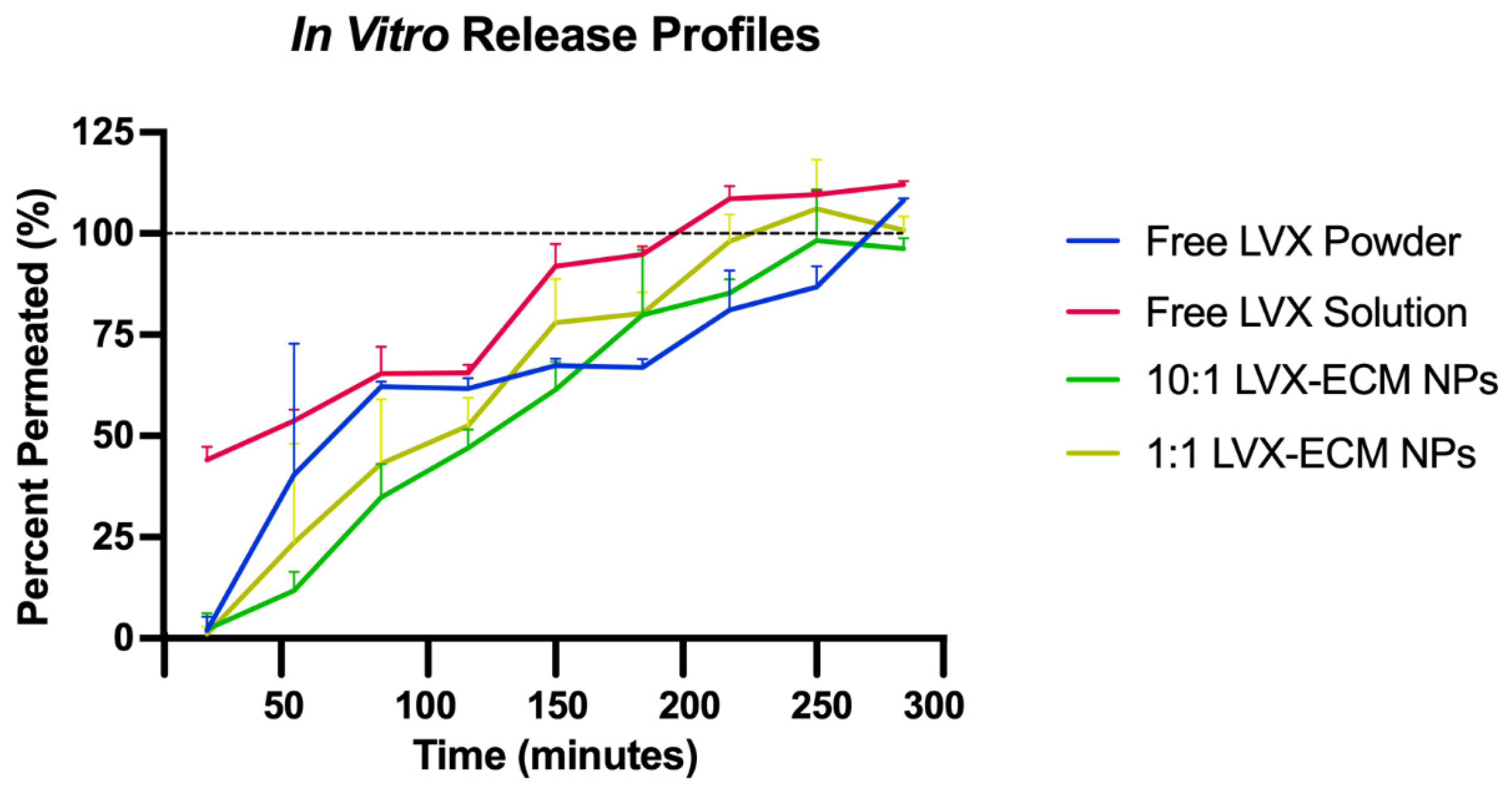
2.2. In Vitro Dissolution and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
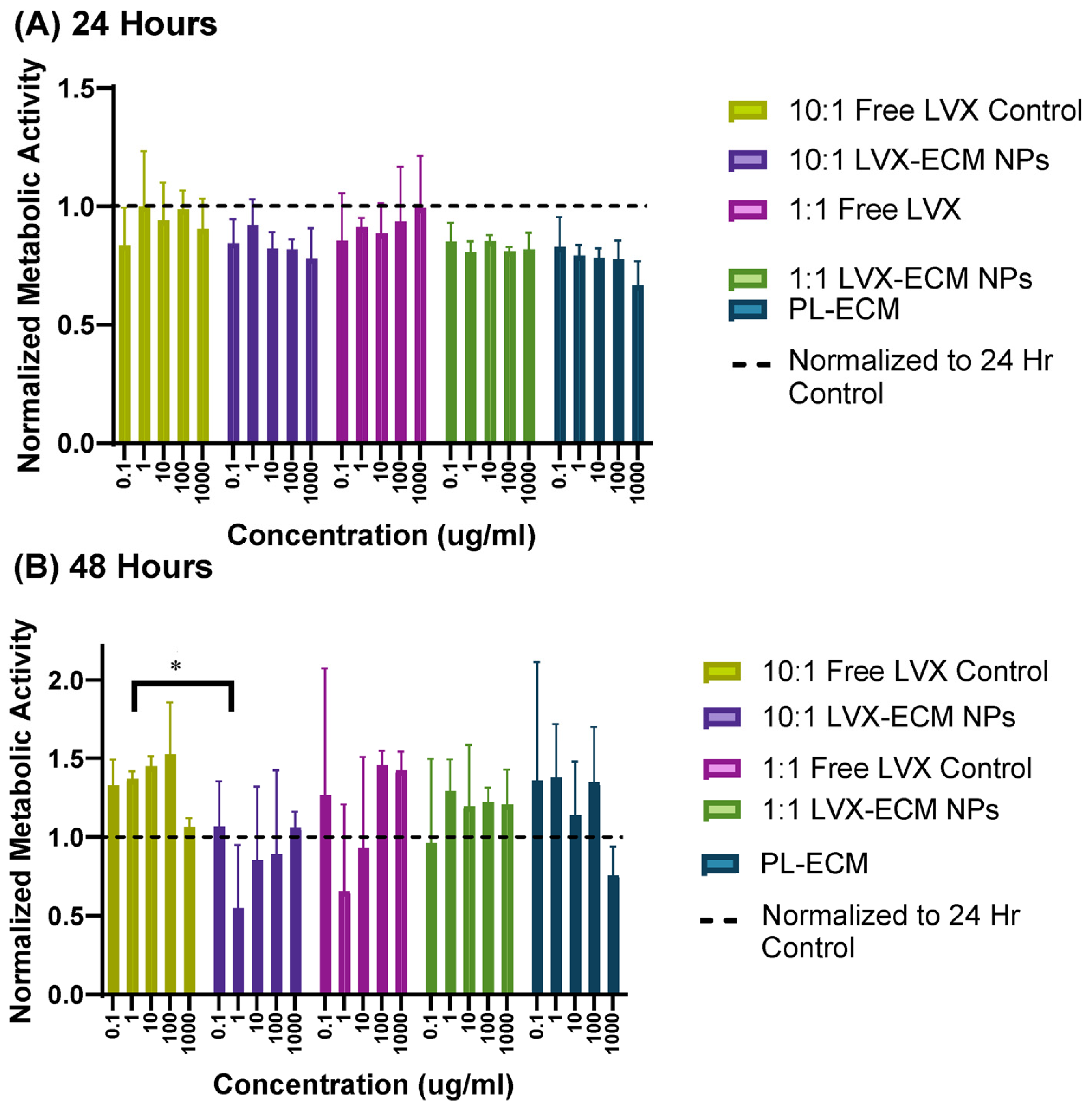
2.3. MTT Assay
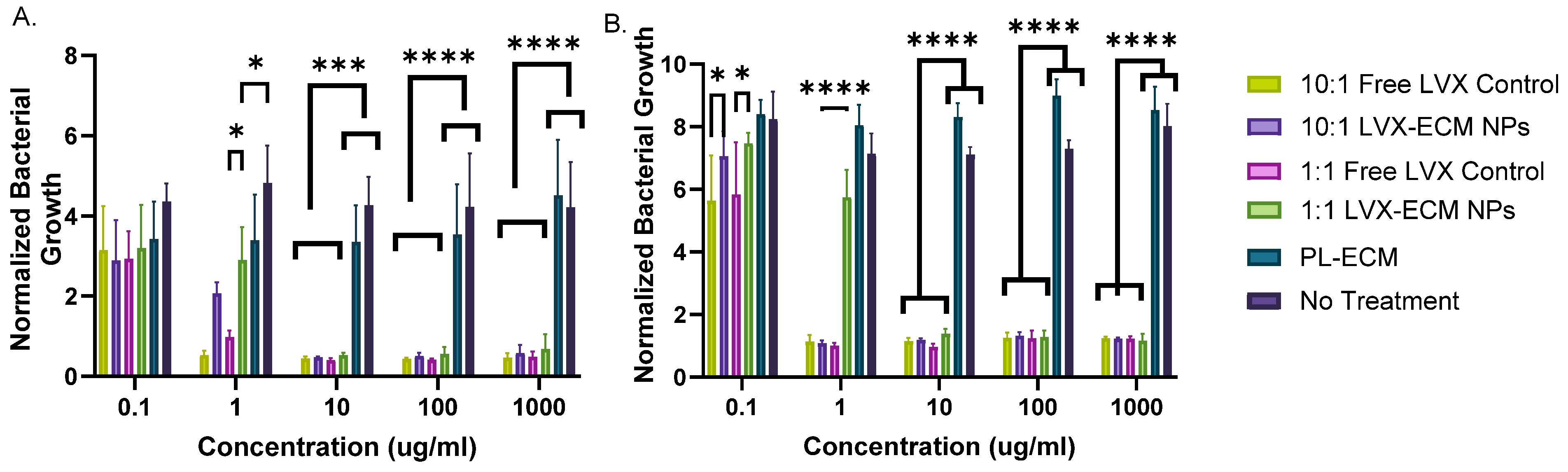
2.4. Antimicrobial Assay
3. Discussion
3.1. Nanoparticle Characterization
3.2. In Vitro Dissolution
3.3. Cell Viability Assay
3.4. Antimicrobial Assay
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Decellularization of Porcine Lung
4.3. Electrospray Deposition Process
4.4. Nanoparticle Size and Charge Characterization
4.5. In Vitro Dissolution and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
4.6. MTT Assay
4.7. Antimicrobial Assay
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. CF Foundation Estimates Increase in CF Population. CFF. July 2022. Available online: https://www.cff.org/news/2022-07/cf-foundation-estimates-increase-cf-population (accessed on 13 August 2023).
- Morrison, C.B.; Markovetz, M.R.; Ehre, C. Mucus, Mucins and Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54 (Suppl. S3), S84–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Definition of Extracellular Matrix—NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms—NCI [Internet]. 2011. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/extracellular-matrix (accessed on 25 January 2024).
- Pinezich, M.R.; Tamargo, M.A.; Fleischer, S.; Reimer, J.A.; Hudock, M.R.; Hozain, A.E.; Kaslow, S.R.; Tipograf, Y.; Soni, R.K.; Gavaudan, O.P.; et al. Pathological remodeling of distal lung matrix in end-stage cystic fibrosis patients. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilliard, T.N.; Regamey, N.; Shute, J.K.; Nicholson, A.G.; Alton, E.W.F.W.; Bush, A.; Davies, J.C. Airway remodelling in children with cystic fibrosis. Thorax 2007, 62, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Conte, G.; Costabile, G.; Baldassi, D.; Rondelli, V.; Bassi, R.; Colombo, D.; Linardos, G.; Fiscarelli, E.V.; Sorrentino, R.; Miro, A.; et al. Hybrid Lipid/Polymer Nanoparticles to Tackle the Cystic Fibrosis Mucus Barrier in siRNA Delivery to the Lungs: Does PEGylation Make the Difference? ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 7565–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, J.S.; Lai, S.K.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Ensign, L.M.; Zeitlin, P.L.; Boyle, M.P.; Hanes, J. The penetration of fresh undiluted sputum expectorated by cystic fibrosis patients by non-adhesive polymer nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2591–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, G.A.; Jung, J.; Hanes, J.; Suk, J.S. The Mucus Barrier to Inhaled Gene Therapy. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 2043–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liang, Y.; Han, R.; Lu, W.L.; Mak, J.C.W.; Zheng, Y. Rational particle design to overcome pulmonary barriers for obstructive lung diseases therapy. J. Control. Release 2019, 314, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elborn, J.S.; Flume, P.A.; Van Devanter, D.R.; Procaccianti, C. Management of chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection with inhaled levofloxacin in people with cystic fibrosis. Future Microbiol. 2021, 16, 1087–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drug Approval Package: Levaquin (Levofloxacin) NDA# 020634/S04 & 0202635/S03. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/98/020634s04.cfm# (accessed on 18 April 2024).
- Quinsair. European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/quinsair (accessed on 18 April 2024).
- Newhouse, M.T.; Hirst, P.H.; Duddu, S.P.; Walter, Y.H.; Tarara, T.E.; Clark, A.R.; Weers, J.G. Inhalation of a Dry Powder Tobramycin PulmoSphere Formulation in Healthy Volunteers. CHEST 2003, 124, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbali, R.M.; Aoun, V.; Moussa, G.; Frei, G.; Tehrani, S.F.; Del’Orto, J.C.; Hildgen, P.; Roullin, V.G.; Chain, J.L. Tailored Nanocarriers for the Pulmonary Delivery of Levofloxacin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Comparative Study. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1906–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, A.H.; Stamer, D.K.; Kyriakides, T.R. The host response to naturally-derived extracellular matrix biomaterials. Semin. Immunol. 2017, 29, 72–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, P.A.; Ritchie, A.M.; Cotman, G.M.; Valentine, M.S.; Dereski, B.S.; Heise, R.L. Electrosprayed extracellular matrix nanoparticles induce a pro-regenerative cell response. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, 2331–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahon, O.R.; Browe, D.C.; Diaz-Payno, P.J.; Pitacco, P.; Cunningham, K.T.; Mills, K.H.; Dunne, A.; Kelly, D.J. Extracellular matrix scaffolds derived from different musculoskeletal tissues drive distinct macrophage phenotypes and direct tissue-specific cellular differentiation. J. Immunol. Regen. Med. 2021, 12, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witherel, C.E.; Sao, K.; Brisson, B.K.; Han, B.; Volk, S.W.; Petrie, R.J.; Han, L.; Spiller, K.L. Regulation of extracellular matrix assembly and structure by hybrid M1/M2 macrophages. Biomaterials 2021, 269, 120667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziki, J.L.; Wang, D.S.; Pineda, C.; Sicari, B.M.; Rausch, T.; Badylak, S.F. Solubilized extracellular matrix bioscaffolds derived from diverse source tissues differentially influence macrophage phenotype. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2017, 105, 138–147. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/jbm.a.35894 (accessed on 18 April 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Suk, J.S. Enhancing nanoparticle penetration through airway mucus to improve drug delivery efficacy in the lung. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, J.; Peng, X.; Liu, X.; Arasappan, D.; Wylie, D.C.; Schwartz, S.H.; Fullmer, J.J.; McWilliams, B.C.; Smyth, H.D.; Ghosh, D. Peptides as surface coatings of nanoparticles that penetrate human cystic fibrosis sputum and uniformly distribute in vivo following pulmonary delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 322, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.S.; Tavares, M.T.; Aguiar-Ricardo, A. Sustainable strategies for nano-in-micro particle engineering for pulmonary delivery. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, M.C.; Sousa, J.J.; Pais, A.A.; Cardoso, O.; Murtinho, D.; Serra, M.E.S.; Tewes, F.; Olivier, J.-C. Optimization of levofloxacin-loaded crosslinked chitosan microspheres for inhaled aerosol therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 96, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islan, G.A.; Tornello, P.C.; Abraham, G.A.; Duran, N.; Castro, G.R. Smart lipid nanoparticles containing levofloxacin and DNase for lung delivery. Design and characterization. Colloids Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2016, 143, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayli, Y.A.; Sahin, S.; Buttini, F.; Balducci, A.G.; Montanari, S.; Vural, I.; Oner, L. Dry powders for the inhalation of ciprofloxacin or levofloxacin combined with a mucolytic agent for cystic fibrosis patients. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandling, E.N.; Rhoads, K.; Ohman, D.E.; Heise, R.L. Electrosprayed Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Extracellular Matrix Nanoparticles Accelerate Cellular Wound Healing and Reduce Gram-Negative Bacterial Growth. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.P.; Baltch, A.L.; Franke, M.A.; Michelsen, P.B.; Bopp, L.H. Levofloxacin penetrates human monocytes and enhances intracellular killing of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2000, 45, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sarikaya, A.; Record, R.; Wu, C.-C.; Tullius, B.; Badylak, S.; Ladisch, M. Antimicrobial Activity Associated with Extracellular Matrices. Tissue Eng. 2002, 8, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Gastélum, G.R.; Aguilar-Medina, E.M.; Soto-Sainz, E.; Ramos-Payán, R.; Silva-Benítez, E.L. Antimicrobial Properties of Extracellular Matrix Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandika, P.; Khan, F.; Heo, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.-M.; Yi, M.; Jung, W.-K. Enhanced wound-healing capability with inherent antimicrobial activities of usnic acid incorporated poly(ε-caprolactone)/decellularized extracellular matrix nanofibrous scaffold. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2022, 140, 213046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, P.A.; Pouliot, R.A.; Mikhaiel, N.S.; Young, B.M.; Heise, R.L. Tunable Hydrogels from Pulmonary Extracellular Matrix for 3D Cell Culture. J. Vis. Exp. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakagami, M.; Li, H.; Venitz, J. In Vivo-Relevant Transwell Dish-Based Dissolution Testing for Orally Inhaled Corticosteroid Products. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample | Size (nm) | Polydispersity Index (PDI) | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10:1 LVX-ECM NP | 525.9 ± 61.99 | 0.51 ± 0.01 | −6.39 ± 1.03 |
| 1:1 LVX-ECM NP | 298.7 ± 16.54 | 0.48 ± 0.06 | −4.14 ± 0.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patel, R.; Moyano, I.; Sakagami, M.; Kang, J.D.; Hylemon, P.B.; Voynow, J.A.; Heise, R.L. Tailored Levofloxacin Incorporated Extracellular Matrix Nanoparticles for Pulmonary Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157453
Patel R, Moyano I, Sakagami M, Kang JD, Hylemon PB, Voynow JA, Heise RL. Tailored Levofloxacin Incorporated Extracellular Matrix Nanoparticles for Pulmonary Infections. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157453
Chicago/Turabian StylePatel, Raahi, Ignacio Moyano, Masahiro Sakagami, Jason D. Kang, Phillip B. Hylemon, Judith A. Voynow, and Rebecca L. Heise. 2025. "Tailored Levofloxacin Incorporated Extracellular Matrix Nanoparticles for Pulmonary Infections" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157453
APA StylePatel, R., Moyano, I., Sakagami, M., Kang, J. D., Hylemon, P. B., Voynow, J. A., & Heise, R. L. (2025). Tailored Levofloxacin Incorporated Extracellular Matrix Nanoparticles for Pulmonary Infections. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157453







