Lasso Peptides—A New Weapon Against Superbugs
Abstract
1. Introduction
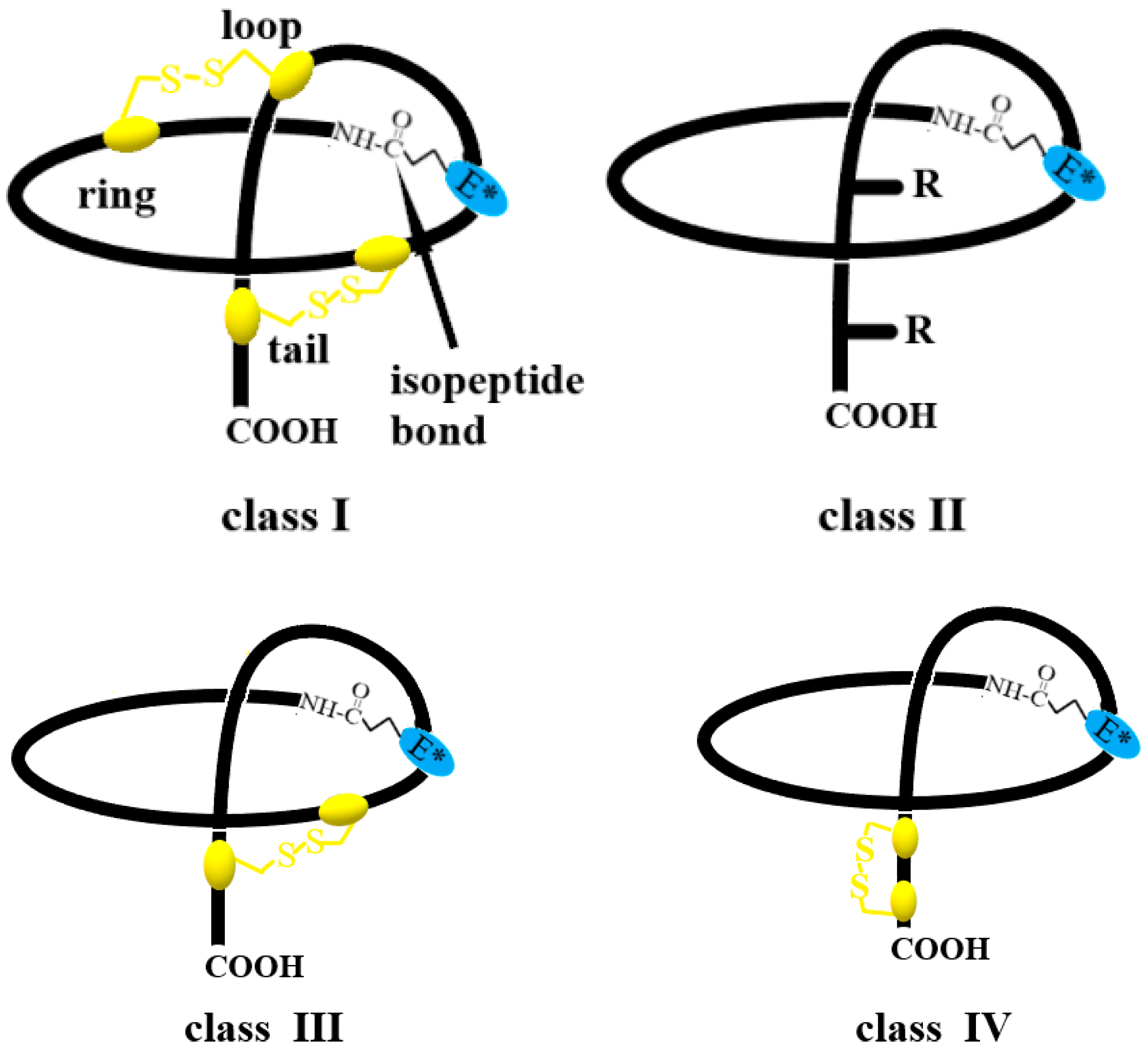
2. Lasso Peptide Structure
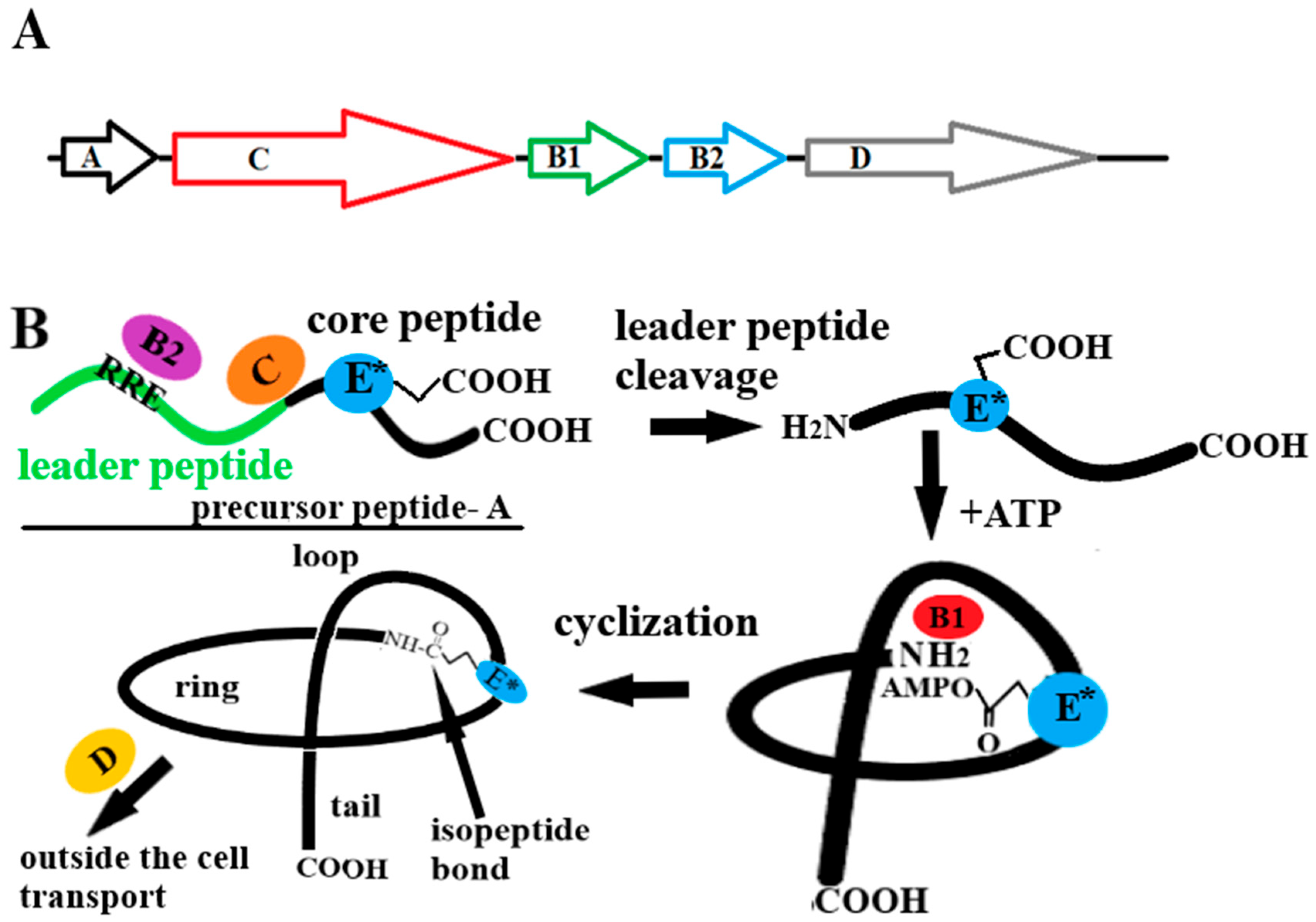
3. Biosynthesis of Lasso Peptides
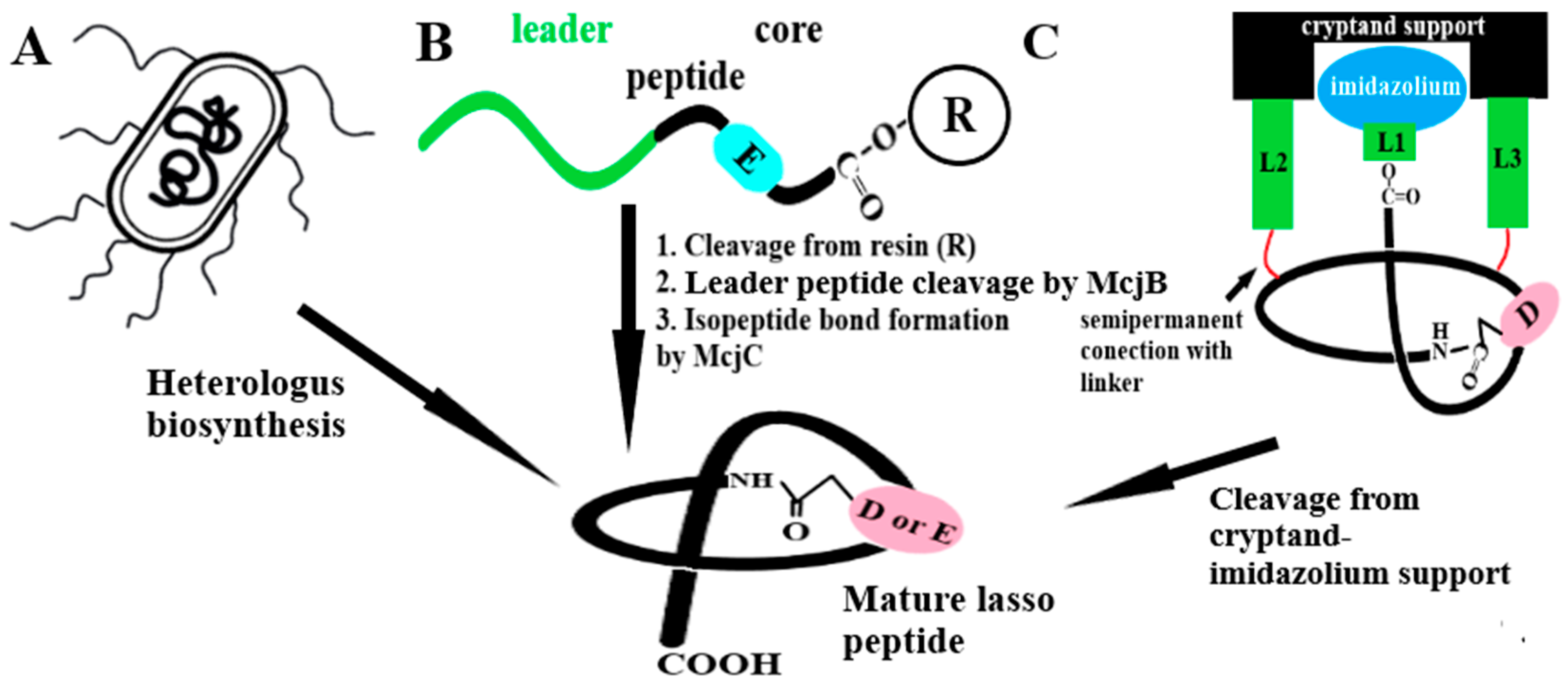
4. Approach to Chemical Synthesis of Lasso Peptides
5. Antibacterial Activities of Lasso Peptides
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | amino acid residue |
| CRAB | carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii |
| DMF | N,N-dimethylformamide |
| LAR-B | Lariocidin B |
| MccJ25 | Microcin J25 |
| MDR | Multi-drug-resistant |
| MHB | cation-adjusted Mueller–Hinton broth |
| MIC | minimum inhibitory concentration |
| MRSA | methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| NMP | N-methylpyrrolidone |
| PTM | post-translational modification |
| RiPP | post-translationally modified peptide |
| RPMI-1640 | nutrient-limited medium |
| RRE | RiPP precursor recognition element |
| SPPS | solid-phase peptide synthesis |
| SPS | solid-phase synthesis |
| STEC | Shiga toxin-producing E. coli |
| WHO BPPL | WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List |
| VA | vancomycin |
| VRE | vancomycin-resistant enterococci |
| VRSA | vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
References
- GBD 2021 Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance 1990–2021: A Systematic Analysis with Forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, S.; Mehra, P.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, V.; Singh, R.; Nepovimova, E.; Chopra, C.; Kuča, K. Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance—Flipsides of the Same Coin. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2022, 28, 2312–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.A.; Wright, G.D. The Past, Present, and Future of Antibiotics. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabo7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240093461 (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- Cheng, C.; Hua, Z.C. Lasso Peptides: Heterologous Production and Potential Medical Application. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 571165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gómez, H.; Tulla-Puche, J. Lasso Peptides: Chemical Approaches and Structural Elucidation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 5065–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Musaimi, O. Lasso Peptides Realm: Insights and Applications. Peptides 2024, 182, 171317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maksimov, M.O.; Pan, S.J.; James Link, A. Lasso Peptides: Structure, Function, Biosynthesis, and Engineering. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegemann, J.D.; Zimmermann, M.; Xie, X.; Marahiel, M.A. Lasso Peptides: An Intriguing Class of Bacterial Natural Products. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1909–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.F.; Li, Y.W.; Ye, Z.H.; Lin, H.B.; Yang, K. Overview of the Preparation Method, Structure and Function, and Application of Natural Peptides and Polypeptides. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenski, S.L.; Thiengmag, S.; Helfrich, E.J.N. Complex Peptide Natural Products: Biosynthetic Principles, Challenges and Opportunities for Pathway Engineering. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2022, 7, 631–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruby, V.J.; Mosberg, H.I. Conformational and Dynamic Considerations in Peptide Structure-Function Studies. Peptides 1982, 3, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mucha, P.; Sikorska, E.; Rekowski, P.; Ruczyński, J. Interaction of Arginine-Rich Cell-Penetrating Peptides with an Artificial Neuronal Membrane. Cells 2022, 11, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazuryk, J.; Puchalska, I.; Koziński, K.; Ślusarz, M.J.; Ruczyński, J.; Rekowski, P.; Rogujski, P.; Płatek, R.; Wiśniewska, M.B.; Piotrowski, A.; et al. PTD4 Peptide Increases Neural Viability in an In Vitro Model of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Niu, W.; Pang, L.; Bian, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, G. Unusual Post-Translational Modifications in the Biosynthesis of Lasso Peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Shortreed, M.R.; Wenger, C.D.; Frey, B.L.; Schaffer, L.V.; Scalf, M.; Smith, L.M. Global Post-Translational Modification Discovery. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucha, P.; Szyk, A.; Rekowski, P.; Barciszewski, J. Structural Requirements for Conserved Arg52 Residue for Interaction of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Trans-Activation Responsive Element with Trans-Activator of Transcription Protein (49–57). Capillary Electrophoresis Mobility Shift Assay. J. Chrom. A 2002, 968, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, Q.; Ren, K.; Xu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, M.; Rao, Z.; Zhang, X. A Review of Antimicrobial Peptides: Structure, Mechanism of Action, and Molecular Optimization Strategies. Fermentation 2024, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharana, T.R.; Nagaraj, R. In Silico Folding of Hydrophobic Peptides That Form β-Hairpin Structures in Solution. J. Pept. Sci. 2022, 28, e3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slósarek, G.; Kalbitzer, H.R.; Mucha, P.; Rekowski, P.; Kupryszewski, G.; Giel-Pietraszuk, M.; Szymański, M.; Barciszewski, J. Mechanism of the Activation of Proteinase Inhibitor Synthesis by Systemin Involves Beta-Sheet Structure, a Specific DNA-Binding Protein Domain. J. Struct. Biol. 1995, 115, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimbarashvili, E.; Samsonidze, N.; Grigolava, M.; Pirtskhalava, M. Small Natural Cyclic Peptides from DBAASP Database. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomón, R.A.; Farías, R.N. Microcin 25, a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide Produced by Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 7428–7435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, R.; Engelborghs, Y. A fluorescence study of tryptophan-histidine interactions in the peptide anantin and in solution. Photochem. Photobiol. 1994, 60, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaweewan, I.; Ohnishi-Kameyama, M.; Kodani, S. Isolation of a New Antibacterial Peptide Achromosin from Streptomyces achromogenes subsp. achromogenes Based on Genome Mining. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metelev, M.; Arseniev, A.; Bushin, L.B.; Kuznedelov, K.; Artamonova, T.O.; Kondratenko, R.; Khodorkovskii, M.; Seyedsayamdost, M.R.; Severinov, K. Acinetodin and Klebsidin, RNA Polymerase Targeting Lasso Peptides Produced by Human Isolates of Acinetobacter gyllenbergii and Klebsiella pneumoniae. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasaka, N.; Kaweewan, I.; Ohnishi-Kameyama, M.; Kodani, S. Isolation of a New Antibacterial Peptide Actinokineosin from Actinokineospora spheciospongiae Based on Genome Mining. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 64, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, C.; Cheung-Lee, W.L.; Elashal, H.E.; Raj, M.; Link, A.J. Albusnodin: An Acetylated Lasso Peptide from Streptomyces albus. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyss, D.F.; Lahm, H.W.; Manneberg, M.; Labhardt, A.M. Anantin—A Peptide Antagonist of the Atrial Natriuretic Factor (ANF). II. Determination of the Primary Sequence by NMR on the Basis of Proton Assignments. J. Antibiot. 1991, 44, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stariha, L.M.; McCafferty, D.G. Discovery of the Class I Antimicrobial Lasso Peptide Arcumycin. ChemBioChem 2021, 22, 2632–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, M.; Hegemann, J.D.; Xie, X.; Marahiel, M.A. The Astexin-1 Lasso Peptides: Biosynthesis, Stability, and Structural Studies. Chem. Biol. 2013, 20, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.D.; Chen, M.Y.; Trick, A.Y.; Le, D.T.; Ferguson, A.L.; Link, A.J. Thermal Unthreading of the Lasso Peptides Astexin-2 and Astexin-3. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 3043–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Hajlasz, N.; Kulik, H.J. Computational Modeling of Conformer Stability in Benenodin-1, a Thermally Actuated Lasso Peptide Switch. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 3398–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potterat, O.; Wagner, K.; Gemmecker, G.; Mack, J.; Puder, C.; Vettermann, R.; Streicher, R. BI-32169, a Bicyclic 19-Peptide with Strong Glucagon Receptor Antagonist Activity from Streptomyces sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1528–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodani, S.; Hemmi, H.; Miyake, Y.; Kaweewan, I.; Nakagawa, H. Heterologous Production of a New Lasso Peptide Brevunsin in Sphingomonas subterranea. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 45, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegemann, J.D.; Zimmermann, M.; Zhu, S.; Klug, D.; Marahiel, M.A. Lasso Peptides from Proteobacteria: Genome Mining Employing Heterologous Expression and Mass Spectrometry. Biopolymers 2013, 100, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knappe, T.A.; Linne, U.; Zirah, S.; Rebuffat, S.; Xie, X.; Marahiel, M.A. Isolation and Structural Characterization of Capistruin, a Lasso Peptide Predicted from the Genome Sequence of Burkholderia thailandensis E264. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 11446–11454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugai, S.; Ohnishi-Kameyama, M.; Kodani, S. Isolation and Identification of a New Lasso Peptide Cattlecin from Streptomyces cattleya Based on Genome Mining. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2017, 60, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegemann, J.D.; Zimmermann, M.; Xie, X.; Marahiel, M.A. Caulosegnins I–III: A Highly Diverse Group of Lasso Peptides Derived from a Single Biosynthetic Gene Cluster. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, S.S.; Trusch, F.; Deng, H.; Raab, A.; Prokes, I.; Busarakam, K.; Asenjo, J.A.; Andrews, B.A.; van West, P.; Bull, A.T.; et al. Chaxapeptin, a Lasso Peptide from Extremotolerant Streptomyces leeuwenhoekii Strain C58 from the Hyperarid Atacama Desert. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 10252–10260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung-Lee, W.L.; Parry, M.E.; Jaramillo Cartagena, A.; Darst, S.A.; Link, A.J. Discovery and Structure of the Antimicrobial Lasso Peptide Citrocin. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 6822–6830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarmusch, S.A.; Feldmann, I.; Blank-Landeshammer, B.; Cortés-Albayay, C.; Castro, J.F.; Andrews, B.; Asenjo, J.A.; Sickmann, A.; Ebel, R.; Jaspars, M. Cutting the Gordian Knot: Early and Complete Amino Acid Sequence Confirmation of Class II Lasso Peptides by HCD Fragmentation. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Garzón, J.F.; Madland, E.; Zehl, M.; Singh, M.; Rezaei, S.; Aachmann, F.L.; Courtade, G.; Urban, E.; Rückert, C.; Busche, T.; et al. Class IV Lasso Peptides Synergistically Induce Proliferation of Cancer Cells and Sensitize Them to Doxorubicin. iScience 2020, 23, 101785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koos, J.D.; Link, A.J. Heterologous and in Vitro Reconstitution of Fuscanodin, a Lasso Peptide from Thermobifida fusca. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Albayay, C.; Jarmusch, S.A.; Trusch, F.; Ebel, R.; Andrews, B.A.; Jaspars, M.; Asenjo, J.A. Downsizing Class II Lasso Peptides: Genome Mining-Guided Isolation of Huascopeptin Containing the First Gly1-Asp7 Macrocycle. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiante, V.; Monteiro, M.C.; Martín, J.; Altwasser, R.; El Aouad, N.; González, I.; Kniemeyer, O.; Mellado, E.; Palomo, S.; de Pedro, N.; et al. Hitting the Caspofungin Salvage Pathway of Human-Pathogenic Fungi with the Novel Lasso Peptide Humidimycin (MDN-0010). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5145–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, E.; Woodward, T.J.; Fields, S.; Brandsen, B.M. Comprehensive Mutational Analysis of the Lasso Peptide Klebsidin. ACS Chem Biol. 2022, 17, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmilic, V.; Asenjo, J.A.; Martínez, I. Predictions to Increase Lasso Peptide Production in the Heterologous Host Streptomyces coelicolor M1152. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2025, 122, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwatsuki, M.; Tomoda, H.; Uchida, R.; Gouda, H.; Hirono, S.; Omura, S. Lariatins, Antimycobacterial Peptides Produced by Rhodococcus sp. K01-B0171, Have a Lasso Structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7486–7491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jangra, M.; Travin, D.Y.; Aleksandrova, E.V.; Kaur, M.; Darwish, L.; Koteva, K.; Klepacki, D.; Wang, W.; Tiffany, M.; Sokaribo, A.; et al. A Broad-Spectrum Lasso Peptide Antibiotic Targeting the Bacterial Ribosome. Nature 2025, 640, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavrish, E.; Sit, C.S.; Cao, S.; Kandror, O.; Spoering, A.; Peoples, A.; Ling, L.; Fetterman, A.; Hughes, D.; Bissell, A.; et al. Lassomycin, a Ribosomally Synthesized Cyclic Peptide, Kills Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Targeting the ATP-Dependent Protease ClpC1P1P2. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietz, J.I.; Schwalen, C.J.; Patel, P.S.; Maxson, T.; Blair, P.M.; Tai, H.C.; Zakai, U.I.; Mitchell, D.A. A New Genome-Mining Tool Redefines the Lasso Peptide Biosynthetic Landscape. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; Martín, J.; Genilloud, O. Identification and Heterologous Expression of the Biosynthetic Gene Cluster Encoding the Lasso Peptide Humidimycin, a Caspofungin Activity Potentiator. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Hegemann, J.D.; Fage, C.D.; Zimmermann, M.; Xie, X.; Linne, U.; Marahiel, M.A. Insights into the Unique Phosphorylation of the Lasso Peptide Paeninodin. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 13662–13678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung-Lee, W.L.; Cao, L.; Link, A.J. Pandonodin: A Proteobacterial Lasso Peptide with an Exceptionally Long C-Terminal Tail. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 2783–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Kanou, F.; Takahashi, H.; Esumi, Y.; Uramoto, M.; Yoshihama, M. Propeptin, a New Inhibitor of Prolyl Endopeptidase Produced by Microbispora. I. Fermentation, Isolation and Biological Properties. J. Antibiot. 1997, 50, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zyubko, T.; Serebryakova, M.; Andreeva, J.; Metelev, M.; Lippens, G.; Dubiley, S.; Severinov, K. Efficient in Vivo Synthesis of Lasso Peptide Pseudomycoidin Proceeds in the Absence of Both the Leader and the Leader Peptidase. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 9699–9707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, Y.; Chiba, S.; Tsukuda, E.; Tanaka, T.; Ogawa, T.; Yamasaki, M.; Yoshida, M.; Kawamoto, I.; Matsuda, Y. RES-701-1, a Novel and Selective Endothelin Type B Receptor Antagonist Produced by Streptomyces sp. RE-701. I. Characterization of Producing Strain, Fermentation, Isolation, Physico-Chemical and Biological Properties. J. Antibiot. 1994, 47, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fréchet, D.; Guitton, J.D.; Herman, F.; Faucher, D.; Helynck, G.; Monegier du Sorbier, B.; Ridoux, J.P.; James-Surcouf, E.; Vuilhorgne, M. Solution Structure of RP 71955, a New 21 Amino Acid Tricyclic Peptide Active against HIV-1 Virus. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunakawa, M.; Hu, S.L.; Hoshino, Y.; Detlefson, D.J.; Hill, S.E.; Furumai, T.; White, R.J.; Nishio, M.; Kawano, K.; Yamamoto, S. Siamycins I and II, New Anti-HIV Peptides: I. Fermentation, Isolation, Biological Activity and Initial Characterization. J. Antibiot. 1995, 48, 433–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaweewan, I.; Hemmi, H.; Komaki, H.; Harada, S.; Kodani, S. Isolation and Structure Determination of a New Lasso Peptide Specialicin Based on Genome Mining. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 6050–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kersten, R.D.; Yang, Y.L.; Xu, Y.; Cimermancic, P.; Nam, S.J.; Fenical, W.; Fischbach, M.A.; Moore, B.S.; Dorrestein, P.C. A Mass Spectrometry-Guided Genome Mining Approach for Natural Product Peptidogenomics. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.J.; Rajniak, J.; Maksimov, M.O.; Link, A.J. The role of a conserved threonine residue in the leader peptide of lasso peptide precursors. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1880–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Ma, X.; Yu, J.; Yang, W.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Ge, Y.; Song, J.; Han, H.; Zhang, W.; et al. Rational Generation of Lasso Peptides Based on Biosynthetic Gene Mutations and Site-Selective Chemical Modifications. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 12353–12364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metelev, M.; Tietz, J.I.; Melby, J.O.; Blair, P.M.; Zhu, L.; Livnat, I.; Severinov, K.; Mitchell, D.A. Structure, Bioactivity, and Resistance Mechanism of Streptomonomicin, an Unusual Lasso Peptide from an Understudied Halophilic Actinomycete. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Um, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kwon, H.; Wen, H.; Kim, S.H.; Kwon, H.C.; Park, S.; Shin, J.; Oh, D.C. Sungsanpin, a Lasso Peptide from a Deep-Sea Streptomycete. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung-Lee, W.L.; Parry, M.E.; Zong, C.; Cartagena, A.J.; Darst, S.A.; Connell, N.D.; Russo, R.; Link, A.J. Discovery of Ubonodin, an Antimicrobial Lasso Peptide Active against Members of the Burkholderia cepacia Complex. ChemBioChem 2020, 21, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Jang, M.; Lee, B.; Hong, Y.S.; Ko, S.K.; Jang, J.H.; Ahn, J.S. Ulleungdin, a Lasso Peptide with Cancer Cell Migration Inhibitory Activity Discovered by the Genome Mining Approach. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 2205–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, S.E.; Mitchell, D.A. Advances in Lasso Peptide Discovery, Biosynthesis, and Function. Trends Genet. 2024, 40, 950–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, H.; Wang, M.; Fage, C.D.; He, Y.; Niu, X.; Han, M.; Li, F.; An, X.; Fan, H.; Song, L.; et al. Discovery and Characterization of Rubrinodin Provide Clues into the Evolution of Lasso Peptides. Biochemistry 2022, 61, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Gómez, H.; Linne, U.; Albericio, F.; Tulla-Puche, J.; Hegemann, J.D. Investigation of the Biosynthesis of the Lasso Peptide Chaxapeptin Using an E. coli-Based Production System. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 2050–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Hora, G.C.A.; Oh, M.; Mifflin, M.C.; Digal, L.; Roberts, A.G.; Swanson, J.M.J. Lasso Peptides: Exploring the Folding Landscape of Nature’s Smallest Interlocked Motifs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 4444–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knappe, T.A.; Manzenrieder, F.; Mas-Moruno, C.; Linne, U.; Sasse, F.; Kessler, H.; Xie, X.; Marahiel, M.A. Introducing lasso peptides as molecular scaffolds for drug design: Engineering of an integrin antagonist. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2011, 50, 8714–8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhart, B.J.; Hudson, G.A.; Dunbar, K.L.; Mitchell, D.A. A Prevalent Peptide-Binding Domain Guides Ribosomal Natural Product Biosynthesis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, S.E.; Yin, S.; Jordan, P.; Brunson, J.K.; Gordon-Nunez, J.; Costa Machado da Cruz, G.; Rosario, C.; Okada, B.K.; Anderson, K.; Pires, T.A.; et al. Substrate interactions guide cyclase engineering and lasso peptide diversification. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2025, 21, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiCaprio, A.J.; Firouzbakht, A.; Hudson, G.A.; Mitchell, D.A. Enzymatic Reconstitution and Biosynthetic Investigation of the Lasso Peptide Fusilassin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegemann, J.D.; Dit-Foque, K.J.; Xie, X. Lasso Peptides: Structure, Biosynthesis, Activities, and Beyond. In Comprehensive Natural Products III; Liu, H.-W., Begley, T.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 206–228. [Google Scholar]
- Montalbán-López, M.; Scott, T.A.; Ramesh, S.; Rahman, I.R.; van Heel, A.J.; Viel, J.H.; Bandarian, V.; Dittmann, E.; Genilloud, O.; Goto, Y.; et al. New Developments in RiPP Discovery, Enzymology and Engineering. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 38, 130–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrild, A.; Svenningsen, T.; Chevrette, M.G.; Tørring, T. Evolution-Guided Discovery of Antimycobacterial Triculamin-Like Lasso Peptides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2025, 64, e202425134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mevaere, J.; Goulard, C.; Schneider, O.; Sekurova, O.N.; Ma, H.; Zirah, S.; Afonso, C.; Rebuffat, S.; Zotchev, S.B.; Li, Y. An Orthogonal System for Heterologous Expression of Actinobacterial Lasso Peptides in Streptomyces Hosts. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Toma, R.S.; Kuthning, A.; Exner, M.P.; Denisiuk, A.; Ziegler, J.; Budisa, N.; Süssmuth, R.D. Site-Directed and Global Incorporation of Orthogonal and Isostructural Noncanonical Amino Acids into the Ribosomal Lasso Peptide Capistruin. ChemBioChem 2015, 16, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Li, Z.; Ye, J.; Wang, X.; Jiang, M.; Deng, Z.; Cao, C.; He, X. Discovery and Characterization of Actinosynnelassin: An Anti-Pseudomonas fluorescens Lasso Peptide Derived from a Large Precursor Open Reading Frame. J. Nat. Prod. 2025, 88, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavel, C.; Fournel-Marotte, K.; Coutrot, F. A pH-sensitive peptide-containing lasso molecular switch. Molecules 2013, 18, 11553–11575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiefelbein, K.; Lang, J.; Schuster, M.; Grigglestone, C.E.; Striga, R.; Bigler, L.; Schuman, M.C.; Zerbe, O.; Li, Y.; Hartrampf, N. Merging Flow Synthesis and Enzymatic Maturation to Expand the Chemical Space of Lasso Peptides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 17261–17269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ting, J.P.; Liu, J.; Al-Azzam, S.; Pandya, P.; Afshar, S. Impact of non-proteinogenic amino acids in the discovery and development of peptide therapeutics. Amino Acids 2020, 52, 1207–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimmidi, R. Synthesis and applications of peptides and peptidomimetics in drug discovery. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 26, e202300028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, S.; Yu, X. Cryptand-Imidazolium Supported Total Synthesis of the Lasso Peptide BI-32169 and Its d-Enantiomer. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 3323–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung-Lee, W.L.; Link, A.J. Genome Mining for Lasso Peptides: Past, Present, and Future. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 46, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; He, B.; Li, J.; Li, Y.X. Challenges and Advances in Genome Mining of Ribosomally Synthesized and Post-Translationally Modified Peptides (RiPPs). Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2020, 5, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Q.; Zhou, B.; Shen, T.; Jiang, T.; Cheng, C.; He, B. The Lasso Structure, Biosynthesis, Bioactivities and Potential Applications of Microcin J25: A Novel Antibacterial Agent with Unique Mechanisms. Eng. Microbiol. 2023, 3, 100096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thokkadam, A.; Do, T.; Ran, X.; Brynildsen, M.P.; Yang, Z.J.; Link, A.J. High-Throughput Screen Reveals the Structure-Activity Relationship of the Antimicrobial Lasso Peptide Ubonodin. ACS Cent. Sci. 2023, 9, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braffman, N.R.; Piscotta, F.J.; Hauver, J.; Campbell, E.A.; Link, A.J.; Darst, S.A. Structural Mechanism of Transcription Inhibition by Lasso Peptides Microcin J25 and Capistruin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1273–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudrioua, A.; Baëtz, B.; Desmadril, S.; Goulard, C.; Groo, A.C.; Lombard, C.; Gueulle, S.; Marugan, M.; Malzert-Fréon, A.; Hartke, A.; et al. Lasso peptides sviceucin and siamycin I exhibit anti-virulence activity and restore vancomycin effectiveness in vancomycin-resistant pathogens. iScience 2025, 28, 111922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Lasso Peptide | Sequence | Class/Ref |
|---|---|---|
| Achromosin | GIGSQTWDTIWLWD | II [24] |
| Acinetodin | GGKGPIFETWVTEGNYYG | II [25] |
| Actinokineosin | GYPFWDNRDIFGGYTFIG | II [26] |
| Albusnodin | GQGGGQSEDKRRAYNC | II [27] |
| Anantin | GFIGWGNDIFGHYSGDF | II [28] |
| Arcumycin | SGQGWDWVDYHHGWYGWWDD | II [29] |
| Astexin-1 | GLSQGVEPDIGOTYFEESRINQD | II [30] |
| Astexin-2 | GLTQIQALDSVSGQFRDQLGLSAD | II [31] |
| Astexin-3 | GPTPMVGLDSVSGQYWDQHAPLAD | II [31] |
| Benenodin-1 | GVGFGRPDSILTQEQAKPM | II [32] |
| BI-32169 | GLPWGC(&)PSDIPGWNTPWAC(&) | III [33] |
| Brevunsin | GDMGEEVIEGLVRDSLYPPAG | II [34] |
| Burhizin | GGAGQYKEVEAGRWSDRIDSDDE | II [35] |
| Capistruin | GTPGFQTPDARVISRFGFN | II [36] |
| Cattlecin | SYHWGDYHDWHHGWYGWWDD | II [37] |
| Caulonodin I | GDVLNAPEPGIGREPTGLSRD | II [35] |
| Caulonodin II | GDVLFAPEPGVGRPPMGLSED | II [35] |
| Caulonodin III | GQIYDHPEVGIGAYGCEGLQR | II [35] |
| Caulonodin IV | SFDVGTIKEGLVSQYYFA | II [35] |
| Caulonodin V | SIGDSGLRESMSSQTYWP | II [35] |
| Caulonodin VI | AGTGVLLPETNQIKRYDPA | II [35] |
| Caulonodin VII | SGIGDVFPEPNMVRRWD | II [35] |
| Caulosegnin I | GAFVGQPEAVNPLGREIQG | II [38] |
| Caulosegnin II | GTLTPGLPEDFLPGHYMPG | II [38] |
| Caulosegnin III | GALVGLLLEDITVARYDPM | II [38] |
| Chaxapeptin | GFGSKPLDSFGLNFF | II [39] |
| Citrocin | GGVGKI LEYFIGGGVGRYG | II [40] |
| Citrulassin | LLGLAGNDRLVLSKN | II [41] |
| Felipeptin A1 | GSRGWGFEPGVRC(&)LIWC(&)D | IV [42] |
| Felipeptin A2 | GGGGRGYEYNKQC(&)LIFC(&) | IV [42] |
| Fuscanodin | WYTAEWGLELIFVFPRFI | II [43] |
| Huascopentin | GYGNAWDSKNGLF | II [44] |
| Humidimycin | C(&1)LGIGSC(&2)DDFAGC(&1)GYAIVC(&2)FW | I [45] |
| Klebsidin | GSDGPIIEFFNPNGVMHYG | II [46] |
| Lagmysin | LAGQGSPDLLGGHSLL | II [47] |
| Lariatin A | GSQLVYREWVGHSNVIKP | II [48] |
| Lariatin B | GSQLVYREWVGHSNVIKPGP | II [48] |
| Lariocidin/LAR | SKKSKPGDGKFGRGVKRG | II [49] |
| Lariocidin B/LAR-B | SK(&) KSKPGDGKFGRGVKR(&) | V* [49] |
| Lassomycin | GLRRLFADQLVGRRNI | II [50] |
| Lp2006 | GRPNWGFENDWSC(&)VRVC(&) | IV [51] |
| Microcin J25/MccJ25 | GGAGHVPEYFVGIGTPISFYG | II [22] |
| Moomysin | SYHWGDYHDWHHGWYGWWDD | II [51] |
| MS-271 | C(&1)LGVGSC(&2)NDFAGC(&1)GYAIVC(&2)FW | I [52] |
| Paeninodin | AGPGTSTPDAFQPDPDEDVHYDS | II [53] |
| Pandonodin | GVLGNDAEGITLLPLC(&)FKPIC(&)IPTLPPLTGGHA | IV [54] |
| Propeptin | GYPWWDYRDLFGGHTFISP | II [55] |
| Pseudomycoidin | AGPGKRLVDQVFEDEDEQGALHHS | II [56] |
| RES-701-1 | GNWHGTAPDWFFNYYW | II [57] |
| RP 71955/aborycin | C(&1)LGIGSC(&2)NDFAGC(&1)GYAVVC(&2)FW | I [58] |
| Siamycin I | C(&1)LGVGSC(&2)NDFAGC(&1)GYAIVC(&2)FW | I [59] |
| Siamycin II | C(&1)LGIGSC(&2)NDFAGC(&1)GYAIVC(&2)FW | I [59] |
| Specialicin | C(&1)LGVGSC(&2)VDFAGC(&1)GYAVVC(&2)FW | I [60] |
| Sphingonodin I | GPGGITGDVGLGENNFG | II [35] |
| Sphingonodin II | GMGSGSTDQNGQPKNLIGG | II [35] |
| SRO15-2005 | GYFVGSYKEYWSRRII | II [61] |
| SSV-2083 | C(&1)VWGGDC(&2)TDFLGC(&1)GTAWIC(&2)V | I [62] |
| Stlassin | LVVIVQADWNAPGWF | I [63] |
| Streptomonomycin | SLGSSPYNDILGYPALIVIYP | II [64] |
| Sungsanpin | GFGSKPIDSFGLSWL | II [65] |
| Ubonodin | GGDGSIAEYFNRPMHIHDWQIMDSGYYG | II [66] |
| Ulleungdin | GFIGWGKDIFGHYGG | II [67] |
| Strain | MIC MHB [µg/mL] | MIC RPMI-1640 [µg/mL] | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus USA300 | 64 | 0.5 | Superbug (MRSA) |
| E. coli BW25113 mcr-1 | 64 | ND | colistin-resistant |
| E. coli C1508 | 32 | 1 | STEC, MDR |
| K. pneumoniae C1559 | >64 | 4 | MDR |
| A. baumannii ATCC17978 | 128 | 1 | |
| A. baumannii C0286* | 8 | 0.5 | Superbag, CRAB |
| Vancomycin (VA) (µg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Strain | Control (VA Only) | +Sviceucin (10 µM) | +Siamycin I (2 µM) |
| E. faecalis V583* | 32 | 2 | 2 |
| E. faecalis JH2-2 08048 | 64 | 2 | <0.5 |
| E. faecalis merz96 | 32 | 1 | 2 |
| S. aureus T-SAR12 VRSA.B | 64 | 2 | 2 |
| E. faecium 1 231 410 | 128 | 128 | 2 |
| E. faecalis HIP11704 | 1024 | 512 | <0.5 |
| E. faecium 1 231 502 | 128 | 128 | 2 |
| E. faecium 1 230 933 | 512 | 256 | 2 |
| S. aureus T-SAR12 VRSA.A | >512 | >512 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mucha, P.; Ruczyński, J.; Prochera, K.; Rekowski, P. Lasso Peptides—A New Weapon Against Superbugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178184
Mucha P, Ruczyński J, Prochera K, Rekowski P. Lasso Peptides—A New Weapon Against Superbugs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178184
Chicago/Turabian StyleMucha, Piotr, Jarosław Ruczyński, Katarzyna Prochera, and Piotr Rekowski. 2025. "Lasso Peptides—A New Weapon Against Superbugs" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178184
APA StyleMucha, P., Ruczyński, J., Prochera, K., & Rekowski, P. (2025). Lasso Peptides—A New Weapon Against Superbugs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178184







