Structural Features of Nucleoproteins from the Recently Discovered Orthonairovirus songlingense and Norwavirus beijiense
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
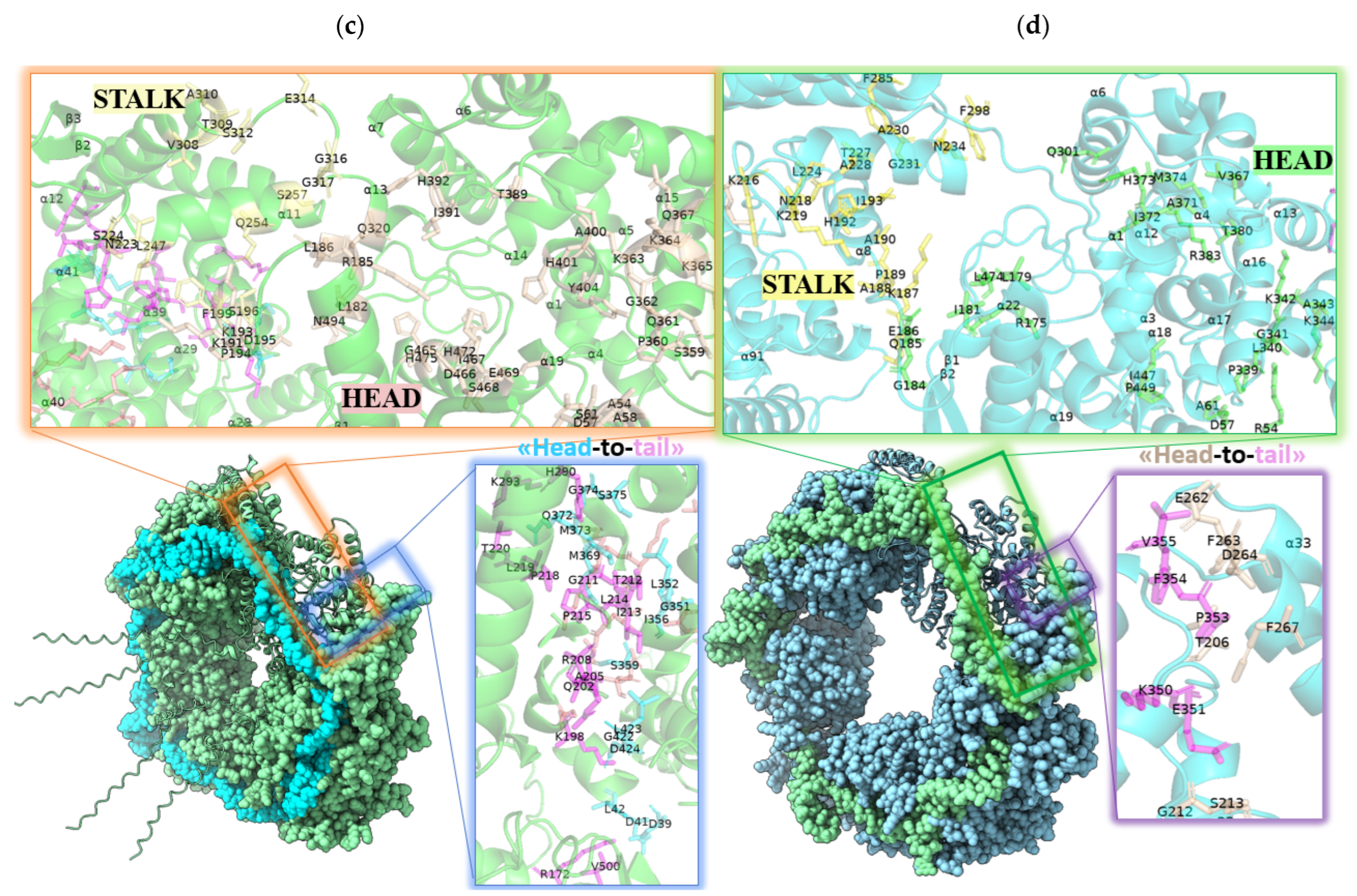
2.1. AlphaFold 3 Tertiary Structure Models of SGLV N and BJNV N
2.2. Recombinant SGLV N and BJNV N
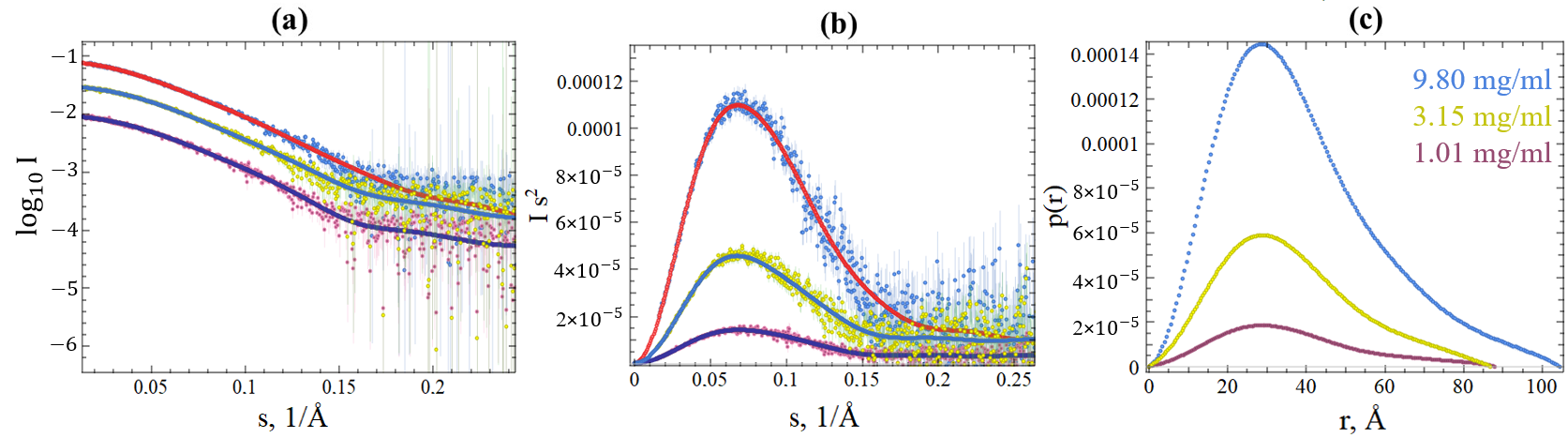
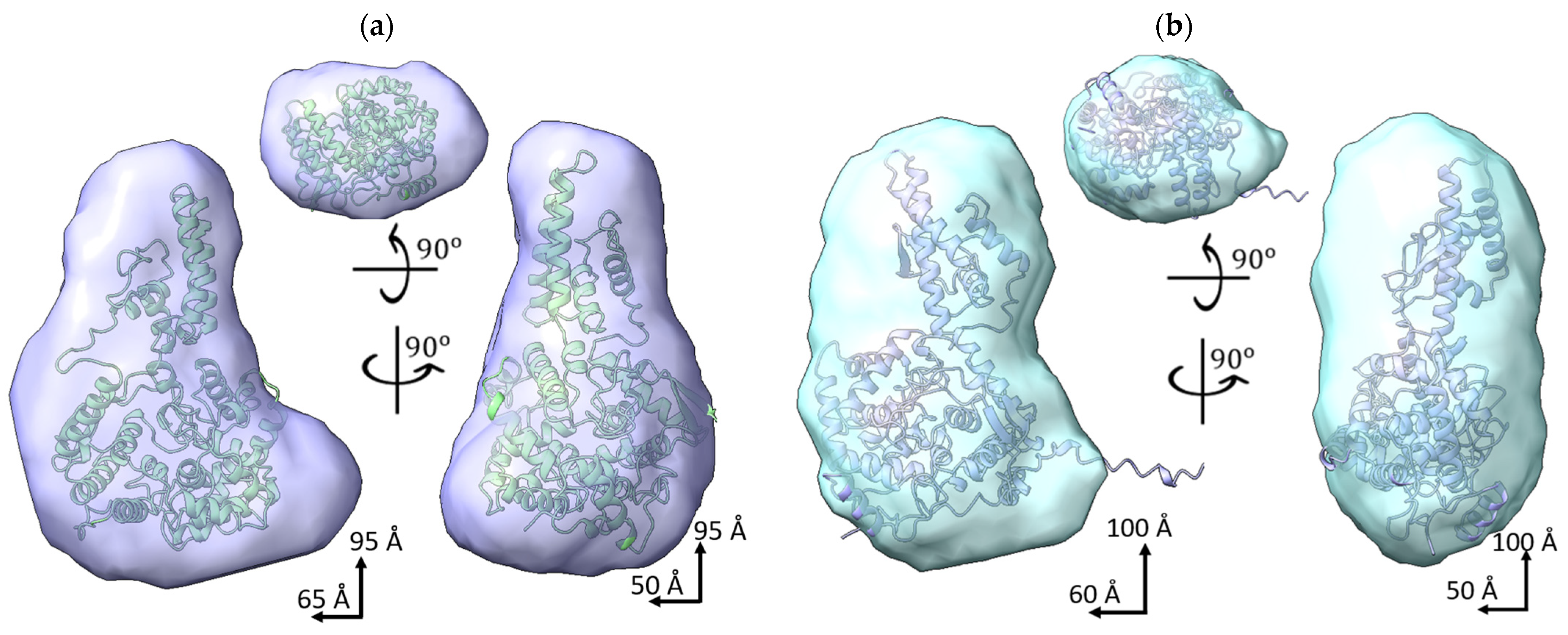
2.3. SAXS Data of SGLV N and BJNV N
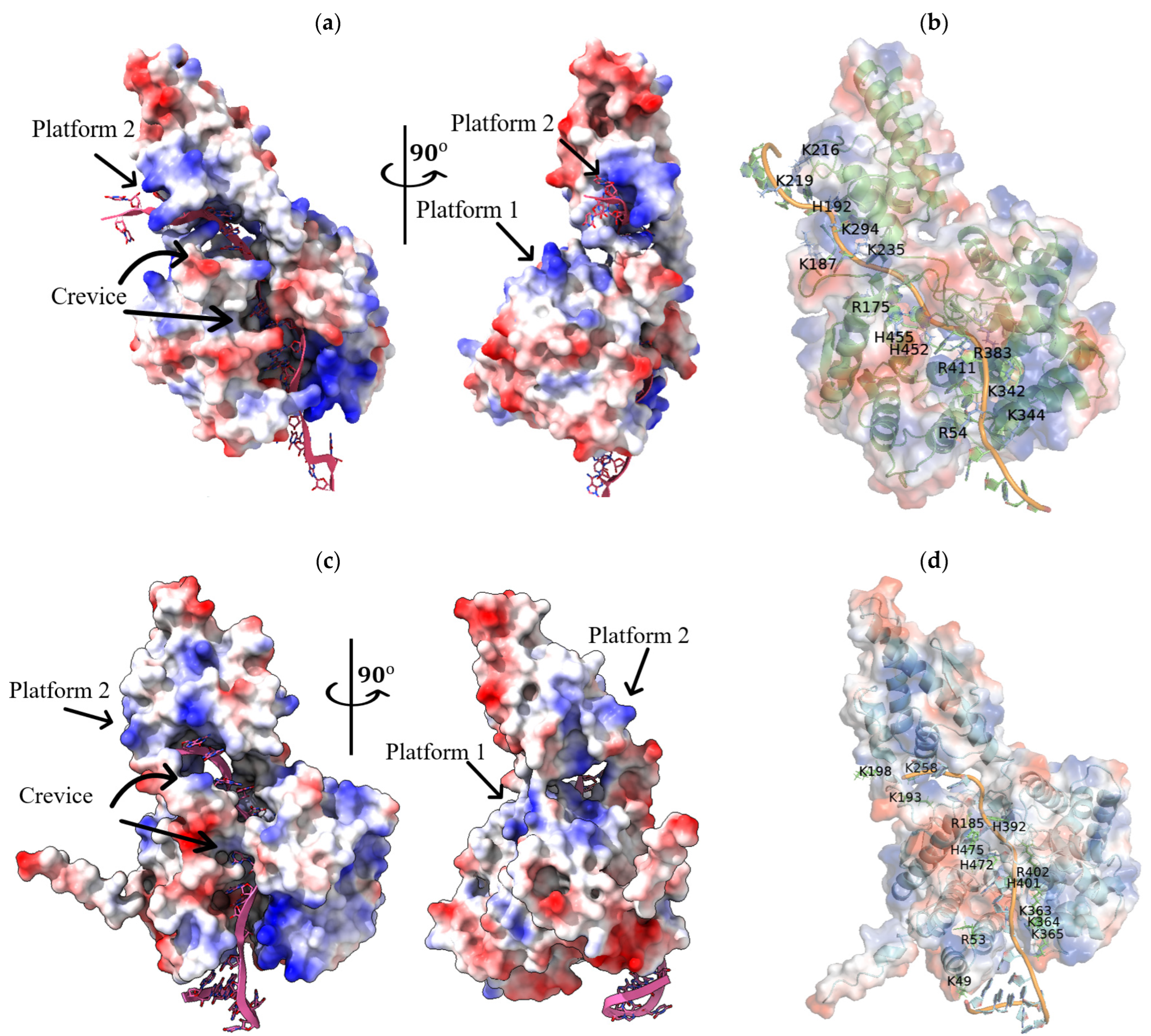
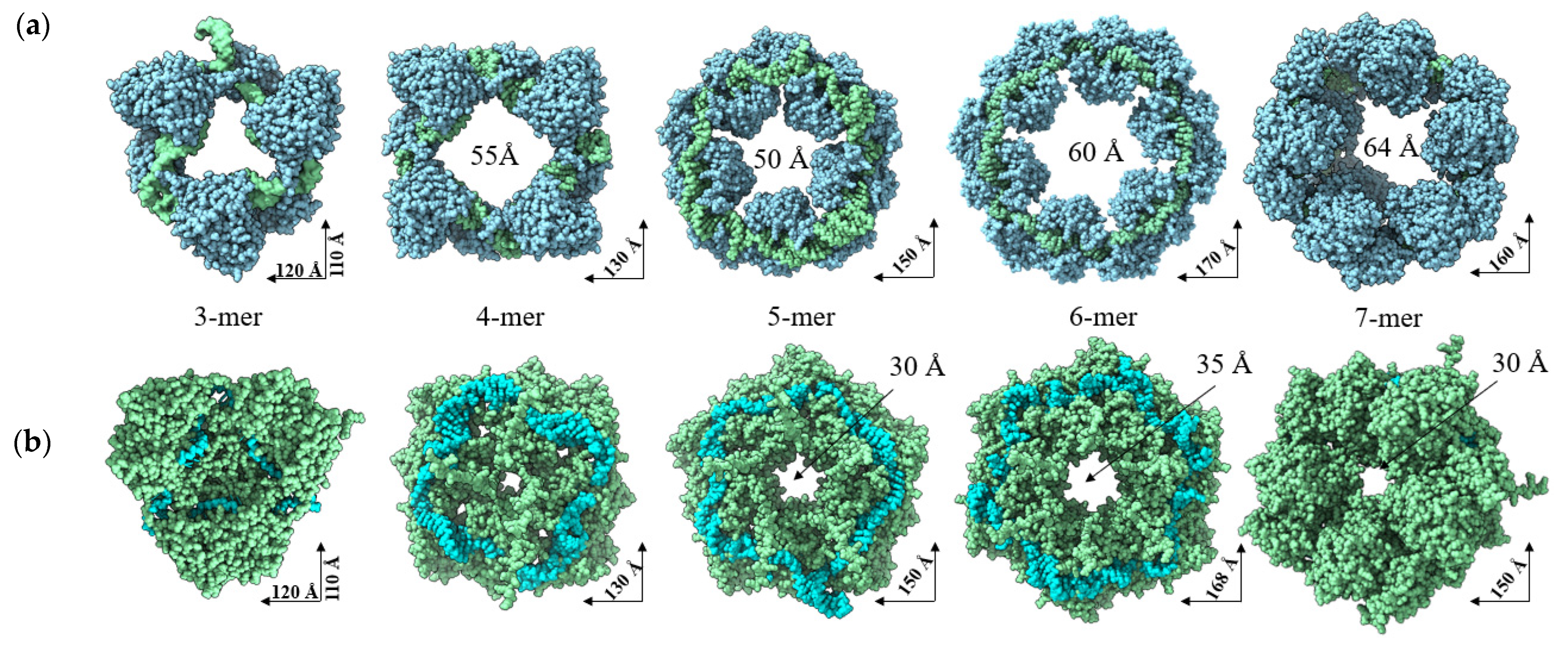
2.4. Interaction of SGLV N and BJNV N with Their ssRNA(−)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthetic Assembly of DNA Copies of Genes Encoding Viral Nucleoproteins
4.2. Production of Recombinant Viral Nucleoproteins in Escherichia coli
4.3. Purification of Recombinant Viral Nucleoproteins
4.4. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Measurement
4.5. Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering (SAXS)
4.6. Tertiary Structure Modeling of Nucleoproteins and Their Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SGLV | Orthonairovirus songlingense, Songling virus |
| YEZV | Orthonairovirus yezoense, Yezo virus |
| BJNV | Norwavirus beijiense, Beiji nairovirus |
| SAXS | Small-angle X-ray scattering |
| CCHFV | Orthonairovirus haemorrhagiae, Crimean–Congo hemorrhagic fever virus |
| ssRNA(−) | Single-stranded RNA of negative polarity |
| N | Nucleoprotein |
| GPC | Glycoprotein precursor |
| RdRp | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
| SEC | Size exclusion chromatography |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
References
- Zhou, H.; Xu, L.; Shi, W. The Human-Infection Potential of Emerging Tick-Borne Viruses Is a Global Public Health Concern. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraga-Fernández, A.; Muñoz-Hernández, C.; Sánchez-Sánchez, M.; Fernández de Mera, I.G.; de la Fuente, J. Exploring the Diversity of Tick-Borne Pathogens: The Case of Bacteria (Anaplasma, Rickettsia, Coxiella and Borrelia) Protozoa (Babesia and Theileria) and Viruses (Orthonairovirus, Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus and Louping Ill Virus) in the European Continent. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 286, 109892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Z.; Xie, S.; Jiang, M.; Song, R.; Ma, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, K.; et al. A Tentative Tamdy Orthonairovirus Related to Febrile Illness in Northwestern China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 2155–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomazatos, A.; von Possel, R.; Pekarek, N.; Holm, T.; Rieger, T.; Baum, H.; Bialonski, A.; Maranda, I.; Erdelyi-Molnár, I.; Spînu, M.; et al. Discovery and Genetic Characterization of a Novel Orthonairovirus in Ixodes Ricinus Ticks from Danube Delta. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 88, 104704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, F.; Yamaguchi, H.; Park, E.; Tatemoto, K.; Sashika, M.; Nakao, R.; Terauchi, Y.; Mizuma, K.; Orba, Y.; Kariwa, H.; et al. A Novel Nairovirus Associated with Acute Febrile Illness in Hokkaido, Japan. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Lv, X.-L.; Zhang, X.; Han, S.-Z.; Wang, Z.-D.; Li, L.; Sun, H.-T.; Ma, L.-X.; Cheng, Z.-L.; Shao, J.-W.; et al. Identification of a New Orthonairovirus Associated with Human Febrile Illness in China. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.-Z.; Bian, C.; Ye, R.-Z.; Cui, X.-M.; Yao, N.-N.; Yang, J.-H.; Chu, Y.-L.; Su, X.-L.; Wu, Y.-F.; Ye, J.-L.; et al. A Series of Patients Infected with the Emerging Tick-Borne Yezo Virus in China: An Active Surveillance and Genomic Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Wei, Z.; Lv, X.; Han, S.; Wang, Z.; Fan, C.; Zhang, X.; Shao, J.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Sui, L.; et al. A New Nairo-like Virus Associated with Human Febrile Illness in China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, R.; Kobayashi, D.; Yamauchi, T.; Park, E.; Nishino, A.; Maeda, K.; Kasai, S.; Itoyama, K.; Isawa, H. Isolation and Characterization of Iwanai Valley Virus, a New Tick-Borne Nairovirus from Ixodes Ovatus Ticks in Hokkaido, Japan. Arch. Virol. 2024, 170, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Xu, W.; Yuan, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Z.; Sui, L.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, Y.; et al. Extensive Diversity of RNA Viruses in Ticks Revealed by Metagenomics in Northeastern China. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0011017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wei, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. The Extensive Diversity of Nairoviruses Reveals the Complexity and High Risk of Tick-Borne Diseases in Northeastern China. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, W.; Nie, K.; Yin, Q.; Fu, S.; Cui, Q.; Xu, S.; Li, F.; et al. Detection and Genetic Analysis of Songling Virus in Haemaphysalis Concinna near the China-North Korea Border. Zoonoses 2024, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Tian, X.; Peng, R.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Hu, X.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, X.; et al. Genomic and Phylogenetic Profiling of RNA of Tick-Borne Arboviruses in Hainan Island, China. Microbes Infect. 2024, 26, 105218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bente, D.A.; Forrester, N.L.; Watts, D.M.; McAuley, A.J.; Whitehouse, C.A.; Bray, M. Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever: History, Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Clinical Syndrome and Genetic Diversity. Antiviral Res. 2013, 100, 159–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabsay, K.R.; Te Velthuis, A.J.W. Negative and Ambisense RNA Virus Ribonucleocapsids: More than Protective Armor. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2023, 87, e0008223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Couch, G.S.; Croll, T.I.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure Visualization for Researchers, Educators, and Developers. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, W.; Ji, W.; Deng, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yang, C.; Deng, F.; Wang, H.; Hu, Z.; et al. Crimean–Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus Nucleoprotein Reveals Endonuclease Activity in Bunyaviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5046–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, S.D.; Surtees, R.; Walter, C.T.; Ariza, A.; Bergeron, É.; Nichol, S.T.; Hiscox, J.A.; Edwards, T.A.; Barr, J.N. Structure, Function, and Evolution of the Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus Nucleocapsid Protein. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 10914–10923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirincal, A.; Doymaz, M.Z. The Role of Nucleocapsid Protein (NP) in the Immunology of Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus (CCHFV). Viruses 2024, 16, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Li, P.; Elliott, R.M.; Dong, C. Structure of Schmallenberg Orthobunyavirus Nucleoprotein Suggests a Novel Mechanism of Genome Encapsidation. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 5593–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Olson, J.; Vakharia, V.; Tao, Y.J. The Crystal Structure and RNA-Binding of an Orthomyxovirus Nucleoprotein. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Dong, H.; Ma, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Mao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; et al. Structural and Functional Diversity of Nairovirus-Encoded Nucleoproteins. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11740–11749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, K.; Saka, N.; Nishio, M. Identification of Critical Residues for RNA Binding of Nairovirus Nucleoprotein. J. Virol. 2024, 98, e0144624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeeva, S.; Pador, S.; Voss, B.; Ganaie, S.S.; Mir, M.A. Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus Nucleocapsid Protein Has Dual RNA Binding Modes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moquin, S.A.; Simon, O.; Karuna, R.; Lakshminarayana, S.B.; Yokokawa, F.; Wang, F.; Saravanan, C.; Zhang, J.; Day, C.W.; Chan, K.; et al. NITD-688, a Pan-Serotype Inhibitor of the Dengue Virus NS4B Protein, Shows Favorable Pharmacokinetics and Efficacy in Preclinical Animal Models. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabb2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gejji, V.; Svoboda, P.; Stefanik, M.; Wang, H.; Salat, J.; Eyer, L.; Ruzek, D.; Fernando, S. An RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Inhibitor for Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus. Virology 2020, 546, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Garzan, A.; Haese, N.; Bostwick, R.; Martinez-Gzegozewska, Y.; Rasmussen, L.; Streblow, D.N.; Haise, M.T.; Pathak, A.K.; Augelli-Szafran, C.E.; et al. Pyrimidone Inhibitors Targeting Chikungunya Virus NsP3 Macrodomain by Fragment-Based Drug Design. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Sneyd, H.; Dekant, R.; Wang, J. Influenza A Virus Nucleoprotein: A Highly Conserved Multi-Functional Viral Protein as a Hot Antiviral Drug Target. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 2271–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Pang, B.; Lai, K.K.; Cheung, N.N.; Dai, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Chan, K.-H.; Chen, H.; Sze, K.-H.; et al. Discovery of a Novel Specific Inhibitor Targeting Influenza A Virus Nucleoprotein with Pleiotropic Inhibitory Effects on Various Steps of the Viral Life Cycle. J. Virol. 2021, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Xiao, Q.; Cui, J.; Dong, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, X.; Ma, L.; Li, Z.; Sun, P.; et al. Identification of Lurasidone as a Potent Inhibitor of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus by Targeting the Viral Nucleoprotein. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1578844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, P.J.; Fleming, K.G. HullRad: Fast Calculations of Folded and Disordered Protein and Nucleic Acid Hydrodynamic Properties. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 856–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-W.; Liu, G.-F.; Wu, H.-J.; Zhou, P.; Hong, C.-X.; Li, N.; Bian, F.-G. BL19U2: Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering Beamline for Biological Macromolecules in Solution at SSRF. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2020, 31, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, J.B. BioXTAS RAW 2: New Developments for a Free Open-Source Program for Small-Angle Scattering Data Reduction and Analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2024, 57, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petoukhov, M.V.; Franke, D.; Shkumatov, A.V.; Tria, G.; Kikhney, A.G.; Gajda, M.; Gorba, C.; Mertens, H.D.T.; Konarev, P.V.; Svergun, D.I. New Developments in the ATSAS Program Package for Small-Angle Scattering Data Analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konarev, P.V.; Volkov, V.V.; Sokolova, A.V.; Koch, M.H.J.; Svergun, D.I. PRIMUS: A Windows PC-Based System for Small-Angle Scattering Data Analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, L.A.; Svergun, D.I.; Taylor, G.W. Structure Analysis by Small-Angle X-Ray and Neutron Scattering; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781475766264. [Google Scholar]
- Svergun, D.I. Determination of the Regularization Parameter in Indirect-Transform Methods Using Perceptual Criteria. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1992, 25, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svergun, D.I. Restoring Low Resolution Structure of Biological Macromolecules from Solution Scattering Using Simulated Annealing. Biophys. J. 1999, 76, 2879–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozin, M.B.; Svergun, D.I. Automated Matching of High- and Low-Resolution Structural Models. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2001, 34, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, V.V.; Svergun, D.I. Uniqueness of Ab Initio Shape Determination in Small-Angle Scattering. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svergun, D.; Barberato, C.; Koch, M.H.J. CRYSOL—A Program to Evaluate X-Ray Solution Scattering of Biological Macromolecules from Atomic Coordinates. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1995, 28, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate Structure Prediction of Biomolecular Interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kempen, M.; Kim, S.S.; Tumescheit, C.; Mirdita, M.; Lee, J.; Gilchrist, C.L.M.; Söding, J.; Steinegger, M. Fast and Accurate Protein Structure Search with Foldseek. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering Key Features in Protein Structures with the New ENDscript Server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
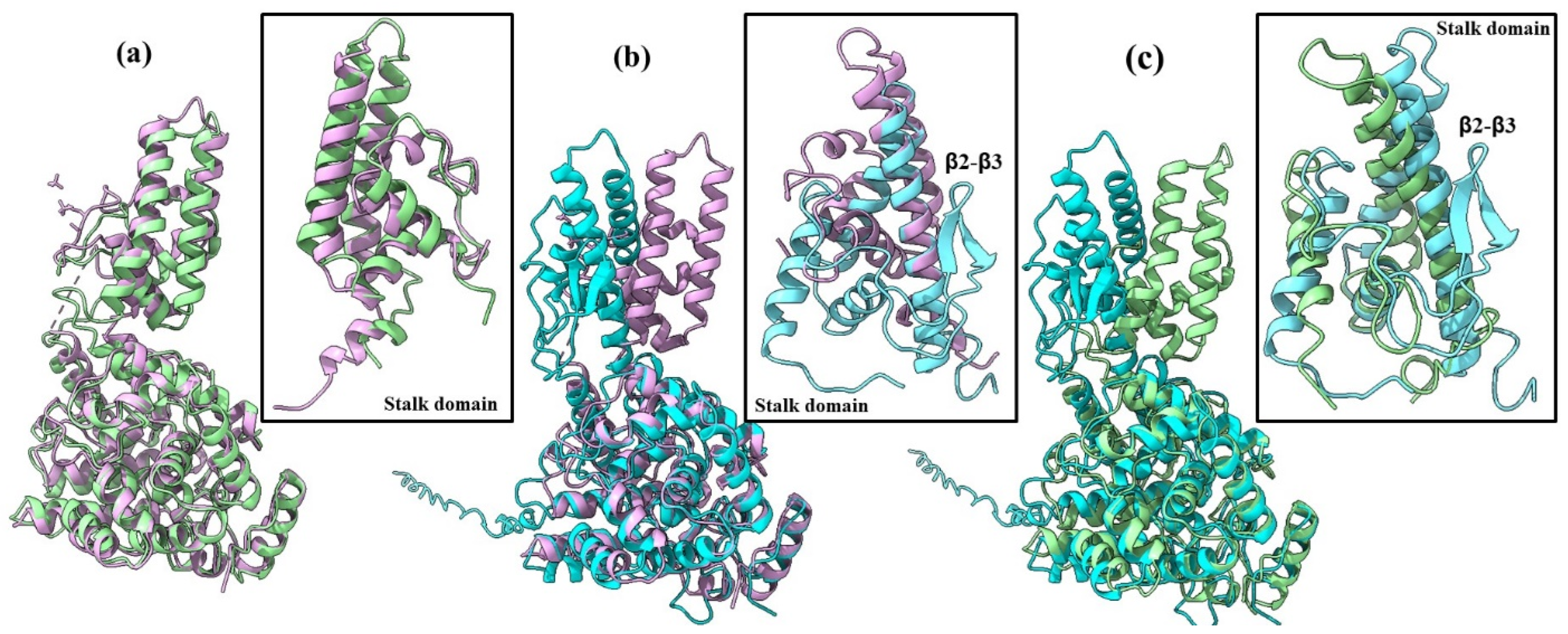

| PDB ID | Name of Virus | TM-Score | RMSD, Å | Aligned Residues, a.a. | Amino Acid Sequence Identity (Blastp) 1, % | Amino Acid Sequence Identity (RSCB) 2, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SGLV N (full-length) | ||||||
| - | BJNV | 0.78 | 4.34 | 365 | 25.0 | 23.0 |
| 4AQF_A | CCHFV | 0.87 | 2.53 | 433 | 35.6 | 34.0 |
| 5A97_C | Hazara virus | 0.83 | 3.52 | 489 | 32.8 | 32.0 |
| 4AQF_C | CCHFV | 0.82 | 3.27 | 413 | 35.4 | 34.0 |
| 4XZE_A | Hazara virus | 0.81 | 3.38 | 381 | 32.8 | 32.0 |
| 4XZC_A | Kupe virus | 0.78 | 3.63 | 367 | 33.9 | 28.1 |
| 3U3I_A | CCHFV | 0.75 | 2.30 | 365 | 36.0 | 38.0 |
| BJNV N (full-length) | ||||||
| - | SGLV | 0.78 | 4.34 | 365 | 25.0 | 23.0 |
| 6Z0O_B | CCHFV | 0.80 | 3.13 | 417 | 22.0 | 22.0 |
| 4AQF_B | CCHFV | 0.77 | 3.48 | 390 | 24.0 | 22.0 |
| 4XZC_B | Kupe virus | 0.76 | 3.40 | 389 | 23.3 | 22.0 |
| 5A97_A | Hazara virus | 0.74 | 3.98 | 369 | 27.6 | 28.0 |
| 4XZA_A | Erve virus | 0.64 | 2.53 | 337 | 22.0 | 25.0 |
| SGLV N head domain | ||||||
| - | BJNV | 0.90 | 2.15 | 348 | 27.0 | 27.0 |
| 4AQF_A | CCHFV | 0.94 | 1.40 | 351 | 39.0 | 40.0 |
| 5A97_C | Hazara virus | 0.93 | 1.72 | 352 | 36.0 | 37.0 |
| 4AQF_C | CCHFV | 0.94 | 1.46 | 345 | 38.0 | 40.0 |
| 4XZE_A | Hazara virus | 0.95 | 1.28 | 355 | 35.0 | 38.0 |
| 4XZC_A | Kupe virus | 0.95 | 1.37 | 355 | 37.0 | 39.0 |
| BJNV N head domain | ||||||
| 6Z0O_B | CCHFV | 0.90 | 2.26 | 342 | 24.0 | 26.0 |
| 4AQF_B | CCHFV | 0.88 | 2.40 | 336 | 25.0 | 27.0 |
| 4XZC_B | Kupe virus | 0.89 | 2.30 | 339 | 24.0 | 26.0 |
| 5A97_A | Hazara virus | 0.84 | 2.31 | 340 | 27.0 | 29.0 |
| 4XZA_A | Erve virus | 0.89 | 2.57 | 337 | 23.0 | 24.0 |
| SGLV N stalk domain | ||||||
| - | BJNV | 0.55 | 3.00 | 85 | 18.0 | 18.0 |
| 4AQF_A | CCHFV | 0.69 | 2.83 | 94 | 17.0 | 15.0 |
| 5A97_C | Hazara virus | 0.69 | 2.68 | 97 | 21.0 | 18.0 |
| 4AQF_C | CCHFV | 0.73 | 2.80 | 99 | 17.0 | 16.0 |
| 4XZE_A | Hazara virus | 0.70 | 2.85 | 95 | 22.0 | 17.0 |
| 4XZC_A | Kupe virus | 0.70 | 2.72 | 92 | 21.0 | 15.0 |
| BJNV N stalk domain | ||||||
| 6Z0O_B | CCHFV | 0.56 | 3.2 | 82 | 16.0 | 14.0 |
| 4AQF_B | CCHFV | 0.57 | 3.2 | 81 | 15.0 | 13.0 |
| 4XZC_B | Kupe virus | 0.58 | 2.9 | 81 | 13.0 | 11.0 |
| 5A97_A | Hazara virus | 0.60 | 3.0 | 83 | 15.0 | 13.0 |
| Sample | Concentration, mg/mL | , nm * | , nm * | V(Porod), * | MW (exp), kDa * | MW (Theory), kDa * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SGLV N | 9.8 | 0.1 | 10.3 | 53.1 [93% CI: 47.2, 57.5] | 54.5 | |
| 3.15 | 0.1 | 8.7 | 52.0 [94% CI: 49.2, 55.0] | 54.5 | ||
| 1.01 | 0.1 | 8.8 | 47.6 [95% CI: 46.2, 51.5] | 54.5 | ||
| BJNV N | 10.7 | 0.1 | 9.7 | 58.1 [91% CI: 53.8, 61.6] | 61.4 | |
| 3.46 | 0.1 | 9.8 | 53.1 [91% CI: 50.3, 56.2] | 61.4 | ||
| 1.12 | 0.1 | 9.9 | 53.2 [91% CI: 53.0, 60.2] | 61.4 |
| Model | , nm * | (Envelope), nm | V (Envelope), | MW, kDa | χ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCHFV N, PDB ID: 4AQF | 2.6 | 9.1 | 52.4 | BJNV N: 1.2 | |
| SGLV N: 1.2 | |||||
| Hazara virus N, PDB ID: 5A97 | 2.5 | 8.8 | 53.1 | BJNV N: 1.3 | |
| SGLV N: 1.3 | |||||
| BJNV N, AlphaFold 3 model | 3.0 | 9.6 | 61.4 | 1.1 | |
| SGLV N, AlphaFold 3 model | 2.5 | 9.1 | 54.5 | 1.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yanshin, A.O.; Ivkina, D.I.; Tuyrin, V.Y.; Osinkina, I.A.; Tishin, A.E.; Olkin, S.E.; Ukladov, E.O.; Radchenko, N.S.; Arkhipov, S.G.; Ryzhykau, Y.L.; et al. Structural Features of Nucleoproteins from the Recently Discovered Orthonairovirus songlingense and Norwavirus beijiense. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157445
Yanshin AO, Ivkina DI, Tuyrin VY, Osinkina IA, Tishin AE, Olkin SE, Ukladov EO, Radchenko NS, Arkhipov SG, Ryzhykau YL, et al. Structural Features of Nucleoproteins from the Recently Discovered Orthonairovirus songlingense and Norwavirus beijiense. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157445
Chicago/Turabian StyleYanshin, Alexey O., Daria I. Ivkina, Vitaliy Yu. Tuyrin, Irina A. Osinkina, Anton E. Tishin, Sergei E. Olkin, Egor O. Ukladov, Nikita S. Radchenko, Sergey G. Arkhipov, Yury L. Ryzhykau, and et al. 2025. "Structural Features of Nucleoproteins from the Recently Discovered Orthonairovirus songlingense and Norwavirus beijiense" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157445
APA StyleYanshin, A. O., Ivkina, D. I., Tuyrin, V. Y., Osinkina, I. A., Tishin, A. E., Olkin, S. E., Ukladov, E. O., Radchenko, N. S., Arkhipov, S. G., Ryzhykau, Y. L., Li, N., Agafonov, A. P., Imatdinov, I. R., & Gladysheva, A. V. (2025). Structural Features of Nucleoproteins from the Recently Discovered Orthonairovirus songlingense and Norwavirus beijiense. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157445








