Anifrolumab Attenuates Follicular Helper T Cell Activation in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
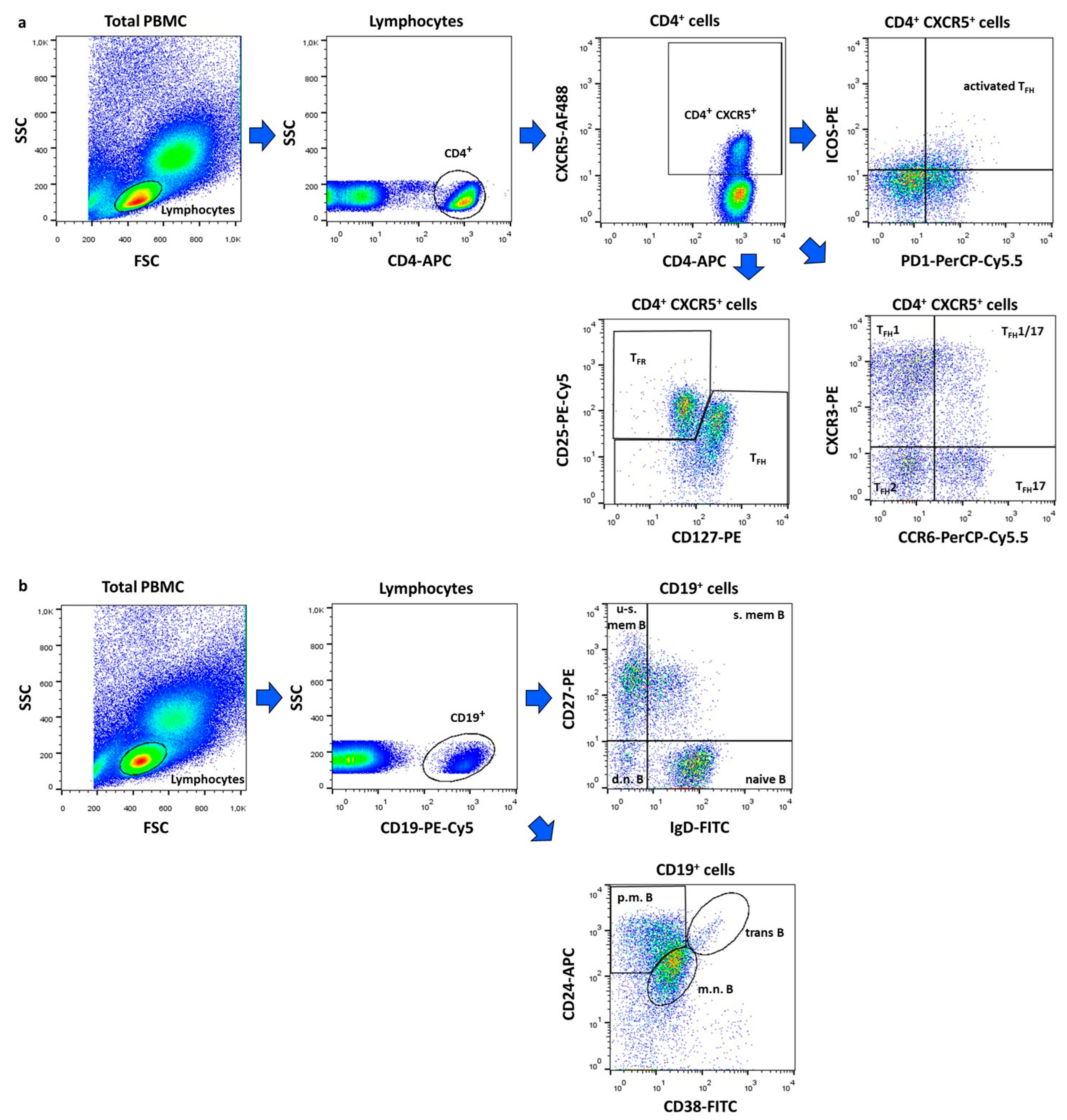
4.2. Flow Cytometric Analysis
4.3. Assessment of Humoral Immune Parameters
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Accapezzato, D.; Caccavale, R.; Paroli, M.P.; Gioia, C.; Nguyen, B.L.; Spadea, L.; Paroli, M. Advances in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fava, A.; Petri, M. Systemic lupus erythematosus: Diagnosis and clinical management. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 96, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crotty, S. T Follicular Helper Cell Biology: A Decade of Discovery and Diseases. Immunity 2019, 50, 1132–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H. T follicular helper cells in space-time. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linterman, M.A.; Pierson, W.; Lee, S.K.; Kallies, A.; Kawamoto, S.; Rayner, T.F.; Srivastava, M.; Divekar, D.P.; Beaton, L.; Hogan, J.J.; et al. Foxp3+ follicular regulatory T cells control the germinal center response. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, L.A.; Buggert, M.; Manne, S.; Herati, R.S.; Sayin, I.; Kuri-Cervantes, L.; Bukh Brody, I.; O’Boyle, K.C.; Kaprielian, H.; Giles, J.R.; et al. T follicular helper cells in human efferent lymph retain lymphoid characteristics. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3185–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, R.; Schmitt, N.; Bentebibel, S.E.; Ranganathan, R.; Bourdery, L.; Zurawski, G.; Foucat, E.; Dullaers, M.; Oh, S.; Sabzghabaei, N.; et al. Human blood CXCR5+ CD4+ T cells are counterparts of T follicular cells and contain specific subsets that differentially support antibody secretion. Immunity 2011, 34, 108–121, Erratum in Immunity 2011, 34, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, K.; Diamond, B. Follicular Helper T Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, K.; Jámbor, I.; Pázmándi, K.; Nagy, N.; Papp, G.; Tarr, T. Altered Circulating Follicular T Helper Cell Subsets and Follicular T Regulatory Cells Are Indicators of a Derailed B Cell Response in Lupus, Which Could Be Modified by Targeting IL-21R. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.Y.; Ho, J.H.; Pasoto, S.G.; Bunin, V.; Kim, S.T.; Carrasco, S.; Borba, E.F.; Gonçalves, C.R.; Costa, P.R.; Kallas, E.G.; et al. Circulating follicular helper-like T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: Association with disease activity. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lindwall, E.; Gauthier, C.; Lyman, J.; Spencer, N.; Alarakhia, A.; Fraser, A.; Ing, S.; Chen, M.; Webb-Detiege, T.; et al. Circulating CXCR5+CD4+helper T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus patients share phenotypic properties with germinal center follicular helper T cells and promote antibody production. Lupus 2015, 24, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, K.; Jámbor, I.; Szántó, A.; Horváth, I.F.; Tarr, T.; Nakken, B.; Szodoray, P.; Papp, G. The Imbalance of Circulating Follicular T Helper Cell Subsets in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome Associates With Serological Alterations and Abnormal B-Cell Distribution. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 639975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Shan, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Feng, J.; Li, C.; Ma, L.; Jiang, Y. High frequencies of activated B cells and T follicular helper cells are correlated with disease activity in patients with new-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 174, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, N.; Gatenby, P.A.; Wilson, A.; Malik, S.; Fulcher, D.A.; Tangye, S.G.; Manku, H.; Vyse, T.J.; Roncador, G.; Huttley, G.A.; et al. Expansion of circulating T cells resembling follicular helper T cells is a fixed phenotype that identifies a subset of severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Wu, Z.B.; Ding, J.; Zheng, Z.H.; Li, X.Y.; Chen, L.N.; Zhu, P. Role of the frequency of blood CD4+ CXCR5+ CCR6+ T cells in autoimmunity in patients with Sjogren’s syndrome. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 422, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Villa, I.; Bautista-Caro, M.B.; Balsa, A.; Aguado-Acin, P.; Bonilla-Hernan, M.G.; Plasencia, C.; Villalba, A.; Nuño, L.; Puig-Kröger, A.; Martín-Mola, E. Constitutively altered frequencies of circulating follicullar helper T cell counterparts and their subsets in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, S.; Zhou, M.; Huang, Y.; Fu, R.; Guo, C.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J.; Gaskin, F.; Fu, S.M.; et al. The ratio of circulating follicular T helper cell to follicular T regulatory cell is correlated with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 183, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, D.; Song, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhao, J.; Wang, H. Increased circulating CD4+CXCR5+FoxP3+ follicular regulatory T cells correlated with severity of systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 56, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarr, T.; Papp, G.; Nagy, N.; Cserép, E.; Zeher, M. Chronic high-dose glucocorticoid therapy triggers the development of chronic organ damage and worsens disease outcome in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Lin, L. Progress of rituximab in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1472019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joy, A.; Muralidharan, A.; Alfaraj, M.; Shantharam, D.; Cherukuri, A.S.S.; Muthukumar, A. The Role of Belimumab in Systemic Lupus Erythematosis: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e25887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frémond, M.L.; David, C.; Richez, C. Anifrolumab: The new frontier in the treatment of genetic interferonopathies. RMD Open 2024, 10, e004780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, T.M.; Ong, S.J.; Mak, A.; Tay, S.H. Type I Interferons in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Journey from Bench to Bedside. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Kusuda, M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Interferons and systemic lupus erythematosus: Pathogenesis, clinical features, and treatments in interferon-driven disease. Mod. Rheumatol. 2023, 33, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.A.; Morand, E.F. Targeting Interferon Signalling in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Lessons Learned. Drugs 2024, 84, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postal, M.; Vivaldo, J.F.; Fernandez-Ruiz, R.; Paredes, J.L.; Appenzeller, S.; Niewold, T.B. Type I interferon in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2020, 67, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Li, T.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Lu, E.; Liu, J.; Qiao, W.; Chen, H. The crucial regulatory role of type I interferon in inflammatory diseases. Cell Biosci. 2023, 13, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucak, H.; Yrlid, U.; Reizis, B.; Kalinke, U.; Johansson-Lindbom, B. Type I interferon signaling in dendritic cells stimulates the development of lymph-node-resident T follicular helper cells. Immunity 2009, 31, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Duan, X.; Zheng, J.; Liang, L.; Wang, F.; Guo, L. IFN-α as an Adjuvant for Adenovirus-Vectored FMDV Subunit Vaccine through Improving the Generation of T Follicular Helper Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rönnblom, L.; Leonard, D. Interferon pathway in SLE: One key to unlocking the mystery of the disease. Lupus Sci. Med. 2019, 6, e000270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunsri, T.; Thawornpan, P.; Tianpothong, P.; Suangtamai, T.; Ngamjanyaporn, P.; Leepiyasakulchai, C.; Wangriatisak, K.; Pisitkun, P.; Chootong, P. Activation of circulating TFH17 cells associated with activated naive and double negative 2 B cell expansion, and disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2024, 26, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Anolik, J.; Cappione, A.; Zheng, B.; Pugh-Bernard, A.; Brooks, J.; Lee, E.-H.; Milner, E.C.B.; Sanz, I. A New Population of Cells Lacking Expression of CD27 Represents a Notable Component of the B Cell Memory Compartment in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 6624–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, M.; Orbai, A.M.; Alarcón, G.S.; Gordon, C.; Merrill, J.T.; Fortin, P.R.; Bruce, I.N.; Isenberg, D.; Wallace, D.J.; Nived, O.; et al. Derivation and validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2677–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladman, D.; Ginzler, E.; Goldsmith, C.; Fortin, P.; Liang, M.; Sanchez-Guerrero, J.; Urowitz, M.; Bacon, P.; Bombardieri, S.; Hanly, J.; et al. The development and initial validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology damage index for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1996, 39, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladman, D.D.; Ibañez, D.; Urowitz, M.B. Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| SLE Patients (n = 10) | Before | 6 Months | 12 Months |
|---|---|---|---|
| C3 g/L, median [Q1–Q3] | 0.925 [0.625–1.183] | 0.955 [0.838–1.185] p = 0.426 | 1.000 [0.868–1.208] p = 0.557 |
| C4 g/L, median [Q1–Q3] | 0.145 [0.090–0.170] | 0.135 [0.085–0.195] p = 0.770 | 0.140 [0.095–0.233] p = 0.606 |
| anti-dsDNA IU/mL, median [Q1–Q3] | 26.5 [9.9–67.6] | 25.5 [13.6–63.3] p = 0.594 | 20.7 [7.2–82.2] p = 0.770 |
| ANA Hep2 titer, median [Q1–Q3] | 1600 [320–3200] | 640 [320–2560] p = 0.250 | 640 [320–1600] p = 0.063 |
| SLE Patients | |
|---|---|
| Age in years, mean ± SD | 45.00 ± 7.17 |
| Female:Male ratio (n) | 9:1 |
| Disease duration in years, mean ± SD | 13.22 ± 9.72 |
| Lupus nephritis (n) | 2 |
| APS (n) | 2 |
| Methylprednisolone (n) | 8 |
| Chloroquine (n) | 8 |
| Azathioprine (n) | 3 |
| Methotrexate (n) | 1 |
| Mycophenolate mofetil (n) | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diós, Á.; Gyetvai, Á.; Papp, G.; Tarr, T. Anifrolumab Attenuates Follicular Helper T Cell Activation in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157397
Diós Á, Gyetvai Á, Papp G, Tarr T. Anifrolumab Attenuates Follicular Helper T Cell Activation in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157397
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiós, Ádám, Ágnes Gyetvai, Gábor Papp, and Tünde Tarr. 2025. "Anifrolumab Attenuates Follicular Helper T Cell Activation in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157397
APA StyleDiós, Á., Gyetvai, Á., Papp, G., & Tarr, T. (2025). Anifrolumab Attenuates Follicular Helper T Cell Activation in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157397








