Interactions Between Prolactin, Intracellular Signaling, and Possible Implications in the Contractility and Pathophysiology of Asthma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Prolactin
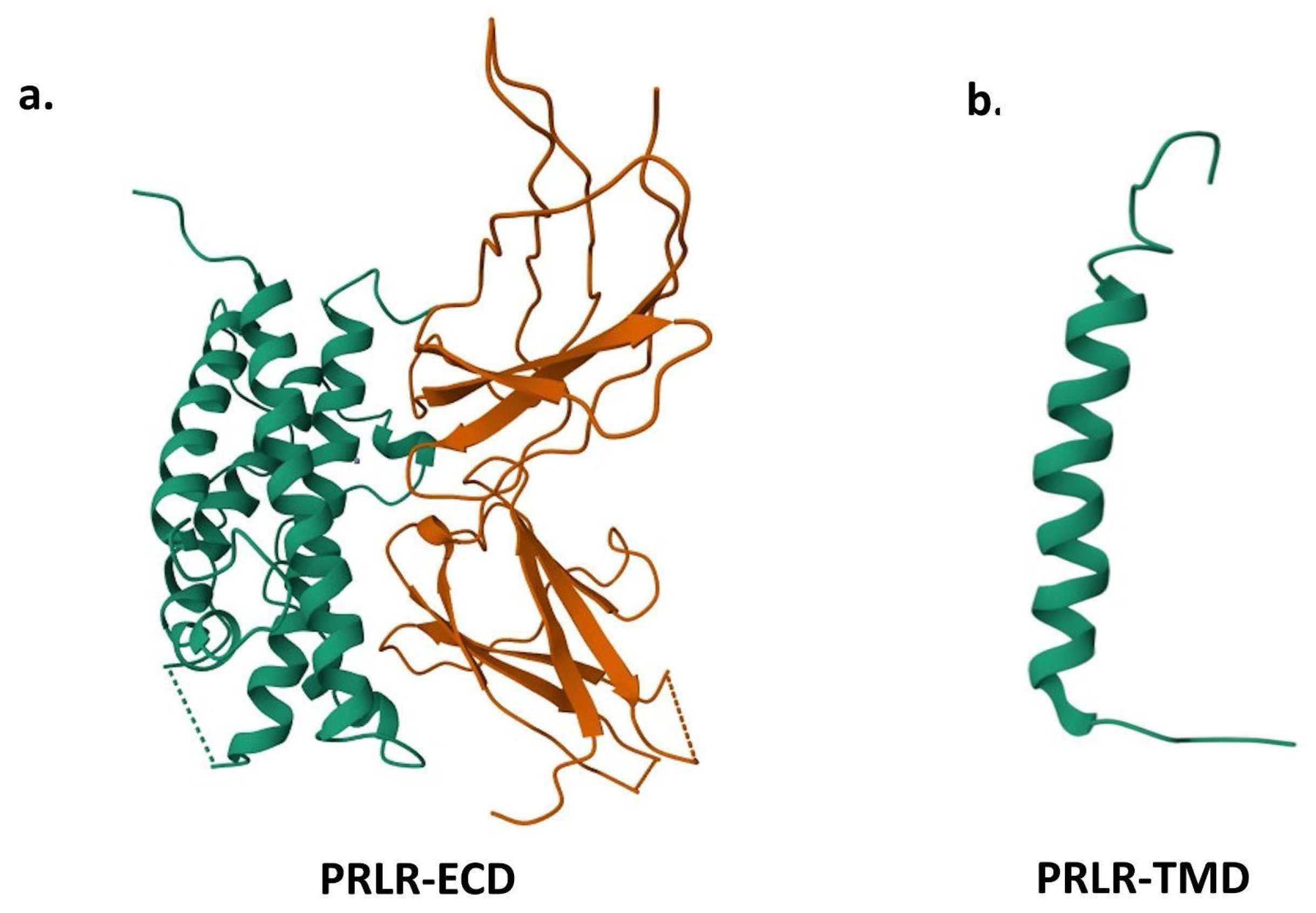
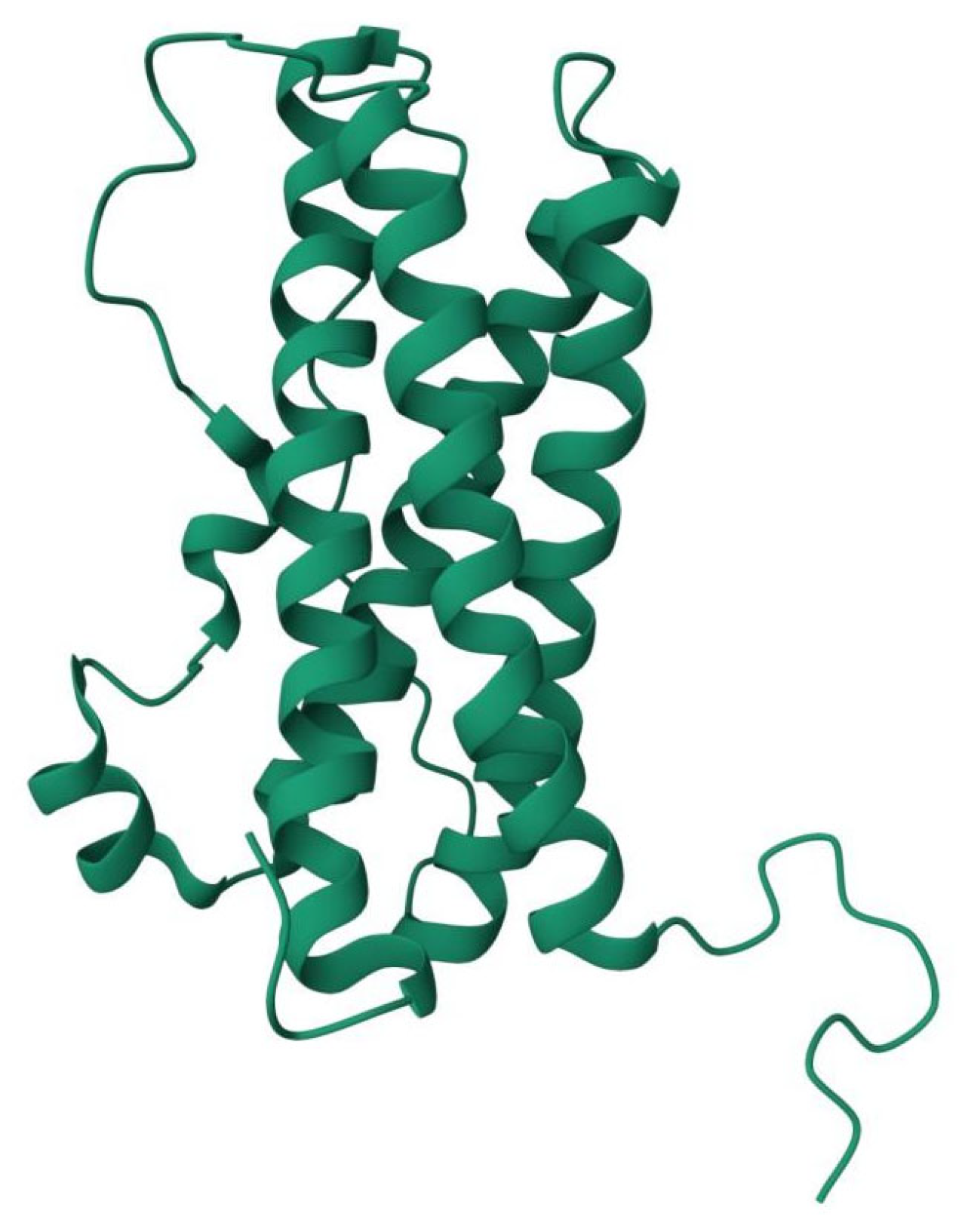
3. Prolactin Receptors
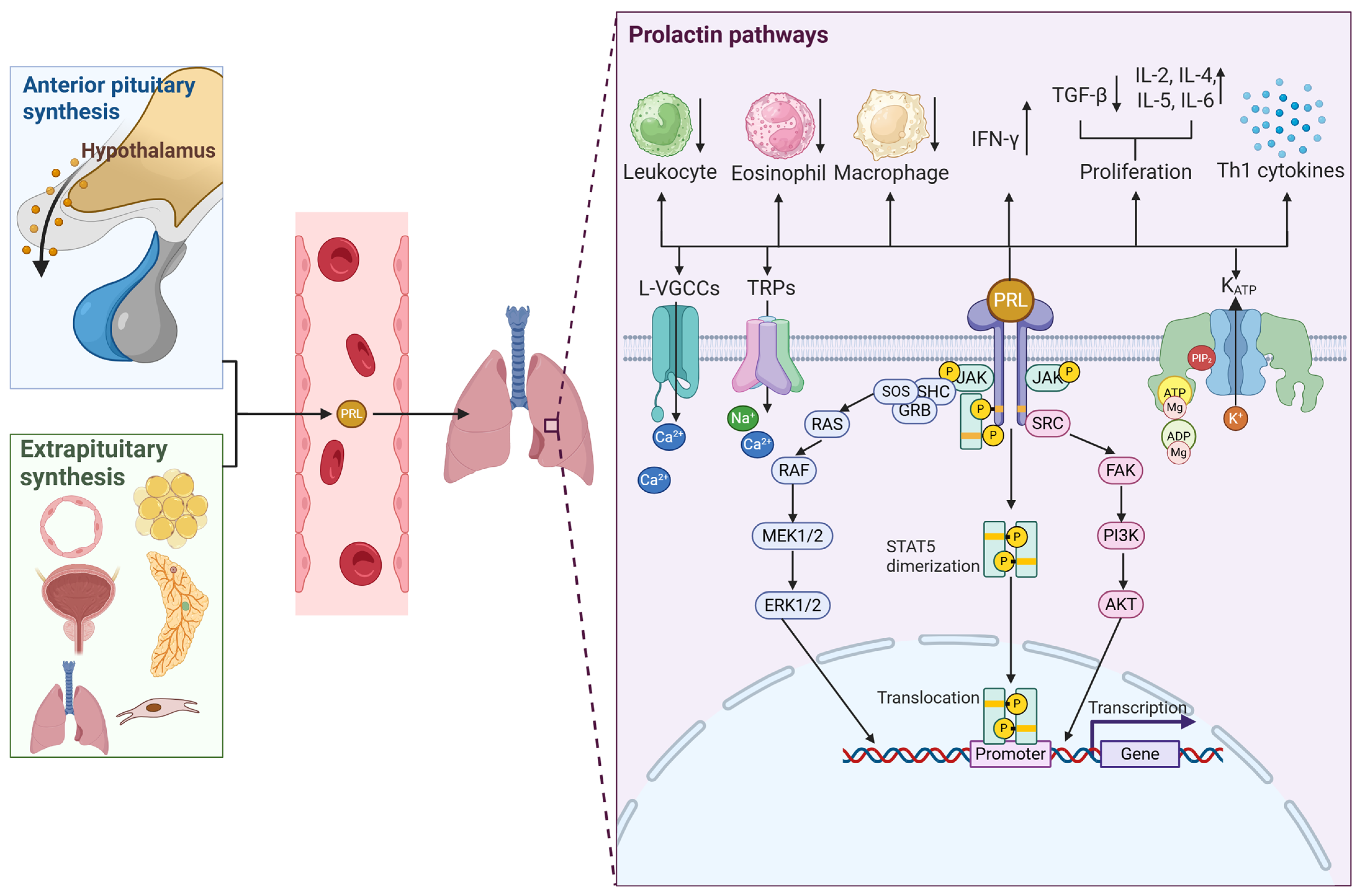
4. Prolactin Functions
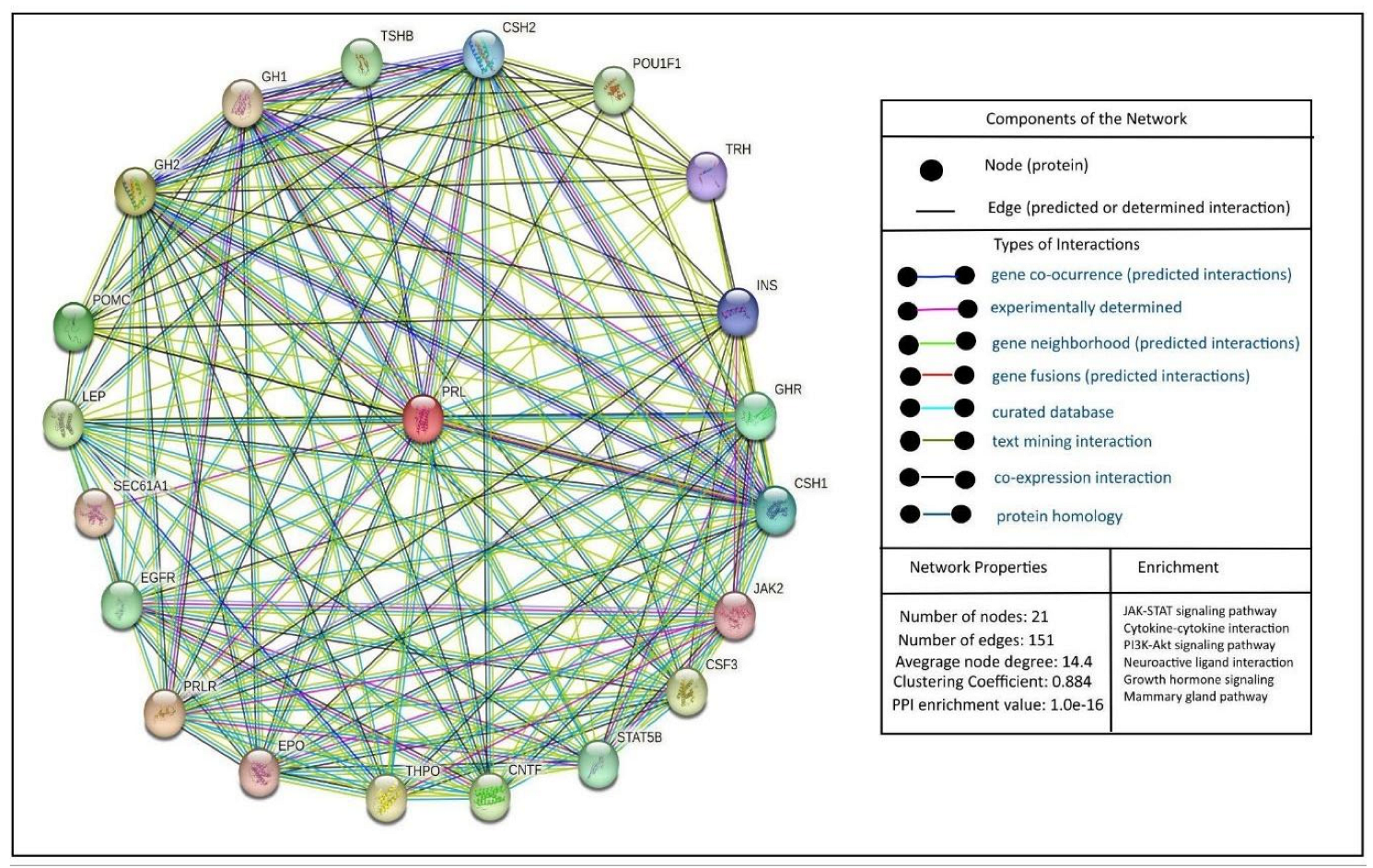
5. Prolactin and Its Interactions
6. Prolactin and the Immune System
7. Prolactin and Autoimmune Diseases
8. Prolactin in Asthma
9. Prolactin and Aging
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PRL | Prolactin |
| GINA | Global Initiative for Asthma |
| HPA | Hypophysis–pituitary–adrenal |
| SLE | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| MS | Multiple sclerosis |
| PRLR | Prolactin receptor |
| PMCA | Plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase |
| NCX | Na+/Ca2+ exchanger |
| ENaC | Epithelial sodium channel |
| ClC4 | Chloride channel |
| L-VGCCs | L-type voltage-gated calcium channels |
| TRPs | Transient receptor potential |
| KATP | ATP-sensitive potassium channels |
| FIL | Leukemia inhibiting factor |
| EPO | Erythropoietin |
| PRFs | PRL-releasing factors |
| PIFs | PRL inhibitory factors |
| GABA | Gamma-aminobutyric acid |
| DOPA | Dihydroxyphenylalanine |
| DC | Dendritic cell |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| SDCs | CD1c-positive dendritic cells |
| OVA | Ovalbumin |
| SLIT | Sublingual immunotherapy |
| ECP | Eosinophil cationic protein |
| ACTH | Adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| PMA | Perimenstrual asthma |
| AHR | Airway hyperresponsiveness |
References
- GINA. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention; GINA: Singapore, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hammad, H.; Lambrecht, B.N. The basic immunology of asthma. Cell 2021, 18, 41469–41485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardet, J.C.; Papi, A.; Reddel, H.K. “As-Needed” Inhaled Corticosteroids for Patients with Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2023, 11, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekking, P.-P.W.; Wener, R.R.; Amelink, M.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Bouvy, M.L.; Bel, E.H. The prevalence of severe refractory asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akcan, N.; Bahceciler, N.N. Headliner in Physiology and Management of Childhood Asthma: Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2020, 16, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, V.J.; Menzies, J.R.; Douglas, A.J. Differential changes in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and prolactin responses to stress in early pregnant mice. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2011, 23, 1066–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russjan, E. The Role of Peptides in Asthma–Obesity Phenotype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.; Kazmi, I.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Alshehri, S.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Imam, S.S.; Nadeem, M.S.; Al-Zahrani, M.H.; Alzarea, S.I.; Alquraini, A. Current Overview on Therapeutic Potential of Vitamin D in Inflammatory Lung Diseases. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Díazcouder, A.; Romero-Nava, R.; Del-Río-Navarro, B.E.; Sánchez-Muñoz, F.; Guzmán-Martín, C.A.; Reyes-Noriega, N.; Rodríguez-Cortés, O.; Leija-Martínez, J.J.; Vélez-Reséndiz, J.M.; Villafaña, S.; et al. The Roles of MicroRNAs in Asthma and Emerging Insights into the Effects of Vitamin D3 Supplementation. Nutrients 2024, 16, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathish, V.; Martin, Y.N.; Prakash, Y.S. Sex steroid signaling: Implications for lung diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 150, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Amaya, J.E.; Hamasato, E.K.; Tobaruela, C.N.; Queiroz-Hazarbassanov, N.; Anselmo Franci, J.A.; Palermo-Neto, J.; Greiffo, F.R.; de Britto, A.A.; Vieira, R.P.; Ligeiro de Oliveira, A.P.; et al. Short-term hyperprolactinemia decreases allergic inflammatory response of the lungs. Life Sci. 2015, 142, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insuela, D.B.R.; Daleprane, J.B.; Coelho, L.P.; Silva, A.R.; e Silva, P.M.; Martins, M.A.; Carvalho, V.F. Glucagon induces airway smooth muscle relaxation by nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 225, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gochicoa-Rangel, L.; Chávez, J.; Del-Río-Hidalgo, R.; Guerrero-Zúñiga, S.; Mora-Romero, U.; Benítez-Pérez, R.; Rodríguez-Moreno, L.; Torre-Bouscoulet, L.; Vargas, M.H. Lung function is related to salivary cytokines and hormones in healthy children. An exploratory cross-sectional study. Physiol. Rep. 2023, 11, e15861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulkhi, A.A.; Shepard, K.V.; Casale, T.B.; Cardet, J.C. Elevated Testosterone Is Associated with Decreased Likelihood of Current Asthma Regardless of Sex. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 3029–3035.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radzikowska, U.; Golebski, K. Sex hormones and asthma: The role of estrogen in asthma development and severity. Allergy 2023, 78, 620–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, E.A.; Miller, V.M.; Prakash, Y.S. Sex Differences and Sex Steroids in Lung Health and Disease. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Martínez, B.S.; Flores-Soto, E.; Sommer, B.; Reyes-García, J.; Arredondo-Zamarripa, D.; Solís-Chagoyán, H.; Lemini, C.; Rivero-Segura, N.A.; Santiago-de-la-Cruz, J.A.; Pérez-Plascencia, C. 17β-estradiol induces hyperresponsiveness in guinea pig airway smooth muscle by inhibiting the plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2024, 590, 112273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, W.; Murphy, V. Asthma in pregnancy: A review. Obstet. Med. 2013, 6, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, D.R.; Perkins, N.; Chen, Z.; Kumar, R.; Grobman, W.; Subramaniam, A.; Biggio, J.; Grantz, K.L.; Sherman, S.; Rohn, M.; et al. Determining the Clinical Course of Asthma in Pregnancy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 793–802.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, W.C.; Meyers, D.A.; Wenzel, S.E.; Teague, W.G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; D’Agostino, R., Jr.; Castro, M.; Curran-Everett, D.; Fitzpatrick, A.M.; et al. Identification of Asthma Phenotypes Using Cluster Analysis in the Severe Asthma Research Program. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, B.; González-Ávila, G.; Flores-Soto, E.; Montaño, L.M.; Solís-Chagoyán, H.; Romero-Martínez, B.S. Phytoestrogen-Based Hormonal Replacement Therapy Could Benefit Women Suffering Late-Onset Asthma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borba, V.V.; Zandman-Goddard, G.; Shoenfeld, Y. Prolactin and Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorshkind, K.; Horseman, N.D. The roles of prolactin, growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor-I, and thyroid hormones in lymphocyte development and function: Insights from genetic models of hormone and hormone receptor deficiency. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 292–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borba, V.V.; Zandman-Goddard, G.; Shoenfeld, Y. Prolactin and autoimmunity: The hormone as an inflammatory cytokine. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 33, 101324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, M.; Binart, N.; Steinman, L.; Pedotti, R. Prolactin: A versatile regulator of inflammation and autoimmune pathology. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.E.; Jacobson, J.D. Roles of prolactin and gonadotropin-releasing hormone in rheumatic diseases. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North. Am. 2000, 26, 713–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.E. Treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus with bromocriptine. Lupus 2001, 10, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duc Nguyen, H.; Hoang, N.M.H.; Ko, M.; Seo, D.; Kim, S.; Jo, W.H.; Bae, J.W.; Kim, M.S. Association between Serum Prolactin Levels and Neurodegenerative Diseases: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neuroimmunomodulation 2022, 29, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Jabir, M.S.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Albuhadily, A.K. The conceivable role of prolactin hormone in Parkinson disease: The same goal but with different ways. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 91, 102075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ippoliti, F.; De Santis, W.; Volterrani, A.; Lenti, L.; Canitano, N.; Lucarelli, S.; Frediani, T. Immunomodulation during sublingual therapy in allergic children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2003, 14, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbacho, A.M.; Valacchi, G.; Kubala, L.; Olano-Martín, E.; Schock, B.C.; Kenny, T.P.; Cross, C.E. Tissue-specific gene expression of prolactin receptor in the acute-phase response induced by lipopolysaccharides. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 287, E750–E757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravčenia, B.; Maślanka, T. Mycophenolate Mofetil, an Inhibitor of Inosine Monophosphate Dehydrogenase, and Tofacitinib, a Janus Kinase Inhibitor, Attenuate Airway Inflammation and Hyperresponsiveness in a Mouse Model of Allergic Asthma. Molecules 2024, 29, 5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bole-Feysot, C.; Goffin, V.; Edery, M.; Binart, N.; Kelly, P.A. Prolactin (PRL) and its receptor: Actions, signal transduction pathways and phenotypes observed in PRL receptor knockout mice. Endocr. Rev. 1998, 19, 225–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeeta Devi, Y.; Halperin, J. Reproductive actions of prolactin mediated through short and long receptor isoforms. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2014, 382, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Salinas, G.; Rivero-Segura, N.A.; Cabrera-Reyes, E.A.; Rodríguez-Chávez, V.; Langley, E.; Cerbon, M. Decoding signaling pathways involved in prolactin-induced neuroprotection: A review. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2021, 61, 100913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorvin, C.M. The prolactin receptor: Diverse and emerging roles in pathophysiology. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2015, 2, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Costa-Brito, A.R.; Gonçalves, I.; Santos, C.R.A. The brain as a source and a target of prolactin in mammals. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 1695–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horseman, N.D.; Gregerson, K.A. Prolactin actions. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 52, R95–R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marano, R.J.; Ben-Jonathan, N. Minireview: Extrapituitary Prolactin: An Update on the Distribution, Regulation, and Functions. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 28, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.J.; Henry, M.A.; Akopian, A.N. Prolactin receptor in regulation of neuronal excitability and channels. Channels 2014, 8, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Salinas, G.; Rodríguez-Chávez, V.; Langley, E.; Cerbon, M. Prolactin-induced neuroprotection against excitotoxicity is mediated via PI3K/AKT and GSK3β/NF-κB in primary cultures of hippocampal neurons. Peptides 2023, 166, 171037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorkkam, N.; Wongdee, K.; Suntornsaratoon, P.; Krishnamra, N.; Charoenphandhu, N. Prolactin stimulates the L-type calcium channel-mediated transepithelial calcium transport in the duodenum of male rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 430, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.T.; Qu, Z.W.; Ren, C.; Gan, X.; Qiu, C.Y.; Hu, W.P. Prolactin potentiates the activity of acid-sensing ion channels in female rat primary sensory neurons. Neuropharmacology 2016, 103, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenlee, M.M.; Mitzelfelt, J.D.; Duke, B.J.; Al-Khalili, O.; Bao, H.F.; Eaton, D.C. Prolactin stimulates sodium and chloride ion channels in A6 renal epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2015, 308, F697–F705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Amaya, J.E.; Marino, L.P.; Tobaruela, C.N.; Namazu, L.B.; Calefi, A.S.; Margatho, R.; Gonçalves, V., Jr.; Queiroz-Hazarbassanov, N.; Klein, M.O.; Palermo-Neto, J.; et al. Attenuated allergic inflammatory response in the lungs during lactation. Life Sci. 2016, 151, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Reyes, E.A.; Limón-Morales, O.; Rivero-Segura, N.A.; Camacho-Arroyo, I.; Cerbón, M. Prolactin function and putative expression in the brain. Endocrine 2017, 57, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, V.; Young, J.; Binart, N. Prolactin-a pleiotropic factor in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddle, O.; Bates, R.W.; Dykshorn, S.W. A new hormone of the anterior pituitary. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1932, 29, 1211–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, R.W.; Lahr, E.L.; Riddle, O. The gross action of prolactin and follicle-stimulating hormone on the mature ovary and sex accessories of fowl. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1935, 111, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.E.; Kanyicska, B.; Lerant, A.; Nagy, G. Prolactin: Structure, function, and regulation of secretion. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 1523–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.; Guyda, H.; Friesen, H. Purification of human prolactin. J. Biol. Chem. 1972, 247, 1955–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattan, D.R.; Kokay, I.C. Prolactin: A Pleiotropic Neuroendocrine Hormone. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 20, 752–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, R.S.; Grattan, D.R. 30 years after: CNS actions of prolactin: Sources, mechanisms and physiological significance. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2019, 31, e12669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huising, M.O.; Kruiswijk, C.P.; Flik, G. Phylogeny and evolution of class-I helical cytokines. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 189, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, P.; Dinan, T.G. Prolactin and dopamine: What is the connection? A review article. J. Psychopharmacol. 2008, 22, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binart, N. Prolactin and pregnancy in mice and humans. Ann. Endocrinol. 2016, 77, 126–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carré, N.; Binart, N. Prolactin and adipose tissue. Biochimie 2014, 97, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanza, M.; Pedotti, R. Prolactin: Friend or Foe in Central Nervous System Autoimmune Inflammation? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guh, Y.J.; Lin, C.H.; Hwang, P.P. Osmoregulation in zebrafish: Ion transport mechanisms and functional regulation. EXCLI J. 2015, 14, 627–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero, J.; Sánchez-Robledo, V.; Carretero-Hernández, M.; Catalano-Iniesta, L.; García-Barrado, M.J.; Iglesias-Osma, M.C.; Blanco, E.J. Prolactin system in the hippocampus. Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 375, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triebel, J.; Robles, J.P.; Zamora, M.; Clapp, C.; Bertsch, T. New horizons in specific hormone proteolysis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 33, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, N.; Adachi, T.; Ishihara, T.; Shimatsu, A. The natural history of macroprolactinaemia. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 166, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, V.; Villa, C.; Auguste, A.; Lamothe, S.; Guillou, A.; Martin, A.; Caburet, S.; Young, J.; Veitia, R.A.; Binart, N. Natural and molecular history of prolactinoma: Insights from a Prlr−/− mouse model. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 6144–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, V.; Young, J.; Chanson, P.; Binart, N. New insights in prolactin: Pathological implications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapp, C.; Aranda, J.; González, C.; Jeziorski, M.C.; Martínez de la Escalera, G. Vasoinhibins: Endogenous regulators of angiogenesis and vascular function. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 17, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macotela, Y.; Ruiz-Herrera, X.; Vázquez-Carrillo, D.I.; Ramírez-Hernandez, G.; Martínez De La Escalera, G.; Clapp, C. The beneficial metabolic actions of prolactin. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1001703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara-Castañeda, E.; Grattan, D.R.; Pasantes-Morales, H.; Pérez-Domínguez, M.; Cabrera-Reyes, E.A.; Morales, T.; Cerbón, M. Prolactin mediates neuroprotection against excitotoxicity in primary cell cultures of hippocampal neurons via its receptor. Brain Res. 2016, 1636, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, G.; Liang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Extra-pituitary prolactin (PRL) and prolactin-like protein (PRL-L) in chickens and zebrafish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 220, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torner, L. Actions of Prolactin in the Brain: From Physiological Adaptations to Stress and Neurogenesis to Psychopathology. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, V.S.; Harris, R.M.; Austin, S.H.; Nava Ultreras, B.; Booth, A.M.; Angelier, F.; Lang, A.S.; Feustel, T.; Lee, C.; Bond, A. Prolactin and prolactin receptor expression in the HPG axis and crop during parental care in both sexes of a biparental bird (Columba livia). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2022, 315, 113940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.B.; Whittington, C.M.; Meyer, A.; Scobell, S.K.; Gauthier, M.E. Prolactin and the evolution of male pregnancy. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2023, 334, 114210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DaSilva, L.; Howard, O.M.; Rui, H.; Kirken, R.A.; Farrar, W.L. Growth signaling and JAK2 association mediated by membrane-proximal cytoplasmic regions of prolactin receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 18267–18270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya-Secchi, R.; Bugge, K.; Seiffert, P.; Petry, A.; Haxholm, G.W.; Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Falsig Pedersen, S.; Arleth, L.; Kragelund, B.B. The prolactin receptor scaffolds Janus kinase 2 via co-structure formation with phosphoinositide-4,5-bisphosphate. eLife 2023, 12, e84645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, W.; Ultsch, M.; De Vos, A.M.; Kossiakoff, A.A. The X-ray structure of a growth hormone–prolactin receptor complex. Nature 1994, 372, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugge, K.; Papaleo, E.; Haxholm, G.W.; Hopper, J.T.; Robinson, C.V.; Olsen, J.G.; Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Kragelund, B.B. A combined computational and structural model of the full-length human prolactin receptor. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laud, K.; Gourdou, I.; Belair, L.; Peyrat, J.P.; Djiane, J. Characterization and modulation of a prolactin receptor mRNA isoform in normal and tumoral human breast tissues. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 85, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, J.M.; Ginsburg, E.; McAndrew, C.W.; Heger, C.D.; Cheston, L.; Rodriguez-Canales, J.; Vonderhaar, B.K.; Goldsmith, P. Characterization of Δ7/11, a functional prolactin-binding protein. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 50, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Jonathan, N.; Mershon, J.L.; Allen, D.L.; Steinmetz, R.W. Extrapituitary prolactin: Distribution, regulation, functions, and clinical aspects. Endocr. Rev. 1996, 17, 639–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grattan, D.R. 60 YEARS OF NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY: The hypothalamo-prolactin axis. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 226, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, P.; Kokay, I.; Sapsford, T.; Bunn, S.; Grattan, D. Prolactin regulation of the HPA axis is not mediated by a direct action upon CRH neurons: Evidence from the rat and mouse. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 222, 3191–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, P.; Martínez-Moreno, C.G.; Lorenson, M.Y.; Walker, A.M.; Morales, T. Prolactin Attenuates Neuroinflammation in LPS-Activated SIM-A9 Microglial Cells by Inhibiting NF-κB Pathways Via ERK1/2. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 42, 2171–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Campos, A.; Giovannini, P.; Parati, E.; Novelli, A.; Caraceni, T.; Müller, E.E. Growth hormone and prolactin stimulation by Madopar in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1981, 44, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera-Reyes, E.A.; Vanoye–Carlo, A.; Rodríguez-Dorantes, M.; Vázquez-Martínez, E.R.; Rivero-Segura, N.A.; Collazo-Navarrete, O.; Cerbón, M. Transcriptomic analysis reveals new hippocampal gene networks induced by prolactin. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reem, G.H.; Ray, D.W.; Davis, J.R. The human prolactin gene upstream promoter is regulated in lymphoid cells by activators of T-cells and by cAMP. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 1999, 22, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torner, L.; Neumann, I.D. The Brain Prolactin System: Involvement in Stress Response Adaptations in Lactation. Stress 2002, 5, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, T.L.; Vukovic, J.; Koudijs, M.M.; Blackmore, D.G.; Mackay, E.W.; Sykes, A.M.; Overall, R.W.; Hamlin, A.S.; Bartlett, P.F. Prolactin Stimulates Precursor Cells in the Adult Mouse Hippocampus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero-Segura, N.A.; Flores-Soto, E.; García De La Cadena, S.; Coronado-Mares, I.; Gomez-Verjan, J.C.; Ferreira, D.G.; Cabrera-Reyes, E.A.; Lopes, L.V.; Massieu, L.; Cerbón, M. Prolactin-induced neuroprotection against glutamate excitotoxicity is mediated by the reduction of [Ca2+]i overload and NF-κB activation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Moratalla, A.; Martín, E.D. Prolactin enhances hippocampal synaptic plasticity in female mice of reproductive age. Hippocampus 2021, 31, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Chávez, V.; Flores-Soto, E.; Molina-Salinas, G.; Martínez-Razo, L.D.; Montaño, L.M.; Cerbón, M. Prolactin reduces the kainic acid-induced increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration, leading to neuroprotection of hippocampal neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 2023, 810, 137344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaya, J.M.; Shoenfeld, Y. Multiple autoimmune disease in a patient with hyperprolactinemia. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2005, 7, 740–741. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira Borba, V.; Sharif, K.; Shoenfeld, Y. Breastfeeding and autoimmunity: Programing health from the beginning. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2018, 79, e12778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Gonzalez, J.; Rosenfeld, G.; Keiser, H.; Peeva, E. Prolactin alters the mechanisms of B cell tolerance induction. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.M.; Garman, R.D.; Keyes, L.; Kavanagh, B.; McPherson, J.M. Prolactin is an antagonist of TGF-beta activity and promotes proliferation of murine B cell hybridomas. Cell Immunol. 1998, 184, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeva, E.; Zouali, M. Spotlight on the role of hormonal factors in the emergence of autoreactive B-lymphocytes. Immunol. Lett. 2005, 101, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athreya, B.H.; Pletcher, J.; Zulian, F.; Weiner, D.B.; Williams, W.V. Subset-specific effects of sex hormones and pituitary gonadotropins on human lymphocyte proliferation in vitro. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1993, 66, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matera, L.; Galetto, A.; Geuna, M.; Vekemans, K.; Ricotti, E.; Contarini, M.; Moro, F.; Basso, G. Individual and combined effect of granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor and prolactin on maturation of dendritic cells from blood monocytes under serum-free conditions. Immunology 2000, 100, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matera, L.; Mori, M.; Galetto, A. Effect of prolactin on the antigen presenting function of monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Lupus 2001, 10, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, R.W. Estrogen, prolactin, and autoimmunity: Actions and interactions. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2001, 1, 995–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera-Lastra, O.; Jara, L.J.; Espinoza, L.R. Prolactin and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2002, 1, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu-Lee, L.Y. Prolactin modulation of immune and inflammatory responses. Recent. Prog. Horm. Res. 2002, 57, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Hou, Y. Prolactin modulates the functions of murine spleen CD11c-positive dendritic cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 1478–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, L.J.; Benitez, G.; Medina, G. Prolactin, dendritic cells, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2008, 7, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikanza, I.C. Prolactin and neuroimmunomodulation: In vitro and in vivo observations. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 876, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walton, P.E.; Cronin, M.J. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma reduce prolactin release in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. 1990, 259, E672–E676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, K.; Masumoto, N.; Kasahara, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Tasaka, K.; Hirota, K.; Miyake, A.; Tanizawa, O. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulates prolactin release from anterior pituitary cells: A possible involvement of intracellular calcium mobilization. Endocrinology 1991, 128, 2785–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theas, S.; Pisera, D.; Duvilanski, B.; De Laurentiis, A.; Pampillo, M.; Lasaga, M.; Seilicovich, A. Estrogens modulate the inhibitory effect of tumor necrosis factor-alpha on anterior pituitary cell proliferation and prolactin release. Endocrine 2000, 12, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, R.; Nguyen, T. Protein S: Function, regulation, and clinical perspectives. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2021, 28, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matera, L.; Mori, M. Cooperation of Pituitary Hormone Prolactin with Interleukin-2 and Interleukin-12 on Production of Interferon-γ by Natural Killer and T Cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 917, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, S.M.; Sodhi, A. Effect of prolactin on nitric oxide and interleukin-1 production of murine peritoneal macrophages: Role of Ca2+ and protein kinase C. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 1997, 19, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.H.; Kessler, M.A.; Schuler, L.A. Regulation of interleukin (IL)-1alpha, IL-1beta, and IL-6 expression by growth hormone and prolactin in bovine thymic stromal cells. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 1997, 128, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.G.; Lee, Y.H. Circulating prolactin level in systemic lupus erythematosus and its correlation with disease activity: A meta-analysis. Lupus 2017, 26, 1260–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praprotnik, S.; Agmon-Levin, N.; Porat-Katz, B.S.; Blank, M.; Meroni, P.L.; Cervera, R.; Miesbach, W.; Stojanovich, L.; Szyper-Kravitz, M.; Rozman, B.; et al. Prolactin’s role in the pathogenesis of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus 2010, 19, 1515–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.E.; Allen, S.H.; Hoffman, R.W.; McMurray, R.W. Prolactin: A stimulator of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 1995, 4, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaños-Miranda, A.; Cárdenas-Mondragón, G. Serum free prolactin concentrations in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus are associated with lupus activity. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, R.; Keisler, D.; Kanuckel, K.; Izui, S.; Walker, S.E. Prolactin influences autoimmune disease activity in the female B/W mouse. J. Immunol. 1991, 147, 3780–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, R.W.; Weidensaul, D.; Allen, S.H.; Walker, S.E. Efficacy of bromocriptine in an open label therapeutic trial for systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 1995, 22, 2084–2091. [Google Scholar]
- Semik-Orzech, A.; Skoczyński, S.; Pierzchała, W. Serum estradiol concentration, estradiol-toprogesterone ratio and sputum IL-5 and IL-8 concentrations are increased in luteal phase of the menstrual cycle in perimenstrual asthma patients. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 49, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Lai, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhou, G. Protective Effects of Herba Houttuyniae Aqueous Extract against OVA-Induced Airway Hyperresponsiveness and Inflammation in Asthmatic Mice. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2022, 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Favela, F.; Legorreta-Haquet, M.V.; Huerta-Villalobos, Y.R.; Yunuen, R.; Chávez-Rueda, K.; Montoya-Díaz, E.; Chávez-Sánchez, L.; Zenteno-Galindo, E. Participación de la prolactina en la respuesta inmune. Bol. Med. Hosp. Infant. Mex. 2012, 69, 329–336. [Google Scholar]
- Crosignani, P.G. Management of hyperprolactinemic infertility. Middle East. Fertil. Soc. J. 2012, 17, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, A.M.P.; Rodríguez, G.G.; Vega, M.M.E. Prolactina y autoinmunidad en piel. Dermatol. Cosmet. Med. Quir. 2013, 11, 148–154. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, S.; Muneyyirci-Delale, O. Stress-Induced Hyperprolactinemia: Pathophysiology and Clinical Approach. Obstet. Gynecol. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, E.; Thébault, S.; Aroña, R.; Martínez de la Escalera, G.; Clapp, C. Prolactin mitigates deficiencies of retinal function associated with aging. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 85, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, Y.Y.; Toledo, J.B.; Nefedov, A.; Polikar, R.; Raghavan, N.; Xie, S.X.; Farnum, M.; Schultz, T.; Baek, Y.; Deerlin, V.V.; et al. Identifying amyloid pathology–related cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease in a multicohort study. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 1, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zverova, M.; Kitzlerova, E.; Fisar, Z.; Jirak, R.; Hroudova, J.; Benakova, H.; Lelkova, P.; Martasek, P.; Raboch, J. Interplay between the APOE Genotype and Possible Plasma Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2018, 15, 938–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, A.S.; Landau, S.; Chaudhuri, K.R. Serum prolactin levels in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Clin. Auton. Res. 2002, 12, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitkowska, M.; Tomasiuk, R.; Czyżyk, M.; Friedman, A. Prolactin and sex hormones levels in males with Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2015, 131, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresovich, J.K.; Xu, Z.; O’Brien, K.M.; Weinberg, C.R.; Sandler, D.P.; Taylor, J.A. Methylation-Based Biological Age and Breast Cancer Risk. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 111, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tworoger, S.S.; Eliassen, A.H.; Sluss, P.; Hankinson, S.E. A prospective study of plasma prolactin concentrations and risk of premenopausal and postmenopausal breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1482–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiloiro, S.; Giampietro, A.; Bianchi, A.; De Marinis, L. Prolactinoma and Bone. Curr. Opin. Endocr. Metab. Res. 2018, 3, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.J.; Sang, H.; Park, S.Y.; Chin, S.O. Effect of Hyperprolactinemia on Bone Metabolism: Focusing on Osteopenia/Osteoporosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Aspect | Prolactin/Asthma Relationship | Proposed Mechanism/Evidence | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drug-induced hyperprolactinemia | ↓ Allergic lung inflammation | Inhibits D2 receptors → ↑ Prolactin → Modulates leukocytes, mucus, and cytokines (IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α) | [11] |
| Pregnancy and Breastfeeding | ↑ Prolactin during breastfeeding = possible protection | Lactating females → ↑ plasma prolactin Modulation of the inflammatory response Stimulates B lymphopoiesis and the secretion of IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α Mast cell involvement Promotes bronchodilation via the β2 pathway | [45,119] |
| Premenstrual phase | Possible indirect effect via hormonal disruption | Hyperprolactinemia → Anovulation → ↓ Progesterone/estrogens → Indirect impact on asthma exacerbations | [120] |
| Stress | ↑ Prolactin associated with stress → potential asthma exacerbation | Activation of the HPA and sympathetic axis → Inflammatory modulation; Hyperprolactinemia as an immunological mediator | [121,122] |
| Environmental factors | Possible proinflammatory role of prolactin | ↑ Cytokines due to pollution → ↑ Prolactin → Modulates respiratory immune response | [119] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calixto, E.; Gomez-Verjan, J.C.; Cerbón, M.; Rodríguez-Chávez, V.; Romero-Martínez, B.S.; Martinez-Enriquez, M.E.; Montaño, L.M.; Solís-Chagoyán, H.; Aquino-Gálvez, A.; Rivero-Segura, N.A.; et al. Interactions Between Prolactin, Intracellular Signaling, and Possible Implications in the Contractility and Pathophysiology of Asthma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157332
Calixto E, Gomez-Verjan JC, Cerbón M, Rodríguez-Chávez V, Romero-Martínez BS, Martinez-Enriquez ME, Montaño LM, Solís-Chagoyán H, Aquino-Gálvez A, Rivero-Segura NA, et al. Interactions Between Prolactin, Intracellular Signaling, and Possible Implications in the Contractility and Pathophysiology of Asthma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157332
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalixto, Eduardo, Juan C. Gomez-Verjan, Marco Cerbón, Valeria Rodríguez-Chávez, Bianca S. Romero-Martínez, María E. Martinez-Enriquez, Luis M. Montaño, Héctor Solís-Chagoyán, Arnoldo Aquino-Gálvez, Nadia A. Rivero-Segura, and et al. 2025. "Interactions Between Prolactin, Intracellular Signaling, and Possible Implications in the Contractility and Pathophysiology of Asthma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157332
APA StyleCalixto, E., Gomez-Verjan, J. C., Cerbón, M., Rodríguez-Chávez, V., Romero-Martínez, B. S., Martinez-Enriquez, M. E., Montaño, L. M., Solís-Chagoyán, H., Aquino-Gálvez, A., Rivero-Segura, N. A., González-Ávila, G., Susunaga Notario, A. d. C., Pérez-Figueroa, G. E., Carbajal, V., Flores-Soto, E., & Sommer, B. (2025). Interactions Between Prolactin, Intracellular Signaling, and Possible Implications in the Contractility and Pathophysiology of Asthma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157332








