Unravelling the Role of Post-Junctional M2 Muscarinic Receptors in Cholinergic Nerve-Mediated Contractions of Airway Smooth Muscle
Abstract
1. Introduction
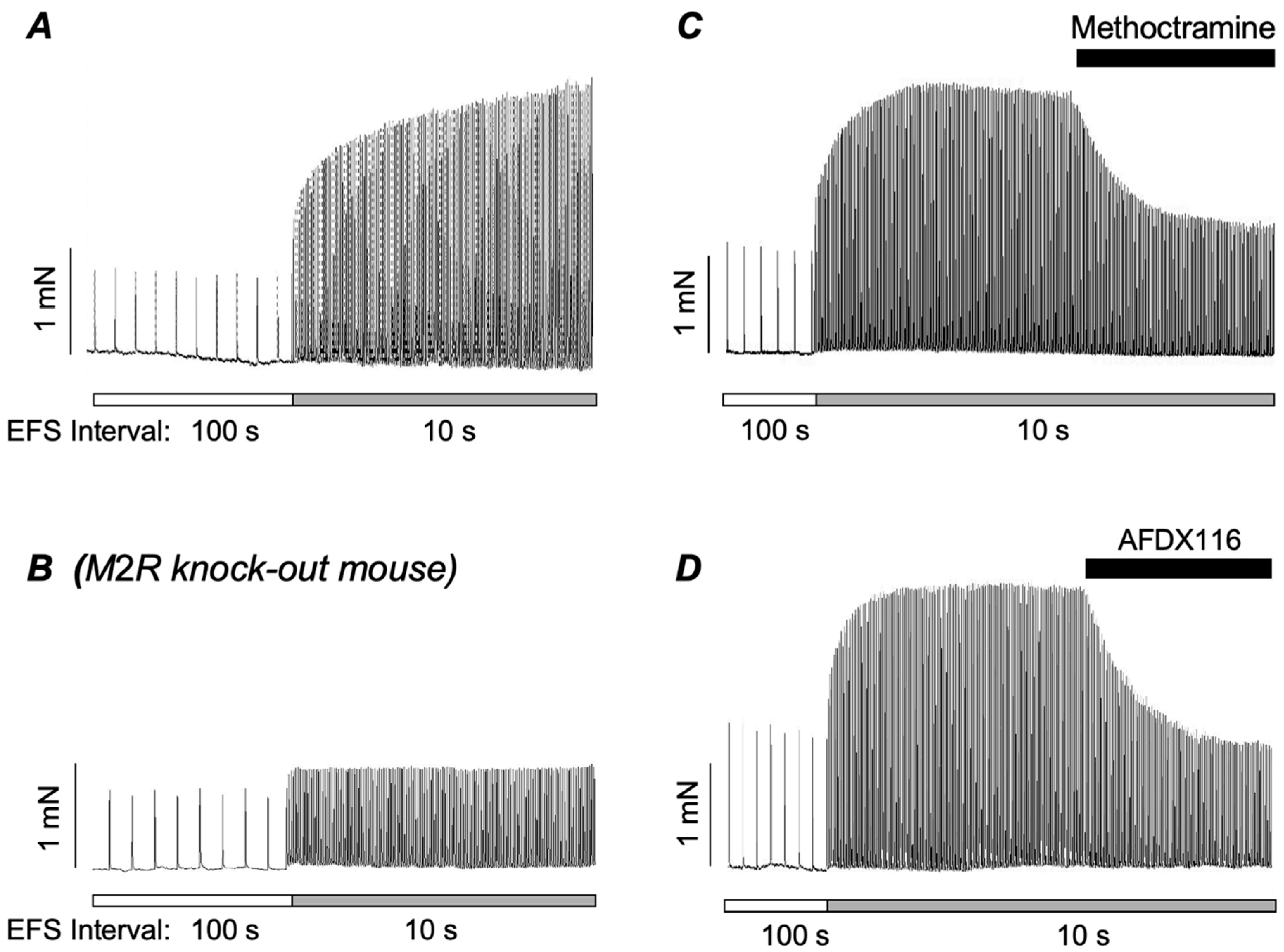
2. Role of Postjunctional M2Rs in the Contraction of ASM
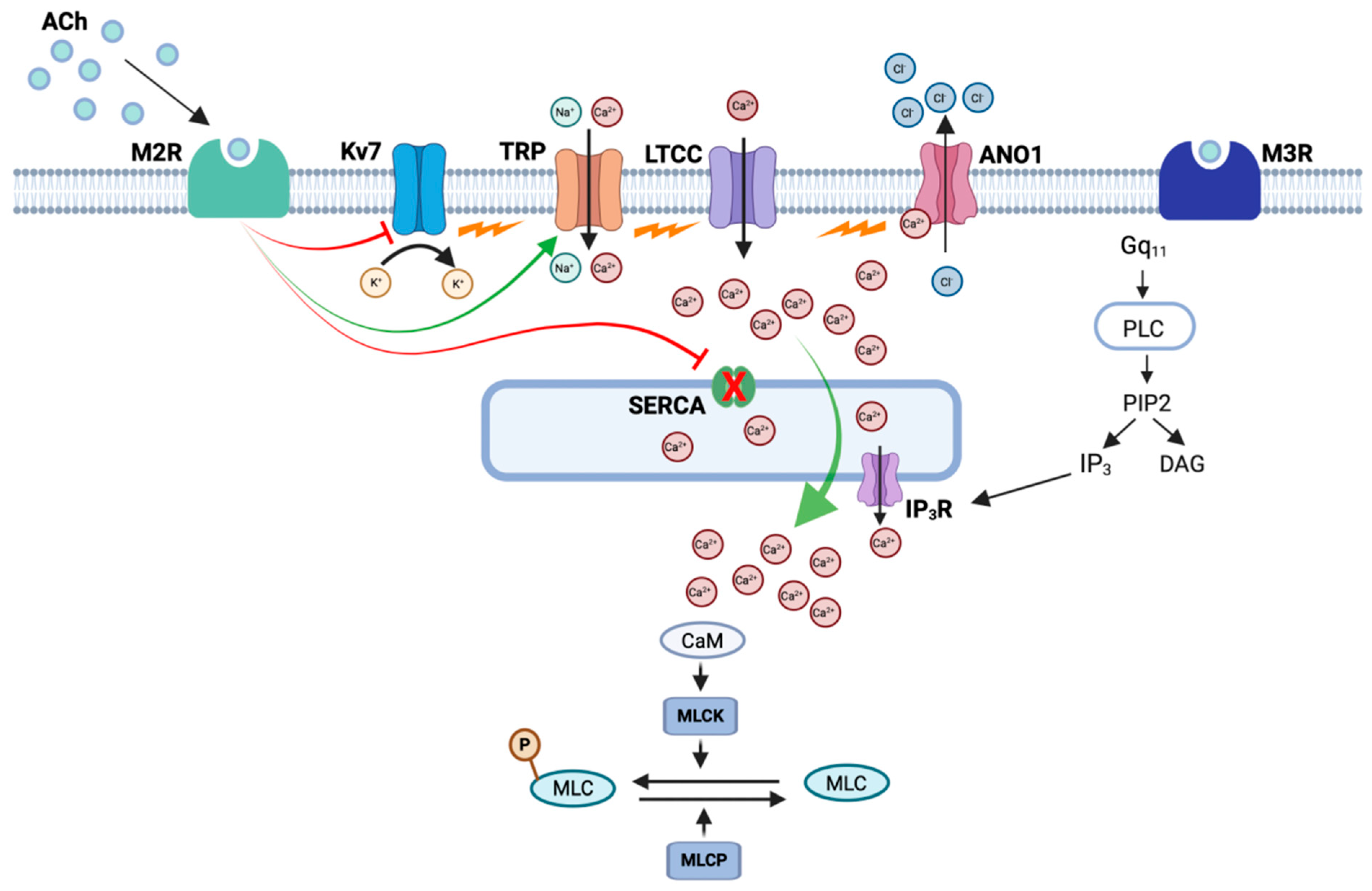
3. Mechanisms Underlying M2R-Dependent Contractions of ASM
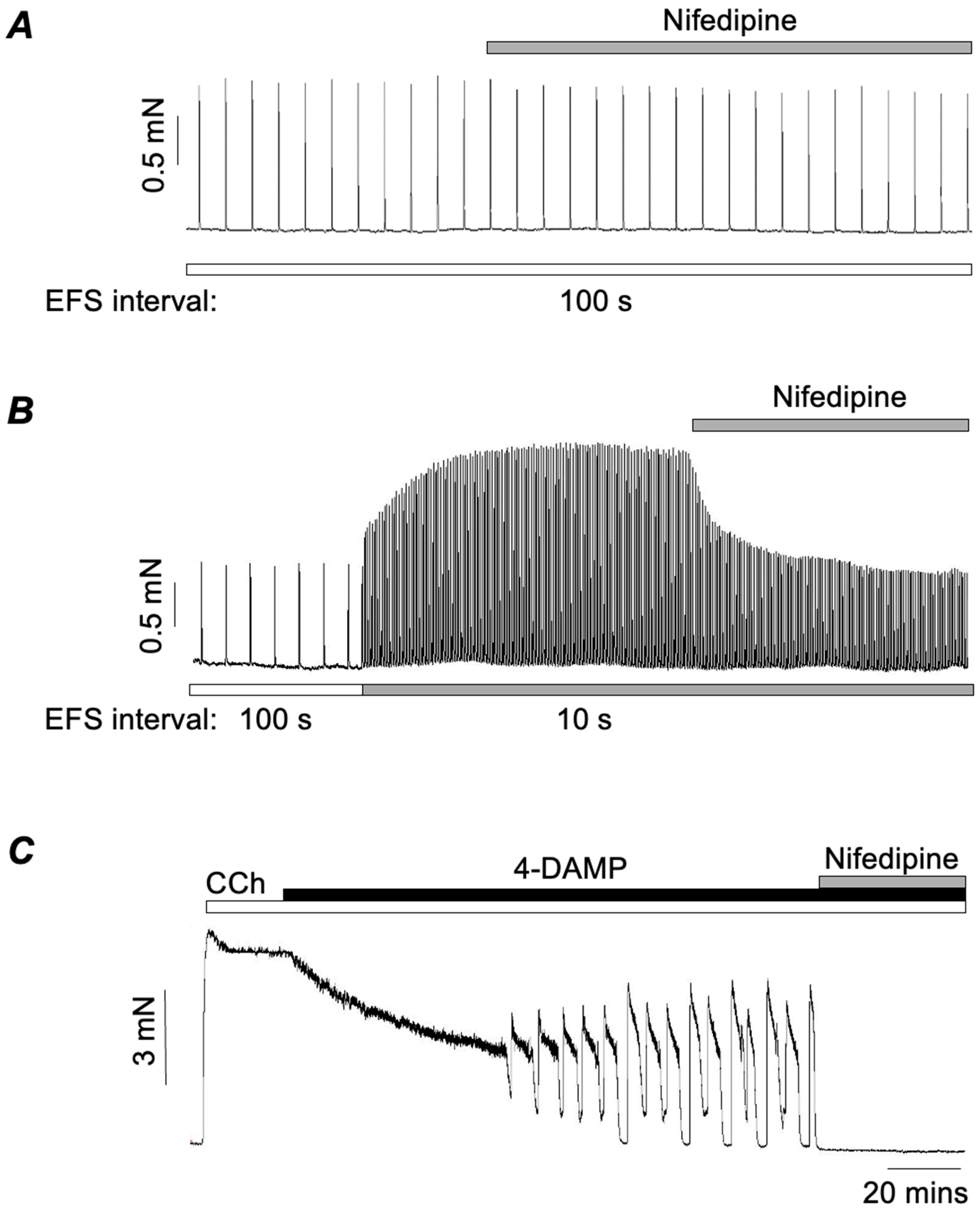
3.1. Role of L-Type Ca2+ Channels in M2R-Mediated Contractions of ASM
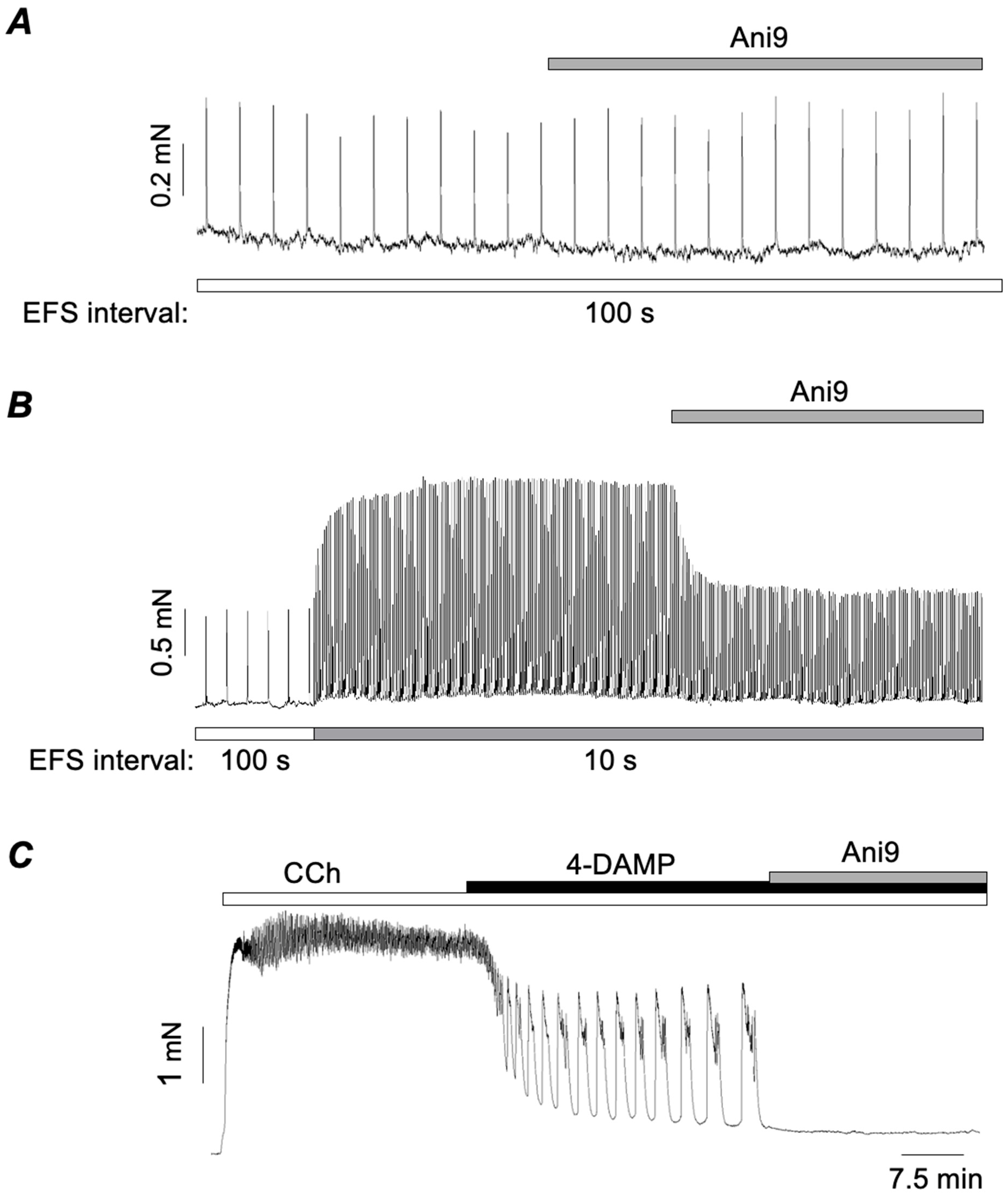
3.2. Role of TMEM16A Ca2+-Activated Cl− Channels in M2R-Dependent Contractions of ASM
3.3. Involvement of K+ Channels or Non-Specific Cation Channels?
4. Modulation of M2R-Dependent Contractions of ASM
5. A Role for M2Rs in Asthma and COPD?
6. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zaagsma, J.; Roffel, A.F.; Meurs, H. Muscarinic control of airway function. Life Sci. 1997, 60, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryer, A.D.; Jacoby, D.B. Muscarinic receptors and control of airway smooth muscle. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 158, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. The role of anticholinergics in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Med. Suppl. 2004, 117 (Suppl. S12), 24S–32S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazzola, M.; Page, C.P.; Calzetta, L.; Matera, M.G. Pharmacology and therapeutics of bronchodilators. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 450–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosens, R.; Gross, N. The mode of action of anticholinergics in asthma. Eur. Respir J. 2018, 52, 1701247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, N.J.; Co, E.; Skorodin, M.S. Cholinergic bronchomotor tone in COPD. Estimates of its amount in comparison with that in normal subjects. Chest 1989, 96, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, N.J.; Skorodin, M.S. Role of the parasympathetic system in airway obstruction due to emphysema. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984, 311, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulson, F.R.; Fryer, A.D. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and airway diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 98, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosens, R.; Zaagsma, J.; Meurs, H.; Halayko, A.J. Muscarinic receptor signaling in the pathophysiology of asthma and COPD. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matera, M.G.; Page, C.P.; Calzetta, L.; Rogliani, P.; Cazzola, M. Pharmacology and Therapeutics of Bronchodilators Revisited. Pharmacol. Rev. 2020, 72, 218–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, D.B.; Fryer, A.D. Anticholinergic therapy for airway diseases. Life Sci. 2001, 68, 2565–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazzola, M.; Rogliani, P.; Matera, M.G. The latest on the role of LAMAs in asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 1288–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazzola, M.; Luigino Calzetta, L.; Matera, M.G. Long-acting muscarinic antagonists and small airways in asthma: Which link? Allergy 2021, 76, 1990–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzola, M.; Rogliani, P.; Matera, M.G. Might It Be Appropriate to Anticipate the Use of Long-Acting Muscarinic Antagonists in Asthma? Drugs 2023, 83, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agache, I.; Adcock, I.M.; Akdis, C.A.; Akdis, M.; Bentabol-Ramos, G.; van den Berge, M.; Boccabella, C.; Canonica, W.G.; Caruso, C.; Couto, M.; et al. The Bronchodilator and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Long-Acting Muscarinic Antagonists in Asthma: An EAACI Position Paper. Allergy 2025, 80, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fryer, A.D.; Maclagan, J. Muscarinic inhibitory receptors in pulmonary parasympathetic nerves in the guinea-pig. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1984, 83, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaber, L.C.; Fryer, A.D.; Maclagan, J. Neuronal muscarinic receptors attenuate vagally-induced contraction of feline bronchial smooth muscle. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1985, 86, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, D.; Fryer, A.D.; Maclagan, J. Postganglionic muscarinic inhibitory receptors in pulmonary parasympathetic nerves in the guinea-pig. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1986, 88, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulfield, M.P.; Birdsall, N.J. International Union of Pharmacology. XVII. Classification of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 1998, 50, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte, K.E. Cholinergic pathways in the lungs and anticholinergic therapy for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2005, 2, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roffel, A.; Meurs, H.; Elzinga, C.; Zaagsma, J. Characterization of the muscarinic receptor subtype involved in phosphoinositide metabolism in bovine tracheal smooth muscle. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1990, 99, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.T.; Vincent, S.G.; Gomeza, J.; Yamada, M.; Wess, J. Loss of Vagally Mediated Bradycardia and Bronchoconstriction in Mice Lacking M2 or M3 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptors. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilvers, E.R.; Batty, I.H.; Barnes, P.J.; Nahorski, S.R. Formation of inositol polyphosphates in airway smooth muscle after muscarinic receptor stimulation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1990, 252, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandordy, B.M.; Cuss, F.M.; Sampson, A.S.; Palmer, J.B.; Barnes, P.J. Phosphatidylinositol response to cholinergic agonists in airway smooth muscle: Relationship to contraction and muscarinic receptor occupancy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1986, 238, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, N.; Magnussen, H.; Rabe, K.F. Pharmacological characterization of the muscarinic receptor subtype mediating contraction of human peripheral airways. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995, 274, 1293–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Muscarinic receptor subtypes in the airways. Life Sci. 1993, 52, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, E.; Molimard, M.; Savineau, J.P.; Marthan, R. Muscarinic stimulation of airway smooth muscle cells. Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 1998, 31, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.G.; Don, H.F.; Brown, J.K. Direct measurement of acetylcholine release in guinea pig trachea. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 1992, 263, L142–L147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aas, P.; Maclagan, J. Evidence for prejunctional M2 muscarinic receptors in pulmonary cholinergic nerves in the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1990, 101, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltze, M.; Galvan, M. Involvement of muscarinic M2 and M3, but not of M1 and M4 receptors in vagally stimulated contractions of rabbit bronchus/trachea. Pulm. Pharmacol. 1994, 7, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Yoshitomi, T. Autoregulation of acetylcholine release from vagus nerve terminals through activation of muscarinic receptors in the dog trachea. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1988, 93, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minette, P.A.; Barnes, P.J. Prejunctional inhibitory muscarinic receptors on cholinergic nerves in human and guinea pig airways. J. Appl. Physiol. 1988, 64, 2532–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.J.; Barnes, P.J.; Takahashi, T.; Tadjkarimi, S.; Yacoub, M.H.; Belvisi, M.G. Evidence for prejunctional muscarinic autoreceptors in human and guinea pig trachea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 152, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berge, R.E.T.; Zaagsma, J.; Roffel, A.F. Muscarinic inhibitory autoreceptors in different generations of human airways. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 154, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.W.; Yu, M.F.; Robinson, N.E.; Derksen, F.J. Acetylcholine re- lease from airway cholinergic nerves in horses with heaves, an airway obstructive disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 151, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minette, P.A.; Lammers, J.W.; Dixon, C.M.; McCusker, M.T.; Barnes, P.J. A muscarinic agonist inhibits reflex bronchoconstriction in normal but not in asthmatic subjects. J. Appl. Physiol. 1989, 67, 2461–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, L.E.; Ahmed, T. Is there loss of protective muscarinic receptor mechanism in asthma? Chest 1989, 96, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryer, A.D.; Wills-Karp, M.J. Dysfunction of M2-muscarinic receptors in pulmonary parasympathetic nerves after antigen challenge. J. Appl. Physiol. 1991, 71, 2255–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryer, A.D.; Jacoby, D.B. Parainfluenza virus infection damages inhibitory M2 muscarinic receptors on pulmonary parasympathetic nerves in the guinea-pig. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1991, 102, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultheis, A.H.; Bassett, D.J.; Fryer, A.D. Ozone-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and loss of neuronal M2 muscarinic receptor function. J. Appl. Physiol. 1994, 76, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eglen, R.M.; Reddy, H.; Watson, N.; Challiss, R. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes in smooth muscle. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1994, 15, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlert, F.J.; Ostrom, R.S.; Sawyer, G.W. Subtypes of the muscarinic receptor in smooth muscle. Life Sci. 1997, 61, 1729–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlert, F.J. Contractile role of M2 and M3 muscarinic receptors in gastrointestinal, airway and urinary bladder smooth muscle. Life Sci. 2003, 74, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wettschureck, N.; Offermanns, S. Mammalian G proteins and their cell type specific functions. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 1159–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locht, C.; Coutte, L.; Mielcarek, N. The ins and outs of pertussis toxin. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 4668–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kume, H.; Mikawa, K.; Takagi, K.; Kotlikoff, M.I. Role of G proteins and KCa channels in the muscarinic and beta-adrenergic regulation of airway smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 1995, 268 Pt 2, L221–L229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirshman, C.A.; Lande, B.; Croxton, T.L. Role of M2 muscarinic receptors in airway smooth muscle contraction. Life Sci. 1999, 64, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unno, T.; Matsuyama, H.; Sakamoto, T.; Uchiyama, M.; Izumi, Y.; Okamoto, H.; Yamada, M.; Wess, J.; Komori, S. M(2) and M(3) muscarinic receptor-mediated contractions in longitudinal smooth muscle of the ileum studied with receptor knockout mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 146, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, I.; Wang, B.; Herlihy, J.T.; Brenner, R. BK channel β1 subunits regulate airway contraction secondary to M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediated depolarization. J. Physiol. 2011, 589 Pt 7, 1803–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stengel, P.W.; Yamada, M.; Wess, J.; Cohen, M.L. M(3)-receptor knockout mice: Muscarinic receptor function in atria, stomach fundus, urinary bladder, and trachea. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2002, 282, R1443–R1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlenz, H.; Kummer, W.; Jositsch, G.; Wess, J.; Krasteva, G.; Shaik, F.A.; Medapati, M.R.; Chelikani, P.; Mahavadi, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; et al. Muscarinic receptor-mediated bronchoconstriction is coupled to caveolae in murine airways. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2010, 298, L626–L636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struckmann, N.; Schwering, S.; Wiegand, S.; Gschnell, A.; Yamada, M.; Kummer, W.; Wess, J.; Haberberger, R.V. Role of muscarinic receptor subtypes in the constriction of peripheral airways: Studies on receptor-deficient mice. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 64, 1444–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkawadri, T.; McGarvey, L.P.; Mullins, N.D.; Hollywood, M.A.; Thornbury, K.D.; Sergeant, G.P. Contribution of Postjunctional M2 Muscarinic Receptors to Cholinergic Nerve-Mediated Contractions of Murine Airway Smooth Muscle. Function 2021, 3, zqab053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-C.; Peng, Y.-J.; Zhang, G.-S.; He, W.-Q.; Qiao, Y.-N.; Dong, Y.-Y.; Gao, Y.-Q.; Chen, C.; Zhang, C.-H.; Li, W.; et al. Myosin light chain kinase is necessary for tonic airway smooth muscle contraction. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 5522–5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Muscarinic receptors in airways: Recent developments. J. Appl. Physiol 1990, 68, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, E.; Guibert, C.; Savineau, J.; Marthan, R. [Ca2+](i) oscillations induced by muscarinic stimulation in airway smooth muscle cells: Receptor subtypes and correlation with the mechanical activity. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 120, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.-H.; Zheng, Y.-M.; Wang, Y.-X. Two distinct signaling pathways for regulation of spontaneous local Ca2+ release by phospholipase C in airway smooth muscle cells. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2007, 453, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, L. Ionic mechanisms and Ca(2+) regulation in airway smooth muscle contraction: Do the data contradict dogma? Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2002, 282, L1161–L1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Zoghbi, J.F.; Karner, C.; Ito, S.; Shepherd, M.; Alrashdan, Y.; Sanderson, M.J. Ion channel regulation of intracellular calcium and airway smooth muscle function. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 22, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Byron, K.L.; Brueggemann, L.I.; Kakad, P.P.; Haick, J.M. Kv7 (KCNQ) Potassium Channels and L-type Calcium Channels in the Regulation of Airway Diameter. In Calcium Signaling in Airway Smooth Muscle Cells; Wang, Y.-X., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, L.J.; Killian, K. Airway smooth muscle as a target of asthma therapy: History and new directions. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kume, H. Large-Conductance Calcium-Activated Potassium Channels. In Calcium Signaling in Airway Smooth Muscle Cells; Wang, Y.-X., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 49–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brueggemann, L.I.; Cribbs, L.L.; Schwartz, J.; Wang, M.; Kouta, A.; Byron, K.L. Mechanisms of PKA-dependent potentiation of Kv7.5 channel activity in human airway smooth muscle cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, L.J.; Sims, S.M. Acetylcholine activates non-selective cation and chloride conductances in canine and guinea-pig tracheal myocytes. J. Physiol. 1992, 453, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Janssen, L.J.; Sims, S.M. Ca(2+)-dependent Cl- current in canine tracheal smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 269, C163–C169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Fleischmann, B.K.; Kotlikoff, M.I. M2 receptor activation of nonselective cation channels in smooth muscle cells: Calcium and Gi/G(o) requirements. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 1997, 273 Pt 1, C500–C508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotlikoff, M.I.; Wang, Y.X. Calcium release and calcium-activated chloride channels in airway smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 158 Pt 3, S109–S114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZhuGe, R.; Sims, S.M.; Tuft, R.A.; Fogarty, K.E.; Walsh, J.V., Jr. Ca21 sparks 12 activate K and Cl channels, resulting in spontaneous transient currents in guinea-pig tracheal myocytes. J. Physiol. 1998, 513, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Rock, J.R.; Harfe, B.D.; Cheng, T.; Huang, X.; Jan, Y.N.; Jan, L.Y. Studies on expression and function of the TMEM16A calcium-activated chloride channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21413–21418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zhang, H.; Wu, M.; Yang, H.; Kudo, M.; Peters, C.J.; Woodruff, P.G.; Solberg, O.D.; Donne, M.L.; Huang, X.; et al. Calcium-activated chloride channel TMEM16A modulates mucin secretion and airway smooth muscle contraction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16354–16359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhao, W.; Sun, J.; Tao, T.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.H.; Chen, Z.; Gao, Y.Q.; She, F.; et al. Inflammatory mediators mediate airway smooth muscle contraction through a G protein-coupled receptor-transmembrane protein 16A-voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel axis and contribute to bronchial hyperresponsiveness in asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1259–1268.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.A.; Xue, A.; Chini, E.N.; Thompson, M.; Sieck, G.C.; Wylam, M.E. Role of transient receptor potential C3 in TNF-alpha-enhanced calcium influx in human airway myocytes. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 35, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, Y.X.; Zheng, Y.M. Molecular expression and functional role of canonical transient receptor potential channels in airway smooth muscle cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 704, 731–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Farley, J.M.; Miles, P.R. The sources of calcium for acetylcholine-induced contractions of dog tracheal smooth muscle. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1978, 207, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, R.; Drumm, B.T.; Alkawadri, T.; Martin, S.L.; Sergeant, G.P.; Hollywood, M.A.; Thornbury, K.D. The TMEM16A blockers benzbromarone and MONNA cause intracellular Ca2+-release in mouse bronchial smooth muscle cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 947, 175677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shieh, C.C.; Petrini, M.F.; Dwyer, T.M.; Farley, J.M. Cromakalim effects of acetylcholine-induced changes in cytosolic calcium and tension in swine trachealis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1992, 260, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Alkawadri, T.; McGarvey, L.P.; Hollywood, M.A.; Thornbury, K.D.; Sergeant, G.P. Role of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels and Ano1 Ca2+-activated Cl-channels in M2 muscarinic receptor-dependent contractions of murine airway smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2025, 328, L301–L312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielsson, J.; Perez-Zoghbi, J.; Bernstein, K.; Barajas, M.B.; Zhang, Y.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, P.K.; Gallos, G.; Emala, C.W. Antagonists of the TMEM16A calcium- activated chloride channel modulate airway smooth muscle tone and intracellular calcium. Anesthesiology 2015, 123, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielsson, J.; Kuforiji, A.S.; Yocum, G.T.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, D.; Gallos, G.; Emala, C.W., Sr. Agonism of the TMEM16A calcium-activated chloride channel modulates airway smooth muscle tone. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2020, 318, L287–L295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Cannell, M.; van Breemen, C. The superficial buffer barrier in vascular smooth muscle. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1992, 70, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; van Breemen, C. The superficial buffer barrier in venous smooth muscle: Sarcoplasmic reticulum refilling and unloading. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 109, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- van Breemen, C.; Chen, Q.; Laher, I. Superficial buffer barrier function of smooth muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1995, 16, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, L.J.; Betti, P.A.; Netherton, S.J.; Walters, D.K. Superficial buffer barrier and preferentially directed release of Ca2+ in canine airway smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 1999, 276, L744–L753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, P.; Inui, M.; Tada, M.; Chiesi, M.; Carafoli, E. Nature and site of phospholamban regulation of the Ca2+ pump of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1989, 342, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colyer, J. Phosphorylation states of phospholamban. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 853, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aickin, C.C.; Brading, A.F. Measurement of intracellular chloride in guinea-pig vas deferens by ion analysis, 36chloride efflux and micro-electrodes. J. Physiol. 1982, 326, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Imaizumi, Y.; Muraki, K.; Takeda, M.; Watanabe, M. Measurement and simulation of non-inactivating Ca current in smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 1989, 256 Pt 1, C880–C885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kume, H.; Kotlikoff, M.I. Muscarinic inhibition of single KCa channels in smooth muscle cells by a pertussis-sensitive G protein. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 1991, 261 Pt 1, C1204–C1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kume, H.; Graziano, M.P.; Kotlikoff, M.I. Stimulatory and inhibitory regulation of calcium-activated potassium channels by guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 11051–11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, X.B.; Wulfsen, I.; Lutz, S.; Utku, E.; Sausbier, U.; Ruth, P.; Wieland, T.; Korth, M. M2 muscarinic receptors induce airway smooth muscle activation via a dual, Gbetagamma-mediated inhibition of large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 21036–21044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brueggemann, L.I.; Kakad, P.P.; Love, R.B.; Solway, J.; Dowell, M.L.; Cribbs, L.L.; Byron, K.L. Kv7 potassium channels in airway smooth muscle cells: Signal transduction intermediates and pharmacological targets for bronchodilator therapy. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2012, 302, L120–L132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brueggemann, L.I.; Haick, J.M.; Neuburg, S.; Tate, S.; Randhawa, D.; Cribbs, L.L.; Byron, K.L. KCNQ (Kv7) potassium channel activators as bronchodilators: Combination with a beta2-adrenergic agonist enhances relaxation of rat airways. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L476–L486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, F.; Gamper, N.; Gao, H. Kv7 Channels and Excitability Disorders. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2021, 267, 185–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Horst, J.; Greenwood, I.A.; Jepps, T.A. Cyclic AMP-Dependent Regulation of Kv7 Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Song, T.; Zheng, Y.M.; Vincent, P.A.; Cai, D.; Rosenberg, P.; Wang, Y.X. Canonical transient receptor potential 3 channels activate NF-κB to mediate allergic airway disease via PKC-α/IκB-α and calcineurin/IκB-β pathways. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Billington, C.K.; Penn, R.B.; Hall, I.P. β2 Agonists. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017, 237, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pera, T.; Penn, R.B. Crosstalk between beta-2-adrenoceptor and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in the airway. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2014, 16, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.B.; Fryer, A.D.; Hirshman, C.A. M2 muscarinic receptors inhibit isoproterenol-induced relaxation of canine airway smooth muscle. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1992, 262, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, N.; Eglen, R.M. Effects of muscarinic M2 and M3 receptor stimulation and antagonism on responses to isoprenaline of guinea-pig trachea in vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 112, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, C.M.; Arjona, N.C.; Grunstein, M.M. Role of muscarinic M2 receptors in regulating beta-adrenergic responsiveness in maturing rabbit airway smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 1995, 269 Pt 1, L783–L790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarria, B.; Naline, E.; Zhang, Y.; Cortijo, J.; Molimard, M.; Moreau, J.; Therond, P.; Advenier, C.; Morcillo, E.J. Muscarinic M2 receptors in acetylcholine-isoproterenol functional antagonism in human isolated bronchus. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2002, 283, L1125–L1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.M.; Koarai, A.; Sturton, R.G.; Nicholson, A.G.; Barnes, P.J.; Donnelly, L.E. A role for M(2) and M(3) muscarinic receptors in the contraction of rat and human small airways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 702, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torphy, T.J.; Rinard, G.A.; Rietow, M.G.; Mayer, S.E. Functional antagonism in canine tracheal smooth muscle: Inhibition by methacholine of the mechanical and biochemical responses to isoproterenol. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1983, 227, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torphy, T.J.; Zheng, C.; Peterson, S.M.; Fiscus, R.R.; Rinard, G.A.; Mayer, S.E. Inhibitory effect of methacholine on drug-induced relaxation, cyclic AMP accumulation, and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activation in canine tracheal smooth muscle. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1985, 233, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panettieri, R.A., Jr. Bronchodilators, receptors and cross-talk: Together is better? Postgrad. Med. 2015, 127, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkawadri, T.; Wong, P.Y.; Fong, Z.; Lundy, F.T.; McGarvey, L.P.; Hollywood, M.A.; Thornbury, K.D.; Sergeant, G.P. M2 Muscarinic Receptor-Dependent Contractions of Airway Smooth Muscle are Inhibited by Activation of β-Adrenoceptors. Function 2022, 3, zqac050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whicker, S.D.; Compton, M.R.; Seale, J.P.; Black, J.L. Effect of sensitization and aerosol antigen challenge in guinea-pigs: Studies of airway receptor function and characteristics. Pulm. Pharmacol. 1990, 3, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, E.-B.; Mak, J.C.W.; Belvisi, M.G.; Nishikawa, M.; Rousell, J.; Barnes, P.J. Muscarinic and adrenergic receptor expression in peripheral lung from normal and asthmatic patients. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 1996, 270, L947–L953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donfack, J.; Kogut, P.; Forsythe, S.; Solway, J.; Ober, C. Sequence variation in the promoter region of the cholinergic receptor muscarinic 3 gene and asthma and atopy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakonarson, H.; Herrick, D.J.; Grunstein, M.M. Mechanism of impaired beta-adrenoceptor responsiveness in atopic sensitized airway smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 1995, 269 Pt 1, L645–L652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, Y.; Sakai, H.; Misawa, M. Possible involvement of G(i3) protein in augmented contraction of bronchial smooth muscle from antigen-induced airway hyperresponsive rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2001, 61, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J.; Chung, K.F.; Page, C.P. Inflammatory mediators and asthma. Pharmacol. Rev. 1988, 40, 49–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broide, D.H.; Lotz, M.; Cuomo, A.J.; Coburn, D.A.; Federman, E.C.; Wasserman, S.I. Cytokines in symptomatic asthma airways. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1992, 89, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kips, J.C.; Tavernier, J.; Pauwels, R.A. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) causes bronchial hyperresponsiveness in rats. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1992, 145, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borish, L.; Joseph, B.Z. Inflammation and the allergic response. Med. Clin. North Am. 1992, 76, 765–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, A.S. The role of cytokines in asthma. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1991, 629, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakonarson, H.; Herrick, D.J.; Serrano, P.G.; Grunstein, M.M. Mechanism of cytokine-induced modulation of beta-adrenoceptor responsiveness in airway smooth muscle. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 2593–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Baines, K.J.; Liu, G.; Hsu, A.C.-Y.; Wang, F.; Chen, Z.; et al. Activated non-neuronal cholinergic system correlates with non-type 2 inflammation and exacerbations in severe asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024, 133, 64–72.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, D. Current and novel bronchodilators in respiratory disease. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2014, 20, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghosh, S.; Alkawadri, T.; Hollywood, M.A.; Thornbury, K.D.; Sergeant, G.P. Unravelling the Role of Post-Junctional M2 Muscarinic Receptors in Cholinergic Nerve-Mediated Contractions of Airway Smooth Muscle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125455
Ghosh S, Alkawadri T, Hollywood MA, Thornbury KD, Sergeant GP. Unravelling the Role of Post-Junctional M2 Muscarinic Receptors in Cholinergic Nerve-Mediated Contractions of Airway Smooth Muscle. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125455
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhosh, Srijit, Tuleen Alkawadri, Mark A. Hollywood, Keith D. Thornbury, and Gerard P. Sergeant. 2025. "Unravelling the Role of Post-Junctional M2 Muscarinic Receptors in Cholinergic Nerve-Mediated Contractions of Airway Smooth Muscle" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125455
APA StyleGhosh, S., Alkawadri, T., Hollywood, M. A., Thornbury, K. D., & Sergeant, G. P. (2025). Unravelling the Role of Post-Junctional M2 Muscarinic Receptors in Cholinergic Nerve-Mediated Contractions of Airway Smooth Muscle. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125455





