Non-Canonical Functions of Adenosine Receptors: Emerging Roles in Metabolism, Immunometabolism, and Epigenetic Regulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
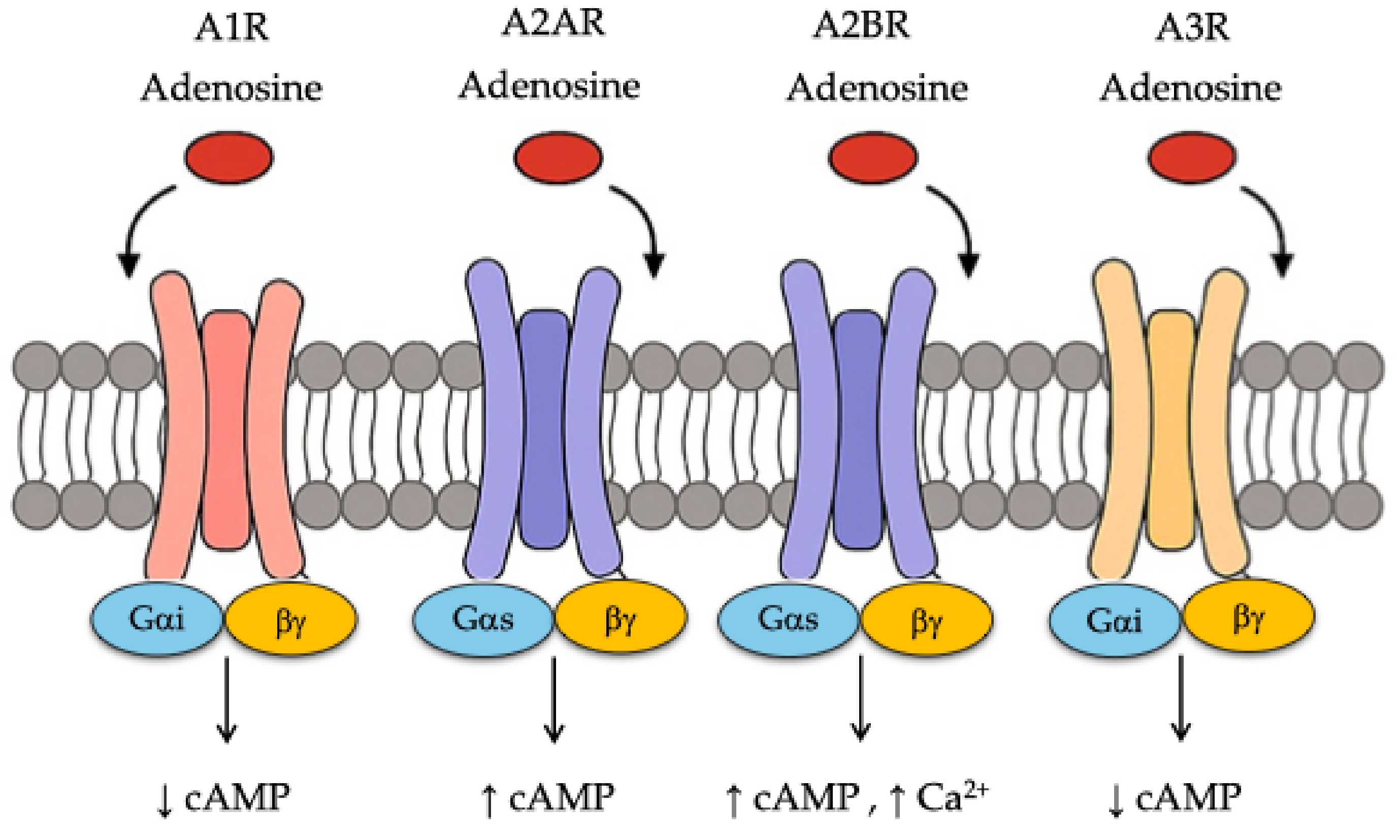
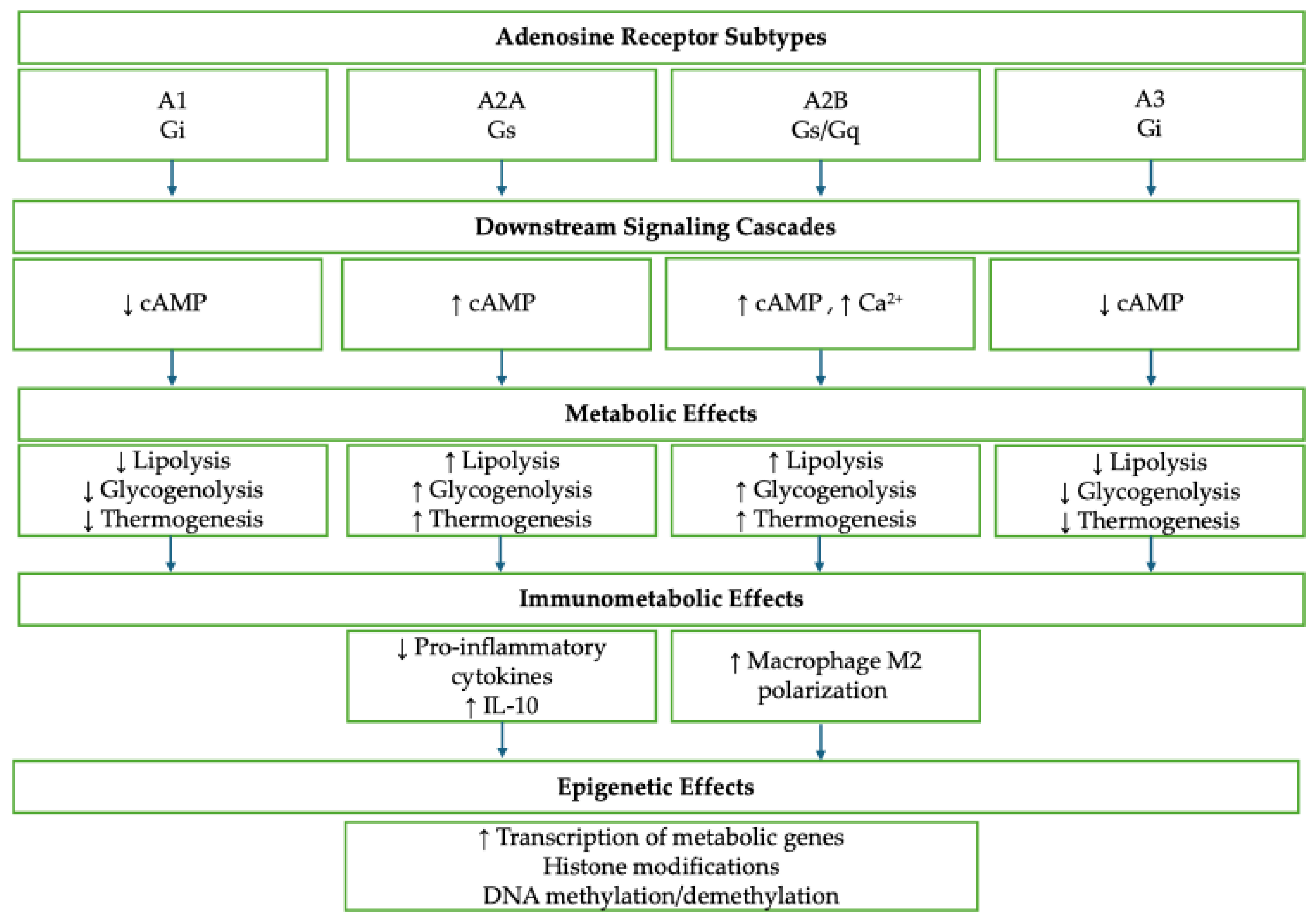
2. Adenosine Receptors and Metabolic Regulation
| Receptor | Tissue(s) | Signaling Pathways | Metabolic Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1R | Adipose, Liver | ↓ cAMP (via Gi), Leptin signaling | ↓ Lipolysis ↓ Gluconeogenesis ↑ Leptin secretion ↓ ATP production | [16,17] |
| A2AR | Heart, Muscle, Immune Cells | AMPK, PI3K-Akt, PGC-1α, NRF1/2 | ↑ FA oxidation ↑ Mitochondrial biogenesis ↑ Adiponectin Protection from ROS injury | [16,21,23,24] |
| A2BR | Liver, Muscle, Adipose | AMPK, PI3K-Akt, PGC-1α, UCP1 | ↑ Glycolysis ↑ Insulin sensitivity ↑ Beige adipocytes ↑ Energy expenditure | [15,20,23] |
| Combined | Systemic | Various | Integration of stress signals Metabolic adaptation Potential therapeutic targets | [16,26] |
3. Immunometabolic Functions of Adenosine Receptors
| Process/Component | Description/Effect | References |
|---|---|---|
| Adenosine production pathway | ATP → AMP (via CD39) → Adenosine (via CD73); both enzymes upregulated in hypoxic tumors | [11] |
| Hypoxia and inflammation | Induce HIF-1α expression → upregulation of CD73 → increased extracellular adenosine | [11,29] |
| Adenosine concentration | >100 µM in solid tumors; correlates with immunosuppression | [30] |
| A2AR (adenosine A2A receptor) | Expressed on CD8+ T cells, Tregs, NK cells; suppresses IFN-γ, granzyme B, perforin; enhances FOXP3 | [31] |
| A2BR (adenosine A2B receptor) | Expressed on macrophages and dendritic cells; promotes IL-10, TGF-β; inhibits antigen presentation | [32] |
| Tregs (regulatory T cells) | A2AR activation enhances suppressive capacity and FOXP3 expression | [33] |
| Macrophage polarization | Adenosine promotes M2 phenotype (pro-tumor) and inhibits M1 phenotype (proinflammatory) | [34] |
| Dendritic cells (DCs) | Adenosine impairs maturation and co-stimulatory molecule expression (CD80, CD86) | [35] |
| Therapeutic strategies | -CD39/CD73 inhibitors reduce adenosine production—A2AR/A2BR antagonists (e.g., ciforadenant, AZD4635)—combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors (PD-1, CTLA-4) | [36,37,38,39] |
| Beyond oncology | Adenosine modulates immune responses in chronic infections and autoimmunity (dual pro-/anti-inflammatory role) | [40] |
4. Epigenetic Regulation via Adenosine Signaling
5. Targeting Adenosine Receptors in Cancer Therapy
6. Targeting Adenosine Receptors in Chronic Inflammatory Disorders
7. Challenges and Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fredholm, B.B.; Ijzerman, A.P.; Jacobson, K.A.; Linden, J.; Müller, C.E. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXXI. Nomenclature and Classification of Adenosine Receptors An Update. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskó, G.; Linden, J.; Cronstein, B.; Pacher, P. Adenosine receptors: Therapeutic aspects for inflammatory and immune diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Dong, C.; Hu, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, G. Unlocking the adenosine receptor mechanism of the tumour immune microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1434118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procopio, M.C.; Lauro, R.; Nasso, C.; Carerj, S.; Squadrito, F.; Bitto, A.; Di Bella, G.; Micari, A.; Irrera, N.; Costa, F. Role of Adenosine and Purinergic Receptors in Myocardial Infarction: Focus on Different Signal Transduction Pathways. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholl, J.N.; Weber, A.F.; Dias, C.K.; Lima, V.P.; Grun, L.K.; Zambonin, D.; Anzolin, E.; Dos Santos Dias, W.W.; Kus, W.P.; Barbé-Tuana, F.; et al. Characterization of purinergic signaling in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from lower- and high-grade gliomas. Purinergic. Signal. 2024, 20, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Xu, Y.; Liang, L.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Liu, H. The progress and prospects of targeting the adenosine pathway in cancer immunotherapy. Biomark. Res. 2025, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yan, S.; Cao, K.; Zeng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Q.; Pan, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Adenosine kinase is critical for neointima formation after vascular injury by inducing aberrant DNA hypermethylation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheu, J.W.; Chiu, D.K.; Kwan, K.K.; Yang, C.; Yuen, V.W.; Goh, C.C.; Chui, N.N.; Shen, W.; Law, C.T.; Li, Q.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor orchestrates adenosine metabolism to promote liver cancer development. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, P.; Bar-Yehuda, S.; Synowitz, M.; Powell, J.D.; Klotz, K.N.; Gessi, S.; Borea, P.A. Adenosine receptors and cancer. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2009, 193, 399–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, V.J.; Radhika, A.; Biju, P.G. Adenosine receptor activation promotes macrophage class switching from LPS-induced acute inflammatory M1 to anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype. Immunobiology 2023, 228, 152362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatfield, S.M.; Kjaergaard, J.; Lukashev, D.; Belikoff, B.; Schreiber, T.H.; Sethumadhavan, S.; Abbott, R.; Philbrook, P.; Thayer, M.; Shujia, D.; et al. Systemic oxygenation weakens the hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factor 1α-dependent and extracellular adenosine-mediated tumor protection. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhulai, G.; Oleinik, E.; Shibaev, M.; Ignatev, K. Adenosine-metabolizing enzymes, adenosine kinase and adenosine deaminase, in cancer. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenici, M.R.; Ferrante, A.; Martire, A.; Chiodi, V.; Pepponi, R.; Tebano, M.T.; Popoli, P. Adenosine A2A receptor as potential therapeutic target in neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 147, 104338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.H.; Song, J. Adenosine and adenosine receptors in metabolic imbalance-related neurological issues. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 177, 116996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnad, T.; Scheibler, S.; Von Kügelgen, I.; Scheele, C.; Kilić, A.; Glöde, A.; Hoffmann, L.S.; Reverte-Salisa, L.; Horn, P.; Mutlu, S.; et al. Adenosine activates brown adipose tissue and recruits beige adipocytes via A2A receptors. Nature 2014, 516, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhalla, A.K.; Chisholm, J.W.; Reaven, G.M.; Belardinelli, L. A1 adenosine receptor: Role in diabetes and obesity. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2009, 193, 271–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston-Cox, H.; Koupenova, M.; Yang, D.; Corkey, B.; Gokce, N.; Farb, M.G.; LeBrasseur, N.; Ravid, K. The A2B adenosine receptor modulates glucose homeostasis and obesity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Y.; Li, H.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, J.; Luo, X.; Ma, L.; McDaniel, K.; Zeng, T.; Chen, Y.; Qian, X.; et al. Regulation of adipose tissue inflammation by adenosine 2A receptor in obese mice. J Endocrinol. 2018, 239, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koupenova, M.; Ravid, K. Adenosine, adenosine receptors and their role in glucose homeostasis and lipid metabolism. J. Cell. Physiol. 2013, 228, 1703–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csóka, B.; Selmeczy, Z.; Koscsó, B.; Németh, Z.H.; Pacher, P.; Murray, P.J.; Kepka-Lenhart, D.; Morris, S.M.; Gause, W.C.; Leibovich, S.J.; et al. Adenosine promotes alternative macrophage activation via A2A and A2B receptors. FASEB J. 2011, 26, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahreyni, A.; Avan, A.; Shabani, M.; Ryzhikov, M.; Fiuji, H.; Soleimanpour, S.; Khazaei, M.; Hassanian, S.M. Therapeutic potential of A2 adenosine receptor pharmacological regulators in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, recent progress, and prospective. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 1295–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeOliveira, C.C.; Paiva Caria, C.R.; Ferreira Gotardo, E.M.; Ribeiro, M.L.; Gambero, A. Role of A1 and A2A adenosine receptor agonists in adipose tissue inflammation induced by obesity in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 799, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aymerich, I.; Foufelle, F.; Ferré, P.; Casado, F.J.; Pastor-Anglada, M. Extracellular adenosine activates AMP-dependent protein kinase (AMPK). J. Cell. Sci. 2006, 119, 1612–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.; Corciulo, C.; Solesio, M.E.; Liang, F.; Pavlov, E.V.; Cronstein, B.N. Adenosine A2A receptor (A2AR) stimulation enhances mitochondrial metabolism and mitigates reactive oxygen speciesmediated mitochondrial injury. FASEB J. PubMed. 2020, 34, 5027–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atif, M.; Alsrhani, A.; Naz, F.; Ullah, M.I.; Alameen, A.A.M.; Imran, M.; Ejaz, H. Adenosine A2A receptor as a potential target for improving cancer immunotherapy. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 10677–10687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faas, M.M.; Saez, T.; de Vos, P. Extracellular ATP and adenosine: The yin and yang in immune responses? Mol. Aspects Med. 2020, 74, 100964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. The Immune Regulatory Role of Adenosine in the Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, B.; Allard, D.; Buisseret, L.; Stagg, J. The Adenosine Pathway in Immuno-Oncology. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beavis, P.A.; Milenkovski, N.; Henderson, M.A.; John, L.B.; Allard, B.; Loi, S.; Kershaw, M.H.; Stagg, J.; Darcy, P.K. Adenosine Receptor 2A Blockade Increases the Efficacy of Anti-PD-1 through Enhanced Antitumor T-cell Responses. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayan, D.; Young, A.; Teng, M.W.L.; Smyth, M.J. Targeting Immunosuppressive Adenosine in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 709–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, A.; Ngiow, S.F.; Madore, J.; Reinhardt, J.; Landsberg, J.; Chitsazan, A.; Rautela, J.; Bald, T.; Barkauskas, D.S.; Ahern, E.; et al. Targeting Adenosine in BRAF-Mutant Melanoma Reduces Tumor Growth and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 4684–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, D.; Sinha, D.; Barkauskas, D.; Young, A.; Kalimutho, M.; Stannard, K.; Caramia, F.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Stagg, J.; Khanna, K.K.; et al. Adenosine 2B Receptor Expression on Cancer Cells Promotes Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4372–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaglio, S.; Dwyer, K.M.; Gao, W.; Friedman, D.; Usheva, A.; Erat, A.; Chen, J.F.; Enjyoji, K.; Linden, J.; Oukka, M.; et al. Adenosine generation catalyzed by CD39 and CD73 expressed on regulatory T cells mediates immune suppression. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chu, Y.; Li, Z.; Yu, X.; Huang, Z.; Xu, J.; Zheng, L. Tumor-derived adenosine promotes macrophage proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, R.D.; Lo, Y.C.; Powell, J.D. A2aR antagonists: Next generation checkpoint blockade for cancer immunotherapy. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willingham, S.B.; Ho, P.Y.; Hotson, A.; Hill, C.; Piccione, E.C.; Hsieh, J.; Liu, L.; Buggy, J.J.; McCaffery, I.; Miller, R.A. A2AR Antagonism with CPI-444 Induces Antitumor Responses and Augments Efficacy to Anti-PD-(L)1 and Anti-CTLA-4 in Preclinical Models. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 10, 1136–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.; Ngiow, S.F.; Barkauskas, D.S.; Sult, E.; Hay, C.; Blake, S.J.; Huang, Q.; Liu, J.; Takeda, K.; Teng, M.W.L.; et al. Co-inhibition of CD73 and A2AR Adenosine Signaling Improves Anti-tumor Immune Responses. Cancer Cell. 2016, 30, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, A.; Allard, D.; Allard, B.; Stagg, J. Targeting the adenosine pathway for cancer immunotherapy. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 42, 101304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sek, K.; Mølck, C.; Stewart, G.D.; Kats, L.; Darcy, P.K.; Beavis, P.A. Targeting Adenosine Receptor Signaling in Cancer Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csóka, B.; Haskó, G. Adenosine, inflammation pathways and therapeutic challenges. Jt. Bone. Spine. 2011, 78, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhang, S.; Shao, B. Epigenetic regulation and therapeutic targets in the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Biomed. 2023, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahavi, D.; Hodge, J.W. Targeting immunosuppressive adenosine signaling: A review of potential immunotherapy combination strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remley, V.A.; Linden, J.; Bauer, T.W.; Dimastromatteo, J. Unlocking antitumor immunity with adenosine receptor blockers. Cancer Drug Resist. 2023, 14, 748–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshari, S.; Barrodia, P.; Singh, A.K. Epigenetic Perspective of Immunotherapy for Cancers. Cells 2023, 12, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.C.; Hsu, K.W.; Wu, K.J. Interrogation of the interplay between DNA N6-methyladenosine (6mA) and hypoxia-induced chromatin accessibility by a randomized empirical model (EnrichShuf). Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2024, 52, 13605–13624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Fan, J.; Thompson, L.F.; Zhang, Y.; Shin, T.; Curiel, T.J.; Zhang, B. CD73 has distinct roles in nonhematopoietic and hematopoietic cells to promote tumor growth in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2371–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, R.D.; Sun, I.M.; Oh, M.H.; Sun, I.H.; Wen, J.; Englert, J.; Powell, J.D. Inhibition of the adenosine A2a receptor modulates expression of T cell coinhibitory receptors and improves effector function for enhanced checkpoint blockade and ACT in murine cancer models. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 67, 1271–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Ding, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Sun, T.; Wei, M.; Wang, X.; Wu, H. The Relationship Between the Network of Non-coding RNAs-Molecular Targets and N6-Methyladenosine Modification in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 772542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, E.; Zhu, Z.; Wahed, S.; Qu, Z.; Storkus, W.J.; Guo, Z.S. Epigenetic modulation of antitumor immunity for improved cancer immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orillion, A.; Hashimoto, A.; Damayanti, N.; Shen, L.; Adelaiye-Ogala, R.; Arisa, S.; Chintala, S.; Ordentlich, P.; Kao, C.; Elzey, B.; et al. Entinostat Neutralizes Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Enhances the Antitumor Effect of PD-1 Inhibition in Murine Models of Lung and Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5187–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, L.; Hotson, A.; Powderly, J.D.; Sznol, M.; Heist, R.S.; Choueiri, T.K.; George, S.; Hughes, B.G.M.; Hellmann, M.D.; Shepard, D.R.; et al. Adenosine 2A Receptor Blockade as an Immunotherapy for Treatment-Refractory Renal Cell Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, C.; Patel, J.S.; Liang, S.H. Development of CD73 Inhibitors in Tumor Immunotherapy and Opportunities in Imaging and Combination Therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 68, 6860–6869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beavis, P.A.; Stagg, J.; Darcy, P.K.; Smyth, M.J. CD73: A potent suppressor of antitumor immune responses. Trends Immunol. 2012, 33, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.V.; Suman, S.; Goruganthu, M.U.L.; Tchekneva, E.E.; Guan, S.; Arasada, R.R.; Antonucci, A.; Piao, L.; Ilgisonis, I.; Bobko, A.A.; et al. Improving combination therapies: Targeting A2B-adenosine receptor to modulate metabolic tumor microenvironment and immunosuppression. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2023, 115, 1404–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Azuma, K.; Kawahara, A.; Kinoshita, T.; Matsuo, N.; Naito, Y.; Tokito, T.; Yamada, K.; Akiba, J.; Hoshino, T. Predictive value of CD73 expression for the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in NSCLC. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonioli, L.; Yegutkin, G.G.; Pacher, P.; Blandizzi, C.; Haskó, G. Anti-CD73 in cancer immunotherapy: Awakening new opportunities. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.A.; Bendell, J.C.; Falchook, G.S.; Bauer, T.M.; Drake, C.G.; Choe, J.H.; George, D.J.; Karlix, J.L.; Ulahannan, S.; Sachsenmeier, K.F.; et al. Phase Ia/b, Open-Label, Multicenter Study of AZD4635 (an Adenosine A2A Receptor Antagonist) as Monotherapy or Combined with Durvalumab, in Patients with Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 4871–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turiello, R.; Pinto, A.; Morello, S. CD73: A Promising Biomarker in Cancer Patients. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 609931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varani, K.; Padovan, M.; Govoni, M.; Vincenzi, F.; Trotta, F.; Borea, P.A. The role of adenosine receptors in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2010, 10, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronstein, B.N.; Naime, D.; Ostad, E. The antiinflammatory mechanism of methotrexate. Increased adenosine release at inflamed sites diminishes leukocyte accumulation in an in vivo model of inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 92, 2675–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Colucci, R.; Ghisu, N.; Blandizzi, C.; Del Tacca, M. A2a receptors mediate inhibitory effects of adenosine on colonic motility in the presence of experimental colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2006, 12, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madi, L.; Ochaion, A.; Rath-Wolfson, L.; Bar-Yehuda, S.; Erlanger, A.; Ohana, G.; Harish, A.; Merimski, O.; Barer, F.; Fishman, P. The A3 adenosine receptor is highly expressed in tumor versus normal cells: Potential target for tumor growth inhibition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 4472–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aherne, C.M.; Saeedi, B.; Collins, C.B.; Masterson, J.C.; McNamee, E.N.; Perrenoud, L.; Rapp, C.R.; Curtis, V.F.; Bayless, A.; Fletcher, A.; et al. Epithelial-specific A2B adenosine receptor signaling protects the colonic epithelial barrier during acute colitis. Mucosal. Immunol. 2015, 8, 1324–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolachala, V.; Ruble, B.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Wang, L.; Mwangi, S.; Figler, H.E.; Figler, R.A.; Srinivasan, S.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Linden, J.; et al. Blockade of adenosine A2B receptors ameliorates murine colitis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 155, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondi, C.O.; Rodriguez, G.; Gould, G.G.; Frazer, A.; Morilak, D.A. Chronic unpredictable stress induces a cognitive deficit and anxiety-like behavior in rats that is prevented by chronic antidepressant drug treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Schneider, D.J.; Blackburn, M.R. Adenosine signaling and the regulation of chronic lung disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 123, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouma, M.G.; van den Wildenberg, F.A.; Buurman, W.A. The anti-inflammatory potential of adenosine in ischemia-reperfusion injury: Established and putative beneficial actions of a retaliatory metabolite. Shock 1997, 8, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, C.; Ding, A. Nonresolving inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laubach, V.E.; French, B.A.; Okusa, M.D. Targeting of adenosine receptors in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2011, 15, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, M.; Akerman, L.; Ziv, M.; Kadurina, M.; Gospodinov, D.; Pavlotsky, F.; Yankova, R.; Kouzeva, V.; Ramon, M.; Silverman, M.H.; et al. Treatment of plaque-type psoriasis with oral CF101: Data from an exploratory randomized phase 2 clinical trial. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 26, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-X. Role of A2B adenosine receptor signaling in adenosine-dependent pulmonary inflammation and injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2173–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cekic, C.; Linden, J. Adenosine A2A receptors intrinsically regulate CD8+ T cells in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7239–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, R.S.; Liew, F.Y.; Talbot, J.; Carregaro, V.; Oliveira, R.D.; Almeida, S.L.; França, R.F.O.; Donate, P.B.; Pinto, L.G.; Ferreira, F.I.S.; et al. Low expression of CD39 on regulatory T cells as a biomarker for resistance to methotrexate therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2509–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cekic, C.; Linden, J. Purinergic regulation of the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, K.N. Adenosine receptors and their ligands. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2000, 362, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredholm, B.B. Adenosine receptors as drug targets. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 1284–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.E.; Jacobson, K.A. Recent developments in adenosine receptor ligands and their potential as novel drugs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2011, 1808, 1290–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, B.; Longhi MSRobson, S.C.; Stagg, J. The ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73: Novel checkpoint inhibitor targets. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 276, 121–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacParland, S.A.; Liu, J.C.; Ma, X.Z.; Innes, B.T.; Bartczak, A.M.; Gage, B.K.; Manuel, J.; Khuu, N.; Echeverri, J.; Linares, I.; et al. Single cell RNA sequencing of human liver reveals distinct intrahepatic macrophage populations. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, P.; Ramkhelawon, B.; Cronstein, B.N. Adenosine metabolism and receptors in aging of the skin, musculoskeletal, immune and cardiovascular systems. Ageing Res. Rev. 2025, 106, 102695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, S.R.; Herring, S.E.; Tchalla, E.Y.I.; Lenhard, A.P.; Bhalla, M.; Bou Ghanem, E.N. Activating A1 adenosine receptor signaling boosts early pulmonary neutrophil recruitment in aged mice in response to Streptococcus pneumoniae infection. Immun. Ageing 2024, 21, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laflamme, C.; Mailhot, G.B.; Pouliot, M. Age-related decline of the acute local inflammation response: A mitigating role for the adenosine A2A receptor. Aging 2017, 9, 2083–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahan Yossef, Y.; Sela Peremen, L.; Telerman, A.; Goldinger, G.; Malitsky, S.; Itkin, M.; Halperin, R.; Peshes Yaloz, N.; Tirosh, A. Single-cell transcriptomics and metabolomic analysis reveal adenosine-derived metabolites over-representation in pseudohypoxic neuroendocrine tumours. Clin. Transl. Med. 2025, 15, e70159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Hong, Y.; Tong, Z.; He, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Song, P.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; et al. Activation of hepatic adenosine A1 receptor ameliorates MASH via inhibiting SREBPs maturation. Cell. Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Pour, N.G.; Tiruvadi-Krishnan, S.; Ray, A.P.; Thakur, N.; Eddy, M.T.; Lamichhane, R. Single-molecule visualization of human A2A adenosine receptor activation by a G protein and constitutively activating mutations. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, N.; Zhang, K.; Chen, X.; Liu, K.; Wang, J.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, W.; Ma, P.; Xu, P.; Cheng, C.; et al. ADORA2A-driven proline synthesis triggers epigenetic reprogramming in neuroendocrine prostate and lung cancers. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e168670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Epigenetic Mechanism | Effects in the Tumor Microenvironment (TME) | Impacted Cell Types/Functions | Therapeutic Implications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA methylation | Silencing of tumor suppressor genes; upregulation of immune checkpoints (e.g., PD-L1, CTLA-4); inhibition of antigen presentation | Tumor cells; cytotoxic T cells (via impaired recognition) | DNMT inhibitors restore gene expression and immunogenicity | [44] |
| Histone modifications | Altered chromatin structure; regulation of immune-related genes; stabilization of Treg phenotype | Tregs; tumor cells | HDAC inhibitors used to reverse suppressive histone marks | [45,46] |
| Chromatin remodeling | Affects accessibility of immune genes and checkpoint molecules; supports tumor-promoting transcriptional programs | TAMs, MDSCs, tumor cells | Targeting specific remodeling enzymes (e.g., EZH2) in clinical testing | [47] |
| Non-coding RNAs | Post-transcriptional regulation of immune modulators and oncogenes | Multiple immune cells and tumor cells | miRNA and lncRNA-based therapies under investigation | [48] |
| Hypoxia-induced epigenetic changes | HIFs regulate epigenetic enzymes → promote angiogenesis, immune suppression, metabolic reprogramming | Tumor cells, immune cells | Indirect targeting via hypoxia modulation and HIF pathway inhibitors | [8] |
| Effect on immune cells | -TAMs/MDSCs: epigenetically driven immunosuppressive phenotypes; Tregs: epigenetically stabilized suppressive function | TAMs, MDSCs, Tregs | Modulation of epigenetic pathways may reprogram immune cells | [42,43] |
| Checkpoint regulation | Epigenetic upregulation of PD-L1, CTLA-4 blocks T cell-mediated killing | Tumor cells, T cells | Combos with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 or CTLA-4 + epigenetic drugs | [27,44] |
| Clinical strategies | Use of DNMT and HDAC inhibitors to enhance tumor immunogenicity; combination with ICI therapies showing synergistic effects | Tumor and immune compartments | Clinical trials testing DNMTi/HDACi + checkpoint inhibitors | [49] |
| Emerging targets | EZH2, BET proteins, and others being explored for immunomodulatory roles | Tumor cells, TME components | Potential to overcome resistance to immunotherapy | [27,47] |
| Disease | Organ/Tissue/ Cells Affected | AR Involved | Signaling Pathway/ Effect | Drug/Intervention | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obesity/Insulin Resistance | Adipose tissue, hepatocytes | A1R | ↓ cAMP → ↓ lipolysis, ↓ gluconeogenesis; ↑ leptin secretion | N^6-cyclopentyladenosine (CPA), GR79236 | [16] |
| Type 2 Diabetes | Liver, skeletal muscle | A2BR | ↑ AMPK, ↑ PI3K/Akt → ↑ glycolysis, ↑ insulin sensitivity | BAY 60-6583 | [20,26] |
| Metabolic Syndrome | Adipocytes | A2AR, A2BR | ↑ Adiponectin secretion; ↑ PGC-1α/UCP1 → beige adipocyte formation | CGS21680, BAY 60-6583 | [15,16] |
| Cardiac/Skeletal Myopathy | Cardiomyocytes, muscle fibers | A2AR | ↑ Mitochondrial biogenesis, ↑ fatty acid oxidation via PGC-1α, NRF1/2 | CGS21680, ATL146e | [21,23] |
| Osteoarthritis/Cartilage Damage | Chondrocytes | A2AR | ↑ Mitochondrial metabolism; ↓ ROS-mediated mitochondrial injury | CGS21680, ATL313 | [24] |
| Cancer (Solid Tumors) | TME, CD8+ T cells, Tregs, NK cells, macrophages | A2AR, A2BR | ↑ FOXP3, ↓ IFN-γ, ↓ granzyme B, ↑ IL-10/TGF-β, ↑ M2 macrophages | Ciforadenant (CPI-444), AZD4635, Oleclumab (MEDI9447), AB928 | [28,39,47,49] |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) | Synovium, monocytes, T cells, fibroblasts | A2AR, A3R | ↓ TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β; ↑ IL-10; modulates PI3K/Akt, NF-κB | Methotrexate, CGS21680, IB-MECA (CF101) | [59] |
| Psoriasis | Skin, keratinocytes, Th17 cells | A2AR, A3R | ↓ IL-17A, IL-22; ↓ keratinocyte proliferation; ↓ neutrophil infiltration | Piclidenoson (CF101) | [69,70] |
| IBD (Ulcerative Colitis, Crohn’s) | Gut epithelium, macrophages, stromal cells | A2BR | ↑ Barrier integrity (acute); ↑ IL-6, IL-8, fibrosis (chronic) | PSB603, CVT-6883 | [63,65,68] |
| COPD/Asthma | Airway epithelium, fibroblasts, mast cells | A2BR | ↑ TGF-β, collagen; airway remodeling, neutrophil recruitment | GS-6201, CVT-6883 | [66,71] |
| Liver Fibrosis/Inflammation | Hepatic stellate cells, fibroblasts | A2AR, A2BR | ↑ Pro-fibrotic cytokines; ↑ collagen synthesis | AB928 (etrumadenant) | [72,73] |
| Autoimmunity (SLE, MS) | Tregs, Th cells, myeloid cells | A2AR, A3R | ↑ FOXP3 expression; ↓ effector T cell activation | Piclidenoson (CF101), Namodenoson (CF102) | [58,62] |
| Chronic Infections | T cells, macrophages | A2AR, A2BR | Promotes T cell exhaustion, pathogen persistence | Ciforadenant, AZD4635 | [40] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pallio, G.; Mannino, F. Non-Canonical Functions of Adenosine Receptors: Emerging Roles in Metabolism, Immunometabolism, and Epigenetic Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157241
Pallio G, Mannino F. Non-Canonical Functions of Adenosine Receptors: Emerging Roles in Metabolism, Immunometabolism, and Epigenetic Regulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157241
Chicago/Turabian StylePallio, Giovanni, and Federica Mannino. 2025. "Non-Canonical Functions of Adenosine Receptors: Emerging Roles in Metabolism, Immunometabolism, and Epigenetic Regulation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157241
APA StylePallio, G., & Mannino, F. (2025). Non-Canonical Functions of Adenosine Receptors: Emerging Roles in Metabolism, Immunometabolism, and Epigenetic Regulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157241







