Interleukin Dynamics and Their Correlation with Tumor Aggressiveness in Colorectal Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Demographic Analysis
2.2. Descriptive Analysis of Interleukin Concentration
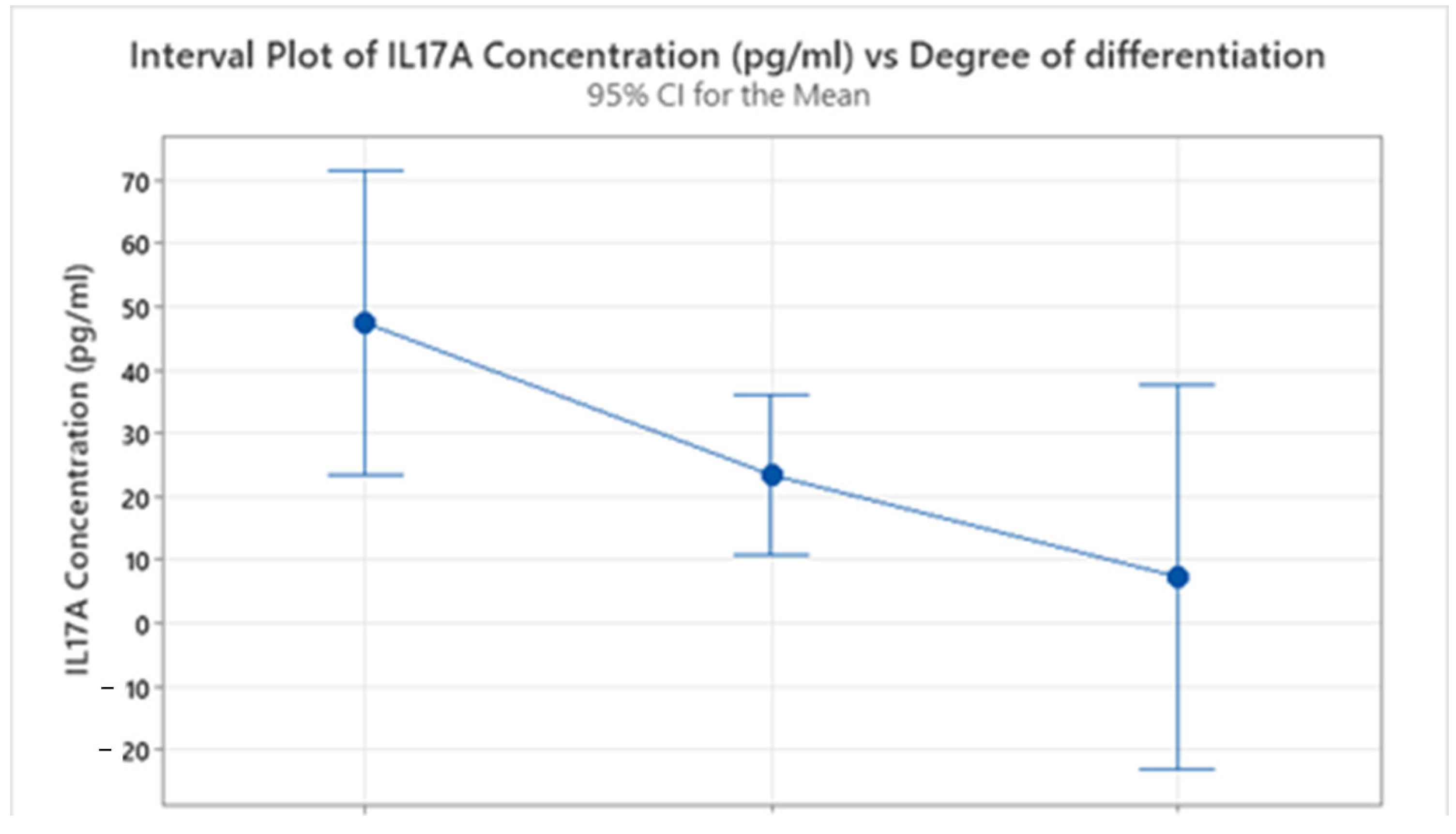
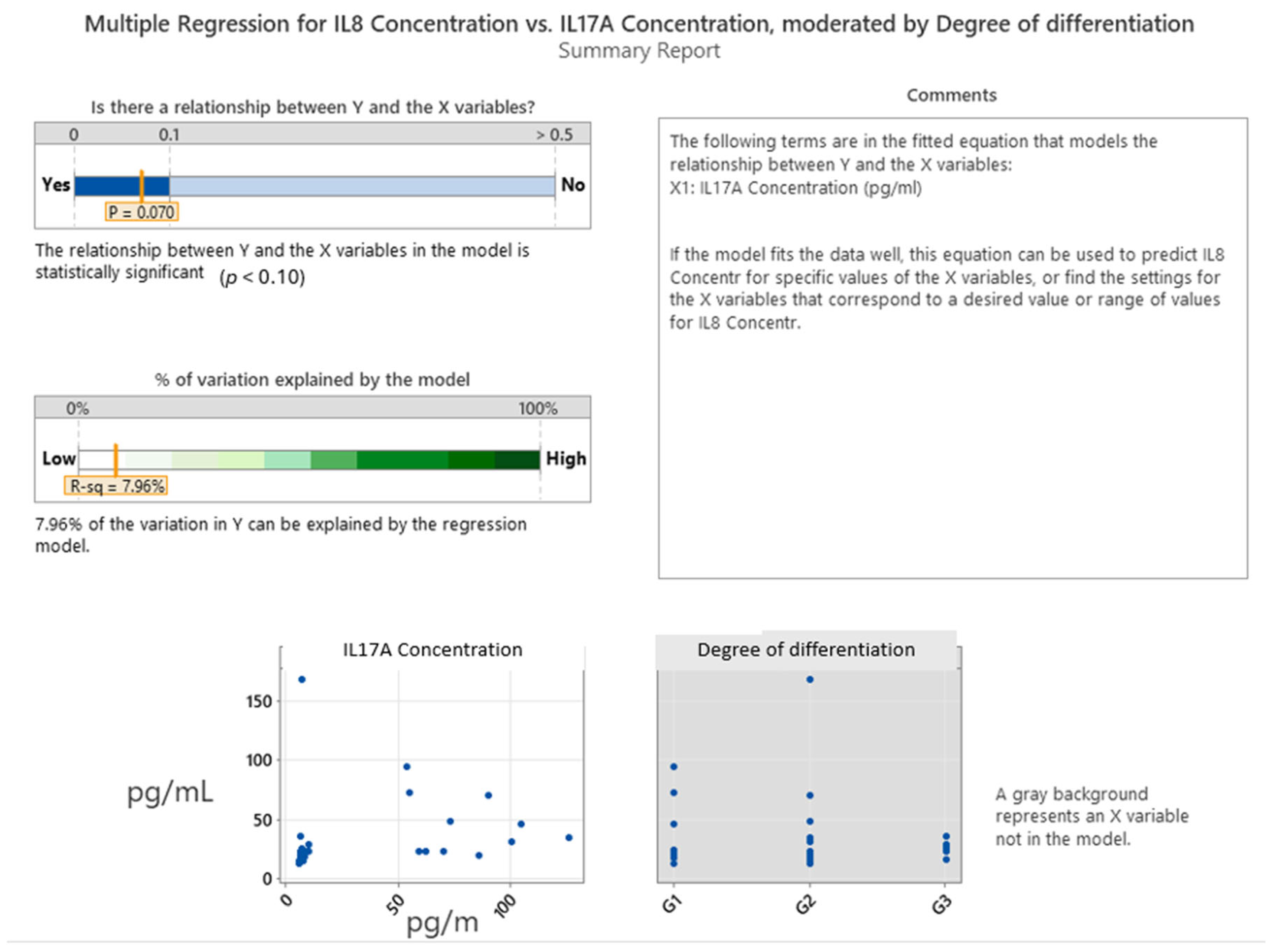
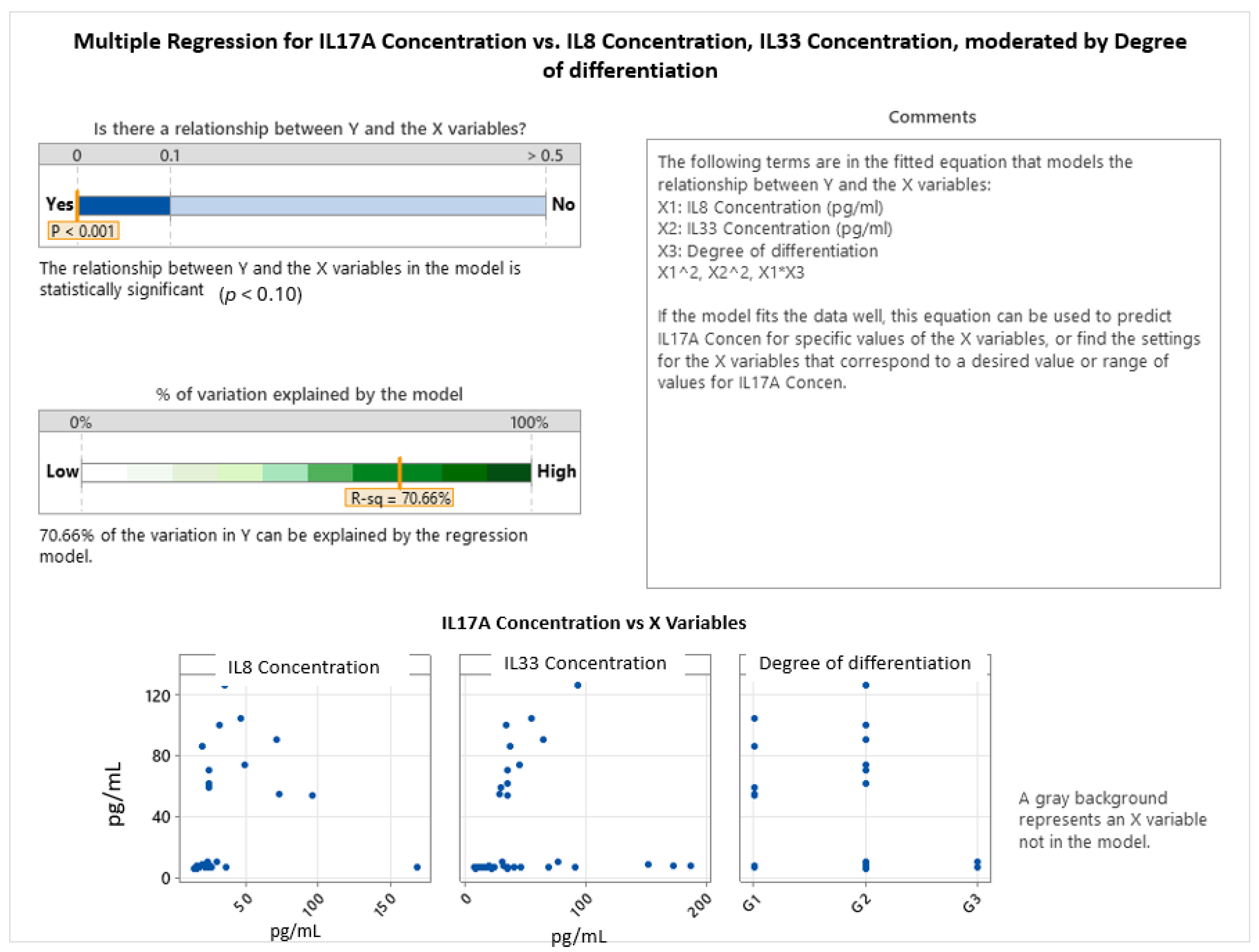
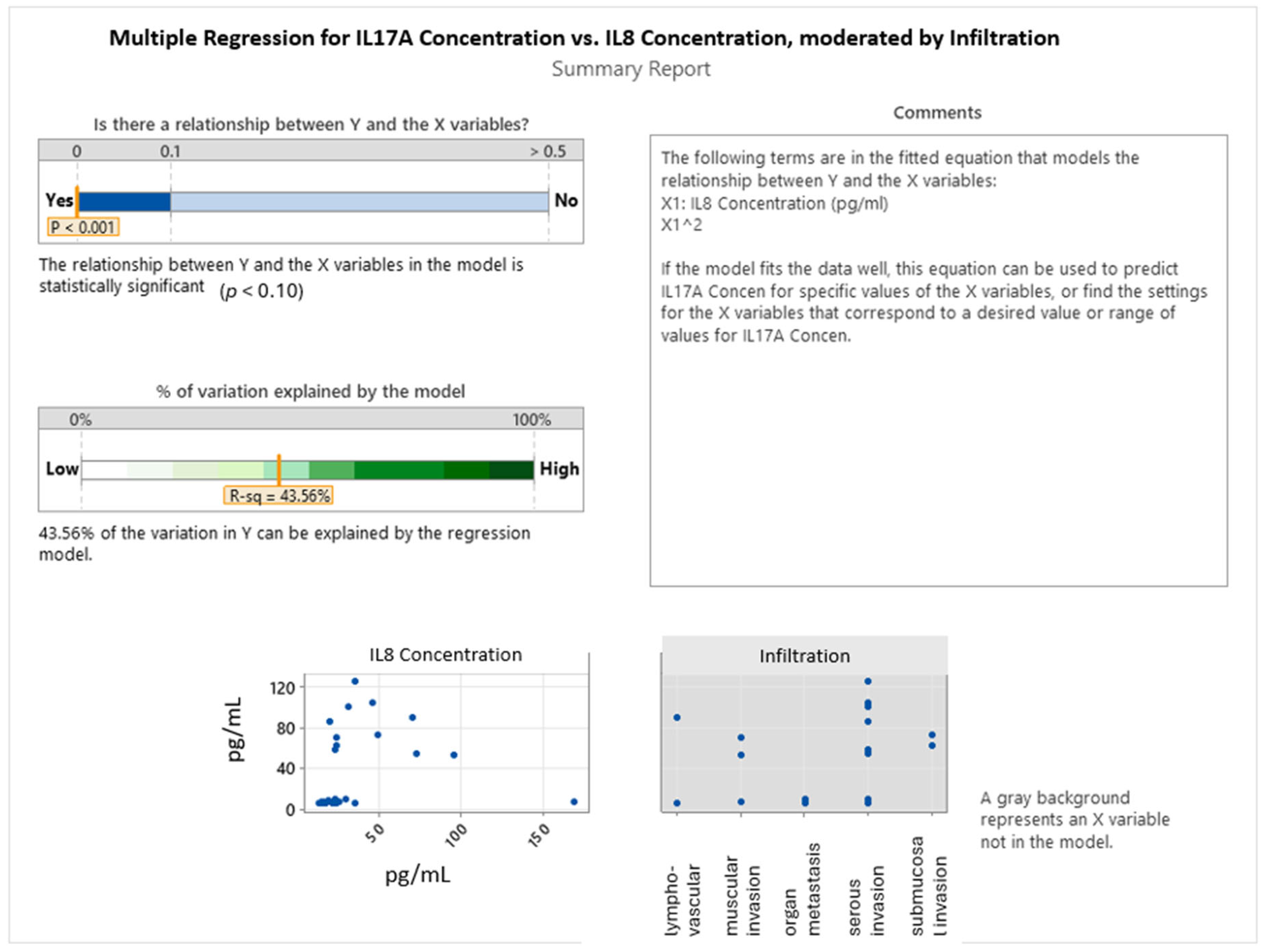
2.3. Interleukin Correlations in Colon Cancer Grading and Invasion
- Degree of differentiation: G1
- Degree of differentiation: G2
- Degree of differentiation: G3
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Blood Sample Collection
4.3. ELISA Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Study Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thuraisingam, R.; Jandova, J.; Pandit, V.; Michailidou, M.; Nfonsam, V.N. Assessing the National Trends in Colon Cancer among Native Americans: A 12 Year SEER Database Study. Am. J. Surg. 2017, 214, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, M. US Colon Cancer Rate Dropped 30% among over 50s in Past Decade. BMJ 2014, 348, g2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.; Acuna-Villaorduna, A.; Goel, S. Incidence Patterns of Early Onset Colon Cancer by Race and Stage in the US. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, e18168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saika, K.; Machii, R. Subsite Distribution of Colon Cancer from Cancer Incidence in Five Continents Vol. X. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 46, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mitry, E.; Rachet, B.; Quinn, M.J.; Cooper, N.; Coleman, M.P. Survival from Cancer of the Colon in England and Wales up to 2001. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 99, S26–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, M.; Singh, K.; Verma, N. Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases Biomarkers. Int. J. Biomed. Adv. Res. 2012, 3, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Leyte, D.J.; Zepeda-García, O.; Domínguez-Pérez, M.; González-Garrido, A.; Villarreal-Molina, T.; Jacobo-Albavera, L. Endothelial Dysfunction, Inflammation and Coronary Artery Disease: Potential Biomarkers and Promising Therapeutical Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normanno, N.; Apostolidis, K.; de Lorenzo, F.; Beer, P.A.; Henderson, R.; Sullivan, R.; Biankin, A.V.; Horgan, D.; Lawler, M. Cancer Biomarkers in the Era of Precision Oncology: Addressing the Needs of Patients and Health Systems. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 84, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farc, O.; Budisan, L.; Zaharie, F.; Țăulean, R.; Vălean, D.; Talvan, E.; Neagoe, I.B.; Zănoagă, O.; Braicu, C.; Cristea, V. Expression and Functional Analysis of Immuno-Micro-RNAs Mir-146a and Mir-326 in Colorectal Cancer. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 7065–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tâlvan, E.-T.; Mohor, C.I.; Chisnoiu, D.; Făgețan, I.M.; Tâlvan, C.-D.; Cristea, V.; Câmpian, R.S. Correlation of Chronic Periodontitis Progression with sTREM-1 and E-Cadherin Salivary Levels. Rev. Romana Med. Lab. 2018, 26, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tâlvan, C.-D.; Budișan, L.; Tâlvan, E.-T.; Grecu, V.; Zănoagă, O.; Mihalache, C.; Cristea, V.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Mohor, C.I. Serum Interleukins 8, 17, and 33 as Potential Biomarkers of Colon Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulubova, M.; Chonov, D.; Aleksandrova, E.; Ivanova, K.; Ignatova, M.M.; Vlaykova, T. Interleukin-6-Positive Immune Cells as a Possible New Immunologic Marker Associated with the Colorectal Cancer Prognosis. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. AIMM 2024, 32, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smagina, E.; Polit’ko, D.; Kumeiko, V.; Gurina, L.; Stenkova, A. Correlation Between Interleukin IL-6/IL-6 Receptor Polymorphisms (IL6–174C>G and IL6R 1073A>C) and RAS/BRAF Mutations in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterol. Insights 2025, 16, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banday, M.Z.; Sameer, A.S.; Chowdri, N.A.; Haq, E. Interleukin-10 -592C/A, but Not -1082A/G Promoter Single Nucleotide Polymorphism, Is Associated with a Decreased Risk of Colorectal Cancer in an Ethnic Kashmiri Population: A Case-Control Study. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 26, 476–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omrane, I.; Marrakchi, R.; Baroudi, O.; Mezlini, A.; Ayari, H.; Medimegh, I.; Stambouli, N.; Kourda, N.; Bouzaienne, H.; Uhrhammer, N.; et al. Significant Association between Interleukin-17A Polymorphism and Colorectal Cancer. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2014, 35, 6627–6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najdaghi, S.; Razi, S.; Rezaei, N. An Overview of the Role of Interleukin-8 in Colorectal Cancer. Cytokine 2020, 135, 155205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Sun, F.; Wang, B.; Liu, S.; Niu, W.; Liu, E.; Peng, C.; Wang, J.; Gao, H.; Liang, B.; et al. Interleukin-8 Promotes Cell Migration through Integrin Avβ6 Upregulation in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014, 354, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conciatori, F.; Bazzichetto, C.; Falcone, I.; Ferretti, G.; Cognetti, F.; Milella, M.; Ciuffreda, L. Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells Properties and Features: Evidence of Interleukin-8 Involvement. Cancer Drug Resist. 2019, 2, 968–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, D.; Wu, P.; Chen, Z.; Li, C.; Huang, J. Prognostic Value, Clinicopathologic Features and Diagnostic Accuracy of Interleukin-8 in Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Jiang, J.-K. The Expression of Interleukin 17 Receptor A Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Colorectal Cancer and Its Knockdown Inhibits Tumor Growth and Modulates Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells in Mice Tumor. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, v197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.-K.; Lin, C.-H.; Chang, T.-A.; Lo, L.-C.; Lin, C.-P.; Lu, R.-H.; Yang, C.-Y. Decreased Interleukin-17RA Expression Is Associated with Good Prognosis in Patients with Colorectal Cancer and Inhibits Tumor Growth and Vascularity in Mice. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Na, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, T. Targeting Interleukin-17 Enhances Tumor Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Colorectal Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, G.; Qiu, Y.; Yu, H.; Kong, Q.; Zhen, B. Interleukin-17 Promotes the Development of Cisplatin Resistance in Colorectal Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Liang, H.; Wu, W. Interleukin-17A mRNA Expression Is Associated with the Prognosis of Patients with Colorectal Cancer: A Pooled Meta-Analysis. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 33, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ji, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, H. IL-33 Promotes the Development of Colorectal Cancer Through Inducing Tumor-Infiltrating ST2L+ Regulatory T Cells in Mice. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1533033818780091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Yuan, A.; Pang, Z.; Zheng, W.; Li, Z.; Goll, R. Contribution of IL-33 to the Pathogenesis of Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Gong, Z.; Meng, J.; Liu, H.; Gao, J. Relationship between serum soluble interleukin-33 levels and clinical features in patients with colorectal cancer and its diagnostic value. Acta medica mediterranea. 2019, 35, 2081–2085. [Google Scholar]
- Eissmann, M.F.; Dijkstra, C.; Wouters, M.A.; Baloyan, D.; Mouradov, D.; Nguyen, P.M.; Davalos-Salas, M.; Putoczki, T.L.; Sieber, O.M.; Mariadason, J.M.; et al. Interleukin 33 Signaling Restrains Sporadic Colon Cancer in an Interferon-γ-Dependent Manner. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tâlvan, C.-D.; Tâlvan, E.-T.; Mohor, C.I.; Budișan, L.; Grecu, V.; Mihalache, M.; Zănoagă, O.; Chira, S.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Cristea, V.; et al. Exploring miRNA Profiles in Colon Cancer: A Focus on miR101-3p, miR106a-5p, and miR326. Cancers 2024, 16, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tâlvan, C.-D.; Tâlvan, E.-T.; Mohor, C.I.; Budișan, L.; Grecu, V.; Mihalache, M.; Neagoe, I.B.; Zănoagă, O.; Oprinca, G.C.; Cristian, A.N. The Impact of miRNA Expression on Colon Cancer Severity, Invasiveness, and Localization. Cancers 2025, 17, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Fonseca, L.M.; da Luz, M.M.P.; Lacerda-Filho, A.; Cabral, M.M.D.A.; da Silva, R.G. Colorectal Carcinoma in Different Age Groups: A Histopathological Analysis. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2012, 27, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulrazzaq, T.A.; Salayi, J.S. Clinicopathological Comparison of Colorectal Cancer in Young and Old Patients. AMJ Adv. Med. J. 2023, 8, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossola, M.; Sofo, L.; Ratto, C.; Bellantone, R.; Doglietto, G.B.; Crucitti, A.; Crucitti, F. Colorectal Cancer in Patients 40 Years of Age and Younger. Ital. J. Surg. Sci. 1989, 19, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mulyati Sri, R.; Khairunnisa, Z.; Nabil Ibnu, S. Relationship Between Age and Depth of Invasion and Histopathological Features in Colorectal Cancer Patients in the Anatomical Pathology Department of Cut Meutia General Hospital (RSUCM) 2018 - 2021. J. Multidisiplin. Madani 2023, 3, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.M.M.D.; Duarte, R.P.; Leão, C.C.A.; Vissoci, C.M.; Alvarenga, A.L.A.T.; Ramos, A.B.S.; Goulart, A.E.C. Colorectal Cancer in Patients under Age 50: A Five-Year Experience. Rev. Colégio Bras. Cir. 2020, 47, e20202406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessman, O.; Bergkvist, L.; Ström, S. Colorectal Cancer in Patients over 75 Years of Age—Determinants of Outcome. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 1997, 23, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozek, W.; Kriwanek, S.; Bonner, E.; Peterlik, M.; Cross, H.S. Mutual Associations between Malignancy, Age, Gender, and Subsite Incidence of Colorectal Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 3721–3726. [Google Scholar]
- Ram, E.; Zbar, A.; Bachar, G.; Krissi, H.; Joubran, S.; Rath-Wolfson, L. Gender Differences in Colorectal Cancer Presentation and Outcome at a Single Israeli Institution: 1989–2002. Acta Chir. Iugosl. 2013, 60, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-J.; Huang, S.-C.; Lin, H.-H.; Lin, C.-C.; Lan, Y.-T.; Wang, H.-S.; Yang, S.-H.; Jiang, J.-K.; Chen, W.-S.; Lin, T.-C.; et al. Differences in Gene Mutations According to Gender among Patients with Colorectal Cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 16, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-E.; Paik, H.Y.; Yoon, H.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, N.; Sung, M.-K. Sex- and Gender-Specific Disparities in Colorectal Cancer Risk. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 5167–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; He, J.; Ren, S.; Wu, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F. Gender Differences in Colorectal Cancer Survival: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 1942–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bărbălan, A.; Streața, I.; Ivan, E.T.; Cherciu, I.; Șurlin, V.; Ioana, M.; Săftoiu, A. Interleukin-8 mRNA Expression in Locally Advanced Colorectal Cancer Patients. Curr. Health Sci. J. 2017, 43, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, B.Y.; Yip, W.K.; Dusa, N.; Mohtarrudin, N.; Seow, H.F. Loss of Interleukin-17RA Expression Is Associated with Tumour Progression in Colorectal Carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. POR 2020, 26, 2291–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Qi, H.; Gundersen, M.D.; Yang, H.; Christiansen, I.; Sørbye, S.W.; Goll, R.; Florholmen, J. Dynamics of the IL-33/ST2 Network in the Progression of Human Colorectal Adenoma to Sporadic Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 2015, 64, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terada, H.; Urano, T.; Konno, H. Association of Interleukin-8 and Plasminogen Activator System in the Progression of Colorectal Cancer. Eur. Surg. Res. 2005, 37, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wu, D.; Min, Z.; Quan, Y. Upregulation of interleukin-17F in Colorectal Cancer Promotes Tumor Invasion by Inducing Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Davis, C.; Shah, S.; Hughes, D.; Ryan, J.C.; Altomare, D.; Peña, M.M.O. IL-33 Promotes Growth and Liver Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer in Mice by Remodeling the Tumor Microenvironment and Inducing Angiogenesis. Mol. Carcinog. 2017, 56, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farc, O.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Zaharie, F.; Budisan, L.; Zănoagă, O.; Cristea, V. Characterization of the Immune Response Through Cytokine Profiling and Correlational Analysis in Colorectal Malignant Tumors. Rom. Arch. Microbiol. Immunol. 2021, 80, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Xu, J.; Su, H.; Zhong, W.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, Z.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, C.; Huang, K. Interleukin-17 Is a Favorable Prognostic Marker for Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2015, 17, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastille, E.; Wasmer, M.-H.; Adamczyk, A.; Vu, V.P.; Mager, L.F.; Phuong, N.N.T.; Palmieri, V.; Simillion, C.; Hansen, W.; Kasper, S.; et al. The IL-33/ST2 Pathway Shapes the Regulatory T Cell Phenotype to Promote Intestinal Cancer. Mucosal Immunol. 2019, 12, 990–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Lu, X.; Bian, H.; Wu, X.; Yang, W.; Qin, Q. IL-33/ST2 Pathway Contributes to Metastasis of Human Colorectal Cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 453, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How to Determine the Right Significance Level for Your Test. Available online: https://www.statsig.com/perspectives/right-significance-level-test (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Hayat, M.J. Understanding Statistical Significance. Nurs. Res. 2010, 59, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, L.B. Understanding Significance Testing; SAGE: Newcastle Upon Tyne, UK, 1990; ISBN 978-0-8039-3568-6. [Google Scholar]
- Haile, Z.T. Power Analysis and Exploratory Research. J. Hum. Lact. 2023, 39, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.D.; Ahmed, I.; Ensor, J.; Takwoingi, Y.; Kirkham, A.; Morris, R.K.; Noordzij, J.P.; Deeks, J.J. Meta-Analysis of Test Accuracy Studies: An Exploratory Method for Investigating the Impact of Missing Thresholds. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petriella, K. Significance Levels 101 for Smarter Experimentation. Available online: https://www.geteppo.com/blog/significance-levels-for-smarter-experimentation (accessed on 1 July 2025).
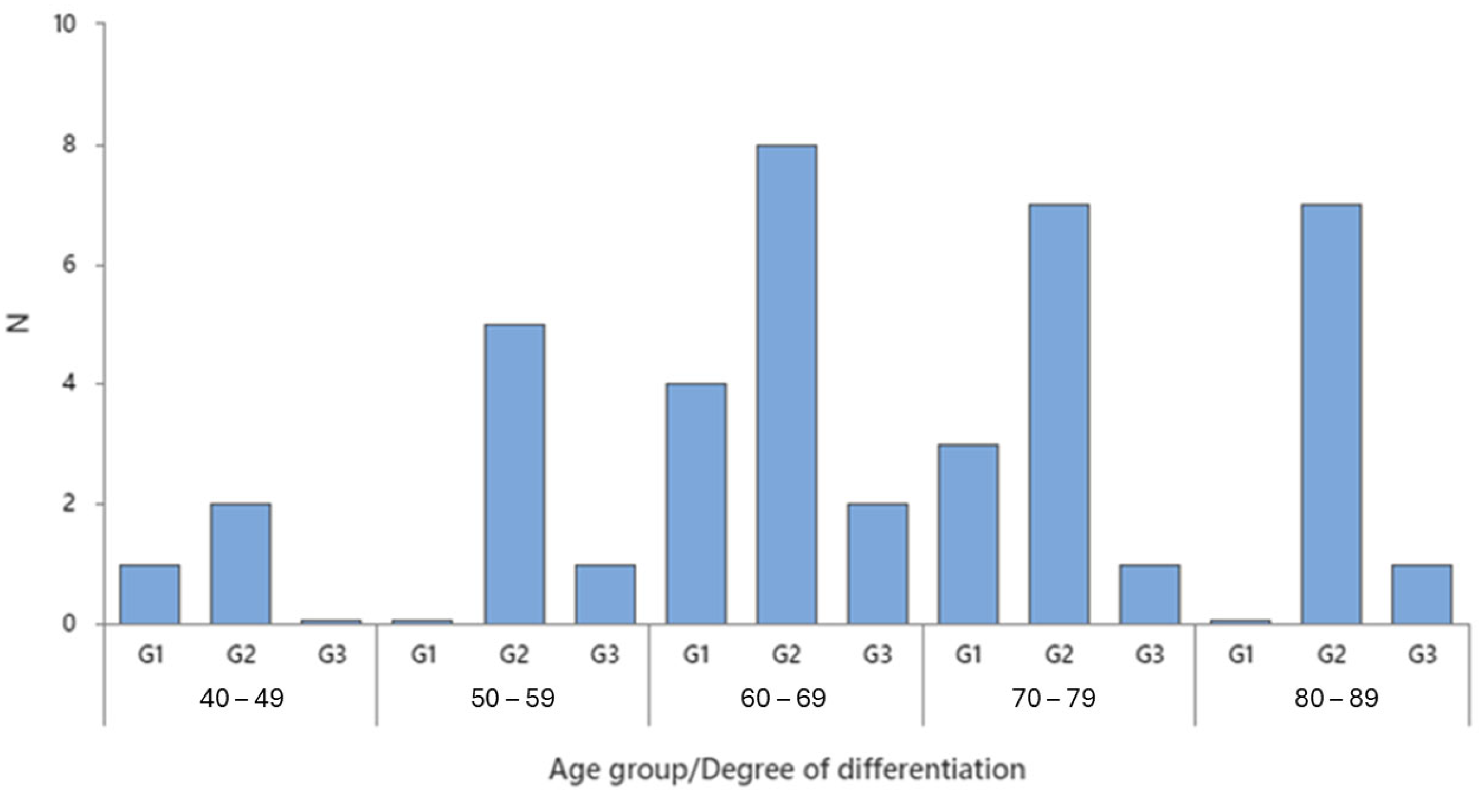

| Gender | Degree of Differentiation | N | N* | Mean Age | SE Mean | StDev | Minimum | Q1 | Median | Q3 | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | G1 | 4 | 0 | 65.00 | 6.57 | 13.14 | 47.00 | 51.50 | 67.50 | 76.00 | 78.00 |
| F | G2 | 15 | 0 | 67.60 | 3.26 | 12.64 | 48.00 | 56.00 | 69.00 | 78.00 | 85.00 |
| F | G3 | 4 | 0 | 70.75 | 5.68 | 11.35 | 59.00 | 60.25 | 70.00 | 82.00 | 84.00 |
| M | G1 | 4 | 0 | 68.00 | 3.19 | 6.38 | 62.00 | 63.00 | 66.50 | 74.50 | 77.00 |
| M | G2 | 14 | 0 | 70.93 | 03.08 | 11.52 | 45.00 | 63.00 | 71.50 | 81.25 | 86.00 |
| M | G3 | 1 | 0 | 62.00 | * | * | 62.00 | * | 62.00 | * | 62.00 |
| Invasion Type | Variable | Gender | N | N* | Mean | SE Mean | StDev | Minimum | Q1 | Median | Q3 | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lymphovascular Invasion | Age | F | 7 | 0 | 62.14 | 3.87 | 10.24 | 48.00 | 51.00 | 64.00 | 73.00 | 75.00 |
| Age | M | 5 | 0 | 71.60 | 4.70 | 10.50 | 59.00 | 62.50 | 68.00 | 82.50 | 83.00 | |
| Muscular Invasion | Age | F | 5 | 0 | 64.00 | 4.38 | 9.80 | 47.00 | 56.00 | 67.00 | 70.50 | 71.00 |
| Age | M | 1 | 0 | 67.00 | * | * | 67.00 | * | 67.00 | * | 67.00 | |
| Organ Metastasis | Age | F | 2 | 0 | 80.00 | 4.00 | 5.66 | 76.00 | * | 80.00 | * | 84.00 |
| Age | M | 2 | 0 | 74.00 | 12.00 | 17.00 | 62.00 | * | 74.00 | * | 86.00 | |
| Serous Invasion | Age | F | 8 | 0 | 73.25 | 4.61 | 13.05 | 51.00 | 60.00 | 78.00 | 84.00 | 85.00 |
| Age | M | 10 | 0 | 67.60 | 3.39 | 10.72 | 45.00 | 61.50 | 67.50 | 77.25 | 81.00 | |
| Submucosal Invasion | Age | F | 1 | 0 | 56.00 | * | * | 56.00 | * | 56.00 | * | 56.00 |
| Age | M | 1 | 0 | 78.00 | * | * | 78.00 | * | 78.00 | * | 78.00 |
| Variable | Degree of Differentiation | N | N* | Mean | SE Mean | StDev | Minimum | Q1 | Median | Q3 | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL8 Concentration (pg/mL) | G1 | 8 | 0 | 39.4 | 10.5 | 29.8 | 13.8 | 18.6 | 24.4 | 66.2 | 95.3 |
| G2 | 29 | 0 | 26.75 | 5.54 | 29.85 | 13.78 | 15.50 | 16.76 | 23.90 | 168.56 | |
| G3 | 5 | 0 | 26.73 | 3.11 | 6.95 | 17.22 | 20.78 | 26.18 | 32.95 | 36.05 | |
| IL17A Concentration (pg/mL) | G1 | 8 | 0 | 47.4 | 13.4 | 37.8 | 6.3 | 6.7 | 54.4 | 79.5 | 104.8 |
| G2 | 29 | 0 | 23.40 | 6.43 | 34.64 | 5.80 | 6.34 | 6.53 | 9.16 | 126.00 | |
| G3 | 5 | 0 | 7.306 | 0.702 | 1.569 | 6.254 | 6.390 | 6.617 | 8.566 | 10.062 | |
| IL33 Concentration (pg/mL) | G1 | 8 | 0 | 48.1 | 20.5 | 57.9 | 6.1 | 14.6 | 31.6 | 50.1 | 186.5 |
| G2 | 29 | 0 | 43.53 | 7.26 | 39.10 | 8.07 | 20.32 | 33.36 | 44.61 | 171.90 | |
| G3 | 5 | 0 | 27.3 | 13.2 | 29.6 | 6.6 | 7.4 | 10.9 | 55.4 | 76.1 |
| Variable | Infiltration | N | N* | Mean | SE Mean | StDev | Minimum | Q1 | Median | Q3 | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL8 Concentration (pg/mL) | lymphovascular invasion | 12 | 0 | 22.57 | 4.52 | 15.66 | 15.39 | 15.62 | 16.53 | 23.65 | 70.85 |
| muscular invasion | 6 | 0 | 32.2 | 12.8 | 31.3 | 13.8 | 15.7 | 21.3 | 42.6 | 95.3 | |
| organ metastasis | 4 | 0 | 24.51 | 5.06 | 10.11 | 14.93 | 15.50 | 23.54 | 34.50 | 36.05 | |
| serous invasion | 18 | 0 | 32.73 | 8.71 | 36.95 | 13.78 | 15.44 | 19.60 | 32.69 | 168.56 | |
| submucosal invasion | 2 | 0 | 36.7 | 12.4 | 17.5 | 24.4 | * | 36.7 | * | 49.1 | |
| IL17A Concentration (pg/mL) | lymphovascular invasion | 12 | 0 | 13.41 | 7.02 | 24.32 | 5.80 | 6.28 | 6.44 | 6.59 | 90.64 |
| muscular invasion | 6 | 0 | 25.1 | 11.9 | 29.2 | 6.3 | 6.4 | 6.9 | 58.1 | 70.5 | |
| organ metastasis | 4 | 0 | 7.297 | 0.924 | 1.847 | 6.254 | 6.277 | 6.436 | 9.178 | 10.062 | |
| serous invasion | 18 | 0 | 34.30 | 9.96 | 42.25 | 5.80 | 6.50 | 7.61 | 65.87 | 126.00 | |
| submucosal invasion | 2 | 0 | 67.88 | 5.73 | 8.11 | 62.14 | * | 67.88 | * | 73.61 | |
| IL33 Concentration (pg/mL) | lymphovascular invasion | 12 | 0 | 35.85 | 7.69 | 26.62 | 9.00 | 12.74 | 28.28 | 59.64 | 91.18 |
| muscular invasion | 6 | 0 | 49.1 | 27.9 | 68.3 | 6.1 | 9.2 | 28.8 | 72.5 | 186.5 | |
| organ metastasis | 4 | 0 | 32.6 | 16.4 | 32.7 | 6.6 | 7.0 | 23.8 | 67.0 | 76.1 | |
| serous invasion | 18 | 0 | 47.2 | 10.7 | 45.5 | 8.1 | 22.0 | 31.9 | 43.5 | 171.9 | |
| submucosal invasion | 2 | 0 | 39.26 | 4.71 | 6.66 | 34.55 | * | 39.26 | * | 43.97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tâlvan, E.-T.; Budișan, L.; Mohor, C.I.; Grecu, V.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Cristea, V.; Oprinca, G.; Cristian, A. Interleukin Dynamics and Their Correlation with Tumor Aggressiveness in Colorectal Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26147027
Tâlvan E-T, Budișan L, Mohor CI, Grecu V, Berindan-Neagoe I, Cristea V, Oprinca G, Cristian A. Interleukin Dynamics and Their Correlation with Tumor Aggressiveness in Colorectal Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):7027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26147027
Chicago/Turabian StyleTâlvan, Elena-Teodora, Liviuta Budișan, Călin Ilie Mohor, Valentin Grecu, Ioana Berindan-Neagoe, Victor Cristea, George Oprinca, and Adrian Cristian. 2025. "Interleukin Dynamics and Their Correlation with Tumor Aggressiveness in Colorectal Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 7027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26147027
APA StyleTâlvan, E.-T., Budișan, L., Mohor, C. I., Grecu, V., Berindan-Neagoe, I., Cristea, V., Oprinca, G., & Cristian, A. (2025). Interleukin Dynamics and Their Correlation with Tumor Aggressiveness in Colorectal Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 7027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26147027










