Isolation and Structural Characterization of Melanins from Red and Yellow Varieties of Stropharia rugosoannulata
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
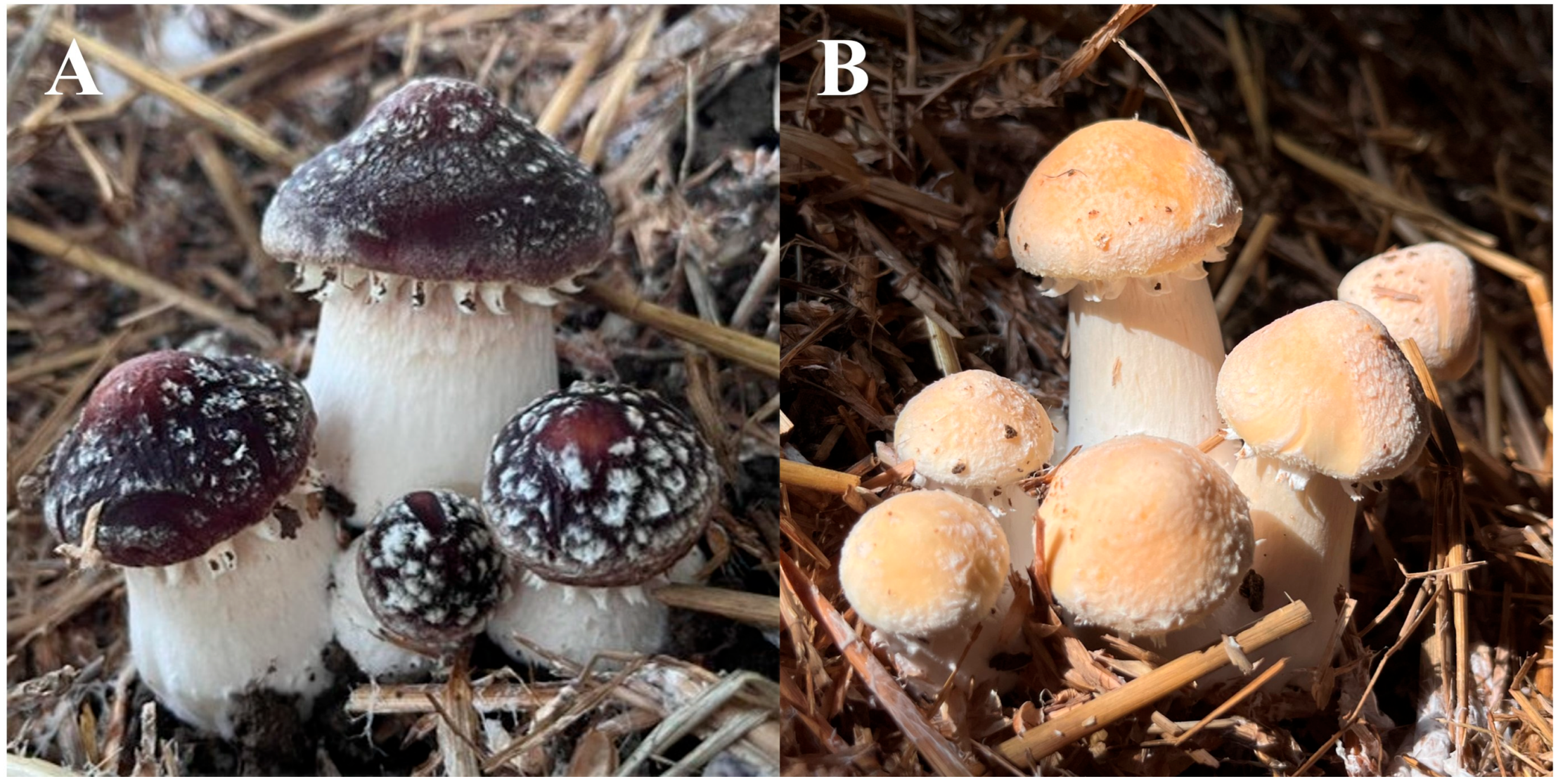
2.1. Isolation of the Pigments
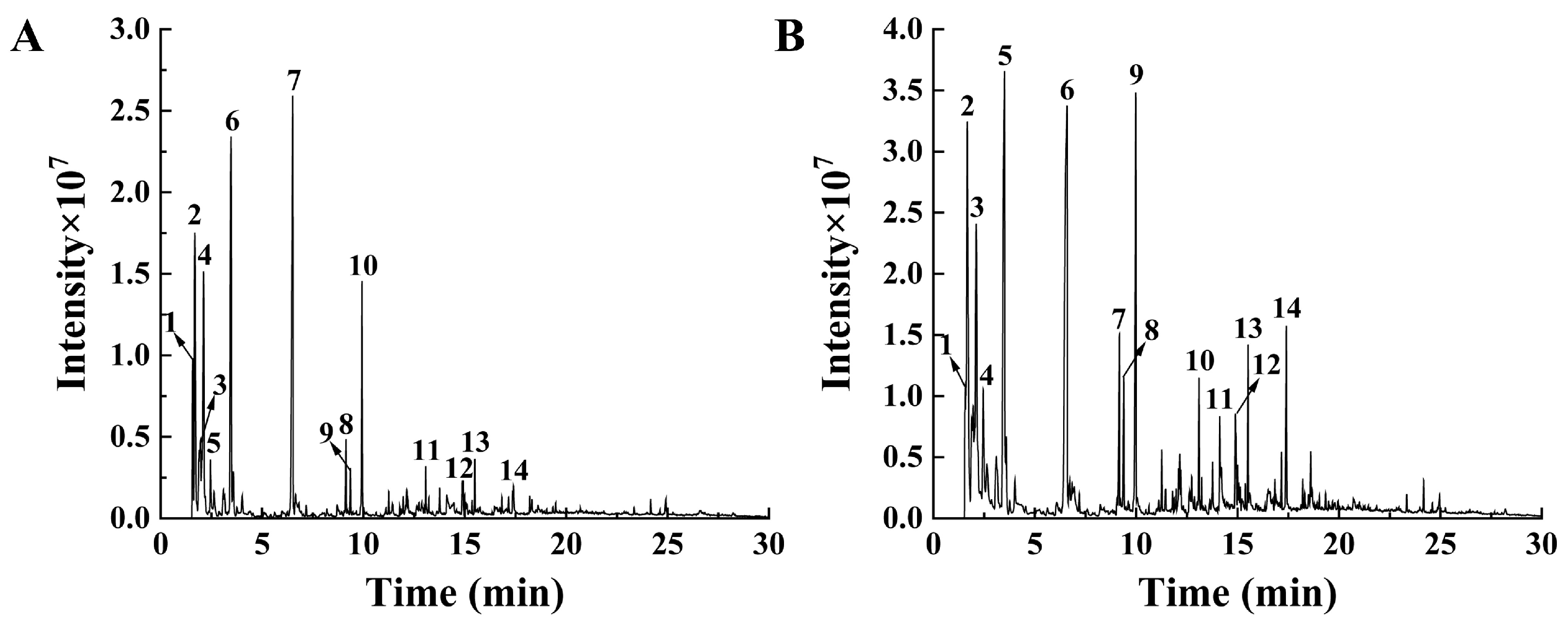
2.2. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
2.3. Chemical Composition Analysis of the Pigments
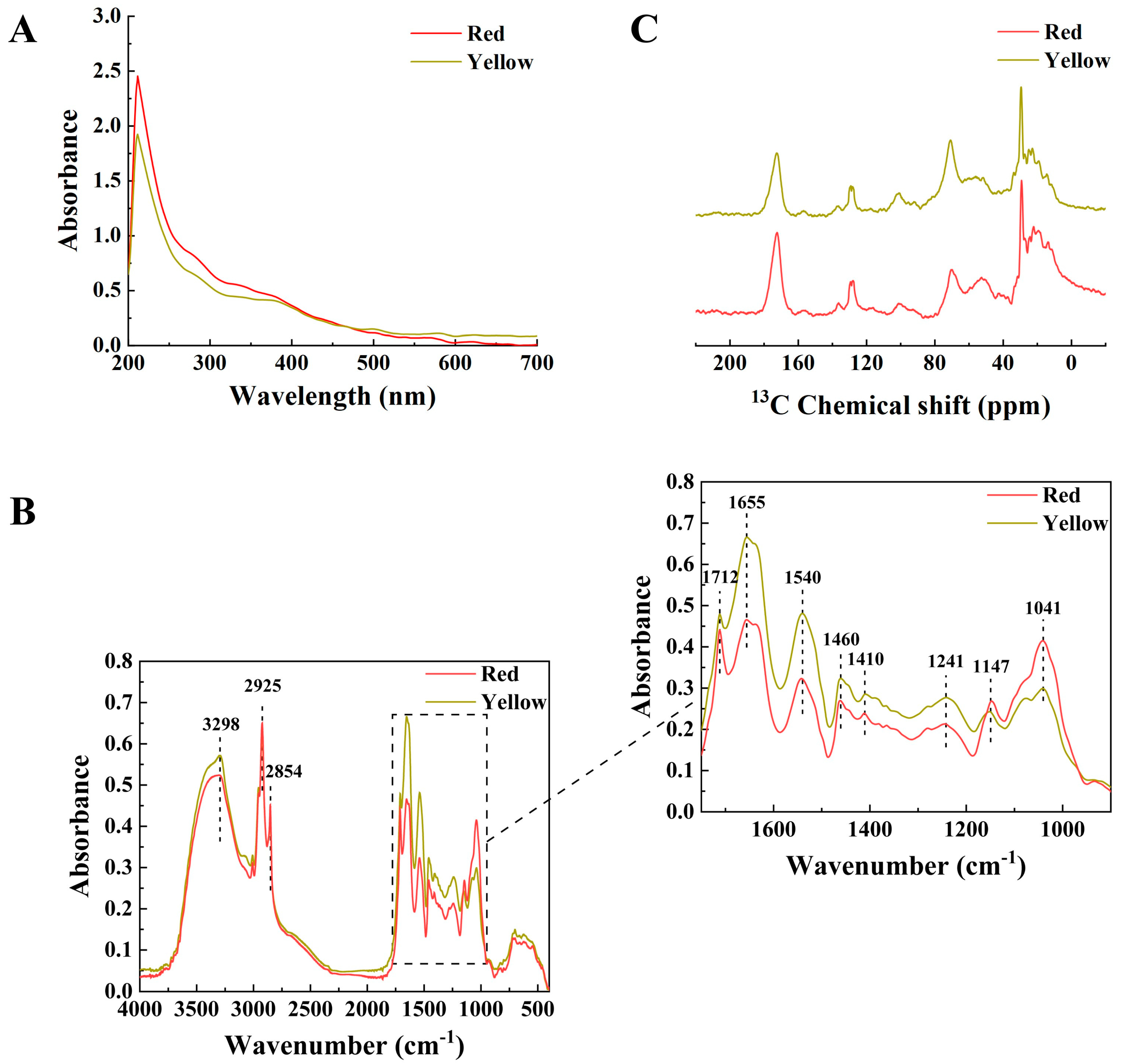
2.3.1. UV–Visible Spectra
2.3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectra
2.3.3. Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectra
2.3.4. Pyrolysis Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (Py-GCMS) Analysis
2.3.5. Elemental Composition Analysis
| Source | Content (%) | Ratio | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O | N | S | C/H | C/O | C/N | ||
| S. rugosoannulata (This study) | Red cap | 55.63 | 7.40 | 30.23 | 5.99 | 0.64 | 7.52 | 1.84 | 9.29 |
| Yellow cap | 52.22 | 6.74 | 29.70 | 5.91 | 0.99 | 7.75 | 1.76 | 8.84 | |
| Synthetic eumelanin [41] | 56.45 | 3.15 | 31.82 | 8.49 | 0.09 | 9.55 | 2.37 | 7.76 | |
| Phaeomelanin [41] | 46.24 | 4.46 | 30.16 | 9.36 | 9.78 | 12.10 | 2.04 | 5.76 | |
| Auricularia auricula [16] | 44.29 | 4.63 | 41.65 | 8.49 | 0.94 | 6.57 | 1.06 | 5.22 | |
| Boletus griseus [37] | 56.38 | 5.86 | 28.04 | 6.17 | 2.44 | 9.62 | 2.01 | 9.13 | |
| Ganoderma lucidum [40] | 54.20 | 6.24 | 33.35 | 5.14 | 1.07 | 8.69 | 1.63 | 10.54 | |
| Morchella sextelata [19] | Brown cap | 49.99 | 6.85 | 35.18 | 7.27 | 0.71 | 7.30 | 1.42 | 6.88 |
| Black cap | 53.55 | 5.84 | 30.10 | 9.28 | 1.23 | 9.17 | 1.78 | 5.77 | |
| Ophiocordyceps sinensis [20] | 50.59 | 6.18 | 33.90 | 8.19 | 1.2 | 8.19 | 1.49 | 6.18 | |
| Pleurotus cornucopiae [13] | Black cap | 52.96 | 7.37 | 28.03 | 11.09 | 0.55 | 7.19 | 1.89 | 4.78 |
| Pleurotus citrinopileatus [13] | Yellow cap | 50.51 | 7.09 | 31.79 | 9.78 | 0.83 | 7.12 | 1.59 | 5.16 |
| Pleurotus djamor [13] | Pink cap | 50.82 | 7.17 | 30.69 | 10.41 | 0.91 | 7.09 | 1.66 | 4.88 |
| Termitomyces albuminosus [34] | 54.68 | 3.54 | 26.92 | 2.49 | 12.36 | 15.43 | 2.03 | 21.94 | |
2.4. Microscopic Analysis of the Pigments
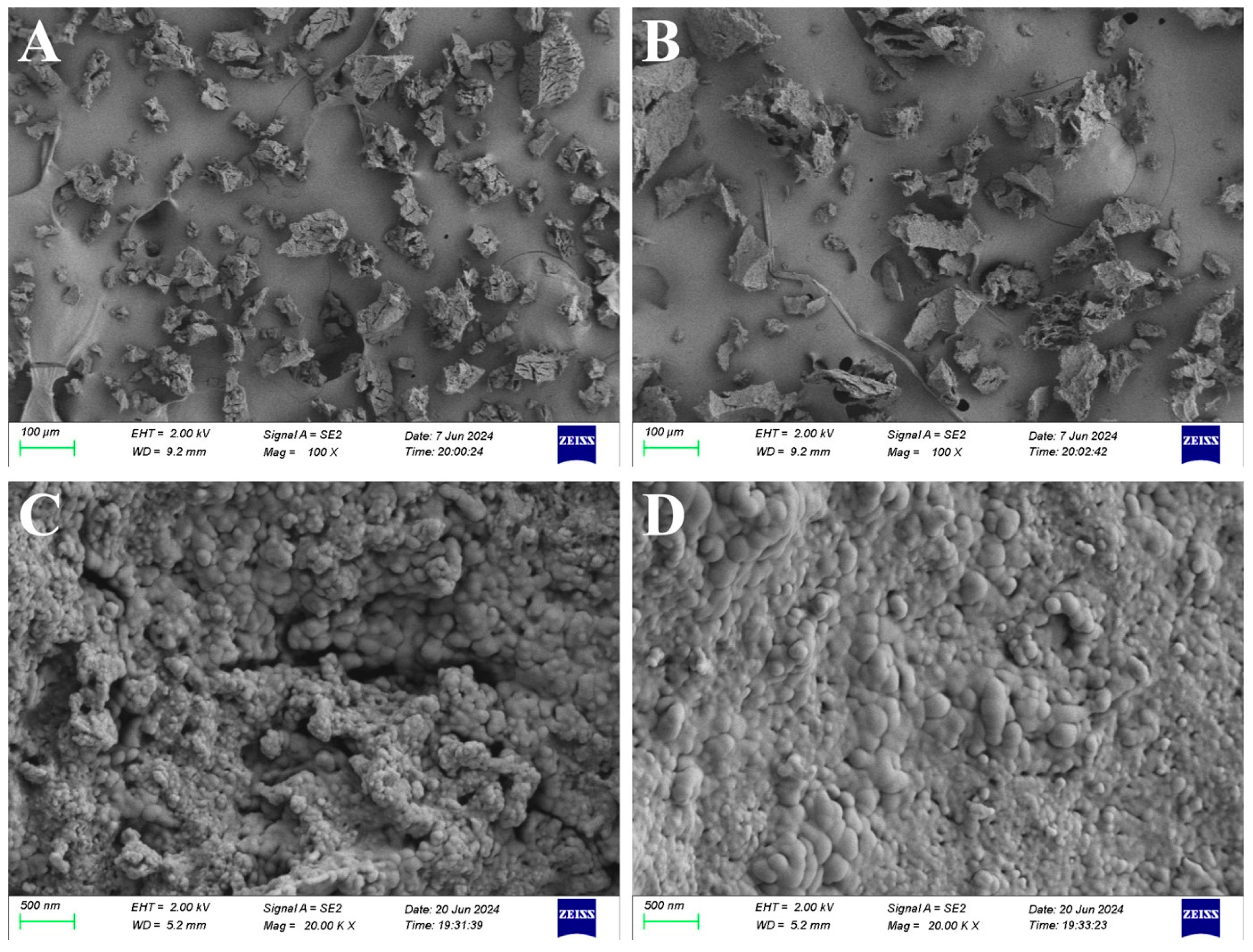
2.4.1. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Analysis
2.4.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Mushroom Samples
3.2. Pigments Isolation and Purification
3.3. HPLC Analysis
3.4. Chemical Composition Analysis of the Pigments
3.4.1. UV–Visible Light Absorption Spectra
3.4.2. FTIR Spectroscopy Analysis
3.4.3. Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy Analysis
3.4.4. Py-GCMS Analysis
3.4.5. Elemental Composition Analysis
3.5. Microscopic Observation of the Pigments
3.5.1. SEM
3.5.2. TEM
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sigurdson, G.T.; Tang, P.; Giusti, M.M. Natural Colorants: Food Colorants from Natural Sources. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, P.T.; Nielsen, S.R.; Borodina, I. Recent Advances in Engineering Microorganisms for the Production of Natural Food Colorants. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2024, 81, 102477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, A.; Rossignol, T.; Park, Y.K. Biotechnological Approaches for Producing Natural Pigments in Yeasts. Trends Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 1644–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, N.; Ren, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, Y.; Xin, H.; Cui, Y. Natural Edible Pigments: A Comprehensive Review of Resource, Chemical Classification, Biosynthesis Pathway, Separated Methods and Application. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.; Aadil, R.M.; Li, B.; Gao, X. Natural Pigments in the Food Industry: Enhancing Stability, Nutritional Benefits, and Gut Microbiome Health. Food Chem. 2024, 460 Pt 1, 140514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, R.; Conlan, X.A.; Goel, M. Fungi as a Potential Source of Pigments: Harnessing Filamentous Fungi. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maria, A.T.; Hasibur, M.H.; Rahman, M.S.; Arif, M.; Nazir, K.H.M.N.H.; Dufossé, L. Fungal Pigments: Carotenoids, Riboflavin, and Polyketides with Diverse Applications. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, X.; Gao, S.; Li, D.; Zhou, J. Production of Natural Pigments Using Microorganisms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 9243–9254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Meng, X.; Mo, C.; Wei, X.; Ma, A. Melanin of Fungi: From Classification to Application. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Nimse, S.B.; Mathew, D.E.; Dhimmar, A.; Sahastrabudhe, H.; Gajjar, A.; Ghadge, V.A.; Kumar, P.; Shinde, P.B. Microbial Melanin: Recent Advances in Biosynthesis, Extraction, Characterization, and Applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 53, 107773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero, R.J.B.; Casadevall, A. Melanin. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, R142–R143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, H.S.R.; Subiramanian, S.R.; Thyagarajan, D.; Mohammed, N.B.; Saravanakumar, V.K.; Govindaraj, M.; Maheswari, K.M.; Karthikeyan, N.; Ramesh Kumar, C. Melanin Biopolymers from Microbial World with Future Perspectives-a Review. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, W. Isolation and Identification of Pigments from Oyster Mushrooms with Black, Yellow and Pink Caps. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weijn, A.; Bastiaan-Net, S.; Wichers, H.J.; Mes, J.J. Melanin Biosynthesis Pathway in Agaricus bisporus Mushrooms. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2013, 55, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribera, J.; Panzarasa, G.; Stobbe, A.; Osypova, A.; Rupper, P.; Klose, D.; Schwarze, F. Scalable Biosynthesis of Melanin by the Basidiomycete Armillaria cepistipes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, X.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Shan, S.; Zhu, H. Production of Natural Melanin by Auricularia auricula and Study on Its Molecular Structure. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.R.; Dai, D.H.; Huang, G.R.; Zhang, Z.D. Isolation and Characterization of Extracellular Melanin Produced by Chroogomphus rutilus D447. Ame. J. Food Technol. 2015, 10, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Liu, Y.; Rong, C.; Song, S.; Zhao, S.; Qin, L.; Wang, S.; Gao, Q. Characterization of Brown Film Formed by Lentinula edodes. Fungal Biol. 2020, 124, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Cui, L.; Wang, X.; Cai, N.; Li, H.; Ren, S.; Li, T.; Shu, L. Synthesis and Structural Characteristics Analysis of Melanin Pigments Induced by Blue Light in Morchella sextelata. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1276457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, C.; Luo, J.; Xie, C.; Wei, J.; Pan, G.; Zhou, Z.; Li, C. Characterization and Biological Activities of Melanin from the Medicinal Fungi Ophiocordyceps sinensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Ma, X.; Zhou, Y.; Bian, Y.; Liu, G.; Cai, Y.; Huang, T.; Dong, H.; Cai, D.; Wan, X.; et al. Genome Sequencing Highlights the Plant Cell Wall Degrading Capacity of Edible Mushroom Stropharia rugosoannulata. J. Microbiol. 2023, 61, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Meng, G.; Ni, S.; Zhang, H.; Dong, C. Genomic Analysis of Stropharia rugosoannulata Reveals Its Nutritional Strategy and Application Potential in Bioremediation. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhao, S.; Hu, C.; Mao, C.; Guo, L.; Yu, H.; Yu, H. Whole Genome Sequence of an Edible Mushroom Stropharia rugosoannulata (Daqiugaigu). J. Fungi 2022, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Chen, W.; Ma, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y. Study on the Relationship between Structure and Taste Activity of the Umami Peptide of Stropharia rugosoannulata Prepared by Ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2022, 90, 106206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, C.F.; Feng, X.; Cheng, L.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Wang, C.T.; Huang, W. Isolation, Characterization and Antioxidant of Polysaccharides from Stropharia rugosoannulata. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Meng, F.; Tang, P.; Huang, D.; Li, Q.; Lin, M. Widely Targeted Metabolomics Analysis of the Changes to Key Non-Volatile Taste Components in Stropharia rugosoannulata under Different Drying Methods. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 884400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Song, T.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Lv, G.; Fan, L.; Feng, W.; Qu, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. From White to Reddish-Brown: The Anthocyanin Journey in Stropharia rugosoannulata Driven by Auxin and Genetic Regulators. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 954–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Yang, H.; Liu, S.; Yu, H.; Li, D.; Li, P.; Xing, R. Melanin: Insights into Structure, Analysis, and Biological Activities for Future Development. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 7528–7543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, P.; Dai, X.; Yao, X.; Zhou, S.; Ma, Q.; Liu, J.; Tian, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Extraction, Physicochemical Properties, and Antioxidant Activity of Natural Melanin from Auricularia heimuer Fermentation. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1131542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wu, W.; Zhang, F.; Hu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, X.; Fu, J. Differences between Water-Soluble and Water-Insoluble Melanin Derived from Inonotus hispidus Mushroom. Food Chem. X 2022, 16, 100498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khouqeer, G.; Alghrably, M.; Madkhali, N.; Dhahri, M.; Jaremko, M.; Emwas, A. Preparation and Characterization of Natural Melanin and Its Nanocomposite Formed by Copper Doping. Nano Sel. 2022, 3, 1598–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pralea, I.E.; Moldovan, R.C.; Petrache, A.M.; Ilies, M.; Heghes, S.C.; Ielciu, I.; Nicoara, R.; Moldovan, M.; Ene, M.; Radu, M.; et al. From Extraction to Advanced Analytical Methods: The Challenges of Melanin Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, S.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Shaikh, F.; Yang, L.; Ye, M. Structure Characterization and Lead Detoxification Effect of Carboxymethylated Melanin Derived from Lachnum sp. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 182, 669–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, R.A.; Kamat, N.M.; Nadkarni, V.S. Purification and Characterisation of a Sulphur Rich Melanin from Edible Mushroom Termitomyces albuminosus Heim. Mycology 2018, 9, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Kwon, S.L.; Hwang, D.H.; Choi, Y.E.; Kim, G.H. Production and Characterization of Melanin Pigments Derived from Amorphotheca resinae. J. Microbiol. 2020, 58, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzierzega-Lecznar, A.; Kurkiewicz, S.; Stepien, K.; Chodurek, E.; Riederer, P.; Gerlach, M. Structural Investigations of Neuromelanin by Pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. J. Neural Transm. 2006, 113, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Xiao, J.; Liu, B.; Zhuang, Y.; Sun, L. Study on the Preparation and Chemical Structure Characterization of Melanin from Boletus griseus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suthar, M.; Dufosse, L.; Singh, S.K. The Enigmatic World of Fungal Melanin: A Comprehensive Review. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Xia, Y. Melanin in Fungi: Advances in Structure, Biosynthesis, Regulation, and Metabolic Engineering. Microb. Cell Factories 2024, 23, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Li, J.; Chang, M.; Cheng, Y.; Geng, X.; Meng, J.; Zhu, M. Comparison of Physicochemical and Biochemical Properties of Natural and Arginine-Modified Melanin from Medicinal Mushroom Ganoderma lucidum. J. Basic Microbiol. 2020, 60, 1014–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Fujita, K. Microanalysis of Eumelanin and Pheomelanin in Hair and Melanomas by Chemical Degradation and Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 144, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.J.; Ju, K.Y.; Lee, J.K. The Synthetic Melanin Nanoparticles Having an Excellent Binding Capacity of Heavy Metal Ions. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2012, 33, 3788–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prados-Rosales, R.; Toriola, S.; Nakouzi, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Stark, R.; Gerfen, G.; Tumpowsky, P.; Dadachova, E.; Casadevall, A. Structural Characterization of Melanin Pigments from Commercial Preparations of the Edible Mushroom Auricularia auricula. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7326–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, E.; Vij, R.; Chrissian, C.; Prados-Rosales, R.; Gil, D.; O’Meally, R.N.; Cordero, R.J.B.; Cole, R.N.; McCaffery, J.M.; Stark, R.E.; et al. The Structural Unit of Melanin in the Cell Wall of the Fungal Pathogen Cryptococcus Neoformans. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 10471–10489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosanchuk, J.D.; Casadevall, A. Budding of Melanized Cryptococcus Neoformans in the Presence or Absence of L-Dopa. Microbiology 2003, 149 Pt 7, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzierzega-Lecznar, A.; Kurkiewicz, S.; Stepien, K. Detection and Quantitation of a Pheomelanin Component in Melanin Pigments Using Pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry System with Multiple Reaction Monitoring Mode. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 47, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Z.-F.; Zhang, W.-W.; Zhao, S.-Y.; Zhang, X.-H.; You, S.-N.; Liu, C.-M.; Zhang, G.-Q. Isolation and Structural Characterization of Melanins from Red and Yellow Varieties of Stropharia rugosoannulata. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6985. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146985
Xie Z-F, Zhang W-W, Zhao S-Y, Zhang X-H, You S-N, Liu C-M, Zhang G-Q. Isolation and Structural Characterization of Melanins from Red and Yellow Varieties of Stropharia rugosoannulata. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6985. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146985
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Zhen-Fei, Wei-Wei Zhang, Shun-Yin Zhao, Xiao-Han Zhang, Shu-Ning You, Chun-Mei Liu, and Guo-Qing Zhang. 2025. "Isolation and Structural Characterization of Melanins from Red and Yellow Varieties of Stropharia rugosoannulata" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6985. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146985
APA StyleXie, Z.-F., Zhang, W.-W., Zhao, S.-Y., Zhang, X.-H., You, S.-N., Liu, C.-M., & Zhang, G.-Q. (2025). Isolation and Structural Characterization of Melanins from Red and Yellow Varieties of Stropharia rugosoannulata. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6985. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146985





