Alterations in P-glycoprotein Expression in the Placenta of Obese Rats and Humans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
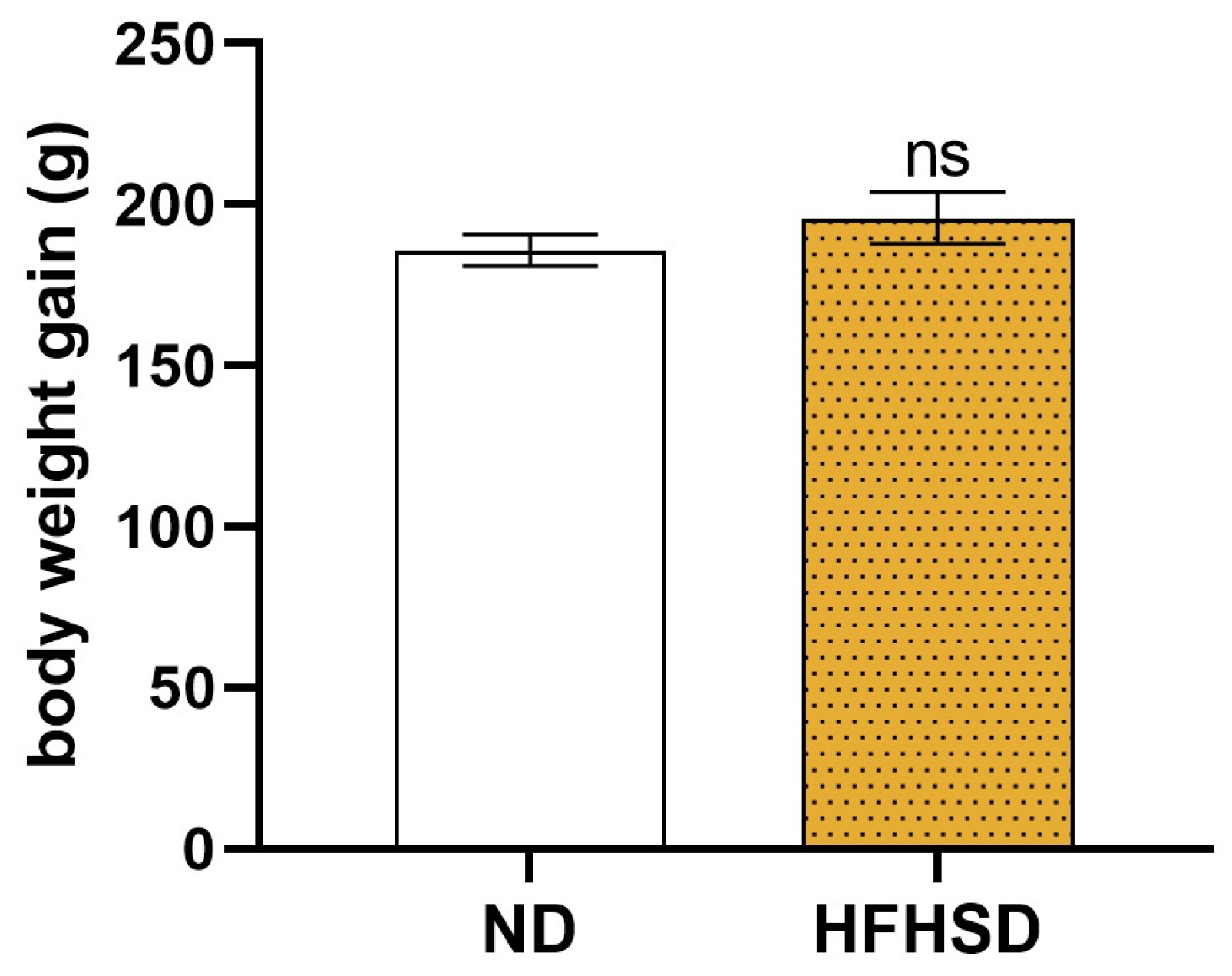
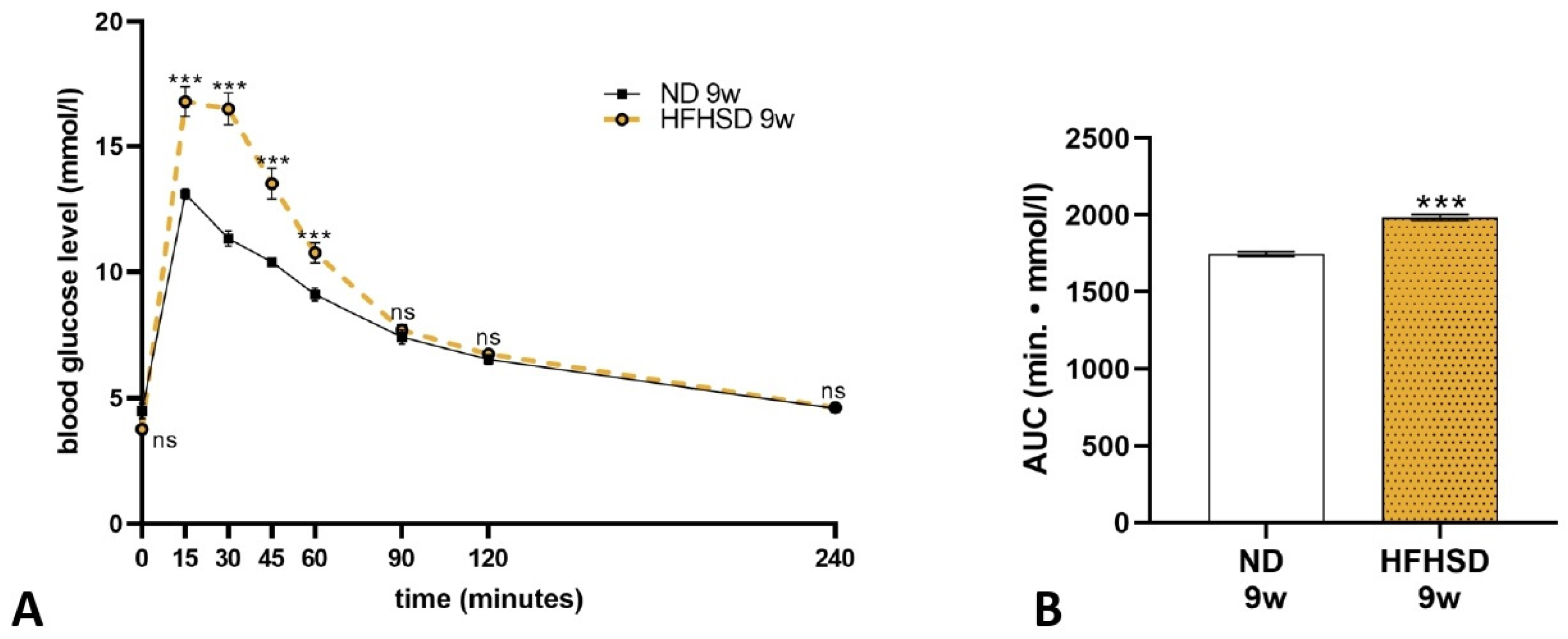
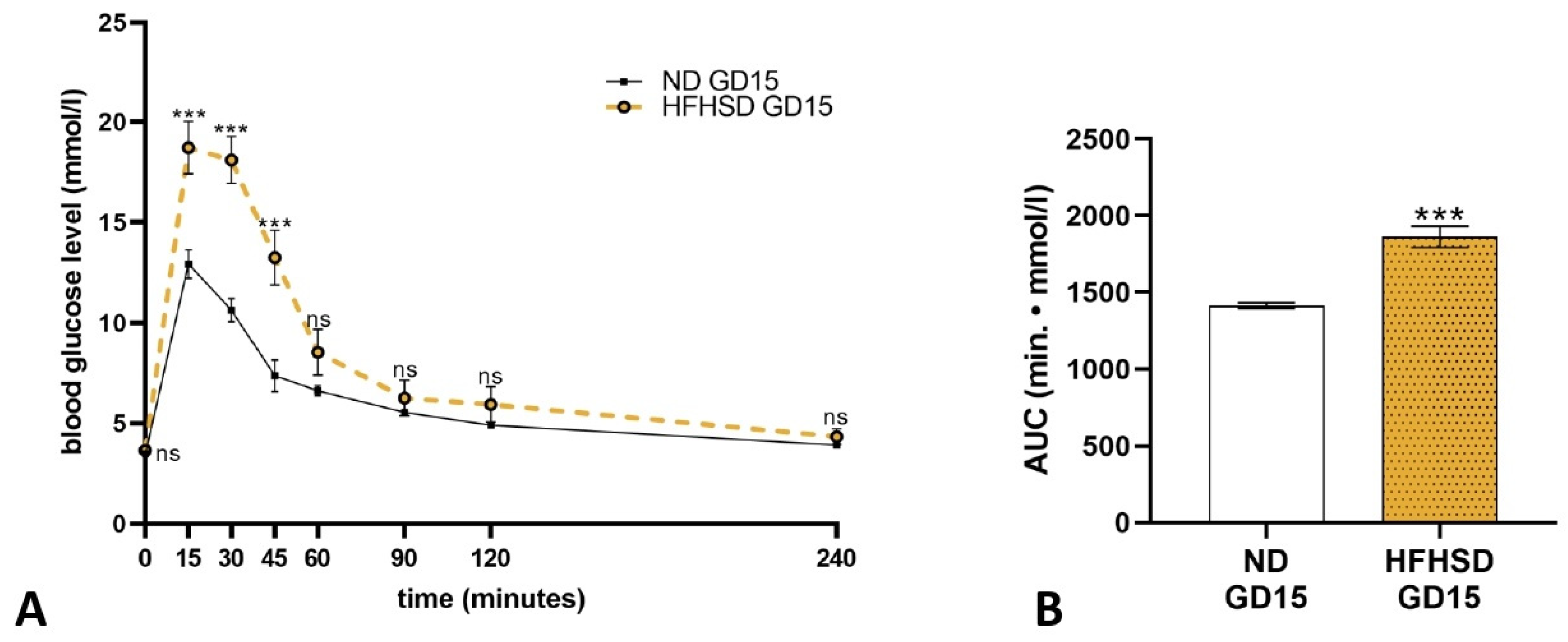
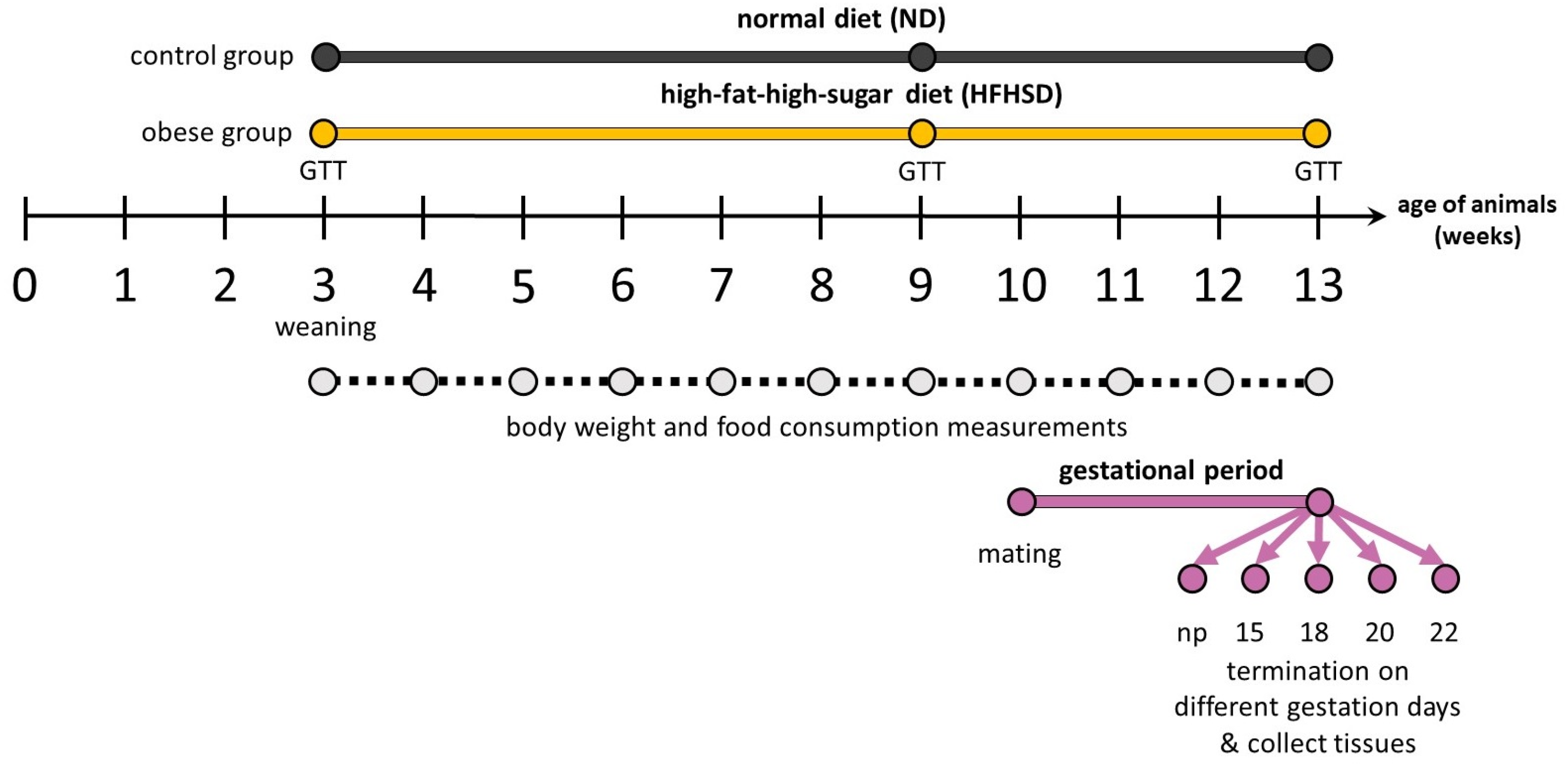
2.1. Effect of HFHSD on Body Weight and Glucose Tolerance in Rats Before and During Pregnancy
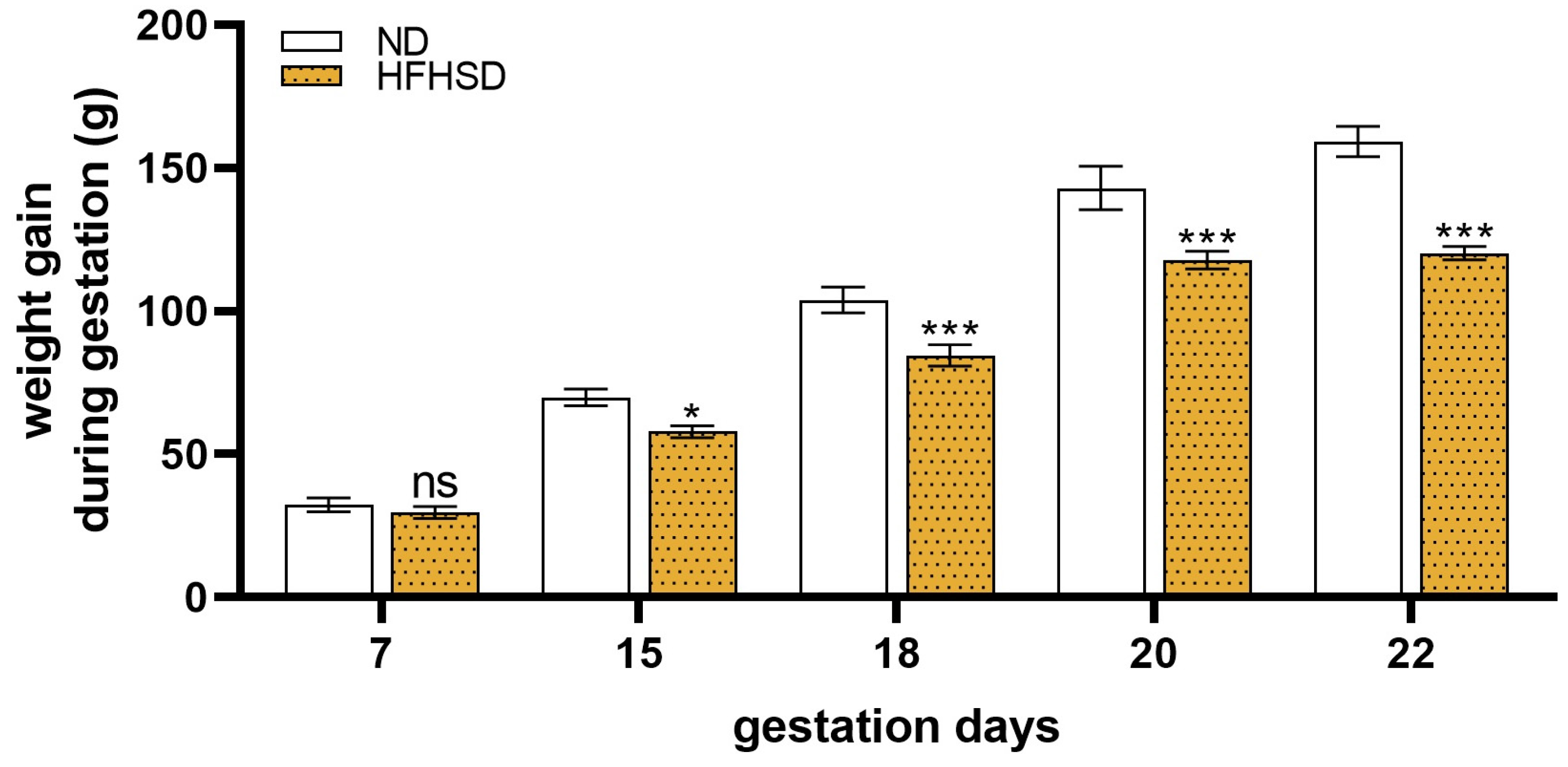
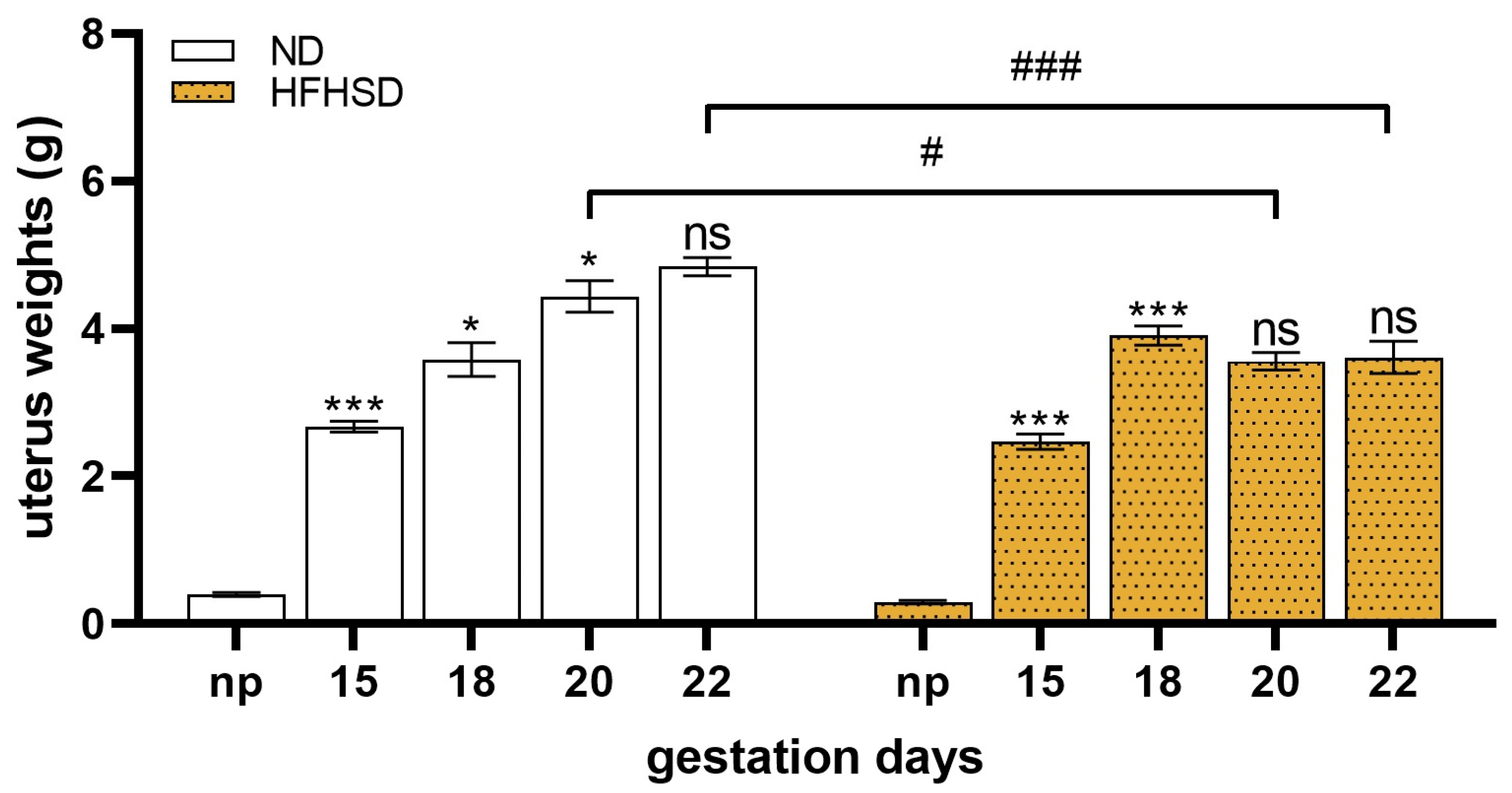
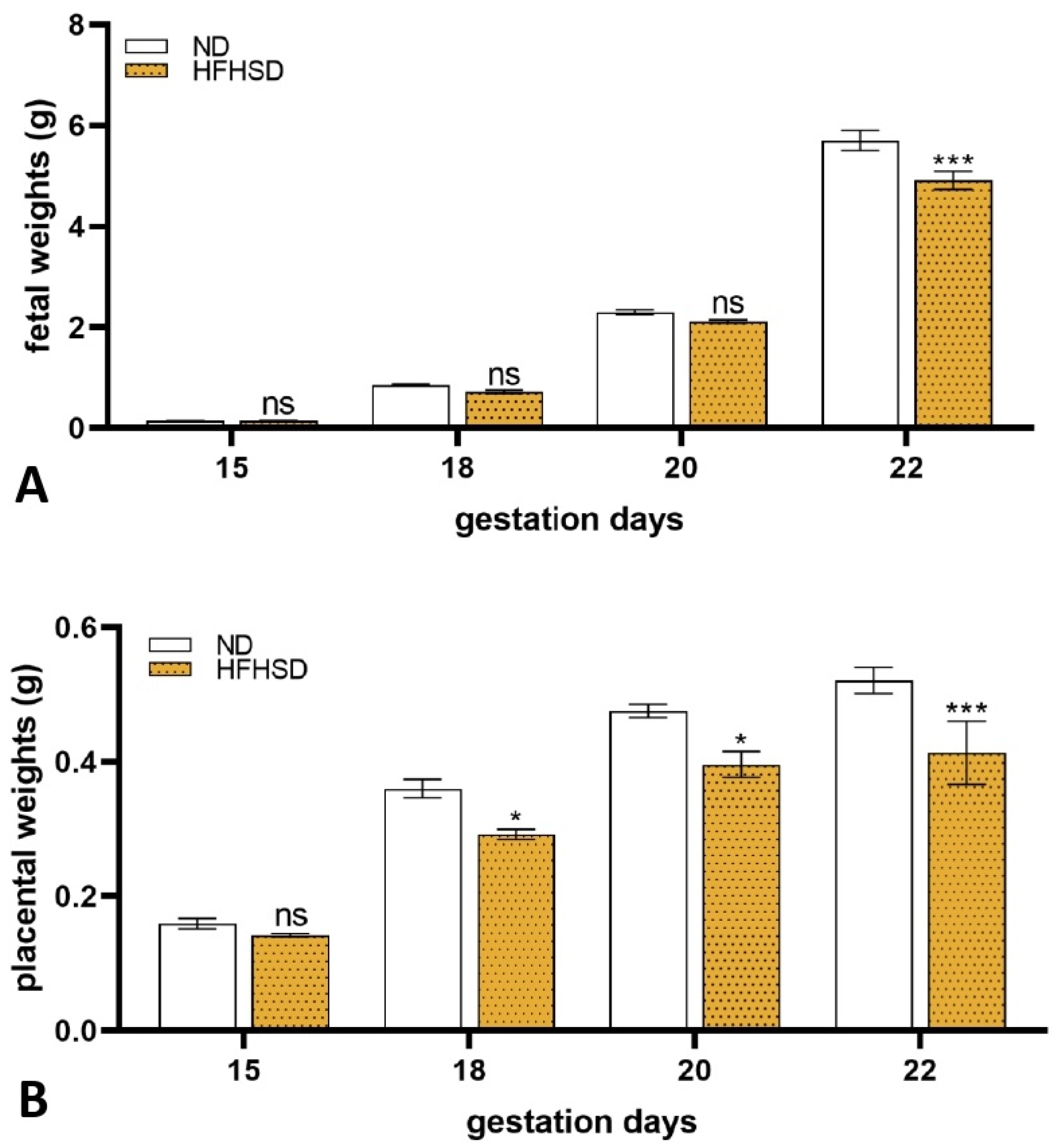
2.2. Changes in the Weights of the Uterus, Fetus, and Placenta in HFHSD Rats
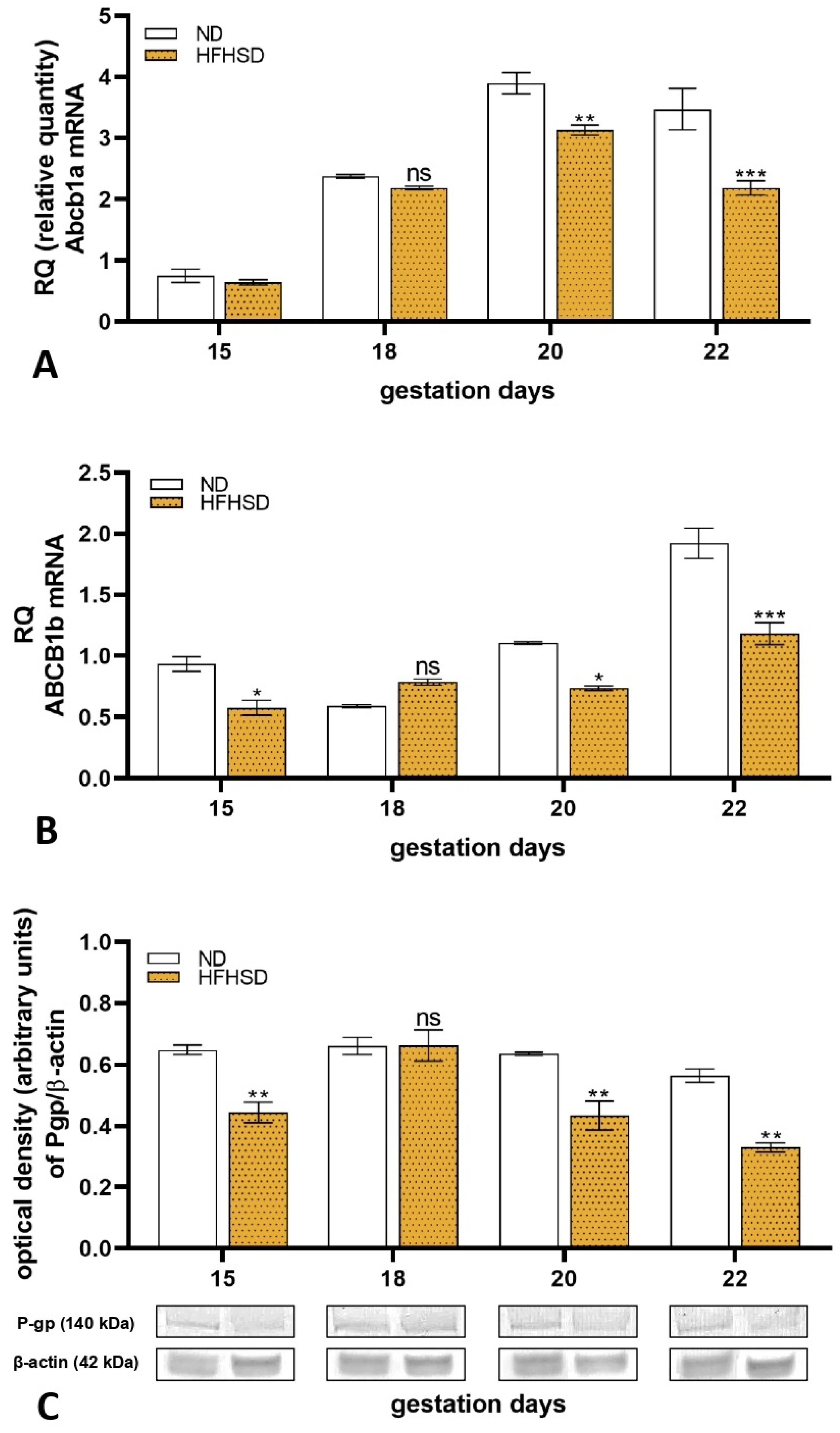
2.3. Changes in Expression of P-glycoprotein in Rat Placenta
2.4. Changes in Expression of P-glycoprotein in Human Placenta
3. Discussion
3.1. Animal Model
3.2. Expression of Placental P-glycoprotein in Obesity
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Housing and Handling of the Animals
4.2. Mating of the Animals
4.3. Experimental Design
4.4. Glucose Tolerance Test
4.5. Human Samples Collection
4.6. RT-PCR Study
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity and Overweight (2024). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 4 June 2024).
- Reichetzeder, C. Overweight and obesity in pregnancy: Their impact on epigenetics. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 1710–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaillard, R. Maternal obesity during pregnancy and cardiovascular development and disease in the offspring. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 30, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langley-Evans, S.C.; Pearce, J.; Ellis, S. Overweight, obesity and excessive weight gain in pregnancy as risk factors for adverse pregnancy outcomes: A narrative review. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2022, 35, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Farias, M.; Fos-Domenech, J.; Serra, D.; Herrero, L.; Sánchez-Infantes, D. White adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity and aging. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 192, 114723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwitz, A.; Birk, R. Adipose Tissue Hyperplasia and Hypertrophy in Common and Syndromic Obesity-The Case of BBS Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorena, K.; Jachimowicz-Duda, O.; Ślęzak, D.; Robakowska, M.; Mrugacz, M. Adipokines and Obesity. Potential Link to Metabolic Disorders and Chronic Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Qiu, T.; Li, L.; Yu, R.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Proud, C.G.; Jiang, T. Pathophysiology of obesity and its associated diseases. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 2403–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wondmkun, Y.T. Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Type 2 Diabetes: Associations and Therapeutic Implications. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 3611–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szatmári, P.; Ducza, E. Changes in Expression and Function of Placental and Intestinal P-gp and BCRP Transporters during Pregnancy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shchulkin, A.V.; Abalenikhina, Y.V.; Kosmachevskaya, O.V.; Topunov, A.F.; Yakusheva, E.N. Regulation of P-Glycoprotein during Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, M.; Nakai, E.; Mizutani, T. Study of oxidized lipids as endogenous substrates of P-gp (ABCB1). Drug Metab. Lett. 2008, 2, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunk, C.E.; Pappas, J.J.; Lye, P.; Kibschull, M.; Javam, M.; Bloise, E.; Lye, S.J.; Szyf, M.; Matthews, S.G. P-Glycoprotein (P-gp)/ABCB1 plays a functional role in extravillous trophoblast (EVT) invasion and is decreased in the pre-eclamptic placenta. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5378–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. ICH Harmonised Guideline, Drug Interaction Studies M12; International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH): Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ich-m12-drug-interaction-studies-scientific-guideline (accessed on 6 June 2024).
- Daud, A.N.; Bergman, J.E.; Bakker, M.K.; Wang, H.; Kerstjens-Frederikse, W.S.; de Walle, H.E.; Groen, H.; Bos, J.H.; Hak, E.; Wilffert, B. P-Glycoprotein-Mediated Drug Interactions in Pregnancy and Changes in the Risk of Congenital Anomalies: A Case-Reference Study. Drug Saf. 2015, 38, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlosky, D.; Barrett, E.; Aleksunes, L.M. Regulation of Placental Efflux Transporters during Pregnancy Complications. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2022, 50, 1364–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, H.; Luo, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yun, D.; Mu, D.; Zhou, K.; Hua, Y. The effect of maternal obesity on the expression and functionality of placental P-glycoprotein: Implications in the individualized transplacental digoxin treatment for fetal heart failure. Placenta 2015, 36, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, K.L.; Kibschull, M.; Matysiak-Zablocki, E.; Nguyen, T.T.N.; Matthews, S.G.; Lye, S.J.; Bloise, E. Maternal malnutrition impacts placental morphology and transporter expression: An origin for poor offspring growth. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 78, 108329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, H.; Martinelli, L.M.; Grynspan, D.; Bloise, E.; Connor, K.L. Preterm Birth Associates With Increased Placental Expression of MDR Transporters Irrespective of Prepregnancy BMI. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 1140–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justesen, S.; Bilde, K.; Olesen, R.H.; Pedersen, L.H.; Ernst, E.; Larsen, A. ABCB1 expression is increased in human first trimester placenta from pregnant women classified as overweight or obese. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geusens, N.; Verlohren, S.; Luyten, C.; Taube, M.; Hering, L.; Vercruysse, L.; Hanssens, M.; Dudenhausen, J.W.; Dechend, R.; Pijnenborg, R. Endovascular trophoblast invasion, spiral artery remodelling and uteroplacental haemodynamics in a transgenic rat model of pre-eclampsia. Placenta 2008, 29, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, T.; Pang, G. Intercellular wireless communication network between mother and fetus in rat pregnancy-a study on directed and weighted network. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2019, 17, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aguilera, N.; Salas-Pérez, F.; Ortíz, M.; Álvarez, D.; Echiburú, B.; Maliqueo, M. Rodent models in placental research. Implications for fetal origins of adult disease. Anim. Reprod. 2022, 19, e20210134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matias, A.M.; Estevam, W.M.; Coelho, P.M.; Haese, D.; Kobi, J.B.B.S.; Lima-Leopoldo, A.P.; Leopoldo, A.S. Differential Effects of High Sugar, High Lard or a Combination of Both on Nutritional, Hormonal and Cardiovascular Metabolic Profiles of Rodents. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastías-Pérez, M.; Serra, D.; Herrero, L. Dietary Options for Rodents in the Study of Obesity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gáspár, R.; Hajagos-Tóth, J.; Schaffer, A.; Kothencz, A.; Siska-Szabó, L.; Ducza, E.; Csányi, A.; Tábi, T.; Bagaméry, F.; Szökő, É.; et al. High Fat High Sucrose Diet Modifies Uterine Contractility and Cervical Resistance in Pregnant Rats: The Roles of Sex Hormones, Adipokines and Cytokines. Life 2022, 12, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hufnagel, A.; Dearden, L.; Fernandez-Twinn, D.S.; Ozanne, S.E. Programming of cardiometabolic health: The role of maternal and fetal hyperinsulinaemia. J. Endocrinol. 2022, 253, R47–R63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, S.; Hayashi, S.; Abe, M.; Hagio, S.; Irie, K.; Kuroda, Y.; Ogawa, I.; Sugiyama, A. Background data on developmental parameters during the gestation period in rats. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 26, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, S.; Tsuji, N.; Sugiyama, A. Morphology and physiology of rat placenta for toxicological evaluation. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2019, 32, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovat, N.E.J.; Legare, D.J.; Gieni, R.S.; Lautt, W.W. Gestational postprandial insulin sensitivity in the Sprague Dawley rat: The putative role of hepatic insulin sensitizing substance in glucose partitioning in pregnancy. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 98, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shynlova, O.; Lye, S.J. Regulation of Parturition. In The Guide to Investigation of Mouse Pregnancy, 1st ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 373–389. [Google Scholar]
- Mendonça, A.C.; Carneiro, E.M.; Bosqueiro, J.R.; Crepaldi-Alves, S.C.; Boschero, A.C. Development of the insulin secretion mechanism in fetal and neonatal rat pancreatic B-cells: Response to glucose, K+, theophylline, and carbamylcholine. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1998, 31, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudet, L.; Ferraro, Z.M.; Wen, S.W.; Walker, M. Maternal obesity and occurrence of fetal macrosomia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 640291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, R.X.; He, X.J.; Hu, C.L. Maternal pre-pregnancy obesity and the risk of macrosomia: A meta-analysis. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2018, 297, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathasivam, R.; Selliah, P.; Sivalingarajah, R.; Mayorathan, U.; Munasinghe, B.M. Placental weight and its relationship with the birth weight of term infants and body mass index of the mothers. J. Int. Med. Res. 2023, 51, 3000605231172895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemény, K.K.; Kozinszky, Z.; Altorjay, Á.T.; Kolcsár, B.; Surányi, A.; Ducza, E. Effect of Obesity on Aquaporin5 Expression in Human Placental and Uterus Tissues. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, S.; Nurulain, S.M.; Rashed, H.; Lotfy, M.; Emerald, S.B.; Koturan, S.; Tekes, K.; Adeghate, E. Diabetes-induced changes in the morphology and nociceptinergic innervation of the rat uterus. J. Mol. Histol. 2016, 47, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo-Silva, V.C.; Santos-Silva, A.; Lourenço, A.S.; Barros-Barbosa, C.M.; Moraes-Souza, R.Q.; Soares, T.S.; Karki, B.; Paula, V.G.; Sinzato, Y.K.; Damasceno, D.C.; et al. Congenital Anomalies Programmed by Maternal Diabetes and Obesity on Offspring of Rats. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 701767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novotna, M.; Libra, A.; Kopecky, M.; Pavek, P.; Fendrich, Z.; Semecky, V.; Staud, F. P-glycoprotein expression and distribution in the rat placenta during pregnancy. Reprod. Toxicol. 2004, 18, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalabis, G.M.; Kostaki, A.; Andrews, M.H.; Petropoulos, S.; Gibb, W.; Matthews, S.G. Multidrug Resistance Phosphoglycoprotein (ABCB1) in the Mouse Placenta: Fetal Protection. Biol. Reprod. 2005, 73, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, R.C.; Osachoff, H.L.; Kennedy, C.J. Short communication: Tissue-specific transcript expression of P-glycoprotein isoforms abcb1a and abcb1b in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) following induction with clotrimazole. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 252, 110538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellfolk, M.; Tornio, A.; Niemi, M.; Leinonen, M.K.; Lahesmaa-Korpinen, A.M.; Malm, H. Placental transporter-mediated drug interactions and offspring congenital anomalies. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 868–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardi, E.; Seidita, I.; Abati, I.; Donati, C.; Bernacchioni, C.; Castiglione, F.; Serena, C.; Mecacci, F.; Bloise, E.; Petraglia, F. The placenta in fetal death: Molecular evidence of dysregulation of inflammatory, proliferative, and fetal protective pathways. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2024, 232, 328.e1–328.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vafai, Y.; Yeung, E.H.; Sundaram, R.; Smarr, M.M.; Gerlanc, N.; Grobman, W.A.; Skupski, D.; Chien, E.K.; Hinkle, S.N.; Newman, R.B.; et al. Prenatal medication use in a prospective pregnancy cohort by pre-pregnancy obesity status. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022, 35, 5799–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewanjee, S.; Dua, T.K.; Bhattacharjee, N.; Das, A.; Gangopadhyay, M.; Khanra, R.; Joardar, S.; Riaz, M.; Feo, V.; Zia-Ul-Haq, M. Natural Products as Alternative Choices for P-Glycoprotein (P-gp) Inhibition. Molecules 2017, 22, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danner, L.; Malard, F.; Valdes, R.; Olivier-Van Stichelen, S. Non-Nutritive Sweeteners Acesulfame Potassium and Sucralose Are Competitive Inhibitors of the Human P-glycoprotein/Multidrug Resistance Protein 1 (PGP/MDR1). Nutrients 2023, 15, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjöstedt, N.; Deng, F.; Rauvala, O.; Tepponen, T.; Kidron, H. Interaction of Food Additives with Intestinal Efflux Transporters. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 3824–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosellini, M.; Turunen, P.; Efferth, T. Impact of Plastic-Related Compounds on P-Glycoprotein and Breast Cancer Resistance Protein In Vitro. Molecules 2023, 28, 2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aouache, R.; Biquard, L.; Vaiman, D.; Miralles, F. Oxidative Stress in Preeclampsia and Placental Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.J.; Dai, R.X.; Hu, C.L. Maternal prepregnancy overweight and obesity and the risk of preeclampsia: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 14, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdu, H.; Ergete, W.; Tadele, A.; Woldekidan, S.; Abebe, A.; Seyoum, G. Toxic effects of 70% ethanol extract of Moringa stenopetala leaf (Baker f.) Cufod. (Moringaceae) on fetus and placenta of pregnant Wistar rats. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.H.; Cho, Y.S.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, C.H.; Seong, H.H.; Baek, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Studies on the induction of pregnancy and the number of fetuses during pregnancy in rats. J. Anim. Reprod. Biotechnol. 2020, 35, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomczynski, P.; Sacchi, N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 162, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Pregnancy Outcome Parameters | ND | HFHSD |
|---|---|---|
| average number of implantation sites | 14.80 ± 1.25 | 13.29 ± 1.88 ** |
| average implantation success (%) | 97.01 ± 3.82 | 95.13 ± 8.6 ns |
| average litter size | 14.42 ± 1.44 | 12.08 ± 2.03 ** |
| Category | Xenobiotics | P-gp Modulation | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| medicinal drugs | analgesic | paracetamol | substrate | [11,16,43] |
| antibiotics | azithromycin | inhibitor | ||
| clarithromycin | inhibitor | |||
| antidiabetics | metformin | substrate | ||
| insulin and analogs | inducer | |||
| antiemetics | metoclopramide | substrate | ||
| antihistamines | (levo)cetirizine | substrate | ||
| (des)loratadine | substrate | |||
| fexofenadine | substrate | |||
| antivirals | tenofovir | substrate | ||
| dolutegravir | substrate | |||
| cardiac glycosides | digoxin | substrate | ||
| glucocorticoids | prednisolone | substrate | ||
| budesonide | substrate | |||
| H2 antagonists | cimetidine | substrate | ||
| ranitidine | substrate | |||
| herbal extracts | alkaloids | capsaicin (Capsicum frutescens) | inhibitor | [46] |
| furanocoumarins | bergamottin (Ginkgo biloba) | inhibitor | ||
| flavonoids | catechins, quercetin (Camellia sinensis) | inhibitor | ||
| dietary constituents | non-nutritive sweeteners | acesulfame potassium | inhibitor | [47,48] |
| sucralose | inhibitor | |||
| food additives | curcumin piperine | inhibitor inhibitor | ||
| environmental contaminant | microplastic-related chemicals | di-isobutyl phthalate | inhibitor | [49] |
| 1,1-bis(3,5-di-tert-butyl-2-hydroxyphenyl)ethane | substrate | |||
| 2,2’-methylenebis (4-methyl-6-tert-butylphenol) | inhibitor | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szatmári, P.; Kemény, K.K.; Surányi, A.; Rachamim, Y.; Ducza, E. Alterations in P-glycoprotein Expression in the Placenta of Obese Rats and Humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146976
Szatmári P, Kemény KK, Surányi A, Rachamim Y, Ducza E. Alterations in P-glycoprotein Expression in the Placenta of Obese Rats and Humans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146976
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzatmári, Péter, Kata Kira Kemény, Andrea Surányi, Yakov Rachamim, and Eszter Ducza. 2025. "Alterations in P-glycoprotein Expression in the Placenta of Obese Rats and Humans" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146976
APA StyleSzatmári, P., Kemény, K. K., Surányi, A., Rachamim, Y., & Ducza, E. (2025). Alterations in P-glycoprotein Expression in the Placenta of Obese Rats and Humans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146976





