SGLT2 Inhibitors: From Structure–Effect Relationship to Pharmacological Response
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. SGLTs Seen as Therapeutic Targets
3.1. SGLT1
3.2. SGLT2
3.3. SGLT3
3.4. SGLT4
3.5. SGLT5
3.6. SGLT6
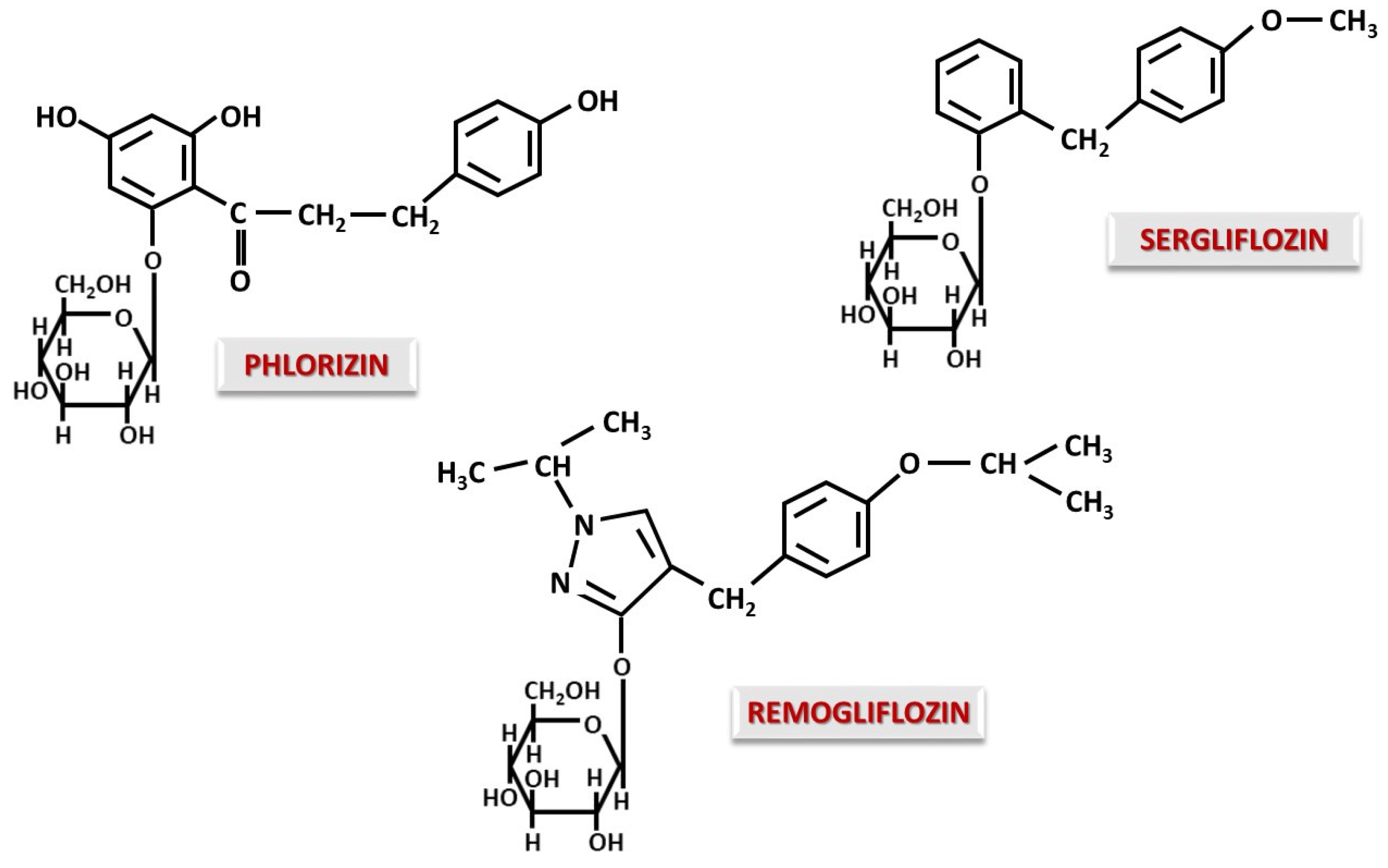
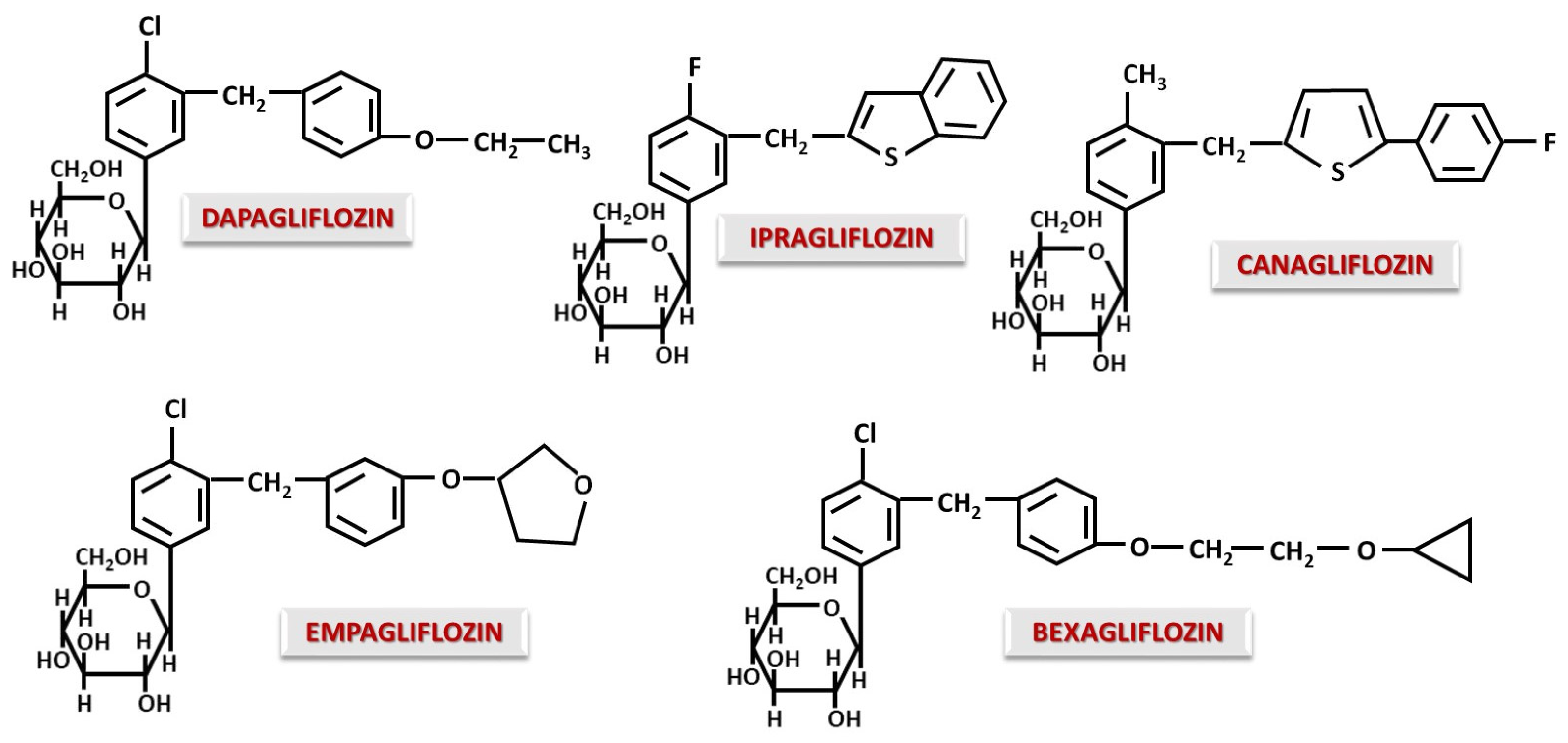
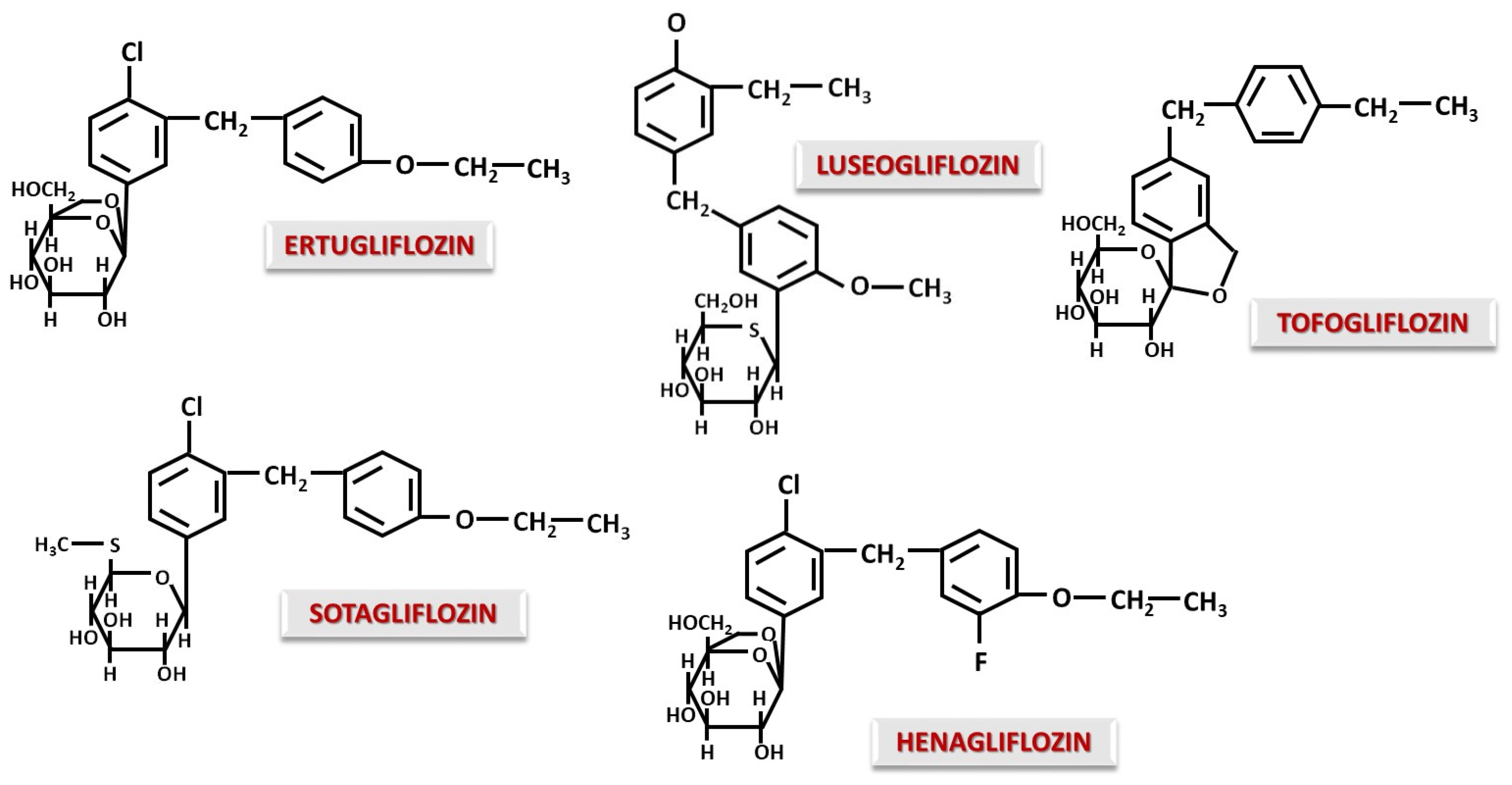
4. Structural Aspects of Compounds with Inhibitory Action on SGLTs
4.1. O-Glucoside Gliflozins
4.2. C-Glucoside Gliflozins
5. Studies That Explain the Global Therapeutic Action of SGLT Inhibitors
5.1. DM2 and Beyond
5.2. CVD
5.2.1. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
5.2.2. Arrhythmias
5.2.3. Coronary Artery Disease
5.3. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
5.4. Renal Diseases
5.5. Obesity
6. Off-Label Uses of SGLTs with Promising Therapeutic Potential and Future Directions
6.1. Anti-Aging and Age-Related Processes
6.2. Allergic Bronchial Asthma
6.3. Other Contributions Worth Considering for Future Use: Rare Forms of Neutropenia
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DM | diabetes mellitus |
| DM1 | type 1 DM |
| DM2 | type 2 DM |
| CVD | cardiovascular disease |
| SGLTs | sodium–glucose cotransporter |
| RAAS | renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system |
| 1,5-AG | 1,5-anhydroglucitol |
| EDKA | euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis |
| HMG-CoA | 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A |
| SCOT | succinyl-CoA-3-oxoacid-CoA transferase |
| BDH | 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase |
| ICAM-1 | intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| VCAM-1 | vascular cell adhesion protein-1 |
| IL | interleukin |
| MCP-1 | monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| NOS | NO synthase |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| TGL | triglyceride |
| TLR9 | toll-like receptor 9 |
| SIRT | sirtuin |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| NAFLD | non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| SREBP-1 | sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 |
| PEPCK-1 | phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase-1 |
| FAS | fatty acid synthase |
| ACC1 | acetyl-CoA-carboxylase-1 |
| SCD1 | sterol-CoA desaturase-1 |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| eGFR | estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| HPTC | human renal proximal tubular epithelial cell |
| EPO | erythropoietin |
| HIF | hypoxia inducible factor |
| AMPK | AMP-activating protein kinase |
| NF-kB | nuclear factor kappa B |
| PDH | pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase-4 |
| BA | bronchial asthma |
| IDF | International Diabetes Federation |
| ADA | American Diabetes Association |
| EASD | European Association for the Study of Diabetes |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| HFD | high-fat diet |
| PGC-1α | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor G coactivator 1-α |
| TFAM | mitochondrial transcription factor A |
| Drp1 | dynamin-related protein 1 |
| Mfn | mitofusin |
| OPA1 | optic atrophy 1 |
| CANVAS | Canagliflozin Cardiovascular Assessment Study |
| FG | Fournier’s gangrene |
References
- Yang, T.; Qi, F.; Guo, F.; Shao, M.; Song, Y.; Ren, G.; Linlin, Z.; Qin, G.; Zhao, Y. An update on chronic complications of diabetes mellitus: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies with a focus on metabolic memory. Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez Alvarez, P.; San Martin, V.T.; Morey-Vargas, O.L. Hyperglycemic crises in adults: A look at the 2024 consensus report. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2025, 92, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Yoon, S.H.; Hwang, I.; Ma, J.H.; Yang, E.; Kim, R.H.; Kim, E.; Yu, J.W. Hyperglycemia enhances brain susceptibility to lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation via astrocyte reprogramming. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Shen, H.; Han, Y.; Han, S.; Lu, Y. Association between stress hyperglycemia ratio index and all-cause mortality in critically ill patients with atrial fibrillation: A retrospective study using the MIMIC-IV database. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittendorfer, B.; Johnson, J.D.; Solinas, G.; Jansson, P.A. Insulin hypersecretion as promoter of body fat gain and hyperglycemia. Diabetes 2024, 73, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Z.; Bian, X.; Song, C.; Zhang, R.; Yuan, S.; Lin, Z.; Zhu, C.; Liu, Q.; Ma, W.; Dou, K. High stress hyperglycemia ratio predicts adverse clinical outcome in patients with coronary three-vessel disease: A large-scale cohort study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Liu, Q.; Li, F. Prevalence, awareness and control of type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk factors in Chinese elderly population. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Wu, W.; Chen, J.; Zhou, H.; Ding, G.; Lai, S.; Kuo, A.T.; Wan, H.; Lin, B.; Wu, H.; et al. Global Burden of type 2 diabetes in non-elderly individuals 1990 to 2021 and projections for 2050: A systematic analysis of the 2021 Global Burden of Disease. Diabetes Metab. 2025, 51, 101660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Gangwar, R.; Zargar, A.A.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, A. Prevalence of Diabetes in India: A Review of IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th Edition. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2024, 20, e130423215752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdinand, K.C. An overview of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Manag. Care 2024, 30, S181–S188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Zhao, L.; Chen, C.; Ren, Z.; Jing, Y.; Qiu, J.; Liu, D. National burden and risk factors of diabetes mellitus in China from1990 to 2021: Results from the Global Burden of Disease study 2021. J. Diabetes 2024, 16, e70012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhatariya, K.; Umpierrez, G.E. Management of Diabetes and Hyperglycemia in Hospitalized Patients. In Endotext [Internet]; Feingold, K.R., Ahmed, S.F., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Corpas, E., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279093/ (accessed on 8 July 2025).
- Zee, B.; Lee, J.; Lai, M.; Chee, P.; Rafferty, J.; Thomas, R.; Owens, D. Digital solution for detection of undiagnosed diabetes using machine learning-based retinal image analysis. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2022, 10, e002914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.L.; Zhong, L.; Lee, S.; Towne, S.D., Jr.; Ory, M.G. Effectiveness and economic impact of a diabetes education program among adults with type 2 diabetes in South Texas. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, P.E.; Ahmed, S.B.; Carrero, J.J.; Foster, B.; Francis, A.; Hall, R.K.; Herrington, W.G.; Hill, G.; Inker, L.A.; Kazancıoğlu, R.; et al. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, S117–S314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maringhini, S.; Zoccali, C. Chronic Kidney Disease Progression—A Challenge. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polychronopoulou, E.; Bourdon, F.; Teta, D. SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetic and non-diabetic kidney transplant recipients: Current knowledge and expectations. Front. Nephrol. 2024, 4, 1332397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, A.; Harhay, M.N.; Ong, A.C.M.; Tummalapalli, S.L.; Ortiz, A.; Fogo, A.B.; Fliser, D.; Roy-Chaudhury, P.; Fontana, M.; Nangaku, M.; et al. American Society of Nephrology; European Renal Association; International Society of Nephrology. Chronic kidney disease and the global public health agenda: An international consensus. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2024, 20, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidu, S.; Alabraba, V.; Davies, S.; Newland-Jones, P.; Fernando, K.; Bain, S.C.; Diggle, J.; Evans, M.; James, J.; Kanumilli, N.; et al. SGLT2 Inhibitors—The New Standard of Care for Cardiovascular, Renal and Metabolic Protection in Type 2 Diabetes: A Narrative Review. Diabetes Ther. 2024, 15, 1099–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgianos, P.I.; Agarwal, R. The Nonsteroidal Mineralocorticoid-Receptor-Antagonist Finerenone in Cardiorenal Medicine: A State-of-the-Art Review of the Literature. Am. J. Hypertens. 2023, 36, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorakopoulou, M.P.; Sarafidis, P. SGLT2 inhibitors and finerenone in non-diabetic CKD: A step into the (near) future? Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 17, sfad272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khullar, D.; Gupta, A.K.; Singh, K. Finerenone: Will It Be a Game-changer? Card. Fail. Rev. 2024, 10, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Li, M.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, T.; Feng, X.; Gao, A.; Zhang, H.; Gao, R. The non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) as a predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in US adults with diabetes or prediabetes: NHANES1999–2018. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Liang, D. The association between the triglyceride-glucose index and the risk of cardiovascular disease in US population aged ≤ 65 years with prediabetes or diabetes: A population-based study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Xie, Q.; Pan, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Peng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, S.; Tong, N. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults: Pathogenesis, prevention and therapy. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2024, 9, 262. [Google Scholar]
- Angelini, G.; Russo, S.; Mingrone, G. Incretin hormones, obesity and gut microbiota. Peptides 2024, 178, 171216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, S.B.; Fenton, R.A.; Rieg, T. Sodium-glucose cotransport. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2015, 24, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, R.; Shinozaki, Y.; Ohta, T. Sodium-glucose cotransporters: Functional properties and pharmaceutical potential. J. Diabetes Investig. 2020, 11, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watabe, E.; Kawanabe, A.; Kamitori, K.; Ichihara, S.; Fujiwara, Y. Sugar binding of sodium-glucose cotransporters analyzed by voltage-clamp fluorometry. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 107215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimek, K.; Chen, X.; Sasaki, T.; Groener, D.; Werner, R.A.; Higuchi, T. PET imaging of sodium-glucose cotransporters (SGLTs): Unveiling metabolic dynamics in diabetes and oncology. Mol. Metab. 2024, 90, 102055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca-Correa, J.I.; Correa-Rotter, R. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Mechanisms of Action: A Review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 777861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koepsell, H. Glucose transporters in the small intestine in health and disease. Pflug. Arch. 2020, 472, 1207–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez Rieg, J.A.; Rieg, T. What does sodium-glucose co-transporter 1 inhibition add: Prospects for dual inhibition. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrannini, E. Sodium-glucose co-transporters and their inhibition: Clinical physiology. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, E.M. SGLT2 Inhibitors: Physiology and Pharmacology. Kidney360 2021, 2, 2027–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevola, R.; Villani, A.; Imbriani, S.; Alfano, M.; Criscuolo, L.; Beccia, D.; Ruocco, R.; Femine, A.D.; Gragnano, F.; Cozzolino, D.; et al. Sodium-glucose co-transporters family: Current evidence, clinical applications and perspectives. Front. Biosci. 2023, 28, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soták, M.; Casselbrant, A.; Rath, E.; Zietek, T.; Strömstedt, M.; Adingupu, D.D.; Karlsson, D.; Fritsch Fredin, M.; Ergang, P.; Pácha, J.; et al. Intestinal sodium/glucose cotransporter 3 expression is epithelial and downregulated in obesity. Life Sci. 2021, 267, 118974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotak, M.; Casselbrant, A.; Strömstedt, M.; Rath, E.; Adingupu, D.; Karlsson, D.; Fredin, M.F.; Ergang, P.; Zietek, T.; Pácha, J.; et al. Intestinal sodium glucose transporter 3 (sglt3) is downregulated in experimental models of obesity and in morbidly obese patients. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 670.46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soták, M.; Marks, J.; Unwin, R.J. Putative tissue location and function of the SLC5 family member SGLT3. Exp. Physiol. 2017, 102, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallon, V.; Nakagawa, T. Renal tubular handling of glucose and fructose in health and disease. Compr. Physiol. 2021, 12, 2995–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamitori, K.; Shirota, M.; Fujiwara, Y. Structural basis of the selective sugar transport in sodium-glucose cotransporters. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Vicente, A.; Cabral, P.D.; Hong, N.J.; Asirwatham, J.; Saez, F.; Garvin, J.L. Fructose reabsorption by rat proximal tubules: Role of Na+-linked cotransporters and the effect of dietary fructose. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2019, 316, F473–F480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulanger, C.; Stephenne, X.; Diederich, J.; Mounkoro, P.; Chevalier, N.; Ferster, A.; Van Schaftingen, E.; Veiga-da-Cunha, M. Successful use of empagliflozin to treat neutropenia in two G6PC3-deficient children: Impact of a mutation in SGLT5. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2022, 45, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, M.E.; Yahya, G.; Popoviciu, M.S.; Cavalu, S.; Abd-Eldayem, M.A.; Saber, S. Unlocking the full potential of SGLT2 inhibitors: Expanding applications beyond glycemic control. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diederich, J.; Mounkoro, P.; Tirado, H.A.; Chevalier, N.; Van Schaftingen, E.; Veiga-da-Cunha, M. SGLT5 is the renal transporter for 1,5-anhydroglucitol, a major player in two rare forms of neutropenia. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2023, 80, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, H.; Takayanagi, K.; Shimizu, T.; Iwashita, T.; Ikari, A.; Maeshima, A.; Hasegawa, H. Possible involvement of up-regulated salt-dependent glucose transporter-5 (SGLT5) in high-fructose diet-induced hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2025, 48, 1068–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baader-Pagler, T.; Eckhardt, M.; Himmelsbach, F.; Sauer, A.; Stierstorfer, B.E.; Hamilton, B.S. SGLT6—A pharmacological target for the treatment of obesity? Adipocyte 2018, 7, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Steenbergen, A.; Balteau, M.; Ginion, A.; Ferté, L.; Battault, S.; de Meester de Ravenstein, C.; Balligand, J.L.; Daskalopoulos, E.P.; Gilon, P.; Despa, F.; et al. Sodium-myoinositol cotransporter-1, SMIT1, mediates the production of reactive oxygen species induced by hyperglycemia in the heart. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, D.; Davidson, S.; Yellon, D. The SGLT family—Sodium-glucose transporters with roles beyond glucose and the kidney. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganwir, P.; Bhadane, R.; Chaturbhuj, G.U. In-silico screening and identification of glycomimetic as potential human sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2024, 110, 108074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helvacı, Ö.; Helvacı, B. Story of Serendipities: From Phlorizin to Gliflozins. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2023, 21, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Cao, J.; Zhao, T.; Liu, Y.; Khan, A.; Cheng, G. The bioavailability, extraction, biosynthesis and distribution of natural dihydrochalcone: Phloridzin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kshirsagar, R.P.; Kulkarni, A.A.; Chouthe, R.S.; Pathan, S.K.; Une, H.D.; Reddy, G.B.; Diwan, P.V.; Ansari, S.A.; Sangshetti, J.N. SGLT inhibitors as antidiabetic agents: A comprehensive review. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 1733–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccari, R.; Ottanà, R. Sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitors as antidiabetic drugs: Current development and future perspectives. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 10848–10881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, R.P.; Babu, R.J.; Srinivas, N.R. Comparative pharmacokinetics of three SGLT-2 inhibitors sergliflozin, remogliflozin and ertugliflozin: An overview. Xenobiotica 2016, 47, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atal, S.; Fatima, Z.; Singh, S.; Balakrishnan, S.; Joshi, R. Remogliflozin: The new low cost SGLT-2 inhibitor for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetol. Int. 2020, 12, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tewari, J.; Qidwai, K.A.; Rana, A.; Tewari, A.; Tewari, V.; Maheshwari, A. Safety and efficacy of remogliflozin in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cureus 2024, 16, e66145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkanski, S. Dapagliflozin—Structure, synthesis, and new indications. Pharmacia 2021, 68, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksud, N.; Bera, S.; Naim, M.J.; Alam, O. Dapagliflozin: A new hope for the therapeutic treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. Rep. 2024, 11, 100167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, R.L.; Gallo, G.; Le, K.P.N.; Volino, L.R. Bexagliflozin: A comprehensive review of a recently approved SGLT2 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Med. Chem. Res. 2024, 33, 1354–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramani, J.; Shah, H.; Vyas, V.K.; Sharma, M. A review on the medicinal chemistry of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2-I): Update from 2010 to present. Eur. J. Med. Chem. Rep. 2022, 6, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumieniczek, A.; Berecka-Rycerz, A.; Dul, M.; Pryjda, A. Standardized Chromatographic and Computational Approaches for Lipophilicity Analysis of Five Gliflozin Antidiabetic Drugs in Relation to Their Biological Activity. Molecules 2025, 30, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantakonstanti, V.V.; Mountanea, O.G.; Papoulidou, K.E.C.; Andreou, T.; Koftis, T.V.; Gallos, J.K. Studies towards the synthesis of ertugliflozin from l-Arabinose. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 5700–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, F.; Moffa, S.; Impronta, F.; Cefalo, C.M.A.; Sun, V.A.; Sorice, G.P.; Mezza, T.; Giaccari, A. Spotlight on ertugliflozin and its potential in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: Evidence to date. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 2905–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, P.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Shi, A. Mechanistic evaluation of the inhibitory effect of four SGLT-2 inhibitors on SGLT 1 and SGLT 2 using physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling approaches. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1142003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, J.C.; Liang, Y.; Sahasrabudhe, V.; Tensfeldt, T.; Fediuk, D.J.; Zhou, S.; Krishna, R.; Dawra, V.K.; Wood, L.S.; Sweeney, K. Meta-analysis of noncompartmental pharmacokinetic parameters of Ertugliflozin to evaluate dose proportionality and UGT1A9 polymorphism effect on exposure. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 61, 1220–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Liu, G.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y.; Shen, J.; Jia, Y. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interactions between Henagliflozin, a novel selective SGLT-2 inhibitor, and Warfarin in healthy chinese subjects. Clin. Ther. 2023, 45, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraizumi, M.; Akashi, T.; Murasaki, K.; Kishida, H.; Kumanomidou, T.; Torimoto, N.; Nureki, O.; Miyaguchi, I. Transport and inhibition mechanism of the human SGLT2–MAP17 glucose transporter. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2024, 31, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cefalo, C.M.A.; Cinti, F.; Moffa, S.; Impronta, F.; Sorice, G.P.; Mezza, T.; Pontecorvi, A.; Giaccari, A. Sotagliflozin, the first dual SGLT inhibitor: Current outlook and perspectives. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuffer, W.; Williams, B.; Trujillo, J.M. A review of sotagliflozin for use in type 1 diabetes. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 10, 2042018819890527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayour, A.A.; Oláh, A.; Ruppert, M.; Barta, B.A.; Merkely, B.; Radovits, T. Effect of pharmacological selectivity of SGLT2 inhibitors on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Requena-Ibáñez, J.A.; Kindberg, K.M.; Santos-Gallego, C.G.; Zafar, M.U.; Badimon, J.J. Sotagliflozin: Two Birds with One Stone? Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsar, B.; Afsar, R.E.; Lentine, K.L. The impact of sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitors on gut microbiota: A scoping review. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2024, 23, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, Y.; Miyagawa, H.; Yoshida, T.; Chuman, H. Binding interaction of SGLT with sugar and thiosugar by the molecular dynamics simulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1848, 2799–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ohtake, Y.; Sato, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Nishimoto, M.; Taka, N.; Takano, K.; Yamamoto, K. Discovery of tofogliflozin, a novel C-arylglucoside with an O-spiroketal ring system, as a highly selective sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 7828–7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashraqi, M.M.; Chaturvedi, N.; Alam, Q.; Alshamrani, S.; Bahnass, M.M.; Ahmad, K.; Alqosaibi, A.I.; Alnamshan, M.M.; Ahmad, S.S.; Beg, M.M.A.; et al. Biocomputational prediction approach targeting FimH by natural SGLT2 inhibitors: A possible way to overcome the uropathogenic effect of SGLT2 inhibitor drugs. Molecules 2021, 26, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katakami, N.; Mita, T.; Yoshii, H.; Shiraiwa, T.; Yasuda, T.; Okada, Y.; Kurozumi, A.; Hatazaki, M.; Kaneto, H.; Osonoi, T.; et al. UTOPIA study investigators. Tofogliflozin long-term effects on atherosclerosis progression and major clinical parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus lacking a history of cardiovascular disease: A 2-year extension study of the UTOPIA trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lou, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Chen, H.; Zheng, T.; Xia, C.; Song, X.; Dong, T.; Li, J.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 6-deoxy O-spiroketal C-arylglucosides as novel renal sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 180, 398–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Młynarska, E.; Czarnik, W.; Dzieża, N.; Jędraszak, W.; Majchrowicz, G.; Prusinowski, F.; Stabrawa, M.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. Type 2 diabetes mellitus: New pathogenetic mechanisms, treatment and the most important complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrannini, G.; Savarese, G.; Cosentino, F. SGLT2 Inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Heart Fail Clin. 2022, 18, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, A.; Vickneson, K.; Singh, J.S. SGLT2-inhibitors; more than just glycosuria and diuresis. Heart Fail Rev. 2021, 26, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.C.H.; Chan, M.C.Y. SGLT2 Inhibitors: The next blockbuster multifaceted drug? Medicina 2023, 59, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iordan, L.; Lazar, S.; Timar, R.; Popescu, S.; Sorescu, T.; Albai, O.; Braha, A.; Timar, B.; Gaita, L. The impact of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibition on insulin resistance and inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes: A retrospective study. Medicina 2025, 61, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, M.R.; Di Meo, I.; Polito, R.; Auriemma, M.C.; Gambardella, A.; di Mauro, G.; Capuano, A.; Paolisso, G. Cognitive impairment and type 2 diabetes mellitus: Focus of SGLT2 inhibitors treatment. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 176, 106062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Li, S.; Kang, B.; Zhou, J. The current role of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus management. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.I.; Yazdi, Z.S.; Beitelshees, A.L. Pharmacological treatment of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e142243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hropot, T.; Battelino, T.; Dovc, K. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors in type 1 diabetes: A scoping review. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2023, 96, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elian, V.; Popovici, V.; Karampelas, O.; Pircalabioru, G.G.; Radulian, G.; Musat, M. Risks and benefits of SGLT-2 inhibitors for type 1 diabetes patients using automated insulin delivery systems—A literature review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
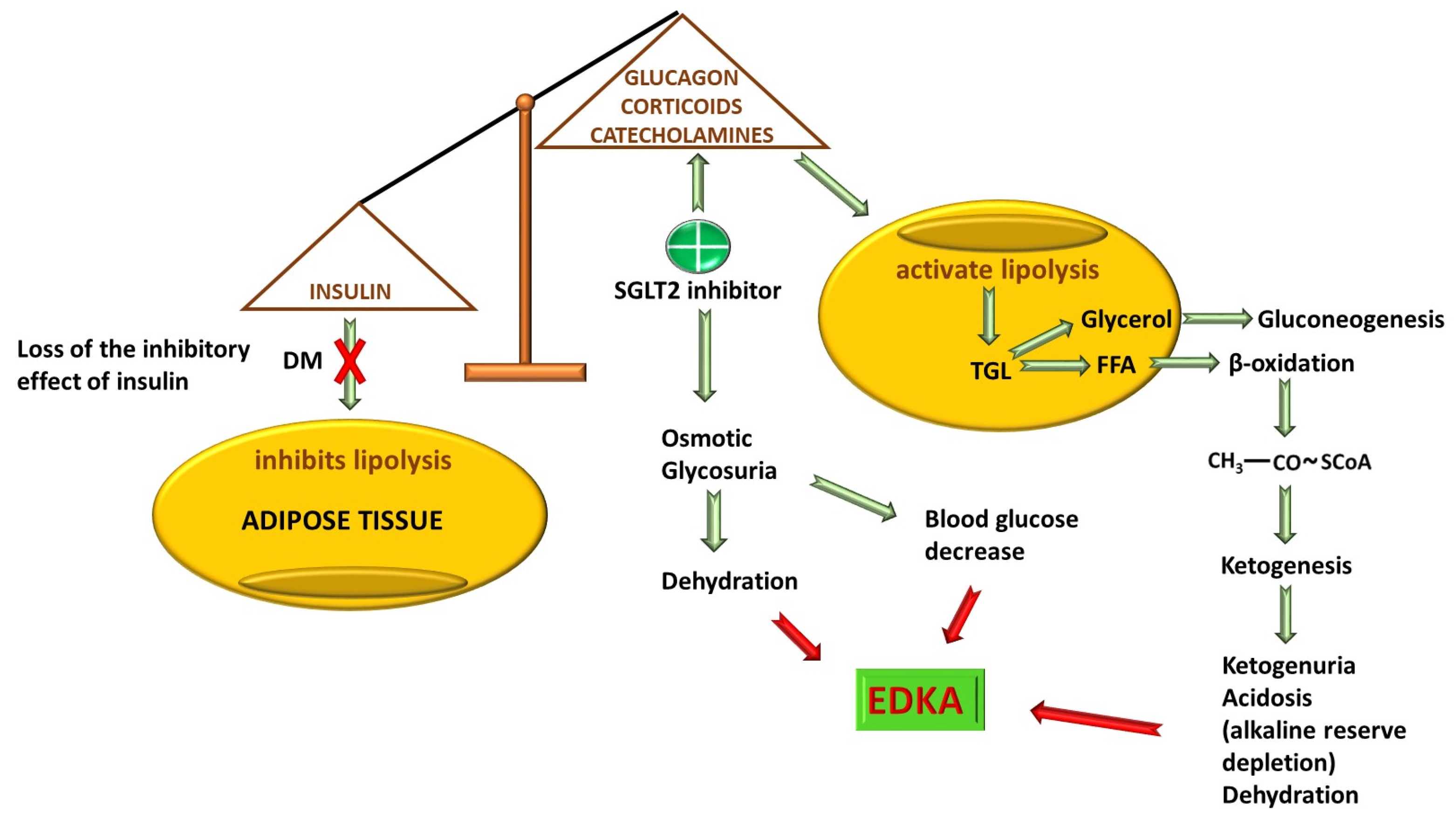
- Patel, K.; Nair, A. A literature review of the therapeutic perspectives of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor-induced euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis. Cureus 2022, 14, e29652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somagutta, M.R.; Agadi, K.; Hange, N.; Jain, M.S.; Batti, E.; Emuze, B.O.; Amos-Arowoshegbe, E.O.; Popescu, S.; Hanan, S.; Kumar, V.R.; et al. Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors: A Focused Review of Pathophysiology, Risk Factors, and Triggers. Cureus 2021, 13, e13665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasa, P.; Chaudhary, S.; Shrivastava, P.K.; Singh, A. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis: A missed diagnosis. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, R.J.; Rabin-Court, A.; Song, J.D.; Cardone, R.L.; Wang, Y.; Kibbey, R.G.; Shulman, G.I. Dehydration and insulinopenia are necessary and sufficient for euglycemic ketoacidosis in SGLT2 inhibitor-treated rats. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, H.S.; Jeong, C.; Yang, Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, J.H.; Sohn, T.S.; Son, H.S.; Yoon, K.H.; et al. Diabetic Ketoacidosis as an Effect of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor: Real World Insights. Diabetes Metab. J. 2024, 48, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bińczyk, W.; Dróżdż, O.; Siudek, B.; Głuszczyk, A.M.; Plizga, J.I.; Grajnert, F.J. The Significance of Precise Diabetes Diagnosis: A Case of Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis Induced by the Introduction of Empagliflozin with Simultaneous Reduction of Insulin Dosage. Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2024, 11, 004567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffei, P.; Bettini, S.; Busetto, L.; Dassie, F. SGLT2 Inhibitors in the Management of Type 1 Diabetes (T1D): An Update on Current Evidence and Recommendations. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 3579–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, J.; Wang, D.; Zhong, R.; Liu, F.; Luo, J.; Tang, P.; Song, X.; Zhang, L. Sodium glucose cotransporter2 inhibitors for type 1 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Prim. Care Diabetes 2024, 18, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, E.; Clement, S.; Garg, R. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis in the era of SGLT-2 inhibitors. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2023, 11, e003666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koceva, A.; Kravos Tramšek, N.A. From sweet to sour: SGLT-2-inhibitor-induced euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juneja, D.; Nasa, P.; Jain, R.; Singh, O. Sodium-glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors induced euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis: A meta summary of case reports. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genc, S.; Evren, B.; Yigit, O.S.; Sahin, I.; Dayanan, R.; Klisic, A.; Erturk, A.; Mercantepe, F. Evolving Clinical Features of Diabetic Ketoacidosis: The Impact of SGLT2 Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almazrouei, R.; Afandi, B.; AlKindi, F.; Govender, R.; Al-Shamsi, S. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes using SGLT2 Inhibitors. Clin. Med. Insights Endocrinol. Diabetes 2023, 16, 11795514231153717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Kumar, T.; Singh, S.; Ambwani, S.; Charan, J.; Varthya, S.B. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis associated with SGLT2 inhibitors: A systematic review and quantitative analysis. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2022, 11, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morace, C.; Lorello, G.; Bellone, F.; Quartarone, C.; Ruggeri, D.; Giandalia, A.; Mandraffino, G.; Minutoli, L.; Squadrito, G.; Russo, G.T.; et al. Ketoacidosis and SGLT2 Inhibitors: A Narrative Review. Metabolites 2024, 14, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampani, E.; Sarafidis, P.; Papagianni, A. Euglycaemic diabetic ketoacidosis as a complication of SGLT-2 inhibitors: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and treatment. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2020, 19, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menghoum, N.; Oriot, P.; Hermans, M.P. Clinical and biochemical characteristics and analysis of risk factors for euglycaemic diabetic ketoacidosis in type 2 diabetic individuals treated with SGLT2 inhibitors: A review of 72 cases over a 4.5-year period. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2021, 15, 102275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selwyn, J.; Pichardo-Lowden, A.R. Managing Hospitalized Patients Taking SGLT2 Inhibitors: Reducing the Risk of Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Diabetology 2023, 4, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.K.H.; Ball, P.A. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis in the setting of acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2024, 15, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, S.; Diaz, V.; Ogbu, I.R.; Sanchez, J.R.P.; Manov, A.E.; Shah, P. Empagliflozin-Associated Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis Masked by Urinary Tract Infection. Cureus 2024, 16, e66408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazan, D.Z.; Esqueda, L.; Ibrahim, A.; Gonzalez, L.; Skubic, J.J.; Reilly, J.; Cavazos, R.; Verduzco, R., Jr. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors and Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Case Series of Three Post-surgical Patients. Cureus 2025, 17, e84665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almascati, Y.; Alhumaiqani, A. Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis Triggered by Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitor Use in a Patient with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cureus 2025, 17, e84170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.; Ahmed, E.; Hamid, S.; Ahmed, M.; Abdalla, H. Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) with Sodium-Glucose Transport Protein 2 (SGLT-2) Inhibitors. Cureus 2025, 17, e79309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshaakh Moh’d Mari, A.; Iwuagwu, C.C.; Johnson, M. Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis, Recurrent Genital Abscess, and Proximal Renal Tubular Acidosis with Concurrent SGLT-2 Inhibitor: More Than an Association. Cureus 2024, 16, e67481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yomogida, D.; Hasegawa, S.; Mizuta, S.; Horikawa, S.; Koshida, Y. Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis with Sepsis and Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients: A Case Series. Cureus 2025, 17, e83920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devkota, B.; Maxwell, T.; Schaedel, J.; Wagener, B.M.; Song, W.; Nooli, N.P. Intraoperative Diagnosis of Sodium-Glucose Transporter-2 Inhibitor-Associated Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Cureus 2024, 16, e71931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, M.; Nakano, M.; Takahashi, H.; Isaka, Y.; Hiura, Y. Euglycemic Ketoacidosis in a Patient without Diabetes Taking Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors for Heart Failure. Am. J. Case Rep. 2024, 25, e943945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhemeiri, M.; Alseddeeqi, E. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis after discontinuing SGLT2 inhibitor. Case Rep. Endocrinol. 2022, 2022, 4101975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secinaro, E.; Ciavarella, S.; Rizzo, G.; Porreca, E.; Vitacolonna, E. SGLT2-inhibitors and euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis in COVID-19 pandemic era: A case report. Acta Diabetol. 2022, 59, 1391–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, S.; Eschler, D.C. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis caused by SGLT2 inhibitors and a ketogenic diet: A case series and review of literature. AACE Clin. Case Rep. 2020, 7, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtas, C.; Rasarmos, A.P.; Naddaf, N. sodium-glucose transport protein 2 inhibitors association with euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis. Case Rep. Endocrinol. 2023, 2023, 6835882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedary, A.; Melder, L.; Pippin, M. A case of euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis associated with a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor. Cureus 2024, 16, e75399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frąk, W.; Hajdys, J.; Radzioch, E.; Szlagor, M.; Młynarska, E.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. Cardiovascular diseases: Therapeutic potential of SGLT-2 inhibitors. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, K.; Wilczopolski, P.; Buławska, D.; Młynarska, E.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. The importance of SGLT-2 inhibitors as both the prevention and the treatment of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triposkiadis, F.; Xanthopoulos, A.; Bargiota, A.; Kitai, T.; Katsiki, N.; Farmakis, D.; Skoularigis, J.; Starling, R.C.; Iliodromitis, E. Diabetes mellitus and heart failure. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tentolouris, A.; Vlachakis, P.; Tzeravini, E.; Eleftheriadou, I.; Tentolouris, N. SGLT2 Inhibitors: A Review of Their Antidiabetic and Cardioprotective Effects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzurović, E.; Mikhailidis, D.P. Impact of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists and sodium-glucose transport protein 2 inhibitors on blood pressure and lipid profile. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2020, 21, 2125–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saisho, Y. SGLT2 Inhibitors: The Star in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes? Diseases 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherbon, A.; Frandes, M.; Dîrpeş, D.; Timar, R.; Timar, B. Impact of SGLT-2 inhibitors on modifiable cardiovascular risk factors in Romanian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2024, 16, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalçın, N.; Aktaş, S.; Uyar, S.; Koca, N. Impact of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Cardiovascular Risk Scores, Metabolic Parameters, and Laboratory Profiles in Type 2 Diabetes. Life 2025, 15, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsimardou, A.; Theofilis, P.; Vordoni, A.; Doumas, M.; Kalaitzidis, R.G. The Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Blood Pressure and Other Cardiometabolic Risk Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajić, S.; Janković, S.; Stojadinović, M.; Filić, K.; Bontić, A.; Pavlović, J.; Mrđa, I.; Petrović, K.; Hadži-Tanović, L.; Žunić, J.; et al. The Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Lipid Profile and Kidney Function in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Regardless of Diabetes and Hypertension Status. Metabolites 2025, 15, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Wen, S.; Gong, M.; Yuan, X.; Xu, D.; Wang, C.; Jin, J.; Zhou, L. Dapagliflozin Activates Neurons in the Central Nervous System and Regulates Cardiovascular Activity by Inhibiting SGLT-2 in Mice. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 2781–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahwin, P.; Martinez, D. The relationship between SGLT2 and systemic blood pressure regulation. Hypertens. Res. 2024, 47, 2094–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laksono, S.; Hosea, G.T.; Nurusshofa, Z. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Pathophysiology and novel therapies. Brown J. Hosp. Med. 2022, 1, 37850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhu, Q.X.; Li, G.Z.; Wang, T.; Zhou, H. Empagliflozin ameliorates diabetic cardiomyopathy probably via activating AMPK/PGC-1α and inhibiting the RhoA/ROCK pathway. World J. Diabetes. 2023, 14, 1862–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Chong, K.; Huang, Y.; Huang, C.; Yin, L. Empagliflozin improves mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy by modulating ketone body metabolism and oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2024, 69, 103010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
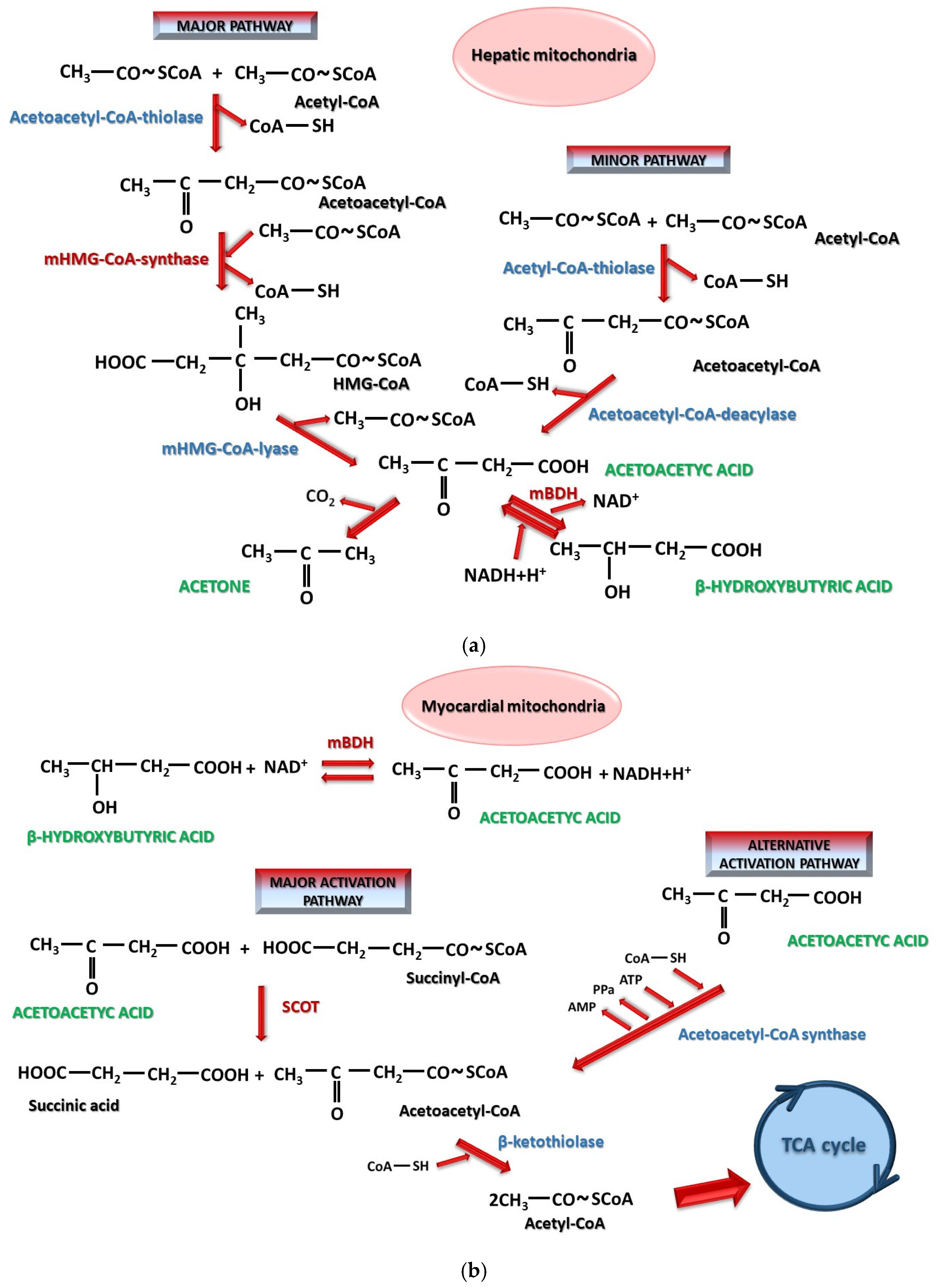
- Arnedo, M.; Latorre-Pellicer, A.; Lucia-Campos, C.; Gil-Salvador, M.; Antoñanzas-Peréz, R.; Gómez-Puertas, P.; Bueno-Lozano, G.; Puisac, B.; Pié, J. More Than One HMG-CoA Lyase: The Classical Mitochondrial Enzyme Plus the Peroxisomal and the Cytosolic Ones. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, L.; Ipek, Ö.; Beaumont, M.; Shevlyakova, M.; Christinat, N.; Masoodi, M.; Greenberg, N.; Gruetter, R.; Cuenoud, B. Nutritional Ketosis Increases NAD+/NADH Ratio in Healthy Human Brain: An in Vivo Study by 31P-MRS. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, T.R.; Puchalska, P.; Crawford, P.A.; Kelly, D.P. Ketones and the Heart: Metabolic Principles and Therapeutic Implications. Circ. Res. 2023, 132, 882–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Delgado, A.P.; Arteaga Herrera, E.; Tumbaco Mite, C.; Delgado Cedeno, P.; Van Loon, M.C.; Badimon, J.J. Renal and Cardiovascular Metabolic Impact Caused by Ketogenesis of the SGLT2 Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodur, N.; Yurista, S.; Province, V.; Rueth, E.; Nguyen, C.; Tang, W.H.W. Ketogenic Diet in Heart Failure: Fact or Fiction? Heart Fail. 2023, 11, 838–844. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, K.L.; Karwi, Q.G.; Wang, F.; Wagg, C.; Zhang, L.; Panidarapu, S.; Chen, B.; Pherwani, S.; Greenwell, A.A.; Oudit, G.Y.; et al. The ketogenic diet does not improve cardiac function and blunts glucose oxidation in ischaemic heart failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 2024, 120, 1126–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedeke, L.; Ma, Y.; Gaspar, R.C.; Nasiri, A.; Lee, J.; Zhang, D.; Galsgaard, K.D.; Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Guerrera, N.; et al. SGLT2 inhibition alters substrate utilization and mitochondrial redox in healthy and failing rat hearts. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e176708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, J.H.; Finck, B.N. Beyond ketosis: The search for the mechanism underlying SGLT2-inhibitor benefit continues. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e187097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolis, A.S.; Manolis, T.A.; Manolis, A.A. Ketone Bodies and Cardiovascular Disease: An Alternate Fuel Source to the Rescue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, B.M.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, B.-W. Ketone Body Induction: Insights into Metabolic Disease Management. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Dyck, J.R.B. Ketones and the cardiovascular system. Nat. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 2, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, R.; Møller, N.; Gormsen, L.C.; Tolbod, L.P.; Hansson, N.H.; Sorensen, J.; Harms, H.J.; Frøkiær, J.; Eiskjaer, H.; Jespersen, N.R.; et al. Cardiovascular Effects of Treatment with the Ketone Body 3-Hydroxybutyrate in Chronic Heart Failure Patients. Circulation 2019, 139, 2129–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papazafiropoulou, A.K.; Georgopoulos, M.M.; Katsilambros, N.L. Ketone bodies and the heart. Arch. Med. Sci. Atheroscler. Dis. 2021, 6, e209–e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, N.; Chacko, L.; Bhattacharya, H.; Vallamkondu, J.; Nag, S.; Dey, A.; Karmakar, T.; Reddy, P.H.; Kandimalla, R.; Dewanjee, S. Exploring the complex relationship between diabetes and cardiovascular complications: Understanding diabetic cardiomyopathy and promising therapies. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patoulias, D.; Fragakis, N.; Rizzo, M. The therapeutic role of SGLT-2 inhibitors in acute heart failure: From pathophysiologic mechanisms to clinical evidence with pooled analysis of relevant studies across safety and efficacy endpoints of interest. Life 2022, 12, 2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhov, L.; Apostol, A.; Dăniluc, L.; Haj Ali, L.; Sandu, O.E.; Bogdan, C.; Andor, M. Implications of heart failure treatment on atrial fibrillation onset: A retrospective study. Medicina 2025, 61, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, D.; Semmler, L.; Oeing, C.U.; Alogna, A.; Schiattarella, G.G.; Pieske, B.M.; Heinzel, F.R.; Hohendanner, F. Implications of SGLT inhibition on redox signalling in atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachteas, P.; Nasoufidou, A.; Karagiannidis, E.; Patoulias, D.; Karakasis, P.; Alexiou, S.; Samaras, A.; Zormpas, G.; Stavropoulos, G.; Tsalikakis, D.; et al. The role of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors in atrial fibrillation: A comprehensive review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, V.C.; Chiu, K.P.; Wang, C.L.; Hsu, C.Y.; Tu, H.T.; Huang, Y.T.; Chang, C.H.; Huang, C.H.; Kuo, C.F.; Chen, S.W.; et al. Electrocardiographic changes associated with SGLT2 inhibitors and non-SGLT2 inhibitors: A multi-center retrospective study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 934193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Hirai, T.; Koya, D.; Kitada, M. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on atherosclerosis: Lessons from cardiovascular clinical outcomes in type 2 diabetic patients and basic researches. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rroji, M.; Spahia, N.; Figurek, A.; Spasovski, G. Targeting diabetic atherosclerosis: The role of GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT2 inhibitors, and nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in vascular protection and disease modulation. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scisciola, L.; Cataldo, V.; Taktaz, F.; Fontanella, R.A.; Pesapane, A.; Ghosh, P.; Franzese, M.; Puocci, A.; De Angelis, A.; Sportiello, L.; et al. Anti-inflammatory role of SGLT2 inhibitors as part of their anti-atherosclerotic activity: Data from basic science and clinical trials. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 1008922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechmann, L.E.; Emanuelsson, F.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Benn, M. SGLT2-inhibition increases total, LDL, and HDL cholesterol and lowers triglycerides: Meta-analyses of 60 randomized trials, overall and by dose, ethnicity, and drug type. Atherosclerosis 2024, 394, 117236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccirillo, F.; Mastroberardino, S.; Nusca, A.; Frau, L.; Guarino, L.; Napoli, N.; Ussia, G.P.; Grigioni, F. Novel antidiabetic agents and their effects on lipid profile: A single shot for several cardiovascular targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osto, E.; Bonacina, F.; Pirillo, A.; Norata, G.D. Neutral effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on lipoprotein metabolism: From clinical evidence to molecular mechanisms. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 188, 106667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, S.S.; Sattar, N.; Salsali, A.; Neubacher, D.; Ginsberg, H.N. Potential contribution of haemoconcentration to changes in lipid variables with empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes: A post hoc analysis of pooled data from four phase 3 randomized clinical trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 2763–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titus, A.S.; Sung, E.A.; Zablocki, D.; Sadoshima, J. Mitophagy for cardioprotection. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2023, 118, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Xiao, C.; Ding, Z.; Zhai, X.; Liu, J.; Yu, M. Canagliflozin Mitigates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy through Enhanced PINK1-Parkin Mitophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M. SGLT2 inhibitors: Role in protective reprogramming of cardiac nutrient transport and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2023, 20, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picca, A.; Faitg, J.; Auwerx, J.; Ferrucci, L.; D’Amico, D. Mitophagy in human health, ageing and disease. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 2047–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Jiang, T.; Dong, D.; Sun, M. The PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway-mediated mitophagy: A forgotten protagonist in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 209, 107466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, R.L.; Inserra, F.; García Menéndez, S.; Mazzei, L.; Ferder, L.; Manucha, W. Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiac Remodeling Due to Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress Involving Gliflozins and Sirtuins. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2023, 25, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.C.; Chen, K.H.; Yue, Y.; Cheng, B.C.; Hsu, T.W.; Chiang, J.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Liu, F.; Xiao, J.; Yip, H.K. SGLT2 inhibitor downregulated oxidative stress via activating AMPK pathway for cardiorenal (CR) protection in CR syndrome rodent fed with high protein diet. J. Mol. Histol. 2024, 55, 803–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koizumi, T.; Watanabe, M.; Yokota, T.; Tsuda, M.; Handa, H.; Koya, J.; Nishino, K.; Tatsuta, D.; Natsui, H.; Kadosaka, T.; et al. Empagliflozin suppresses mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation and mitigates the inducibility of atrial fibrillation in diabetic rats. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1005408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muszyński, P.; Cieślińska, M.; Dziemidowicz, M.; Bonda-Ostaszewska, E.; Hirnle, T.; Bonda, T.A. The Influence of Empagliflozin on the Expression of Mitochondrial Regulatory Proteins in Human Myocardium in an Ex Vivo Model of Short-Term Atrial Tachypacing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, H.; Yang, X.; Shi, J.; Sheng, X.; Wang, L.; Li, T.; Quan, H.; Zhai, X.; Li, W. Effects of dapagliflozin monotherapy and combined aerobic exercise on skeletal muscle mitochondrial quality control and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 169, 115852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Peng, D. New insights into the molecular mechanisms of SGLT2 inhibitors on ventricular remodeling. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 118, 110072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-C.; Lin, M.-H.; Su, H.-T.; Ho, M.-Y.; Yeh, J.-K.; Tsai, M.-L.; Hsieh, I.-C.; Wen, M.-S. TLR9 binding to Beclin 1 and mitochondrial SIRT3 by a sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor protects the heart from Doxorubicin toxicity. Biology 2020, 9, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Xu, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, F.; Tu, Z.; Qian, J.; Xu, S.; Xu, Y.; Hwa, J.; Li, J.; et al. Cardioprotective mechanism of SGLT2 inhibitor against myocardial infarction is through reduction of autosis. Protein Cell. 2022, 13, 336–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piperis, C.; Marathonitis, A.; Anastasiou, A.; Theofilis, P.; Mourouzis, K.; Giannakodimos, A.; Tryfou, E.; Oikonomou, E.; Siasos, G.; Tousoulis, D. Multifaceted Impact of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Heart Failure Patients: Exploring Diverse Mechanisms of Action. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, V.C.-C.; Li, Y.-R.; Wang, C.-Y. Impact of sodium–glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors on cardiac protection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Zhu, X.; Cai, X.; Yang, W.; Lv, F.; Nie, L.; Ji, L. SGLT2 inhibitors and lower limb complications: An updated meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potier, L.; Mohammedi, K.; Velho, G.; Roussel, R. SGLT2 inhibitors and lower limb complications: The diuretic-induced hypovolemia hypothesis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miceli, G.; Basso, M.G.; Pennacchio, A.R.; Cocciola, E.; Pintus, C.; Cuffaro, M.; Profita, M.; Rizzo, G.; Sferruzza, M.; Tuttolomondo, A. The potential impact of SGLT2-I in diabetic foot prevention: Promising pathophysiologic implications, state of the art, and future perspectives—A narrative review. Medicina 2024, 60, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimellaro, A.; Cavallo, M.; Mungo, M.; Suraci, E.; Spagnolo, F.; Addesi, D.; Pintaudi, M.; Pintaudi, C. Cardiovascular effectiveness and safety of antidiabetic drugs in patients with type 2 diabetes and peripheral artery disease: Systematic review. Medicina 2024, 60, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nani, A.; Carrara, F.; Paulesu, C.M.E.; Dalle Fratte, C.; Padroni, M.; Enisci, S.; Bilancio, M.C.; Romio, M.S.; Bertuzzi, F.; Pintaudi, B. Association of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors with osteomyelitis and other lower limb safety outcomes in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanner, C.; Iliev, H.; Duarte, N.; Schueler, E.; Soares, A.R.; Thanam, V.; Pfarr, E. Safety of Empagliflozin: An Individual Participant-Level Data Meta-Analysis from Four Large Trials. Adv Ther. 2024, 41, 2826–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.X.; Liu, T.T.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, Q.; Geng, X.H.; Man, C.X.; Li, J.Y.; Mao, X.Y.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, H. Safety of sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1275060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, E.L.; D’Andrea, E.; Wexler, D.J.; Patorno, E.; Paik, J.M. Safety of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in patients with CKD and type 2 diabetes: Population-based US Cohort Study. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 18, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Adachi, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Iida, S.; Katsuyama, H. Metabolic-dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease—Its pathophysiology, association with atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease, and treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirarchi, L.; Amodeo, S.; Citarrella, R.; Licata, A.; Soresi, M.; Giannitrapani, L. SGLT2 inhibitors as the most promising influencers on the outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Dalbeni, A. Treatments for NAFLD: State of art. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Xu, X.; Guo, L.; Li, J.; Li, L. Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on type 2 diabetes mellitus with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 635556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasiri-Ansari, N.; Nikolopoulou, C.; Papoutsi, K.; Kyrou, I.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Kyriakopoulos, G.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Kalotychou, V.; Randeva, M.S.; Chatha, K.; et al. Empagliflozin attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in high fat diet fed ApoE(−/−) mice by activating autophagy and reducing ER stress and apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Lian, D.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Mu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B. SGLT-2 inhibitors for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A review. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2023, 28, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Androutsakos, T.; Nasiri-Ansari, N.; Bakasis, A.-D.; Kyrou, I.; Efstathopoulos, E.; Randeva, H.S.; Kassi, E. SGLT-2 inhibitors in NAFLD: Expanding their role beyond diabetes and cardioprotection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, R.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Xing, J. Mechanism of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Important role of lipid metabolism. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2024, 12, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaznadar, F.; Petrovic, A.; Khaznadar, O.; Roguljic, H.; Bojanic, K.; Kuna Roguljic, L.; Siber, S.; Smolic, R.; Bilic-Curcic, I.; Wu, G.Y.; et al. Biomarkers for assessing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, D.H.; Joo, S.K.; Koo, B.K.; Lim, S.; Lee, W.; Kim, W. Outcomes of various classes of oral antidiabetic drugs on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. JAMA Intern. Med. 2024, 184, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troise, D.; Mercuri, S.; Infante, B.; Losappio, V.; Cirolla, L.; Netti, G.S.; Ranieri, E.; Stallone, G. mTOR and SGLT-2 inhibitors: Their synergistic effect on age-related processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, C.J.; Day, C.; Bellary, S. Renal protection with SGLT2 inhibitors: Effects in acute and chronic kidney disease. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2022, 22, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. DAPA-CKD trial committees and investigators. Dapagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassif, M.E.; Windsor, S.L.; Borlaug, B.A.; Kitzman, D.W.; Shah, S.J.; Tang, F.; Khariton, Y.; Malik, A.O.; Khumri, T.; Umpierrez, G.; et al. The SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: A multicenter randomized trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1954–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, C.A.M.; Azevedo, L.C.P.; Rea-Neto, Á.; Campos, N.S.; Amendola, C.P.; Kozesinski-Nakatani, A.C.; David-João, P.G.; Lobo, S.M.; Filiponi, T.C.; Almeida, G.M.B.; et al. DEFENDER Investigators. Dapagliflozin for Critically Ill Patients with Acute Organ Dysfunction: The DEFENDER Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 332, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Fernandez, B.; Sarafidis, P.; Soler, M.J.; Ortiz, A. EMPA-KIDNEY: Expanding the range of kidney protection by SGLT2 inhibitors. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosenzon, O.; Wiviott, S.D.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Dwyer, J.P.; Cahn, A.; Goodrich, E.L.; Rozenberg, A.; Schechter, M.; Yanuv, I.; Murphy, S.A.; et al. The Effect of Dapagliflozin on Albuminuria in DECLARE-TIMI 58. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1805–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, R.; Obi, Y.; Dossabhoy, N.R.; Shafi, T. Is there a role for SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with end-stage kidney disease? Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2024, 26, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, L. SGLT2 inhibitors across the spectrum of chronic kidney disease: A narrative review. Postgrad. Med. 2024, 136, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, A. SGLT2 inhibitors and kidney protection: Mechanisms beyond tubuloglomerular feedback. Kidney360 2024, 5, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kravtsova, O.; Bohovyk, R.; Levchenko, V.; Palygin, O.; Klemens, C.A.; Rieg, T.; Staruschenko, A. SGLT2 inhibition effect on salt-induced hypertension, RAAS, and Na+ transport in Dahl SS rats. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2022, 322, F692–F707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, B.; Fuhrmann, D.C.; Schubert, R.; Geiger, H.; Speer, T.; Baer, P.C. Gliflozins have an anti-inflammatory effect on renal proximal tubular epithelial cells in a diabetic and inflammatory microenvironment in vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirklbauer, M.; Bernd, M.; Fuchs, L.; Staudinger, P.; Corazza, U.; Leierer, J.; Mayer, G.; Schramek, H. Empagliflozin inhibits basal and IL-1β-mediated MCP-1/CCL2 and endothelin-1 expression in human proximal tubular cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita-Yagi, A.; Ozeki-Okuno, N.; Watanabe-Uehara, N.; Komaki, K.; Umehara, M.; Sawada-Yamauchi, H.; Minamida, A.; Sunahara, Y.; Matoba, Y.; Nakamura, I.; et al. The importance of proinflammatory failed-repair tubular epithelia as a predictor of diabetic kidney disease progression. iScience 2024, 27, 109020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
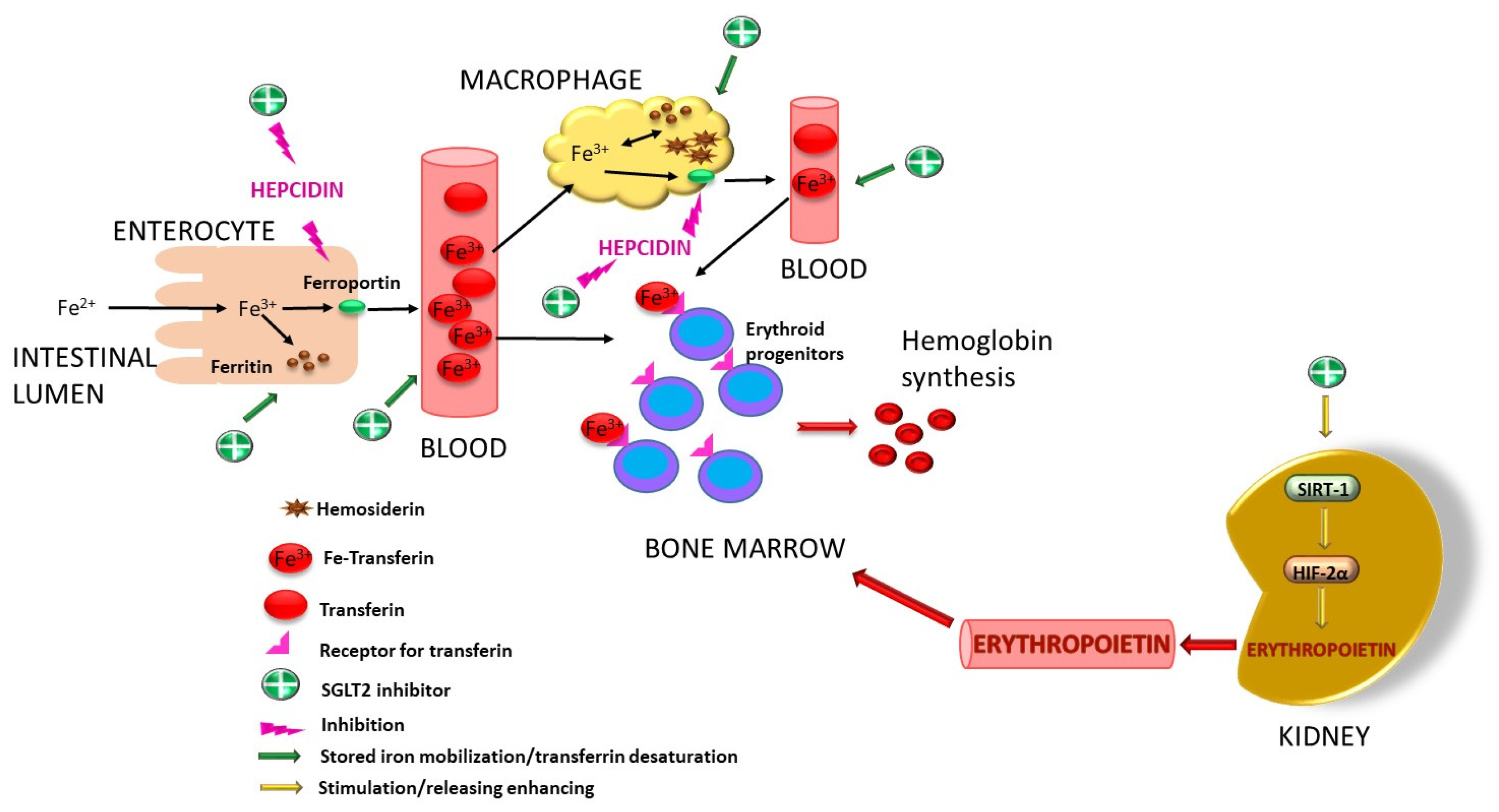
- Peng, B.; Kong, G.; Yang, C.; Ming, Y. Erythropoietin and its derivatives: From tissue protection to immune regulation. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M. Mechanisms of enhanced renal and hepatic erythropoietin synthesis by sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 5027–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M. Mechanistic and clinical comparison of the erythropoietic effects of SGLT2 inhibitors and prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors in patients with chronic kidney disease and renal anemia. Am. J. Nephrol. 2024, 55, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tziastoudi, M.; Pissas, G.; Golfinopoulos, S.; Filippidis, G.; Dousdampanis, P.; Eleftheriadis, T.; Stefanidis, I. Sodium–Glucose Transporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors and Iron Deficiency in Heart Failure and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Literature Review. Life 2023, 13, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M. Alleviation of Anemia by SGLT2 Inhibitors in Patients with CKD: Mechanisms and Results of Long-Term Placebo-Controlled Trials. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques Vidas, M.; Portolés, J.; Cobo, M.; Gorriz, J.L.; Nuñez, J.; Cases, A. Anemia Management in the Cardiorenal Patient: A Nephrological Perspective. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2025, 14, e037363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docherty, K.F.; Welsh, P.; Verma, S.; De Boer, R.A.; O’Meara, E.; Bengtsson, O.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Hammarstedt, A.; Langkilde, A.M.; et al. DAPA-HF Investigators and Committees. Iron Deficiency in Heart Failure and Effect of Dapagliflozin: Findings From DAPA-HF. Circulation 2022, 146, 980–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshino, A.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Jongs, N.; Badve, S.V.; Arnott, C.; Neal, B.; Jardine, M.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Pollock, C.; Perkovic, V.; et al. Canagliflozin and iron metabolism in the CREDENCE trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2025, 40, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshino, A.; Neuen, B.L.; Jongs, N.; Pollock, C.; Greasley, P.J.; Andersson, E.M.; Hammarstedt, A.; Karlsson, C.; Langkilde, A.M.; Wada, T.; et al. Effects of dapagliflozin and dapagliflozin-saxagliptin on erythropoiesis, iron and inflammation markers in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: Data from the DELIGHT trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murashima, M.; Tanaka, T.; Kasugai, T.; Tomonari, T.; Ide, A.; Ono, M.; Mizuno, M.; Suzuki, T.; Hamano, T. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and anemia among diabetes patients in real clinical practice. J. Diabetes Investig. 2022, 13, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docherty, K.F.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Kalra, P.R.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Lang, N.N.; Petrie, M.C.; Robertson, M.; Ford, I. Intravenous iron and SGLT2 inhibitors in iron-deficient patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. ESC Heart Fail. 2024, 11, 1875–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittipibul, V.; Cox, Z.L.; Chesdachai, S.; Fiuzat, M.; Lindenfeld, J.; Mentz, R.J. Genitourinary tract infections in patients taking SGLT2 Inhibitors: JACC review topic of the week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 83, 1568–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendt, R.; Schmerler, D.; Müller-Hechler, C.; Weichold, C.; Craatz, D.; Beige, J. Candida sepsis from local infection in a patient with a urostomy on SGLT2 inhibitor therapy. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 98, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iordan, L.; Avram, V.F.; Timar, B.; Sturza, A.; Popescu, S.; Albai, O.; Timar, R.Z. Safety of SGLT2 inhibitors and urinary tract infections in clinical practice—A cross-sectional study. Medicina 2024, 60, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgojo-Martínez, J.J.; Górriz, J.L.; Cebrián-Cuenca, A.; Castro Conde, A.; Velasco Arribas, M. Clinical recommendations for managing genitourinary adverse effects in patients treated with SGLT-2 inhibitors: A multidisciplinary expert consensus. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferwani, P.; Maldar, A.; Shah, N.; Chauhan, P.; Chadha, M. Prevalence of bacterial urinary tract infection among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors: A prospective real-world setting study. J. ASEAN Fed. Endocr. Soc. 2022, 37, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H. Case literature analysis of Fournier’s gangrene caused by sodium-glucose protein-2 inhibitors. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1301105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, T.; Gousy, N.; Bellamkonda, A.; Dutta, J.; Zaman, C.F.; Zakia, U.B.; Tasha, T.; Dutta, P.; Deb Roy, P.; Gomez, A.M.; et al. Fournier’s Gangrene: A Coexistence or Consanguinity of SGLT-2 Inhibitor Therapy. Cureus 2022, 14, e27773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, L.; Asmar, O.; Mandal, A.; Tridente, A.; Hardy, K.; Shokrollahi, K. Perspectives From a Regional Plastic Surgery Centre on Evidence for the Purported Link Between SGLT2 Inhibitors and Fournier’s Gangrene. Front. Surg. 2021, 8, 754101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mederle, A.L.; Dumitrescu, P.; Borza, C.; Kundnani, N.R. Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions Associated with SGLT2 Inhibitors. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suciu, I.-M.; Greluș, A.; Cozlac, A.-R.; Suciu, B.-S.; Stoica, S.; Luca, S.; Luca, C.-T.; Gaiță, D.-I. Fournier’s Gangrene as an Adverse Event Following Treatment with Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors. Medicina 2024, 60, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidegger, I.; Zwierzina, M.; Boeckhaus, J.; Krane, V.; Gross, O. Fournier’s Gangrene in a Patient with CKD Without Diabetes Possibly Related to Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Therapy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2024, 9, 1531–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratama, K.G.; Tandarto, K.; Hengky, A. Weight loss effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors in patients with obesity without diabetes: A systematic review. Acta Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janež, A.; Fioretto, P. SGLT2 Inhibitors and the clinical implications of associated weight loss in type 2 diabetes: A narrative review. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 2249–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccirillo, F.; Lanciotti, M.; Nusca, A.; Frau, L.; Spanò, A.; Liporace, P.; Ussia, G.P.; Grigioni, F. Sodium-glucose transporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) and myocardial ischemia: Another compelling reason to consider these agents regardless of diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radlinger, B.; Ress, C.; Folie, S.; Salzmann, K.; Lechuga, A.; Weiss, B.; Salvenmoser, W.; Graber, M.; Hirsch, J.; Holfeld, J.; et al. Empagliflozin protects mice against diet-induced obesity, insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 754–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaborit, B.; Ancel, P.; Abdullah, A.E.; Maurice, F.; Abdesselam, I.; Calen, A.; Soghomonian, A.; Houssays, M.; Varlet, I.; Eisinger, M.; et al. Effect of empagliflozin on ectopic fat stores and myocardial energetics in type 2 diabetes: The EMPACEF study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinte, L.C.; Castellano-Castillo, D.; Ghosh, A.; Melrose, K.; Gasser, E.; Noé, F.; Massier, L.; Dong, H.; Sun, W.; Hoffmann, A.; et al. Adipose tissue retains an epigenetic memory of obesity after weight loss. Nature 2024, 636, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanasie, G.; Bojin, F.; Tatu, R.F.; Sisu, A.M.; Cristea, M.; Puscasiu, D.A.; Nemes, E.A.; Tatu, C.A. In vitro effects of biomaterials on mesenchymal stem cells viability and proliferation. Mater. Plast. 2017, 54, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurmuz, M.; Bojin, F.; Ionac, M.; Tatu, F.; Puscasiu, D.; Tatu, C. Plastic adherence method for isolation of stem cells derived from infrapatellar fat pad. Mater. Plast. 2016, 53, 553–556. [Google Scholar]
- Yip, J.M.X.; Chiang, G.S.H.; Lee, I.C.J.; Lehming-Teo, R.; Dai, K.; Dongol, L.; Wang, L.Y.-T.; Teo, D.; Seah, G.T.; Lehming, N. Mitochondria and the repurposing of diabetes drugs for off-label health benefits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scisciola, L.; Olivieri, F.; Ambrosino, C.; Barbieri, M.; Rizzo, M.R.; Paolisso, G. On the wake of metformin: Do anti-diabetic SGLT2 inhibitors exert anti-aging effects? Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 92, 102131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiNicolantonio, J.J.; McCarty, M.F.; O’Keefe, J.H. Nutraceutical activation of Sirt1: A review. Open Heart 2022, 9, e002171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Grotta, R.; Frigé, C.; Matacchione, G.; Olivieri, F.; de Candia, P.; Ceriello, A.; Prattichizzo, F. Repurposing SGLT-2 inhibitors to target aging: Available evidence and molecular mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönberger, E.; Mihaljević, V.; Steiner, K.; Šarić, S.; Kurevija, T.; Majnarić, L.T.; Bilić Ćurčić, I.; Canecki-Varžić, S. Immunomodulatory effects of SGLT2 inhibitors—Targeting inflammation and oxidative stress in aging. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasleen, B.; Vishal, G.K.; Sameera, M.; Fahad, M.; Brendan, O.; Deion, S.; Pemminati, S. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors: Benefits versus risk. Cureus 2023, 15, e33939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, T.; Jia, S.; Zhao, J.; Wan, B.; Liu, G. Fine mapping-based multi-omics analysis interprets the gut-lung axis function of SGLT2 inhibitors. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1447327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-E.; Im, D.-S. SGLT2 Inhibitors Empagliflozin and Canagliflozin ameliorate allergic asthma responses in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Hu, R.; Zou, H. Relative efficacy of five SGLT2 inhibitors: A network meta-analysis of 20 cardiovascular and respiratory outcomes. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1419729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, Y.; Jo, T.; Inoue, N.; Suzukawa, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Kumazawa, R.; Ishimaru, M.; Matsui, H.; Yokoyama, A.; Tanaka, G.; et al. Association of novel antihyperglycemic drugs versus metformin with a decrease in asthma exacerbations. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2024, 12, 2035–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga-da-Cunha, M.; Wortmann, S.B.; Grünert, S.C.; Van Schaftingen, E. Treatment of the Neutropenia Associated with GSD1b and G6PC3 Deficiency with SGLT2 Inhibitors. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mateoc, T.; Dumitrascu, A.-L.; Flangea, C.; Puscasiu, D.; Vlad, T.; Popescu, R.; Marina, C.; Vlad, D.-C. SGLT2 Inhibitors: From Structure–Effect Relationship to Pharmacological Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6937. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146937
Mateoc T, Dumitrascu A-L, Flangea C, Puscasiu D, Vlad T, Popescu R, Marina C, Vlad D-C. SGLT2 Inhibitors: From Structure–Effect Relationship to Pharmacological Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6937. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146937
Chicago/Turabian StyleMateoc, Teodora, Andrei-Luca Dumitrascu, Corina Flangea, Daniela Puscasiu, Tania Vlad, Roxana Popescu, Cristina Marina, and Daliborca-Cristina Vlad. 2025. "SGLT2 Inhibitors: From Structure–Effect Relationship to Pharmacological Response" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6937. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146937
APA StyleMateoc, T., Dumitrascu, A.-L., Flangea, C., Puscasiu, D., Vlad, T., Popescu, R., Marina, C., & Vlad, D.-C. (2025). SGLT2 Inhibitors: From Structure–Effect Relationship to Pharmacological Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6937. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146937






